|
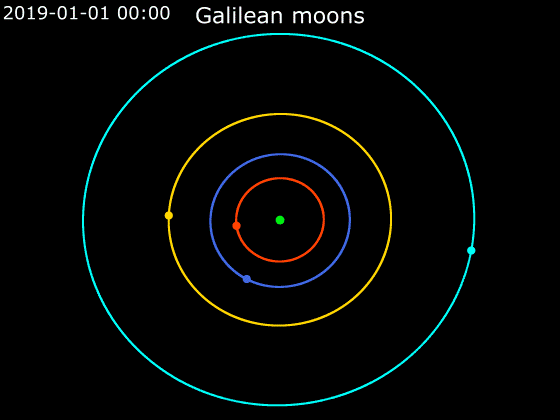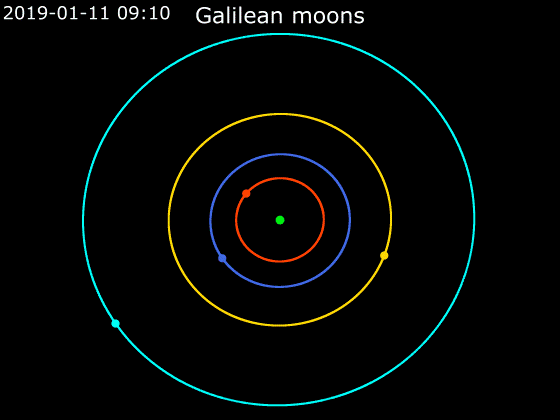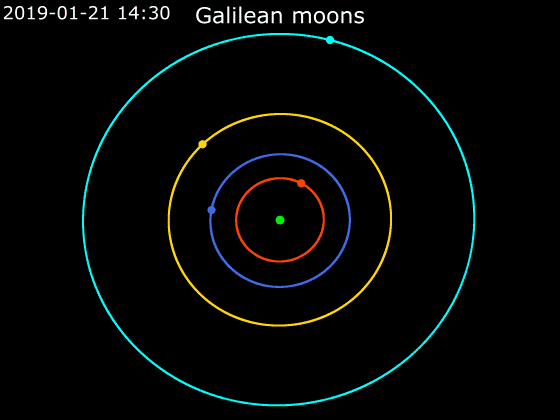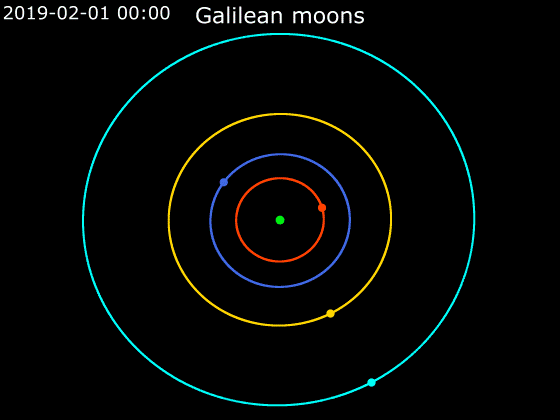
Io (moon)
Io (), or Jupiter I, is the innermost and third-largest of the four Galilean moons of the planet Jupiter. Slightly larger than Earth’s moon, Io is the fourth-largest moon in the Solar System, has the highest density of any moon, the strongest surface gravity of any moon, and the lowest amount of water (by atomic ratio) of any known astronomical object in the Solar System. It was discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei and was named after the mythological character Io, a priestess of Hera who became one of Zeus's lovers. With over 400 active volcanoes, Io is the most geologically active object in the Solar System. This extreme geologic activity is the result of tidal heating from friction generated within Io's interior as it is pulled between Jupiter and the other Galilean moons—Europa, Ganymede and Callisto. Several volcanoes produce plumes of sulfur and sulfur dioxide that climb as high as above the surface. Io's surface is also dotted with more than 100 mountains t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo (spacecraft)
''Galileo'' was an American robotic space probe that studied the planet Jupiter and its moons, as well as the asteroids Gaspra and Ida. Named after the Italian astronomer Galileo Galilei, it consisted of an orbiter and an entry probe. It was delivered into Earth orbit on October 18, 1989, by , during STS-34. ''Galileo'' arrived at Jupiter on December 7, 1995, after gravitational assist flybys of Venus and Earth, and became the first spacecraft to orbit an outer planet. The Jet Propulsion Laboratory built the ''Galileo'' spacecraft and managed the ''Galileo'' program for NASA. West Germany Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm supplied the propulsion module. NASA's Ames Research Center managed the atmospheric probe, which was built by Hughes Aircraft Company. At launch, the orbiter and probe together had a mass of and stood tall. Spacecraft are normally stabilized either by spinning around a fixed axis or by maintaining a fixed orientation with reference to the Sun and a star. ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of Australia). The Moon is a planetary-mass object with a differentiated rocky body, making it a satellite planet under the geophysical definitions of the term and larger than all known dwarf planets of the Solar System. It lacks any significant atmosphere, hydrosphere, or magnetic field. Its surface gravity is about one-sixth of Earth's at , with Jupiter's moon Io being the only satellite in the Solar System known to have a higher surface gravity and density. The Moon orbits Earth at an average distance of , or about 30 times Earth's diameter. Its gravitational influence is the main driver of Earth's tides and very slowly lengthens Earth's day. The Moon's orbit around Earth has a sidereal period of 27.3 days. During each synod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
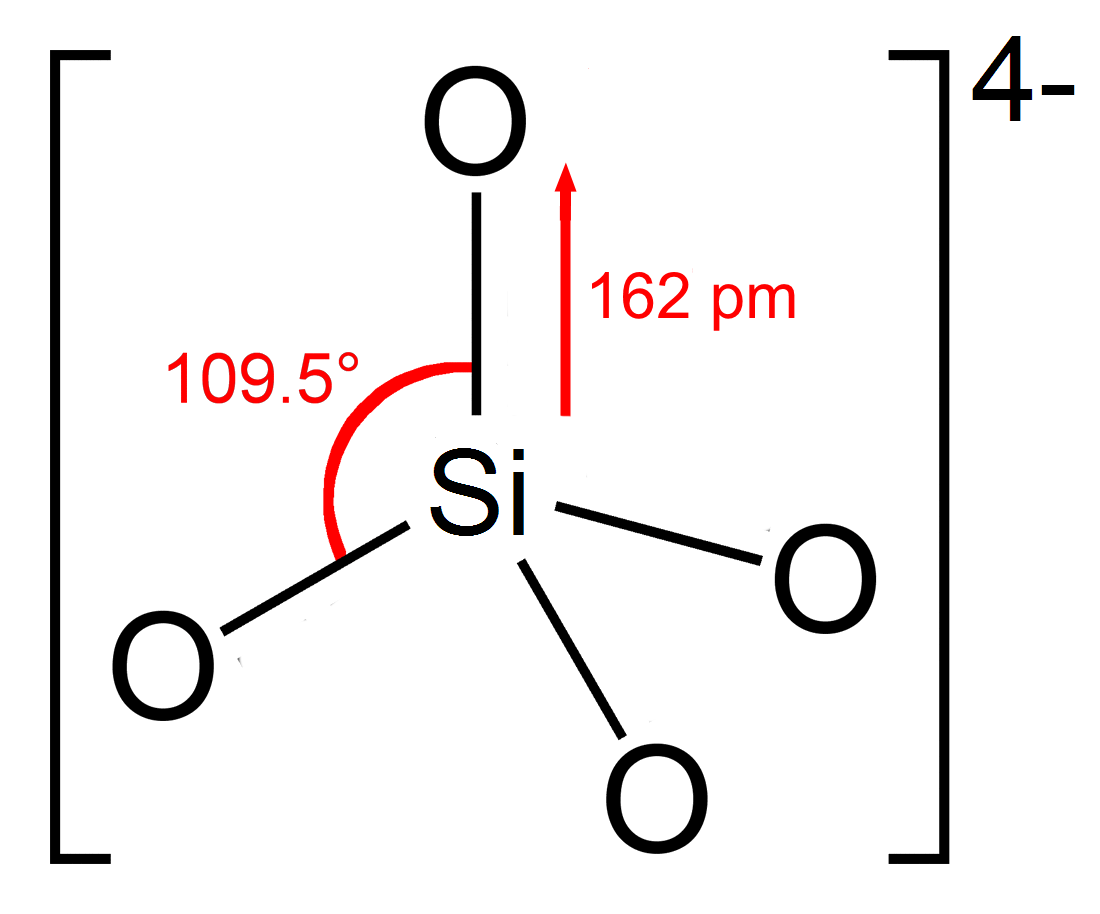
Silicate
In chemistry, a silicate is any member of a family of polyatomic anions consisting of silicon and oxygen, usually with the general formula , where . The family includes orthosilicate (), metasilicate (), and pyrosilicate (, ). The name is also used for any salt of such anions, such as sodium metasilicate; or any ester containing the corresponding chemical group, such as tetramethyl orthosilicate. The name "silicate" is sometimes extended to any anions containing silicon, even if they do not fit the general formula or contain other atoms besides oxygen; such as hexafluorosilicate .Most commonly, silicates are encountered as silicate minerals. For diverse manufacturing, technological, and artistic needs, silicates are versatile materials, both natural (such as granite, gravel, and garnet) and artificial (such as Portland cement, ceramics, glass, and waterglass). Structural principles In all silicates, silicon atom occupies the center of an idealized tetrahedron whose c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callisto (moon)
Callisto (), or Jupiter IV, is the second-largest moon of Jupiter, after Ganymede. It is the third-largest moon in the Solar System after Ganymede and Saturn's largest moon Titan, and the largest object in the Solar System that may not be properly differentiated. Callisto was discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei. With a diameter of , Callisto is about 99% the diameter of the planet Mercury, but only about a third of its mass. It is the fourth Galilean moon of Jupiter by distance, with an orbital radius of about . It is not in an orbital resonance like the three other Galilean satellites— Io, Europa, and Ganymede—and is thus not appreciably tidally heated. Callisto's rotation is tidally locked to its orbit around Jupiter, so that the same hemisphere always faces inward. Because of this, there is a sub-Jovian point on Callisto's surface, from which Jupiter would appear to hang directly overhead. It is less affected by Jupiter's magnetosphere than the other inner sate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ganymede (moon)
Ganymede, a satellite of Jupiter (Jupiter III), is the largest and most massive of the Solar System's moons. The ninth-largest object (including the Sun) of the Solar System, it is the largest without a substantial atmosphere (albeit not the most massive one, which is Mercury). It has a diameter of , making it 26 percent larger than the planet Mercury by volume, although it is only 45 percent as massive. Possessing a metallic core, it has the lowest moment of inertia factor of any solid body in the Solar System and is the only moon known to have a magnetic field. Outward from Jupiter, it is the seventh satellite and the third of the Galilean moons, the first group of objects discovered orbiting another planet. Ganymede orbits Jupiter in roughly seven days and is in a 1:2:4 orbital resonance with the moons Europa and Io, respectively. Ganymede is composed of approximately equal amounts of silicate rock and water. It is a fully differentiated body with an iron-rich, li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Europa (moon)
Europa , or Jupiter II, is the smallest of the four Galilean moons orbiting Jupiter, and the sixth-closest to the planet of all the 80 known moons of Jupiter. It is also the sixth-largest moon in the Solar System. Europa was discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei and was named after Europa, the Phoenician mother of King Minos of Crete and lover of Zeus (the Greek equivalent of the Roman god Jupiter). Slightly smaller than Earth's Moon, Europa is primarily made of silicate rock and has a water-ice crust and probably an iron–nickel core. It has a very thin atmosphere, composed primarily of oxygen. Its white- beige surface is striated by light tan cracks and streaks, but craters are relatively few. In addition to Earth-bound telescope observations, Europa has been examined by a succession of space-probe flybys, the first occurring in the early 1970s. In September 2022, the ''Juno'' spacecraft flew within about 200 miles of Europa for a more recent close-up view. Europa has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: *Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into ''static friction'' (" stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and ''kinetic friction'' between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features, known as asperities (see Figure 1). *Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other. *Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces. *Skin friction is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body. *Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Heating Of Io
Tidal heating of Io (also known as tidal working) occurs through the tidal friction processes between Jupiter and its moon. Orbital and rotational energy are dissipated as heat in the crust of the moon. Io has a similar mass and size as the Moon, but Io is the most geologically active body in the Solar System. This is caused by the heating mechanism of Io. The major heating source of Earth and its moon is radioactive heating, but the heating source on Io is tidal heating. As Jupiter is very massive, the side of Io nearest to Jupiter has a slightly larger gravitational pull than the opposite side. This difference in gravitational forces cause distortion of Io’s shape. Differently from the Earth’s only moon, Jupiter has two other large moons (Europa and Ganymede) that are in an orbital resonance with it. Io is the innermost of this set of resonant moons, and their interactions maintain its orbit in an eccentric (elliptical) state. The varying distance between Jupiter and Io cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label= genitive Boeotian Aeolic and Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label= genitive el, Δίας, ''Días'' () is the sky and thunder god in ancient Greek religion, who rules as king of the gods on Mount Olympus. His name is cognate with the first element of his Roman equivalent Jupiter.''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. His mythology and powers are similar, though not identical, to those of Indo-European deities such as Jupiter, Perkūnas, Perun, Indra, Dyaus, and Zojz. Entry: "Dyaus" Zeus is the child of Cronus and Rhea, the youngest of his siblings to be born, though sometimes reckoned the eldest as the others required disgorging from Cronus's stomach. In most traditions, he is married to Hera, by whom he is usually said to have fathered Ares, Eileithyia, Hebe, and Hephaestus. At the oracle of Dodona, his consort was said to be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hera
In ancient Greek religion, Hera (; grc-gre, Ἥρα, Hḗrā; grc, Ἥρη, Hḗrē, label=none in Ionic and Homeric Greek) is the goddess of marriage, women and family, and the protector of women during childbirth. In Greek mythology, she is queen of the twelve Olympians and Mount Olympus, sister and wife of Zeus, and daughter of the Titans Cronus and Rhea. One of her defining characteristics in myth is her jealous and vengeful nature in dealing with any who offend her, especially Zeus' numerous adulterous lovers and illegitimate offspring. Her iconography usually presents her as a dignified, matronly figure, upright or enthroned, crowned with a '' polos'' or diadem, sometimes veiled as a married woman. She is the patron goddess of lawful marriage. She presides over weddings, blesses and legalises marital unions, and protects women from harm during childbirth. Her sacred animals include the cow, cuckoo and the peacock. She is sometimes shown holding a pomegranate, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Object
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often used interchangeably. However, an astronomical body or celestial body is a single, tightly bound, contiguous entity, while an astronomical or celestial ''object'' is a complex, less cohesively bound structure, which may consist of multiple bodies or even other objects with substructures. Examples of astronomical objects include planetary systems, star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies, while asteroids, moons, planets, and stars are astronomical bodies. A comet may be identified as both body and object: It is a ''body'' when referring to the frozen nucleus of ice and dust, and an ''object'' when describing the entire comet with its diffuse coma and tail. History Astronomical objects such as stars, planets, nebulae, asteroids and comet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







_Pompeian_Art.jpg)
