
A megalith is a large
stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The word was first used in 1849 by the British antiquarian
Algernon Herbert
Algernon Herbert (12 July 1792 – 11 June 1855) was an English antiquary.
Biography
Herbert was the sixth and youngest son of Henry Herbert, 1st Earl of Carnarvon by Elizabeth Alicia Maria, elder daughter of Charles Wyndham, 2nd Earl of Egremo ...
in reference to
Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connectin ...
and derives from the
Ancient Greek words "
mega
Mega or MEGA may refer to:
Science
* mega-, a metric prefix denoting 106
* Mega (number), a certain very large integer in Steinhaus–Moser notation
* "mega-" a prefix meaning "large" that is used in taxonomy
* Gravity assist, for ''Moon-Earth ...
" for great and "
lithos
Lithos is a glyphic sans-serif typeface designed by Carol Twombly in 1989 for Adobe Systems. Lithos is inspired by the unadorned, geometric letterforms of the engravings found on Ancient Greek public buildings. The typeface consists of only cap ...
" for stone. Most extant megaliths were erected between the
Neolithic period (although earlier
Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
examples are known) through the
Chalcolithic period and into the
Bronze Age.
At that time, the beliefs that developed were dynamism and animism, because Indonesia experienced the megalithic age or the great stone age in 2100 to 4000 BC. So that humans ancient tribe worship certain objects that are considered to have supernatural powers. Some relics of the megalithic era are menhirs (stone monuments) and dolmens (stone tables).
Types and definitions
While "megalith" is often used to describe a single piece of stone, it also can be used to denote one or more rocks hewn in definite shapes for special purposes.
It has been used to describe structures built by people from many parts of the world living in many different periods. The most widely known megaliths are not
tombs.
Single stones
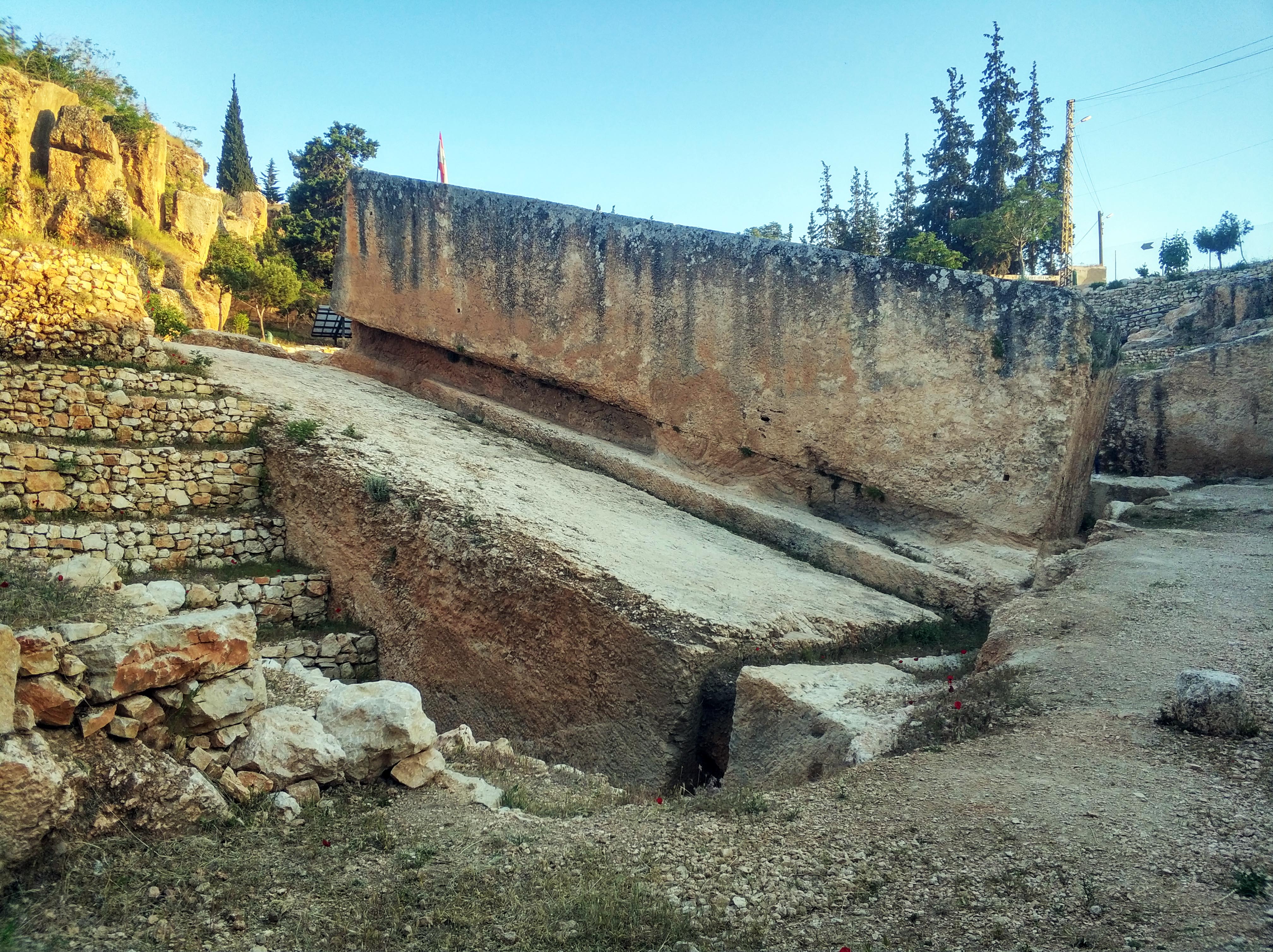


;Menhir:
Menhir is the name used in
Western Europe for a single upright stone erected in
prehistoric
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of ...
times; sometimes called a "standing stone".
;Monolith: Any single standing stone erected in prehistoric times.
;Capstone style: Single megaliths placed horizontally, often over burial chambers, without the use of support stones.
Multiple stones
;Alignments: Multiple megaliths placed in relation to each other with intention. Often placed in
rows or
spirals. Some alignments, such as the
Carnac Stones in
Brittany,
France consist of thousands of stones.
;Megalithic walls: Also called ''
Cyclopean walls''
;Stone circles: In most languages
stone circles are called "cromlechs" (a word in the
Welsh language); the word "
cromlech" is sometimes used with that meaning in English.
;Dolmen: A
Dolmen
A dolmen () or portal tomb is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more upright megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the early Neolithic (40003000 BCE) and were somet ...
is the building is a stone table, consisting of a wide stone supported by several other stones
;Cist: A
Cist is a small stone-built coffin-like box or
ossuary used to hold the
bodies of the dead. Burials are megalithic forms very similar to dolmens in structure. These type of burials were completely underground.
Timeline
Mesolithic
* 7400 BC: A 12 m long
monolith probably weighing around 15,000 kg found submerged 40 m under water in the
Strait of Sicily
The Strait of Sicily (also known as Sicilian Strait, Sicilian Channel, Channel of Sicily, Sicilian Narrows and Pantelleria Channel; it, Canale di Sicilia or the Stretto di Sicilia; scn, Canali di Sicilia or Strittu di Sicilia, ar, مضيق ص ...
south-west of
Sicily. Its origin and purpose are unknown.
Neolithic

* 9000 BC: Constructions in Asia Minor (
Göbekli Tepe,
Nevalı Çori and other sites); perhaps proto-
Hattian, a yet to be named culture (the oldest discovered ceremonial structures in the world).
* 7000 BC: Construction in
proto-Canaanite Israel (
Atlit Yam).
* 6000 BC: Constructions in Portugal (
Almendres Cromlech,
Évora) - Possibly first standing stones in Portugal.
* 5000 BC: Emergence of the Atlantic
Neolithic period, the age of agriculture along the western shores of Europe during the sixth millennium BC pottery culture of
La Almagra, Spain nearby, perhaps precedent from Africa.
* 4800 BC: Constructions in
Brittany,
France (
Barnenez
The Cairn of Barnenez (also: Barnenez Tumulus, Barnenez Mound; in Breton ''Karn Barnenez''; in French: ''Cairn de Barnenez'' or ''Tumulus de Barnenez'') is a Neolithic monument located near Plouezoc'h, on the Kernéléhen peninsula in northern ...
) and
Poitou (
Bougon
Bougon () is a commune in the Deux-Sèvres department in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region in western France.
See also
*Communes of the Deux-Sèvres department
The following is a list of the 256 communes of the Deux-Sèvres department of France. ...
).
* 4500 BC: Constructions in south
Egypt (
Nabta Playa).
* 4300 BC: Constructions in south
Spain (
Dolmen de Alberite
A dolmen () or portal tomb is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more upright megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the early Neolithic (40003000 BCE) and were somet ...
,
Cádiz).
* 4000 BC: Constructions in Brittany (
Carnac
Carnac (; br, italic=no, Karnag, ) is a commune beside the Gulf of Morbihan on the south coast of Brittany in the Morbihan department in north-western France.
Its inhabitants are called ''Carnacois'' in French. Carnac is renowned for the C ...
), Portugal (
Great Dolmen of Zambujeiro, Évora), France (central and southern),
Corsica
Corsica ( , Upper , Southern ; it, Corsica; ; french: Corse ; lij, Còrsega; sc, Còssiga) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of ...
, Spain (
Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
), England and
Wales, Constructions in Andalusia, Spain (
Villa Martín, Cádiz), Construction in
proto-Canaanite Israel c. 4000~3000 BC: Constructions in the rest of the proto-Canaanite
Levant, e.g.
Rujm el-Hiri
Rujm el-Hiri ( ar, رجم الهري, ''Rujm al-Hīrī''; he, גִּלְגַּל רְפָאִים ''Gilgal Refā'īm'' or ''Rogem Hiri'') is an ancient megalithic monument consisting of concentric circles of stone with a tumulus at center. It is ...
and
dolmens.
* 3700 BC: Constructions in Ireland (
Knockiveagh and elsewhere).
* 3600 BC: Constructions in
Malta (
Skorba
The Skorba temples are megalithic remains on the northern edge of Żebbiegħ, in Malta, which have provided detailed and informative insight into the earliest periods of Malta's neolithic culture. The site was only excavated in the early 1960s, ...
temples).

* 3600 BC: Constructions in England (
Maumbury Rings and
Godmanchester), and
Malta (
Ġgantija and
Mnajdra temples).
* 3500 BC: Constructions in Spain (
Málaga
Málaga (, ) is a municipality of Spain, capital of the Province of Málaga, in the autonomous community of Andalusia. With a population of 578,460 in 2020, it is the second-most populous city in Andalusia after Seville and the sixth most pop ...
and
Guadiana
The Guadiana River (, also , , ), or Odiana, is an international river defining a long stretch of the Portugal-Spain border, separating Extremadura and Andalusia (Spain) from Alentejo and Algarve (Portugal). The river's basin extends from the e ...
), Ireland (south-west), France (
Arles and the north), Malta (and elsewhere in the Mediterranean), Belgium (north-east), and Germany (central and south-west).
* 3400 BC: Constructions in Sardinia (circular graves), Ireland (
Newgrange), Netherlands (north-east), Germany (northern and central) Sweden and Denmark.
* 3300 BC: Constructions in France (
Carnac stones)
* 3200 BC: Constructions in Malta (
Ħaġar Qim and
Tarxien
Tarxien ( mt, Ħal Tarxien) is a town in the South Eastern Region of Malta. Its population stood at 8583 in March 2014.
The town is most notable for the Tarxien Temples, a megalithic temple complex which is among the oldest freestanding structur ...
).
* 3100 BC: Constructions in Russia (
Dolmens of North Caucasus
Concentrations of megaliths, dolmens ( ady, исп-унэ) and stone labyrinths dating between the end of the 4th millennium and the beginning of the 2nd millennium B.C. have been found (but little studied) throughout the Caucasus Mountains, inc ...
)
* 3000 BC: Constructions in Sardinia (earliest construction phase of the prehistoric altar of
Monte d'Accoddi), France (
Saumur
Saumur () is a commune in the Maine-et-Loire department in western France.
The town is located between the Loire and Thouet rivers, and is surrounded by the vineyards of Saumur itself, Chinon, Bourgueil, Coteaux du Layon, etc.. Saumur statio ...
,
Dordogne,
Languedoc,
Biscay, and the Mediterranean coast), Spain (
Los Millares), Sicily, Belgium (
Ardennes
The Ardennes (french: Ardenne ; nl, Ardennen ; german: Ardennen; wa, Årdene ; lb, Ardennen ), also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in Be ...
), and
Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north ...
, as well as the first
henges (circular earthworks) in Britain.
Chalcolithic
* 2500 BC: Constructions in Brittany (
Le Menec,
Kermario and elsewhere), Italy (
Otranto), Sardinia, and
Scotland (northeast), plus the climax of the megalithic
Bell-beaker culture
The Bell Beaker culture, also known as the Bell Beaker complex or Bell Beaker phenomenon, is an archaeological culture named after the inverted-bell beaker drinking vessel used at the very beginning of the European Bronze Age. Arising from ar ...
in
Iberia, Germany, and the
British Isles (stone circle at
Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connectin ...
). With the bell-beakers, the Neolithic period gave way to the
Chalcolithic, the age of copper.
* 2500 BC: Tombs at
Algarve,
Portugal. Additionally, a problematic dating (by
optically stimulated luminescence) of Quinta da Queimada Menhir in western Algarve indicates "a very early period of megalithic activity in the Algarve, older than in the rest of Europe and in parallel, to some extent, with the famous Anatolian site of Göbekli Tepe"
* c. 2400 BC: The Bell-beaker culture was dominant in Britain, and hundreds of smaller
stone circles were built in the British Isles at this time.
Stone Age
* 2100 BC:The highest plateau Lampung, West Lampung Regency, Batu Brak Liwa, Indonesia Megalith Site.
Bronze Age
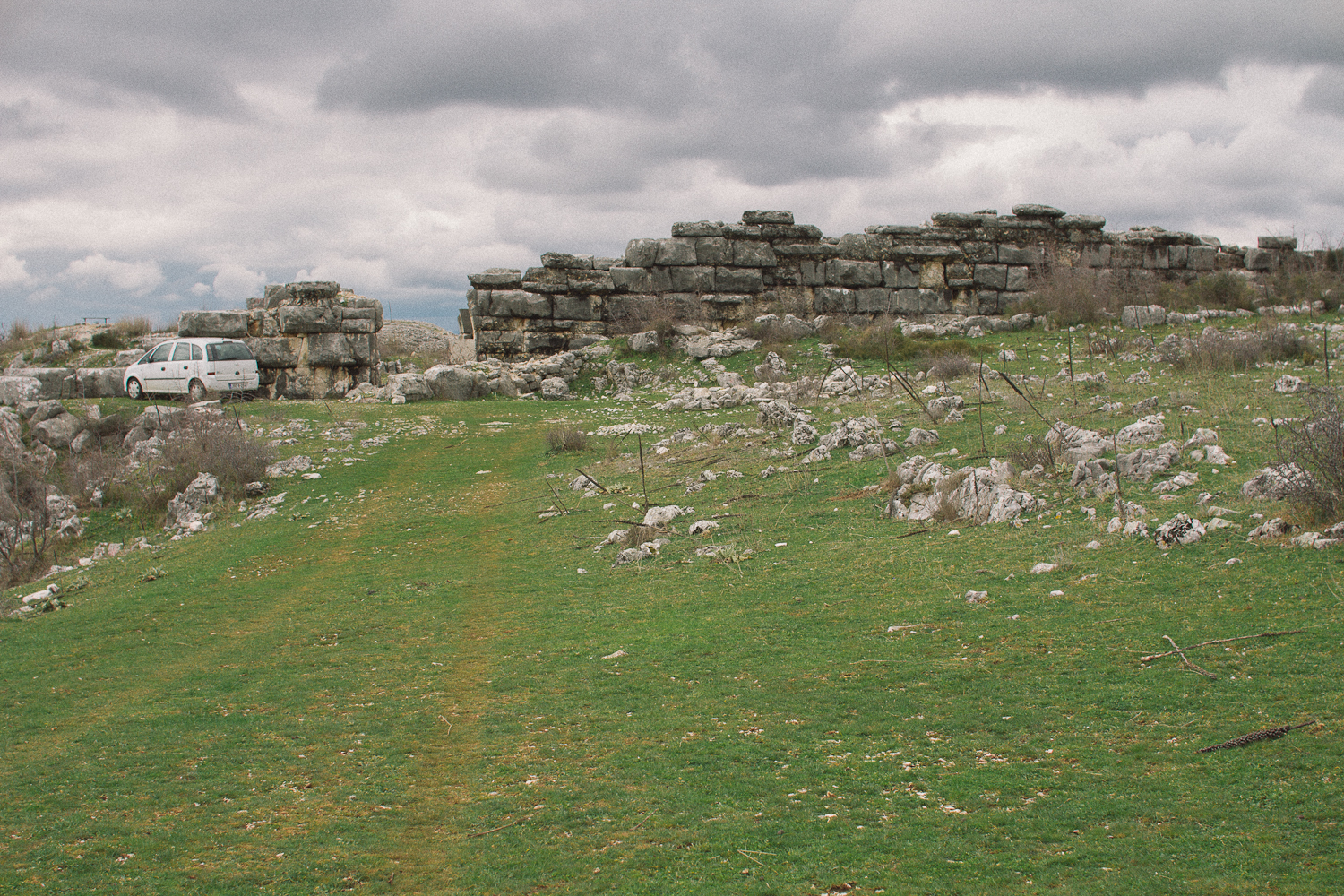

* 2000 BC: Constructions in Brittany (
Er Grah), Italy : (
Bari
Bari ( , ; nap, label= Barese, Bare ; lat, Barium) is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Bari and of the Apulia region, on the Adriatic Sea, southern Italy. It is the second most important economic centre of mainland Southern Italy a ...
); Sicily (
Cava dei Servi, Cava Lazzaro
Cava may refer to:
People Sports
* José Luis Cabrera Cava (born 1982), a Spanish retired footballer
* Michela Cava, a Canadian-born women's ice hockey player
* Nicholas la Cava (born 1986), an American rower
* Tony LaCava (1961), an American ...
);, and Scotland (
Callanish
Callanish ( gd, Calanais) is a village (township) on the west side of the Isle of Lewis, in the Outer Hebrides (Western Isles), Scotland. Callanish is within the parish of Uig. A linear settlement with a jetty, it is on a headland jutting into ...
). The Chalcolithic period gave way to the
Bronze Age in western and northern Europe.
* 1800 BC: Constructions in Italy (
Giovinazzo, in Sardinia started the
nuragic civilisation
The Nuragic civilization, also known as the Nuragic culture, was a civilization or culture on Sardinia (Italy), the second largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, which lasted from the 18th century BC (Middle Bronze Age) (or from t ...
).
* 1500 BC: Constructions in Portugal (
Alter Pedroso and
Mourela).
* 1400 BC: Burial of the
Egtved Girl in Denmark, whose body is today one of the best-preserved examples of its kind.
* 1200 BC: Last vestiges of the megalithic tradition in the Mediterranean and elsewhere come to an end during the general population upheaval known to ancient history as the
Invasions of the Sea Peoples. Megalithic construction persisted in
Egypt into the Iron Age.
Geographic distribution of megaliths
Megalithic sites in Turkey

Göbekli Tepe
At a number of sites in southeastern Turkey, ceremonial complexes with large T-shaped megalithic
orthostats, dating from the
Pre-Pottery Neolithic (PPN, 9600–7000 cal BC), have been discovered.
At the most famous of these sites,
Göbekli Tepe, parts of the oldest level (III) have been
C14-dated as far back as to the mid-10th millennium BC (cal). On this level, 20 great stone circles (up to 20 meters in diameter) with standing stones up to 7 meters high have been identified. At least 5 of these circles have so far (as of 2019) been excavated. Many of the standing stones are richly ornamented with carved reliefs of "
ars, boars, snakes, foxes, wildcats, aurochs, gazelle, quadruped reptiles, birds, spiders, insects, quadrupeds, scorpions" and other animals; in addition, some of the stones are carved in low profile with stylized human features (arms, hands, loincloths, but ''no heads'').
On the younger level (II) rectangular structures with smaller megaliths have been excavated. In the surrounding area, several village sites incorporating elements similar to those of Göbekli Tepe have been identified. Four of these have Göbekli Tepe's characteristic T-shaped standing stones, though only one of them,
Nevalı Çori, has so far been excavated. At Göbekli Tepe itself, no traces of habitation have so far been found, nor any trace of agriculture or cultivated plants, though bones of wild animals and traces of wild edible plants, along with many grinding stones, have been unearthed. It is thus assumed that these structures (which have been characterized as the first known ceremonial architecture)
were erected by
hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fungi, ...
s.
Göbekli Tepe's oldest structures are about 7,000 years older than the
Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connectin ...
megaliths, although it is doubtful that any of the European megalithic traditions (
see below) are derived from them.
Middle Eastern megaliths
 Dolmens
Dolmens and
standing stones
A menhir (from Brittonic languages: ''maen'' or ''men'', "stone" and ''hir'' or ''hîr'', "long"), standing stone, orthostat, or lith is a large human-made upright stone, typically dating from the European middle Bronze Age. They can be foun ...
have been found in large areas of the Middle East starting at the
Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
border in the north of
Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
close to
Aleppo
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
, southwards down to
Yemen. They can be encountered in
Lebanon, Syria,
Iran,
Israel,
Jordan, and
Saudi Arabia. The largest concentration can be found in southern Syria and along the
Jordan Rift Valley; these are threatened with destruction. They date from the late Chalcolithic or Early Bronze Age. Megaliths have also been found on
Kharg Island
Kharg or Khark Island ( fa, جزیره خارک) is a continental island in the Persian Gulf belonging to Iran. The island is located off the coast of Iran and northwest of the Strait of Hormuz. Its total area is . Administered by the adjacent ...
and
Pirazmian in
Iran, at
Barda Balka
Barda Balka is an archeological site near the Little Zab and Chamchamal in the north of modern-day Iraq.
The site was discovered on a hilltop in 1949 by Sayid Fuad Safar and Naji al-Asil from the Directorate General of Antiquities, Iraq. It was la ...
in
Iraq.

A semicircular arrangement of megaliths was found in Israel at
Atlit Yam, a site that is now under the sea. It is a very early example, dating from the
7th millennium BC.
The most concentrated occurrence of dolmens in particular is in a large area on both sides of the
Jordan Rift Valley, with greater predominance on the eastern side. They occur first and foremost on the
Golan Heights, the
Hauran
The Hauran ( ar, حَوْرَان, ''Ḥawrān''; also spelled ''Hawran'' or ''Houran'') is a region that spans parts of southern Syria and northern Jordan. It is bound in the north by the Ghouta oasis, eastwards by the al-Safa (Syria), al-Safa ...
, and in Jordan, which probably has the largest concentration of dolmen in the Middle East. In Saudi Arabia, only very few dolmen have been identified so far in the
Hejaz
The Hejaz (, also ; ar, ٱلْحِجَاز, al-Ḥijāz, lit=the Barrier, ) is a region in the west of Saudi Arabia. It includes the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif, and Baljurashi. It is also known as the "Western Provin ...
. They seem, however, to re-emerge in Yemen in small numbers, and thus could indicate a continuous tradition related to those of
Somalia and
Ethiopia.

The standing stone has a very ancient tradition in the Middle East, dating back from
Mesopotamian times. Although not always 'megalithic' in the true sense, they occur throughout the area and can reach 5 metres or more in some cases (such as at
Ader
The Ader was a French automobile designed and built by Clément Ader, a pioneer in flight and telephone service.
The Ader car was built in Levallois-Perret, Seine, by his Société Industrielle des Téléphones-Voitures Système Ader
between 19 ...
in Jordan). This phenomenon can also be traced through many passages from the
Old Testament
The Old Testament (often abbreviated OT) is the first division of the Christian biblical canon, which is based primarily upon the 24 books of the Hebrew Bible or Tanakh, a collection of ancient religious Hebrew writings by the Israelites. The ...
, such as those related to
Jacob, the grandson of
Abraham, who poured oil over a stone that he erected after his famous dream in which angels climbed to heaven (Genesis 28:10-22). Jacob is also described as putting up stones at other occasions, whereas
Moses
Moses hbo, מֹשֶׁה, Mōše; also known as Moshe or Moshe Rabbeinu (Mishnaic Hebrew: מֹשֶׁה רַבֵּינוּ, ); syr, ܡܘܫܐ, Mūše; ar, موسى, Mūsā; grc, Mωϋσῆς, Mōÿsēs () is considered the most important pro ...
erected twelve pillars symbolizing the tribes of Israel. The tradition of venerating standing stones continued in
Nabatean times.
Related phenomena, such as cupholes, rock-cut tombs and circles, also occur in the Middle East.
European megaliths

The most common type of megalithic construction in Europe is the
portal tomb—a chamber consisting of upright stones (
orthostats) with one or more large flat capstones forming a roof. Many portal tombs have been found to contain human remains, but it is debated if their primary function was use as burial sites. The megalithic structures in the northwest of France are believed to be the oldest in Europe based on radiocarbon dating. Though generally known as "dolmens", the term most accepted by archaeologists is "portal tomb". Local names for portal tombs exist in multiple locations, such as ''anta'' in
Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
and Portugal, ''stazzone'' in
Sardinia, ''hunebed'' in the Netherlands, ''Hünengrab'' in Germany, ''dysse'' in Denmark, and ''cromlech'' in
Wales. It is assumed that most portal tombs were originally covered by earthen mounds.
The second-most-common tomb type is the
passage grave. It normally consists of a square, circular, or cruciform chamber with a slabbed or
corbelled
In architecture, a corbel is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal jutting from a wall to carry a superincumbent weight, a type of bracket. A corbel is a solid piece of material in the wall, whereas a console is a piece applied to the st ...
roof, accessed by a long, straight passageway, with the whole structure covered by a circular mound of earth. Sometimes it is also surrounded by an external stone kerb. Prominent examples include the sites of
Brú na Bóinne and
Carrowmore in Ireland,
Maes Howe
Maeshowe (or Maes Howe; non, Orkhaugr) is a Neolithic chambered cairn and passage grave situated on Mainland Orkney, Scotland. It was probably built around . In the archaeology of Scotland, it gives its name to the Maeshowe type of chambered c ...
in
Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north ...
, and
Gavrinis
Gavrinis ( br, Gavriniz) is a small island in the Gulf of Morbihan in Brittany, France. It contains the Gavrinis tomb, a megalithic monument notable for its abundance of megalithic art in the European Neolithic. Administratively, it is part of ...
in France.

The third tomb type is a diverse group known as
gallery graves. These are axially arranged chambers placed under elongated mounds. The Irish
court tomb
The court cairn or court tomb is a megalithic type of chambered cairn or gallery grave. During the period, 3900–3500 BCE, more than 390 court cairns were built in Ireland and over 100 in southwest Scotland. The Neolithic (New Stone Age ...
s, British
long barrows, and German ''Steinkisten'' belong to this group.
Standing stones, or
menhirs
A menhir (from Brittonic languages: ''maen'' or ''men'', "stone" and ''hir'' or ''hîr'', "long"), standing stone, orthostat, or lith is a large human-made upright stone, typically dating from the European middle Bronze Age. They can be foun ...
as they are known in France, are very common throughout Europe, where some 50,000 examples have been noted. Some of these are thought to have an astronomical function as a marker or foresight. In some areas, long and complex "alignments" of such stones exist, the largest known example being located at
Carnac
Carnac (; br, italic=no, Karnag, ) is a commune beside the Gulf of Morbihan on the south coast of Brittany in the Morbihan department in north-western France.
Its inhabitants are called ''Carnacois'' in French. Carnac is renowned for the C ...
in
Brittany, France.
In parts of Britain and Ireland a relatively common type of megalithic construction is the
stone circle
A stone circle is a ring of standing stones. Most are found in Northwestern Europe – especially in Britain, Ireland, and Brittany – and typically date from the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, with most being built from 3000 BC. The be ...
, of which examples include
Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connectin ...
,
Avebury,
Ring of Brodgar
The Ring of Brodgar (or Brogar, or Ring o' Brodgar) is a Neolithic henge and stone circle about 6 miles north-east of Stromness on Mainland, the largest island in Orkney, Scotland. It is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site known as the Heart ...
and
Beltany. These, too, display evidence of astronomical alignments, both solar and lunar. Stonehenge, for example, is famous for its
solstice alignment. Examples of stone circles are also found in the rest of Europe. The circle at
Lough Gur, near Limerick in Ireland has been dated to the Beaker period, approximately contemporaneous with Stonehenge. The stone circles are assumed to be of later date than the tombs, straddling the
Neolithic and the
Bronze Ages.

Tombs

Megalithic tombs are aboveground burial chambers, built of large stone slabs (megaliths) laid on edge and covered with earth or other, smaller stones. They are a type of
chamber tomb, and the term is used to describe the structures built across
Atlantic Europe
Atlantic Europe is a geographical term for the western portion of Europe which borders the Atlantic Ocean. The term may refer to the idea of Atlantic Europe as a cultural unit and/or as a biogeographical region.
It comprises the Atlantic Isles ...
, the Mediterranean, and neighbouring regions, mostly during the
Neolithic period, by Neolithic farming communities. They differ from the contemporary
long barrows through their structural use of stone.
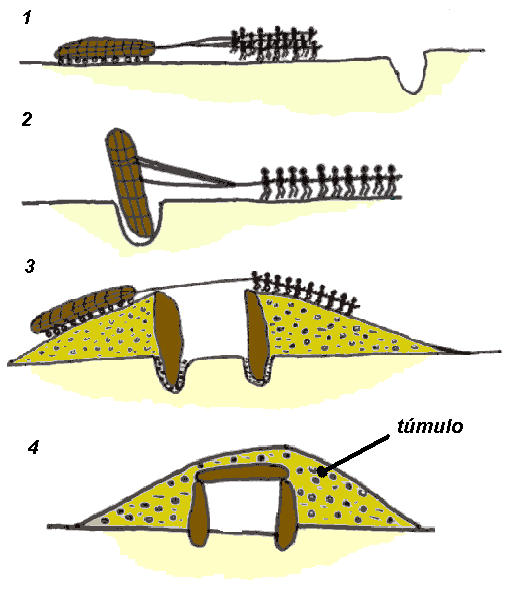
There is a huge variety of megalithic tombs. The free-standing single chamber
dolmen
A dolmen () or portal tomb is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more upright megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the early Neolithic (40003000 BCE) and were somet ...
s and
portal dolmen
A dolmen () or portal tomb is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more upright megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the early Neolithic (40003000 BCE) and were somet ...
s found in
Brittany, Denmark, Germany, Ireland, Netherlands, Sweden,
Wales, and elsewhere consist of a large flat stone supported by three, four, or more standing stones. They were covered by a stone
cairn
A cairn is a man-made pile (or stack) of stones raised for a purpose, usually as a marker or as a burial mound. The word ''cairn'' comes from the gd, càrn (plural ).
Cairns have been and are used for a broad variety of purposes. In prehis ...
or earth
barrow
Barrow may refer to:
Places
England
* Barrow-in-Furness, Cumbria
** Borough of Barrow-in-Furness, local authority encompassing the wider area
** Barrow and Furness (UK Parliament constituency)
* Barrow, Cheshire
* Barrow, Gloucestershire
* Barro ...
.
In Italy, dolmens can be found especially in
Sardinia. There are more than 100 dolmen dating to the Neolithic (3500–2700 BC) and the most famous is called ''Dolmen di Sa Coveccada'' (near
Mores). During the
Bronze Age, the
Nuragic civilization built c. 800
Giants' grave, a type of megalithic
gallery grave that can be found throughout
Sardinia with different structures. The earliest megalithic tombs in Sardinia are the circular graves of the so-called
Arzachena culture
The Arzachena culture was a pre-Nuragic culture of the Late Neolithic Age occupying Gallura (the northeastern part of Sardinia) and part of southern Corsica from approximately the 4th to the 3rd millennium BC. It takes its name from the Sardin ...
, also found in
Corsica
Corsica ( , Upper , Southern ; it, Corsica; ; french: Corse ; lij, Còrsega; sc, Còssiga) is an island in the Mediterranean Sea and one of the 18 regions of France. It is the fourth-largest island in the Mediterranean and lies southeast of ...
,
southern France
Southern France, also known as the South of France or colloquially in French language, French as , is a defined geographical area consisting of the regions of France that border the Atlantic Ocean south of the Marais Poitevin,Louis Papy, ''Le midi ...
and eastern Spain.

Dolmens are also in Apulia and in Sicily. In this latter region, they are small structures located in Mura Pregne (
Palermo
Palermo ( , ; scn, Palermu , locally also or ) is a city in southern Italy, the capital (political), capital of both the autonomous area, autonomous region of Sicily and the Metropolitan City of Palermo, the city's surrounding metropolitan ...
), Sciacca (
Agrigento), Monte Bubbonia (
Caltanissetta), Butera (Caltanissetta), Cava Lazzaro (
Siracusa), Cava dei Servi (
Ragusa Ragusa is the historical name of Dubrovnik. It may also refer to:
Places Croatia
* the Republic of Ragusa (or Republic of Dubrovnik), the maritime city-state of Ragusa
* Cavtat (historically ' in Italian), a town in Dubrovnik-Neretva County, Cro ...
), Avola (Siracusa), and
Argimusco
One of the "megaliths" in the Argimusco plateau.
The Argimusco is a high plateau situated just north of Mount Etna in Sicily, southern Italy, between the Nebrodi and Peloritani Mountains. It lies within the boundaries of the communes of Montalb ...
in
Montalbano Elicona
Montalbano Elicona ( Sicilian: ''Muntarbanu'') is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Metropolitan City of Messina in the Italian region Sicily, located about east of Palermo and about southwest of Messina on the Nebrodi mountains at the bord ...
(
Messina
Messina (, also , ) is a harbour city and the capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of more than 219,000 inhabitants in ...
). Dating to the Early Bronze Age (2200–1800 BC), the prehistoric Sicilian buildings were covered by a circular mound of earth. In the dolmen of Cava dei Servi, archaeologists found numerous human bone fragments and some splinters of Castelluccian ceramics (Early Bronze Age) which confirmed the burial purpose of the artefact.

Examples with outer areas, not used for burial, are also known. The
Court Cairns of southwest
Scotland and northern Ireland, the
Severn-Cotswold tombs of southwest England and the
transepted gallery grave
A gallery grave is a form of megalithic tomb built primarily during the Neolithic, Neolithic Age in Europe in which the main Long gallery, gallery of the tomb is entered without first passing through an antechamber or hallway. There are at least f ...
s of the
Loire region in France share many internal features, although the links between them are not yet fully understood. That they often have antechambers or forecourts is thought to imply a desire on the part of the builders to emphasize a special
ritual or physical separation of the dead from the living.

Megalithic tombs appear to have been used by communities for the long-term deposition of the remains of their dead, and some seem to have undergone alteration and enlargement. The organization and effort required to erect these large stones suggest that the societies concerned placed great emphasis on the proper treatment of their dead. The
ritual significance of the tombs is supported by the presence of
pre-historic art carved into the stones at some sites. Hearths and deposits of pottery and animal bone found by archaeologists around some tombs also implies that some form of burial feast or sacrificial rites took place there.
Further examples of megalithic tombs include the stalled cairn at
Midhowe in Orkney and the passage grave at
Bryn Celli Ddu on
Anglesey. There are also extensive grave sites with up to 60 megaliths at
Louisenlund and
Gryet
Gryet, some west of Nexø and just north of Bodilsker on the Danish island of Bornholm, is a site with one of Denmark's largest collections of megaliths with tall upright stones standing among the trees in a little wood.
The site
Gryet is on ...
on the Danish island of
Bornholm
Bornholm () is a Danish island in the Baltic Sea, to the east of the rest of Denmark, south of Sweden, northeast of Germany and north of Poland.
Strategically located, Bornholm has been fought over for centuries. It has usually been ruled by ...
.
Despite its name, the
Stone Tomb
Kamyana Mohyla ( uk, Кам'яна Могила; literally: "stone grave") is an archaeological site in the Molochna River (literally: "Milk river") valley, about a mile from the village of Terpinnia, Zaporizhzhia Oblast, Ukraine. Petroglyphs ...
in
Ukraine was not a tomb but rather a sanctuary.
Other structures

In association with the megalithic constructions across Europe, there are often large
earthworks
Earthworks may refer to:
Construction
*Earthworks (archaeology), human-made constructions that modify the land contour
* Earthworks (engineering), civil engineering works created by moving or processing quantities of soil
*Earthworks (military), m ...
of various designs—ditches and banks (like the
Dorset Cursus), broad terraces, circular enclosures known as
henges, and frequently artificial mounds such as
Silbury Hill in England and
Monte d'Accoddi in
Sardinia (the prehistoric step pyramid).
Spread of megalithic architecture in Europe
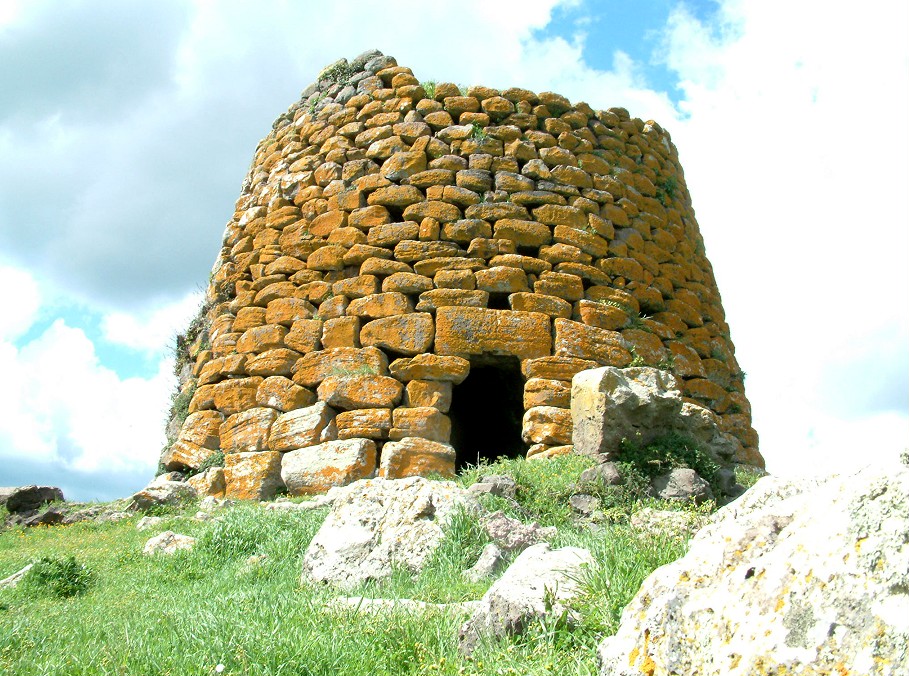

In Europe megaliths are, in general, constructions erected during the
Neolithic or late Stone Age and
Chalcolithic or Copper Age (4500–1500 BC). The megalithic structures of
Malta are believed to be the oldest in Europe. Perhaps the most famous megalithic structure is
Stonehenge
Stonehenge is a prehistoric monument on Salisbury Plain in Wiltshire, England, west of Amesbury. It consists of an outer ring of vertical sarsen standing stones, each around high, wide, and weighing around 25 tons, topped by connectin ...
in England.
In Sardinia, in addition to dolmens, menhirs and circular graves there are also more than 8000 megalithic structure made by a Nuragic civilisation, called
Nuraghe: buildings similar to towers (sometimes with really complex structures) made using only rocks. They are often near
giant's grave or the other megalithic monuments.

The French
Comte de Caylus
Anne Claude de Tubières-Grimoard de Pestels de Lévis, ''comte de Caylus'', marquis d'Esternay, baron de Bransac (Anne Claude Philippe; 31 October, 16925 September 1765), was a French antiquarian, proto-archaeologist and man of letters.
Born in ...
was the first to describe the
Carnac stones.
Pierre Jean-Baptiste Legrand d'Aussy Pierre Jean-Baptiste Legrand d'Aussy (3 June 1737 - 6 December 1800) was a French antiquarian and historian, who introduced the terms ''menhir'' and '' dolmen'', both taken from the Breton language, into antiquarian terminology. He interpreted me ...
introduced the terms ''
menhir'' and ''
dolmen
A dolmen () or portal tomb is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more upright megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the early Neolithic (40003000 BCE) and were somet ...
'', both taken from the
Breton language
Breton (, ; or in Morbihan) is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family spoken in Brittany, part of modern-day France. It is the only Celtic language still widely in use on the European mainland, albeit as a member of t ...
, into antiquarian terminology. He mistakenly interpreted megaliths as Gallic tombs. In Britain, the
antiquarian
An antiquarian or antiquary () is an fan (person), aficionado or student of antiquities or things of the past. More specifically, the term is used for those who study history with particular attention to ancient artifact (archaeology), artifac ...
s
Aubrey
Aubrey is traditionally a male English given name. The name is from the French derivation Aubry of the Germanic given name Alberic / Old High German given name Alberich, which consists of the elements ALF "elf" and RIK "king", from Proto-Germani ...
and
Stukeley conducted early research into megaliths. In 1805,
Jacques Cambry published a book called ''Monuments celtiques, ou recherches sur le culte des Pierres, précédées d'une notice sur les Celtes et sur les Druides, et suivies d'Etymologie celtiques'', where he proposed a
Celt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
ic stone cult. This unproven connection between
druids and megaliths has haunted the public imagination ever since. In Belgium, there are the
Wéris megaliths
The Wéris megaliths are a group of megalithic monuments found near the village of Wéris, in the Luxembourg (Belgium), province of Luxembourg, in Belgium.
Description
The megalithic remains at Wéris are scattered over region more than long, and ...
at Wéris, a little town situated in the
Ardennes
The Ardennes (french: Ardenne ; nl, Ardennen ; german: Ardennen; wa, Årdene ; lb, Ardennen ), also known as the Ardennes Forest or Forest of Ardennes, is a region of extensive forests, rough terrain, rolling hills and ridges primarily in Be ...
. In the Netherlands, megalithic structures can be found in the northeast of the country, mostly in the province of
Drenthe
Drenthe () is a province of the Netherlands located in the northeastern part of the country. It is bordered by Overijssel to the south, Friesland to the west, Groningen to the north, and the German state of Lower Saxony to the east. As of Nov ...
.
Knowth
Knowth (; ga, Cnóbha) is a Neolithic passage grave and an ancient monument of the World Heritage Site of Brú na Bóinne located 8.4 km west of Drogheda in Ireland's valley of the River Boyne. It is the largest passage grave of the Brú ...
is a
passage grave of the
Brú na Bóinne neolithic complex in Ireland, dating from c. 3500–3000 BC. It contains more than a third of the total number of examples of
megalithic art
Megalithic art refers to art either painted or carved onto megaliths in prehistoric Europe.
Elizabeth Shee Twohig has coined the term Megalithic art in her study of The Megalithic Art of Western Europe. Her original definition of Megalithic a ...
in all Europe, with over 200 decorated stones found during excavations.
African megaliths
North Africa
Nabta Playa at the southwest corner of the western Egyptian desert was once a large lake in the
Nubian Desert, located 500 miles south of modern-day
Cairo. By the 5th millennium BC, the peoples in
Nabta Playa had fashioned an astronomical device that accurately marks the summer
solstice. Findings indicate that the region was occupied only seasonally, likely only in the summer when the local lake filled with water for grazing
cattle. There are other megalithic stone circles in the southwestern desert.
At
Nabta Playa, located in
Egypt and broader region of the Eastern
Sahara
, photo = Sahara real color.jpg
, photo_caption = The Sahara taken by Apollo 17 astronauts, 1972
, map =
, map_image =
, location =
, country =
, country1 =
, ...
, there is a megalithic cultural complex (e.g.,
sacrificed cow burial site,
solar calendar
A solar calendar is a calendar whose dates indicate the season or almost equivalently the apparent position of the Sun relative to the stars. The Gregorian calendar, widely accepted as a standard in the world, is an example of a solar calendar.
T ...
,
altar) that dates between 4000 BCE and 2000 BCE.
Likely part of Copper Age and Bronze Age
cultural traditions of megalith-building, megaliths (e.g.,
dolmens) were constructed in
Mediterranean North Africa.
West Africa
In
Cross-River State, Nigeria, there are
megalithic monoliths of an anthropomorphic nature.
At
Tondidarou
Tondidarou is a small town and megalithic archaeological site in Niafunké Cercle, Timbuktu Region, Mali, northwest of Niafunké, about 150 kilometres south-west of Timbuktu. The site, located on the eastern bank of Lac Tagadji, was discovered by ...
, in the Malian Lakes Region, there are megaliths of an anthropomorphic nature (e.g., face, navel,
scarifications
Scarification involves scratching, etching, burning/branding, or superficially cutting designs, pictures, or words into the skin as a permanent body modification or body art. The body modification can take roughly 6–12 months to heal. In the p ...
) that date between 600 CE and 700 CE.
Between 1350 BCE and 1500/1600 CE,
Senegambian megaliths (e.g.,
tumuli) were constructed for the purpose of
ancestral reverence.
Central Africa
In the northwestern region of the
Central African Republic, there are
megaliths that were created for various purposes (e.g., burial, ritual performances).
Between late 3rd millennium BCE and mid-2nd millennium CE, megaliths (e.g., monuments, cairn burials) were constructed in the regions (e.g., Eastern
Adamawa,
Oubanguian
The Ubangi River (), also spelled Oubangui, is the largest right-bank tributary of the Congo River in the region of Central Africa. It begins at the confluence of the Mbomou (mean annual discharge 1,350 m3/s) and Uele Rivers (mean annual discharge ...
Ridge,
Chad/Congo watershed) in Central African Republic and Cameroon, throughout various periods (e.g., Balimbé: 2000 BCE – 1000 BCE; Early Gbabiri: 950 BCE – 200 BCE; Late Gbabiri: 200 BCE – 500 CE; Bouboun: 500 CE – 1600 CE), for various purposes (e.g., ritual practices, territorial marking).
Eastern Africa
In the
Ethiopian Highlands of
Harar, the earliest construction of megaliths occurred.
From this region and its megalith-building tradition (e.g., dolmens,
tumuli with burial chambers organized in cemeteries), the subsequent traditions in other areas of
Ethiopia likely developed.
In the late 1st millennium BCE, the urban civilization of
Axum
Axum, or Aksum (pronounced: ), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia with a population of 66,900 residents (as of 2015).
It is the site of the historic capital of the Aksumite Empire, a naval and trading power that ruled the whole region ...
developed a megalithic
stelae-building tradition, which commemorated Axumite royalty and elites, that persisted until the
Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
period of
Axum
Axum, or Aksum (pronounced: ), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia with a population of 66,900 residents (as of 2015).
It is the site of the historic capital of the Aksumite Empire, a naval and trading power that ruled the whole region ...
.
In the Sidamo Province, the megalithic monoliths of the stelae-building cultural tradition were utilized as tombstones in cemeteries (e.g., Arussi, Konso, Sedene, Tiya, Tuto Felo), and have engraved anthropomorphic features (e.g., swords, masks), phallic form, and some of that served as markers of territory.
Sidamo Province has the most megaliths in Ethiopia.
In 2nd millennium BCE, Namoratunga (Monolith Circles) megaliths were constructed as burials the eastern
Turkana region of northwestern
Kenya.
Namoratunga
The Nasura Pillar Site, registered as GcJh3 and also known as Namoratunga II, is an Archaeology, archaeological site on the west side of Lake Turkana in Kenya dating to the Pastoral Neolithic. Namoratunga means "people of stone" in the Turkana ...
, a group of megaliths dated 300 BC, was used by
Cushitic-speaking people as an alignment with star systems tuned to a lunar calendar of 354 days. This site was excavated by B. N. Lynch and L. H. Robins of
Michigan State University
Michigan State University (Michigan State, MSU) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in East Lansing, Michigan. It was founded in 1855 as the Agricultural College of the State of Michigan, the fi ...
.
Additionally,
Tiya
Tiya is a town in central Ethiopia. It is situated in the Gurage Zone of the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples Region south of Addis Ababa. It is also the location of the Tiya archaeological site, famous for its unique stelae.
Demogra ...
in central
Ethiopia has a number of old megaliths. Some of these ancient structures feature engravings, and the area is a World Heritage Site. Megaliths are also found within the Valley of Marvels in the East Hararghe area.
Southern Africa
In the mid-2nd millennium CE, the megalithic funerary monuments of
Madagascar were constructed amid the
emergent period of the
Merina Kingdom.
Some of the megaliths remain utilized by
Malagasy-speakers for funerary practices (e.g., ceremony of turning the dead) in present-day.
Asian megaliths

Megalithic burials are found in Northeast and Southeast Asia. They are found mainly in the
Korean Peninsula. They are also found in the
Liaoning
Liaoning () is a coastal province in Northeast China that is the smallest, southernmost, and most populous province in the region. With its capital at Shenyang, it is located on the northern shore of the Yellow Sea, and is the northernmost ...
,
Shandong
Shandong ( , ; ; alternately romanized as Shantung) is a coastal province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the East China region.
Shandong has played a major role in Chinese history since the beginning of Chinese civilizati ...
, and
Zhejiang in China, the East Coast of
Taiwan,
Kyūshū
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surround ...
and
Shikoku in Japan,
Đồng Nai Province in
Vietnam and
South Asia. Some living megalithic traditions are found on the island of
Sumba
Sumba ( id, Pulau Sumba) is an island in eastern Indonesia. It is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands and is in the province of East Nusa Tenggara. Sumba has an area of , and the population was 779,049 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as a ...
and
Nias in
Indonesia. The greatest concentration of megalithic burials is in Korea. Archaeologists estimate that there are 15,000 to 100,000 southern megaliths in the Korean Peninsula. Typical estimates hover around the 30,000 mark for the entire peninsula, which in itself constitutes some 40% of all dolmens worldwide (see
Dolmen
A dolmen () or portal tomb is a type of single-chamber megalithic tomb, usually consisting of two or more upright megaliths supporting a large flat horizontal capstone or "table". Most date from the early Neolithic (40003000 BCE) and were somet ...
).
North East Asia
=Northern style
=
Northeast Asian megalithic traditions originated from
Gojoseon, which was in modern-day
Manchuria and
North Korea. This was prominent within the
Liao River
The Liao River () is the principal river in southern Northeast China, and one of the seven main river systems in China. Its name derived from the Liao region, a historical name for southern Manchuria, from which the Liaoning province, Liaodong P ...
basin in particular in the early phases. The practice of erecting megalithic burials spread quickly from the Liao River Basin and into the Korean Peninsula, where the structure of megaliths is geographically and chronologically distinct. The earliest megalithic burials are called "northern" or "table-style" because they feature an above-ground burial chamber formed by heavy stone slabs that form a rectangular cist. An oversized capstone is placed over the stone slab burial chamber, giving the appearance of a table-top. These megalithic burials date to the early part of the
Mumun pottery period (c. 1500–850 BC) and are distributed, with a few exceptions, north of the
Han River. Few northern-style megaliths in North Korea and Manchuria contain
grave goods such as
Liaoning bronze daggers, prompting some archaeologists to interpret the burials as the graves of chiefs or preeminent individuals. However, whether a result of grave-robbery or intentional mortuary behaviour, most northern megaliths contain no grave goods.
=Southern style
=

Southern-style megalithic burials are distributed in the southern
Korean Peninsula. It is thought that most of them date to the latter part of the Early
Mumun or to the Middle Mumun Period. Southern-style megaliths are typically smaller in scale than northern megaliths. The interment area of southern megaliths has an underground burial chamber made of earth or lined with thin stone slabs. A massive capstone is placed over the interment area and is supported by smaller propping stones. Most of the megalithic burials on the
Korean Peninsula are of the southern type.
As with northern megaliths, southern examples contain few, if any, artifacts. However, a small number of megalithic burials contain fine red-burnished pottery, bronze daggers, polished groundstone daggers, and greenstone ornaments. Southern megalithic burials are often found in groups, spread out in lines that are parallel with the direction of streams. Megalithic cemeteries contain burials that are linked together by low stone platforms made from large river cobbles. Broken red-burnished pottery and charred wood found on these platforms has led archaeologists to hypothesize that these platform were sometimes used for ceremonies and rituals. The capstones of many southern megaliths have 'cup-marks' carvings. A small number of capstones have human and dagger representations.
=Capstone style
=

These megaliths are distinguished from other types by the presence of a burial shaft, sometimes up to 4 m in depth, which is lined with large cobbles.
[Bale, Martin T.]
Excavations of Large-scale Megalithic Burials at Yulha-ri, Gimhae-si, Gyeongsang Nam-do
in ''Early Korea Project''. Korea Institute, Harvard University. Retrieved 10 October 2007 A large capstone is placed over the burial shaft without propping stones. Capstone-style megaliths are the most monumental type in the
Korean Peninsula, and they are primarily distributed near or on the south coast of Korea. It seems that most of these burials date to the latter part of the Middle Mumun (c. 700–550 BC), and they may have been built into the early part of the Late Mumun. An example is found near modern
Changwon
Changwon () is the capital city of Gyeongsangnam-do, on the southeast coast of South Korea. With a population of 1.07 million , Changwon is South Korea's ninth-most populous city.
A port city, Changwon is bordered by Masan Bay to the south ...
at Deokcheon-ni, where a small cemetery contained a capstone burial (No. 1) with a massive, rectangularly shaped, stone and earthen platform. Archaeologists were not able to recover the entire feature, but the low platform was at least 56×18 m in size.
Southeast Asia
=Living megalith culture of Indonesia
=

The
Indonesian archipelago is the host of
Austronesian
Austronesian may refer to:
*The Austronesian languages
*The historical Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, M ...
and
Melanesians megalith cultures both past and present. Living megalith cultures can be found on
Nias, an isolated island off the western coast of
North Sumatra
North Sumatra ( id, Sumatra Utara) is a province of Indonesia located on the northern part of the island of Sumatra. Its capital and largest city is Medan. North Sumatra is Indonesia's fourth most populous province after West Java, East Java and ...
, the
Batak
Batak is a collective term used to identify a number of closely related Austronesian ethnic groups predominantly found in North Sumatra, Indonesia, who speak Batak languages. The term is used to include the Karo, Pakpak, Simalungun, Toba, ...
people in the interior of North Sumatra, on
Sumba
Sumba ( id, Pulau Sumba) is an island in eastern Indonesia. It is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands and is in the province of East Nusa Tenggara. Sumba has an area of , and the population was 779,049 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as a ...
island in
East Nusa Tenggara and also
Toraja people from the interior of
South Sulawesi
South Sulawesi ( id, Sulawesi Selatan) is a province in the southern peninsula of Sulawesi. The Selayar Islands archipelago to the south of Sulawesi is also part of the province. The capital is Makassar. The province is bordered by Central Sula ...
. These megalith cultures remained preserved, isolated and undisturbed well into the late 19th century.
Several megalith sites and structures are also found across Indonesia. Menhirs, dolmens, stone tables, and ancestral stone statues were discovered in various sites in
Java,
Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
,
Sulawesi
Sulawesi (), also known as Celebes (), is an island in Indonesia. One of the four Greater Sunda Islands, and the world's eleventh-largest island, it is situated east of Borneo, west of the Maluku Islands, and south of Mindanao and the Sulu Ar ...
,
Lesser Sunda Islands
The Lesser Sunda Islands or nowadays known as Nusa Tenggara Islands ( id, Kepulauan Nusa Tenggara, formerly ) are an archipelago in Maritime Southeast Asia, north of Australia. Together with the Greater Sunda Islands to the west they make up t ...
, and
New Guinea.
The
Cipari megalith site also in West Java displays monoliths, stone terraces, and sarcophagi.
Lore Lindu National Park
Lore Lindu National Park is a protected area of forest on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi, in the province of Central Sulawesi. The Indonesian national park is 2,180 km2 covering both lowland and montane forests (200 to 2,610 meters abov ...
in
Central Sulawesi
Central Sulawesi (Indonesian: ''Sulawesi Tengah'') is a province of Indonesia located at the centre of the island of Sulawesi. The administrative capital and largest city is located in Palu. The 2010 census recorded a population of 2,635,009 for ...
houses ancient megalith relics such as ancestral stone statues, mostly located in the Bada, Besoa and Napu valleys.
South Asia

Megaliths in South Asia are dated before 3000 BC, with recent findings dated back to 5000 BC in southern India. Megaliths are found in almost all parts of South Asia. There is also a broad time evolution with the megaliths in central India and the upper Indus valley where the oldest megaliths are found, while those in the east are of much later date.
A large fraction of these are assumed to be associated with burial or post burial rituals, including memorials for those whose remains may or may not be available. The case-example is that of Brahmagiri, which was excavated by Wheeler (1975) and helped establish the culture sequence in south Indian prehistory. However, there is another distinct class of megaliths that do not seem to be associated with burials.
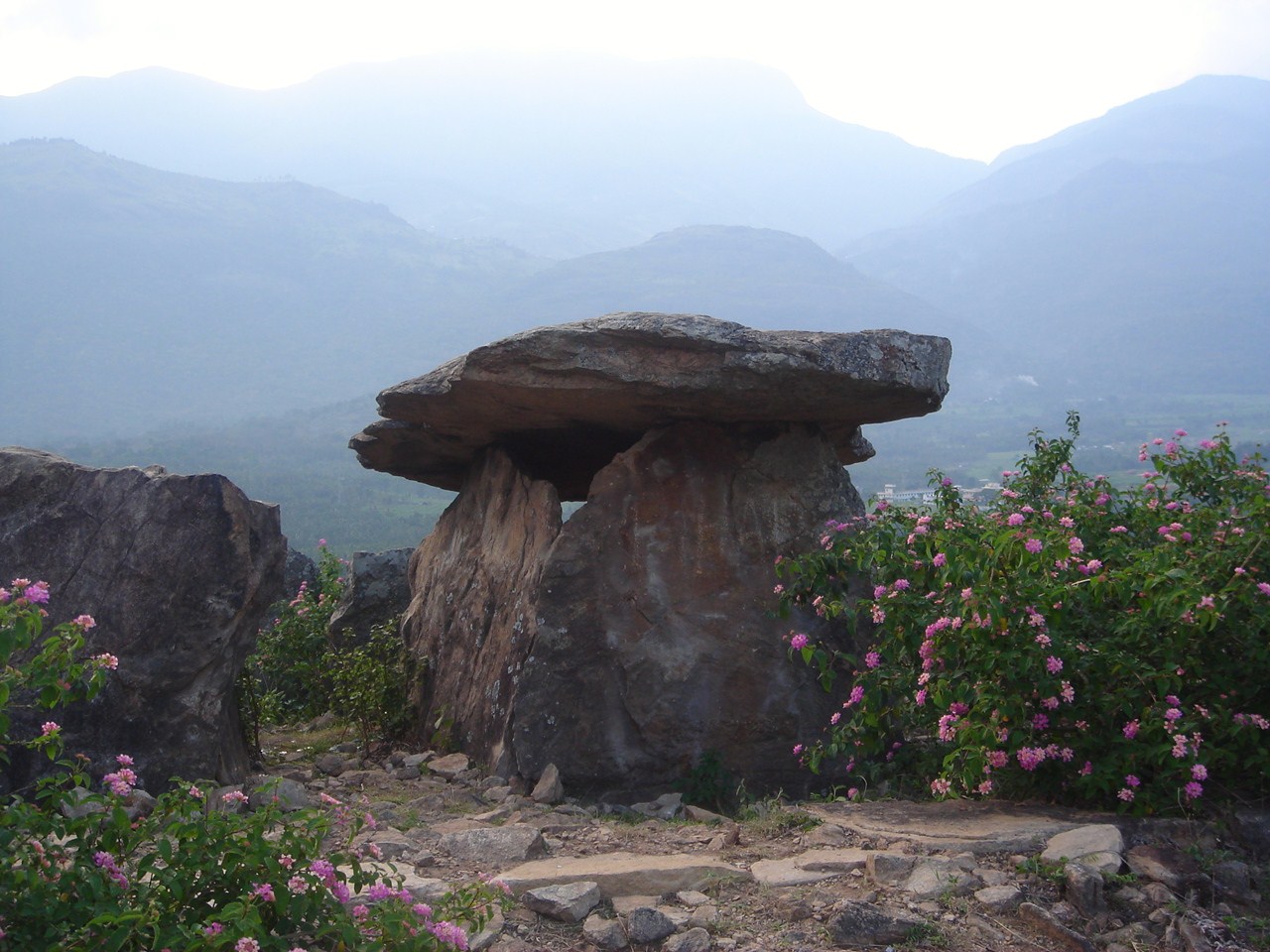

In South Asia, megaliths of all kinds are noted; these vary from
Menhirs
A menhir (from Brittonic languages: ''maen'' or ''men'', "stone" and ''hir'' or ''hîr'', "long"), standing stone, orthostat, or lith is a large human-made upright stone, typically dating from the European middle Bronze Age. They can be foun ...
,
Rock-cut burial, chamber tomb,
dolmens, stone alignment, stone circles and
anthropomorphic figures
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities. It is considered to be an innate tendency of human psychology.
Personification is the related attribution of human form and characteristics t ...
. These are broadly classified into two (potentially overlapping) classes (after Moorti, 1994, 2008): ''Sepulchral'' (containing remains of the dead), or memorial stones where mortal remains along with funerary objects are placed; and ''Non-sepulchral'' including large patterned placement of stones over a wide area. The 'non-sepulchral' type is associated with astronomy and cosmology in South Asia and in other parts of the world (Menon and Vahia, 2010).
In the context of prehistoric anthropomorphic figures in India, (Rao 1988/1999, Upinder Singh 2008) note that it is unclear what these giant anthropomorphs symbolize. They usually occur in association with megalithic monuments and are located in megalithic burial grounds, and may have been connected with ancestor worship.
Melanesian megaliths
Megaliths occur in many parts of
Melanesia, mainly in
Milne Bay Province,
Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
and
Vanuatu. Few excavations has been made and little is known about the structures.
The megalith tomb Otuyam at
Kiriwina has been dated to be approximately 2,000 years old which indicates that megaliths are an old custom in Melanesia. However very few megaliths have been dated. The constructions have been used for different rituals. For example, tombs, sacrifices and rituals of fecundity. Dance sites exist next to some megaliths. In some places in Melanesia rituals are continued to be held at the sacred megalith sites. The fact that the beliefs are alive is a reason that most excavations have been stopped at the sites.
Micronesian megaliths
Megalithic structures in Micronesia reach their most developed form on the islands of
Pohnpei
Pohnpei "upon (''pohn'') a stone altar (''pei'')" (formerly known as Ponape or Ascension, Proto-Chuukic-Pohnpeic: ''*Fawo ni pei)'' is an island of the Senyavin Islands which are part of the larger Caroline Islands group. It belongs to Pohnpei ...
and
Kosrae in the Eastern Caroline Islands. On these two islands there was extensive use of prismatic basalt columns to build upland building complexes such as those at Salapwuk on Pohnpei and Menka on Kosrae. These building sites, remote from the ocean, appear to have been abandoned early. Megalithic building then shifted to constructing networks of artificial islands on the coast that supported a multitude of common, royal and religious structures. Dating of the structures is difficult but the complex at
Nan Madol on Pohnpei was probably inhabited as early as c. 800, probably as artificial islands, with the more elaborate buildings and religious structures added to the site from 1000 to 1400 AD.
Modern theories
Purposes
Megaliths were used for a variety of purposes ranging from serving as boundary markers of territory, to a reminder of past events, and to being part of the society's religion. Common motifs including crooks and axes seem to be symbols of political power, much as the crook was a symbol of Egyptian pharaohs. Amongst the
indigenous peoples of India,
Malaysia,
Polynesia, North Africa, North America, and South America, the worship of these stones, or the use of these stones to symbolize a spirit or deity, is a possibility. In the early 20th century, some scholars believed that all megaliths belonged to one global "Megalithic culture" (
hyperdiffusionism, e. g. "the Manchester school", by
Grafton Elliot Smith and
William James Perry William Perry may refer to:
Business
* William Perry (Queensland businessman) (1835–1891), businessman and politician in Queensland, Australia
* William H. Perry (businessman) (1832–1906), American businessman and entrepreneur
Politics and ...
), but this has long been disproved by modern dating methods. Nor is it believed any longer that there was a pan-European megalithic culture, although regional cultures existed, even within such small areas as the British Isles. The archaeologist Euan Mackie wrote, "Likewise it cannot be doubted that important regional cultures existed in the Neolithic period and can be defined by different kinds of stone circles and local pottery styles (Ruggles & Barclay 2000: figure 1). No-one has ever been rash enough to claim a nationwide unity of all aspects of Neolithic archaeology!".
Methods of construction
Much scholarship over history has suggested that Stone Age peoples moved the large stones on cylindrical wooden rollers. However, there is some disagreement with this theory, specifically as experiments have indicated that this method is impractical on uneven ground. In some contemporary megalith building cultures, such as in
Sumba
Sumba ( id, Pulau Sumba) is an island in eastern Indonesia. It is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands and is in the province of East Nusa Tenggara. Sumba has an area of , and the population was 779,049 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as a ...
,
Indonesia, great emphasis is placed on the social status of moving heavy stones without the relief of rollers. In the majority of documented contemporary megalithic-building communities, the stones have been placed on timber sledges and dragged without rollers.
Types of megalithic structure
The types of megalithic structure can be divided into two categories, the "polylithic type" and the "monolithic type". Different megalithic structures include:
Contemporary megalith-building cultures
The Toraja of Indonesia
The megalithic culture of the
Toraja people in the mountainous region of
South Sulawesi
South Sulawesi ( id, Sulawesi Selatan) is a province in the southern peninsula of Sulawesi. The Selayar Islands archipelago to the south of Sulawesi is also part of the province. The capital is Makassar. The province is bordered by Central Sula ...
,
Indonesia dates back to around 2500–1000 BC.
The Marapu of Indonesia
In West
Sumba
Sumba ( id, Pulau Sumba) is an island in eastern Indonesia. It is one of the Lesser Sunda Islands and is in the province of East Nusa Tenggara. Sumba has an area of , and the population was 779,049 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as a ...
,
Indonesia, the more than 20,000 followers of the
Marapu animist
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning 'breath, Soul, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct Spirituality, spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things—Animal, animals, Plant, plants, Ro ...
religion construct monolithic tombs by hand. Originally built with slave labor, the large tombs of nobles are now built by a class of dependents who are paid either in animals or cash (an amount equal to $0.65–0.90 per day). The tombs are planned long in advance, with families sometimes going into extreme debt to finance the construction. In 1971, one leading family sacrificed 350 buffalo over the course of a year in order to feed the 1,000 people necessary to drag the capstone 3 km from the quarry to the tombsite.
Quarrying the stones for a tomb can take almost a month and typically involves 20-40 laborours, sometimes subcontracted by a relative. It can be months or years before the stones are actually transported to the gravesite, which is done traditionally by hand, using a wooden sled and rollers with the help of many members of the family's clan. Building the sled itself can take several days, and typically males between the ages of 10-60 are assembled to pull the stone from the quarry to the tombsite. Smaller capstones may be moved by a few hundred members of a clan, but larger ones can involve upwards of 2,000 individuals over many days.
Sometimes the stones are draped with woven cloths given as gifts by relatives of the owner. The sidewalls are smaller and usually require fewer participants. The entire process is accompanied by large feasts and ritual singers provided by the owner. Some contemporary practitioners now choose to use large machinery and trucks to move the stones.
Once on site, the stones were traditionally assembled and mortared with a mix of water buffalo dung and ash, but are now more commonly cemented together. Typically, the walls are assembled first, and then the capstone is incrementally elevated to the height of the walls by means of a wood scaffolding which is inserted log by log at alternating ends. Once the capstone is at the correct height beside the walls it is slid into place above the tomb. Alternately, some tombs are constructed by dragging the capstone up a fabricated ramp and then assembling the sidewalls below it, before removing the ramp structure to let the capstone rest upon the walls. Often, but not always, the finished structure is decorated by a professional stone carver with symbolic motifs. The carving alone can at times take over a month to complete.
References in literature and fiction
Gallery
File:Moai Rano raraku.jpg, Easter Island's Moai at Rano Raraku
File:Inside the remains of the burial chamber, Mane Braz, Brittany.jpg, Inside the burial chamber at Mane Braz
Mane Braz is a Megalithic tomb located 2 km southeast of Erdeven, Brittany, France. The site comprises four side chambers and two small dolmens. It is built into a hill and appears to be the remains of a tumulus
A tumulus (plural tu ...
, Brittany, France
File:Almendres_cromlech_3.jpg, Menhirs at the Almendres Cromlech, Évora, Portugal
File:abakan08.jpg, Megalithic tomb in Khakasiya
Khakassia (russian: Хакасия; kjh, Хакасия, Хакас Чирі, ''Khakasiya'', ''Khakas Çiri''), officially the Republic of Khakassia (russian: Республика Хакасия, r=Respublika Khakasiya, ; kjh, Хакас Рес ...
, Russian Federation
File:Guam Dolmen Sites.JPG, Capstones of southern-style megalithic burials in Guam-ri, Jeollabuk-do, Korea
File:Ales stenar bred.jpg, Ale's Stones at Kåseberga, around ten kilometres south east of Ystad, Sweden
File:BrynCelliDdu3.jpg, Bryn Celli Ddu in Wales
File:Talaiot.jpg, Talaiot in Majorca
Mallorca, or Majorca, is the largest island in the Balearic Islands, which are part of Spain and located in the Mediterranean.
The capital of the island, Palma, is also the capital of the autonomous community of the Balearic Islands. The Bal ...
File:Sa ena e thomes 2.jpg, Giant's grave near Dorgali in Sardinia, Italy
File:Deer-stone.jpg, Deer stone near Mörön
Mörön ( mn, Мөрөн;, lit=river), also spelled Murun, is the administrative center of Khövsgöl Aimag (province) in northern Mongolia. Before 1933, Khatgal had been the aimag capital.
It has 12,286 families and a population of 46,918, an ...
in Mongolia
File:Bretagne Morbihan Locmariaquer 14015.jpg, the Great Menhir of Er Grah in Brittany, the largest known single stone erected by Neolithic man, which later fell down
File:Taula-Menorca.jpg, ''Taula
A taula (meaning 'table' in Catalan) is a Stonehenge-esque stone monument found on the Balearic island of Menorca. Taulas can be up to 5 metres high and consist of a vertical pillar (a monolith or several smaller stones on top of each other) wi ...
'' in Talati de Dalt, Menorca
File:Tiya Stèles.JPG, Megaliths with engraved figures in Tiya
Tiya is a town in central Ethiopia. It is situated in the Gurage Zone of the Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples Region south of Addis Ababa. It is also the location of the Tiya archaeological site, famous for its unique stelae.
Demogra ...
, southern Ethiopia
File:Dolmen di Avola.JPG, Dolmen of Avola
Avola (; scn, Àvula/, becoming / if preceded by vowel; la, Abola) is a city and in the province of Syracuse, Sicily (southern Italy).
History
The foundation of the city in an area previously inhabited by the Sicani and invaded by the Si ...
(Sicily, Italy)
File:Dolmen kueijiyeh.jpg, Dolmen at the Kuejiyeh dolmen field close to Madaba, Jordan
File:Dolmen de Menga 07.jpg, Dolmen of Menga in Antequera
Antequera () is a city and municipality in the Comarca de Antequera, province of Málaga, part of the Spanish autonomous community of Andalusia. It is known as "the heart of Andalusia" (''el corazón de Andalucía'') because of its central locat ...
, Spain
See also
*
Bilger's rocks
*
British megalith architecture
British megalith architecture is the study of those ancient cultures that built megalithic sites on the British Isles, including the research and documentation of these sites. The classification sometimes used of these cultures based on geologica ...
*
Irish megalithic tombs
Megalithic monuments in Ireland typically represent one of several types of megalithic tombs: court cairns, passage tombs, portal tombs and wedge tombs. The remains of over 1,000 such megalithic tombs have been recorded around Ireland.
Types Co ...
*
List of megalithic sites
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to:
People
* List (surname)
Organizations
* List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America
* SC Germania List, German rugby union ...
*
Megalithic monuments in Europe
*
Megaliths in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
*
Megaliths in the Urals
*
Nature worship
Nature worship also called naturism or physiolatry is any of a variety of religious, spiritual and devotional practices that focus on the worship of the nature spirits considered to be behind the natural phenomena visible throughout nature. A nat ...
*
Nordic megalith architecture
Nordic megalith architecture is an ancient architectural style found in Northern Europe, especially Scandinavia and North Germany, that involves large slabs of stone arranged to form a structure. It emerged in northern Europe, predominantly betwee ...
*
Plain of Jars ranging from the
Khorat Plateau in Thailand in the south, through Laos and to
Dima Hasao of northerneastern India.
*
Standing stone
A menhir (from Brittonic languages: ''maen'' or ''men'', "stone" and ''hir'' or ''hîr'', "long"), standing stone, orthostat, or lith is a large human-made upright rock (geology), stone, typically dating from the European middle Bronze Age. T ...
*
Stone slab
*
Straße der Megalithkultur
The Route of Megalithic Culture (german: Straße der Megalithkultur) was first created as a tourist route that meanders from Osnabrück to Oldenburg in North-West Germany. Signposted with brown road signs it links many places of archaeological ...
– tourist route from Osnabrück to Oldenburg via some 33 Megalithic sites.
*
Unidentified submerged object
An unidentified submerged object (USO) is an unidentified object submerged in water. This term does not necessarily refer to an object of paranormal activity origin.
See also
* Baltic Sea anomaly
* Bimini Road
* Cuban underwater formation
* Elta ...
*
Yonaguni Monument
*
Stone circles of Junapani
The stone circles of Junapani are prehistoric megalithic circles in Junapani, near Nagpur in the Indian state of Maharashtra. There are about 300 such stone circles noted around Junapani. They were first excavated by J. H. Rivett-Carnac in 18 ...
Notes
References
Articles
* A Fleming, "Megaliths and post-modernism. The case of Wales". ''Antiquity'', 2005.
* A Fleming, "Phenomenology and the Megaliths of Wales: a Dreaming Too Far?". ''Oxford Journal of Archaeology'', 1999
* A Sherratt, "The Genesis of Megaliths". ''World Archaeology''. 1990. (JSTOR)
* A Thom, "Megaliths and Mathematics". ''Antiquity'', 1966.
*
* G Kubler, "Period, Style and Meaning in Ancient American Art". ''New Literary History'', Vol. 1, No. 2, A Symposium on Periods (Winter, 1970), pp. 127–144.
* HJ Fleure, HJE Peake, "Megaliths and Beakers". ''The Journal of the Royal Anthropological Institute of Great Britain and Ireland'', Vol. 60, Jan. - Jun., 1930 (Jan. - Jun., 1930), pp. 47–71.
* J McKim Malville, F Wendorf, AA Mazar, R Schild, "Megaliths and Neolithic astronomy in southern Egypt". ''Nature'', 1998.
* KL Feder, "Irrationality and Popular Archaeology". ''American Antiquity'', Vol. 49, No. 3 (July 1984), pp. 525–541.
*
* MW Ovenden, DA Rodger, "Megaliths and Medicine Wheels". ''Bulletin of the American Astronomical Society'', 1978
Books
* Asthana, S. (1976). ''History and archaeology of India's contacts with other countries, from earliest times to 300 B.C.''. Delhi: B.R. Pub. Corp.
* Deo, S. B. (1973). ''Problem of South Indian megaliths''. Dharwar: Kannada Research Institute, Karnatak University.
* Goblet d'Alviella, E., & Wicksteed, P. H. (1892). ''Lectures on the origin and growth of the conception of God as illustrated by anthropology and history''. London: Williams and Norgate.
* Goudsward, D., & Stone, R. E. (2003). ''America's Stonehenge: the ''. Boston: Branden Books.
* Illustrated Encyclopedia of Humankind (The): ''Worlds Apart'' (1994) Weldon Owen Pty Limited
* Keane, A. H. (1896).
Ethnology'. Cambridge: University Press.
* Johnson, Walter (1908)
''Folk-Memory: Or, The Continuity of British Archaeology'' Oxford: Clarendon Press.
* Lancaster Brown, P. (1976). ''Megaliths, myths, and men: an introduction to astro-archaeology''. New York: Taplinger Pub. Co.
* Moffett, M., Fazio, M. W., & Wodehouse, L. (2004). ''A world history of architecture''. Boston: McGraw-Hill.
* Nelson, Sarah M. (1993) ''The Archaeology of Korea''. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
* O'Kelly, M. J., et al. (1989). ''Early Ireland: An Introduction to Irish Prehistory''. Cambridge University Press.
* Parker, Joanne (editor) (2009). ''Written On Stone: The Cultural Reception of British Prehistoric Monuments'' (Cambridge Scholars Publishing; 2009).
* Patton, Mark (1993). ''Statements in Stone: monuments and society in Neolithic Brittany''. Routledge. 209 pages.
* Piccolo, Salvatore (2013). Ancient Stones: ''The Prehistoric Dolmens of Sicily''. Thornham/Norfolk: Brazen Head Publishing.
* Pohribný, Jan (photo) & Richards, J (introduction) (2007). ''Magic Stones; the secret world of ancient megaliths''. London: Merrell.
* Pozzi, Alberto (2013). ''Megalithism - Sacred and Pagan Architecture in Prehistory''. Universal Publisher.
* Scheltema, H.G. (2008). ''Megalithic Jordan; an introduction and field guide''. Amman, Jordan: The American Center of Oriental Research.
* Stukeley, W., Burl, A., & Mortimer, N. (2005). ''Stukeley's 'Stonehenge': an unpublished manuscript, 1721-1724''. New Haven
onn.
Walmart, Inc., like many large retail and grocery chain stores, offers private brands (also called house brands or store brands), which are lower-priced alternatives to name brand products.
Apparel brands
Major brands
In March 2018, to better ...
Yale University Press.
* Subbayya, K. K. (1978). ''Archaeology of Coorg with special reference to megaliths''. Mysore: Geetha Book House.
* Tyler, J. M. (1921). ''The new stone age in northern Europe''. New York: C. Scribner's Sons.
External links
Catalog of megalithsMegalithicIreland.comDolmens, Menhirs & Stones-Circles in the South of FranceMegaliths in Charente-Maritime, FranceDolmen Path - Russian MegalithsThe Megalithic Portal and Megalith MapIndex of Megalithic monuments in IrelandThe Modern AntiquarianModern Megalith-Building
{{Authority control
Stone Age
Sacred rocks
Burial monuments and structures
 A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The word was first used in 1849 by the British antiquarian
A megalith is a large stone that has been used to construct a prehistoric structure or monument, either alone or together with other stones. There are over 35,000 in Europe alone, located widely from Sweden to the Mediterranean sea.
The word was first used in 1849 by the British antiquarian 
 ;Menhir: Menhir is the name used in Western Europe for a single upright stone erected in
;Menhir: Menhir is the name used in Western Europe for a single upright stone erected in  * 9000 BC: Constructions in Asia Minor ( Göbekli Tepe, Nevalı Çori and other sites); perhaps proto- Hattian, a yet to be named culture (the oldest discovered ceremonial structures in the world).
* 7000 BC: Construction in proto-Canaanite Israel ( Atlit Yam).
* 6000 BC: Constructions in Portugal ( Almendres Cromlech, Évora) - Possibly first standing stones in Portugal.
* 5000 BC: Emergence of the Atlantic Neolithic period, the age of agriculture along the western shores of Europe during the sixth millennium BC pottery culture of La Almagra, Spain nearby, perhaps precedent from Africa.
* 4800 BC: Constructions in Brittany, France (
* 9000 BC: Constructions in Asia Minor ( Göbekli Tepe, Nevalı Çori and other sites); perhaps proto- Hattian, a yet to be named culture (the oldest discovered ceremonial structures in the world).
* 7000 BC: Construction in proto-Canaanite Israel ( Atlit Yam).
* 6000 BC: Constructions in Portugal ( Almendres Cromlech, Évora) - Possibly first standing stones in Portugal.
* 5000 BC: Emergence of the Atlantic Neolithic period, the age of agriculture along the western shores of Europe during the sixth millennium BC pottery culture of La Almagra, Spain nearby, perhaps precedent from Africa.
* 4800 BC: Constructions in Brittany, France ( * 3600 BC: Constructions in England ( Maumbury Rings and Godmanchester), and Malta ( Ġgantija and Mnajdra temples).
* 3500 BC: Constructions in Spain (
* 3600 BC: Constructions in England ( Maumbury Rings and Godmanchester), and Malta ( Ġgantija and Mnajdra temples).
* 3500 BC: Constructions in Spain ( * 2000 BC: Constructions in Brittany ( Er Grah), Italy : (
* 2000 BC: Constructions in Brittany ( Er Grah), Italy : (
 The standing stone has a very ancient tradition in the Middle East, dating back from Mesopotamian times. Although not always 'megalithic' in the true sense, they occur throughout the area and can reach 5 metres or more in some cases (such as at
The standing stone has a very ancient tradition in the Middle East, dating back from Mesopotamian times. Although not always 'megalithic' in the true sense, they occur throughout the area and can reach 5 metres or more in some cases (such as at  The third tomb type is a diverse group known as gallery graves. These are axially arranged chambers placed under elongated mounds. The Irish
The third tomb type is a diverse group known as gallery graves. These are axially arranged chambers placed under elongated mounds. The Irish 
 Megalithic tombs are aboveground burial chambers, built of large stone slabs (megaliths) laid on edge and covered with earth or other, smaller stones. They are a type of chamber tomb, and the term is used to describe the structures built across
Megalithic tombs are aboveground burial chambers, built of large stone slabs (megaliths) laid on edge and covered with earth or other, smaller stones. They are a type of chamber tomb, and the term is used to describe the structures built across  There is a huge variety of megalithic tombs. The free-standing single chamber
There is a huge variety of megalithic tombs. The free-standing single chamber  Dolmens are also in Apulia and in Sicily. In this latter region, they are small structures located in Mura Pregne (
Dolmens are also in Apulia and in Sicily. In this latter region, they are small structures located in Mura Pregne ( Megalithic tombs appear to have been used by communities for the long-term deposition of the remains of their dead, and some seem to have undergone alteration and enlargement. The organization and effort required to erect these large stones suggest that the societies concerned placed great emphasis on the proper treatment of their dead. The ritual significance of the tombs is supported by the presence of pre-historic art carved into the stones at some sites. Hearths and deposits of pottery and animal bone found by archaeologists around some tombs also implies that some form of burial feast or sacrificial rites took place there.
Further examples of megalithic tombs include the stalled cairn at Midhowe in Orkney and the passage grave at Bryn Celli Ddu on Anglesey. There are also extensive grave sites with up to 60 megaliths at Louisenlund and
Megalithic tombs appear to have been used by communities for the long-term deposition of the remains of their dead, and some seem to have undergone alteration and enlargement. The organization and effort required to erect these large stones suggest that the societies concerned placed great emphasis on the proper treatment of their dead. The ritual significance of the tombs is supported by the presence of pre-historic art carved into the stones at some sites. Hearths and deposits of pottery and animal bone found by archaeologists around some tombs also implies that some form of burial feast or sacrificial rites took place there.
Further examples of megalithic tombs include the stalled cairn at Midhowe in Orkney and the passage grave at Bryn Celli Ddu on Anglesey. There are also extensive grave sites with up to 60 megaliths at Louisenlund and  In association with the megalithic constructions across Europe, there are often large
In association with the megalithic constructions across Europe, there are often large  In Europe megaliths are, in general, constructions erected during the Neolithic or late Stone Age and Chalcolithic or Copper Age (4500–1500 BC). The megalithic structures of Malta are believed to be the oldest in Europe. Perhaps the most famous megalithic structure is
In Europe megaliths are, in general, constructions erected during the Neolithic or late Stone Age and Chalcolithic or Copper Age (4500–1500 BC). The megalithic structures of Malta are believed to be the oldest in Europe. Perhaps the most famous megalithic structure is  The French
The French  Megalithic burials are found in Northeast and Southeast Asia. They are found mainly in the Korean Peninsula. They are also found in the
Megalithic burials are found in Northeast and Southeast Asia. They are found mainly in the Korean Peninsula. They are also found in the  Southern-style megalithic burials are distributed in the southern Korean Peninsula. It is thought that most of them date to the latter part of the Early Mumun or to the Middle Mumun Period. Southern-style megaliths are typically smaller in scale than northern megaliths. The interment area of southern megaliths has an underground burial chamber made of earth or lined with thin stone slabs. A massive capstone is placed over the interment area and is supported by smaller propping stones. Most of the megalithic burials on the Korean Peninsula are of the southern type.
As with northern megaliths, southern examples contain few, if any, artifacts. However, a small number of megalithic burials contain fine red-burnished pottery, bronze daggers, polished groundstone daggers, and greenstone ornaments. Southern megalithic burials are often found in groups, spread out in lines that are parallel with the direction of streams. Megalithic cemeteries contain burials that are linked together by low stone platforms made from large river cobbles. Broken red-burnished pottery and charred wood found on these platforms has led archaeologists to hypothesize that these platform were sometimes used for ceremonies and rituals. The capstones of many southern megaliths have 'cup-marks' carvings. A small number of capstones have human and dagger representations.
Southern-style megalithic burials are distributed in the southern Korean Peninsula. It is thought that most of them date to the latter part of the Early Mumun or to the Middle Mumun Period. Southern-style megaliths are typically smaller in scale than northern megaliths. The interment area of southern megaliths has an underground burial chamber made of earth or lined with thin stone slabs. A massive capstone is placed over the interment area and is supported by smaller propping stones. Most of the megalithic burials on the Korean Peninsula are of the southern type.
As with northern megaliths, southern examples contain few, if any, artifacts. However, a small number of megalithic burials contain fine red-burnished pottery, bronze daggers, polished groundstone daggers, and greenstone ornaments. Southern megalithic burials are often found in groups, spread out in lines that are parallel with the direction of streams. Megalithic cemeteries contain burials that are linked together by low stone platforms made from large river cobbles. Broken red-burnished pottery and charred wood found on these platforms has led archaeologists to hypothesize that these platform were sometimes used for ceremonies and rituals. The capstones of many southern megaliths have 'cup-marks' carvings. A small number of capstones have human and dagger representations.
 These megaliths are distinguished from other types by the presence of a burial shaft, sometimes up to 4 m in depth, which is lined with large cobbles.Bale, Martin T.
These megaliths are distinguished from other types by the presence of a burial shaft, sometimes up to 4 m in depth, which is lined with large cobbles.Bale, Martin T. The Indonesian archipelago is the host of
The Indonesian archipelago is the host of  Megaliths in South Asia are dated before 3000 BC, with recent findings dated back to 5000 BC in southern India. Megaliths are found in almost all parts of South Asia. There is also a broad time evolution with the megaliths in central India and the upper Indus valley where the oldest megaliths are found, while those in the east are of much later date. A large fraction of these are assumed to be associated with burial or post burial rituals, including memorials for those whose remains may or may not be available. The case-example is that of Brahmagiri, which was excavated by Wheeler (1975) and helped establish the culture sequence in south Indian prehistory. However, there is another distinct class of megaliths that do not seem to be associated with burials.
Megaliths in South Asia are dated before 3000 BC, with recent findings dated back to 5000 BC in southern India. Megaliths are found in almost all parts of South Asia. There is also a broad time evolution with the megaliths in central India and the upper Indus valley where the oldest megaliths are found, while those in the east are of much later date. A large fraction of these are assumed to be associated with burial or post burial rituals, including memorials for those whose remains may or may not be available. The case-example is that of Brahmagiri, which was excavated by Wheeler (1975) and helped establish the culture sequence in south Indian prehistory. However, there is another distinct class of megaliths that do not seem to be associated with burials.