Tau protein on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The tau proteins (abbreviated from tubulin associated unit) are a group of six highly soluble 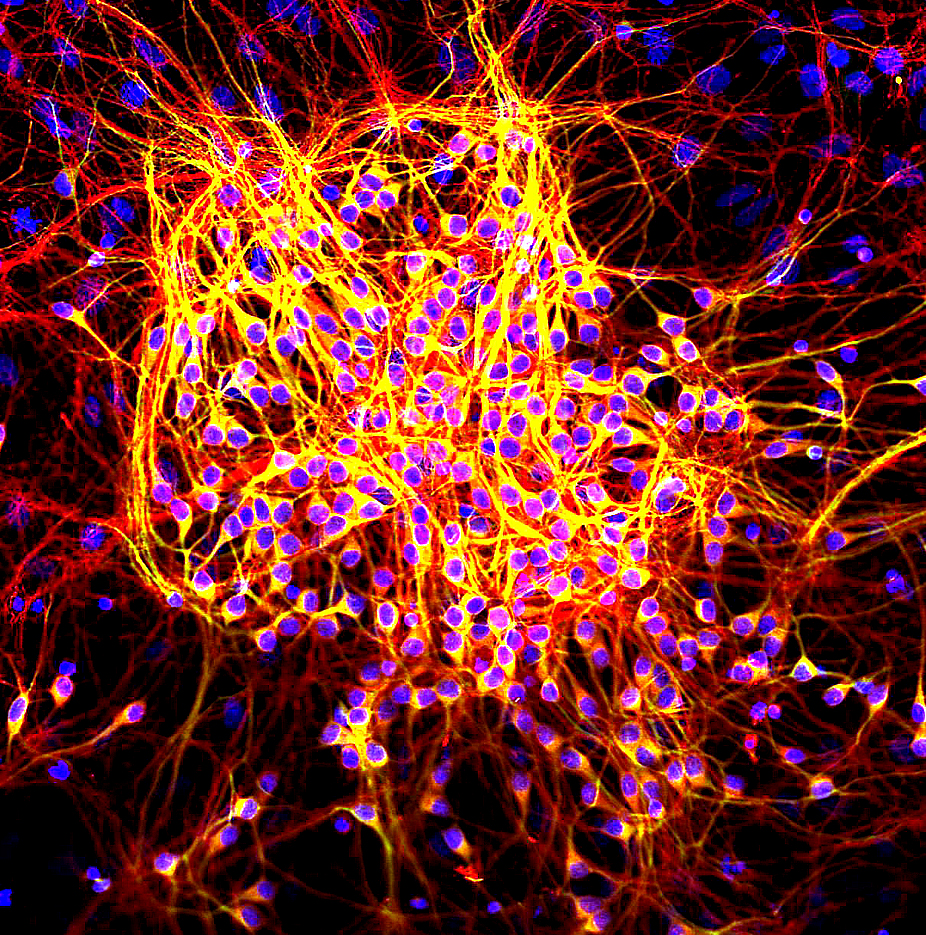
GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on MAPT-Related Disorders
CSF tau-positive man * {{DEFAULTSORT:Tau Protein Proteins
protein isoforms
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isof ...
produced by alternative splicing
Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be i ...
from the gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
''MAPT'' (microtubule-associated protein In cell biology, microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) are proteins that interact with the microtubules of the cellular cytoskeleton. MAPs are integral to: the stability of the cell and its internal structures and the transport of components within ...
tau). They have roles primarily in maintaining the stability of microtubules
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 11 a ...
in axons
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action p ...
and are abundant in the neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa ...
s of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
(CNS), where the cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting o ...
has the highest abundance. They are less common elsewhere but are also expressed at very low levels in CNS astrocyte
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of e ...
s and oligodendrocyte
Oligodendrocytes (), or oligodendroglia, are a type of neuroglia whose main functions are to provide support and insulation to axons in the central nervous system of jawed vertebrates, equivalent to the function performed by Schwann cells in the ...
s.
Pathologies and dementia
Dementia is a disorder which manifests as a set of related symptoms, which usually surfaces when the brain is damaged by injury or disease. The symptoms involve progressive impairments in memory, thinking, and behavior, which negatively affe ...
s of the nervous system
In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes ...
such as Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As ...
and Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms beco ...
are associated with tau proteins that have become hyperphosphorylated
Hyperphosphorylation occurs when a biochemical with multiple phosphorylation sites is fully saturated. Hyperphosphorylation is one of the signaling mechanisms used by the cell to regulate mitosis. When these mechanisms fail, developmental problems ...
insoluble aggregates called neurofibrillary tangles
Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) are aggregates of hyperphosphorylated tau protein that are most commonly known as a primary biomarker of Alzheimer's disease. Their presence is also found in numerous other diseases known as tauopathies. Little is ...
. The tau proteins were identified in 1975 as heat-stable proteins essential for microtubule assembly, and since then they have been characterized as intrinsically disordered proteins
In molecular biology, an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure, typically in the absence of its macromolecular interaction partners, such as other proteins or RNA. IDPs ra ...
.

Function
Microtubule stabilization
Tau proteins are found more often in neurons than in non-neuronal cells in humans. One of tau's main functions is to modulate the stability of axonalmicrotubule
Microtubules are polymers of tubulin that form part of the cytoskeleton and provide structure and shape to eukaryotic cells. Microtubules can be as long as 50 micrometres, as wide as 23 to 27 nm and have an inner diameter between 1 ...
s.'''' Other nervous system microtubule-associated proteins In cell biology, microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) are proteins that interact with the microtubules of the cellular cytoskeleton. MAPs are integral to: the stability of the cell and its internal structures and the transport of components with ...
(MAPs) may perform similar functions, as suggested by tau knockout mice
A knockout mouse, or knock-out mouse, is a genetically modified mouse (''Mus musculus'') in which researchers have inactivated, or "knocked out", an existing gene by replacing it or disrupting it with an artificial piece of DNA. They are importan ...
that did not show abnormalities in brain development – possibly because of compensation in tau deficiency by other MAPs.
Although tau is present in dendrites
Dendrites (from Greek δένδρον ''déndron'', "tree"), also dendrons, are branched protoplasmic extensions of a nerve cell that propagate the electrochemical stimulation received from other neural cells to the cell body, or soma, of the ...
at low levels, where it is involved in postsynaptic scaffolding, it is active primarily in the distal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
portions of axons
An axon (from Greek ἄξων ''áxōn'', axis), or nerve fiber (or nerve fibre: see spelling differences), is a long, slender projection of a nerve cell, or neuron, in vertebrates, that typically conducts electrical impulses known as action p ...
, where it provides microtubule stabilization but also flexibility as needed. Tau proteins interact with tubulin
Tubulin in molecular biology can refer either to the tubulin protein superfamily of globular proteins, or one of the member proteins of that superfamily. α- and β-tubulins polymerize into microtubules, a major component of the eukaryotic cytoske ...
to stabilize microtubules and promote tubulin assembly into microtubules. Tau has two ways of controlling microtubule stability: isoforms
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some iso ...
and phosphorylation
In chemistry, phosphorylation is the attachment of a phosphate group to a molecule or an ion. This process and its inverse, dephosphorylation, are common in biology and could be driven by natural selection. Text was copied from this source, wh ...
.
In addition to its microtubule-stabilizing function, Tau has also been found to recruit signaling proteins and to regulate microtubule-mediated axonal transport.
mRNA translation
Tau is a negative regulator of mRNAtranslation
Translation is the communication of the meaning of a source-language text by means of an equivalent target-language text. The English language draws a terminological distinction (which does not exist in every language) between ''transla ...
in both ''Drosophila'', mouse, and human brains, through its binding to ribosome
Ribosomes ( ) are macromolecular machines, found within all cells, that perform biological protein synthesis (mRNA translation). Ribosomes link amino acids together in the order specified by the codons of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules to fo ...
s, which results in impaired ribosomal function, reduction of protein synthesis
Protein biosynthesis (or protein synthesis) is a core biological process, occurring inside cells, balancing the loss of cellular proteins (via degradation or export) through the production of new proteins. Proteins perform a number of critical ...
and altered synaptic function.'''' Tau interacts specifically with several ribosomal proteins, including the crucial regulator of translation rpS6
Ribosomal protein S6 (rpS6 or eS6) is a component of the 40S ribosomal subunit and is therefore involved in translation. Mouse model studies have shown that phosphorylation of eS6 is involved in the regulation of cell size, cell proliferation, an ...
.
Behavior
The primary non-cellular functions of tau is to negatively regulatelong-term memory
Long-term memory (LTM) is the stage of the Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model in which informative knowledge is held indefinitely. It is defined in contrast to short-term and working memory, which persist for only about 18 to 30 seconds. Long-t ...
and to facilitate habituation
Habituation is a form of non-associative learning in which an innate (non-reinforced) response to a stimulus decreases after repeated or prolonged presentations of that stimulus. Responses that habituate include those that involve the intact org ...
(a form of non-associative learning), two higher and more integrated physiological functions. Since regulation of tau is critical for memory, this could explain the linkage between tauopathies and cognitive impairment.
In mice, while the reported tau knockout strains present without overt phenotype when young, when aged, they show some muscle weakness, hyperactivity, and impaired fear conditioning
Pavlovian fear conditioning is a behavioral paradigm in which organisms learn to predict aversive events. It is a form of learning in which an aversive stimulus (e.g. an electrical shock) is associated with a particular neutral context (e.g., a ...
. However, neither spatial learning in mice, nor short-term memory (learning) in ''Drosophila'' seems to be affected by the absence of tau.
In addition, tau knockout mice have abnormal sleep-wake cycle
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., endogenous) and responds to ...
, with increased wakefulness periods and decreased non-rapid eye movements (NREM) sleep time.
Other functions
Other typical functions of tau includecellular signalling
In biology, cell signaling (cell signalling in British English) or cell communication is the ability of a cell to receive, process, and transmit signals with its environment and with itself. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular ...
, neuronal development, neuroprotection
Neuroprotection refers to the relative preservation of neuronal structure and/or function. In the case of an ongoing insult (a neurodegenerative insult) the relative preservation of neuronal integrity implies a reduction in the rate of neuronal lo ...
and apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes ( morphology) and death. These changes in ...
. Atypical, non-standard roles of tau are also under current investigation, such as its involvement in chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
stability, its interaction with the cellular transcriptome
The transcriptome is the set of all RNA transcripts, including coding and non-coding, in an individual or a population of cells. The term can also sometimes be used to refer to all RNAs, or just mRNA, depending on the particular experiment. The t ...
, its interaction with other cytoskeletal or synaptic proteins, its involvement in myelination
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be ...
or in brain insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism ...
signaling, its role in the exposure to chronic stress
Chronic stress is the physiological or psychological response induced by a long-term internal or external stressor. The stressor, either physically present or recollected, will produce the same effect and trigger a chronic stress response. There i ...
and in depression, etc.
Genetics
In humans, the ''MAPT'' gene for encoding tau protein is located onchromosome 17
Chromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 83 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 2.5 and 3% of the total D ...
q21, containing 16 exon
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequen ...
s. The major tau protein in the human brain is encoded
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communication ...
by 11 exons. Exons 2, 3 and 10 are alternatively spliced
Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may b ...
, which leads to the formation of six tau isoforms. In the human brain, tau proteins constitute a family of six isoforms
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some iso ...
with a range of 352–441 amino acids. Tau isoforms are different in having either zero, one, or two inserts of 29 amino acids at the N-terminal part (exons 2 and 3) and three or four repeat-regions at the C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is ...
part (exon 10). Thus, the longest isoform in the CNS has four repeats (R1, R2, R3 and R4) and two inserts (441 amino acids total), while the shortest isoform has three repeats (R1, R3 and R4) and no insert (352 amino acids total).
The ''MAPT'' gene has two haplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share ...
s, H1 and H2, in which the gene appears in inverted orientations. Haplogroup H2 is common only in Europe and in people with European ancestry. Haplogroup H1 appears to be associated with increased probability of certain dementias, such as Alzheimer's disease. The presence of both haplogroups in Europe means that recombination between inverted haplotypes can result in the lack of one of the functioning copies of the gene, resulting in congenital defects.
Structure
Six tau isoforms exist in human brain tissue, and they are distinguished by their number of binding domains. Three isoforms have three binding domains and the other three have four binding domains. The binding domains are located in the carboxy-terminus of the protein and are positively charged (allowing it to bind to the negatively charged microtubule). The isoforms with four binding domains are better at stabilizing microtubules than those with three binding domains. Tau is aphosphoprotein
A phosphoprotein is a protein that is posttranslationally modified by the attachment of either a single phosphate group, or a complex molecule such as 5'-phospho-DNA, through a phosphate group. The target amino acid is most often serine, threonin ...
with 79 potential Serine (Ser) and Threonine (Thr) phosphorylation sites on the longest tau isoform. Phosphorylation has been reported on approximately 30 of these sites in normal tau proteins.
Phosphorylation of tau is regulated by a host of kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
s, including PKN, a serine/threonine kinase. When PKN is activated, it phosphorylates tau, resulting in disruption of microtubule organization. Phosphorylation of tau is also developmentally regulated. For example, fetal tau is more highly phosphorylated in the embryonic CNS than adult tau. The degree of phosphorylation in all six isoforms decreases with age due to the activation of phosphatase
In biochemistry, a phosphatase is an enzyme that uses water to cleave a phosphoric acid monoester into a phosphate ion and an alcohol. Because a phosphatase enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of its substrate, it is a subcategory of hydrolase ...
s. Like kinases, phosphatases too play a role in regulating the phosphorylation of tau. For example, PP2A and PP2B are both present in human brain tissue and have the ability to dephosphorylate Ser396. The binding of these phosphatases to tau affects tau's association with microtubules.
Phosphorylation of tau has also been suggested to be regulated by ''O''-GlcNAc modification at various Ser and Thr residues.
Mechanism
The accumulation of hyperphosphorylated tau in neurons is associated with neurofibrillary degeneration. The actual mechanism of how tau propagates from one cell to another is not well identified. Also, other mechanisms, including tau release and toxicity, are unclear. As tau aggregates, it replaces tubulin, which in turn enhances fibrilization of tau. Several propagation methods have been proposed that occur by synaptic contact such as synaptic cell adhesion proteins, neuronal activity and other synaptic and non-synaptic mechanisms. The mechanism of tau aggregation is still not completely elucidated, but several factors favor this process, including tau phosphorylation and zinc ions.Release
Tau involves in uptake and release process, which is known as seeding. Uptake of tau protein mechanism requires the presence of heparan sulfate proteoglycans at the cell surface, which happen bymacropinocytosis
In cellular biology, pinocytosis, otherwise known as fluid endocytosis and bulk-phase pinocytosis, is a mode of endocytosis in which small molecules dissolved in extracellular fluid are brought into the cell through an invagination of the cell me ...
. On the other hand, tau release depends on neuronal activity. Many factors influence tau release, for example, type of isoforms or ''MAPT'' mutations that change the extracellular level of tau. According to Asai and his colleagues, the spreading of tau protein occurs from the entorhinal cortex
The entorhinal cortex (EC) is an area of the brain's allocortex, located in the medial temporal lobe, whose functions include being a widespread network hub for memory, navigation, and the perception of time.Integrating time from experience in th ...
to the hippocampal region in the early stages of the disease. They also suggested that microglia
Microglia are a type of neuroglia (glial cell) located throughout the brain and spinal cord. Microglia account for about 7% of cells found within the brain. As the resident macrophage cells, they act as the first and main form of active immune de ...
were also involved in the transport process, and their actual role is still unknown.
Toxicity
Tau causes toxic effects through its accumulation inside cells. Many enzymes are involved in toxicity mechanism such as PAR-1 kinase. This enzyme stimulates phosphorylation of serine 262 and 356, which in turn leads to activate other kinases (GSK-3
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) is a serine/threonine protein kinase that mediates the addition of phosphate molecules onto serine and threonine amino acid residues. First discovered in 1980 as a regulatory kinase for its namesake, glycogen ...
and CDK5) that cause disease-associated phosphoepitopes. The degree of toxicity is affected by different factors, such as the degree of microtubule binding. Toxicity could also happen by neurofibrillary tangle
Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) are aggregates of hyperphosphorylated tau protein that are most commonly known as a primary biomarker of Alzheimer's disease. Their presence is also found in numerous other diseases known as tauopathies. Little is ...
s (NFTs), which leads to cell death and cognitive decline.
Clinical significance
Hyperphosphorylation
Hyperphosphorylation occurs when a biochemical with multiple phosphorylation sites is fully saturated. Hyperphosphorylation is one of the signaling mechanisms used by the cell to regulate mitosis. When these mechanisms fail, developmental problems ...
of the tau protein (tau inclusions, pTau) can result in the self-assembly
Self-assembly is a process in which a disordered system of pre-existing components forms an organized structure or pattern as a consequence of specific, local interactions among the components themselves, without external direction. When the ...
of tangles of paired helical filaments and straight filaments, which are involved in the pathogenesis
Pathogenesis is the process by which a disease or disorder develops. It can include factors which contribute not only to the onset of the disease or disorder, but also to its progression and maintenance. The word comes from Greek πάθος ''pat ...
of Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As ...
, frontotemporal dementia
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), or frontotemporal degeneration disease, or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of frontal and temporal lobes. FTDs broadly present as ...
and other tauopathies. All of the six tau isoforms are present in an often hyperphosphorylated state in paired helical filaments in the Alzheimer's disease brain. In other neurodegenerative diseases
A neurodegenerative disease is caused by the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, in the process known as neurodegeneration. Such neuronal damage may ultimately involve cell death. Neurodegenerative diseases include amyotrophi ...
, the deposition of aggregates enriched in certain tau isoforms has been reported. When misfolded
Protein folding is the physical process by which a protein chain is translated to its native three-dimensional structure, typically a "folded" conformation by which the protein becomes biologically functional. Via an expeditious and reproduc ...
, this otherwise very soluble protein can form extremely insoluble aggregates that contribute to a number of neurodegenerative diseases. Tau protein has a direct effect on the breakdown of a living cell caused by tangles that form and block nerve synapses
In the nervous system, a synapse is a structure that permits a neuron (or nerve cell) to pass an electrical or chemical signal to another neuron or to the target effector cell.
Synapses are essential to the transmission of nervous impulses fr ...
."Alzheimer's Brain Tangles." Alzheimer's Association, www.alz.org/braintour/tangles.asp.
Gender-specific tau gene expression across different regions of the human brain has recently been implicated in gender differences in the manifestations and risk for tauopathies. Some aspects of how the disease functions also suggest that it has some similarities to prion
Prions are misfolded proteins that have the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein. They characterize several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and many other animals. It i ...
proteins.
Tau hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease
Thetau hypothesis The biochemistry of Alzheimer's disease, the most common cause of dementia, is not yet very well understood. Alzheimer's disease (AD) has been identified as a proteopathy: a protein misfolding disease due to the accumulation of abnormally folded a ...
states that excessive or abnormal phosphorylation of tau results in the transformation of normal adult tau into paired-helical-filament (PHF) tau and neurofibrillary tangle
Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) are aggregates of hyperphosphorylated tau protein that are most commonly known as a primary biomarker of Alzheimer's disease. Their presence is also found in numerous other diseases known as tauopathies. Little is ...
s (NFTs). The stage of the disease determines NFTs' phosphorylation. In AD, at least 19 amino acids are phosphorylated; pre-NFT phosphorylation occurs at serine 119, 202 and 409, while intra-NFT phosphorylation happens at serine 396 and threonine 231. Through its isoforms and phosphorylation, tau protein interacts with tubulin to stabilize microtubule assembly. All of the six tau isoforms are present in an often hyperphosphorylated state in paired helical filaments (PHFs) in the AD brain.
Tau mutations have many consequences, including microtubule dysfunction and alteration of the expression level of tau isoforms. Mutations that alter function and isoform expression of tau lead to hyperphosphorylation. The process of tau aggregation in the absence of mutations is not known but might result from increased phosphorylation, protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
action or exposure to polyanions, such as glycosaminoglycans
Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) or mucopolysaccharides are long, linear polysaccharides consisting of repeating disaccharide units (i.e. two-sugar units). The repeating two-sugar unit consists of a uronic sugar and an amino sugar, except in the case ...
. Hyperphosphorylated tau disassembles microtubules and sequesters normal tau, MAPT 1 (microtubule associated protein tau 1), MAPT 2 and ubiquitin
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Fo ...
into tangles of PHFs. This insoluble structure damages cytoplasmic
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The ...
functions and interferes with axonal transport
Axonal transport, also called axoplasmic transport or axoplasmic flow, is a cellular process responsible for movement of mitochondria, lipids, synaptic vesicles, proteins, and other organelles to and from a neuron's cell body, through the cytopla ...
, which can lead to cell death.
Hyperphosphorylated forms of tau protein are the main component of PHFs of NFTs in the brain of AD patients. It has been well demonstrated that regions of tau six-residue segments, namely PHF6 (VQIVYK) and PHF6* (VQIINK), can form tau PHF aggregation in AD. Apart from the PHF6, some other residue sites like Ser285, Ser289, Ser293, Ser305 and Tyr310, located near the C-terminal of the PHF6 sequences, play key roles in the phosphorylation of tau. Hyperphosphorylated tau differs in its sensitivity and its kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule don ...
as well as alkaline phosphatase
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.1, alkaline phosphomonoesterase; phosphomonoesterase; glycerophosphatase; alkaline phosphohydrolase; alkaline phenyl phosphatase; orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase (alkaline optimum), systematic ...
activity and is, along with beta-amyloid
Amyloid beta (Aβ or Abeta) denotes peptides of 36–43 amino acids that are the main component of the amyloid plaques found in the brains of people with Alzheimer's disease. The peptides derive from the amyloid precursor protein (APP), which is ...
, a component of the pathologic lesion seen in Alzheimer disease. A recent hypothesis identifies the decrease of reelin signaling as the primary change in Alzheimer's disease that leads to the hyperphosphorylation of tau via a decrease in GSK3β inhibition.
A68 is a name sometimes given (mostly in older publications) to the hyperphosphorylated
Hyperphosphorylation occurs when a biochemical with multiple phosphorylation sites is fully saturated. Hyperphosphorylation is one of the signaling mechanisms used by the cell to regulate mitosis. When these mechanisms fail, developmental problems ...
form of tau protein found in the brains of individuals with Alzheimer's disease.
In 2020, researchers from two groups published studies indicating that an immunoassay
An immunoassay (IA) is a biochemical test that measures the presence or concentration of a macromolecule or a small molecule in a solution through the use of an antibody (usually) or an antigen (sometimes). The molecule detected by the immunoa ...
blood test for the p-tau-217 form of the protein could diagnose Alzheimer's up to decades before dementia symptoms were evident.
Traumatic brain injury
Repetitive mildtraumatic brain injury
A traumatic brain injury (TBI), also known as an intracranial injury, is an injury to the brain caused by an external force. TBI can be classified based on severity (ranging from mild traumatic brain injury TBI/concussionto severe traumatic br ...
(TBI) is a central component of contact sports
Contact sports are sports that emphasize or require physical contact between players. Some sports, such as mixed martial arts, are scored on impacting an opponent, while others, including rugby football, gridiron football and Australian rules foot ...
, especially American football
American football (referred to simply as football in the United States and Canada), also known as gridiron, is a team sport played by two teams of eleven players on a rectangular field with goalposts at each end. The offense, the team wi ...
, and the concussive force of military blasts. It can lead to chronic traumatic encephalopathy
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a neurodegenerative disease linked to repeated trauma to the head. The encephalopathy symptoms can include behavioral problems, mood problems, and problems with thinking. The disease often gets worse ...
(CTE), a condition characterized by fibrillar tangles of hyperphosphorylated tau. After severe traumatic brain injury, high levels of tau protein in extracellular fluid in the brain are linked to poor outcomes.
*
Prion-like propagation hypothesis
The term "prion-like" is often used to describe several aspects of tau pathology in various tauopathies, likeAlzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As ...
and frontotemporal dementia
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), or frontotemporal degeneration disease, or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of frontal and temporal lobes. FTDs broadly present as ...
. True prion
Prions are misfolded proteins that have the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein. They characterize several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and many other animals. It i ...
s are defined by their ability to induce misfolding of native proteins to perpetuate the pathology. True prions, like PRNP
Major prion protein (PrP), is encoded in the human by the ''PRNP'' gene also known as CD230 (cluster of differentiation 230). Expression of the protein is most predominant in the nervous system but occurs in many other tissues throughout the bo ...
, are also infectious with the capability to cross species. Since tau has yet to be proven to be infectious it is not considered to be a true prion but instead a "prion-like" protein. Much like true prions, pathological tau aggregates have been shown to have the capacity to induce misfolding of native tau protein. Both misfolding competent and non-misfolding competent species of tau aggregates have been reported, indicating a highly specific mechanism.
Interactions
Tau protein has been shown tointeract
Advocates for Informed Choice, doing business as, dba interACT or interACT Advocates for Intersex Youth, is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization using innovative strategies to advocate for the legal and human rights of children with intersex trai ...
with:
* Alpha-synuclein
Alpha-synuclein is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''SNCA'' gene. Alpha-synuclein is a neuronal protein that regulates synaptic vesicle trafficking and subsequent neurotransmitter release.
It is abundant in the brain, while smaller a ...
,
* FYN,
* Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src
* S100B, and
* YWHAZ
14-3-3 protein zeta/delta (14-3-3ζ) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''YWHAZ'' gene on chromosome 8. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the 14-3-3 protein family and a central hub protein for many signal transduction pat ...
.
See also
*Tauopathy
Tauopathy belongs to a class of neurodegenerative diseases involving the aggregation of tau protein into neurofibrillary or gliofibrillary tangles in the human brain. Tangles are formed by hyperphosphorylation of the microtubule protein known ...
, a class of diseases associated with accumulated tau proteins
* Dementia pugilistica
Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) is a neurodegenerative disease linked to repeated trauma to the head. The encephalopathy symptoms can include behavioral problems, mood problems, and problems with thinking. The disease often gets worse o ...
* Alzheimer's disease
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and progressively worsens. It is the cause of 60–70% of cases of dementia. The most common early symptom is difficulty in remembering recent events. As ...
* Primary age-related tauopathy Primary age-related tauopathy (PART) is a neuropathological designation introduced in 2014 to describe the neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) that are commonly observed in the brains of normally aged and cognitively impaired individuals that can occur ...
* Aging-related tau astrogliopathy
* Corticobasal degeneration
* Progressive supranuclear palsy
Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a late-onset degenerative disease involving the gradual deterioration and death of specific volumes of the brain. The condition leads to symptoms including loss of balance, slowing of movement, difficulty ...
* Proteopathy
* Pick's disease
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD), or frontotemporal degeneration disease, or frontotemporal neurocognitive disorder, encompasses several types of dementia involving the progressive degeneration of frontal and temporal lobes. FTDs broadly present a ...
* Frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17
Frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17) is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative tauopathy and Parkinson plus syndrome. FTDP-17 is caused by mutations in the MAPT (microtubule associated protein tau) gene locat ...
* Prion
Prions are misfolded proteins that have the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein. They characterize several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and many other animals. It i ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
*GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on MAPT-Related Disorders
CSF tau-positive man * {{DEFAULTSORT:Tau Protein Proteins