|
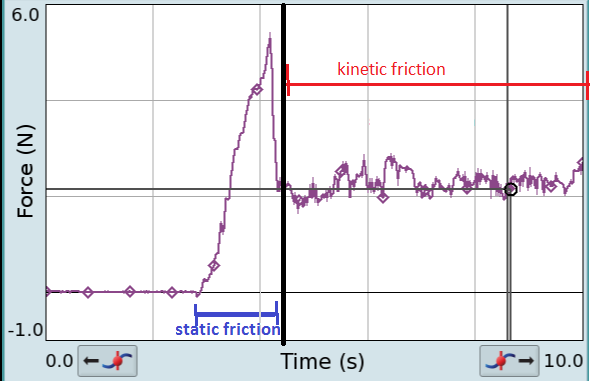
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: *Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into ''static friction'' (" stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and ''kinetic friction'' between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features, known as asperities (see Figure 1). *Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other. *Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces. *Skin friction is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body. *Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction Between Surfaces
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: *Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into ''static friction'' (" stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and ''kinetic friction'' between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features, known as asperities (see Figure 1). *Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other. *Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces. *Skin friction is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body. *Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribology
Tribology is the science and engineering of interacting surfaces in relative motion. It includes the study and application of the principles of friction, lubrication and wear. Tribology is highly interdisciplinary, drawing on many academic fields, including physics, chemistry, materials science, mathematics, biology and engineering. People who work in the field of tribology are referred to as ''tribologists''. The fundamental objects of study in tribology are tribosystems, which are physical systems of contacting surfaces. In lubricated tribosystems, contact stress can create tribofilms. Subfields of tribology include biotribology, nanotribology, space tribology and tribotronics. Etymology The word ''tribology'' derives from the Greek root τριβ- of the verb , ''tribo'', "I rub" in classic Greek, and the suffix '' -logy'' from , '' -logia'' "study of", "knowledge of". Peter Jost coined the word in 1966, in the eponymous report which highlighted the cost of frictio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sliding (motion)
Sliding is a type of frictional motion between two surfaces in contact. This can be contrasted to rolling motion. Both types of motion may occur in bearings. The relative motion or tendency toward such motion between two surfaces is resisted by friction. Friction may damage or 'wear' the surfaces in contact. However, wear can be reduced by lubrication. The science and technology of friction, lubrication, and wear is known as tribology. Sliding may occur between two objects of arbitrary shape, whereas rolling friction is the frictional force associated with the rotational movement of a somewhat disclike or other circular object along a surface. Generally, the frictional force of rolling friction is less than that associated with sliding kinetic friction. Typical values for the coefficient of rolling friction are less than that of sliding friction. Correspondingly sliding friction typically produces greater sound and thermal bi-products. One of the most common examples of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Force
In physics, a force is an influence that can change the motion of an object. A force can cause an object with mass to change its velocity (e.g. moving from a state of rest), i.e., to accelerate. Force can also be described intuitively as a push or a pull. A force has both magnitude and direction, making it a vector quantity. It is measured in the SI unit of newton (N). Force is represented by the symbol (formerly ). The original form of Newton's second law states that the net force acting upon an object is equal to the rate at which its momentum changes with time. If the mass of the object is constant, this law implies that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on the object, is in the direction of the net force, and is inversely proportional to the mass of the object. Concepts related to force include: thrust, which increases the velocity of an object; drag, which decreases the velocity of an object; and torque, which pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drag (physics)
In fluid dynamics, drag (sometimes called air resistance, a type of friction, or fluid resistance, another type of friction or fluid friction) is a force acting opposite to the relative motion of any object moving with respect to a surrounding fluid. This can exist between two fluid layers (or surfaces) or between a fluid and a solid surface. Unlike other resistive forces, such as dry friction, which are nearly independent of velocity, the drag force depends on velocity. Drag force is proportional to the velocity for low-speed flow and the squared velocity for high speed flow, where the distinction between low and high speed is measured by the Reynolds number. Even though the ultimate cause of drag is viscous friction, turbulent drag is independent of viscosity. Drag forces always tend to decrease fluid velocity relative to the solid object in the fluid's path. Examples Examples of drag include the component of the net aerodynamic or hydrodynamic force acting opposite to the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubricant
A lubricant (sometimes shortened to lube) is a substance that helps to reduce friction between surfaces in mutual contact, which ultimately reduces the heat generated when the surfaces move. It may also have the function of transmitting forces, transporting foreign particles, or heating or cooling the surfaces. The property of reducing friction is known as lubricity. In addition to industrial applications, lubricants are used for many other purposes. Other uses include cooking ( oils and fats in use in frying pans, in baking to prevent food sticking), bioapplications on humans (e.g. lubricants for artificial joints), ultrasound examination, medical examination, and sexual intercourse. It is mainly used to reduce friction and to contribute to a better and efficient functioning of a mechanism. History Lubricants have been in some use for thousands of years. Calcium soaps have been identified on the axles of chariots dated to 1400 BC. Building stones were slid on oil-impregrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Land Vehicle
A vehicle (from la, vehiculum) is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles (motorcycles, cars, trucks, buses, mobility scooters for disabled people), railed vehicles (trains, trams), watercraft (ships, boats, underwater vehicles), amphibious vehicles (screw-propelled vehicles, hovercraft), aircraft (airplanes, helicopters, aerostats) and spacecraft.Halsey, William D. (Editorial Director): ''MacMillan Contemporary Dictionary'', page 1106. MacMillan Publishing, 1979. Land vehicles are classified broadly by what is used to apply steering and drive forces against the ground: wheeled, tracked, railed or skied. ISO 3833-1977 is the standard, also internationally used in legislation, for road vehicles types, terms and definitions. History * The oldest boats found by archaeological excavation are logboats, with the oldest logboat found, the Pesse canoe found in a bog in the Netherlands, being carbon dated to 804 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stiction
Stiction is the static friction that needs to be overcome to enable relative motion of stationary objects in contact. The term is a portmanteau of the words ''static'' and ''friction'', and is perhaps also influenced by the verb '' to stick''. Any solid objects pressing against each other (but not sliding) will require some threshold of force parallel to the surface of contact in order to overcome static adhesion. Stiction is a ''threshold'', not a continuous force. However, stiction might also be an illusion made by the rotation of kinetic friction. In situations where two surfaces with areas below the micrometer scale come into close proximity (as in an accelerometer), they may adhere together. At this scale, electrostatic and/or Van der Waals and hydrogen bonding forces become significant. The phenomenon of two such surfaces being adhered together in this manner is also called stiction. Stiction may be related to hydrogen bonding or residual contamination. Automobiles Sticti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guillaume Amontons
Guillaume Amontons (31 August 1663 – 11 October 1705) was a French scientific instrument inventor and physicist. He was one of the pioneers in studying the problem of friction, which is the resistance to motion when bodies make contact. He is also known for his work on thermodynamics, the concept of absolute zero, and early engine design. Life Guillaume was born in Paris, France. His father was a lawyer from Normandy who had moved to the French capital. While still young, Guillaume lost his hearing and became mostly deaf. According to one biographer, Fontenelle, while studying perpetual motion, he became convinced of the importance of studying machines from a mathematical perspective. He never attended a university, but was able to study mathematics, the physical sciences, and celestial mechanics. He also spent time studying the skills of drawing, surveying, and architecture. He died in Paris, France. Work He was supported in his research career by the government, and was e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traction (engineering)
Traction, or tractive force, is the force used to generate motion between a body and a tangential surface, through the use of dry friction, though the use of shear force of the surface is also commonly used. Traction can also refer to the ''maximum'' tractive force between a body and a surface, as limited by available friction; when this is the case, traction is often expressed as the ratio of the maximum tractive force to the normal force and is termed the ''coefficient of traction'' (similar to coefficient of friction). It is the force which makes an object move over the surface by overcoming all the resisting forces like friction, normal loads(load acting on the tiers in negative 'Z' axis), air resistance, rolling resistance, etc. Definitions Traction can be defined as: In vehicle dynamics, tractive force is closely related to the terms tractive effort and drawbar pull, though all three terms have different definitions. Coefficient of traction The ''coefficient of tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conservative Force
In physics, a conservative force is a force with the property that the total work done in moving a particle between two points is independent of the path taken. Equivalently, if a particle travels in a closed loop, the total work done (the sum of the force acting along the path multiplied by the displacement) by a conservative force is zero. A conservative force depends only on the position of the object. If a force is conservative, it is possible to assign a numerical value for the potential at any point and conversely, when an object moves from one location to another, the force changes the potential energy of the object by an amount that does not depend on the path taken, contributing to the mechanical energy and the overall conservation of energy. If the force is not conservative, then defining a scalar potential is not possible, because taking different paths would lead to conflicting potential differences between the start and end points. Gravitational force is an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Energy
In physical sciences, mechanical energy is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy. The principle of conservation of mechanical energy states that if an isolated system is subject only to conservative forces, then the mechanical energy is constant. If an object moves in the opposite direction of a conservative net force, the potential energy will increase; and if the speed (not the velocity) of the object changes, the kinetic energy of the object also changes. In all real systems, however, nonconservative forces, such as frictional forces, will be present, but if they are of negligible magnitude, the mechanical energy changes little and its conservation is a useful approximation. In elastic collisions, the kinetic energy is conserved, but in inelastic collisions some mechanical energy may be converted into thermal energy. The equivalence between lost mechanical energy and an increase in temperature was discovered by James Prescott Joule. Many devices are used to con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |