|
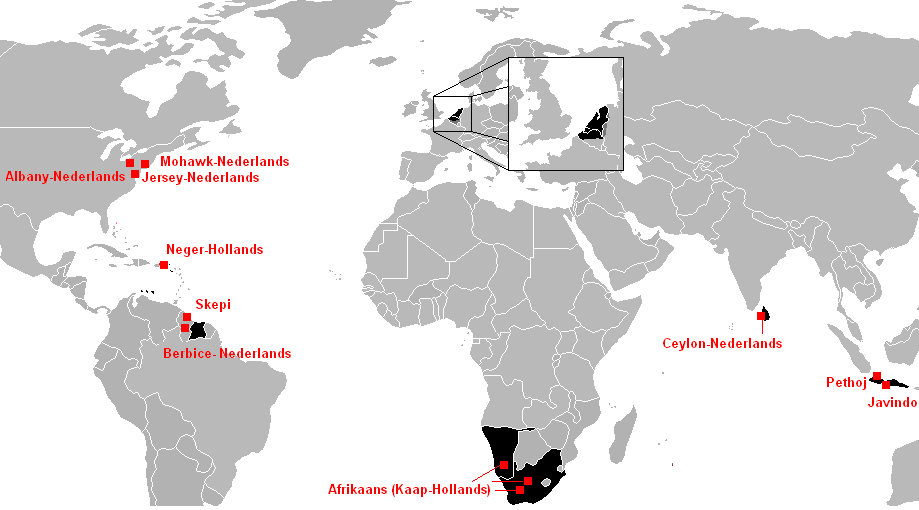
Dutch-based Creole Languages
A Dutch creole is a creole language that has been substantially influenced by the Dutch language. Most Dutch-based creoles originated in Dutch colonies in the Americas and Southeast Asia, after the 17th century expansion of Dutch maritime power. Almost all of them are now extinct, while two known varieties are classified as "critically endangered". The extinction has generally been attributed to a wilful cultural and generational language shift towards standard Dutch or the majority language of the area with each successive generation. Afrikaans is considered to be a daughter language of Dutch and it, by contrast, is vibrant and has completely displaced Dutch in southern Africa. Though not a majority-held position, it is considered by some linguists to be a creole because of its simpler grammar relative to Dutch. List Some important Dutch creoles are the following: Dutch has also made a significant contribution to other creoles: * Papiamento : based mostly on Portuguese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohawk Dutch
Mohawk Dutch is a now extinct Dutch-based creole language mainly spoken during the 17th century west of Albany, New York in the area around the Mohawk River, by the Dutch colonists who traded with or to a lesser extent mixed with the local population from the Mohawk nation. At the height of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands's North American colony of New Netherland, there were 18 languages spoken within Dutch-controlled territory. Dutch settlers frequently married indigenous women, most commonly from the Mohawk, with whom they were strong allies. The resulting children often drifted between the territory of the Iroquois Confederacy and New Netherland, forming among themselves a creole taking elements from both languages. The language disappeared in the 20th century. One lullaby purported to be in Mohawk Dutch was recorded as part of the research for the Dictionary of American Regional English; it is mostly German with one Dutch diminutive suffix (whose German equival ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Central German
West Central German (german: Westmitteldeutsch) belongs to the Central, High German dialect family of German. Its dialects are Franconian and comprise the parts of the Rhinelandic continuum located south of the Benrath line isogloss, including the following sub-families: * Central Franconian () ** Ripuarian (), spoken in North Rhine-Westphalia (including ) and German-speaking Belgium and a small edge in the south of the Dutch province of Limbourg. ** Moselle Franconian (; french: francique luxembourgeois) in Rhineland-Palatinate, Saarland and France *** Luxembourgish (; lb, Lëtzebuergesch; or ) in Luxembourg, Belgium and France *** Hunsrik (), spoken in Brazil and derived from the dialect of Moselle Franconian * Rhine Franconian (; ) ** Palatinate Franconian (; ), spoken in Rhineland-Palatinate *** Lorraine Franconian (; ) in the French region of Lorraine *** Bukovina German () in Bukovina (extinct) *** Pennsylvania German () in historical communities in North America ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variety (linguistics)
In sociolinguistics, a variety, also called an isolect or lect, is a specific form of a language or language cluster. This may include languages, dialects, registers, styles, or other forms of language, as well as a standard variety.Meecham, Marjorie and Janie Rees-Miller. (2001) "Language in social contexts." In W. O'Grady, J. Archibald, M. Aronoff and J. Rees-Miller (eds) ''Contemporary Linguistics''. pp. 537-590. Boston: Bedford/St. Martin's. The use of the word "variety" to refer to the different forms avoids the use of the term ''language'', which many people associate only with the standard language, and the term ''dialect'', which is often associated with non-standard varieties thought of as less prestigious or "correct" than the standard.Schilling-Estes, Natalies. (2006) "Dialect variation." In R.W. Fasold and J. Connor-Linton (eds) ''An Introduction to Language and Linguistics''. pp. 311-341. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. Linguists speak of both standard and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennsylvania Dutch (language)
Pennsylvania Dutch (, or ), referred to as Pennsylvania German in scholarly literature, is a variety of Palatine German, also known as Palatine Dutch, spoken by the Old Order Amish, Old Order Mennonites, Fancy Dutch, and other descendants of German immigrants in the United States and Canada. There are possibly more than 300,000 native speakers of Pennsylvania Dutch in the United States and Canada. It has traditionally been the dialect of the Pennsylvania Dutch, descendants of late 17th- and early to late 18th-century immigrants to Pennsylvania, Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, and North Carolina primarily from Southern Germany and, less so, from the eastern France regions of Alsace and Lorraine, and parts of Switzerland. Although the term Pennsylvania Dutch is often taken to refer to the Amish and related Old Order groups, it does not imply a connection to any particular religious group. The word Dutch does not refer to the Dutch language or people, but is derived from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sranan Tongo
Sranan Tongo (also Sranantongo "Surinamese tongue," Sranan, Surinaams, Surinamese, Surinamese Creole) is an English-based creole language that is spoken as a ''lingua franca'' by approximately 550,000 people in Suriname. Developed originally among slaves from West Africa and English colonists, its use as a ''lingua franca'' expanded after the Dutch took over the colony in 1667, and 85% of the vocabulary comes from English and Dutch. It also became the common language among the indigenous peoples and the indentured laborers imported by the Dutch; these groups included speakers of Javanese, Sarnami Hindustani, Saramaccan, and varieties of Chinese. Origins The Sranan Tongo words for "to know" and "small children" are and (respectively derived from Portuguese and ). The Portuguese were the first European explorers of the West African coast. A trading pidgin language developed between them and Africans, and later explorers, including the English, also used this creole. Based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suriname
Suriname (; srn, Sranankondre or ), officially the Republic of Suriname ( nl, Republiek Suriname , srn, Ripolik fu Sranan), is a country on the northeastern Atlantic coast of South America. It is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north, French Guiana to the east, Guyana to the west, and Brazil to the south. At just under , it is the smallest sovereign state in South America. It has a population of approximately , dominated by descendants from the slaves and labourers brought in from Africa and Asia by the Dutch Empire and Republic. Most of the people live by the country's (north) coast, in and around its capital and largest city, Paramaribo. It is also one of the least densely populated countries on Earth. Situated slightly north of the equator, Suriname is a tropical country dominated by rainforests. Its extensive tree cover is vital to the country's efforts to mitigate climate change and maintain carbon negativity. A developing country with a relativel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saramaccan Language
Saramaccan () is a creole language spoken by about 58,000 ethnic African people near the Saramacca and the upper Suriname River, as well as in Paramaribo, capital of Suriname (formerly also known as Dutch Guiana). The language also has 25,000 speakers in French Guiana and 8,000 in the Netherlands. It has three main dialects. The speakers are mostly descendants of fugitive slaves who were native to West and Central Africa; they form a group called Saamacca, also spelled Saramaka. Linguists consider Saramaccan notable because its vocabulary is based on two European source languages, English (30%) and Portuguese (20%), and various West and Central African languages (50%), but it diverges considerably from all of them. The African component accounts for about 50% once ritual use is taken into account, the highest percentage in the Americas. It is derived from Niger–Congo languages of West Africa, especially Fon and other Gbe languages, as well as Akan and Central African la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curaçao
Curaçao ( ; ; pap, Kòrsou, ), officially the Country of Curaçao ( nl, Land Curaçao; pap, Pais Kòrsou), is a Lesser Antilles island country in the southern Caribbean Sea and the Dutch Caribbean region, about north of the Venezuela coast. It is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Together with Aruba and Bonaire, it forms the ABC islands. Collectively, Curaçao, Aruba, and other Dutch islands in the Caribbean are often called the Dutch Caribbean. Curaçao was formerly part of the Curaçao and Dependencies colony from 1815 to 1954 and later the Netherlands Antilles from 1954 to 2010, as Island Territory of Curaçao ( nl, Eilandgebied Curaçao, links=no, pap, Teritorio Insular di Kòrsou, links=no), and is now formally called the Country of Curaçao. It includes the main island of Curaçao and the much smaller, uninhabited island of Klein Curaçao ("Little Curaçao"). Curaçao has a population of 158,665 (January 2019 est.), with an area of ; its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonaire
Bonaire (; , ; pap, Boneiru, , almost pronounced ) is a Dutch island in the Leeward Antilles in the Caribbean Sea. Its capital is the port of Kralendijk, on the west ( leeward) coast of the island. Aruba, Bonaire and Curaçao form the ABC islands, 80 km (50 miles) off the coast of Venezuela. Unlike much of the Caribbean region, the ABC islands lie outside Hurricane Alley. The islands have an arid climate that attracts visitors seeking warm, sunny weather all year round. Bonaire is a popular snorkeling and scuba diving destination because of its multiple shore diving sites and easy access to the island's fringing reefs. As of 1 January 2019, the island's population totaled 20,104 permanent residents, an increase of about 1,200 since 2015. The island's total land area is ; it is long from north to south, and ranges from wide from east to west. A short west of Bonaire across the sea is the uninhabited islet Klein Bonaire with a total land area of . Klein Bonaire has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aruba
Aruba ( , , ), officially the Country of Aruba ( nl, Land Aruba; pap, Pais Aruba) is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands physically located in the mid-south of the Caribbean Sea, about north of the Venezuela peninsula of Paraguaná Peninsula, Paraguaná and northwest of Curaçao. It measures long from its northwestern to its southeastern end and across at its widest point. Together with Bonaire and Curaçao, Aruba forms a group referred to as the ABC islands (Leeward Antilles), ABC islands. Collectively, these and the other three Dutch substantial islands in the Caribbean are often called the Dutch Caribbean, of which Aruba has about one-third of the population. In 1986, it became a Kingdom of the Netherlands#Constituent countries, constituent country within the Kingdom of the Netherlands, and acquired the formal name the Country of Aruba. Aruba is one of the four countries that form the Kingdom of the Netherlands, along with the Netherlands, Curaçao, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papiamento
Papiamento () or Papiamentu (; nl, Papiaments) is a Portuguese-based creole language spoken in the Dutch Caribbean. It is the most widely spoken language on the Caribbean ABC islands (Aruba, Bonaire, Curaçao), with official status in Aruba and Curaçao. Papiamento is also a recognised language in the Dutch public bodies of Sint-Eustatius and Saba.Papiamento can be used in relations with the Dutch government. The language, spelled in Aruba and in Bonaire and Curaçao, is largely based on colonial-era Portuguese and Spanish (including Judaeo-Portuguese), and has been influenced considerably by Dutch and Venezuelan Spanish. Due to lexical similarities between Spanish and Portuguese, it is difficult to pinpoint the exact origin of some words. Though there are different theories about its origins, most linguists now believe that Papiamento emerged from the Spanish and Portuguese creole languages that developed in the West African coasts, as it has many similarities with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |