|
Data Transformation Services
Data Transformation Services (DTS) is a Microsoft database tool with a set of objects and utilities to allow the automation of extract, transform and load operations to or from a database. The objects are DTS packages and their components, and the utilities are called DTS tools. DTS was included with earlier versions of Microsoft SQL Server, and was almost always used with SQL Server databases, although it could be used independently with other databases. DTS allows data to be transformed and loaded from heterogeneous sources using OLE DB, ODBC, or text-only files, into any supported database. DTS can also allow automation of data import or transformation on a scheduled basis, and can perform additional functions such as FTPing files and executing external programs. In addition, DTS provides an alternative method of version control and backup for packages when used in conjunction with a version control system, such as Microsoft Visual SourceSafe. DTS has been superseded by SQL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
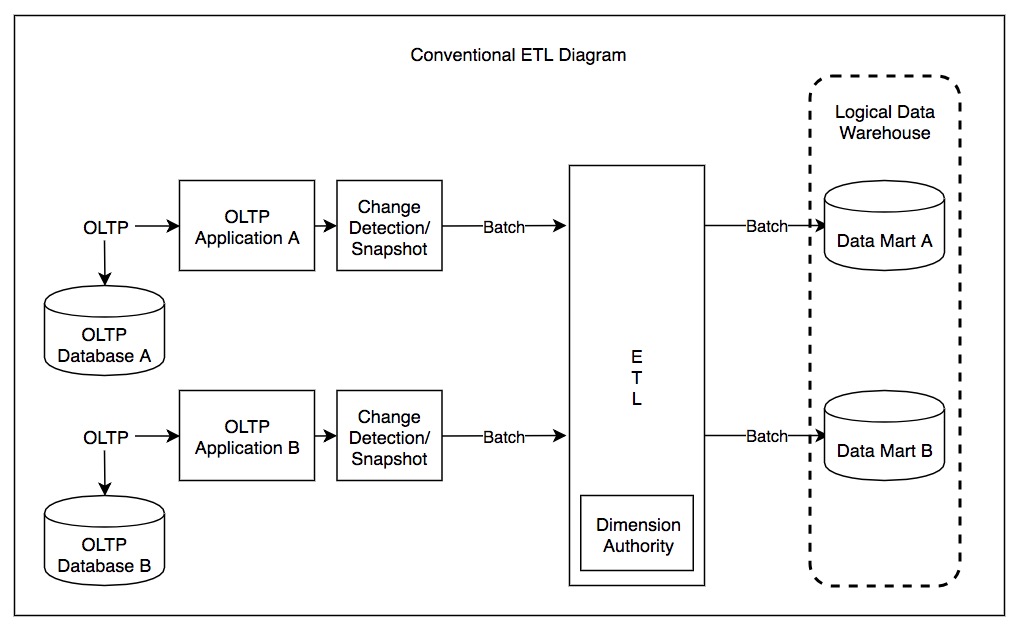
Extract, Transform, Load
Extract, transform, load (ETL) is a three-phase computing process where data is ''extracted'' from an input source, ''transformed'' (including cleaning), and ''loaded'' into an output data container. The data can be collected from one or more sources and it can also be output to one or more destinations. ETL processing is typically executed using software applications but it can also be done manually by system operators. ETL software typically automates the entire process and can be run manually or on recurring schedules either as single jobs or aggregated into a batch of jobs. A properly designed ETL system extracts data from source systems and enforces data type and data validity standards and ensures it conforms structurally to the requirements of the output. Some ETL systems can also deliver data in a presentation-ready format so that application developers can build applications and end users can make decisions. The ETL process is often used in data warehousing. ETL sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metadata
Metadata (or metainformation) is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including: * Descriptive metadata – the descriptive information about a resource. It is used for discovery and identification. It includes elements such as title, abstract, author, and keywords. * Structural metadata – metadata about containers of data and indicates how compound objects are put together, for example, how pages are ordered to form chapters. It describes the types, versions, relationships, and other characteristics of digital materials. * Administrative metadata – the information to help manage a resource, like resource type, and permissions, and when and how it was created. * Reference metadata – the information about the contents and quality of Statistical data type, statistical data. * Statistical metadata – also called process data, may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Retrieval
Information retrieval (IR) in computing and information science is the task of identifying and retrieving information system resources that are relevant to an Information needs, information need. The information need can be specified in the form of a search query. In the case of document retrieval, queries can be based on full-text search, full-text or other content-based indexing. Information retrieval is the science of searching for information in a document, searching for documents themselves, and also searching for the metadata that describes data, and for databases of texts, images or sounds. Automated information retrieval systems are used to reduce what has been called information overload. An IR system is a software system that provides access to books, journals and other documents; it also stores and manages those documents. Web search engines are the most visible IR applications. Overview An information retrieval process begins when a user enters a query into the sys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copy And Paste
Cut, copy, and paste are essential Command (computing), commands of modern human–computer interaction and user interface design. They offer an interprocess communication technique for transferring data (computing), data through a computer's user interface. The ''cut'' command removes the Selection (user interface), selected data from its original position, and the ''copy'' command creates a duplicate; in both cases the selected data is kept in temporary storage called the Clipboard (computing), clipboard. Clipboard data is later inserted wherever a ''paste'' command is issued. The data remains available to any application supporting the feature, thus allowing easy data transfer between applications. The command names are an interface metaphor based on the physical procedure used in manuscript print editing to create a page layout, like with paper. The commands were pioneered into computing by Xerox PARC (company), PARC in 1974, popularized by Apple Computer in the 1983 Apple Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icon (computing)
In computing, an icon is a pictogram or ideogram displayed on a computer screen in order to help the user navigate a computer system. It can serve as an electronic hyperlink or file shortcut to access the program or data. The user can activate an icon using a mouse, pointer, finger, or voice commands. Their placement on the screen, also in relation to other icons, may provide further information to the user about their usage. In activating an icon, the user can move directly into and out of the identified function without knowing anything further about the location or requirements of the file or code. Icons as parts of the graphical user interface of a computer system, in conjunction with window (computing), windows, Menu (computing), menus and a pointing device (mouse), belong to the much larger topic of the history of the graphical user interface that has largely supplanted the text-based interface for casual use. Overview The computing definition of "icon" can include three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphical Tool
A graphical user interface, or GUI, is a form of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices through graphical icons and visual indicators such as secondary notation. In many applications, GUIs are used instead of text-based UIs, which are based on typed command labels or text navigation. GUIs were introduced in reaction to the perceived steep learning curve of command-line interfaces (CLIs), which require commands to be typed on a computer keyboard. The actions in a GUI are usually performed through direct manipulation of the graphical elements. Beyond computers, GUIs are used in many handheld mobile devices such as MP3 players, portable media players, gaming devices, smartphones and smaller household, office and industrial controls. The term ''GUI'' tends not to be applied to other lower-display resolution types of interfaces, such as video games (where head-up displays (''HUDs'') are preferred), or not including flat screens like volumetric disp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SQL Server Agent
SQL Server Agent is a component of Microsoft SQL Server which schedules jobs and handles other automated tasks. It runs as a Windows service so it can start automatically when the system boots or it can be started manually. Typical system tasks performed include scheduling maintenance plans (such as backups), handling Reporting Services subscriptions and performing log shipping Log shipping is the process of automating the backup of transaction log files on a primary (production) database server, and then restoring them onto a standby server. This technique is supported by Microsoft SQL Server,T-SQL or command line statement are also common. SQLAgent has support for operators and alerts, so that administrators can be notified, e.g. by email. References ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wizard (software)
A software wizard or setup assistant or multi-step form is a user interface that leads a user through a sequence of small steps, such as a dialog box to configure a program for the first time. They are used to make complex, unfamiliar tasks easier by breaking them into smaller pieces. History Before the 1990s, "wizard" was a common term for a technical expert, comparable to "hacker." The 1985 textbook Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs was nicknamed the "Wizard Book" for the illustration on its cover; its first chapter says, "A computational process is indeed much like a sorcerer's idea of a spirit." When developing the first version of its desktop publishing software, Microsoft Publisher, around 1991, Microsoft wanted to help users create well-presented documents in spite of their lack of graphic design skills. Microsoft reasoned that, no matter the tools a program offered, users would not know how best to use them. Publisher's "Page Wizards" instead provided a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Global Variable
In computer programming, a global variable is a variable with global scope, meaning that it is visible (hence accessible) throughout the program, unless shadowed. The set of all global variables is known as the ''global environment'' or ''global state.'' In compiled languages, global variables are generally static variables, whose extent (lifetime) is the entire runtime of the program, though in interpreted languages (including command-line interpreters), global variables are generally dynamically allocated when declared, since they are not known ahead of time. In some languages, all variables are global, or global by default, while in most modern languages variables have limited scope, generally lexical scope, though global variables are often available by declaring a variable at the top level of the program. In other languages, however, global variables do not exist; these are generally modular programming languages that enforce a module structure, or class-based object-or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Transformation Service
Data Transformation Services (DTS) is a Microsoft database tool with a set of objects and utilities to allow the automation of extract, transform and load operations to or from a database. The objects are DTS packages and their components, and the utilities are called DTS tools. DTS was included with earlier versions of Microsoft SQL Server, and was almost always used with SQL Server databases, although it could be used independently with other databases. DTS allows data to be transformed and loaded from heterogeneous sources using OLE DB, ODBC, or text-only files, into any supported database. DTS can also allow automation of data import or transformation on a scheduled basis, and can perform additional functions such as FTPing files and executing external programs. In addition, DTS provides an alternative method of version control and backup for packages when used in conjunction with a version control system, such as Microsoft Visual SourceSafe. DTS has been superseded by SQL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object Model
In computing, object model has two related but distinct meanings: # The properties of objects in general in a specific computer programming language, technology, notation or methodology that uses them. Examples are the object models of ''Java'', the ''Component Object Model (COM)'', or ''Object-Modeling Technique (OMT)''. Such object models are usually defined using concepts such as class, generic function, message, inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation. There is an extensive literature on formalized object models as a subset of the formal semantics of programming languages. # A collection of objects or classes through which a program can examine and manipulate some specific parts of its world. In other words, the object-oriented interface to some service or system. Such an interface is said to be the ''object model of'' the represented service or system. For example, the Document Object Model (DOM) is a collection of objects that represent a page in a web browser, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ActiveX Data Objects
In computing, Microsoft's ActiveX Data Objects (ADO) comprises a set of Component Object Model (COM) objects for accessing data sources. A part of MDAC (Microsoft Data Access Components), it provides a middleware layer between programming languages and OLE DB (a means of accessing data stores, whether databases or not, in a uniform manner). ADO allows a developer to write programs that access data without knowing how the database is implemented; developers must be aware of the database for connection only. No knowledge of SQL is required to access a database when using ADO, although one can use ADO to execute SQL commands directly (with the disadvantage of introducing a dependency upon the type of database used). Microsoft introduced ADO in October 1996, positioning the software as a successor to Microsoft's earlier object layers for accessing data sources, including RDO (Remote Data Objects) and DAO (Data Access Objects). ADO is made up of four collections and twelve o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |