|
Wichí
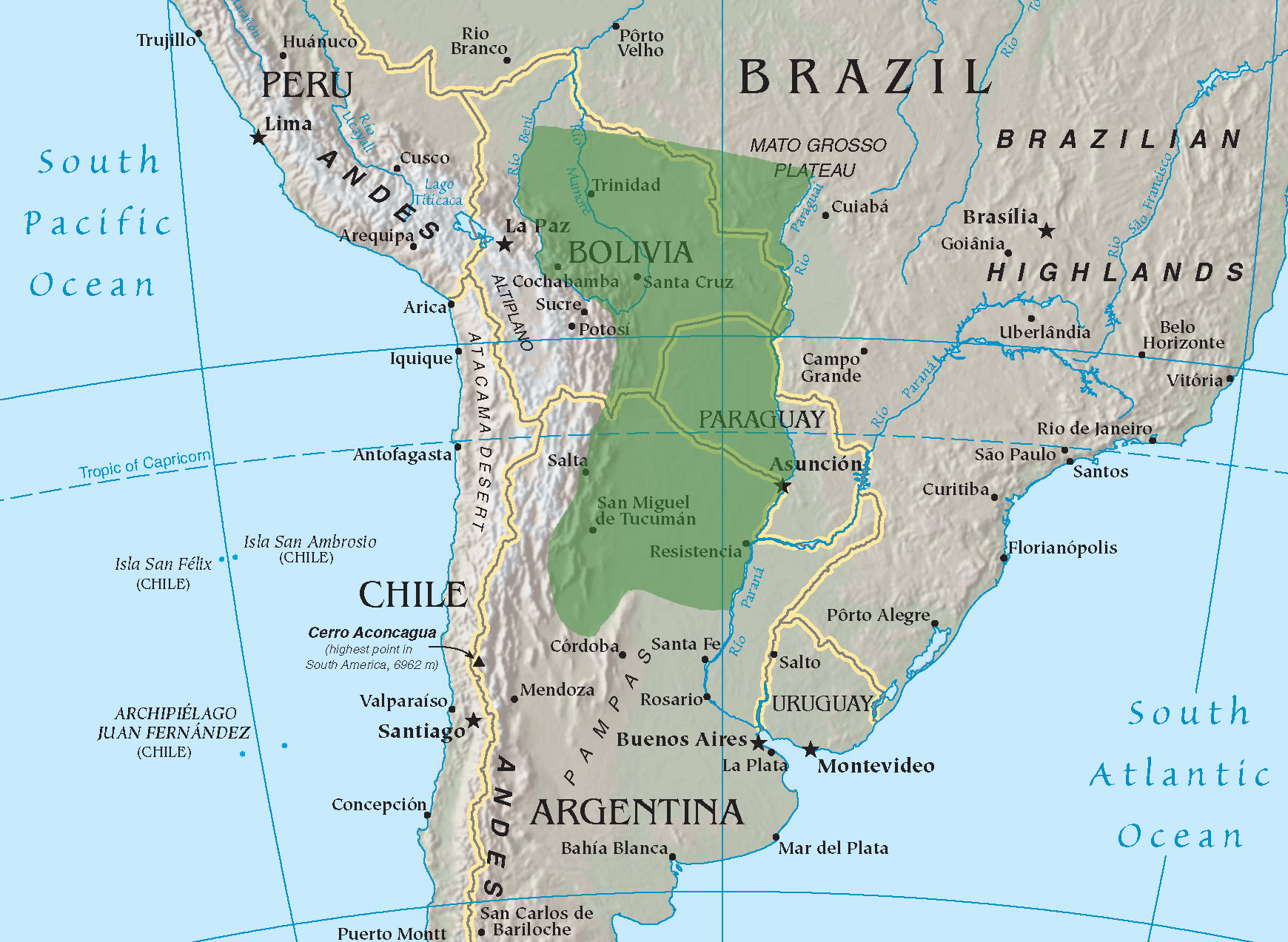
The Wichí are an indigenous people of South America. They are a large group of tribes ranging about the headwaters of the Bermejo River and the Pilcomayo River, in Argentina and Bolivia. Notes on designation This ethnic group was named by the English settlers and is still widely known as Mataco. The etymology of the term is obscure but in several sources, it is cited that the Wichí find the term derogatory. Among the group exists a folk etymology for this term, which relates it to the Spanish verb ''matar'', to kill. Thus their preferred name, their own word for themselves, is Wichí, pronounced , and their language, ''Wichí Lhamtés'' . There is a pronunciation variant in some areas of Bolivia, , where the self-denomination of the group is Weenhayek wichi, translated by Alvarsson (1988) as "''the different people''" (pl. ''Weenhayey''). Weenhayey informers of Alvarsson state that the old name was Olhamelh (), meaning simply ''us''. The subgroups within Wichí have been ide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wichí Languages
The Wichí languages are an indigenous language family spoken by the Wichí in northwestern Argentina and far-southeastern Bolivia, part of the Matacoan languages, Matacoan family. They are also known as Mataco, Wichi, Wichí Lhamtés, Weenhayek, Noctenes, Matahuayo, Matako, Weʃwo. The name ''Mataco'' is common but pejorative. Status Currently, the Argentine government does not have education in indigenous languages in schools. Because the Wichí have to be fluent in Spanish to access government services, and children are only educated in Spanish, Wichí children only speak Spanish among themselves. This has made all Wichí dialects vulnerable to extinction. In 2010, the province of Chaco province, Chaco in Argentina declared Wichí as one of four provincial official languages alongside Spanish and the indigenous Moqoit language, Moqoit and Qom language, Qom. Languages They include the following languages: *Noktén language, Noktén (a.k.a. Noctén, Wichí Lhamtés Nocten), s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wichí Lhamtés Güisnay
Wichí Lhamtés Güisnay or Wiznay is a Wichí language. Wichí Lhamtés Güisnay had an estimated 15,000 speakers in 1999 in Argentina. The language is centered in the Pilcomayo River region. Other names for the language include Güisnay, Mataco, Mataco Güisnay, Mataco Pilcomayo, and Wichí Lhamtés. A grammar book has been written for the language."Wichí Lhamtés Güisnay." ''Ethnologue.'' Retrieved 30 Jan 2012. The Wichí languages are predominantly suffixing and ; verbal words have between 2 and 15 morphemes. Alienable and inalienable [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wichí Lhamtés Vejoz
Wichí Lhamtés Vejoz is a Mataco-Guaicuru language of Argentina and Bolivia. Speakers are concentrated in northern parts of Chaco, Formosa, Salta, Jujuy Provinces, as well as west of Toba, the upper Bermejo River valley, and Pilcomayo River. The language is also called ''Mataco Vejoz'' and ''Vejos''. The Wichí languages are predominantly suffixing and polysynthetic; verbal words have between 2 and 15 morphemes. Alienable and inalienable possession is distinguished. The phonological inventory is large, with simple, glottalized and aspirated stops and sonorants. The number of vowels varies with the language (five or six). Phonology * // is heard as after palatal consonants. * // is heard as when preceding uvular consonants. * /, / sounds can be heard as before uvular consonants. * // can be heard as in syllable-final position. See also *Wichí Lhamtés Nocten Wichí Lhamtés Nocten, or Weenhayek, is a Wichí language primarily spoken in Bolivia, where an estim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wichí Lhamtés Nocten
Wichí Lhamtés Nocten, or Weenhayek, is a Wichí language primarily spoken in Bolivia, where an estimated 1,810 Wichí people spoke it in 1994. An additional one hundred people spoke the language in Argentina in 1994. In Bolivia, the language is spoken in the north-central Tarija Department, southwest of Pilcomayo River, and in Cordillera de Pirapo. In Argentina, it is spoken in from the northern border south to Tartagal, Salta Tartagal () is a tropical city in northern Argentina, in the province of Salta. It is located in the northeast of the province, within the General José de San Martín Department, of which it is the capital. It is located in the Yungas jungle, at .... The language is also called Mataco, Bolivian, Mataco Nocten, Nocten, Noctenes, Oktenai, and Weenhayek; the last name is used in the Bolivian constitution of 2009. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matacoan Languages
Matacoan (also ''Mataguayan, Matákoan, Mataguayo, Mataco–Mataguayo, Matacoano, Matacoana'') is a language family of northern Argentina, western Paraguay, and southeastern Bolivia. Family division Matacoan consists of four clusters of languages. The family also has a clear binary split between Wichí-Chorote and Maká-Nivaclé according to Nikulin (2019).Nikulin, Andrey V. 2019. The classification of the languages of the South American Lowlands: State-of-the-art and challenges / Классификация языков востока Южной Америки'. Illič-Svityč (Nostratic) Seminar / Ностратический семинар, Higher School of Economics, October 17, 2019. Gordon (2005) in '' Ethnologue'' divides Wichí into three separate languages and Chorote into two languages. ;Matacoan * Wichí-Chorote ** Wichí (also known as Mataco, Wichi, Wichí Lhamtés, Weenhayek, Noctenes, Matahuayo, Matako, Weʃwo. The name ''Mataco'' is common but pejorative.) ***''Ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaco Province
Chaco (; Wichi: ''To-kós-wet''), officially the Province of Chaco ( es, provincia del Chaco ), is one of the 23 provinces in Argentina. Its capital and largest city, is Resistencia. It is located in the north-east of the country. It is bordered by Salta and Santiago del Estero to the west, Formosa to the north, Corrientes to the east, and Santa Fe to the south. It also has an international border with the Paraguayan Department of Ñeembucú. With an area of , and a population of 1,055,259 as of 2010, it is the twelfth most extensive, and the ninth most populated, of the twenty-three Argentine provinces. In 2010, Chaco became the second province in Argentina to adopt more than one official language. These languages are the Kom, Moqoit and Wichí languages, spoken by the Toba, Mocovi and Wichí peoples respectively. Chaco has historically been among Argentina's poorest regions, and currently ranks last both by per capita GDP and on the Human Development Index. Etymology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world. It shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a federal state subdivided into twenty-three provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, and a part of Antarctica. The earliest recorded human prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toba (tribe)
The Toba people, also known as the Qom people, are one of the largest indigenous groups in Argentina who historically inhabited the region known today as the Pampas of the Central Chaco. During the 16th century, the Qom inhabited a large part of what is today northern Argentina, in the current provinces of Salta, Chaco, Santiago del Estero, Formosa and the province of Gran Chaco in the southeast of the Department of Tarija in Bolivia (which the Qom have inhabited since the 20th century). Currently, many Toba, due to persecution in their rural ancestral regions, live in the suburbs of San Ramón de la Nueva Orán, Salta, Tartagal, Resistencia, Charata, Formosa, Rosario and Santa Fe and in Greater Buenos Aires. Nearly 130,000 people currently identify themselves as Toba or Qom. With more than 120,000 Qom living in Argentina, the Qom community is one of the largest indigenous communities in the country. Like most indigenous groups in South America, the Qom have a long hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salta Province
Salta () is a province of Argentina, located in the northwest of the country. Neighboring provinces are from the east clockwise Formosa, Chaco, Santiago del Estero, Tucumán and Catamarca. It also surrounds Jujuy. To the north it borders Bolivia and Paraguay and to the west lies Chile. History Before the Spanish conquest, numerous native peoples (now called Diaguitas and Calchaquíes) lived in the valleys of what is now Salta Province; they formed many different tribes, the Quilmes and Humahuacas among them, which all shared the Cacán language. The Atacamas lived in the Puna, and the Wichís (Matacos), in the Chaco region. The first conquistador to venture into the area was Diego de Almagro in 1535; he was followed by Diego de Rojas. Hernando de Lerma founded San Felipe de Lerma in 1582, following orders of the viceroy Francisco de Toledo, Count of Oropesa; the name of the city was soon changed to "San Felipe de Salta". By 1650, the city had around five hundred inhabitan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg , flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center , flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square patchwork with the (top left to bottom right) diagonals forming colored stripes (green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, white, green, blue, purple, red, orange, yellow, from top right to bottom left) , other_symbol = , other_symbol_type = Dual flag: , image_coat = Escudo de Bolivia.svg , national_anthem = " National Anthem of Bolivia" , image_map = BOL orthographic.svg , map_width = 220px , alt_map = , image_map2 = , alt_map2 = , map_caption = , capital = La Paz Sucre , largest_city = , official_languages = Spanish , languages_type = Co-official languages , languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bermejo River
The Bermejo River (Spanish, Río Bermejo) is a river in South America that flows from Bolivia to the Paraguay River in Argentina. The river is generally called Bermejo in spite of its different names along its way, but it also has its own Native American names; in Wichí it is called Teuco, and in Guaraní it is called Ypitá. In the plains of Argentina's Gran Chaco the Bermejo forms wetlands and splits into two branches. The southern branch is the bed of the old Bermejo River, now an intermittent stream called Río Bermejito. The northern branch is now the main stem of the Bermejo and is called the Teuco River (''Río Teuco''), Bermejo Nuevo, or simply the Bermejo River. The two branches rejoin at , near Villa Río Bermejito, forming the Lower Bermejo River. The Bermejo River is long and has a drainage basin of in area. Its mean annual discharge is irregular and varies between and . The river is born in a mountain range known as Sierra de Santa Victoria around coordinates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glottalization
Glottalization is the complete or partial closure of the glottis during the articulation of another sound. Glottalization of vowels and other sonorants is most often realized as creaky voice (partial closure). Glottalization of obstruent consonants usually involves complete closure of the glottis; another way to describe this phenomenon is to say that a glottal stop is made simultaneously with another consonant. In certain cases, the glottal stop can even wholly replace the voiceless consonant. The term 'glottalized' is also used for ejective and implosive consonants; see glottalic consonant for examples. There are two other ways to represent glottalization of sonorants in the IPA: (a) the same way as ejectives, with an apostrophe; or (b) with the under-tilde for creaky voice. For example, the Yapese word for "sick" with a glottalized ''m'' could be transcribed as either or . (In some typefaces, the apostrophe will occur above the m.) Types Glottalization varies along three p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |