|
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, sometimes referred to as Latin languages or Neo-Latin languages, are the various modern languages that evolved from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages in the Indo-European language family. The five most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are Spanish (489 million), Portuguese (283 million), French (77 million), Italian (67 million) and Romanian (24 million), which are all national languages of their respective countries of origin. By most measures, Sardinian and Italian are the least divergent from Latin, while French has changed the most. However, all Romance languages are closer to each other than to classical Latin. There are more than 900 million native speakers of Romance languages found worldwide, mainly in the Americas, Europe, and parts of Africa. The major Romance languages also have many non-native speakers and are in widespread use as linguae francae.M. Paul Lewis,Summary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
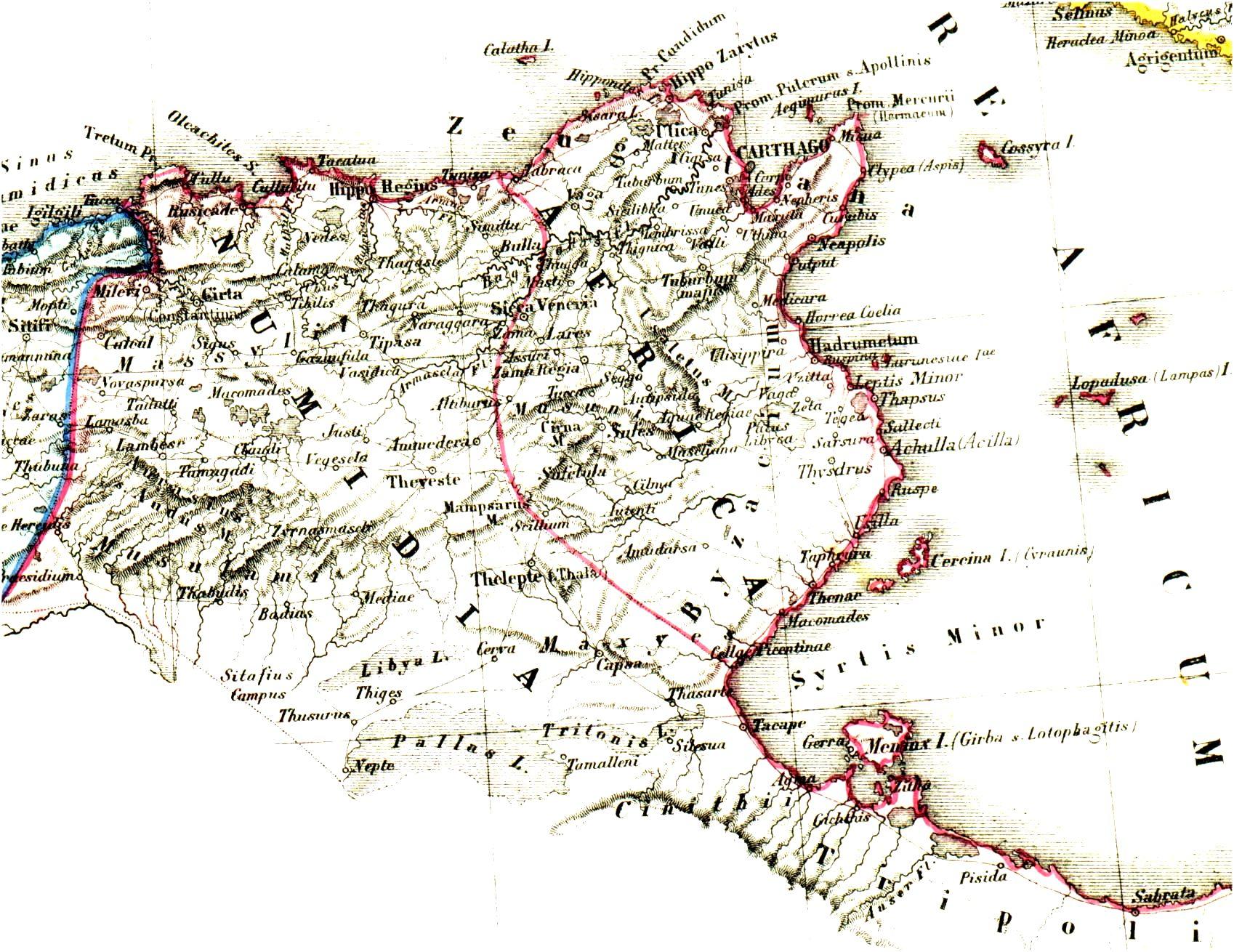
African Romance
African Romance or African Latin is an extinct Romance language that was spoken in the Roman province of Africa by the Roman Africans during the later Roman and early Byzantine Empires, and several centuries after the annexation of the region by the Umayyad Caliphate in 696 AD. African Romance is poorly attested as it was mainly a spoken, vernacular language, a ''sermo rusticus.'' There is little doubt, however, that by the early 3rd century AD, some native provincial variety of Latin was fully established in Africa.' This language, which developed under Byzantine rule, continued through to the 12th century in various places along the North African coast and the immediate littoral,' with evidence that it may have persisted up to the 14th century,' and possibly even the 15th century,' or later' in certain areas of the interior. Background The Roman province of Africa was organized in 146 BC following the defeat of Carthage in the Third Punic War. The city of Carthag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Latium
Old Latium ( la, Latium vetus or ') is a region of the Italian peninsula bounded to the north by the river Tiber, to the east by the central Apennine mountains, to the west by the Mediterranean Sea and to the south by Monte Circeo. It was the territory of the Latins, an Italic tribe which included the early inhabitants of the city of Rome. Later it was also settled by various Italic tribes such as the Rutulians, Volscians, Aequi, and Hernici. The region was referred to as "old" to distinguish it from the expanded region, Latium, that included the region to the south of Old Latium, between Monte Circeo and the river Garigliano – the so-called Latium adiectum ("attached Latium"). It corresponded to the central part of the modern administrative region of Lazio, Italy, and it covered an area measuring of roughly 50 Roman miles. It was calculated by Mommsen that the region's area was about 1860 square kilometres. Settlement Literary tradition Dionysius of Halicarnassus has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sardinian Language
Sardinian or Sard ( , or ) is a Romance languages, Romance language spoken by the Sardinians on the Western Mediterranean island of Sardinia. Many Romance linguists consider it the language that is closest to Latin among all its genealogical descendants. However, it has also incorporated elements of a Pre-Latin (mostly Paleo-Sardinian language, Paleo-Sardinian and, to a much lesser degree, Punic language, Punic) Stratum (linguistics)#substratum, substratum, as well as a Byzantine Greek, Catalan language, Catalan, Spanish and Italian superstratum. These elements originate in the political history of Sardinia, whose indigenous society experienced for centuries competition and at times conflict with a series of colonizing newcomers: before the Middle Ages, it was for a time a Byzantine empire, Byzantine possession; then, after a significant period of self-rule with the Judicates, it came during the late Middle Ages into the Iberian sphere of influence; and finally, from the earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Latin
Classical Latin is the form of Literary Latin recognized as a literary standard by writers of the late Roman Republic and early Roman Empire. It was used from 75 BC to the 3rd century AD, when it developed into Late Latin. In some later periods, it was regarded as good or proper Latin, with following versions viewed as debased, degenerate, or corrupted. The word ''Latin'' is now understood by default to mean "Classical Latin"; for example, modern Latin textbooks almost exclusively teach Classical Latin. Cicero and his contemporaries of the late republic referred to the Latin language, in contrast to other languages such as Greek, as or . They distinguished the common vernacular, however, as Vulgar Latin (''sermo vulgaris'' and ''sermo vulgi''), in contrast to the higher register that they called , sometimes translated as "Latinity". ''Latinitas'' was also called ("speech of the good families"), ''sermo urbanus'' ("speech of the city"), and in rare cases ''sermo nobilis' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Language
Romanian (obsolete spellings: Rumanian or Roumanian; autonym: ''limba română'' , or ''românește'', ) is the official and main language of Romania and the Republic of Moldova. As a minority language it is spoken by stable communities in the countries surrounding Romania (Bulgaria, Hungary, Serbia, and Ukraine), and by the large Romanian diaspora. In total, it is spoken by 28–29 million people as an L1+ L2, of whom 23–24 millions are native speakers. In Europe, Romanian is rated as a medium level language, occupying the tenth position among thirty-seven official languages. Romanian is part of the Eastern Romance sub-branch of Romance languages, a linguistic group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin which separated from the Western Romance languages in the course of the period from the 5th to the 8th centuries. To distinguish it within the Eastern Romance languages, in comparative linguistics it is called ''Daco-Romanian'' as opposed to its closest r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Language
Italian (''italiano'' or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. Together with Sardinian, Italian is the least divergent language from Latin. Spoken by about 85 million people (2022), Italian is an official language in Italy, Switzerland ( Ticino and the Grisons), San Marino, and Vatican City. It has an official minority status in western Istria (Croatia and Slovenia). Italian is also spoken by large immigrant and expatriate communities in the Americas and Australia.Ethnologue report for language code:ita (Italy) – Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.), 2005. Ethnologue: Languages of the World, Fifteenth edition. Dallas, Tex.: SIL International. Online version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Language
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. It descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire, as did all Romance languages. French evolved from Gallo-Romance, the Latin spoken in Gaul, and more specifically in Northern Gaul. Its closest relatives are the other langues d'oïl—languages historically spoken in northern France and in southern Belgium, which French (Francien) largely supplanted. French was also influenced by native Celtic languages of Northern Roman Gaul like Gallia Belgica and by the ( Germanic) Frankish language of the post-Roman Frankish invaders. Today, owing to France's past overseas expansion, there are numerous French-based creole languages, most notably Haitian Creole. A French-speaking person or nation may be referred to as Francophone in both English and French. French is an official language in 29 countries across multiple continents, most of which are members of the '' Organisation internationale de la Francopho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese Language
Portuguese ( or, in full, ) is a western Romance language of the Indo-European language family, originating in the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. It is an official language of Portugal, Brazil, Cape Verde, Angola, Mozambique, Guinea-Bissau and São Tomé and Príncipe, while having co-official language status in East Timor, Equatorial Guinea, and Macau. A Portuguese-speaking person or nation is referred to as "Lusophone" (). As the result of expansion during colonial times, a cultural presence of Portuguese speakers is also found around the world. Portuguese is part of the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in the medieval Kingdom of Galicia and the County of Portugal, and has kept some Celtic phonology in its lexicon. With approximately 250 million native speakers and 24 million L2 (second language) speakers, Portuguese has approximately 274 million total speakers. It is usually listed as the sixth-most spoken language, the third-mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Language
Spanish ( or , Castilian) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from colloquial Latin spoken on the Iberian peninsula. Today, it is a world language, global language with more than 500 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain. Spanish is the official language of List of countries where Spanish is an official language, 20 countries. It is the world's list of languages by number of native speakers, second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's list of languages by total number of speakers, fourth-most spoken language overall after English language, English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani language, Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance languages, Romance language. The largest population of native speakers is in Mexico. Spanish is part of the Iberian Romance languages, Ibero-Romance group of languages, which evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Languages By Number Of Native Speakers
This article ranks human languages by their number of native speakers. However, all such rankings should be used with caution, because it is not possible to devise a coherent set of linguistic criteria for distinguishing languages in a dialect continuum. For example, a language is often defined as a set of varieties that are mutually intelligible, but independent national standard languages may be considered to be separate languages even though they are largely mutually intelligible, as in the case of Danish and Norwegian. Conversely, many commonly accepted languages, including German, Italian and even English, encompass varieties that are not mutually intelligible. While Arabic is sometimes considered a single language centred on Modern Standard Arabic, other authors describe its mutually unintelligible varieties as separate languages. Similarly, Chinese is sometimes viewed as a single language because of a shared culture and common literary language. It is also common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch, and Spanish, have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, of which there are eight groups with languages still alive today: Albanian, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic, Germanic, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian, and Italic; and another nine subdivisions that are now extinct. Today, the individual Indo-European languages with the most native speakers are English, Hindi–Urdu, Spanish, Bengali, French, Russian, Portuguese, German, and Punjabi, each with over 100 million native speakers; many others are small and in danger of extinction. In total, 46% of the world's population (3.2 billion people) speaks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania State University Press
The Penn State University Press, also known as The Pennsylvania State University Press, was established in 1956 and is a non-profit publisher of scholarly books and journals. It is the independent publishing branch of the Pennsylvania State University and is a division of the Penn State University Library system. Penn State University Press publishes books and journals of interest to scholars and general audiences. As a part of a land-grant university with a mandate to serve the citizens of the commonwealth of Pennsylvania, it also specializes in works about Penn State University, Pennsylvania, and the mid-Atlantic region. The areas of scholarship the Press is best known for are art history, medieval studies, Latin American studies, rhetoric and communication, religious studies, and Graphic Medicine. In 2016 the Press launched PSU Press Unlocked, an open access platform featuring over 70 books and journals. The Press acquired academic publisher Eisenbrauns, which specializes in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |