|
Database Testing
Database testing usually consists of a layered process, including the user interface (UI) layer, the business layer, the data access layer and the database itself. The UI layer deals with the interface design of the database, while the business layer includes databases supporting business strategies. Purposes Databases, the collection of interconnected files on a server, storing information, may not deal with the same ''type'' of data, i.e. databases may be heterogeneous. As a result, many kinds of implementation and integration errors may occur in large database systems, which negatively affect the system's performance, reliability, consistency and security. Thus, it is important to test in order to obtain a database system which satisfies the ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability) of a database management system. One of the most critical layers is the data access layer, which deals with databases directly during the communication process. Dat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
User Interface
In the industrial design field of human–computer interaction, a user interface (UI) is the space where interactions between humans and machines occur. The goal of this interaction is to allow effective operation and control of the machine from the human end, while the machine simultaneously feeds back information that aids the operators' decision-making process. Examples of this broad concept of user interfaces include the interactive aspects of computer operating systems, hand tools, heavy machinery operator controls and Unit operation, process controls. The design considerations applicable when creating user interfaces are related to, or involve such disciplines as, ergonomics and psychology. Generally, the goal of user interface design is to produce a user interface that makes it easy, efficient, and enjoyable (user-friendly) to operate a machine in the way which produces the desired result (i.e. maximum usability). This generally means that the operator needs to provide mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
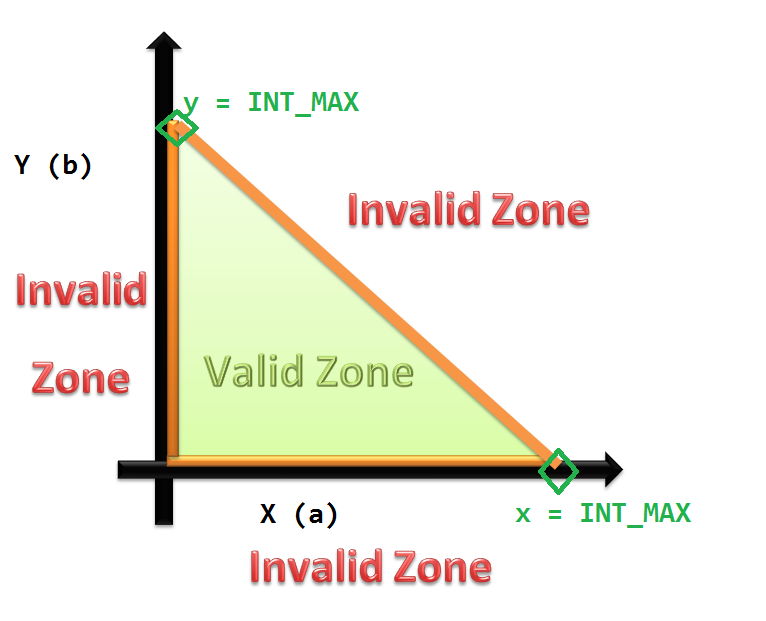
Equivalence Partitioning
Equivalence partitioning or equivalence class partitioning (ECP) is a software testing technique that divides the input data of a software unit into partitions of equivalent data from which test cases can be derived. In principle, test cases are designed to cover each partition at least once. This technique tries to define test cases that uncover classes of errors, thereby reducing the total number of test cases that must be developed. An advantage of this approach is reduction in the time required for testing software due to lesser number of test cases. Equivalence partitioning is typically applied to the inputs of a tested component, but may be applied to the outputs in rare cases. The equivalence partitions are usually derived from the requirements specification for input attributes that influence the processing of the test object. The fundamental concept of ECP comes from equivalence class which in turn comes from equivalence relation. A software system is in effect a comput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unit Testing
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior. Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the Integration testing, integration or System testing, system level. History Unit testing, as a principle for testing separately smaller parts of large software systems, dates back to the early days of software engineering. In June 1956 at US Navy's Symposium on Advanced Programming Methods for Digital Computers, H.D. Benington presented the Semi-Automatic Ground Environment, SAGE project. It featured a specification-based approach where the coding phase was followed by "parameter testing" to validate component subprograms against their specification, followed then by an "assembly testing" for parts put together. In 1964, a similar approach is described for the software of the Project Mercury, Mercury project, where individual units developed by dif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Testing
Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations. Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the Quality (business), quality of software and the risk of its failure to a User (computing), user or sponsor. Software testing can determine the Correctness (computer science), correctness of software for specific Scenario (computing), scenarios but cannot determine correctness for all scenarios. It cannot find all software bug, bugs. Based on the criteria for measuring correctness from an test oracle, oracle, software testing employs principles and mechanisms that might recognize a problem. Examples of oracles include specifications, Design by Contract, contracts, comparable products, past versions of the same product, inferences about intended or expected purpose, user or customer expectations, relevant standards, and applicable laws. Software testing is often dynamic in nature; running the software to verify actual output ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Database Normalization
Database normalization is the process of structuring a relational database in accordance with a series of so-called '' normal forms'' in order to reduce data redundancy and improve data integrity. It was first proposed by British computer scientist Edgar F. Codd as part of his relational model. Normalization entails organizing the columns (attributes) and tables (relations) of a database to ensure that their dependencies are properly enforced by database integrity constraints. It is accomplished by applying some formal rules either by a process of ''synthesis'' (creating a new database design) or ''decomposition'' (improving an existing database design). Objectives A basic objective of the first normal form defined by Codd in 1970 was to permit data to be queried and manipulated using a "universal data sub-language" grounded in first-order logic. An example of such a language is SQL, though it is one that Codd regarded as seriously flawed. The objectives of normalization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Transformation Services
Data Transformation Services (DTS) is a Microsoft database tool with a set of objects and utilities to allow the automation of extract, transform and load operations to or from a database. The objects are DTS packages and their components, and the utilities are called DTS tools. DTS was included with earlier versions of Microsoft SQL Server, and was almost always used with SQL Server databases, although it could be used independently with other databases. DTS allows data to be transformed and loaded from heterogeneous sources using OLE DB, ODBC, or text-only files, into any supported database. DTS can also allow automation of data import or transformation on a scheduled basis, and can perform additional functions such as FTPing files and executing external programs. In addition, DTS provides an alternative method of version control and backup for packages when used in conjunction with a version control system, such as Microsoft Visual SourceSafe. DTS has been superseded by SQL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Load Testing
Load testing is the process of putting demand on a structure or system and measuring its response. Software load testing Physical load testing Many types of machinery, engines, structures, and motors are load tested. The load may be at a designated safe working load (SWL), full load, or at an aggravated level of load. The governing contract, technical specification or test method contains the details of conducting the test. The purpose of a mechanical load test is to verify that all the component parts of a structure including materials, base-fixings are fit for task and loading it is designed for. Several types of load testing are employed * Static testing is when a designated constant load is applied for a specified time. * Dynamic testing is when a variable or moving load is applied. * Cyclical testing consists of repeated loading and unloading for specified cycles, durations and conditions. The ''Supply of Machinery (Safety) Regulation 1992 UK'' state that load testi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server is a proprietary relational database management system developed by Microsoft using Structured Query Language (SQL, often pronounced "sequel"). As a database server, it is a software product with the primary function of storing and retrieving data as requested by other software applications—which may run either on the same computer or on another computer across a network (including the Internet). Microsoft markets at least a dozen different editions of Microsoft SQL Server, aimed at different audiences and for workloads ranging from small single-machine applications to large Internet-facing applications with many concurrent users. History The history of Microsoft SQL Server begins with the first Microsoft SQL Server product—SQL Server 1.0, a 16-bit server for the OS/2 operating system in 1989—and extends to the current day. Its name is entirely descriptive, it being '' server'' software that responds to queries in the '' SQL'' language. Mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PHPUnit
PHPUnit is a unit testing framework for the PHP programming language. It is an instance of the xUnit architecture for unit testing frameworks that originated with SUnit and became popular with JUnit. PHPUnit was created by Sebastian Bergmann and its development is hosted on GitHub. Purpose PHPUnit is based on the idea that developers should be able to find mistakes in their newly committed code quickly and assert that no code regression has occurred in other parts of the code base. Much like other unit testing frameworks, PHPUnit uses assertions to verify that the behavior of the specific component - or ''"unit"'' - being tested behaves as expected. Benefits The goal of unit testing is to isolate each part of the program and show that the individual parts are correct. A unit test provides a strict, written contract that the piece of code must satisfy. As a result, unit tests find problems early in the development cycle. PHPUnit can output test results in a number of differe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Test Fixture
A test fixture is a device used to consistently test some item, device, or piece of software. Test fixtures are used in the testing of electronics, software and physical devices. Electronics In testing electronic equipment such as circuit boards, electronic components, and chips, a test fixture is a device or setup designed to hold the device under test in place and allow it to be tested by being subjected to controlled electronic test signals. Examples are a bed of nails tester or smart fixture. Test fixtures can come in different shapes, sizes, and functions. There are several different types of test fixtures, including In-circuit testing, In-Circuit Test Fixtures, Functional testing (manufacturing), Functional Test Fixtures, and Wireless Test Fixtures. In Circuit Test (ICT) fixtures individually test each component on a Printed circuit board, PCB, while functional test fixtures assess the entire board's functionality. Functional test fixtures simulate real-world conditions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclomatic Complexity
Cyclomatic complexity is a software metric used to indicate the complexity of a program. It is a quantitative measure of the number of linearly independent paths through a program's source code. It was developed by Thomas J. McCabe, Sr. in 1976. Cyclomatic complexity is computed using the control-flow graph of the program. The nodes of the graph correspond to indivisible groups of commands of a program, and a directed edge connects two nodes if the second command might be executed immediately after the first command. Cyclomatic complexity may also be applied to individual functions, modules, methods, or classes within a program. One testing strategy, called basis path testing by McCabe who first proposed it, is to test each linearly independent path through the program. In this case, the number of test cases will equal the cyclomatic complexity of the program. Description Definition There are multiple ways to define cyclomatic complexity of a section of source code. One com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |