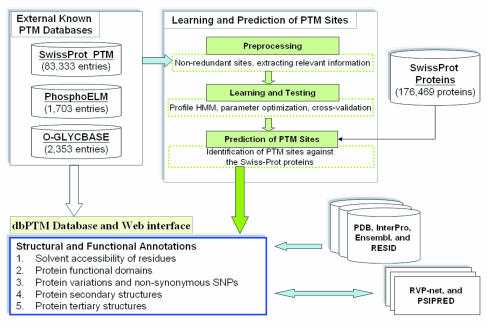
|
C-terminal
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-translational Modification
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signaling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones. Post-translational modifications can occur on the amino acid side chains or at the protein's C- or N- termini. They can extend the chemical repertoire of the 20 standard amino acids by modifying an existing functional group or introducing a new one such as phosphate. Phosphorylation is a highly effective mechanism for regulating the activity of enzymes and is the most common post-translational modification. Many eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins also have carbohydrate molecules attached to them in a process called glycosyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posttranslational Modification
Post-translational modification (PTM) is the covalent and generally enzymatic modification of proteins following protein biosynthesis. This process occurs in the endoplasmic reticulum and the golgi apparatus. Proteins are synthesized by ribosomes translating mRNA into polypeptide chains, which may then undergo PTM to form the mature protein product. PTMs are important components in cell signal transduction, signaling, as for example when prohormones are converted to hormones. Post-translational modifications can occur on the amino acid side chains or at the protein's C-terminus, C- or N-terminus, N- termini. They can extend the chemical repertoire of the 20 standard amino acids by modifying an existing functional group or introducing a new one such as phosphorylation, phosphate. Phosphorylation is a highly effective mechanism for regulating the activity of enzymes and is the most common post-translational modification. Many eukaryotic and prokaryotic proteins also have carbohydra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. A 550 kDa complex of 12 subunits, RNAP II is the most studied type of RNA polymerase. A wide range of transcription factors are required for it to bind to upstream gene promoters and begin transcription. Discovery Early studies suggested a minimum of two RNAPs: one which synthesized rRNA in the nucleolus, and one which synthesized other RNA in the nucleoplasm, part of the nucleus but outside the nucleolus. In 1969, science experimentalists Robert Roeder and William Rutter definitively discovered an additional RNAP that was responsible for transcription of some kind of RNA in the nucleoplasm. The finding was obtained by the use of ion-exchange chromatography via DEAE coated Sephadex beads. The technique separated the enzymes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol (), or glycophosphatidylinositol, or GPI in short, is a phosphoglyceride that can be attached to the C-terminus of a protein during posttranslational modification. The resulting GPI-anchored proteins play key roles in a wide variety of biological processes. GPI is composed of a phosphatidylinositol group linked through a carbohydrate-containing linker (glucosamine and mannose glycosidically bound to the inositol residue) and via an ethanolamine phosphate (EtNP) bridge to the C-terminal amino acid of a mature protein. The two fatty acids within the hydrophobic phosphatidyl-inositol group anchor the protein to the cell membrane. Synthesis Glycosylated (GPI-anchored) proteins contain a signal sequence, thus directing them to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). The protein is co-translationally inserted in the ER membrane via a translocon and is attached to the ER membrane by its hydrophobic C terminus; the majority of the protein extends into the ER lume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the formation of new protein products. They do this by cleaving the peptide bonds within proteins by hydrolysis, a reaction where water breaks bonds. Proteases are involved in many biological functions, including digestion of ingested proteins, protein catabolism (breakdown of old proteins), and cell signaling. In the absence of functional accelerants, proteolysis would be very slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteases can be found in all forms of life and viruses. They have independently evolved multiple times, and different classes of protease can perform the same reaction by completely different catalytic mechanisms. Hierarchy of proteases Based on catalytic residue Proteases can be classified into seven broad groups: * Serine protease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capping Enzyme
A capping enzyme (CE) is an enzyme that catalyzes the attachment of the 5' cap to messenger RNA molecules that are in the process of being synthesized in the cell nucleus during the first stages of gene expression. The addition of the cap occurs co-transcriptionally, after the growing RNA molecule contains as little as 25 nucleotides. The enzymatic reaction is catalyzed specifically by the phosphorylated carboxyl-terminal domain (CTD) of RNA polymerase II. The 5' cap is therefore specific to RNAs synthesized by this polymerase rather than those synthesized by RNA polymerase I or RNA polymerase III. Pre-mRNA undergoes a series of modifications - 5' capping, splicing and 3' polyadenylation before becoming mature mRNA that exits the nucleus to be translated into functional proteins and capping of the 5' end is the first of these modifications. Three enzymes, RNA triphosphatase, guanylyltransferase (or CE), and methyltransferase are involved in the addition of the methylated 5' cap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
G Protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell to its interior. Their activity is regulated by factors that control their ability to bind to and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP) to guanosine diphosphate (GDP). When they are bound to GTP, they are 'on', and, when they are bound to GDP, they are 'off'. G proteins belong to the larger group of enzymes called GTPases. There are two classes of G proteins. The first function as monomeric small GTPases (small G-proteins), while the second function as heterotrimeric G protein complexes. The latter class of complexes is made up of '' alpha'' (α), ''beta'' (β) and ''gamma'' (γ) subunits. In addition, the beta and gamma subunits can form a stable dimeric complex referred to as the beta-gamma complex . Heterotrimeric G proteins located within the cell are activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenylation
Prenylation (also known as isoprenylation or lipidation) is the addition of hydrophobic molecules to a protein or a biomolecule. It is usually assumed that prenyl groups (3-methylbut-2-en-1-yl) facilitate attachment to cell membranes, similar to lipid anchors like the GPI anchor, though direct evidence of this has not been observed. Prenyl groups (also called isoprenyl groups, having one hydrogen atom more than isoprene) have been shown to be important for protein–protein binding through specialized prenyl-binding domains. Protein prenylation Protein prenylation involves the transfer of either a farnesyl or a geranylgeranyl moiety to C-terminal cysteine(s) of the target protein. There are three enzymes that carry out prenylation in the cell, farnesyl transferase, Caax protease and geranylgeranyl transferase I. Farnesylation is a type of prenylation, a post-translational modification of proteins by which an isoprenyl group is added to a cysteine residue. It is an important pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapeptide Structural Formulae V
A tetrapeptide is a peptide, classified as an oligopeptide, since it only consists of four amino acids joined by peptide bonds. Many tetrapeptides are pharmacologically active, often showing affinity and specificity for a variety of receptors in protein-protein signaling. Present in nature are both linear and cyclic tetrapeptides (CTPs), the latter of which mimics protein reverse turns which are often present on the surface of proteins and druggable targets. Tetrapeptides may be cyclized by a fourth peptide bond or other covalent bonds. Examples of tetrapeptides are: * Tuftsin (L-threonyl-L-lysyl-L-prolyl-L-arginine) is a peptide related primarily to the immune system function. * Rigin (glycyl-L-glutaminyl-L-prolyl-L-arginine) is a tetrapeptide with functions similar to those of tuftsin. * Postin (Lys-Pro-Pro-Arg) is the N-terminal tetrapeptide of cystatin C and an antagonist of tuftsin. * Endomorphin-1 (H-Tyr-Pro-Trp-Phe-NH2) and endomorphin-2 (H-Tyr-Pro-Phe-Phe-NH2) are pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ER Retention
ER retention refers to proteins that are retained in the endoplasmic reticulum, or ER, after folding; these are known as ER resident proteins. Protein localization to the ER often depends on certain sequences of amino acids located at the N terminus or C terminus. These sequences are known as signal peptides, molecular signatures, or sorting signals. The classical ER retention signal is the C-terminal KDEL sequence for lumen bound proteins and KKXX (signal sequence is located in cytoplasm) for transmembrane localization. These signals allow for retrieval from the Golgi apparatus by ER retention receptors, effectively maintaining the protein in the ER. Other mechanisms for ER retention are being studied but are not as well characterized as signal retention. ER retention receptors proteins *KDELR1 *KDELR2 *KDELR3 See also * KKXX (amino acid sequence) * KDEL (amino acid sequence) * Signal peptide *Protein targeting :''This article deals with protein targeting in eukaryotes unless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminal End
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |