|
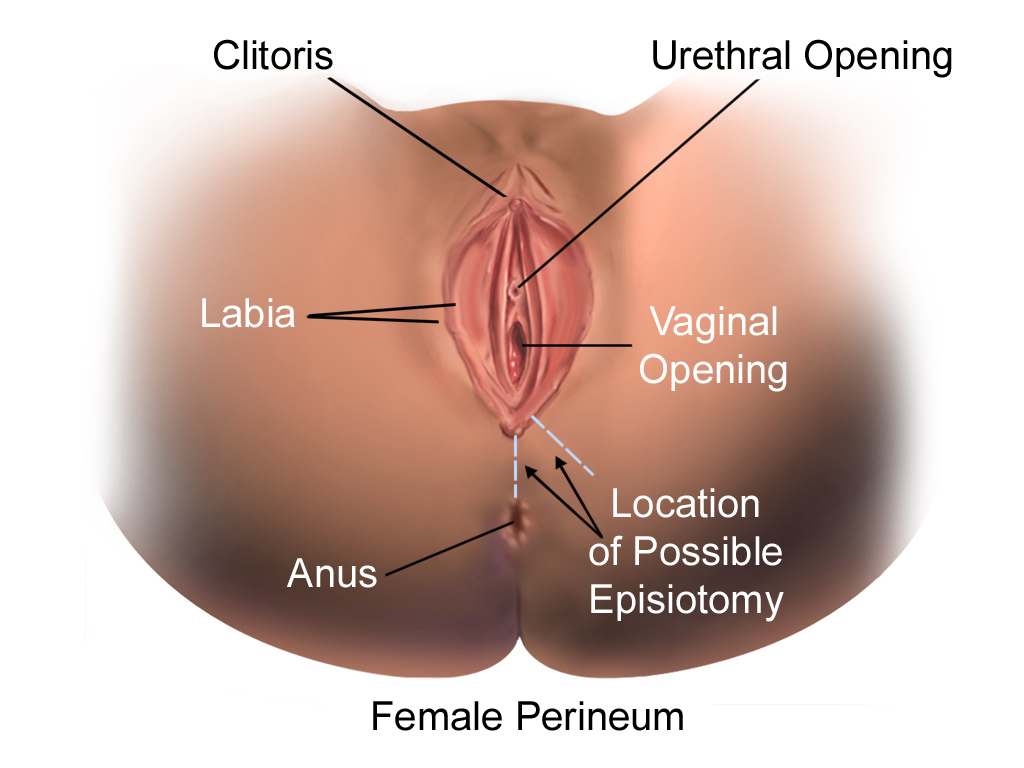
Episiotomy
Episiotomy, also known as perineotomy, is a surgical incision of the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall generally done by a midwife or obstetrician. Episiotomy is usually performed during second stage of labor to quickly enlarge the opening for the baby to pass through. The incision, which can be done from the posterior midline of the vulva straight toward the anus or at an angle to the right or left (medio-lateral episiotomy), is performed under local anesthetic ( pudendal anesthesia), and is sutured after delivery. Its routine use is no longer recommended, as perineal massage is an alternative painless method of enlarging the opening for baby. Despite this, it is one of the most common surgical procedures specific to women. In the United States, as of 2012, it was performed in 12% of vaginal births. It is still widely practiced in many parts of the world, including Korea, Japan, Taiwan, China, and Spain. Uses Vaginal tears can occur during childbirth, most often at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineal Tear
A perineal tear is a laceration of the skin and other soft tissue structures which, in women, separate the vagina from the anus. Perineal tears mainly occur in women as a result of vaginal childbirth, which strains the perineum. It is the most common form of obstetric injury. Tears vary widely in severity. The majority are superficial and may require no treatment, but severe tears can cause significant bleeding, long-term pain or dysfunction. A perineal tear is distinct from an episiotomy, in which the perineum is intentionally incised to facilitate delivery. Episiotomy, a very rapid birth, or large fetal size can lead to more severe tears which may require surgical intervention. Anatomy In women, an anatomical area known as the perineum separates the opening of the vagina from that of the anus. Each opening is surrounded by a wall, and the anal wall is separated from the vaginal wall by a mass of soft tissue including: * The muscles of the anus (corrugator cutis ani, the intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineal Massage
Antenatal perineal massage (APM) or Birth Canal Widening (BCW) is the massage (painless stretching) of a pregnant woman's perineum – the skin and deep tissues around the opening to the vagina or ('birth canal' – when a baby is in this passage), performed in the 4 to 6 weeks before childbirth, i.e., 25 weeks onwards, just in case the baby is born at 28 weeks and usually on six consecutive days, and continued weekly until birth. The practice aims to gently mimic the 'massaging' action of a baby's head on the opening to the birth canal (vagina) prior to birth, to achieve the 10cm diameter opening without using the back of baby's head, i.e., doing some of the hard work of labour (birth) before the start of labour, making birth less stressful on the baby and mother. The intention is also to attempt to: prevent tearing of the perineum during birth; eliminate the need for an episiotomy Episiotomy, also known as perineotomy, is a surgical incision of the perineum and the posterior v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pudendal Anesthesia
Pudendal anesthesia, also known as a pudendal block, or saddle block, is a form of local anesthesia commonly used in the practice of obstetrics to relieve pain during the delivery of baby by forceps. The pudendal nerve block prevents fainting during forceps delivery which was common before pudendal nerve block use was available. The anesthesia is produced by blocking the pudendal nerves near the ischial spine of the pelvis. The ischial spine separates the greater and lesser sciatic foramina at the exit of the bony pelvis. The pudendal block gets its name because a local anesthetic, such as lidocaine or chloroprocaine, is injected into the pudendal canal where the pudendal nerve is located. This allows quick pain relief to the perineum, vulva, and vagina. A pudendal block is usually given in the second stage of labor just before delivery of the baby. It relieves pain around the vagina and rectum as the baby comes down the birth canal. It is also helpful just before an episiotomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frenulum Of Labia Minora
The frenulum of labia minora (''fourchette'' or ''posterior commissure of the labia minora'') is a frenulum where the labia minora meet posteriorly. Pathology The fourchette may be torn during delivery due to the sudden stretching of the vulval orifice, or during copulation. To prevent this tearing in a haphazard manner, obstetricians and, less frequently, midwives may perform an episiotomy, which is a deliberate cut made in the perineum starting from the fourchette and continuing back along the perineum toward the anus. Sometimes this surgical cut may extend to involve the perineal body and thus reduce anal sphincter function. Thus some obstetricians have opted to perform a posterior-lateral cut in the perineum to prevent this potential complication from occurring. The fourchette may also be torn in acts of violence wherein forced entry occurs such as rape. When the fourchette is torn, the bleeding which ensues sometimes requires surgical suturing for containment. Ety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineal Body
The perineum in humans is the space between the anus and scrotum in the male, or between the anus and the vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis (pubic arch) and the coccyx (tail bone), including the perineal body and surrounding structures. There is some variability in how the boundaries are defined. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees. The perineum is an erogenous zone. The word perineum entered English from late Latin via Greek περίναιος ~ περίνεος ''perinaios, perineos'', itself from περίνεος, περίνεοι 'male genitals' and earlier περίς ''perís'' 'penis' through influence from πηρίς ''pērís'' 'scrotum'. The term was originally understood as a purely male body-part with the perineal raphe seen as a continuation of the scrotal septum since masculinization causes the development of a large anogenital distance in men, in comparison to the corresponding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perineum
The perineum in humans is the space between the anus and scrotum in the male, or between the anus and the vulva in the female. The perineum is the region of the body between the pubic symphysis (pubic arch) and the coccyx (tail bone), including the perineal body and surrounding structures. There is some variability in how the boundaries are defined. The perineal raphe is visible and pronounced to varying degrees. The perineum is an erogenous zone. The word perineum entered English from late Latin via Greek περίναιος ~ περίνεος ''perinaios, perineos'', itself from περίνεος, περίνεοι 'male genitals' and earlier περίς ''perís'' 'penis' through influence from πηρίς ''pērís'' 'scrotum'. The term was originally understood as a purely male body-part with the perineal raphe seen as a continuation of the scrotal septum since masculinization causes the development of a large anogenital distance in men, in comparison to the correspond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
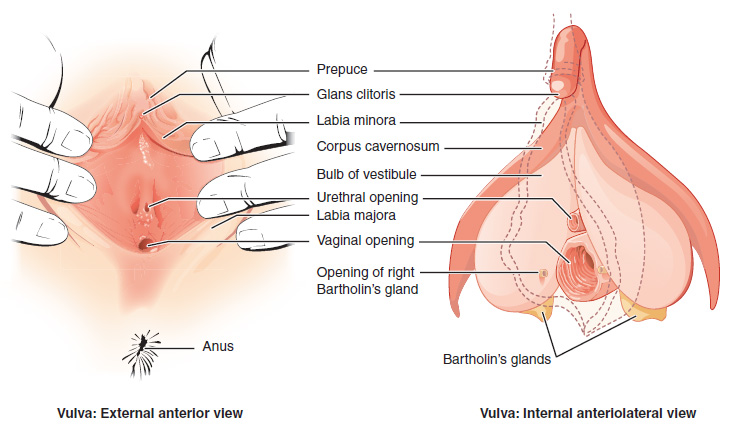
Vulva
The vulva (plural: vulvas or vulvae; derived from Latin for wrapper or covering) consists of the external female sex organs. The vulva includes the mons pubis (or mons veneris), labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vestibular bulbs, vulval vestibule, urinary meatus, the vaginal opening, hymen, and Bartholin's and Skene's vestibular glands. The urinary meatus is also included as it opens into the vulval vestibule. Other features of the vulva include the pudendal cleft, sebaceous glands, the urogenital triangle (anterior part of the perineum), and pubic hair. The vulva includes the entrance to the vagina, which leads to the uterus, and provides a double layer of protection for this by the folds of the outer and inner labia. Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the three pudendal arteries. The internal pudendal veins give drainage. Afferent l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulbospongiosus
The bulbospongiosus muscle (bulbocavernosus in older texts) is one of the superficial muscles of the perineum. It has a slightly different origin, insertion and function in males and females. In males, it covers the bulb of the penis. In females, it covers the vestibular bulb. In both sexes, it is innervated by the deep or muscular branch of the perineal nerve, which is a branch of the pudendal nerve. Structure In males, the bulbospongiosus is located in the middle line of the perineum, in front of the anus. It consists of two symmetrical parts, united along the median line by a tendinous perineal raphe. It arises from the central tendinous point of the perineum and from the median perineal raphe in front. In females, there is no union, nor a tendinous perineal raphe; the parts are disjoint primarily and arise from the same central tendinous point of the perineum, which is the tendon that is formed at the point where the bulbospongiosus muscle, superficial transverse perinea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the circulatory system is also known as ''peripheral blood'', and the blood cells it carries, ''peripheral blood cells''. Blood is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume), and contains proteins, glucose, mineral ions, hormones, carbon dioxide (plasma being the main medium for excretory product transportation), and blood cells themselves. Albumin is the main protein in plasma, and it functions to regulate the colloidal osmotic pressure of blood. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells (also called RBCs or erythrocytes), white blood cells (also called WBCs or leukocytes) and platelets (also called thrombocytes). The most abundant cells in verte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Postpartum Pelvic Floor Dysfunction
Pelvic floor dysfunction is a term used for a variety of disorders that occur when pelvic floor muscles and ligaments are impaired. The condition affects up to 50 percent of women who have given birth. Although this condition predominantly affects women, up to 16 percent of men are affected as well. Symptoms can include pelvic pain, pressure, pain during sex, urinary incontinence (UI), overactive bladder, bowel incontinence, incomplete emptying of feces, constipation, myofascial pelvic pain and pelvic organ prolapse. When pelvic organ prolapse occurs, there may be visible organ protrusion or a lump felt in the vagina or anus. Common treatments for pelvic floor dysfunction are surgery, medication, physical therapy and lifestyle modifications. The term "pelvic floor dysfunction" has been criticized since it does not represent a particular pelvic floor disorder. It has therefore been recommended that the term not be used in medical literature without additional clarification. Epid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
External Anal Sphincter
The external anal sphincter (or sphincter ani externus ) is a flat plane of skeletal muscle fibers, elliptical in shape and intimately adherent to the skin surrounding the margin of the anus. Anatomy The external anal sphincter measures about 8 to 10 cm in length, from its anterior to its posterior extremity, and is about 2.5 cm opposite the anus, the sphincter muscle retracts on defecating. It consists of two layers: ''superficial'' and ''deep''. * The superficial layer, constitutes the main portion of the muscle, and arises from a narrow tendinous band, the anococcygeal raphe, which stretches from the tip of the coccyx to the posterior margin of the anus; it forms two flattened planes of muscular tissue, which encircle the anus and meet in front to be inserted into the central tendinous point of the perineum, joining with the superficial transverse perineal muscle, the levator ani, and the bulbospongiosus muscle also known as the bulbocavernosus. * The deeper laye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Anal Sphincter
The internal anal sphincter, IAS, (or sphincter ani internus) is a ring of smooth muscle that surrounds about 2.5–4.0 cm of the anal canal; its inferior border is in contact with, but quite separate from, the external anal sphincter. It is myogenic in nature and playing phasic and tonic state for relaxation and contraction. This myogenic tone is based on Ca2+/Calmodulin/MLCK/RhoA/ROCK signaling cascade pathway. Recent studies suggested, BDNF is the member of the neurotrophin family; having next target for basal IAS and NANC relaxation. It is about 5 mm thick, and is formed by an aggregation of the involuntary circular fibers of the rectum. Its lower border is about 6 mm from the orifice of the anus. Actions Its action is entirely involuntary, and it is in a state of continuous maximal contraction. It helps the Sphincter ani externus to occlude the anal aperture and aids in the expulsion of the feces. Sympathetic fibers from the superior rectal and hypogastric pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |