database storage structures on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
 The introduction of the term ''database'' coincided with the availability of direct-access storage (disks and drums) from the mid-1960s onwards. The term represented a contrast with the tape-based systems of the past, allowing shared interactive use rather than daily
The introduction of the term ''database'' coincided with the availability of direct-access storage (disks and drums) from the mid-1960s onwards. The term represented a contrast with the tape-based systems of the past, allowing shared interactive use rather than daily
 The use of primary keys (user-oriented identifiers) to represent cross-table relationships, rather than disk addresses, had two primary motivations. From an engineering perspective, it enabled tables to be relocated and resized without expensive database reorganization. But Codd was more interested in the difference in semantics: the use of explicit identifiers made it easier to define update operations with clean mathematical definitions, and it also enabled query operations to be defined in terms of the established discipline of first-order predicate calculus; because these operations have clean mathematical properties, it becomes possible to rewrite queries in provably correct ways, which is the basis of query optimization. There is no loss of expressiveness compared with the hierarchic or network models, though the connections between tables are no longer so explicit.
In the hierarchic and network models, records were allowed to have a complex internal structure. For example, the salary history of an employee might be represented as a "repeating group" within the employee record. In the relational model, the process of normalization led to such internal structures being replaced by data held in multiple tables, connected only by logical keys.
For instance, a common use of a database system is to track information about users, their name, login information, various addresses and phone numbers. In the navigational approach, all of this data would be placed in a single variable-length record. In the relational approach, the data would be ''normalized'' into a user table, an address table and a phone number table (for instance). Records would be created in these optional tables only if the address or phone numbers were actually provided.
As well as identifying rows/records using logical identifiers rather than disk addresses, Codd changed the way in which applications assembled data from multiple records. Rather than requiring applications to gather data one record at a time by navigating the links, they would use a declarative query language that expressed what data was required, rather than the access path by which it should be found. Finding an efficient access path to the data became the responsibility of the database management system, rather than the application programmer. This process, called query optimization, depended on the fact that queries were expressed in terms of mathematical logic.
Codd's paper inspired teams at various universities to research the subject, including one at
The use of primary keys (user-oriented identifiers) to represent cross-table relationships, rather than disk addresses, had two primary motivations. From an engineering perspective, it enabled tables to be relocated and resized without expensive database reorganization. But Codd was more interested in the difference in semantics: the use of explicit identifiers made it easier to define update operations with clean mathematical definitions, and it also enabled query operations to be defined in terms of the established discipline of first-order predicate calculus; because these operations have clean mathematical properties, it becomes possible to rewrite queries in provably correct ways, which is the basis of query optimization. There is no loss of expressiveness compared with the hierarchic or network models, though the connections between tables are no longer so explicit.
In the hierarchic and network models, records were allowed to have a complex internal structure. For example, the salary history of an employee might be represented as a "repeating group" within the employee record. In the relational model, the process of normalization led to such internal structures being replaced by data held in multiple tables, connected only by logical keys.
For instance, a common use of a database system is to track information about users, their name, login information, various addresses and phone numbers. In the navigational approach, all of this data would be placed in a single variable-length record. In the relational approach, the data would be ''normalized'' into a user table, an address table and a phone number table (for instance). Records would be created in these optional tables only if the address or phone numbers were actually provided.
As well as identifying rows/records using logical identifiers rather than disk addresses, Codd changed the way in which applications assembled data from multiple records. Rather than requiring applications to gather data one record at a time by navigating the links, they would use a declarative query language that expressed what data was required, rather than the access path by which it should be found. Finding an efficient access path to the data became the responsibility of the database management system, rather than the application programmer. This process, called query optimization, depended on the fact that queries were expressed in terms of mathematical logic.
Codd's paper inspired teams at various universities to research the subject, including one at
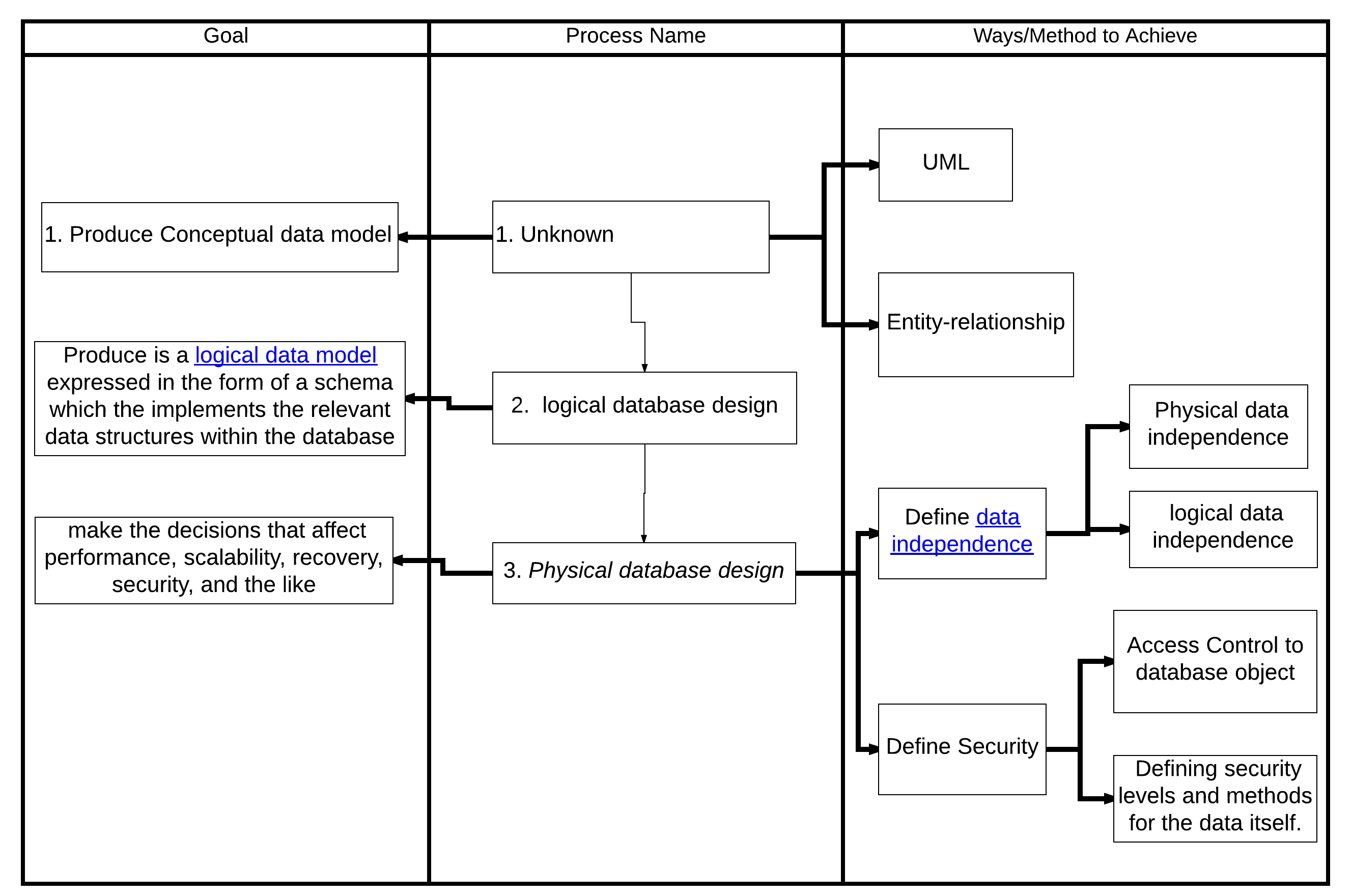 The first task of a database designer is to produce a
The first task of a database designer is to produce a
 A database model is a type of data model that determines the logical structure of a database and fundamentally determines in which manner
A database model is a type of data model that determines the logical structure of a database and fundamentally determines in which manner
Encyclopedia of Database Systems
4100 p. 60 illus. . * Gray, J. and Reuter, A. ''Transaction Processing: Concepts and Techniques'', 1st edition, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 1992. * Kroenke, David M. and David J. Auer. ''Database Concepts.'' 3rd ed. New York: Prentice, 2007. * Raghu Ramakrishnan and Johannes Gehrke,
Database Management Systems
'. *
Database System Concepts
'. * * Teorey, T.; Lightstone, S. and Nadeau, T. ''Database Modeling & Design: Logical Design'', 4th edition, Morgan Kaufmann Press, 2005. . *
CMU Database courses playlist
' *
MIT OCW 6.830 , Fall 2010 , Database Systems
' *
Berkeley CS W186
'
DB File extension
nbsp;– information about files with the DB extension {{Authority control
computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and softw ...
, a database is an organized collection of data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
or a type of data store
A data store is a repository for persistently storing and managing collections of data which include not just repositories like databases, but also simpler store types such as simple files, emails, etc.
A ''database'' is a collection of data that ...
based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
that interacts with end user
In product development, an end user (sometimes end-user) is a person who ultimately uses or is intended to ultimately use a product. The end user stands in contrast to users who support or maintain the product, such as sysops, system administrato ...
s, applications
Application may refer to:
Mathematics and computing
* Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks
** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a ...
, and the database itself to capture and analyze the data. The DBMS additionally encompasses the core facilities provided to administer the database. The sum total of the database, the DBMS and the associated applications can be referred to as a database system. Often the term "database" is also used loosely to refer to any of the DBMS, the database system or an application associated with the database.
Before digital storage and retrieval of data have become widespread, index cards were used for data storage
Data storage is the recording (storing) of information (data) in a storage medium. Handwriting, phonographic recording, magnetic tape, and optical discs are all examples of storage media. Biological molecules such as RNA and DNA are con ...
in a wide range of applications and environments: in the home to record and store recipes, shopping lists, contact information and other organizational data; in business to record presentation notes, project research and notes, and contact information; in schools as flash cards or other visual aids; and in academic research to hold data such as bibliographical citations or notes in a card file
A (German language, German: 'slipbox', plural ) or card file consists of small items of information stored on (German: 'slips'), paper slips or cards, that may be linked to each other through Index term, subject headings or other metadata such ...
. Professional book indexers used index cards in the creation of book indexes until they were replaced by indexing software
Indexing software consists of computer application software, applications that help to build an index (publishing), index (like this one:Index of branches of science).
Features
There are several methodologies for indexing:
* Standalone indexin ...
in the 1980s and 1990s.
Small databases can be stored on a file system, while large databases are hosted on computer clusters or cloud storage
Cloud storage is a model of computer data storage in which data, said to be on "the cloud", is stored remotely in logical pools and is accessible to users over a network, typically the Internet. The physical storage spans multiple servers (so ...
. The design of databases spans formal techniques and practical considerations, including data modeling
Data modeling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying certain formal techniques. It may be applied as part of broader Model-driven engineering (MDE) concept.
Overview
Data modeli ...
, efficient data representation and storage, query language
A query language, also known as data query language or database query language (DQL), is a computer language used to make queries in databases and information systems. In database systems, query languages rely on strict theory to retrieve informa ...
s, security
Security is protection from, or resilience against, potential harm (or other unwanted coercion). Beneficiaries (technically referents) of security may be persons and social groups, objects and institutions, ecosystems, or any other entity or ...
and privacy
Privacy (, ) is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively.
The domain of privacy partially overlaps with security, which can include the concepts of a ...
of sensitive data, and distributed computing
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems, defined as computer systems whose inter-communicating components are located on different networked computers.
The components of a distributed system commu ...
issues, including supporting concurrent access and fault tolerance
Fault tolerance is the ability of a system to maintain proper operation despite failures or faults in one or more of its components. This capability is essential for high-availability, mission-critical, or even life-critical systems.
Fault t ...
.
Computer scientists
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to applied disciplines (including the design an ...
may classify database management systems according to the database model
A database model is a type of data model that determines the logical structure of a database. It fundamentally determines in which manner data can be stored, organized and manipulated. The most popular example of a database model is the relatio ...
s that they support. Relational database
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970.
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured for ...
s became dominant in the 1980s. These model data as rows and columns
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member ...
in a series of tables, and the vast majority use SQL
Structured Query Language (SQL) (pronounced ''S-Q-L''; or alternatively as "sequel")
is a domain-specific language used to manage data, especially in a relational database management system (RDBMS). It is particularly useful in handling s ...
for writing and querying data. In the 2000s, non-relational databases became popular, collectively referred to as NoSQL
NoSQL (originally meaning "Not only SQL" or "non-relational") refers to a type of database design that stores and retrieves data differently from the traditional table-based structure of relational databases. Unlike relational databases, which ...
, because they use different query language
A query language, also known as data query language or database query language (DQL), is a computer language used to make queries in databases and information systems. In database systems, query languages rely on strict theory to retrieve informa ...
s.
Terminology and overview
Formally, a "database" refers to a set of related data accessed through the use of a "database management system" (DBMS), which is an integrated set ofcomputer software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
that allows users
Ancient Egyptian roles
* User (ancient Egyptian official), an ancient Egyptian nomarch (governor) of the Eighth Dynasty
* Useramen, an ancient Egyptian vizier also called "User"
Other uses
* User (computing), a person (or software) using an ...
to interact with one or more databases and provides access to all of the data contained in the database (although restrictions may exist that limit access to particular data). The DBMS provides various functions that allow entry, storage and retrieval of large quantities of information and provides ways to manage how that information is organized.
Because of the close relationship between them, the term "database" is often used casually to refer to both a database and the DBMS used to manipulate it.
Outside the world of professional information technology
Information technology (IT) is a set of related fields within information and communications technology (ICT), that encompass computer systems, software, programming languages, data processing, data and information processing, and storage. Inf ...
, the term ''database'' is often used to refer to any collection of related data (such as a spreadsheet
A spreadsheet is a computer application for computation, organization, analysis and storage of data in tabular form. Spreadsheets were developed as computerized analogs of paper accounting worksheets. The program operates on data entered in c ...
or a card index) as size and usage requirements typically necessitate use of a database management system.
Existing DBMSs provide various functions that allow management of a database and its data which can be classified into four main functional groups:
* Data definition – Creation, modification and removal of definitions that detail how the data is to be organized.
* Update – Insertion, modification, and deletion of the data itself.
* Retrieval – Selecting data according to specified criteria (e.g., a query, a position in a hierarchy, or a position in relation to other data) and providing that data either directly to the user, or making it available for further processing by the database itself or by other applications. The retrieved data may be made available in a more or less direct form without modification, as it is stored in the database, or in a new form obtained by altering it or combining it with existing data from the database.
* Administration – Registering and monitoring users, enforcing data security, monitoring performance, maintaining data integrity, dealing with concurrency control, and recovering information that has been corrupted by some event such as an unexpected system failure.
Both a database and its DBMS conform to the principles of a particular database model
A database model is a type of data model that determines the logical structure of a database. It fundamentally determines in which manner data can be stored, organized and manipulated. The most popular example of a database model is the relatio ...
. "Database system" refers collectively to the database model, database management system, and database.
Physically, database servers are dedicated computers that hold the actual databases and run only the DBMS and related software. Database servers are usually multiprocessor
Multiprocessing (MP) is the use of two or more central processing units (CPUs) within a single computer system. The term also refers to the ability of a system to support more than one processor or the ability to allocate tasks between them. The ...
computers, with generous memory and RAID
RAID (; redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical Computer data storage, data storage components into one or more logical units for th ...
disk arrays used for stable storage. Hardware database accelerators, connected to one or more servers via a high-speed channel, are also used in large-volume transaction processing environments. DBMSs are found at the heart of most database applications. DBMSs may be built around a custom multitasking kernel with built-in networking support, but modern DBMSs typically rely on a standard operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware and software resources, and provides common daemon (computing), services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems scheduler (computing), schedule tasks for ...
to provide these functions.
Since DBMSs comprise a significant market
Market is a term used to describe concepts such as:
*Market (economics), system in which parties engage in transactions according to supply and demand
*Market economy
*Marketplace, a physical marketplace or public market
*Marketing, the act of sat ...
, computer and storage vendors often take into account DBMS requirements in their own development plans.
Databases and DBMSs can be categorized according to the database model(s) that they support (such as relational or XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing data. It defines a set of rules for encoding electronic document, documents in a format that is both human-readable and Machine-r ...
), the type(s) of computer they run on (from a server cluster to a mobile phone
A mobile phone or cell phone is a portable telephone that allows users to make and receive calls over a radio frequency link while moving within a designated telephone service area, unlike fixed-location phones ( landline phones). This rad ...
), the query language
A query language, also known as data query language or database query language (DQL), is a computer language used to make queries in databases and information systems. In database systems, query languages rely on strict theory to retrieve informa ...
(s) used to access the database (such as SQL or XQuery
XQuery (XML Query) is a query language and functional programming language designed to query and transform collections of structured and unstructured data, primarily in the form of XML. It also supports text data and, through implementation-sp ...
), and their internal engineering, which affects performance, scalability
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work. One definition for software systems specifies that this may be done by adding resources to the system.
In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that ...
, resilience, and security.
History
The sizes, capabilities, and performance of databases and their respective DBMSs have grown in orders of magnitude. These performance increases were enabled by the technology progress in the areas of processors,computer memory
Computer memory stores information, such as data and programs, for immediate use in the computer. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the terms ''RAM,'' ''main memory,'' or ''primary storage.'' Archaic synonyms for main memory include ...
, computer storage
Computer data storage or digital data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and Data storage, recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers.
The cent ...
, and computer network
A computer network is a collection of communicating computers and other devices, such as printers and smart phones. In order to communicate, the computers and devices must be connected by wired media like copper cables, optical fibers, or b ...
s. The concept of a database was made possible by the emergence of direct access storage media
Data storage is the recording (storing) of information (data) in a storage medium. Handwriting, phonographic recording, magnetic tape, and optical discs are all examples of storage media. Biological molecules such as RNA and DNA are cons ...
such as magnetic disks, which became widely available in the mid-1960s; earlier systems relied on sequential storage of data on magnetic tape
Magnetic tape is a medium for magnetic storage made of a thin, magnetizable coating on a long, narrow strip of plastic film. It was developed in Germany in 1928, based on the earlier magnetic wire recording from Denmark. Devices that use magnetic ...
. The subsequent development of database technology can be divided into three eras based on data model or structure: navigational
Navigation is a field of study that focuses on the process of monitoring and controlling the movement of a craft or vehicle from one place to another.Bowditch, 2003:799. The field of navigation includes four general categories: land navigation, ...
, SQL/ relational, and post-relational.
The two main early navigational data model
A data model is an abstract model that organizes elements of data and standardizes how they relate to one another and to the properties of real-world entities. For instance, a data model may specify that the data element representing a car be ...
s were the hierarchical model
A hierarchical database model is a data model in which the data is organized into a tree-like structure. The data are stored as records which is a collection of one or more fields. Each field contains a single value, and the collection of fields i ...
and the CODASYL
CODASYL, the Conference/Committee on Data Systems Languages, was a consortium formed in 1959 to guide the development of a standard programming language that could be used on many computers. This effort led to the development of the programming ...
model ( network model). These were characterized by the use of pointers
Pointer may refer to:
People with the name
* Pointer (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name)
* Pointer Williams (born 1974), American former basketball player
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Pointer'' (journal), the ...
(often physical disk addresses) to follow relationships from one record to another.
The relational model
The relational model (RM) is an approach to managing data using a structure and language consistent with first-order predicate logic, first described in 1969 by English computer scientist Edgar F. Codd, where all data are represented in terms of t ...
, first proposed in 1970 by Edgar F. Codd
Edgar Frank "Ted" Codd (19 August 1923 – 18 April 2003) was a British computer scientist who, while working for IBM, invented the relational model for database management, the theoretical basis for relational databases and relational database ...
, departed from this tradition by insisting that applications
Application may refer to:
Mathematics and computing
* Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks
** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a ...
should search for data by content, rather than by following links. The relational model employs sets of ledger-style tables, each used for a different type of entity
An entity is something that Existence, exists as itself. It does not need to be of material existence. In particular, abstractions and legal fictions are usually regarded as entities. In general, there is also no presumption that an entity is Lif ...
. Only in the mid-1980s did computing hardware become powerful enough to allow the wide deployment of relational systems (DBMSs plus applications). By the early 1990s, however, relational systems dominated in all large-scale data processing
Data processing is the collection and manipulation of digital data to produce meaningful information. Data processing is a form of ''information processing'', which is the modification (processing) of information in any manner detectable by an o ...
applications, and they remain dominant: IBM Db2, Oracle
An oracle is a person or thing considered to provide insight, wise counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. If done through occultic means, it is a form of divination.
Descript ...
, MySQL
MySQL () is an Open-source software, open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). Its name is a combination of "My", the name of co-founder Michael Widenius's daughter My, and "SQL", the acronym for Structured Query Language. A rel ...
, and Microsoft SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server is a proprietary relational database management system developed by Microsoft using Structured Query Language (SQL, often pronounced "sequel"). As a database server, it is a software product with the primary function of ...
are the most searched DBMS
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and ana ...
. The dominant database language, standardized SQL for the relational model, has influenced database languages for other data models.
Object database
An object database or object-oriented database is a database management system in which information is represented in the form of objects as used in object-oriented programming. Object databases are different from relational databases which are ...
s were developed in the 1980s to overcome the inconvenience of object–relational impedance mismatch
Object–relational impedance mismatch is a set of difficulties going between data in relational data stores and data in domain-driven object models. Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) is the standard method for storing data in a ded ...
, which led to the coining of the term "post-relational" and also the development of hybrid object–relational database
An object–relational database (ORD), or object–relational database management system (ORDBMS), is a database management system (DBMS) similar to a relational database, but with an object-oriented database model: objects, classes and inherit ...
s.
The next generation of post-relational databases in the late 2000s became known as NoSQL
NoSQL (originally meaning "Not only SQL" or "non-relational") refers to a type of database design that stores and retrieves data differently from the traditional table-based structure of relational databases. Unlike relational databases, which ...
databases, introducing fast key–value stores and document-oriented database
A document-oriented database, or document store, is a computer program and data storage system designed for storing, retrieving and managing document-oriented information, also known as semi-structured data.
Document-oriented databases are one ...
s. A competing "next generation" known as NewSQL
NewSQL is a class of relational database management system, relational database management systems that seek to provide the scalability of NoSQL systems for online transaction processing (OLTP) workloads while maintaining the ACID guarantees of a t ...
databases attempted new implementations that retained the relational/SQL model while aiming to match the high performance of NoSQL compared to commercially available relational DBMSs.
1960s, navigational DBMS
 The introduction of the term ''database'' coincided with the availability of direct-access storage (disks and drums) from the mid-1960s onwards. The term represented a contrast with the tape-based systems of the past, allowing shared interactive use rather than daily
The introduction of the term ''database'' coincided with the availability of direct-access storage (disks and drums) from the mid-1960s onwards. The term represented a contrast with the tape-based systems of the past, allowing shared interactive use rather than daily batch processing
Computerized batch processing is a method of running software programs called jobs in batches automatically. While users are required to submit the jobs, no other interaction by the user is required to process the batch. Batches may automatically ...
. The Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the principal historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP), a University of Oxford publishing house. The dictionary, which published its first editio ...
cites a 1962 report by the System Development Corporation
System Development Corporation (SDC) was a computer software company based in Santa Monica, California. Initially created as a division of the RAND Corporation in December 1955 (under the name System Development Division) and established as an ind ...
of California as the first to use the term "data-base" in a specific technical sense.
As computers grew in speed and capability, a number of general-purpose database systems emerged; by the mid-1960s a number of such systems had come into commercial use. Interest in a standard began to grow, and Charles Bachman
Charles William Bachman III (December 11, 1924 – July 13, 2017) was an American computer scientist, who spent his entire career as an industrial researcher, developer, and manager rather than in academia. He was particularly known for his ...
, author of one such product, the Integrated Data Store (IDS), founded the Database Task Group within CODASYL
CODASYL, the Conference/Committee on Data Systems Languages, was a consortium formed in 1959 to guide the development of a standard programming language that could be used on many computers. This effort led to the development of the programming ...
, the group responsible for the creation and standardization of COBOL
COBOL (; an acronym for "common business-oriented language") is a compiled English-like computer programming language designed for business use. It is an imperative, procedural, and, since 2002, object-oriented language. COBOL is primarily ...
. In 1971, the Database Task Group delivered their standard, which generally became known as the ''CODASYL approach'', and soon a number of commercial products based on this approach entered the market.
The CODASYL approach offered applications the ability to navigate around a linked data set which was formed into a large network. Applications could find records by one of three methods:
#Use of a primary key (known as a CALC key, typically implemented by hashing)
#Navigating relationships (called ''sets'') from one record to another
#Scanning all the records in a sequential order
Later systems added B-tree
In computer science, a B-tree is a self-balancing tree data structure that maintains sorted data and allows searches, sequential access, insertions, and deletions in logarithmic time. The B-tree generalizes the binary search tree, allowing fo ...
s to provide alternate access paths. Many CODASYL databases also added a declarative query language for end users (as distinct from the navigational API
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build ...
). However, CODASYL databases were complex and required significant training and effort to produce useful applications.
IBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
also had its own DBMS in 1966, known as Information Management System
The IBM Information Management System (IMS) is a joint hierarchical database and information management system that supports transaction processing. Development began in 1966 to keep track of the bill of materials for the Saturn V rocket of the ...
(IMS). IMS was a development of software written for the Apollo program
The Apollo program, also known as Project Apollo, was the United States human spaceflight program led by NASA, which Moon landing, landed the first humans on the Moon in 1969. Apollo followed Project Mercury that put the first Americans in sp ...
on the System/360
The IBM System/360 (S/360) is a family of mainframe computer systems announced by IBM on April 7, 1964, and delivered between 1965 and 1978. System/360 was the first family of computers designed to cover both commercial and scientific applicati ...
. IMS was generally similar in concept to CODASYL, but used a strict hierarchy for its model of data navigation instead of CODASYL's network model. Both concepts later became known as navigational databases due to the way data was accessed: the term was popularized by Bachman's 1973 Turing Award
The ACM A. M. Turing Award is an annual prize given by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) for contributions of lasting and major technical importance to computer science. It is generally recognized as the highest distinction in the fi ...
presentation ''The Programmer as Navigator''. IMS is classified by IBM as a hierarchical database
A hierarchical database model is a data model in which the data is organized into a tree-like structure. The data are stored as records which is a collection of one or more fields. Each field contains a single value, and the collection of fields i ...
. IDMS and Cincom Systems' TOTAL databases are classified as network databases. IMS remains in use .
1970s, relational DBMS
Edgar F. Codd
Edgar Frank "Ted" Codd (19 August 1923 – 18 April 2003) was a British computer scientist who, while working for IBM, invented the relational model for database management, the theoretical basis for relational databases and relational database ...
worked at IBM in San Jose, California
San Jose, officially the City of San José ( ; ), is a cultural, commercial, and political center within Silicon Valley and the San Francisco Bay Area. With a city population of 997,368 and a metropolitan area population of 1.95 million, it is ...
, in an office primarily involved in the development of hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
systems. He was unhappy with the navigational model of the CODASYL approach, notably the lack of a "search" facility. In 1970, he wrote a number of papers that outlined a new approach to database construction that eventually culminated in the groundbreaking ''A Relational Model of Data for Large Shared Data Banks''.
The paper described a new system for storing and working with large databases. Instead of records being stored in some sort of linked list
In computer science, a linked list is a linear collection of data elements whose order is not given by their physical placement in memory. Instead, each element points to the next. It is a data structure consisting of a collection of nodes whi ...
of free-form records as in CODASYL, Codd's idea was to organize the data as a number of " tables", each table being used for a different type of entity. Each table would contain a fixed number of columns containing the attributes of the entity. One or more columns of each table were designated as a primary key
In the relational model of databases, a primary key is a designated attribute (column) that can reliably identify and distinguish between each individual record in a table. The database creator can choose an existing unique attribute or combinati ...
by which the rows of the table could be uniquely identified; cross-references between tables always used these primary keys, rather than disk addresses, and queries would join tables based on these key relationships, using a set of operations based on the mathematical system of relational calculus
The relational calculus consists of two calculi, the tuple relational calculus and the domain relational calculus, that is part of the relational model for databases and provide a declarative way to specify database queries. The raison d'être ...
(from which the model takes its name). Splitting the data into a set of normalized tables (or ''relations'') aimed to ensure that each "fact" was only stored once, thus simplifying update operations. Virtual tables called ''views'' could present the data in different ways for different users, but views could not be directly updated.
Codd used mathematical terms to define the model: relations, tuples, and domains rather than tables, rows, and columns. The terminology that is now familiar came from early implementations. Codd would later criticize the tendency for practical implementations to depart from the mathematical foundations on which the model was based.
University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California), is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Berkeley, California, United States. Founded in 1868 and named after t ...
led by Eugene Wong and Michael Stonebraker, who started INGRES using funding that had already been allocated for a geographical database project and student programmers to produce code. Beginning in 1973, INGRES delivered its first test products which were generally ready for widespread use in 1979. INGRES was similar to System R in a number of ways, including the use of a "language" for data access
Data access is a generic term referring to a process which has both an IT-specific meaning and other connotations involving access rights in a broader legal and/or political sense. In the former it typically refers to software and activities relat ...
, known as QUEL. Over time, INGRES moved to the emerging SQL standard.
IBM itself did one test implementation of the relational model, PRTV
PRTV (''Peterlee Relational Test Vehicle'') was the world's first relational database management system that could handle significant data volumes.
It was a relational query system with powerful query facilities, but very limited update facility ...
, and a production one, Business System 12, both now discontinued. Honeywell
Honeywell International Inc. is an American publicly traded, multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Charlotte, North Carolina. It primarily operates in four areas of business: aerospace, building automation, industrial automa ...
wrote MRDS for Multics
Multics ("MULTiplexed Information and Computing Service") is an influential early time-sharing operating system based on the concept of a single-level memory.Dennis M. Ritchie, "The Evolution of the Unix Time-sharing System", Communications of t ...
, and now there are two new implementations: Alphora Dataphor and Rel. Most other DBMS implementations usually called ''relational'' are actually SQL DBMSs.
In 1970, the University of Michigan began development of the MICRO Information Management System based on D.L. Childs' Set-Theoretic Data model. The university in 1974 hosted a debate between Codd and Bachman which Bruce Lindsay of IBM later described as "throwing lightning bolts at each other!". MICRO was used to manage very large data sets by the US Department of Labor
The United States Department of Labor (DOL) is one of the executive departments of the U.S. federal government. It is responsible for the administration of federal laws governing occupational safety and health, wage and hour standards, unemp ...
, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, and researchers from the University of Alberta
The University of Alberta (also known as U of A or UAlberta, ) is a public research university located in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. It was founded in 1908 by Alexander Cameron Rutherford, the first premier of Alberta, and Henry Marshall Tory, t ...
, the University of Michigan
The University of Michigan (U-M, U of M, or Michigan) is a public university, public research university in Ann Arbor, Michigan, United States. Founded in 1817, it is the oldest institution of higher education in the state. The University of Mi ...
, and Wayne State University
Wayne State University (WSU) is a public university, public research university in Detroit, Michigan, United States. Founded in 1868, Wayne State consists of 13 schools and colleges offering approximately 375 programs. It is Michigan's third-l ...
. It ran on IBM mainframe computers using the Michigan Terminal System
The Michigan Terminal System (MTS) is one of the first time-sharing computer operating systems.. Created in 1967 at the University of Michigan for use on IBM System/360, IBM S/360-67, S/370 and compatible mainframe computers, it was developed and ...
. The system remained in production until 1998.
Integrated approach
In the 1970s and 1980s, attempts were made to build database systems with integrated hardware and software. The underlying philosophy was that such integration would provide higher performance at a lower cost. Examples were IBM System/38, the early offering ofTeradata
Teradata Corporation is an American software company that provides cloud database and Analytics, analytics-related software, products, and services. The company was formed in 1979 in Brentwood, California, as a collaboration between researchers a ...
, and the Britton Lee, Inc. database machine.
Another approach to hardware support for database management was ICL's CAFS accelerator, a hardware disk controller with programmable search capabilities. In the long term, these efforts were generally unsuccessful because specialized database machines could not keep pace with the rapid development and progress of general-purpose computers. Thus most database systems nowadays are software systems running on general-purpose hardware, using general-purpose computer data storage. However, this idea is still pursued in certain applications by some companies like Netezza
IBM Netezza (pronounced ne-teez-a) is a subsidiary of American technology company IBM that designs and markets high-performance data warehouse appliances and advanced analytics applications for the most demanding analytic uses including enterpr ...
and Oracle ( Exadata).
Late 1970s, SQL DBMS
IBM formed a team led by Codd that started working on a prototype system, '' System R'' despite opposition from others at the company. The first version was ready in 1974/5, and work then started on multi-table systems in which the data could be split so that all of the data for a record (some of which is optional) did not have to be stored in a single large "chunk". Subsequent multi-user versions were tested by customers in 1978 and 1979, by which time a standardizedquery language
A query language, also known as data query language or database query language (DQL), is a computer language used to make queries in databases and information systems. In database systems, query languages rely on strict theory to retrieve informa ...
– SQL – had been added. Codd's ideas were establishing themselves as both workable and superior to CODASYL, pushing IBM to develop a true production version of System R, known as ''SQL/DS'', and, later, ''Database 2'' ( IBM Db2).
Larry Ellison's Oracle Database (or more simply, Oracle
An oracle is a person or thing considered to provide insight, wise counsel or prophetic predictions, most notably including precognition of the future, inspired by deities. If done through occultic means, it is a form of divination.
Descript ...
) started from a different chain, based on IBM's papers on System R. Though Oracle V1 implementations were completed in 1978, it was not until Oracle Version 2 when Ellison beat IBM to market in 1979.
Stonebraker went on to apply the lessons from INGRES to develop a new database, Postgres, which is now known as PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL ( ) also known as Postgres, is a free and open-source software, free and open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) emphasizing extensibility and SQL compliance. PostgreSQL features transaction processing, transactions ...
. PostgreSQL is often used for global mission-critical applications (the .org and .info domain name registries use it as their primary data store
A data store is a repository for persistently storing and managing collections of data which include not just repositories like databases, but also simpler store types such as simple files, emails, etc.
A ''database'' is a collection of data that ...
, as do many large companies and financial institutions).
In Sweden, Codd's paper was also read and Mimer SQL was developed in the mid-1970s at Uppsala University
Uppsala University (UU) () is a public university, public research university in Uppsala, Sweden. Founded in 1477, it is the List of universities in Sweden, oldest university in Sweden and the Nordic countries still in operation.
Initially fou ...
. In 1984, this project was consolidated into an independent enterprise.
Another data model, the entity–relationship model
An entity–relationship model (or ER model) describes interrelated things of interest in a specific domain of knowledge. A basic ER model is composed of entity types (which classify the things of interest) and specifies relationships that can e ...
, emerged in 1976 and gained popularity for database design
Database design is the organization of data according to a database model. The designer determines what data must be stored and how the data elements interrelate. With this information, they can begin to fit the data to the database model.Teorey, T ...
as it emphasized a more familiar description than the earlier relational model. Later on, entity–relationship constructs were retrofitted as a data modeling
Data modeling in software engineering is the process of creating a data model for an information system by applying certain formal techniques. It may be applied as part of broader Model-driven engineering (MDE) concept.
Overview
Data modeli ...
construct for the relational model, and the difference between the two has become irrelevant.
1980s, on the desktop
Besides IBM and various software companies such asSybase
Sybase, Inc. was an enterprise software and services company. The company produced software relating to relational databases, with facilities located in California and Massachusetts. Sybase was acquired by SAP in 2010; SAP ceased using the Syba ...
and Informix Corporation, most large computer hardware vendors by the 1980s had their own database systems such as DEC's VAX Rdb/VMS. The decade ushered in the age of desktop computing. The new computers empowered their users with spreadsheets like Lotus 1-2-3
Lotus 1-2-3 is a discontinued spreadsheet program from Lotus Software (later part of IBM). It was the first killer application of the IBM PC, was hugely popular in the 1980s, and significantly contributed to the success of IBM PC-compatibles ...
and database software like dBASE
dBase (also stylized dBASE) was one of the first database management systems for microcomputers and the most successful in its day. The dBase system included the core database engine, a query system, a Form (programming), forms engine, and a pr ...
. The dBASE product was lightweight and easy for any computer user to understand out of the box. C. Wayne Ratliff, the creator of dBASE, stated: "dBASE was different from programs like BASIC, C, FORTRAN, and COBOL in that a lot of the dirty work had already been done. The data manipulation is done by dBASE instead of by the user, so the user can concentrate on what he is doing, rather than having to mess with the dirty details of opening, reading, and closing files, and managing space allocation." dBASE was one of the top selling software titles in the 1980s and early 1990s.
1990s, object-oriented
By the start of the decade databases had become a billion-dollar industry in about ten years. The 1990s, along with a rise inobject-oriented programming
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of '' objects''. Objects can contain data (called fields, attributes or properties) and have actions they can perform (called procedures or methods and impl ...
, saw a growth in how data in various databases were handled. Programmers and designers began to treat the data in their databases as objects. That is to say that if a person's data were in a database, that person's attributes, such as their address, phone number, and age, were now considered to belong to that person instead of being extraneous data. This allows for relations between data to be related to objects and their attributes and not to individual fields. The term "object–relational impedance mismatch
Object–relational impedance mismatch is a set of difficulties going between data in relational data stores and data in domain-driven object models. Relational Database Management Systems (RDBMS) is the standard method for storing data in a ded ...
" described the inconvenience of translating between programmed objects and database tables. Object database
An object database or object-oriented database is a database management system in which information is represented in the form of objects as used in object-oriented programming. Object databases are different from relational databases which are ...
s and object–relational database
An object–relational database (ORD), or object–relational database management system (ORDBMS), is a database management system (DBMS) similar to a relational database, but with an object-oriented database model: objects, classes and inherit ...
s attempt to solve this problem by providing an object-oriented language (sometimes as extensions to SQL) that programmers can use as alternative to purely relational SQL. On the programming side, libraries known as object–relational mappings (ORMs) attempt to solve the same problem.
2000s, NoSQL and NewSQL
Database sales grew rapidly during thedotcom bubble
The dot-com bubble (or dot-com boom) was a stock market bubble that ballooned during the late-1990s and peaked on Friday, March 10, 2000. This period of market growth coincided with the widespread adoption of the World Wide Web and the Intern ...
and, after its end, the rise of ecommerce
E-commerce (electronic commerce) refers to commercial activities including the electronic buying or selling products and services which are conducted on online platforms or over the Internet. E-commerce draws on technologies such as mobile comm ...
. The popularity of open source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use and view the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open source model is a decentrali ...
databases such as MySQL
MySQL () is an Open-source software, open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). Its name is a combination of "My", the name of co-founder Michael Widenius's daughter My, and "SQL", the acronym for Structured Query Language. A rel ...
has grown since 2000, to the extent that Ken Jacobs of Oracle said in 2005 that perhaps "these guys are doing to us what we did to IBM".
XML database
An XML database is a data persistence software system that allows data to be specified, and stored, in XML format. This data can be queried, transformed, exported and returned to a calling system. XML databases are a flavor of document-oriented ...
s are a type of structured document-oriented database that allows querying based on XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing data. It defines a set of rules for encoding electronic document, documents in a format that is both human-readable and Machine-r ...
document attributes. XML databases are mostly used in applications where the data is conveniently viewed as a collection of documents, with a structure that can vary from the very flexible to the highly rigid: examples include scientific articles, patents, tax filings, and personnel records.
NoSQL
NoSQL (originally meaning "Not only SQL" or "non-relational") refers to a type of database design that stores and retrieves data differently from the traditional table-based structure of relational databases. Unlike relational databases, which ...
databases are often very fast, do not require fixed table schemas, avoid join operations by storing denormalized data, and are designed to scale horizontally.
In recent years, there has been a strong demand for massively distributed databases with high partition tolerance, but according to the CAP theorem
In database theory, the CAP theorem, also named Brewer's theorem after computer scientist Eric Brewer (scientist), Eric Brewer, states that any distributed data store can provide at most Inconsistent triad, two of the following three guarantees:
; ...
, it is impossible for a distributed system
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems, defined as computer systems whose inter-communicating components are located on different networked computers.
The components of a distributed system commun ...
to simultaneously provide consistency
In deductive logic, a consistent theory is one that does not lead to a logical contradiction. A theory T is consistent if there is no formula \varphi such that both \varphi and its negation \lnot\varphi are elements of the set of consequences ...
, availability, and partition tolerance guarantees. A distributed system can satisfy any two of these guarantees at the same time, but not all three. For that reason, many NoSQL databases are using what is called eventual consistency to provide both availability and partition tolerance guarantees with a reduced level of data consistency.
NewSQL
NewSQL is a class of relational database management system, relational database management systems that seek to provide the scalability of NoSQL systems for online transaction processing (OLTP) workloads while maintaining the ACID guarantees of a t ...
is a class of modern relational databases that aims to provide the same scalable performance of NoSQL systems for online transaction processing (read-write) workloads while still using SQL and maintaining the ACID
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
guarantees of a traditional database system.
Use cases
Databases are used to support internal operations of organizations and to underpin online interactions with customers and suppliers (seeEnterprise software
Enterprise software, also known as enterprise application software (EAS), is computer software used to satisfy the needs of an organization rather than its individual users. Enterprise software is an integral part of a computer-based information ...
).
Databases are used to hold administrative information and more specialized data, such as engineering data or economic models. Examples include computerized library
A library is a collection of Book, books, and possibly other Document, materials and Media (communication), media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or electron ...
systems, flight reservation systems, computerized parts inventory system
Inventory control or stock control is the process of managing stock held within a warehouse, store or other storage location, including auditing actions concerned with "checking a shop's stock". These processes ensure that the right amount of suppl ...
s, and many content management system
A content management system (CMS) is computer software used to manage the creation and modification of digital content ( content management).''Managing Enterprise Content: A Unified Content Strategy''. Ann Rockley, Pamela Kostur, Steve Manning. New ...
s that store website
A website (also written as a web site) is any web page whose content is identified by a common domain name and is published on at least one web server. Websites are typically dedicated to a particular topic or purpose, such as news, educatio ...
s as collections of webpages in a database.
Classification
One way to classify databases involves the type of their contents, for example: bibliographic, document-text, statistical, or multimedia objects. Another way is by their application area, for example: accounting, music compositions, movies, banking, manufacturing, or insurance. A third way is by some technical aspect, such as the database structure or interface type. This section lists a few of the adjectives used to characterize different kinds of databases. * Anin-memory database
An in-memory database (IMDb, or main memory database system (MMDB) or memory resident database) is a database management system that primarily relies on main memory for computer data storage. It is contrasted with database management systems that e ...
is a database that primarily resides in main memory
Computer data storage or digital data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers.
The central processin ...
, but is typically backed-up by non-volatile computer data storage. Main memory databases are faster than disk databases, and so are often used where response time is critical, such as in telecommunications network equipment.
* An active database
In computing, an active database is a database that includes an event-driven architecture (often in the form of ECA rules) that can respond to conditions both inside and outside the database. Possible uses include security monitoring, alerting, s ...
includes an event-driven architecture which can respond to conditions both inside and outside the database. Possible uses include security monitoring, alerting, statistics gathering and authorization. Many databases provide active database features in the form of database trigger
A database trigger is procedural code that is automatically executed in response to certain Event (computing), events on a particular Table (database), table or View (database), view in a database. The trigger is mostly used for maintaining the Dat ...
s.
* A cloud database
A cloud database is a database that typically runs on a cloud computing platform and access to the database is provided as-a-service. There are two common deployment models: users can run databases on the cloud independently, using a virtual machin ...
relies on cloud technology. Both the database and most of its DBMS reside remotely, "in the cloud", while its applications are both developed by programmers and later maintained and used by end-users through a web browser
A web browser, often shortened to browser, is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's scr ...
and Open APIs.
* Data warehouse
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for Business intelligence, reporting and data analysis and is a core component of business intelligence. Data warehouses are central Re ...
s archive data from operational databases and often from external sources such as market research firms. The warehouse becomes the central source of data for use by managers and other end-users who may not have access to operational data. For example, sales data might be aggregated to weekly totals and converted from internal product codes to use UPCs so that they can be compared with ACNielsen data. Some basic and essential components of data warehousing include extracting, analyzing, and mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
data, transforming, loading, and managing data so as to make them available for further use.
* A deductive database
A deductive database is a database system that can make deductions (i.e. conclude additional facts) based on rules and facts stored in its database. Datalog is the language typically used to specify facts, rules and queries in deductive database ...
combines logic programming
Logic programming is a programming, database and knowledge representation paradigm based on formal logic. A logic program is a set of sentences in logical form, representing knowledge about some problem domain. Computation is performed by applyin ...
with a relational database.
* A distributed database
A distributed database is a database in which data is stored across different physical locations. It may be stored in multiple computers located in the same physical location (e.g. a data centre); or maybe dispersed over a computer network, netwo ...
is one in which both the data and the DBMS span multiple computers.
* A document-oriented database
A document-oriented database, or document store, is a computer program and data storage system designed for storing, retrieving and managing document-oriented information, also known as semi-structured data.
Document-oriented databases are one ...
is designed for storing, retrieving, and managing document-oriented, or semi structured, information. Document-oriented databases are one of the main categories of NoSQL databases.
* An embedded database system is a DBMS which is tightly integrated with an application software that requires access to stored data in such a way that the DBMS is hidden from the application's end-users and requires little or no ongoing maintenance.
*End-user databases consist of data developed by individual end-users. Examples of these are collections of documents, spreadsheets, presentations, multimedia, and other files. Several products exist to support such databases.
* A federated database system
A federated database system (FDBS) is a type of Meta (prefix), meta-database management system (DBMS), which transparently maps multiple autonomous Database management system, database systems into a single federated database. The constituent data ...
comprises several distinct databases, each with its own DBMS. It is handled as a single database by a federated database management system (FDBMS), which transparently integrates multiple autonomous DBMSs, possibly of different types (in which case it would also be a heterogeneous database system A heterogeneous database system is an automated (or semi-automated) system for the integration of heterogeneous, disparate database management systems to present a user with a single, unified query interface.
Heterogeneous database systems (HDBs) ...
), and provides them with an integrated conceptual view.
* Sometimes the term ''multi-database'' is used as a synonym for federated database, though it may refer to a less integrated (e.g., without an FDBMS and a managed integrated schema) group of databases that cooperate in a single application. In this case, typically middleware
Middleware is a type of computer software program that provides services to software applications beyond those available from the operating system. It can be described as "software glue".
Middleware makes it easier for software developers to imple ...
is used for distribution, which typically includes an atomic commit protocol (ACP), e.g., the two-phase commit protocol
In transaction processing, databases, and computer networking, the two-phase commit protocol (2PC, ''tupac'') is a type of Atomic commit, atomic commitment protocol (ACP). It is a distributed algorithm that coordinates all the processes that pa ...
, to allow distributed (global) transactions across the participating databases.
* A graph database
A graph database (GDB) is a database that uses graph structures for semantic queries with nodes, edges, and properties to represent and store data. A key concept of the system is the graph (or edge or relationship). The graph relates the dat ...
is a kind of NoSQL database that uses graph structures with nodes, edges, and properties to represent and store information. General graph databases that can store any graph are distinct from specialized graph databases such as triplestore
A triplestore or RDF store is a purpose-built database for the storage and retrieval of triples through semantic queries. A triple is a data entity composed of subject– predicate– object, like "Bob is 35" (i.e., Bob's age measured in years i ...
s and network databases.
* An array DBMS is a kind of NoSQL DBMS that allows modeling, storage, and retrieval of (usually large) multi-dimensional arrays
An array is a systematic arrangement of similar objects, usually in rows and columns.
Things called an array include:
{{TOC right
Music
* In twelve-tone and serial composition, the presentation of simultaneous twelve-tone sets such that the ...
such as satellite images and climate simulation output.
* In a hypertext
Hypertext is E-text, text displayed on a computer display or other electronic devices with references (hyperlinks) to other text that the reader can immediately access. Hypertext documents are interconnected by hyperlinks, which are typic ...
or hypermedia
Hypermedia, an extension of hypertext, is a nonlinear medium of information that includes graphics, audio, video, plain text and hyperlinks. This designation contrasts with the broader term ''multimedia'', which may include non-interactive linear ...
database, any word or a piece of text representing an object, e.g., another piece of text, an article, a picture, or a film, can be hyperlink
In computing, a hyperlink, or simply a link, is a digital reference providing direct access to Data (computing), data by a user (computing), user's point and click, clicking or touchscreen, tapping. A hyperlink points to a whole document or to ...
ed to that object. Hypertext databases are particularly useful for organizing large amounts of disparate information. For example, they are useful for organizing online encyclopedia
An online encyclopedia, also called an Internet encyclopedia, is a digital encyclopedia accessible through the Internet. Some examples include pre-World Wide Web services that offered the '' Academic American Encyclopedia'' beginning in 1980, Enc ...
s, where users can conveniently jump around the text. The World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW or simply the Web) is an information system that enables Content (media), content sharing over the Internet through user-friendly ways meant to appeal to users beyond Information technology, IT specialists and hobbyis ...
is thus a large distributed hypertext database.
* A knowledge base
In computer science, a knowledge base (KB) is a set of sentences, each sentence given in a knowledge representation language, with interfaces to tell new sentences and to ask questions about what is known, where either of these interfaces migh ...
(abbreviated KB, kb or Δ) is a special kind of database for knowledge management
Knowledge management (KM) is the set of procedures for producing, disseminating, utilizing, and overseeing an organization's knowledge and data. It alludes to a multidisciplinary strategy that maximizes knowledge utilization to accomplish organ ...
, providing the means for the computerized collection, organization, and retrieval of knowledge
Knowledge is an Declarative knowledge, awareness of facts, a Knowledge by acquaintance, familiarity with individuals and situations, or a Procedural knowledge, practical skill. Knowledge of facts, also called propositional knowledge, is oft ...
. Also a collection of data representing problems with their solutions and related experiences.
* A mobile database Mobile computing devices (e.g., smartphones and Personal digital assistant, PDAs) store and share data over a mobile network, or access a database which is actually stored by the mobile device. This could be a list of contacts, price information, di ...
can be carried on or synchronized from a mobile computing device.
* Operational databases store detailed data about the operations of an organization. They typically process relatively high volumes of updates using transactions. Examples include customer databases that record contact, credit, and demographic information about a business's customers, personnel databases that hold information such as salary, benefits, skills data about employees, enterprise resource planning
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is the integrated management of main business processes, often in real time and mediated by software and technology. ERP is usually referred to as a category of business management software—typically a suit ...
systems that record details about product components, parts inventory, and financial databases that keep track of the organization's money, accounting and financial dealings.
* A parallel database A parallel database system seeks to improve performance through parallelization of various operations, such as loading data, building indexes and evaluating queries. Although data may be stored in a distributed fashion, the distribution is governed ...
seeks to improve performance through parallelization
Parallel computing is a type of computation in which many calculations or processes are carried out simultaneously. Large problems can often be divided into smaller ones, which can then be solved at the same time. There are several different for ...
for tasks such as loading data, building indexes and evaluating queries.
::The major parallel DBMS architectures which are induced by the underlying hardware architecture are:
::* Shared memory architecture
A shared-memory architecture (SM) is a distributed computing architecture in which the nodes share the same memory as well as the same storage.{{Cite web , title=Memory: Shared vs Distributed - UFRC , url=https://help.rc.ufl.edu/doc/Memory:_Shared_ ...
, where multiple processors share the main memory space, as well as other data storage.
::* Shared disk architecture, where each processing unit (typically consisting of multiple processors) has its own main memory, but all units share the other storage.
::* Shared-nothing architecture
A shared-nothing architecture (SN) is a distributed computing architecture in which each update request is satisfied by a single node (processor/memory/storage unit) in a computer cluster. The intent is to eliminate contention among nodes. Nodes do ...
, where each processing unit has its own main memory and other storage.
* Probabilistic database Most real databases contain data whose correctness is uncertain. In order to work with such data, there is a need to quantify the integrity of the data. This is achieved by using probabilistic databases.
A probabilistic database is an uncertain da ...
s employ fuzzy logic
Fuzzy logic is a form of many-valued logic in which the truth value of variables may be any real number between 0 and 1. It is employed to handle the concept of partial truth, where the truth value may range between completely true and completely ...
to draw inferences from imprecise data.
* Real-time databases process transactions fast enough for the result to come back and be acted on right away.
* A spatial database
A spatial database is a general-purpose database (usually a relational database) that has been enhanced to include spatial data that represents objects defined in a geometric space, along with tools for querying and analyzing such data.
Most ...
can store the data with multidimensional features. The queries on such data include location-based queries, like "Where is the closest hotel in my area?".
* A temporal database
A temporal database stores data relating to time instances. It offers temporal data types and stores information relating to past, present and future time.
Temporal databases can be uni-temporal, bi-temporal or tri-temporal.
More specifically the ...
has built-in time aspects, for example a temporal data model and a temporal version of SQL
Structured Query Language (SQL) (pronounced ''S-Q-L''; or alternatively as "sequel")
is a domain-specific language used to manage data, especially in a relational database management system (RDBMS). It is particularly useful in handling s ...
. More specifically the temporal aspects usually include valid-time and transaction-time.
* A terminology-oriented database builds upon an object-oriented database
An object database or object-oriented database is a database management system in which information is represented in the form of objects as used in object-oriented programming. Object databases are different from relational databases which are ...
, often customized for a specific field.
* An unstructured data
Unstructured data (or unstructured information) is information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner. Unstructured information is typically plain text, text-heavy, but may contain data such ...
database is intended to store in a manageable and protected way diverse objects that do not fit naturally and conveniently in common databases. It may include email messages, documents, journals, multimedia objects, etc. The name may be misleading since some objects can be highly structured. However, the entire possible object collection does not fit into a predefined structured framework. Most established DBMSs now support unstructured data in various ways, and new dedicated DBMSs are emerging.
Database management system
Connolly and Begg define database management system (DBMS) as a "software system that enables users to define, create, maintain and control access to the database." Examples of DBMS's includeMySQL
MySQL () is an Open-source software, open-source relational database management system (RDBMS). Its name is a combination of "My", the name of co-founder Michael Widenius's daughter My, and "SQL", the acronym for Structured Query Language. A rel ...
, MariaDB
MariaDB is a community-developed, commercially supported Fork (software development), fork of the MySQL relational database management system (RDBMS), intended to remain free and open-source software under the GNU General Public License. Developm ...
, PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL ( ) also known as Postgres, is a free and open-source software, free and open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) emphasizing extensibility and SQL compliance. PostgreSQL features transaction processing, transactions ...
, Microsoft SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server is a proprietary relational database management system developed by Microsoft using Structured Query Language (SQL, often pronounced "sequel"). As a database server, it is a software product with the primary function of ...
, Oracle Database
Oracle Database (commonly referred to as Oracle DBMS, Oracle Autonomous Database, or simply as Oracle) is a proprietary multi-model database management system produced and marketed by Oracle Corporation.
It is a database commonly used for ru ...
, and Microsoft Access
Microsoft Access is a database management system (DBMS) from Microsoft that combines the relational database, relational Access Database Engine (ACE) with a graphical user interface and software-development tools. It is a member of the Microsof ...
.
The DBMS acronym is sometimes extended to indicate the underlying database model
A database model is a type of data model that determines the logical structure of a database. It fundamentally determines in which manner data can be stored, organized and manipulated. The most popular example of a database model is the relatio ...
, with RDBMS for the relational, OODBMS for the object (oriented) and ORDBMS for the object–relational model. Other extensions can indicate some other characteristics, such as DDBMS for a distributed database management systems.
The functionality provided by a DBMS can vary enormously. The core functionality is the storage, retrieval and update of data. Codd proposed the following functions and services a fully-fledged general purpose DBMS should provide:
* Data storage, retrieval and update
* User accessible catalog or data dictionary
A data dictionary, or metadata repository, as defined in the ''IBM Dictionary of Computing'', is a "centralized repository of information about data such as meaning, relationships to other data, origin, usage, and format". ''Oracle Corporation, ...
describing the metadata
* Support for transactions and concurrency
* Facilities for recovering the database should it become damaged
* Support for authorization of access and update of data
* Access support from remote locations
* Enforcing constraints to ensure data in the database abides by certain rules
It is also generally to be expected the DBMS will provide a set of utilities for such purposes as may be necessary to administer the database effectively, including import, export, monitoring, defragmentation and analysis utilities. The core part of the DBMS interacting between the database and the application interface sometimes referred to as the database engine
A database engine (or storage engine) is the underlying software component that a database management system (DBMS) uses to create, read, update and delete (CRUD) data from a database. Most database management systems include their own application ...
.
Often DBMSs will have configuration parameters that can be statically and dynamically tuned, for example the maximum amount of main memory on a server the database can use. The trend is to minimize the amount of manual configuration, and for cases such as embedded databases the need to target zero-administration is paramount.
The large major enterprise DBMSs have tended to increase in size and functionality and have involved up to thousands of human years of development effort throughout their lifetime.
Early multi-user DBMS typically only allowed for the application to reside on the same computer with access via terminals or terminal emulation software. The client–server architecture was a development where the application resided on a client desktop and the database on a server allowing the processing to be distributed. This evolved into a multitier architecture
In software engineering, multitier architecture (often referred to as ''n''-tier architecture) is a client–server architecture in which presentation, application processing and data management functions are physically separated. The most wide ...
incorporating application server
An application server is a server that hosts applications or software that delivers a business application through a communication protocol. For a typical web application, the application server sits behind the web servers.
An application ser ...
s and web server
A web server is computer software and underlying Computer hardware, hardware that accepts requests via Hypertext Transfer Protocol, HTTP (the network protocol created to distribute web content) or its secure variant HTTPS. A user agent, co ...
s with the end user interface via a web browser
A web browser, often shortened to browser, is an application for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's scr ...
with the database only directly connected to the adjacent tier.
A general-purpose DBMS will provide public application programming interface
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software Interface (computing), interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that des ...
s (API) and optionally a processor for database languages such as SQL
Structured Query Language (SQL) (pronounced ''S-Q-L''; or alternatively as "sequel")
is a domain-specific language used to manage data, especially in a relational database management system (RDBMS). It is particularly useful in handling s ...
to allow applications to be written to interact with and manipulate the database. A special purpose DBMS may use a private API and be specifically customized and linked to a single application. For example, an email
Electronic mail (usually shortened to email; alternatively hyphenated e-mail) is a method of transmitting and receiving Digital media, digital messages using electronics, electronic devices over a computer network. It was conceived in the ...
system performs many of the functions of a general-purpose DBMS such as message insertion, message deletion, attachment handling, blocklist lookup, associating messages an email address and so forth however these functions are limited to what is required to handle email.
Application
External interaction with the database will be via an application program that interfaces with the DBMS. This can range from a database tool that allows users to execute SQL queries textually or graphically, to a website that happens to use a database to store and search information.Application program interface
Aprogrammer
A programmer, computer programmer or coder is an author of computer source code someone with skill in computer programming.
The professional titles Software development, ''software developer'' and Software engineering, ''software engineer' ...
will code
In communications and information processing, code is a system of rules to convert information—such as a letter, word, sound, image, or gesture—into another form, sometimes shortened or secret, for communication through a communicati ...
interactions to the database (sometimes referred to as a datasource) via an application program interface (API) or via a database language. The particular API or language chosen will need to be supported by DBMS, possibly indirectly via a preprocessor
In computer science, a preprocessor (or precompiler) is a Computer program, program that processes its input data to produce output that is used as input in another program. The output is said to be a preprocessed form of the input data, which i ...
or a bridging API. Some API's aim to be database independent, ODBC
In computing, Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) is a standard application programming interface (API) for accessing database management systems (DBMS). The designers of ODBC aimed to make it independent of database systems and operating systems. An ...
being a commonly known example. Other common API's include JDBC
Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) is an application programming interface (API) for the Java (programming language), Java programming language which defines how a client may access a database. It is a Java-based data access technology used for Java ...
and ADO.NET.
Database languages
Database languages are special-purpose languages, which allow one or more of the following tasks, sometimes distinguished as sublanguages: * Data control language (DCL) – controls access to data; *Data definition language
In the context of SQL, data definition or data description language (DDL) is a syntax for creating and modifying database objects such as tables, indices, and users. DDL statements are similar to a computer programming language for defining d ...
(DDL) – defines data types such as creating, altering, or dropping tables and the relationships among them;
* Data manipulation language
A data manipulation language (DML) is a computer programming language used for adding (inserting), deleting, and modifying (updating) data in a database. A DML is often a sublanguage of a broader database language such as SQL, with the DML com ...
(DML) – performs tasks such as inserting, updating, or deleting data occurrences;
* Data query language (DQL) – allows searching for information and computing derived information.
Database languages are specific to a particular data model. Notable examples include:
* SQL combines the roles of data definition, data manipulation, and query in a single language. It was one of the first commercial languages for the relational model, although it departs in some respects from the relational model as described by Codd (for example, the rows and columns of a table can be ordered). SQL became a standard of the American National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private nonprofit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organiz ...
(ANSI) in 1986, and of the International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO ; ; ) is an independent, non-governmental, international standard development organization composed of representatives from the national standards organizations of member countries.
M ...
(ISO) in 1987. The standards have been regularly enhanced since and are supported (with varying degrees of conformance) by all mainstream commercial relational DBMSs.
* OQL is an object model language standard (from the Object Data Management Group The Object Data Management Group (ODMG) was conceived in the summer of 1991 at a breakfast with object database vendors that was organized by Rick Cattell of Sun Microsystems. In 1998, the ODMG changed its name from the Object Database Management Gr ...
). It has influenced the design of some of the newer query languages like JDOQL and EJB QL.
* XQuery
XQuery (XML Query) is a query language and functional programming language designed to query and transform collections of structured and unstructured data, primarily in the form of XML. It also supports text data and, through implementation-sp ...
is a standard XML query language implemented by XML database systems such as MarkLogic
MarkLogic is an American software business that develops and provides an enterprise NoSQL database, which is also named ''MarkLogic''. They have offices in the United States, Europe, Asia, and Australia.
In February 2023, MarkLogic was acquired ...
and eXist
eXist-db (or eXist for short) is an open source software project for NoSQL databases built on XML technology. It is classified as both a NoSQL document-oriented database system and a native XML database (and it provides support for XML, JSON, HTM ...
, by relational databases with XML capability such as Oracle and Db2, and also by in-memory XML processors such as Saxon
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
.
* SQL/XML combines XQuery
XQuery (XML Query) is a query language and functional programming language designed to query and transform collections of structured and unstructured data, primarily in the form of XML. It also supports text data and, through implementation-sp ...
with SQL.
A database language may also incorporate features like:
* DBMS-specific configuration and storage engine management
* Computations to modify query results, like counting, summing, averaging, sorting, grouping, and cross-referencing
* Constraint enforcement (e.g. in an automotive database, only allowing one engine type per car)
* Application programming interface version of the query language, for programmer convenience
Storage
Database storage is the container of the physical materialization of a database. It comprises the ''internal'' (physical) ''level'' in the database architecture. It also contains all the information needed (e.g.,metadata
Metadata (or metainformation) is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including:
* Descriptive ...
, "data about the data", and internal data structure
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization and storage format that is usually chosen for Efficiency, efficient Data access, access to data. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships amo ...
s) to reconstruct the ''conceptual level'' and ''external level'' from the internal level when needed. Databases as digital objects contain three layers of information which must be stored: the data, the structure, and the semantics. Proper storage of all three layers is needed for future preservation
Preservation may refer to:
Heritage and conservation
* Preservation (library and archival science), activities aimed at prolonging the life of a record while making as few changes as possible
* ''Preservation'' (magazine), published by the Nat ...
and longevity of the database. Putting data into permanent storage is generally the responsibility of the database engine
A database engine (or storage engine) is the underlying software component that a database management system (DBMS) uses to create, read, update and delete (CRUD) data from a database. Most database management systems include their own application ...
a.k.a. "storage engine". Though typically accessed by a DBMS through the underlying operating system (and often using the operating systems' file systems as intermediates for storage layout), storage properties and configuration settings are extremely important for the efficient operation of the DBMS, and thus are closely maintained by database administrators. A DBMS, while in operation, always has its database residing in several types of storage (e.g., memory and external storage). The database data and the additional needed information, possibly in very large amounts, are coded into bits. Data typically reside in the storage in structures that look completely different from the way the data look at the conceptual and external levels, but in ways that attempt to optimize (the best possible) these levels' reconstruction when needed by users and programs, as well as for computing additional types of needed information from the data (e.g., when querying the database).
Some DBMSs support specifying which character encoding
Character encoding is the process of assigning numbers to graphical character (computing), characters, especially the written characters of human language, allowing them to be stored, transmitted, and transformed using computers. The numerical v ...
was used to store data, so multiple encodings can be used in the same database.
Various low-level database storage structures are used by the storage engine to serialize the data model so it can be written to the medium of choice. Techniques such as indexing may be used to improve performance. Conventional storage is row-oriented, but there are also column-oriented and correlation database
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistic ...
s.
Materialized views
Often storage redundancy is employed to increase performance. A common example is storing ''materialized views'', which consist of frequently needed ''external views'' or query results. Storing such views saves the expensive computing them each time they are needed. The downsides of materialized views are the overhead incurred when updating them to keep them synchronized with their original updated database data, and the cost of storage redundancy.Replication
Occasionally a database employs storage redundancy by database objects replication (with one or more copies) to increase data availability (both to improve performance of simultaneous multiple end-user accesses to the same database object, and to provide resiliency in a case of partial failure of a distributed database). Updates of a replicated object need to be synchronized across the object copies. In many cases, the entire database is replicated.Virtualization
With data virtualization, the data used remains in its original locations and real-time access is established to allow analytics across multiple sources. This can aid in resolving some technical difficulties such as compatibility problems when combining data from various platforms, lowering the risk of error caused by faulty data, and guaranteeing that the newest data is used. Furthermore, avoiding the creation of a new database containing personal information can make it easier to comply with privacy regulations. However, with data virtualization, the connection to all necessary data sources must be operational as there is no local copy of the data, which is one of the main drawbacks of the approach.Security
Database security
Database security concerns the use of a broad range of information security controls to protect databases against compromises of their confidentiality, integrity and availability. It involves various types or categories of controls, such as tech ...
deals with all various aspects of protecting the database content, its owners, and its users. It ranges from protection from intentional unauthorized database uses to unintentional database accesses by unauthorized entities (e.g., a person or a computer program).
Database access control deals with controlling who (a person or a certain computer program) are allowed to access what information in the database. The information may comprise specific database objects (e.g., record types, specific records, data structures), certain computations over certain objects (e.g., query types, or specific queries), or using specific access paths to the former (e.g., using specific indexes or other data structures to access information). Database access controls are set by special authorized (by the database owner) personnel that uses dedicated protected security DBMS interfaces.
This may be managed directly on an individual basis, or by the assignment of individuals and privileges to groups, or (in the most elaborate models) through the assignment of individuals and groups to roles which are then granted entitlements. Data security prevents unauthorized users from viewing or updating the database. Using passwords, users are allowed access to the entire database or subsets of it called "subschemas". For example, an employee database can contain all the data about an individual employee, but one group of users may be authorized to view only payroll data, while others are allowed access to only work history and medical data. If the DBMS provides a way to interactively enter and update the database, as well as interrogate it, this capability allows for managing personal databases.
Data security
Data security or data protection means protecting digital data, such as those in a database, from destructive forces and from the unwanted actions of unauthorized users, such as a cyberattack or a data breach.
Technologies
Disk encryption
...
in general deals with protecting specific chunks of data, both physically (i.e., from corruption, or destruction, or removal; e.g., see physical security
Physical security describes security measures that are designed to deny unauthorized access to facilities, equipment, and resources and to protect personnel and property from damage or harm (such as espionage, theft, or terrorist attacks). Physi ...
), or the interpretation of them, or parts of them to meaningful information (e.g., by looking at the strings of bits that they comprise, concluding specific valid credit-card numbers; e.g., see data encryption
In cryptography, encryption (more specifically, encoding) is the process of transforming information in a way that, ideally, only authorized parties can decode. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plai ...
).
Change and access logging records who accessed which attributes, what was changed, and when it was changed. Logging services allow for a forensic database audit later by keeping a record of access occurrences and changes. Sometimes application-level code is used to record changes rather than leaving this in the database. Monitoring can be set up to attempt to detect security breaches. Therefore, organizations must take database security seriously because of the many benefits it provides. Organizations will be safeguarded from security breaches and hacking activities like firewall intrusion, virus spread, and ransom ware. This helps in protecting the company's essential information, which cannot be shared with outsiders at any cause.
Transactions and concurrency
Database transactions can be used to introduce some level offault tolerance
Fault tolerance is the ability of a system to maintain proper operation despite failures or faults in one or more of its components. This capability is essential for high-availability, mission-critical, or even life-critical systems.
Fault t ...
and data integrity
Data integrity is the maintenance of, and the assurance of, data accuracy and consistency over its entire Information Lifecycle Management, life-cycle. It is a critical aspect to the design, implementation, and usage of any system that stores, proc ...
after recovery from a crash. A database transaction is a unit of work, typically encapsulating a number of operations over a database (e.g., reading a database object, writing, acquiring or releasing a lock
Lock(s) or Locked may refer to:
Common meanings
*Lock and key, a mechanical device used to secure items of importance
*Lock (water navigation), a device for boats to transit between different levels of water, as in a canal
Arts and entertainme ...
, etc.), an abstraction supported in database and also other systems. Each transaction has well defined boundaries in terms of which program/code executions are included in that transaction (determined by the transaction's programmer via special transaction commands).
The acronym ACID
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. Hydron, hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid–base theory, Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis ...
describes some ideal properties of a database transaction: atomicity, consistency
In deductive logic, a consistent theory is one that does not lead to a logical contradiction. A theory T is consistent if there is no formula \varphi such that both \varphi and its negation \lnot\varphi are elements of the set of consequences ...
, isolation, and durability
Durability is the ability of a physical product to remain functional, without requiring excessive maintenance or repair, when faced with the challenges of normal operation over its design lifetime. There are several measures of durability in us ...
.
Migration
A database built with one DBMS is not portable to another DBMS (i.e., the other DBMS cannot run it). However, in some situations, it is desirable to migrate a database from one DBMS to another. The reasons are primarily economical (different DBMSs may have different total costs of ownership or TCOs), functional, and operational (different DBMSs may have different capabilities). The migration involves the database's transformation from one DBMS type to another. The transformation should maintain (if possible) the database related application (i.e., all related application programs) intact. Thus, the database's conceptual and external architectural levels should be maintained in the transformation. It may be desired that also some aspects of the architecture internal level are maintained. A complex or large database migration may be a complicated and costly (one-time) project by itself, which should be factored into the decision to migrate. This is in spite of the fact that tools may exist to help migration between specific DBMSs. Typically, a DBMS vendor provides tools to help import databases from other popular DBMSs.Building, maintaining, and tuning
After designing a database for an application, the next stage is building the database. Typically, an appropriate general-purpose DBMS can be selected to be used for this purpose. A DBMS provides the neededuser interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine fro ...
s to be used by database administrators to define the needed application's data structures within the DBMS's respective data model. Other user interfaces are used to select needed DBMS parameters (like security related, storage allocation parameters, etc.).
When the database is ready (all its data structures and other needed components are defined), it is typically populated with initial application's data (database initialization, which is typically a distinct project; in many cases using specialized DBMS interfaces that support bulk insertion) before making it operational. In some cases, the database becomes operational while empty of application data, and data are accumulated during its operation.
After the database is created, initialized and populated it needs to be maintained. Various database parameters may need changing and the database may need to be tuned ( tuning) for better performance; application's data structures may be changed or added, new related application programs may be written to add to the application's functionality, etc.
Backup and restore
Sometimes it is desired to bring a database back to a previous state (for many reasons, e.g., cases when the database is found corrupted due to a software error, or if it has been updated with erroneous data). To achieve this, a backup operation is done occasionally or continuously, where each desired database state (i.e., the values of its data and their embedding in database's data structures) is kept within dedicated backup files (many techniques exist to do this effectively). When it is decided by a database administrator to bring the database back to this state (e.g., by specifying this state by a desired point in time when the database was in this state), these files are used to restore that state.Static analysis
Static analysis techniques for software verification can be applied also in the scenario of query languages. In particular, the *Abstract interpretation
In computer science, abstract interpretation is a theory of sound approximation of the semantics of computer programs, based on monotonic functions over ordered sets, especially lattices. It can be viewed as a partial execution of a computer pro ...
framework has been extended to the field of query languages for relational databases as a way to support sound approximation techniques. The semantics of query languages can be tuned according to suitable abstractions of the concrete domain of data. The abstraction of relational database systems has many interesting applications, in particular, for security purposes, such as fine-grained access control, watermarking, etc.
Miscellaneous features
Other DBMS features might include: * Database logs – This helps in keeping a history of the executed functions. * Graphics component for producing graphs and charts, especially in a data warehouse system. *Query optimizer
Query optimization is a feature of many relational database management systems and other databases such as NoSQL and graph databases. The query optimizer attempts to determine the most efficient way to execute a given query by considering the pos ...
– Performs query optimization on every query to choose an efficient ''query plan A query plan (or query execution plan) is a sequence of steps used to access data in a SQL relational database management system. This is a specific case of the relational model concept of access plans.
Since SQL is declarative, there are typical ...
'' (a partial order (tree) of operations) to be executed to compute the query result. May be specific to a particular storage engine.
* Tools or hooks for database design, application programming, application program maintenance, database performance analysis and monitoring, database configuration monitoring, DBMS hardware configuration (a DBMS and related database may span computers, networks, and storage units) and related database mapping (especially for a distributed DBMS), storage allocation and database layout monitoring, storage migration, etc.
Increasingly, there are calls for a single system that incorporates all of these core functionalities into the same build, test, and deployment framework for database management and source control. Borrowing from other developments in the software industry, some market such offerings as "DevOps
DevOps is the integration and automation of the software development and information technology operations. DevOps encompasses necessary tasks of software development and can lead to shortening development time and improving the development life ...
for database".
Design and modeling
 The first task of a database designer is to produce a
The first task of a database designer is to produce a conceptual data model
A conceptual schema or conceptual data model is a high-level description of informational needs underlying the design of a database. It typically includes only the core concepts and the main relationships among them. This is a high-level model wi ...
that reflects the structure of the information to be held in the database. A common approach to this is to develop an entity–relationship model
An entity–relationship model (or ER model) describes interrelated things of interest in a specific domain of knowledge. A basic ER model is composed of entity types (which classify the things of interest) and specifies relationships that can e ...
, often with the aid of drawing tools. Another popular approach is the Unified Modeling Language
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) is a general-purpose visual modeling language that is intended to provide a standard way to visualize the design of a system.
UML provides a standard notation for many types of diagrams which can be roughly ...
. A successful data model will accurately reflect the possible state of the external world being modeled: for example, if people can have more than one phone number, it will allow this information to be captured. Designing a good conceptual data model requires a good understanding of the application domain; it typically involves asking deep questions about the things of interest to an organization, like "can a customer also be a supplier?", or "if a product is sold with two different forms of packaging, are those the same product or different products?", or "if a plane flies from New York to Dubai via Frankfurt, is that one flight or two (or maybe even three)?". The answers to these questions establish definitions of the terminology used for entities (customers, products, flights, flight segments) and their relationships and attributes.
Producing the conceptual data model sometimes involves input from business processes, or the analysis of workflow
Workflow is a generic term for orchestrated and repeatable patterns of activity, enabled by the systematic organization of resources into processes that transform materials, provide services, or process information. It can be depicted as a seque ...
in the organization. This can help to establish what information is needed in the database, and what can be left out. For example, it can help when deciding whether the database needs to hold historic data as well as current data.
Having produced a conceptual data model that users are happy with, the next stage is to translate this into a schema
Schema may refer to:
Science and technology
* SCHEMA (bioinformatics), an algorithm used in protein engineering
* Schema (genetic algorithms), a set of programs or bit strings that have some genotypic similarity
* Schema.org, a web markup vocab ...
that implements the relevant data structures within the database. This process is often called logical database design, and the output is a logical data model A logical data model or logical schema is a data model of a specific problem domain expressed independently of a particular database management product or storage technology (physical data model) but in terms of data structures such as relational ta ...
expressed in the form of a schema. Whereas the conceptual data model is (in theory at least) independent of the choice of database technology, the logical data model will be expressed in terms of a particular database model supported by the chosen DBMS. (The terms ''data model'' and ''database model'' are often used interchangeably, but in this article we use ''data model'' for the design of a specific database, and ''database model'' for the modeling notation used to express that design).
The most popular database model for general-purpose databases is the relational model, or more precisely, the relational model as represented by the SQL language. The process of creating a logical database design using this model uses a methodical approach known as normalization
Normalization or normalisation refers to a process that makes something more normal or regular. Science
* Normalization process theory, a sociological theory of the implementation of new technologies or innovations
* Normalization model, used in ...
. The goal of normalization is to ensure that each elementary "fact" is only recorded in one place, so that insertions, updates, and deletions automatically maintain consistency.
The final stage of database design is to make the decisions that affect performance, scalability, recovery, security, and the like, which depend on the particular DBMS. This is often called ''physical database design'', and the output is the physical data model
A physical data model (or database design) is a representation of a data design as implemented, or intended to be implemented, in a database management system. In the Project lifecycle, lifecycle of a project it typically derives from a logical ...
. A key goal during this stage is data independence, meaning that the decisions made for performance optimization purposes should be invisible to end-users and applications. There are two types of data independence: Physical data independence and logical data independence. Physical design is driven mainly by performance requirements, and requires a good knowledge of the expected workload and access patterns, and a deep understanding of the features offered by the chosen DBMS.
Another aspect of physical database design is security. It involves both defining access control
In physical security and information security, access control (AC) is the action of deciding whether a subject should be granted or denied access to an object (for example, a place or a resource). The act of ''accessing'' may mean consuming ...
to database objects as well as defining security levels and methods for the data itself.
Models
 A database model is a type of data model that determines the logical structure of a database and fundamentally determines in which manner
A database model is a type of data model that determines the logical structure of a database and fundamentally determines in which manner data
Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ...
can be stored, organized, and manipulated. The most popular example of a database model is the relational model (or the SQL approximation of relational), which uses a table-based format.
Common logical data models for databases include:
* Navigational databases
**Hierarchical database model
A hierarchical database model is a data model in which the data is organized into a tree-like structure. The data are stored as records which is a collection of one or more fields. Each field contains a single value, and the collection of fields i ...
** Network model
**Graph database
A graph database (GDB) is a database that uses graph structures for semantic queries with nodes, edges, and properties to represent and store data. A key concept of the system is the graph (or edge or relationship). The graph relates the dat ...
*Relational model
The relational model (RM) is an approach to managing data using a structure and language consistent with first-order predicate logic, first described in 1969 by English computer scientist Edgar F. Codd, where all data are represented in terms of t ...
*Entity–relationship model
An entity–relationship model (or ER model) describes interrelated things of interest in a specific domain of knowledge. A basic ER model is composed of entity types (which classify the things of interest) and specifies relationships that can e ...
** Enhanced entity–relationship model
*Object model
In computing, object model has two related but distinct meanings:
# The properties of objects in general in a specific computer programming language, technology, notation or methodology that uses them. Examples are the object models of ''Java'', ...
* Document model
* Entity–attribute–value model
*Star schema
In computing, the star schema or star model is the simplest style of data mart Logical schema, schema and is the approach most widely used to develop data warehouses and dimensional data marts. The star schema consists of one or more fact tables ...
An object–relational database combines the two related structures.
Physical data model
A physical data model (or database design) is a representation of a data design as implemented, or intended to be implemented, in a database management system. In the Project lifecycle, lifecycle of a project it typically derives from a logical ...
s include:
*Inverted index
In computer science, an inverted index (also referred to as a postings list, postings file, or inverted file) is a database index storing a mapping from content, such as words or numbers, to its locations in a table, or in a document or a set of d ...
* Flat file
Other models include:
* Multidimensional model
* Array model
*Multivalue model
A MultiValue database is a type of NoSQL and multidimensional database. It is typically considered synonymous with PICK, a database originally developed as the Pick operating system.
MultiValue databases include commercial products from Rocket Sof ...
Specialized models are optimized for particular types of data:
*XML database
An XML database is a data persistence software system that allows data to be specified, and stored, in XML format. This data can be queried, transformed, exported and returned to a calling system. XML databases are a flavor of document-oriented ...
*Semantic model
The term conceptual model refers to any model that is formed after a conceptualization or generalization process. Conceptual models are often abstractions of things in the real world, whether physical or social. Semantic studies are relevant to va ...
*Content store A content repository or content store is a database of digital content with an associated set of data management, search and access methods allowing application-independent access to the content, rather like a digital library, but with the ability ...
* Event store
* Time series model
External, conceptual, and internal views
A database management system provides three views of the database data: * The external level defines how each group of end-users sees the organization of data in the database. A single database can have any number of views at the external level. * The conceptual level (or ''logical level'') unifies the various external views into a compatible global view. It provides the synthesis of all the external views. It is out of the scope of the various database end-users, and is rather of interest to database application developers and database administrators. * The internal level (or ''physical level'') is the internal organization of data inside a DBMS. It is concerned with cost, performance, scalability and other operational matters. It deals with storage layout of the data, using storage structures such asindexes
Index (: indexes or indices) may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Index (A Certain Magical Index), Index (''A Certain Magical Index''), a character in the light novel series ''A Certain Magical Index''
* The Index, a ...
to enhance performance. Occasionally it stores data of individual views (materialized view
In computing, a materialized view is a database object that contains the results of a query. For example, it may be a local copy of data located remotely, or may be a subset of the rows and/or columns of a table or join result, or may be a summa ...
s), computed from generic data, if performance justification exists for such redundancy. It balances all the external views' performance requirements, possibly conflicting, in an attempt to optimize overall performance across all activities.
While there is typically only one conceptual and internal view of the data, there can be any number of different external views. This allows users to see database information in a more business-related way rather than from a technical, processing viewpoint. For example, a financial department of a company needs the payment details of all employees as part of the company's expenses, but does not need details about employees that are in the interest of the human resources
Human resources (HR) is the set of people who make up the workforce of an organization, business sector, industry, or economy. A narrower concept is human capital, the knowledge and skills which the individuals command. Similar terms include ' ...
department. Thus different departments need different ''views'' of the company's database.
The three-level database architecture relates to the concept of ''data independence'' which was one of the major initial driving forces of the relational model. The idea is that changes made at a certain level do not affect the view at a higher level. For example, changes in the internal level do not affect application programs written using conceptual level interfaces, which reduces the impact of making physical changes to improve performance.
The conceptual view provides a level of indirection between internal and external. On the one hand it provides a common view of the database, independent of different external view structures, and on the other hand it abstracts away details of how the data are stored or managed (internal level). In principle every level, and even every external view, can be presented by a different data model. In practice usually a given DBMS uses the same data model for both the external and the conceptual levels (e.g., relational model). The internal level, which is hidden inside the DBMS and depends on its implementation, requires a different level of detail and uses its own types of data structure types.
Research
Database technology has been an active research topic since the 1960s, both inacademia
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the go ...
and in the research and development groups of companies (for example IBM Research
IBM Research is the research and development division for IBM, an American Multinational corporation, multinational information technology company. IBM Research is headquartered at the Thomas J. Watson Research Center in Yorktown Heights, New York ...
). Research activity includes theory
A theory is a systematic and rational form of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the conclusions derived from such thinking. It involves contemplative and logical reasoning, often supported by processes such as observation, experimentation, ...
and development of prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototype ...
s. Notable research topics have included models
A model is an informative representation of an object, person, or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin , .
Models can be divided int ...
, the atomic transaction concept, related concurrency control
In information technology and computer science, especially in the fields of computer programming, operating systems, multiprocessors, and databases, concurrency control ensures that correct results for concurrent operations are generated, whil ...
techniques, query languages and query optimization
Query optimization is a feature of many relational database management systems and other databases such as NoSQL and graph databases. The query optimizer attempts to determine the most efficient way to execute a given query by considering the po ...
methods, RAID
RAID (; redundant array of inexpensive disks or redundant array of independent disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical Computer data storage, data storage components into one or more logical units for th ...
, and more.
The database research area has several dedicated academic journal
An academic journal (or scholarly journal or scientific journal) is a periodical publication in which Scholarly method, scholarship relating to a particular academic discipline is published. They serve as permanent and transparent forums for the ...
s (for example, '' ACM Transactions on Database Systems''-TODS, ''Data and Knowledge Engineering
''Data & Knowledge Engineering'' is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal in the area of database systems and knowledge base systems. It is published by Elsevier and was established in 1985. The editor-in-chief is P.P. Chen (Louisiana State Uni ...
''-DKE) and annual conferences
A conference is a meeting, often lasting a few days, which is organized on a particular subject, or to bring together people who have a common interest. Conferences can be used as a form of group decision-making, although discussion, not always d ...
(e.g., ACM SIGMOD, ACM PODS, VLDB, IEEE
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) is an American 501(c)(3) organization, 501(c)(3) public charity professional organization for electrical engineering, electronics engineering, and other related disciplines.
The IEEE ...
ICDE).
See also
*Comparison of database tools
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of available database administration tools. Please see individual product articles for further information. This article is neither all-inclusive nor necessarily up to dat ...
* Comparison of object database management systems
* Comparison of object–relational database management systems
* Comparison of relational database management systems
The following tables compare general and technical information for a number of relational database management systems. Please see the individual products' articles for further information. Unless otherwise specified in footnotes, comparisons are ba ...
* Data hierarchy
Data hierarchy refers to the systematic organization of data, often in hierarchical form. Data organization involves characters, fields, records, files and so on. This concept is a starting point when trying to see what makes up data and whether da ...
* Data bank
In database management and information architecture, a data bank or databank is a repository of information about one or more subjects, that is, a database which is organized in a way that facilitates local or remote information retrieval and is a ...
* Data store
A data store is a repository for persistently storing and managing collections of data which include not just repositories like databases, but also simpler store types such as simple files, emails, etc.
A ''database'' is a collection of data that ...
* Database theory
Database theory encapsulates a broad range of topics related to the study and research of the theoretical realm of databases and database management systems.
Theoretical aspects of data management include, among other areas, the foundations of q ...
* Database testing
Database testing usually consists of a layered process, including the user interface (UI) layer, the business layer, the data access layer and the database itself. The UI layer deals with the interface design of the database, while the business l ...
* Database-centric architecture
Database-centric Architecture or data-centric architecture has several distinct meanings, generally relating to software architectures in which databases play a crucial role. Often this description is meant to contrast the design to an alternative ...
* Datalog
Datalog is a declarative logic programming language. While it is syntactically a subset of Prolog, Datalog generally uses a bottom-up rather than top-down evaluation model. This difference yields significantly different behavior and properties ...
* Database-as-IPC
In computer programming, Database-as-Inter-process communication, IPC may be considered an anti-pattern where a disk persisted table in a database is used as the message queue store for routine inter-process communication (IPC) or subscribed data ...
* DBOS
DBOS (Database-Oriented Operating System) is a database-oriented operating system meant to simplify and improve the scalability, security and resilience of large-scale distributed applications. It started in 2020 as a joint open source project with ...
* Flat-file database
A flat-file database is a database stored in a file called a flat file. Records follow a uniform format, and there are no structures for indexing or recognizing relationships between records. The file is simple. A flat file can be a plain t ...
* INP (database)
* Journal of Database Management
* Question-focused dataset
Notes
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* Ling Liu and Tamer M. Özsu (Eds.) (2009).Encyclopedia of Database Systems
4100 p. 60 illus. . * Gray, J. and Reuter, A. ''Transaction Processing: Concepts and Techniques'', 1st edition, Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, 1992. * Kroenke, David M. and David J. Auer. ''Database Concepts.'' 3rd ed. New York: Prentice, 2007. * Raghu Ramakrishnan and Johannes Gehrke,
Database Management Systems
'. *
Abraham Silberschatz
Avi Silberschatz (; born in Haifa, Israel) is an Israeli computer scientist and researcher. He is known for having authored many influential texts in computer science. He finished high school at the Hebrew Reali School in Haifa and graduated ...
, Henry F. Korth
Henry Francis Korth is a professor of Computer Science and Engineering. He is a fellow of the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) and of the IEEE. He is one of the coauthors of the university textbook ''Database System Concepts''.
Early ...
, S. Sudarshan, Database System Concepts
'. * * Teorey, T.; Lightstone, S. and Nadeau, T. ''Database Modeling & Design: Logical Design'', 4th edition, Morgan Kaufmann Press, 2005. . *
CMU Database courses playlist
' *
MIT OCW 6.830 , Fall 2010 , Database Systems
' *
Berkeley CS W186
'
External links
DB File extension
nbsp;– information about files with the DB extension {{Authority control