Zen 3 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Zen 3 is the name for a CPU
File:AMD@7nm(12nmIOD)@Zen3@Vermeer@Ryzen 5 5600X@100-000000064 BG 2042SUS 9JF6228V00014 DSCx2.jpg, A de-lidded Ryzen 5 5600X. Only one 6-core CCD is present. The contacts for a second CCD are visible.
File:AMD@7nm(12nmIOD)@Zen3@Vermeer@Ryzen 5 5600X@100-000000064 BG 2042SUS 9JF6228V00014 DSCx4@IR.jpg, Close-up of the CCD, taken under infrared lighting. This die was damaged by the de-lidding process.
File:AMD@7nm(12nmIOD)@Zen3@Vermeer@Ryzen 5 5600X@100-000000064 BG 2042SUS 9JF6228V00014 DSCx3@IR.jpg, Close-up of the I/O die
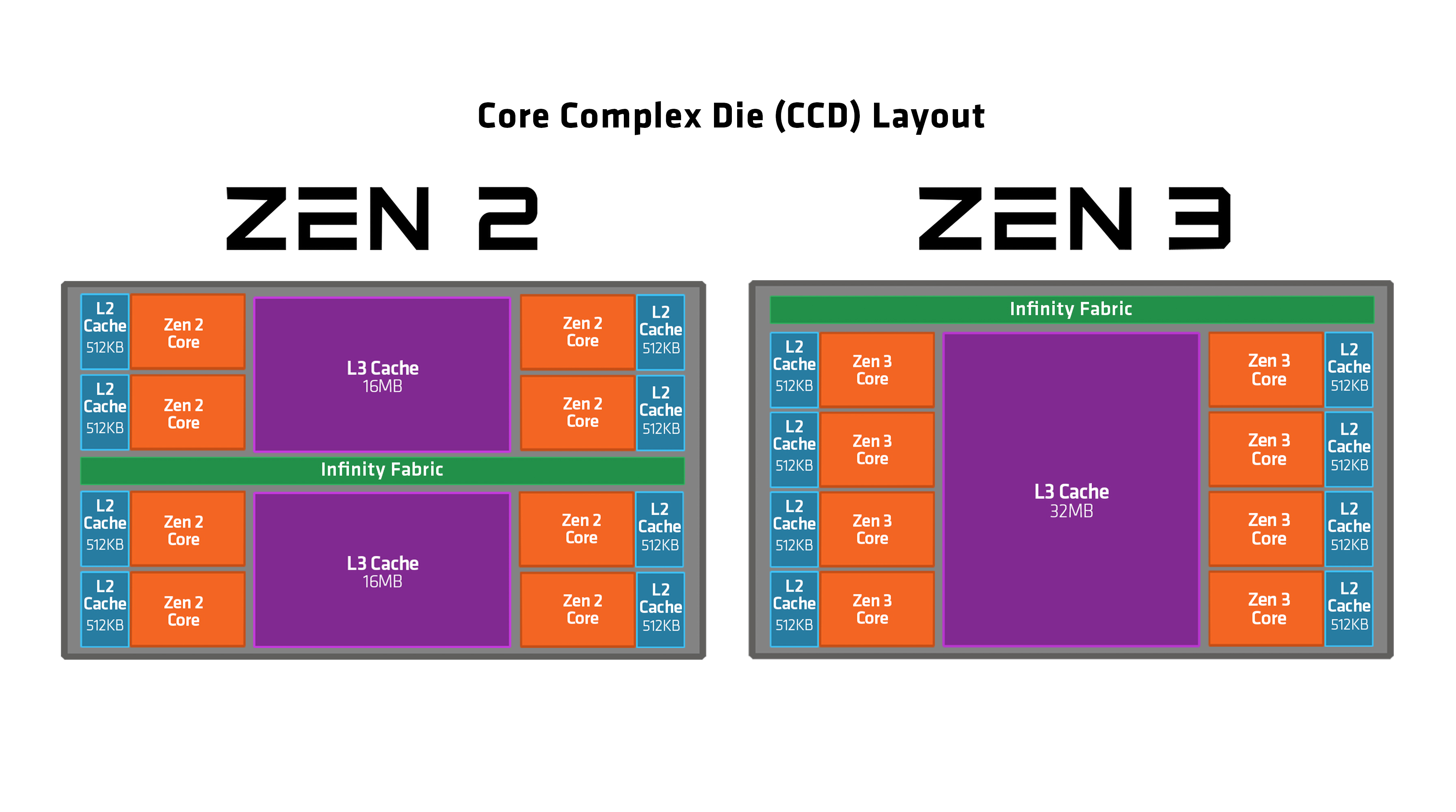
In Zen 3, a single 32MB L3 cache pool is shared among all 8 cores in a chiplet, vs. Zen 2's two 16MB pools each shared among 4 cores in a core complex, of which there were two per chiplet. This new arrangement improves the cache hit rate as well as performance in situations that require cache data to be exchanged among cores, but increases cache latency from 39 cycles in Zen 2 to 46 clock cycles and halves per-core cache bandwidth, although both problems are partially mitigated by higher clock speeds. Total cache bandwidth on all 8 cores combined remains the same due to power consumption concerns. L2 cache capacity and latency remain the same at 512KB and 12 cycles. All cache read and write operations are done at 32 bytes per cycle.
On April 20, 2022, AMD released the R7 5800X3D. It features, for the first time in a desktop PC product, 3D-stacked vertical L3 cache. Its extra 64MB comes via a TSMC N7 (7nm) "3D V Cache" die direct copper to copper hybrid bonded right on top of the 8-core Zen 3 CCD's usual 32MB, increasing the CPU's total L3 cache capacity to 96MB and bringing significant performance improvements for gaming in particular; now rivalling contemporary high-end consumer processors while being much more power efficient and running on older, cheaper motherboards using affordable DDR4 memory. And despite now spanning multiple dies and being three times larger (96MB vs 32MB), the L3 cache's performance remains nearly identical; with X3D only adding around ≈+2ns via an additional three to four cycles of latency. It would later be followed by the Ryzen 5 5600X3D and Ryzen 7 5700X3D for lower-end market segments, and succeeded by the Ryzen 7000X3D family of 3D V Cache equipped Zen 4 processors on the newer socket AM5 platform.
 Zen 3 has made the following improvements over Zen 2:
* An increase of 19% in
Zen 3 has made the following improvements over Zen 2:
* An increase of 19% in
microarchitecture
In electronics, computer science and computer engineering, microarchitecture, also called computer organization and sometimes abbreviated as μarch or uarch, is the way a given instruction set architecture (ISA) is implemented in a particular ...
by AMD
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California and maintains significant operations in Austin, Texas. AMD is a hardware and fabless company that de ...
, released on November 5, 2020. It is the successor to Zen 2 and uses TSMC
Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company Limited (TSMC or Taiwan Semiconductor) is a Taiwanese multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company. It is one of the world's most valuable semiconductor companies, the world' ...
's 7 nm
In semiconductor manufacturing, the "7 nm" process is a term for the MOSFET technology node following the 10 nm process, "10 nm" node, defined by the International Roadmap for Devices and Systems (IRDS), which was preceded by the International T ...
process for the chiplets and GlobalFoundries
GlobalFoundries Inc. is a multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company located in the Cayman Islands and headquartered in Malta, New York. Created by the divestiture of the manufacturing arm of AMD in March 2009, the ...
's 14 nm process for the I/O die on the server chips and 12 nm for desktop chips. Zen 3 powers Ryzen 5000 mainstream desktop processors (codenamed "Vermeer") and Epyc
Epyc (stylized as EPYC) is a brand of multi-core x86-64 microprocessors designed and sold by AMD, based on the company's Zen microarchitecture. Introduced in June 2017, they are specifically targeted for the server and embedded system market ...
server processors (codenamed "Milan"). Zen 3 is supported on motherboards with 500 series chipsets; 400 series boards also saw support on select B450 / X470 motherboards with certain BIOSes. Zen 3 is the last microarchitecture before AMD switched to DDR5 memory and new sockets, which are AM5 for the desktop "Ryzen" chips alongside SP5 and SP6 for the EPYC server platform and sTRX8. According to AMD, Zen 3 has a 19% higher instructions per cycle
In computer architecture, instructions per cycle (IPC), commonly called instructions per clock, is one aspect of a processor's performance: the average number of instructions executed for each clock cycle. It is the multiplicative inverse of c ...
(IPC) on average than Zen 2.
On April 1, 2022, AMD released the new Ryzen 6000 series for laptops/mobile, using an improved Zen 3+ architecture featuring notable architectural improvements to power efficiency and power management
Power management is a feature of some electrical appliances, especially copiers, computers, computer CPUs, computer GPUs and computer peripherals such as monitors and printers, that turns off the power or switches the system to a low-power ...
. And slightly later, on April 20, 2022, AMD would also release the Ryzen 7 5800X3D desktop processor, which increased gaming performance by around +15% on average by using for the very first time in a PC product, a 3D vertically stacked L3 cache. Specifically in the form of a 64MB L3 cache "3D V Cache" die made on the same TSMC N7 process as the 8-core Zen 3 CCD which it gets direct copper to copper hybrid bonded to.
Features
As the first largely "ground up redesign" of the Zen CPU core since the architecture family's original release in early 2017 with Zen 1/Ryzen 1000, Zen 3 was a significant architectural improvement over its predecessors; having a very significant IPC increase of +19% over the prior Zen 2 architecture in addition to being capable of reaching higher clock speeds. Like Zen 2, Zen 3 is composed of up to 2 core complex dies (CCD) along with a separate IO die containing the I/O components. A Zen 3 CCD is composed of a single core complex (CCX) containing 8 CPU cores and 32MB of shared L3 cache, this is in contrast to Zen 2 where each CCD is composed of 2 CCX, each containing 4 cores paired with 16MB of L3 cache. The new configuration allows all 8 cores of the CCX to directly communicate with each other and the L3 Cache instead of having to use the IO die through the Infinity Fabric. Zen 3 (along with AMD's RDNA2 GPUs) also implemented Resizable BAR, an optional feature introduced in PCIe2.0, that was branded as ''Smart Access Memory'' (SAM). This technology allows CPU to directly access all of compatible video card'sVRAM
Video random-access memory (VRAM) is dedicated computer memory used to store the pixels and other graphics data as a framebuffer to be rendered on a computer monitor. It often uses a different technology than other computer memory, in order to ...
. Intel and Nvidia have since implemented this feature as well.
Improvements
 Zen 3 has made the following improvements over Zen 2:
* An increase of 19% in
Zen 3 has made the following improvements over Zen 2:
* An increase of 19% in instructions per clock
In computer architecture, instructions per cycle (IPC), commonly called instructions per clock, is one aspect of a processor's performance: the average number of instructions executed for each clock cycle. It is the multiplicative inverse of c ...
* The base core chiplet
A chiplet is a tiny integrated circuit (IC) that contains a well-defined subset of functionality. It is designed to be combined with other chiplets on an interposer in a single package to create a complex component such as a computer processor. E ...
has a single eight-core complex (versus two four-core complexes in Zen 2)
* A unified 32MB L3 cache pool equally available to all 8 cores in a chiplet, vs Zen 2's two 16MB pools each shared among 4 cores in a core complex.
**On mobile: A unified 16MB L3
*A unified 8-core CCX (from 2x 4-core CCX per CCD)
* Increased branch prediction
In computer architecture, a branch predictor is a digital circuit that tries to guess which way a branch (e.g., an if–then–else structure) will go before this is known definitively. The purpose of the branch predictor is to improve the flow ...
bandwidth. L1 branch target buffer size increased to 1024 entries (vs 512 in Zen 2)
*New instructions
** VAES256-bit Vector AES instructions
** INVLPGBBroadcast TLB flushing
** CET_SS Control-flow Enforcement Technology / Shadow Stack
* Improved integer units
** 96 entry integer scheduler (up from 92)
** 192 entry physical register file (up from 180)
** 10 issue per cycle (up from 7)
** 256 entry reorder-buffer (up from 224)
** fewer cycles for DIV/IDIV ops (10...20 from 16...46)
* Improved floating point units
** 6 μOP dispatch width (up from 4)
** FMA latency reduced by 1 cycle (down from 5 to 4)
* Additional 64MB 3D vertically stacked dense library L3 cache (in -X3D models)
Feature tables
CPUs
APUs
APU features tableProducts
200px, AMD Ryzen 7 5800X On October 8, 2020, AMD announced four Zen 3-based desktop Ryzen processors, consisting of one Ryzen 5, one Ryzen 7, and two Ryzen 9 CPUs and featuring between 6 and 16 cores.Desktop CPUs
The Ryzen 5000 series desktop CPUs are codenamed ''Vermeer''. The models in the second table are based on ''Cezanne''APUs
Apus is a small constellation in the Southern Celestial Hemisphere, southern sky. It represents a bird-of-paradise, and its name means "without feet" in Greek language, Greek because the bird-of-paradise was once wrongly believed to lack feet. ...
with the integrated GPU disabled. Meanwhile the Ryzen Threadripper Pro 5000 series were codenamed ''Chagall''.
5100, 5500, and 5700 have no ECC support like non-Pro Ryzen 5000 Desktop APUs.
Desktop APUs
Cezanne
Mobile APUs
Cezanne
Barceló
Barceló-R
Embedded CPUs
Server CPUs
TheEpyc
Epyc (stylized as EPYC) is a brand of multi-core x86-64 microprocessors designed and sold by AMD, based on the company's Zen microarchitecture. Introduced in June 2017, they are specifically targeted for the server and embedded system market ...
server line of chips based on Zen 3 is named Milan and is the final generation of chips using the SP3 socket. Epyc Milan was released on March 15, 2021.
Zen 3+
Zen 3+ is the codename for a refresh of the Zen 3 microarchitecture, which focuses on power efficiency improvements. It was released in April 2022 with the Ryzen 6000 series of mobile processors.Features and improvements
Zen 3+ has 50 new or enhanced power management features over Zen 3, and also provides an adaptive power management framework, as well as new deep sleep states. Altogether, this brings improvements to efficiency both during idle, and when under load, with up to 30% performance-per-watt increase over Zen 3, as well as longer battery life. IPC is identical to that of Zen 3; the performance improvements of Ryzen 6000 over Ryzen 5000 mobile processors stem from it having a higher efficiency (hence more performance in power-constrained form factors like laptops), as well as the increased clock speeds from being built on the smaller TSMC N6 node. The ''Rembrandt'' implementation of Zen 3+ also has support for DDR5 and LPDDR5 memory.Products
Rembrandt
On April 1, 2022, AMD released the Ryzen 6000 series of mobile APUs, codenamed Rembrandt. It introduces PCIe 4.0 and DDR5/LPDDR5 for the first time in an APU for the laptop and also introduced RDNA2 integrated graphics to the PC. It is built on TSMC's 6 nm node.Rembrandt-R
Rembrandt-R is the codename for a refresh of Rembrandt codenamed processors, released as the Ryzen 7035 series of mobile APUs in January 2023.References
{{AMD processor roadmap AMD microarchitectures AMD x86 microprocessors Computer-related introductions in 2020 X86 microarchitectures