Extract, Transform, Load on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Extract, transform, load (ETL) is a three-phase
 In
In
computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and softw ...
process where data is ''extracted'' from an input source, ''transformed'' (including cleaning
Cleaning is the process of removing unwanted substances, such as dirt, infectious agents, and other impurities, from an object or environment. Cleaning is often performed for beauty, aesthetic, hygiene, hygienic, Function (engineering), function ...
), and ''loaded'' into an output data container. The data can be collected from one or more sources and it can also be output to one or more destinations. ETL processing is typically executed using software application
Application software is any computer program that is intended for end-user use not computer operator, operating, system administration, administering or computer programming, programming the computer. An application (app, application program, sof ...
s but it can also be done manually by system operators. ETL software typically automates the entire process and can be run manually or on recurring schedules either as single jobs or aggregated into a batch of jobs.
A properly designed ETL system extracts data from source systems and enforces data type and data validity standards and ensures it conforms structurally to the requirements of the output. Some ETL systems can also deliver data in a presentation-ready format so that application developers can build applications and end users can make decisions.
The ETL process is often used in data warehousing
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for Business intelligence, reporting and data analysis and is a core component of business intelligence. Data warehouses are central Re ...
. ETL systems commonly integrate data from multiple applications (systems), typically developed and supported by different vendor
In a supply chain, a vendor, supplier, provider or a seller, is an enterprise that contributes goods or services. Generally, a supply chain vendor manufactures inventory/stock items and sells them to the next link in the chain. Today, these term ...
s or hosted on separate computer hardware. The separate systems containing the original data are frequently managed and operated by different stakeholders. For example, a cost accounting system may combine data from payroll, sales, and purchasing.
Data extraction involves extracting data from homogeneous or heterogeneous sources; data transformation processes data by data cleaning and transforming it into a proper storage format/structure for the purposes of querying and analysis; finally, data loading describes the insertion of data into the final target database such as an operational data store, a data mart
A data mart is a structure/access pattern specific to ''data warehouse'' environments. The data mart is a subset of the data warehouse that focuses on a specific business line, department, subject area, or team. Whereas data warehouses have an en ...
, data lake or a data warehouse.
ETL and its variant ELT (extract, load, transform), are increasingly used in cloud-based data warehousing. Applications involve not only batch processing, but also real-time streaming.
Phases
Extract
ETL processing involves extracting the data from the source system(s). In many cases, this represents the most important aspect of ETL, since extracting data correctly sets the stage for the success of subsequent processes. Most data-warehousing projects combine data from different source systems. Each separate system may also use a different data organization and/or format. Common data-source formats includerelational database
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970.
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured for ...
s, flat-file database
A flat-file database is a database stored in a file called a flat file. Records follow a uniform format, and there are no structures for indexing or recognizing relationships between records. The file is simple. A flat file can be a plain t ...
s, XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing data. It defines a set of rules for encoding electronic document, documents in a format that is both human-readable and Machine-r ...
, and JSON
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation, pronounced or ) is an open standard file format and electronic data interchange, data interchange format that uses Human-readable medium and data, human-readable text to store and transmit data objects consi ...
, but may also include non-relational database structures such as IBM Information Management System
The IBM Information Management System (IMS) is a joint hierarchical database model, hierarchical database and information management system that supports transaction processing. Development began in 1966 to keep track of the bill of materials for ...
or other data structures such as Virtual Storage Access Method (VSAM) or Indexed Sequential Access Method (ISAM), or even formats fetched from outside sources by means such as a web crawler
Web crawler, sometimes called a spider or spiderbot and often shortened to crawler, is an Internet bot that systematically browses the World Wide Web and that is typically operated by search engines for the purpose of Web indexing (''web spider ...
or data scraping
Data scraping is a technique where a computer program extracts data from Human-readable medium, human-readable output coming from another program.
Description
Normally, Data transmission, data transfer between programs is accomplished using data ...
. The streaming of the extracted data source and loading on-the-fly to the destination database is another way of performing ETL when no intermediate data storage is required.
An intrinsic part of the extraction involves data validation to confirm whether the data pulled from the sources has the correct/expected values in a given domain (such as a pattern/default or list of values). If the data fails the validation rules, it is rejected entirely or in part. The rejected data is ideally reported back to the source system for further analysis to identify and to rectify incorrect records or perform data wrangling.
Transform
In the data transformation stage, a series of rules or functions are applied to the extracted data in order to prepare it for loading into the end target. An important function of transformation isdata cleansing
Data cleansing or data cleaning is the process of identifying and correcting (or removing) corrupt, inaccurate, or irrelevant records from a dataset, table, or database. It involves detecting incomplete, incorrect, or inaccurate parts of the dat ...
, which aims to pass only "proper" data to the target. The challenge when different systems interact is in the relevant systems' interfacing and communicating. Character sets that may be available in one system may not be in others.
In other cases, one or more of the following transformation types may be required to meet the business and technical needs of the server or data warehouse:
* Selecting only certain columns to load: (or selecting null
Null may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Astronomy
*Nuller, an optical tool using interferometry to block certain sources of light Computing
*Null (SQL) (or NULL), a special marker and keyword in SQL indicating that a data value do ...
columns not to load). For example, if the source data has three columns (aka "attributes"), roll_no, age, and salary, then the selection may take only roll_no and salary. Or, the selection mechanism may ignore all those records where salary is not present (salary = null).
* Translating coded values: (''e.g.'', if the source system codes male as "1" and female as "2", but the warehouse codes male as "M" and female as "F")
* Encoding free-form values: (''e.g.'', mapping "Male" to "M")
* Deriving a new calculated value: (''e.g.'', sale_amount = qty * unit_price)
* Sorting or ordering the data based on a list of columns to improve search performance
* Joining data from multiple sources (''e.g.'', lookup, merge) and deduplicating the data
* Aggregating (for example, rollup – summarizing multiple rows of data – total sales for each store, and for each region, etc.)
* Generating surrogate-key values
* Transposing or pivoting (turning multiple columns into multiple rows or vice versa)
* Splitting a column into multiple columns (''e.g.'', converting a comma-separated list, specified as a string in one column, into individual values in different columns)
* Disaggregating repeating columns
* Looking up and validating the relevant data from tables or referential files
* Applying any form of data validation; failed validation may result in a full rejection of the data, partial rejection, or no rejection at all, and thus none, some, or all of the data is handed over to the next step depending on the rule design and exception handling; many of the above transformations may result in exceptions, e.g., when a code translation parses an unknown code in the extracted data
Load
The load phase loads the data into the end target, which can be any data store including a simple delimited flat file or adata warehouse
In computing, a data warehouse (DW or DWH), also known as an enterprise data warehouse (EDW), is a system used for Business intelligence, reporting and data analysis and is a core component of business intelligence. Data warehouses are central Re ...
. Depending on the requirements of the organization, this process varies widely. Some data warehouses may overwrite existing information with cumulative information; updating extracted data is frequently done on a daily, weekly, or monthly basis. Other data warehouses (or even other parts of the same data warehouse) may add new data in a historical form at regular intervals – for example, hourly. To understand this, consider a data warehouse that is required to maintain sales records of the last year. This data warehouse overwrites any data older than a year with newer data. However, the entry of data for any one year window is made in a historical manner. The timing and scope to replace or append are strategic design choices dependent on the time available and the business
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for ...
needs. More complex systems can maintain a history and audit trail
An audit trail (also called audit log) is a security-relevant chronological record, set of records, and/or destination and source of records that provide documentary evidence of the sequence of activities that have affected at any time a specific ...
of all changes to the data loaded in the data warehouse.
As the load phase interacts with a database, the constraints defined in the database schema – as well as in triggers activated upon data load – apply (for example, uniqueness, referential integrity, mandatory fields), which also contribute to the overall data quality performance of the ETL process.
* For example, a financial institution might have information on a customer in several departments and each department might have that customer's information listed in a different way. The membership department might list the customer by name, whereas the accounting department might list the customer by number. ETL can bundle all of these data elements and consolidate them into a uniform presentation, such as for storing in a database or data warehouse.
* Another way that companies use ETL is to move information to another application permanently. For instance, the new application might use another database vendor and most likely a very different database schema. ETL can be used to transform the data into a format suitable for the new application to use.
* An example would be an expense and cost recovery system such as used by accountants
An accountant is a practitioner of accounting or accountancy.
Accountants who have demonstrated competency through their professional associations' certification exams are certified to use titles such as Chartered Accountant, Chartered Certifie ...
, consultant
A consultant (from "to deliberate") is a professional (also known as ''expert'', ''specialist'', see variations of meaning below) who provides advice or services in an area of specialization (generally to medium or large-size corporations). Cons ...
s, and law firm
A law firm is a business entity formed by one or more lawyers to engage in the practice of law. The primary service rendered by a law firm is to advise consumer, clients (individuals or corporations) about their legal rights and Obligation, respon ...
s. The data usually ends up in the time and billing system, although some businesses may also utilize the raw data for employee productivity reports to Human Resources (personnel dept.) or equipment usage reports to Facilities Management.
Additional phases
A real-life ETL cycle may consist of additional execution steps, for example: # Cycle initiation # Build reference data # Extract (from sources) # Validate # Transform ( clean, applybusiness rule A business rule defines or constrains some aspect of a business. It may be expressed to specify an action to be taken when certain conditions are true or may be phrased so it can only resolve to either true or false. Business rules are intended to a ...
s, check for data integrity
Data integrity is the maintenance of, and the assurance of, data accuracy and consistency over its entire Information Lifecycle Management, life-cycle. It is a critical aspect to the design, implementation, and usage of any system that stores, proc ...
, create aggregates or disaggregates)
# Stage (load into staging tables, if used)
# Audit reports (for example, on compliance with business rules. Also, in case of failure, helps to diagnose/repair)
# Publish (to target tables)
# Archive
An archive is an accumulation of historical records or materials, in any medium, or the physical facility in which they are located.
Archives contain primary source documents that have accumulated over the course of an individual or organ ...
Design Challenges
ETL processes can involve considerable complexity, and significant operational problems can occur with improperly designed ETL systems.Data variations
The range of data values or data quality in an operational system may exceed the expectations of designers at the time validation and transformation rules are specified. Data profiling of a source during data analysis can identify the data conditions that must be managed by transform rules specifications, leading to an amendment of validation rules explicitly and implicitly implemented in the ETL process. Data warehouses are typically assembled from a variety of data sources with different formats and purposes. As such, ETL is a key process to bring all the data together in a standard, homogeneous environment. Design analysis should establish thescalability
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work. One definition for software systems specifies that this may be done by adding resources to the system.
In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that ...
of an ETL system across the lifetime of its usage – including understanding the volumes of data that must be processed within service level agreement
A service-level agreement (SLA) is an agreement between a service provider and a customer. Particular aspects of the service – quality, availability, responsibilities – are agreed between the service provider and the service user.
T ...
s. The time available to extract from source systems may change, which may mean the same amount of data may have to be processed in less time. Some ETL systems have to scale to process terabytes of data to update data warehouses with tens of terabytes of data. Increasing volumes of data may require designs that can scale from daily batch to multiple-day micro batch to integration with message queue
In computer science, message queues and mailboxes are software-engineering components typically used for inter-process communication (IPC), or for inter- thread communication within the same process. They use a queue for messaging – the ...
s or real-time change-data-capture for continuous transformation and update.
Uniqueness of keys
Unique keys play an important part in all relational databases, as they tie everything together. A unique key is a column that identifies a given entity, whereas aforeign key
A foreign key is a set of attributes in a table that refers to the primary key of another table, linking these two tables. In the context of relational databases, a foreign key is subject to an inclusion dependency constraint that the tuples ...
is a column in another table that refers to a primary key. Keys can comprise several columns, in which case they are composite keys. In many cases, the primary key is an auto-generated integer that has no meaning for the business entity
In law, a legal person is any person or legal entity that can do the things a human person is usually able to do in law – such as enter into contracts, lawsuit, sue and be sued, ownership, own property, and so on. The reason for the term "''le ...
being represented, but solely exists for the purpose of the relational database – commonly referred to as a surrogate key.
As there is usually more than one data source getting loaded into the warehouse, the keys are an important concern to be addressed. For example: customers might be represented in several data sources, with their Social Security number
In the United States, a Social Security number (SSN) is a nine-digit number issued to United States nationality law, U.S. citizens, Permanent residence (United States), permanent residents, and temporary (working) residents under section 205(c)(2 ...
as the primary key in one source, their phone number in another, and a surrogate in the third. Yet a data warehouse may require the consolidation of all the customer information into one dimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coo ...
.
A recommended way to deal with the concern involves adding a warehouse surrogate key, which is used as a foreign key from the fact table.
Usually, updates occur to a dimension's source data, which obviously must be reflected in the data warehouse.
If the primary key of the source data is required for reporting, the dimension already contains that piece of information for each row. If the source data uses a surrogate key, the warehouse must keep track of it even though it is never used in queries or reports; it is done by creating a lookup table
In computer science, a lookup table (LUT) is an array data structure, array that replaces runtime (program lifecycle phase), runtime computation of a mathematical function (mathematics), function with a simpler array indexing operation, in a proc ...
that contains the warehouse surrogate key and the originating key.Golfarelli/Rizzi, Data Warehouse Design, p. 291 This way, the dimension is not polluted with surrogates from various source systems, while the ability to update is preserved.
The lookup table is used in different ways depending on the nature of the source data.
There are 5 types to consider; three are included here:
;Type 1
:The dimension row is simply updated to match the current state of the source system; the warehouse does not capture history; the lookup table is used to identify the dimension row to update or overwrite
;Type 2
:A new dimension row is added with the new state of the source system; a new surrogate key is assigned; source key is no longer unique in the lookup table
;Fully logged
:A new dimension row is added with the new state of the source system, while the previous dimension row is updated to reflect it is no longer active and time of deactivation.
Performance
ETL vendors benchmark their record-systems at multiple TB (terabytes) per hour (or ~1 GB per second) using powerful servers with multiple CPUs, multiple hard drives, multiple gigabit-network connections, and much memory. In real life, the slowest part of an ETL process usually occurs in the database load phase. Databases may perform slowly because they have to take care of concurrency, integrity maintenance, and indices. Thus, for better performance, it may make sense to employ: * ''Direct path extract'' method or bulk unload whenever is possible (instead of querying the database) to reduce the load on source system while getting high-speed extract * Most of the transformation processing outside of the database * Bulk load operations whenever possible Still, even using bulk operations, database access is usually the bottleneck in the ETL process. Some common methods used to increase performance are: * Partition tables (and indices): try to keep partitions similar in size (watch fornull values that can skew the partitioning)
* Do all validation in the ETL layer before the load: disable integrity
Integrity is the quality of being honest and having a consistent and uncompromising adherence to strong moral and ethical principles and values.
In ethics, integrity is regarded as the honesty and Honesty, truthfulness or of one's actions. Integr ...
checking (disable constraint ...) in the target database tables during the load
* Disable triggers (disable trigger ...) in the target database tables during the load: simulate their effect as a separate step
* Generate IDs in the ETL layer (not in the database)
* Drop the indices (on a table or partition) before the load – and recreate them after the load (SQL: drop index ...; create index ...)
* Use parallel bulk load when possible – works well when the table is partitioned or there are no indices (Note: attempting to do parallel loads into the same table (partition) usually causes locks – if not on the data rows, then on indices)
* If a requirement exists to do insertions, updates, or deletions, find out which rows should be processed in which way in the ETL layer, and then process these three operations in the database separately; you often can do bulk load for inserts, but updates and deletes commonly go through an API
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build ...
(using SQL)
Whether to do certain operations in the database or outside may involve a trade-off. For example, removing duplicates using distinct may be slow in the database; thus, it makes sense to do it outside. On the other side, if using distinct significantly (x100) decreases the number of rows to be extracted, then it makes sense to remove duplications as early as possible in the database before unloading data.
A common source of problems in ETL is a big number of dependencies among ETL jobs. For example, job "B" cannot start while job "A" is not finished. One can usually achieve better performance by visualizing all processes on a graph, and trying to reduce the graph making maximum use of parallelism, and making "chains" of consecutive processing as short as possible. Again, partitioning of big tables and their indices can really help.
Another common issue occurs when the data are spread among several databases, and processing is done in those databases sequentially. Sometimes database replication may be involved as a method of copying data between databases – it can significantly slow down the whole process. The common solution is to reduce the processing graph to only three layers:
* Sources
* Central ETL layer
* Targets
This approach allows processing to take maximum advantage of parallelism. For example, if you need to load data into two databases, you can run the loads in parallel (instead of loading into the first – and then replicating into the second).
Sometimes processing must take place sequentially. For example, dimensional (reference) data are needed before one can get and validate the rows for main "fact" tables.
Parallel computing
Some ETL software implementations include parallel processing. This enables a number of methods to improve overall performance of ETL when dealing with large volumes of data. ETL applications implement three main types of parallelism: * Data: By splitting a single sequential file into smaller data files to provide parallel access *Pipeline
A pipeline is a system of Pipe (fluid conveyance), pipes for long-distance transportation of a liquid or gas, typically to a market area for consumption. The latest data from 2014 gives a total of slightly less than of pipeline in 120 countries ...
: allowing the simultaneous running of several components on the same data stream
In connection-oriented communication, a data stream is the transmission of a sequence of digitally encoded signals to convey information. Typically, the transmitted symbols are grouped into a series of packets.
Data streaming has become u ...
, e.g. looking up a value on record 1 at the same time as adding two fields on record 2
* Component: The simultaneous running of multiple processes on different data streams in the same job, e.g. sorting one input file while removing duplicates on another file
All three types of parallelism usually operate combined in a single job or task.
An additional difficulty comes with making sure that the data being uploaded is relatively consistent. Because multiple source databases may have different update cycles (some may be updated every few minutes, while others may take days or weeks), an ETL system may be required to hold back certain data until all sources are synchronized. Likewise, where a warehouse may have to be reconciled to the contents in a source system or with the general ledger, establishing synchronization and reconciliation points becomes necessary.
Failure recovery
Data warehousing procedures usually subdivide a big ETL process into smaller pieces running sequentially or in parallel. To keep track of data flows, it makes sense to tag each data row with "row_id", and tag each piece of the process with "run_id". In case of a failure, having these IDs help to roll back and rerun the failed piece. Best practice also calls for ''checkpoints'', which are states when certain phases of the process are completed. Once at a checkpoint, it is a good idea to write everything to disk, clean out some temporary files, log the state, etc.Implementations
An established ETL framework may improve connectivity andscalability
Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work. One definition for software systems specifies that this may be done by adding resources to the system.
In an economic context, a scalable business model implies that ...
. A good ETL tool must be able to communicate with the many different relational database
A relational database (RDB) is a database based on the relational model of data, as proposed by E. F. Codd in 1970.
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) is a type of database management system that stores data in a structured for ...
s and read the various file formats used throughout an organization. ETL tools have started to migrate into enterprise application integration, or even enterprise service bus, systems that now cover much more than just the extraction, transformation, and loading of data. Many ETL vendors now have data profiling, data quality
Data quality refers to the state of qualitative or quantitative pieces of information. There are many definitions of data quality, but data is generally considered high quality if it is "fit for tsintended uses in operations, decision making and ...
, and metadata
Metadata (or metainformation) is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including:
* Descriptive ...
capabilities. A common use case for ETL tools include converting CSV files to formats readable by relational databases. A typical translation of millions of records is facilitated by ETL tools that enable users to input CSV-like data feeds/files and import them into a database with as little code as possible.
ETL tools are typically used by a broad range of professionals – from students in computer science looking to quickly import large data sets to database architects in charge of company account management, ETL tools have become a convenient tool that can be relied on to get maximum performance. ETL tools in most cases contain a GUI that helps users conveniently transform data, using a visual data mapper, as opposed to writing large programs to parse files and modify data types.
While ETL tools have traditionally been for developers and IT staff, research firm Gartner wrote that the new trend is to provide these capabilities to business users so they can themselves create connections and data integrations when needed, rather than going to the IT staff. Gartner refers to these non-technical users as Citizen Integrators.
Variations
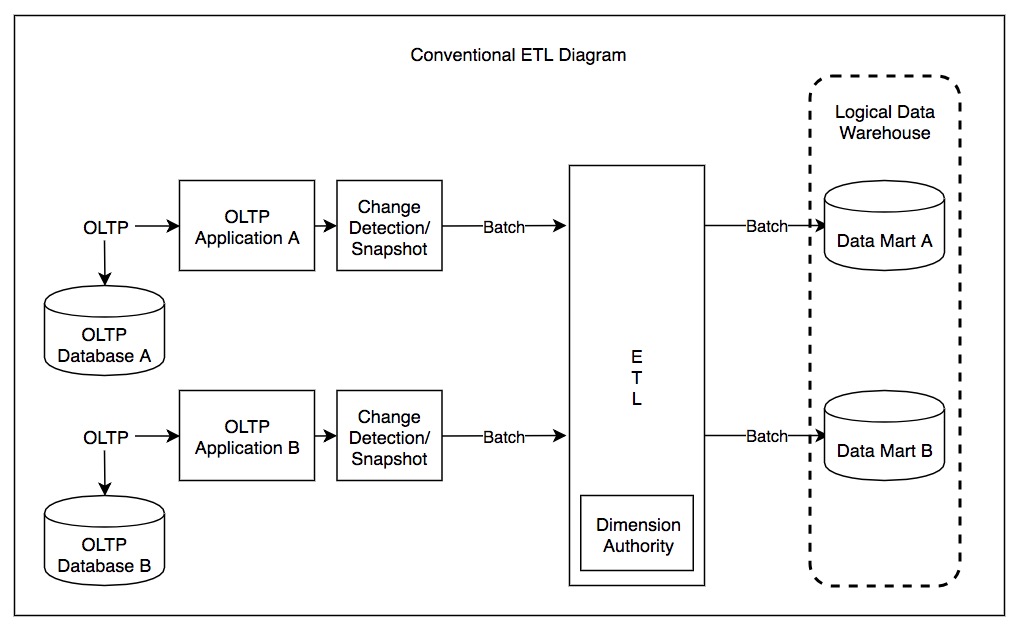
In online transaction processing
 In
In online transaction processing
Online transaction processing (OLTP) is a type of database system used in transaction-oriented applications, such as many operational systems. "Online" refers to the fact that such systems are expected to respond to user requests and process them i ...
(OLTP) applications, changes from individual OLTP instances are detected and logged into a snapshot, or batch, of updates. An ETL instance can be used to periodically collect all of these batches, transform them into a common format, and load them into a data lake or warehouse.
Virtual ETL
Data virtualization can be used to advance ETL processing. The application of data virtualization to ETL allowed solving the most common ETL tasks ofdata migration
Data migration is the process of selecting, preparing, extracting, and transforming data and permanently transferring it from one computer storage system to another. Additionally, the validation of migrated data for completeness and the decommi ...
and application integration for multiple dispersed data sources. Virtual ETL operates with the abstracted representation of the objects or entities gathered from the variety of relational, semi-structured, and unstructured data
Unstructured data (or unstructured information) is information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner. Unstructured information is typically plain text, text-heavy, but may contain data such ...
sources. ETL tools can leverage object-oriented modeling and work with entities' representations persistently stored in a centrally located hub-and-spoke architecture. Such a collection that contains representations of the entities or objects gathered from the data sources for ETL processing is called a metadata repository and it can reside in memory or be made persistent. By using a persistent metadata repository, ETL tools can transition from one-time projects to persistent middleware, performing data harmonization and data profiling consistently and in near-real time.
Extract, load, transform (ELT)
Extract, load, transform (ELT) is a variant of ETL where the extracted data is loaded into the target system first.Amazon Web Services, Data Warehousing on AWS, p. 9 The architecture for the analytics pipeline shall also consider where to cleanse and enrich data as well as how to conform dimensions. Some of the benefits of an ELT process include speed and the ability to more easily handle both unstructured and structured data.Ralph Kimball
Ralph Kimball (born July 18, 1944) is an author on the subject of data warehousing and business intelligence. He is one of the original architects of data warehousing and is known for long-term convictions that data warehouses must be designed to ...
and Joe Caserta's book The Data Warehouse ETL Toolkit, (Wiley, 2004), which is used as a textbook for courses teaching ETL processes in data warehousing, addressed this issue.
Cloud-based data warehouses like Amazon Redshift
Amazon Redshift is a data warehouse product which forms part of the larger cloud-computing platform Amazon Web Services. It is built on top of technology from the massive parallel processing (MPP) data warehouse company ParAccel (later acqui ...
, Google BigQuery, Microsoft Azure Synapse Analytics and Snowflake Inc. have been able to provide highly scalable computing power. This lets businesses forgo preload transformations and replicate raw data into their data warehouses, where it can transform them as needed using SQL.
After having used ELT, data may be processed further and stored in a data mart.
Most data integration tools skew towards ETL, while ELT is popular in database and data warehouse appliances. Similarly, it is possible to perform TEL (Transform, Extract, Load) where data is first transformed on a blockchain (as a way of recording changes to data, e.g., token burning) before extracting and loading into another data store.
See also
* Architectural pattern (EA reference architecture) * CMS Pipelines * Create, read, update and delete (CRUD) *Data cleansing
Data cleansing or data cleaning is the process of identifying and correcting (or removing) corrupt, inaccurate, or irrelevant records from a dataset, table, or database. It involves detecting incomplete, incorrect, or inaccurate parts of the dat ...
*Data integration
Data integration refers to the process of combining, sharing, or synchronizing data from multiple sources to provide users with a unified view.
There are a wide range of possible applications for data integration, from commercial (such as when a ...
*Data mart
A data mart is a structure/access pattern specific to ''data warehouse'' environments. The data mart is a subset of the data warehouse that focuses on a specific business line, department, subject area, or team. Whereas data warehouses have an en ...
* Data mesh, a domain-oriented data architecture
*Data migration
Data migration is the process of selecting, preparing, extracting, and transforming data and permanently transferring it from one computer storage system to another. Additionally, the validation of migrated data for completeness and the decommi ...
* Data transformation (computing)
*Electronic data interchange
Electronic data interchange (EDI) is the concept of businesses electronically communicating information that was traditionally communicated on paper, such as purchase orders, advance ship notices, and invoices. Technical standards for EDI exist to ...
(EDI)
*Enterprise architecture
Enterprise architecture (EA) is a business function concerned with the structures and behaviours of a business, especially business roles and processes that create and use business data. The international definition according to the Federation of ...
* Legal Electronic Data Exchange Standard (LEDES)
* Metadata discovery
*Online analytical processing
In computing, online analytical processing (OLAP) (), is an approach to quickly answer multi-dimensional analytical (MDA) queries. The term ''OLAP'' was created as a slight modification of the traditional database term online transaction proces ...
(OLAP)
*Online transaction processing
Online transaction processing (OLTP) is a type of database system used in transaction-oriented applications, such as many operational systems. "Online" refers to the fact that such systems are expected to respond to user requests and process them i ...
(OLTP)
* Spatial ETL
References
{{Authority control Data warehousing