Languages of Argentina on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 From the Mataco or Mataguyao group:
* Iyojwa'ja Chorote, Ch'orti', Yofuaha or Eklenjuy is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family and is a distinct language from Chorote Iyo'wujwa. It was spoken in 2007 by some 800 people in the Salta Province.
* Chorote iyo'wujwa, Ch'orti', Manjuy, Majui is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family. There were some 1,500 speakers accounted for in 2007, 50 percent of which were monolingual.
* Nivaclé is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family, It has about 200 speakers in the Northeast of the Formosa Province. The term "chulupí" and similar terms are pejoratives and are like the word "guaycurú" (that in Guarani means something like "barbarians") which comes from the Guarani invaders.
*
From the Mataco or Mataguyao group:
* Iyojwa'ja Chorote, Ch'orti', Yofuaha or Eklenjuy is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family and is a distinct language from Chorote Iyo'wujwa. It was spoken in 2007 by some 800 people in the Salta Province.
* Chorote iyo'wujwa, Ch'orti', Manjuy, Majui is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family. There were some 1,500 speakers accounted for in 2007, 50 percent of which were monolingual.
* Nivaclé is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family, It has about 200 speakers in the Northeast of the Formosa Province. The term "chulupí" and similar terms are pejoratives and are like the word "guaycurú" (that in Guarani means something like "barbarians") which comes from the Guarani invaders.
*
 In addition to surviving indigenous languages, before the contact with Europeans and during some time during the
In addition to surviving indigenous languages, before the contact with Europeans and during some time during the
Academia Argentina de Letras - Argentine Academy
Asociación de Centros de Idiomas - Association of Language Centres
Spanish in Argentina
The Dante Alighieri Society of Buenos Aires
{{Authority control

Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
is the language that is predominantly understood and spoken as a first, or second language by nearly all of the population of Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
. According to the latest estimations, the population is currently greater than 45 million.
English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
is another important language in Argentina and is obligatory in primary school instruction in various provinces. Argentina is the only Latin American country characterized as "high aptitude" in English, being placed 15th globally in the year 2015, according to a report from the English Aptitude Index. In 2017, Argentina fell ten places from its best position and fell to 25th place, though it continues to be the second highest ranked Ibero-American
Ibero-America ( es, Iberoamérica, pt, Ibero-América) or Iberian America is a region in the Americas comprising countries or territories where Spanish or Portuguese are predominant languages (usually former territories of Portugal or Spain). P ...
, after Portugal.
Guarani and Quechua
Quechua may refer to:
*Quechua people, several indigenous ethnic groups in South America, especially in Peru
*Quechuan languages, a Native South American language family spoken primarily in the Andes, derived from a common ancestral language
**So ...
are other important languages in Argentina with 200,000 speakers and 65,000 speakers respectively.
Fifteen Indigenous American languages currently exist and five others (today extinct) existed in different regions. The vernacular Indigenous American languages (native to the Argentine territory) are spoken by very few people. In addition there is Lunfardo
Lunfardo (; from the Italian ''lombardo'' or inhabitant of Lombardy in the local dialect) is an argot originated and developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries in the lower classes in Buenos Aires and from there spread to other urban are ...
, a slang or a type of pidgin with original words from many languages, among these languages are ones from the Italian Peninsula, like Piedmontese
Piedmontese (; autonym: or , in it, piemontese) is a language spoken by some 2,000,000 people mostly in Piedmont, northwestern region of Italy. Although considered by most linguists a separate language, in Italy it is often mistakenly reg ...
, Ligurian, and others like Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
, etc., and have been seen in the Río de la Plata
The Río de la Plata (, "river of silver"), also called the River Plate or La Plata River in English, is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River at Punta Gorda. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean and fo ...
area since at least 1880. There is also Portuñol
Portuñol (Spanish spelling) or Portunhol (Portuguese spelling) () is a portmanteau of the words portugués/português ("Portuguese") and español/espanhol ("Spanish"), and is the name often given to any non-systematic mixture of Portuguese and ...
, a pidgin of Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
and Spanish spoken since approximately 1960 in the areas of Argentina that border Brazil.
Another native language is Argentine Sign Language
Argentine Sign Language (Spanish: ''Lengua de señas argentina''; LSA) is used in Argentina. Deaf people attend separate schools, and use local sign languages out of class. A manual alphabet for spelling Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items f ...
(LSA), which is signed by deaf communities. It emerged in 1885.
After the above-mentioned languages German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
follows (around 200,000, including a significant number of the Volga German
The Volga Germans (german: Wolgadeutsche, ), russian: поволжские немцы, povolzhskiye nemtsy) are ethnic Germans who settled and historically lived along the Volga River in the region of southeastern European Russia around Saratov ...
dialect and of the Plautdietsch language). Multitude of Old World and immigrant languages are spoken in their respective ethnic communities throughout the country; these are namely Albanian, Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
, Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
, Asturian, Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
, Belarusian, Bosnian, Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
, Catalan
Catalan may refer to:
Catalonia
From, or related to Catalonia:
* Catalan language, a Romance language
* Catalans, an ethnic group formed by the people from, or with origins in, Northern or southern Catalonia
Places
* 13178 Catalan, asteroid #1 ...
, Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
, Croatian, Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
* Czech, ...
, Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
, Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
, Estonian, Finnish
Finnish may refer to:
* Something or someone from, or related to Finland
* Culture of Finland
* Finnish people or Finns, the primary ethnic group in Finland
* Finnish language, the national language of the Finnish people
* Finnish cuisine
See also ...
, French, Galician, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
, Hungarian, Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
, Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
, Korean
Korean may refer to:
People and culture
* Koreans, ethnic group originating in the Korean Peninsula
* Korean cuisine
* Korean culture
* Korean language
**Korean alphabet, known as Hangul or Chosŏn'gŭl
**Korean dialects and the Jeju language
** ...
, Latvian, Lithuanian, Macedonian, Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
, Occitan Occitan may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania territory in parts of France, Italy, Monaco and Spain.
* Something of, from, or related to the Occitania administrative region of France.
* Occitan language, spoken in parts o ...
, Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
, Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
, Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
, Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
*** Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
** Romanian cuisine, tradition ...
, Russian
Russian(s) refers to anything related to Russia, including:
*Russians (, ''russkiye''), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*Rossiyane (), Russian language term for all citizens and peo ...
, Serbian, Slovene, Swedish
Swedish or ' may refer to:
Anything from or related to Sweden, a country in Northern Europe. Or, specifically:
* Swedish language, a North Germanic language spoken primarily in Sweden and Finland
** Swedish alphabet, the official alphabet used by ...
, Turkish, Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
,
Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
and Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ve ...
. Most of these languages have, with the exception of Chinese and Plautdietsch, very few speakers and are usually only spoken in family environments.
Official language
The Republic ofArgentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
has not established, legally, an official language; however, Spanish has been utilized since the founding of the Argentine state by the administration of the Republic and is used in education in all public establishments, so much so that in basic and secondary levels there is a mandatory subject of Spanish (a subject called "language.") Since 1952, The Argentine Academy of Letters
The ''Academia Argentina de Letras'' is the academy in charge of studying and prescribing the use of the Spanish language in Argentina. Since its establishment, on August 13, 1931, it has maintained ties with the Royal Spanish Academy and the othe ...
, which was founded in 1931, has regularly collaborated with The Royal Spanish Academy to register local variants.
Even though the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
establishes the jurisdiction of the National Congress "to recognize the ethnic and cultural pre-existence of indigenous peoples of Argentina.," the native languages have not been recognized as official, except in the provinces of Chaco and Corrientes
Corrientes (; Guaraní: Taragüí, literally: "Currents") is the capital city of the province of Corrientes, Argentina, located on the eastern shore of the Paraná River, about from Buenos Aires and from Posadas, on National Route 12. It ha ...
.
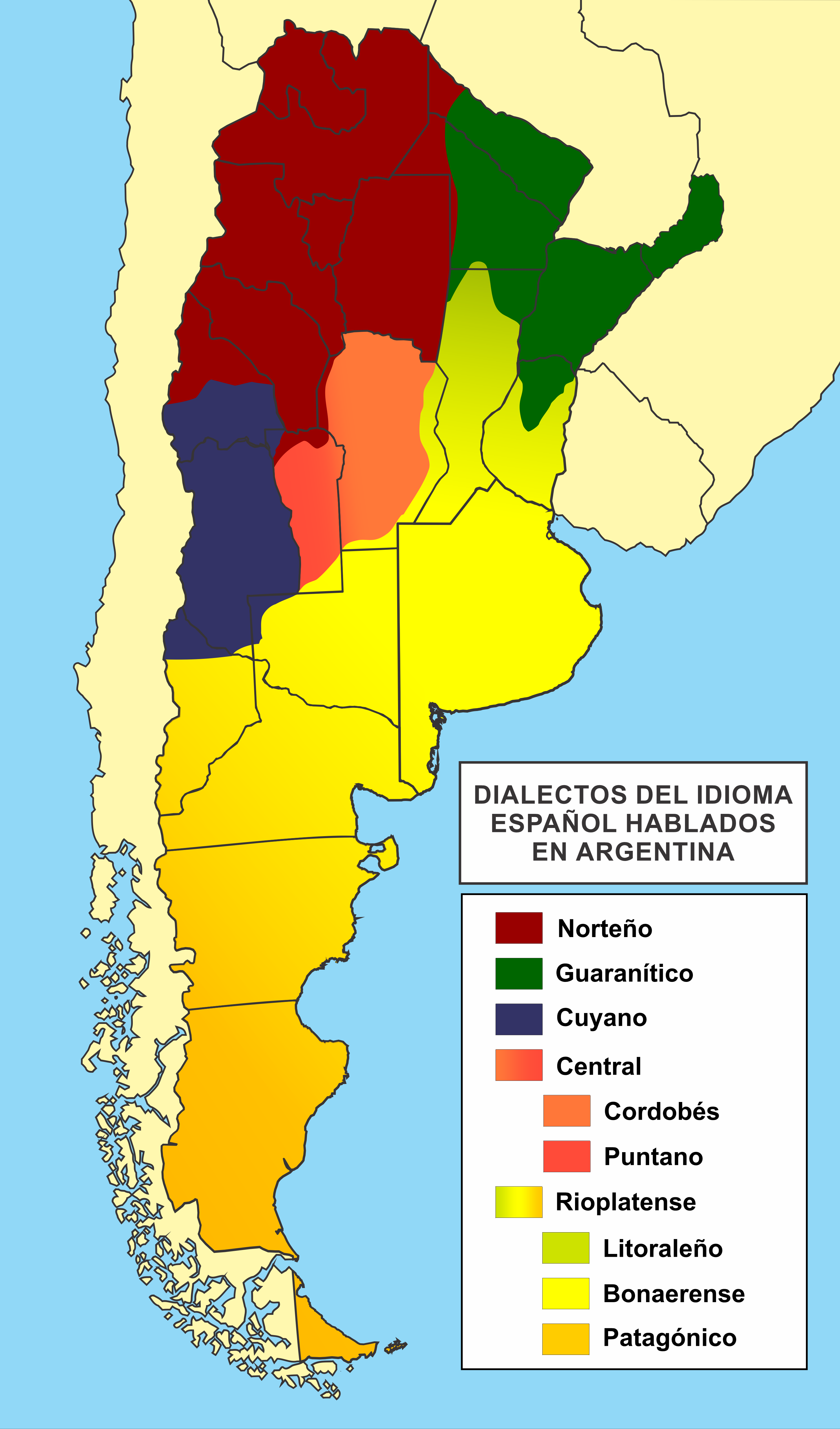
The most prevalent dialect in Argentina is '' Rioplatense'', whose speakers are located primarily in the basin of the Río de la Plata
The Río de la Plata (, "river of silver"), also called the River Plate or La Plata River in English, is the estuary formed by the confluence of the Uruguay River and the Paraná River at Punta Gorda. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean and fo ...
. There is also Cuyo Spanish
Cuyo Spanish or Cuyano Spanish (Castellano Cuyano) is the dialect of Spanish that evolved in the historical province of Cuyo and that is now spoken in the Argentine provinces of Mendoza and San Juan. To a lesser extent it is also spoken in the ...
and Cordobés Spanish. In the north, Andean Spanish
Andean Spanish is a dialect of Spanish spoken in the central Andes, from southern Colombia, with influence as far south as northern Chile and Northwestern Argentina, passing through Ecuador, Peru, and Bolivia. It is influenced principally by ...
is spoken and in the northeast there is a great influence from Paraguayan Spanish
Paraguayan Spanish ( es, español paraguayo) is the set of dialects of the Spanish language spoken in Paraguay. In addition, it influences the speech of the Argentine provinces of Misiones, Corrientes, Formosa, and, to a lesser extent, Chaco. ...
.
Argentina is one of several Spanish-speaking countries (along with Uruguay
Uruguay (; ), officially the Oriental Republic of Uruguay ( es, República Oriental del Uruguay), is a country in South America. It shares borders with Argentina to its west and southwest and Brazil to its north and northeast; while bordering ...
, Paraguay
Paraguay (; ), officially the Republic of Paraguay ( es, República del Paraguay, links=no; gn, Tavakuairetã Paraguái, links=si), is a landlocked country in South America. It is bordered by Argentina to the south and southwest, Brazil to th ...
, El Salvador, Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the countr ...
, Honduras and Costa Rica) that almost universally use what is known as ''voseo
In Spanish grammar, () is the use of as a second-person singular pronoun, along with its associated verbal forms, in certain regions where the language is spoken. In those regions it replaces , i.e. the use of the pronoun and its verbal fo ...
''—the use of the pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase.
Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not c ...
''vos'' instead of ''tú'' (the familiar "you") as well as its corresponding verb forms.
A phonetic study conducted by the Laboratory for Sensory Investigations of ONICETand the University of Toronto
The University of Toronto (UToronto or U of T) is a public university, public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park (Toronto), Queen's Park. It was founded by royal charter in 1827 ...
showed that the intonation Porteño Spanish is unlike that of other Spanish varieties, and suggested that it may be a result of convergence with Italian. Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
immigration influenced ''Lunfardo
Lunfardo (; from the Italian ''lombardo'' or inhabitant of Lombardy in the local dialect) is an argot originated and developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries in the lower classes in Buenos Aires and from there spread to other urban are ...
'', the slang spoken in the Río de la Plata region, permeating the vernacular vocabulary of other regions as well.
As in other large countries, the accents vary depending on geographical location. Extreme differences in pronunciation can be heard within Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
. One notable pronunciation difference found in Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
is the "sh" sounding y and ll. In most Spanish speaking countries the letters y and ll are pronounced somewhat like the "y" in yo-yo, however in most parts of Argentina they are pronounced like "sh" in English (such as "shoe") or like "zh" (such as the sound the makes in "measure").
In many of the central and north-eastern areas of the country, the trilled /r/ takes on the same sound as the and ('zh' - a voiced palatal fricative sound, similar to the "s" in the English pronunciation of the word "vision".) For Example, "Río Segundo" sounds like "Zhio Segundo" and "Corrientes" sounds like "Cozhientes".
The ISO639 code for Argentine Spanish is "es-AR".
Classification
The Indo-European languages spoken in Argentina by stable communities fall into five branches:Romance
Romance (from Vulgar Latin , "in the Roman language", i.e., "Latin") may refer to:
Common meanings
* Romance (love), emotional attraction towards another person and the courtship behaviors undertaken to express the feelings
* Romance languages, ...
(Spanish, Italian, and Portuguese), West Germanic
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages). The West Germanic branch is classically subdivided into ...
(English, Plautdietsch and standard German), Celtic languages
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edwar ...
(Welsh), and Central Indo-Aryan (Romani).
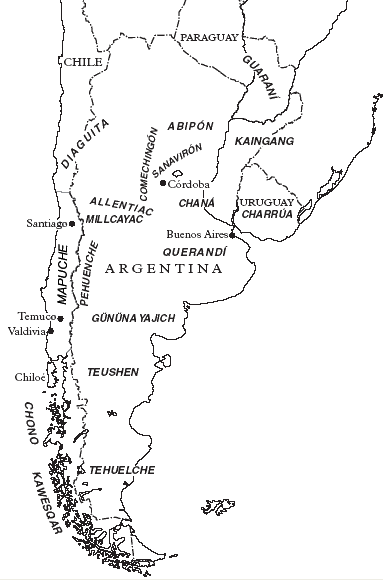
On the other hand, the indigenous languages of Argentina
This is a list of Indigenous languages that are or were spoken in the present territory of Argentina.
Although the official language of Argentina is Spanish, several Indigenous languages are in use. Most are spoken only within their respective in ...
are very diverse and fall into different linguistic families...
(†): Extinct language
Living languages
In addition to Spanish, the following living languages are registered in Argentina with local growth:Other European languages
*Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
is spoken by more than 1.5 million people in Argentina; it is the second most spoken native language in the nation. Italian immigration
The Italian diaspora is the large-scale emigration of Italians from Italy.
There were two major Italian diasporas in Italian history. The first diaspora began around 1880, two decades after the Risorgimento, Unification of Italy, and ended in the ...
, which effectively began in the middle of the 19th century and reached its peak in the first two decades of the 20th century, made a lasting and significant impact on the pronunciation and vernacular of Argentina's variety of Spanish, giving it an Italian flair. In fact, Italian dialects (not Standard Italian) have contributed so much to Rioplatense that many foreigners mistake it for Italian.
* Portuñol
Portuñol (Spanish spelling) or Portunhol (Portuguese spelling) () is a portmanteau of the words portugués/português ("Portuguese") and español/espanhol ("Spanish"), and is the name often given to any non-systematic mixture of Portuguese and ...
is spoken in areas that border Brazil. It is a pidgin of Spanish and Portuguese.
* German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
conserved by the descendants of the immigrants coming directly from Germany as well as other German-speaking countries like Switzerland and Austria. Descendants of Volga Germans
The Volga Germans (german: Wolgadeutsche, ), russian: поволжские немцы, povolzhskiye nemtsy) are ethnic Germans who settled and historically lived along the Volga River in the region of southeastern European Russia around Saratov a ...
of the Volga River in Russia, speak German especially in the Santa Fe and Entre Ríos provinces, part of La Pampa
La Pampa () is a sparsely populated province of Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it ...
, and various sectors of the Buenos Aires Province.
* Lunfardo
Lunfardo (; from the Italian ''lombardo'' or inhabitant of Lombardy in the local dialect) is an argot originated and developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries in the lower classes in Buenos Aires and from there spread to other urban are ...
, a dialect that originated in Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
, is strongly influenced by immigrant languages; primarily by dialects from different Italian regions, but also from Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
, Galician, French, English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
and Yiddish
Yiddish (, or , ''yidish'' or ''idish'', , ; , ''Yidish-Taytsh'', ) is a West Germanic language historically spoken by Ashkenazi Jews. It originated during the 9th century in Central Europe, providing the nascent Ashkenazi community with a ve ...
. They provided numerous lexical and syntactic elements to the Argentine language, as well as the typical pronunciation of Rioplatense Spanish
Rioplatense Spanish (), also known as Rioplatense Castilian, is a variety of Spanish spoken mainly in and around the Río de la Plata Basin of Argentina and Uruguay. It is also referred to as River Plate Spanish or Argentine Spanish. It is ...
. Lunfardo has exercised a strong influence on the informal speech throughout the country, especially through its use in tango
Tango is a partner dance and social dance that originated in the 1880s along the Río de la Plata, the natural border between Argentina and Uruguay. The tango was born in the impoverished port areas of these countries as the result of a combina ...
lyrics and Porteño poetry.
* Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
spoken in Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and g ...
: Indo-European language of the Brittonic Celtic languages
The Celtic languages ( usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edwar ...
group, spoken as a second language
A person's second language, or L2, is a language that is not the native language (first language or L1) of the speaker, but is learned later. A second language may be a neighbouring language, another language of the speaker's home country, or a fo ...
by descendants of Welsh immigrants from the second half of the 19th century) in Chubut Province
Chubut ( es, Provincia del Chubut, ; cy, Talaith Chubut) is a province in southern Argentina, situated between the 42nd parallel south (the border with Río Negro Province), the 46th parallel south (bordering Santa Cruz Province), the Andes rang ...
. An estimation in 2017 indicates that the number of speakers was no greater than 5,000.
* Plautdietch or low German, spoken by Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radi ...
colonies disseminated especially in the La Pampa Province, although it is also spoken in small communities in other provinces.
*English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
is the native language of the population of the Falkland Islands. The islands are part of Argentina according to its constitution, although in reality they are British Overseas Territories.
* See also: Belgranodeutsch, Paraná-Wolga-Deutsch and Argentinien-schwyzertütsch dialect.
Sign language
Argentine Sign Language
Argentine Sign Language (Spanish: ''Lengua de señas argentina''; LSA) is used in Argentina. Deaf people attend separate schools, and use local sign languages out of class. A manual alphabet for spelling Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items f ...
, understood by around two million deaf people of Argentina, their instructors, descendants, and others. There are different regional variants, such as in Cordoba.
Quechuan languages
Southern Quechua
Southern Quechua ( qu, Urin qichwa, es, quechua sureño), or simply Quechua (Qichwa or Qhichwa), is the most widely spoken of the major regional groupings of mutually intelligible dialects within the Quechua language family, with about 6.9 mil ...
: from the family of Quechuan languages. There are seven variations present that are marked by their geographical origin, detailed here are South Bolivian Quechua
South Bolivian Quechua, also known as Central Bolivian Quechua, is a dialect of Southern Quechua spoken in Bolivia and adjacent areas of Argentina, where it is also known as ''Colla''. It is not to be confused with North Bolivian Quechua, which ...
and Santiagueño Quechua:
* South Bolivian Quechua
South Bolivian Quechua, also known as Central Bolivian Quechua, is a dialect of Southern Quechua spoken in Bolivia and adjacent areas of Argentina, where it is also known as ''Colla''. It is not to be confused with North Bolivian Quechua, which ...
is spoken by inhabitants of Puna and their descendants. This same variety is spoken in all of Jujuy
San Salvador de Jujuy (), commonly known as Jujuy and locally often referred to as San Salvador, is the capital and largest city of Jujuy Province in northwest Argentina. Also, it is the seat of the Doctor Manuel Belgrano Department. It lies near ...
, Salta
Salta () is the capital and largest city in the Argentine province of the same name. With a population of 618,375 according to the 2010 census, it is also the 7th most-populous city in Argentina. The city serves as the cultural and economic ce ...
, and Tucumán; after Spanish it is the second most widespread language of the country and the most important Indigenous language of the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
. In 2004, there were speakers.
* Santiagueño Quechua: which is different from Bolivian Quechua, though it has an 81 percent lexical similarity, is spoken by 100,000 people, according to data from Censabella (1999), even though other estimations raise the figure to 140,000 or 160,000 speakers in the Santiago del Estero Province
Santiago del Estero (), also known simply as Santiago, is a province in the north of Argentina. Neighboring provinces, clockwise from the north, are Salta, Chaco, Santa Fe, Córdoba, Catamarca and Tucumán.
History
The indigenous inhabita ...
, southeast of the Salta Province and Buenos Aires. A department for its study and conservation exists in the National University of Santiago del Estero. The smallest calculation of talks about a minimum of 60,000 speakers in 2000. Its speakers are currently composed of a Creoyle population that does not self-recognize as indigenous (even though it admits an indigenous past).
Tupi-Guarani languages
In the provinces ofCorrientes
Corrientes (; Guaraní: Taragüí, literally: "Currents") is the capital city of the province of Corrientes, Argentina, located on the eastern shore of the Paraná River, about from Buenos Aires and from Posadas, on National Route 12. It ha ...
, Misiones
Misiones (, ''Missions'') is one of the 23 provinces of Argentina, located in the northeastern corner of the country in the Mesopotamia region. It is surrounded by Paraguay to the northwest, Brazil to the north, east and south, and Corrientes P ...
, Chaco, Formosa, Entre Ríos, and Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires ( or ; ), officially the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires ( es, link=no, Ciudad Autónoma de Buenos Aires), is the capital and primate city of Argentina. The city is located on the western shore of the Río de la Plata, on South ...
dialects of Argentine Guarani are spoken or known by nearly one million people, including Paraguayan immigrants that speak Paraguayan Guarani or Jopara. In Corrientes, the Argentine Guarani dialect was decreed co-official in 2004 and made obligatory in educational instruction and the government.
* Chiripa is a language family of Tupi-Guarani, subgroup I. There are a few speakers in the Misiones Province and among Paraguayan immigrants.
* Mbyá is from the Tupi-Guarani family, subgroup I. It has a 75 percent lexical similarity with Paraguayan Guarani. In 2012, some speakers were counted in the Misiones Province.
* Eastern Bolivian Guarani
Eastern may refer to:
Transportation
*China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai
*Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways
*Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991
*Eastern Air Li ...
is also from the Tupi-Guarani family, subgroup I. Some 15 000 speakers in the provinces of Salta and Formosa.
* Correntino Guarani or Argentine Guarani pertains to the Tupi-Guarani family. It is spoken (together with Spanish) by nearly 70 percent of the population with an origin from the Corrientes Province (around 350,000 speakers). The Correntino government decreed in 2004 the co-officiality of the Guarani language and its obligatory use in teaching and government, even though it still has not been regulated.
* Kaiwá, called pai tavyterá in Paraguay, is from the Tupi-Guarani family, subgroup I. It is spoken by no more than 510 people in Misiones Province.
* Tapieté from the Tupi-Guarani family, subgroup I, is spoken by some 100 speakers of a village near Tartagal, Salta
Tartagal () is a tropical city in northern Argentina, in the province of Salta. It is located in the northeast of the province, within the General José de San Martín Department, of which it is the capital. It is located in the Yungas jungle, at ...
.
* Missionary Guarani Jesuit was an old variety of Guarani spoken by Jesuit Missionaries became extinct around 1800.
Mapuche
TheMapuche language
Mapuche (, Mapuche & Spanish: , or Mapudungun; from ' 'land' and ' 'speak, speech') is an Araucanian language related to Huilliche spoken in south-central Chile and west-central Argentina by the Mapuche people (from ''mapu'' 'land' and ''che ...
is an isolated language that had approximately speakers in the provinces of Neuquén
Neuquén (; arn, Nehuenken) is the capital city of the Argentine province of Neuquén and of the Confluencia Department, located in the east of the province. It occupies a strip of land west of the confluence of the Limay and Neuquén river ...
, Río Negro, Chubut, and Santa Cruz in 2004, with an ethnic population of people.
Aymara
Central Aymara
Aymara (; also ) is an Aymaran language spoken by the Aymara people of the Bolivian Andes. It is one of only a handful of Native American languages with over one million speakers.The other native American languages with more than one million s ...
is a language of the Aymaran
Aymaran (also Jaqi or Aru) is one of the two dominant language families in the central Andes alongside Quechuan. The family consists of Aymara, widely spoken in Bolivia, and the endangered Jaqaru and Kawki languages of Peru.
Hardman (1978) prop ...
group, spoken by inhabitants of Jujuy
San Salvador de Jujuy (), commonly known as Jujuy and locally often referred to as San Salvador, is the capital and largest city of Jujuy Province in northwest Argentina. Also, it is the seat of the Doctor Manuel Belgrano Department. It lies near ...
, of the North of Salta, besides the immigrants of Puna and of Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = National seal
, national_motto = "Firm and Happy f ...
.
Mataco-Guaicuru languages
 From the Mataco or Mataguyao group:
* Iyojwa'ja Chorote, Ch'orti', Yofuaha or Eklenjuy is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family and is a distinct language from Chorote Iyo'wujwa. It was spoken in 2007 by some 800 people in the Salta Province.
* Chorote iyo'wujwa, Ch'orti', Manjuy, Majui is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family. There were some 1,500 speakers accounted for in 2007, 50 percent of which were monolingual.
* Nivaclé is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family, It has about 200 speakers in the Northeast of the Formosa Province. The term "chulupí" and similar terms are pejoratives and are like the word "guaycurú" (that in Guarani means something like "barbarians") which comes from the Guarani invaders.
*
From the Mataco or Mataguyao group:
* Iyojwa'ja Chorote, Ch'orti', Yofuaha or Eklenjuy is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family and is a distinct language from Chorote Iyo'wujwa. It was spoken in 2007 by some 800 people in the Salta Province.
* Chorote iyo'wujwa, Ch'orti', Manjuy, Majui is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family. There were some 1,500 speakers accounted for in 2007, 50 percent of which were monolingual.
* Nivaclé is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family, It has about 200 speakers in the Northeast of the Formosa Province. The term "chulupí" and similar terms are pejoratives and are like the word "guaycurú" (that in Guarani means something like "barbarians") which comes from the Guarani invaders.
* Wichí Lhamtés Güisnay
Wichí Lhamtés Güisnay or Wiznay is a Wichí language. Wichí Lhamtés Güisnay had an estimated 15,000 speakers in 1999 in Argentina. The language is centered in the Pilcomayo River region. Other names for the language include Güisnay, Mataco ...
is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family and is spoken by some people in the Pilcomayo River
Pilcomayo (in Hispanicized spelling) (Quechua Pillkumayu or Pillku Mayu, ''pillku'' red, ''mayu'' river, "red river", Guarani Ysyry Araguay ) is a river in central South America. At long, it is the longest western tributary of the Paraguay River ...
area, Formosa. The term "mataco" used to name the languages and towns of the Wichí people
The Wichí are an indigenous people of South America. They are a large group of tribes ranging about the headwaters of the Bermejo River and the Pilcomayo River, in Argentina and Bolivia.
Notes on designation
This ethnic group was named by the ...
is a pejorative and comes from the invaders that were speakers of Runasimi (Quechua).
* Wichí Lhamtés Vejoz
Wichí Lhamtés Vejoz is a Mataco-Guaicuru language of Argentina and Bolivia. Speakers are concentrated in northern parts of Chaco, Formosa, Salta, Jujuy Provinces, as well as west of Toba, the upper Bermejo River valley, and Pilcomayo River. Th ...
is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family. There are calculated to be speakers distributed throughout the Chaco, Formosa, and Salta Provinces. Its main area of influence, in general, is found at the west of the area of the Toba people
The Toba people, also known as the Qom people, are one of the largest indigenous groups in Argentina who historically inhabited the region known today as the Pampas of the Central Chaco. During the 16th century, the Qom inhabited a large part of ...
, along the superior course of the Pilcomayo River. It is unintelligible with other languages of Gran Chaco
The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato ...
, and is also spoken in Bolivia.
From the Guaicuru group:
* Mocoví
The Mocoví ( Mocoví: ''moqoit'') are an indigenous people of the Gran Chaco region of South America. They speak the Mocoví language and are one of the ethnic groups belonging to the Guaycuru peoples. In the 2010 Argentine census, 22,439 peopl ...
is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family. In 2012, there were some speakers in Formosa, in the south of Chaco and the Northeast of the Santa Fe Province.
* Pilagá is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family and is spoken by some 2000 to 5000 people in the basins of the Pilcomayo and Bermejo rivers, providences Formosa and Chaco. In 2004, it was spoken by 4000 people.
* Qom is also from the Mataco-Guaicuru family. Spoken in the year 2006 by 40,000 to 60,000 people in the East of Formosa and Chaco. In 2000 it was spoken by 21,410 indigenous people (19,800 in Argentina).
In danger of extinction
* Tehuelche is from the Chonan family. In the 1966 census, there were hardly 200 speakers registered in Santa Cruz.Extinct languages
 In addition to surviving indigenous languages, before the contact with Europeans and during some time during the
In addition to surviving indigenous languages, before the contact with Europeans and during some time during the Colonization of the Americas
During the Age of Discovery, a large scale European colonization of the Americas took place between about 1492 and 1800. Although Norse colonization of North America, the Norse had explored and colonized areas of the North Atlantic, colonizin ...
in Argentina they spoke the following languages, that are currently extinct:
* Abipón is from the Mataco-Guaicuru family and was spoken by the Abipón people, and was related to Kadiweu. There do not appear to be living speakers of this language.
* Cacán was spoken by the Diaguita
The Diaguita people are a group of South American indigenous people native to the Chilean Norte Chico and the Argentine Northwest. Western or Chilean Diaguitas lived mainly in the Transverse Valleys which incised in a semi-arid environment. Ea ...
and Calchaquí The Calchaquí or Kalchakí were a tribe of South American Indians of the Diaguita group, now extinct, who formerly occupied northern Argentina. Stone and other remains prove them to have reached a high degree of civilization. Under the leadership ...
people in northern Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
and Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
. It became extinct during the late 17th century or early 18th century. The language was documented by the Jesuit Alonso de Bárcena, but the manuscript is lost. Genetic affiliation of the language remains unclear, and due to the extremely limited number of known words, it has not been possible to conclusively link it to any existing language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ''ancestral language'' or ''parental language'', called the proto-language of that family. The term "family" reflects the tree model of language origination in h ...
.
* Chané
Chané is the collective name for the southernmost Arawakan-speaking peoples. They lived in the plains of the northern Gran Chaco and in the foothills of the Andes in Paraguay, Brazil, Bolivia, and Argentina. The historical Chané are divided i ...
is from that Arawakan language family, without a subgroup classification. It has been compared to Guana or Kashika language of Paraguay, or Terêna from Brazil, but both are distinct. It was spoken in Salta
Salta () is the capital and largest city in the Argentine province of the same name. With a population of 618,375 according to the 2010 census, it is also the 7th most-populous city in Argentina. The city serves as the cultural and economic ce ...
some 300 years ago. The ethnic group is named Izoceño, and now they speak Guarani.
* Kunza was the language of the Atacama people
The Atacama people, also called Atacameño, are indigenous people from the Atacama Desert and altiplano region in the north of Chile and Argentina and southern Bolivia, mainly Antofagasta Region.
According to the Argentinean Census in 2010, 13,93 ...
and is also extinct in Chile. Due to the lack of information it is considered an isolated language.
* Henia-Camiare was spoken by the Comechingón people. There are not sufficient elements to establish its connection to another language, nor is it possible to try to reconstruct it.
* Querandí
The Querandí were one of the Het peoples, indigenous South Americans who lived in the Pampas area of Argentina; specifically, they were the eastern Didiuhet. The name Querandí was given by the Guaraní people, as they would consume animal fat i ...
is the language of the old inhabitants of Pampas
The Pampas (from the qu, pampa, meaning "plain") are fertile South American low grasslands that cover more than and include the Argentine provinces of Buenos Aires, La Pampa, Santa Fe, Entre Ríos, and Córdoba; all of Uruguay; and Brazi ...
also known as the Querandí
The Querandí were one of the Het peoples, indigenous South Americans who lived in the Pampas area of Argentina; specifically, they were the eastern Didiuhet. The name Querandí was given by the Guaraní people, as they would consume animal fat i ...
people. Its existence as the only language is speculative. The few known words of the language have been related to Puelche and the Chonan languages
The Chonan languages are a family of indigenous American languages which were spoken in Tierra del Fuego and Patagonia. Two Chon languages are well attested: Selk'nam (or Ona), spoken by the people of the same name who occupied territory in th ...
.
* Allentiac and Millcayac are languages from the Huarpean family that were spoken in the Cuyo region. The shortage of remaining elements hinders better classification of these languages.
* Lule-toconoté is considered to be of the Lule-Vilela family. Some authors affirm that Lule and Toconoté language were not the same language, spoken by the people that inhabited part of what is today known as Santiago del Estero and by those that migrated to Chaco in the mid-17th century.
* Ona
Ona or ONA may refer to:
Anthropology
* Ona people, an indigenous people of southern Argentina and Chile
** Ona language, a language once spoken in Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego
* Ona, a pre-Aksumite culture in Sembel, Eritrea
Geography
* On ...
is from the Chonan family that went extinct in the 1990s or early 2000s.
* Puelche is possibly loosely related to the Chonan languages. Rodolfo Casamiquela worked with the last speakers in the middle of the 20th century.
* Yaghan was spoken by aboriginal people in the Southern coastal areas of Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of the Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla ...
. It became extinct in Argentina in the beginning of the 20th century, even though it was conserved in a grand dictionary elaborated by Thomas Bridges and some important words gave name to places in Argentina such as Ushuaia
Ushuaia ( , ) is the capital of Tierra del Fuego, Antártida e Islas del Atlántico Sur Province, Argentina. With a population of nearly 75,000 and a location below the 54th parallel south latitude, Ushuaia claims the title of world's souther ...
, Lapataia, Tolhuin
Tolhuin is a town in the province of Tierra del Fuego, Argentina. It has 2,949 inhabitants as per the . It is located on the eastern shore of Lake Fagnano, in the southern part of the Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego. It is the third largest settlem ...
, etc. Cristina Calderón
Cristina Calderón Harban (24 May 1928 – 16 February 2022) was a Chilean ethnographer, craftswoman, writer and cultural activist who was the last living full-blooded Yaghan person after the death of her 84-year-old sister Úrsula in 2005. By ...
is an elderly Chilean woman living in Navarino Island
Navarino Island () is a Chilean island located between Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, to the north, and Cape Horn, to the south. The island forms part of the Commune of Cabo de Hornos, the southernmost commune in Chile and in the world, belong ...
, and the last living full-bloded Yaghan person; after the death of her sister Úrsula in 2005, Cristina became the last living native speaker of the Yaghan language..
* Missionary Guarani was spoken in the area of the Misiones Jesuit Guaranies, between 1632 and 1767, disappearing permanently around 1870, but left important written documents.
* Manek'enk
The Haush or Manek'enk were an indigenous people who lived on the Mitre Peninsula of the Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego. They were related culturally and linguistically to the Ona or Selk'nam people who also lived on the Isla Grande de Tierra ...
(or Haush), the language of the Haush people
The Haush or Manek'enk were an indigenous people who lived on the Mitre Peninsula of the Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego. They were related culturally and linguistically to the Ona or Selk'nam people who also lived on the Isla Grande de Tierra ...
, was spoken on the far eastern tip of the island of Tierra del Fuego. It was part of the Chonan language family. Before 1850, an estimated 300 people spoke Manek'enk; the last speaker died around 1920.
See also
*Demographics of Argentina
This is a demography of Argentina including population density, ethnicity, economic status and other aspects of the population.
In the , Argentina had a population of 40,117,096 inhabitants, and preliminary results from the counted 47,327,407 ...
* Indigenous peoples in Argentina
Argentina has 35 indigenous groups (often referred to as Argentine Amerindians or Native Argentines) according to the Complementary Survey of the Indigenous Peoples of 2004, the Argentine government's first attempt in nearly 100 years to recogni ...
* Immigration to Argentina
Immigration to Argentina began in several millennia BCE with the arrival of different populations from Asia to the Americas through Beringia, according to the most accepted theories, and were slowly populating the Americas. Upon arrival of ...
* List of indigenous languages of Argentina
Notes
References
Further reading
* Argentina *External links
Academia Argentina de Letras - Argentine Academy
Asociación de Centros de Idiomas - Association of Language Centres
Spanish in Argentina
The Dante Alighieri Society of Buenos Aires
{{Authority control