The Time Machine'' (1895) was a commercial success; in it, he introduced the notion of time travel. In some instances, science fiction inspired new technology and scientific research. Explorer
Ernest Shackleton
Sir Ernest Henry Shackleton (15 February 1874 – 5 January 1922) was an Anglo-Irish Antarctic explorer who led three British expeditions to the Antarctic. He was one of the principal figures of the period known as the Heroic Age of ...
acknowledged that the novel ''Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea'' by Jules Verne was an inspiration.
As reading became more pronounced in the 19th century with public notes, broadsides, catchpennies and printed songs becoming common street literature, it informed and entertained the public before newspapers became readily available in the later 19th century. Advertisements and local news, such as offers of rewards for catching criminals or for the return of stolen goods, appeared on public notices and handbills, while cheaply printed sheets – broadsheets and ballads – covered political or criminal news such murders, trials, executions, disasters and rescues.
Chapbook
A chapbook is a small publication of up to about 40 pages, sometimes bound with a saddle stitch.
In early modern Europe a chapbook was a type of printed street literature. Produced cheaply, chapbooks were commonly small, paper-covered bookle ...
s would also be common place, these were simple reading matter that were small, cheap forms of literature for children and adults that were sold on the streets, their subjects included fiction writing to disaster updates. Their readership would have been largely among the poor, and among children of the middle class.
A 2015 study investigated the frequency at which difficult vocabulary from the
WORDSUM
Wordsum is a 10-item vocabulary test that has been included as an item on the General Social Survey (GSS) in most survey years since 1974. Each of the test's items ranges in difficulty from very easy to very difficult. It is widely used in research ...
test were employed in about 5.9 million English-language texts published between 1850 and 2005. The researchers found that the more difficult of words were in declining usage and that there was a negative correlation between the use of such words and
completed fertility. On the other hand, simpler words entered increasingly common use, an effect of rising literacy.
In another study, from 2017, researchers employed
Google's Ngram Viewer, an enormous archive of scanned books, periodicals, and other printed materials dating back to the sixteenth century. They found that the use of difficult vocabulary increased substantially between the mid-1700s and mid-1800s before declining steadily till the present day.
Entertainment

Popular forms of entertainment varied by social class. Victorian Britain, like the periods before it, was interested in literature, theatre and
the arts
The arts are a very wide range of human practices of creative expression, storytelling and cultural participation. They encompass multiple diverse and plural modes of thinking, doing and being, in an extremely broad range of media. Both ...
(see
Aesthetic movement
Aestheticism (also the Aesthetic movement) was an art movement in the late 19th century which privileged the aesthetic value of literature, music and the arts over their socio-political functions. According to Aestheticism, art should be prod ...
and
Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood
The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood (later known as the Pre-Raphaelites) was a group of English painters, poets, and art critics, founded in 1848 by William Holman Hunt, John Everett Millais, Dante Gabriel Rossetti, William Michael Rossetti, James ...
), and music, drama, and opera were widely attended.
Michael Balfe
Michael William Balfe (15 May 1808 – 20 October 1870) was an Irish composer, best remembered for his operas, especially ''The Bohemian Girl''.
After a short career as a violinist, Balfe pursued an operatic singing career, while he began to co ...
was the most popular British
grand opera composer of the period, while the most popular musical theatre was a series of fourteen
comic operas
Comic opera, sometimes known as light opera, is a sung dramatic work of a light or comic nature, usually with a happy ending and often including spoken dialogue.
Forms of comic opera first developed in late 17th-century Italy. By the 1730s, a ne ...
by
Gilbert and Sullivan
Gilbert and Sullivan was a Victorian era, Victorian-era theatrical partnership of the dramatist W. S. Gilbert (1836–1911) and the composer Arthur Sullivan (1842–1900), who jointly created fourteen comic operas between 1871 and 1896, of which ...
, although there was also
musical burlesque and the beginning of
Edwardian musical comedy
Edwardian musical comedy was a form of British musical theatre that extended beyond the reign of King Edward VII in both directions, beginning in the early 1890s, when the Gilbert and Sullivan operas' dominance had ended, until the rise of the A ...
in the 1890s.
Drama ranged from
low comedy
Low comedy, also known as lowbrow humor, in association to comedy, is a dramatic or literary form of popular entertainment without any primary purpose other than to create laughter through boasting, boisterous jokes, drunkenness, scolding, figh ...
to
Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
(see
Henry Irving
Sir Henry Irving (6 February 1838 – 13 October 1905), christened John Henry Brodribb, sometimes known as J. H. Irving, was an English stage actor in the Victorian era, known as an actor-manager because he took complete responsibility ( ...
).
Melodrama
A modern melodrama is a dramatic work in which the plot, typically sensationalized and for a strong emotional appeal, takes precedence over detailed characterization. Melodramas typically concentrate on dialogue that is often bombastic or exces ...
—literally 'musical drama'—was introduced in Revolutionary France and reached Great Britain from there during the Victorian era. It was a particularly widespread and influential theatrical genre thanks to its appeal to the working-class and artisans. However, its popularity decline in the late nineteenth century. Even so, it continued to influence the novels of the era.
Gentlemen went to dining clubs, like the
Beefsteak Club
Beefsteak Club is the name or nickname of several 18th- and 19th-century male dining clubs in Britain and Australia that celebrated the beefsteak as a symbol of patriotic and often Whig concepts of liberty and prosperity.
The first beefsteak clu ...
or the
Savage Club. Gambling at cards in establishments popularly called
casino
A casino is a facility for certain types of gambling. Casinos are often built near or combined with hotels, resorts, restaurants, retail shopping, cruise ships, and other tourist attractions. Some casinos are also known for hosting live entertai ...
s was wildly popular during the period: so much so that evangelical and reform movements specifically targeted such establishments in their efforts to stop gambling, drinking, and prostitution.
Brass bands and 'The
Bandstand' became popular in the Victorian era. The bandstand was a simple construction that not only created an ornamental focal point but also served acoustic requirements whilst providing shelter from the changeable
British weather. It was common to hear the sound of a brass band whilst strolling through
parklands. At this time musical recording was still very much a novelty.
The Victorian era marked the golden age of the British circus.
Astley's Amphitheatre
Astley's Amphitheatre was a performance venue in London opened by Philip Astley in 1773, considered the first modern circus ring. It was burned and rebuilt several times, and went through many owners and managers. Despite no trace of the theatr ...
in Lambeth,
London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, featuring equestrian acts in a 42-foot wide circus ring, was the center of the 19th-century circus. The permanent structure sustained three fires but as an institution lasted a full century, with
Andrew Ducrow
Andrew Ducrow (1793–1842) was a British circus performer, often called "Colossus of equestrians". He was the originator of horsemanship acts and proprietor of Astley's Amphitheatre and remains one of the few giants of equestrian drama whose na ...
and
William Batty
William Batty (1801–1868) was an equestrian performer, circus proprietor, and longtime operator of Astley's Amphitheatre in London. Batty was one of the most successful circus proprietors in Victorian England and helped launch the career ...
managing the theatre in the middle part of the century.
William Batty
William Batty (1801–1868) was an equestrian performer, circus proprietor, and longtime operator of Astley's Amphitheatre in London. Batty was one of the most successful circus proprietors in Victorian England and helped launch the career ...
would also build his 14,000-person arena, known commonly as Batty's Hippodrome, in Kensington Gardens, and draw crowds from the
Crystal Palace Exhibition
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary structure in which it was held), was an international exhibition which took pl ...
. Traveling circuses, like
Pablo Fanque's, dominated the British provinces, Scotland, and Ireland (Fanque would enjoy fame again in the 20th century when John Lennon would buy an 1843 poster advertising his circus and adapt the lyrics for
The Beatles
The Beatles were an English Rock music, rock band, formed in Liverpool in 1960, that comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are regarded as the Cultural impact of the Beatles, most influential band of al ...
song, ''
Being for the Benefit of Mr. Kite!''). Fanque also stands out as a black man who achieved great success and enjoyed great admiration among the British public only a few decades after Britain had abolished slavery.

Another form of entertainment involved "spectacles" where paranormal events, such as
mesmerism
Animal magnetism, also known as mesmerism, was a protoscientific theory developed by German doctor Franz Mesmer in the 18th century in relation to what he claimed to be an invisible natural force (''Lebensmagnetismus'') possessed by all livi ...
, communication with the dead (by way of
mediumship
Mediumship is the practice of purportedly mediating communication between familiar spirits or ghost, spirits of the dead and living human beings. Practitioners are known as "mediums" or "spirit mediums". There are different types of mediumship o ...
or channeling),
ghost
A ghost is the soul or spirit of a dead person or animal that is believed to be able to appear to the living. In ghostlore, descriptions of ghosts vary widely from an invisible presence to translucent or barely visible wispy shapes, to rea ...
conjuring and the like, were carried out to the delight of crowds and participants. Such activities were more popular at this time than in other periods of recent Western history.
Natural history became increasingly an "amateur" activity. Particularly in Britain and the United States, this grew into specialist hobbies such as the
study of birds, butterflies, seashells (
malacology
Malacology is the branch of invertebrate zoology that deals with the study of the Mollusca (mollusks or molluscs), the second-largest phylum of animals in terms of described species after the arthropods. Mollusks include snails and slugs, clams, ...
/
conchology
Conchology () is the study of mollusc shells. Conchology is one aspect of malacology, the study of molluscs; however, malacology is the study of molluscs as whole organisms, whereas conchology is confined to the study of their shells. It includ ...
), beetles and wildflowers. Amateur
collectors
Collector(s) may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Collector (character), a fictional character in the Marvel Comics universe
* ''Collector'' (2011 film), a 2011 Indian Malayalam film
* ''Collector'' (2016 film), a 2016 Russian film
* ''Collec ...
and natural history entrepreneurs played an important role in building the large natural history collections of the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries.
Middle-class Victorians used the train services to visit the seaside, helped by the
Bank Holiday Act of 1871, which created many fixed holidays. Large numbers traveling to quiet fishing villages such as
Worthing
Worthing () is a seaside town in West Sussex, England, at the foot of the South Downs, west of Brighton, and east of Chichester. With a population of 111,400 and an area of , the borough is the second largest component of the Brighton and Hov ...
,
Morecambe
Morecambe ( ) is a seaside town and civil parish in the City of Lancaster district in Lancashire, England. It is in Morecambe Bay on the Irish Sea.
Name
The first use of the name was by John Whitaker in his ''History of Manchester'' (1771), w ...
and
Scarborough Scarborough or Scarboro may refer to:
People
* Scarborough (surname)
* Earl of Scarbrough
Places Australia
* Scarborough, Western Australia, suburb of Perth
* Scarborough, New South Wales, suburb of Wollongong
* Scarborough, Queensland, sub ...
began turning them into major tourist centres, and people like
Thomas Cook saw tourism and even overseas travel as viable businesses.
Sports

The Victorian era saw the introduction and development of many modern sports. Often originating in the public schools, they exemplified new ideals of manliness.
Cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
, cycling,
croquet, horse-riding, and many water activities are examples of some of the popular sports in the Victorian era.
The modern game of tennis originated in Birmingham, England, between 1859 and 1865. The world's oldest tennis tournament, the
Wimbledon championships
The Wimbledon Championships, commonly known simply as Wimbledon, is the oldest tennis tournament in the world and is widely regarded as the most prestigious. It has been held at the All England Lawn Tennis and Croquet Club, All England Club in ...
, was first played in London in 1877. Britain was an active competitor in all the
Olympic Games
The modern Olympic Games or Olympics (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques) are the leading international sporting events featuring summer and winter sports competitions in which thousands of athletes from around the world participate in a var ...
starting in 1896.
High culture
Gothic Revival architecture
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic, neo-Gothic, or Gothick) is an architectural movement that began in the late 1740s in England. The movement gained momentum and expanded in the first half of the 19th century, as increasingly ...
became increasingly significant during the period, leading to the
Battle of the Styles The Battle of the Styles is a term used to refer to the conflict between supporters of the Gothic style and the Classical style in architecture. In Britain this led to public debates between Decimus Burton and Augustus Pugin.
Later in the century ...
between Gothic and
Classical ideals.
Charles Barry
Sir Charles Barry (23 May 1795 – 12 May 1860) was a British architect, best known for his role in the rebuilding of the Palace of Westminster (also known as the Houses of Parliament) in London during the mid-19th century, but also responsi ...
's architecture for the new
Palace of Westminster
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parli ...
, which had been badly damaged in an
1834 fire, was built in the
medieval style of
Westminster Hall
The Palace of Westminster serves as the meeting place for both the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons and the House of Lords, the two houses of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Informally known as the Houses of Parli ...
, the surviving part of the building. It constructed a narrative of cultural continuity, set in opposition to the violent disjunctions of
Revolutionary France, a comparison common to the period, as expressed in Carlyle's ''
The French Revolution: A History'' (1837) and
Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
' ''
A Tale of Two Cities'' (1859) and ''
Great Expectations
''Great Expectations'' is the thirteenth novel by Charles Dickens and his penultimate completed novel. It depicts the education of an orphan nicknamed Pip (Great Expectations), Pip (the book is a ''bildungsroman''; a coming-of-age story). It ...
'' (1861). Gothic was also supported by critic
John Ruskin
John Ruskin (8 February 1819 20 January 1900) was an English writer, philosopher, art critic and polymath of the Victorian era. He wrote on subjects as varied as geology, architecture, myth, ornithology, literature, education, botany and politi ...
, who argued that it epitomised communal and inclusive social values, as opposed to Classicism, which he considered to epitomise mechanical standardisation.
The middle of the 19th century saw
The Great Exhibition
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary structure in which it was held), was an international exhibition which took pl ...
of 1851, the first
World's Fair
A world's fair, also known as a universal exhibition or an expo, is a large international exhibition designed to showcase the achievements of nations. These exhibitions vary in character and are held in different parts of the world at a specif ...
, which showcased the greatest innovations of the century. At its centre was
the Crystal Palace
The Crystal Palace was a cast iron and plate glass structure, originally built in Hyde Park, London, Hyde Park, London, to house the Great Exhibition of 1851. The exhibition took place from 1 May to 15 October 1851, and more than 14,000 exhibit ...
, a modular glass and iron structure – the first of its kind. It was condemned by Ruskin as the very model of mechanical dehumanisation in design but later came to be presented as the prototype of
Modern architecture
Modern architecture, or modernist architecture, was an architectural movement or architectural style based upon new and innovative technologies of construction, particularly the use of glass, steel, and reinforced concrete; the idea that form ...
. The
emergence of photography, showcased at the Great Exhibition, resulted in significant changes in Victorian art with Queen Victoria being the first British monarch to be photographed.
In general, various styles of painting were popular during the Victorian period, Classicism, Neoclassicism, Romanticism, Impressionism, and Post-impressionism. In 1848,
Dante Rossetti and
William Holman Hunt
William Holman Hunt (2 April 1827 – 7 September 1910) was an English painter and one of the founders of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. His paintings were notable for their great attention to detail, vivid colour, and elaborate symbolism. ...
created the
Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood
The Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood (later known as the Pre-Raphaelites) was a group of English painters, poets, and art critics, founded in 1848 by William Holman Hunt, John Everett Millais, Dante Gabriel Rossetti, William Michael Rossetti, James ...
whose stated aim was to produce paintings of photographic quality, taking inspiration from a variety of sources, from the works of William Shakespeare to Mother Nature herself. The growing popularity of romantic love spilled over into literature and fine arts.
Gallery of selected Victorian paintings
File:Henry Boddington - Norfolk Hamlet 1840.jpg, ''Norfolk Hamlet'' (1840) by Henry John Boddington
File:William Holman Hunt 001.jpg, ''The Hireling Shepherd
''The Hireling Shepherd'' (1851) is a painting by the Pre-Raphaelite artist William Holman Hunt. It represents a shepherd neglecting his flock in favour of an attractive country girl to whom he shows a death's-head hawkmoth. The meaning of the ...
'' (1851) by William Holman Hunt
William Holman Hunt (2 April 1827 – 7 September 1910) was an English painter and one of the founders of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. His paintings were notable for their great attention to detail, vivid colour, and elaborate symbolism. ...
File:Monarch of the Glen, Edwin Landseer, 1851.jpg, ''Monarch of the Glen'' (1851) by Edwin Landseer
File:Dante Gabriel Rossetti - Proserpine.JPG, ''Proserpine'' (1874) by Dante Rossetti
File:Miranda - John William Waterhouse.jpg, ''Miranda'' (1875) by John William Waterhouse
John William Waterhouse (6 April 184910 February 1917) was an English painter known for working first in the Academic style and for then embracing the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood's style and subject matter. His artworks were known for their dep ...
File:Frederick Leighton - Biondina.jpg, ''Biondina'' (1879) by Frederick Leighton
Frederic Leighton, 1st Baron Leighton, (3 December 1830 – 25 January 1896), known as Sir Frederic Leighton between 1878 and 1896, was a British painter, draughtsman, and sculptor. His works depicted historical, biblical, and classical antiqui ...
File:Frank Bramley - A Hopeless Dawn 1888.jpg, ''A Hopeless Dawn'' (1888) by Frank Bramley
Frank Bramley RA (6 May 1857 – 9 August 1915) was an English post-impressionist genre painter of the Newlyn School.
Personal life
Bramley was born in Sibsey, near Boston, in Lincolnshire to Charles Bramley from Fiskerton also in Lincoln ...
File:John Simmons - Titania sleeping in the moonlight protected by her fairies.jpg, ''Titania Sleeping in the Moonlight Protected by Her Fairies'' by John Simmons, inspired by Shakespeare's ''A Midsummer Night's Dream''.
File:Leighton-God Speed!.jpg, ''God Speed!'' (1900) by Edmund Leighton

Journalism
In 1817,
Thomas Barnes became general editor of ''
The Times
''The Times'' is a British daily national newspaper based in London. It began in 1785 under the title ''The Daily Universal Register'', adopting its current name on 1 January 1788. ''The Times'' and its sister paper ''The Sunday Times'' (fou ...
''; he was a political radical, a sharp critic of parliamentary hypocrisy and a champion of freedom of the press. Under Barnes and his successor in 1841,
John Thadeus Delane, the influence of ''The Times'' rose to great heights, especially in politics and in the financial district (the
City of London
The City of London is a city, ceremonial county and local government district that contains the historic centre and constitutes, alongside Canary Wharf, the primary central business district (CBD) of London. It constituted most of London fr ...
). It spoke of reform. ''The Times'' originated the practice of sending
war correspondents to cover particular conflicts.
W. H. Russell
Sir William Howard Russell, (28 March 182011 February 1907) was an Irish reporter with ''The Times'', and is considered to have been one of the first modern war correspondents. He spent 22 months covering the Crimean War, including the Sieg ...
wrote immensely influential dispatches on the
Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the de ...
of 1853–1856; for the first time, the public could read about the reality of warfare. Russell wrote one dispatch that highlighted the surgeons' "inhumane barbarity" and the lack of ambulance care for wounded troops. Shocked and outraged, the public reacted in a backlash that led to major reforms especially in the provision of nursing, led by
Florence Nightingale
Florence Nightingale (; 12 May 1820 – 13 August 1910) was an English Reform movement, social reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing. Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during t ...
.
The ''
Manchester Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...
'' was founded in Manchester in 1821 by a group of
non-conformist businessmen. Its most famous editor,
Charles Prestwich Scott
Charles Prestwich Scott (26 October 1846 – 1 January 1932), usually cited as C. P. Scott, was a British journalist, publisher and politician. Born in Bath, Somerset, he was the editor of the ''Manchester Guardian'' (now ''the Guardian'') ...
, made the ''Guardian'' into a world-famous newspaper in the 1890s. ''
The Daily Telegraph
''The Daily Telegraph'', known online and elsewhere as ''The Telegraph'', is a national British daily broadsheet newspaper published in London by Telegraph Media Group and distributed across the United Kingdom and internationally.
It was fo ...
'' in 1856 became the first penny newspaper in London. It was funded by advertising revenue based on a large audience.
Leisure
At mid-century, the idea of a large amphitheatre for musical performances and conferences for the learned captured the imagination of not just Henry Cole, Secretary of the Science and Art Department, but also Prince Albert. By 1857, Cole planned to build one with "due regard to the
principles of sound." After the Prince's death in 1861, this project had the additional goal of commemorating him. The
Royal Albert Hall
The Royal Albert Hall is a concert hall on the northern edge of South Kensington, London. One of the UK's most treasured and distinctive buildings, it is held in trust for the nation and managed by a registered charity which receives no govern ...
opened on 29 March 1871. Lieutenant-Colonel Henry Scott, R.E., who managed the construction, estimated there was enough space for 7,165 people plus 1,200 performers; the theoretical limit was 10,000. As desired by the Prince, it did not rely on public funds but was purely privately funded.
Opportunities for leisure activities increased dramatically as real wages continued to grow and hours of work continued to decline. In urban areas the nine-hour workday became increasingly the norm; the Factory Act 1874 limited the working week to 56.5 hours, encouraging the movement towards an eventual eight-hour workday. Furthermore, a system of routine annual holidays came into play, starting with white-collar workers and moving into the working-class. Some 200 seaside resorts emerged thanks to cheap hotels and inexpensive railway fares, widespread bank holidays and the fading of many religious prohibitions against secular activities on Sundays.
By the late Victorian era the leisure industry had emerged in all cities. It provided scheduled entertainment of suitable length at convenient locales at inexpensive prices. These included sporting events, music halls, and popular theatre. By 1880 football was no longer the preserve of the social elite, as it attracted large working-class audiences. Average attendance was 5000 in 1905, rising to 23,000 in 1913. That amounted to 6 million paying customers with a weekly turnover of £400,000. Sports by 1900 generated some three percent of the total gross national product. Professional sports were the norm, although some new activities reached an upscale amateur audience, such as lawn tennis and golf. Women were now allowed in some sports, such as archery, tennis, badminton and gymnastics.
Demographics
Demographic transition
Britain had the lead in rapid economic and population growth. At the time,
Thomas Malthus
Thomas Robert Malthus (; 13/14 February 1766 – 29 December 1834) was an English cleric, scholar and influential economist in the fields of political economy and demography.
In his 1798 book '' An Essay on the Principle of Population'', Mal ...
believed this lack of growth outside Britain was due the carrying capacity of their local environments. That is, the tendency of a population to expand geometrically while resources grew more slowly, reaching a crisis (such as famine, war, or epidemic) which would reduce the population to a more sustainable size.
["Malthus, An Essay on the Principle of Population: Library of Economics"] Great Britain escaped the '
Malthusian trap
Malthusianism is the idea that population growth is potentially exponential while the growth of the food supply or other resources is linear, which eventually reduces living standards to the point of triggering a population die off. This event, c ...
' because the scientific and technological breakthroughs of the Industrial Revolution dramatically improved living standards, reducing mortality and increasing longevity.
The Victorian era was a time of unprecedented population growth in Britain. The population rose from 13.9 million in 1831 to 32.5 million in 1901. Two major contributory factors were fertility rates and mortality rates. Britain was the first country to undergo the
demographic transition
In demography, demographic transition is a phenomenon and theory which refers to the historical shift from high birth rates and high death rates in societies with minimal technology, education (especially of women) and economic development, to lo ...
and the
Agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating Plant, plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of Sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of Domestication, domesticated species created food ...
and
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
s.
Economist
Gary Becker argued that at first, falling fertility is due to urbanisation and lower infant mortality rates, which diminished the benefits and increased the costs of raising children. In other words, it became more economically sensible to invest more in fewer children. This is known as the first demographic transition. This trend continued till around 1950. (The
second demographic transition
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds eac ...
occurred due to the significant cultural shifts of the 1960s, leading to the decline in the desire for children.)
Fertility rates and mortality rates
The demographic transition is when a population shifts from being one of high child mortality rates and high fertility rates to one that is low in both. Western nations completed this transition by the early 1900s. It occurred in two stages. Initially, child mortality rates dropped significantly due to improved healthcare and sanitation and better nutrition, yet fertility rates remained high, leading to a population boom. Gradually, fertility rates fell as people became more affluent and had better access to contraception. By 1900, the
infant mortality rate
Infant mortality is the death of young children under the age of 1. This death toll is measured by the infant mortality rate (IMR), which is the probability of deaths of children under one year of age per 1000 live births. The under-five morta ...
in England was 10 percent, down from an estimated 25 percent in the Middle Ages.
There was no catastrophic epidemic or famine in England or Scotland in the nineteenth century—it was the first century in which a major epidemic did not occur throughout the whole country, and deaths per 1000 of population per year in England and Wales fell from 21.9 from 1848 to 1854 to 17 in 1901 (cf, for instance, 5.4 in 1971).
[ ] Social class had a significant effect on mortality rates: the upper classes had a lower rate of premature death early in the nineteenth century than poorer classes did.
In the Victorian era,
fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that would be born to a woman over her lifetime if:
# she were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through her lifetime
# she were t ...
s increased in every decade until 1901, when the rates started evening out. There were several reasons for this. One is biological: with improving living standards, a higher proportion of women were biologically able to have children. Another possible explanation is social. In the 19th century, the marriage rate increased, and people were getting married at a very young age until the end of the century, when the average age of marriage started to increase again slowly. The reasons why people got married younger and more frequently are uncertain. One theory is that greater prosperity allowed people to finance marriage and new households earlier than previously possible. With more births within marriage, it seems inevitable that marriage rates and birth rates would rise together.
Birth rates were originally measured by the '
crude birth rate' – births per year divided by total population. This is indeed a crude measure, as key groups and their fertility rates are not clear. It is likely to be affected mainly by changes in the age distribution of the population. The Net Reproduction Rate was then introduced as an alternative measure: it measures the average fertility rate of women of child-bearing ages.
High rates of birth also occurred because of a lack of
birth control
Birth control, also known as contraception, anticonception, and fertility control, is the use of methods or devices to prevent unwanted pregnancy. Birth control has been used since ancient times, but effective and safe methods of birth contr ...
. Mainly because women lacked knowledge of birth control methods and the practice was seen as unrespectable. The evening out of fertility rates at the beginning of the 20th century was mainly the result of a few big changes: availability of forms of birth control, and changes in people's attitude towards sex.
In the olden days, people typically had had as many children as they could afford in order to ensure at least a few of them would survive to adulthood and have children of their own due to high child mortality rates. Moreover, it was the poor who had had an incentive to curb their fertility whereas the rich had lacked such a need due to greater wealth and lower child mortality rates. This changed due to the Industrial Revolution. Standards of living improved and mortality rates fell. People no longer needed to have as many children as before to ensure the propagation of their genes. The link between poverty and child mortality weakened. In addition, societal attitude towards contraception warmed, leading to the negative correlation between intelligence and fertility.
Factors linked to general intelligence, such as socioeconomic status and educational attainment, were also found to be negatively correlated with fertility starting from the nineteenth century.
Environmental and health standards rose throughout the Victorian era. Improvements in nutrition may also have played a role, though its importance is still debated.
Economy, industry, and trade
Progress
Life in the late 1700s had been little different from life in the late Middle Ages. But the nineteenth century saw dramatic technological development. Someone alive in 1804 would know about the electric telegraph, the steam ship, the circular saw, the bicycle, and the steam-powered locomotive. If this person lived to 1870, he or she would have heard of the invention of the electric light bulb, the typewriter, the calculator, the rubber tyre, the washing machine, the internal combustion engine, plastic, and dynamite.
Engineering prowess, especially in communication and transportation, made Great Britain the leading industrial powerhouse and trading nation of the world at that time.
According to historians David Brandon and Alan Brooke, the
new system of railways after 1830 brought into being our modern world:
:They stimulated demand for building materials, coal, iron and, later, steel. Excelling in the bulk movement of coal, they provided the fuel for the furnaces of industry and for domestic fireplaces. Millions of people were able to travel who had scarcely ever travelled before. Railways enabled mail, newspapers, periodicals and cheap literature to be distributed easily, quickly and cheaply allowing a much wider and faster dissemination of ideas and information. They had a significant impact on improving diet....
nd enableda proportionately smaller agricultural industry was able to feed a much larger urban population....They employed huge quantities of labour both directly and indirectly. They helped Britain to become the ‘Workshop of the World’ by reducing transport costs not only of raw materials but of finished goods, large amounts of which were exported....
day’s global corporations originated with the great limited liability railway companies....By the third quarter of the nineteenth century, there was scarcely any person living in Britain whose life had not been altered in some way by the coming of the railways. Railways contributed to the transformation of Britain from a rural to a predominantly urban society.
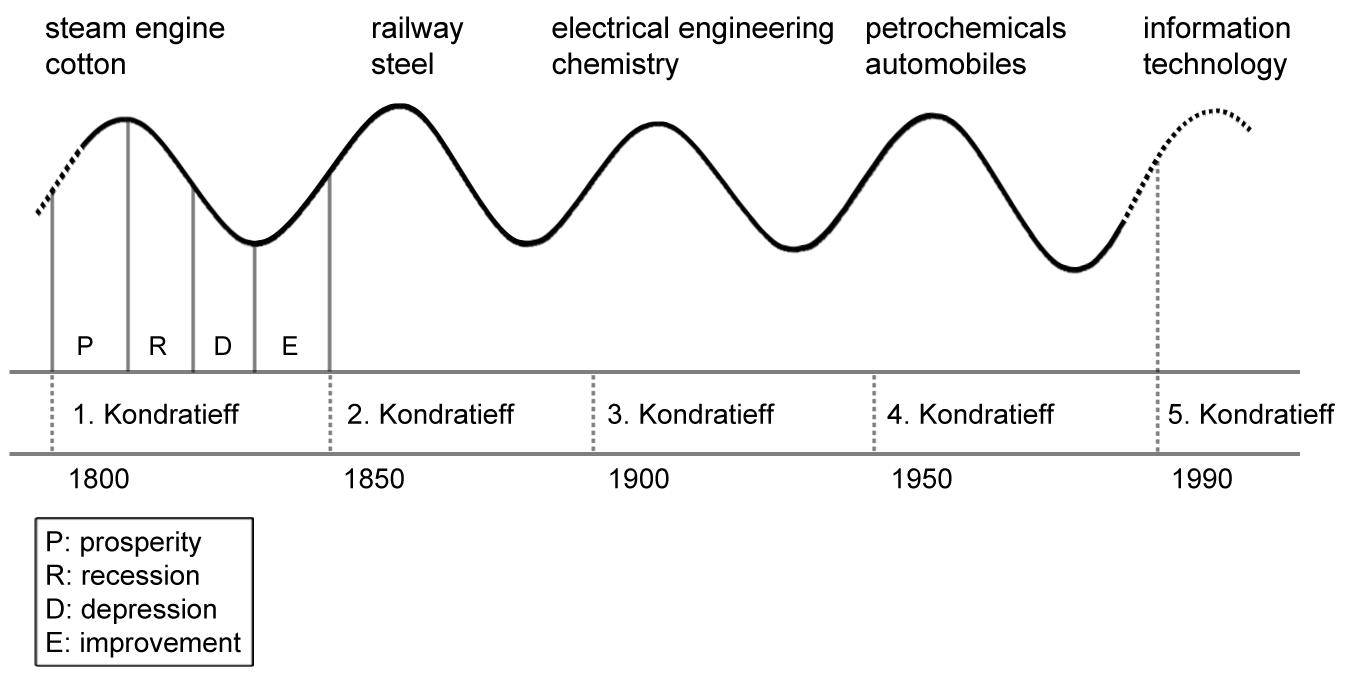
Historians have characterised the mid-Victorian era (1850–1870) as Britain's "Golden Years".
It was not till the two to three decades following the Second World War that substantial economic growth was seen again. In the long-term view, the mid-Victorian boom was one upswing in the
Kondratiev cycle (see figure).
There was prosperity, as the national income per person grew by half. Much of the prosperity was due to the increasing industrialisation, especially in textiles and machinery, as well as to the worldwide network of exports that produced profits for British merchants. British entrepreneurs built railways in India and many independent nations. There was peace abroad (apart from the short Crimean War, 1854–56), and social peace at home. Opposition to the new order melted away, says Porter. The
Chartist movement peaked as a democratic movement among the working class in 1848; its leaders moved to other pursuits, such as trade unions and cooperative societies. The working class ignored foreign agitators like Karl Marx in their midst, and joined in celebrating the new prosperity. Employers typically were paternalistic and generally recognised the trade unions. Companies provided their employees with welfare services ranging from housing, schools and churches, to libraries, baths, and gymnasia. Middle-class reformers did their best to assist the working classes' aspirations to middle-class norms of "respectability".
There was a spirit of libertarianism, says Porter, as people felt they were free. Taxes were very low, and government restrictions were minimal. There were still problem areas, such as occasional riots, especially those motivated by anti-Catholicism. Society was still ruled by the aristocracy and the gentry, who controlled high government offices, both houses of Parliament, the church, and the military. Becoming a rich businessman was not as prestigious as inheriting a title and owning a landed estate. Literature was doing well, but the fine arts languished as the Great Exhibition of 1851 showcased Britain's industrial prowess rather than its sculpture, painting or music. The educational system was mediocre; the main universities (outside Scotland) were likewise mediocre.
Historian
Llewellyn Woodward has concluded:
: For leisure or work, for getting or for spending, England was a better country in 1879 than in 1815. The scales were less weighted against the weak, against women and children, and against the poor. There was greater movement, and less of the fatalism of an earlier age. The public conscience was more instructed, and the content of liberty was being widened to include something more than freedom from political constraint ... Yet England in 1871 was by no means an earthly paradise. The housing and conditions of life of the working class in town & country were still a disgrace to an age of plenty.
In December 1844,
Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers
The Rochdale Society of Equitable Pioneers, founded in 1844, was an early consumers' co-operative, and one of the first to pay a patronage dividend, forming the basis for the modern co-operative movement.
Although other co-operatives preceded it, ...
founded what is considered the first
cooperative
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically-control ...
in the world. The founding members were a group of 28, around half of which were weavers, who decided to band together to open a store owned and managed democratically by the members, selling food items they could not otherwise afford. Ten years later, the British co-operative movement had grown to nearly 1,000 co-operatives. The movement also spread across the world, with the first
cooperative financial institution founded in 1850 in Germany.
File:From 'Street Life in London', 1877, by John Thomson and Adolphe Smith- (6960859488).jpg, From ''Street Life in London'', 1877, by John Thomson and Adolphe Smith. "...the inhabitants of Church Lane were nearly all what I may term “street folks” – living, buying, selling, transacting all their business in the open street. It was a celebrated resort for tramps and costers of every description."
File:The Sellers of Shell-fish (6924988264).jpg, A street stall in London during the 1870s
File:Kemna Lokomotiven.jpg, Many European companies, such as steam-machine producer J. Kemna, modeled themselves on English industry.
Housing
The very rapid growth in population in the 19th century in the cities included the new industrial and manufacturing cities, as well as service centres such as Edinburgh and London. The critical factor was financing, which was handled by building societies that dealt directly with large contracting firms. Private renting from housing landlords was the dominant tenure. P. Kemp says this was usually of advantage to tenants. People moved in so rapidly that there was not enough capital to build adequate housing for everyone, so low income newcomers squeezed into increasingly overcrowded slums. Clean water, sanitation, and public health facilities were inadequate; the death rate was high, especially infant mortality, and tuberculosis among young adults.
Cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
from polluted water and typhoid were endemic. Unlike rural areas, there were no famines such as the one which devastated Ireland in the 1840s.
Poverty
19th-century Britain saw a huge population increase accompanied by rapid urbanisation stimulated by the
Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
. Wage rates improved steadily; real wages (after taking inflation into account) were 65 percent higher in 1901, compared to 1871. Much of the money was saved, as the number of depositors in savings banks rose from 430,000 in 1831, to 5.2 million in 1887, and their deposits from £14 million to over £90 million. People flooded into industrial areas and commercial cities faster than housing could be built, resulting in overcrowding and lagging sanitation facilities such as fresh water and sewage.
These problems were magnified in London, where the population grew at record rates. Large houses were turned into flats and tenements, and as landlords failed to maintain these dwellings,
slum
A slum is a highly populated urban residential area consisting of densely packed housing units of weak build quality and often associated with poverty. The infrastructure in slums is often deteriorated or incomplete, and they are primarily inh ...
housing developed.
Kellow Chesney
Kellow Chesney (3 March 1914 – July 2004) was a journalist, publisher's reader, editor and writer.
His most notable book was ''The Victorian Underworld'', first published in 1970. The writer William Gibson has stated that his depiction of t ...
described the situation as follows: "Hideous slums, some of them acres wide, some no more than crannies of obscure misery, make up a substantial part of the metropolis... In big, once handsome houses, thirty or more people of all ages may inhabit a single room."
[Barbara Daniels]
Poverty and Families in the Victorian Era
Significant changes happened in the British
Poor Law
In English and British history, poor relief refers to government and ecclesiastical action to relieve poverty. Over the centuries, various authorities have needed to decide whose poverty deserves relief and also who should bear the cost of hel ...
system in
England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is Eng ...
,
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
, and
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
. These included a large expansion in
workhouses (or
poorhouses
A poorhouse or workhouse is a government-run (usually by a county or municipality) facility to support and provide housing for the dependent or needy.
Workhouses
In England, Wales and Ireland (but not in Scotland), ‘workhouse’ has been the ...
in Scotland), although with changing populations during the era.
Child labour
The early Victorian era before the reforms of the 1840s became notorious for
the employment of young children in factories and mines and as
chimney sweeps. Child labour played an important role in the Industrial Revolution from its outset: novelist
Charles Dickens
Charles John Huffam Dickens (; 7 February 1812 – 9 June 1870) was an English writer and social critic. He created some of the world's best-known fictional characters and is regarded by many as the greatest novelist of the Victorian e ...
, for example, worked at the age of 12 in a
blacking factory, with his family in a
debtors' prison. Reformers wanted the children in school: in 1840 only about 20 percent of the children in London had any schooling. By 1860 about half of the children between 5 and 15 were in school (including
Sunday school
A Sunday school is an educational institution, usually (but not always) Christian in character. Other religions including Buddhism, Islam, and Judaism have also organised Sunday schools in their temples and mosques, particularly in the West.
Su ...
).
[Child Labor](_blank)
David Cody, Hartwick College
The children of the poor were expected to help towards the family budget, often working long hours in dangerous jobs for low wages.
Agile boys were employed by the chimney sweeps; small children were employed to scramble under machinery to retrieve cotton bobbins; and children were also employed to work in
coal mines
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from ...
, crawling through tunnels too narrow and low for adults. Children also worked as errand boys,
crossing sweeper
A crossing sweeper was a person working as a street sweeper who would sweep a path ahead of people crossing dirty urban streets in exchange for a gratuity. This practice was an informal occupation among the urban poor, primarily during the 19th ...
s, shoe blacks, or sold matches, flowers, and other cheap goods.
Some children undertook work as apprentices to respectable trades, such as building, or as
domestic servants
A domestic worker or domestic servant is a person who works within the scope of a residence. The term "domestic service" applies to the equivalent occupational category. In traditional English contexts, such a person was said to be "in service ...
(there were over 120,000 domestic servants in London in the mid 19th century). Working hours were long: builders might work 64 hours a week in summer and 52 in winter, while domestic servants were theoretically on duty 80-hours a week.
Mother bides at home, she is troubled with bad breath, and is sair weak in her body from early labour. I am wrought with sister and brother, it is very sore work; cannot say how many rakes or journeys I make from pit's bottom to wall face and back, thinks about 30 or 25 on the average; the distance varies from 100 to 250 fathom. I carry about 1 cwt. and a quarter on my back; have to stoop much and creep through water, which is frequently up to the calves of my legs.
:— Isabella Read, 12 years old, coal-bearer, testimony gathered by Ashley's Mines Commission 1842
As early as 1802 and 1819,
Factory Acts
The Factory Acts were a series of acts passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom to regulate the conditions of industrial employment.
The early Acts concentrated on regulating the hours of work and moral welfare of young children employed ...
were passed to limit the working hours of children in factories and
cotton mills to 12 hours per day. These acts were largely ineffective and after radical agitation, by for example the "Short Time Committees" in 1831, a
Royal Commission recommended in 1833 that children aged 11–18 should work a maximum of 12 hours per day, children aged 9–11 a maximum of eight hours, and children under the age of nine should no longer be permitted to work. This act, however, only applied to the
textile industry
The textile industry is primarily concerned with the design, production and distribution of yarn, cloth and clothing. The raw material may be natural, or synthetic using products of the chemical industry.
Industry process
Cotton manufacturi ...
, and further agitation led to another act in 1847 limiting both adults and children to 10-hour working days.
Mathematics, science, technology, and engineering
Professionalisation of science
Founded in 1799 with the stated purpose of "diffusing the Knowledge, and facilitating the general Introduction, of Useful Mechanical Inventions and Improvements; and for teaching, by Courses of Philosophical Lectures and Experiments, the application of Science to the common Purposes of Life," the
Royal Institution
The Royal Institution of Great Britain (often the Royal Institution, Ri or RI) is an organisation for scientific education and research, based in the City of Westminster. It was founded in 1799 by the leading British scientists of the age, inc ...
was a proper scientific institution with laboratories, a lecture hall, libraries, and offices. In its first years, the Institution was dedicated to the improvement of agriculture using chemistry, prompted by trade restrictions with Europe. Such practical concerns continued through the next two centuries. However, it soon became apparent that additional funding was required in order for the Institution to continue. Some well-known experts were hired as lecturers and researchers. The most successful of them all was Sir
Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for t ...
, whose lectures concerned a myriad of topics and were so popular that the original practical purpose of the Institution faded away. It became increasingly dominated by research in basic science.
The professionalisation of science began in the aftermath of the French Revolution and soon spread to other parts of the Continent, including the German lands. It was slow to reach Britain, however. Master of Trinity College
William Whewell
William Whewell ( ; 24 May 17946 March 1866) was an English polymath, scientist, Anglican priest, philosopher, theologian, and historian of science. He was Master of Trinity College, Cambridge. In his time as a student there, he achieved dist ...
coined the term ''scientist'' in 1833 to describe the new professional breed specialists and experts studying what was still commonly known as ''natural philosophy''.
In 1840, Whewell wrote, "We need very much a name to describe a cultivator of science in general. I should incline to call him a Scientist." The new term signalled the recognition of the importance of empiricism and inductive reasoning. But this term was slow to catch on. As biologist
Thomas Huxley
Thomas Henry Huxley (4 May 1825 – 29 June 1895) was an English biologist and anthropologist specialising in comparative anatomy. He has become known as "Darwin's Bulldog" for his advocacy of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution.
The storie ...
indicated in 1852, the prospect of earning a decent living as a scientist remained remote despite the prestige of the occupation. It was possible for a scientist to "earn praise but not pudding," he wrote. Since its birth, the
Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
of London had been a club of gentlemanly amateurs, though some of whom were the very best in their fields, people like Charles Darwin and James Prescott Joule. But the Society reformed itself in the 1830s and 1840s. By 1847, it only admitted the new breed of professionals.
The Victorians were impressed by science and progress and felt that they could improve society in the same way as they were improving technology. Britain was the leading world centre for advanced engineering and technology. Its engineering firms were in worldwide demand for designing and constructing railways.
Ease of discovery and rate of progress
A necessary part of understanding scientific progress is the ease of scientific discovery. In many cases, from planetary science to mammalian biology, the ease of discovery since the 1700s and 1800s can be fitted to an exponentially decaying curve. But the rate of progress is also dependent on other factors, such as the number of researchers, the level of funding, and advances in technology. Thus the number of new species of mammals discovered between the late 1700s and late 1800s followed grew exponentially before leveling off in the 1900s; the general shape is known as the
logistic curve
A logistic function or logistic curve is a common S-shaped curve (sigmoid function, sigmoid curve) with equation
f(x) = \frac,
where
For values of x in the domain of real numbers from -\infty to +\infty, the S-curve shown on the right is ...
. In other cases, a branch of study reached the point of saturation. For instance, the last major internal human organ, the
paraythyroid gland, was discovered in 1880 by Ivar Viktor Sandström.
This does not mean that basic science was coming an end. Despite the despondency of many Victorian-era scientists, who thought that all that remained was measuring quantities to the next decimal place and that new discoveries would not change the contemporary scientific paradigm, as the nineteenth century became the twentieth, science witnessed truly revolutionary discoveries, such as radioactivity, and basic science continued its advance, though a number of twentieth-century scientists shared the same pessimism as their late-Victorian counterparts.
Mathematics and statistics

In the field of statistics, the nineteenth century saw significant innovations in data visualisation.
William Playfair, who created charts of all sorts, justified it thus, "a man who has carefully investigated a printed table, finds, when done, that he has only a very faint and partial idea of what he has read; and that like a figure imprinted on sand, is soon totally erased and defaced." For example, in a chart showing the relationship between population and government revenue of some European nations, he used the areas of circles to represent the geographical sizes of those nations. In the same graph he used the slopes of lines to indicate the tax burden of a given population. While serving as nurse during the Crimean War,
Florence Nightingale
Florence Nightingale (; 12 May 1820 – 13 August 1910) was an English Reform movement, social reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing. Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during t ...
drew the first pie charts representing the monthly fatality rates of the conflict, distinguishing deaths due to battle wounds (innermost section), those due to infectious disease (outer section), and to other causes (middle section). (See figure.) Her charts clearly showed that most deaths resulted from disease, which led the general public to demand improved sanitation at field hospitals. Although bar charts representing frequencies were first used by the Frenchman A. M. Guerry in 1833, it was the statistician
Karl Pearson
Karl Pearson (; born Carl Pearson; 27 March 1857 – 27 April 1936) was an English mathematician and biostatistician. He has been credited with establishing the discipline of mathematical statistics. He founded the world's first university st ...
who gave them the name ''
histogram
A histogram is an approximate representation of the distribution of numerical data. The term was first introduced by Karl Pearson. To construct a histogram, the first step is to " bin" (or "bucket") the range of values—that is, divide the ent ...
s''. Pearson used them in an 1895 article mathematically analyzing biological evolution. One such histogram showed that buttercups with large numbers of petals were rarer.
Normal distribution
In statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is
:
f(x) = \frac e^
The parameter \mu ...
s, expressible in the form
, arose in various works on probability and the theory of errors. Belgian sociologist and statistician
Adolphe Quetelet
Lambert Adolphe Jacques Quetelet FRSF or FRSE (; 22 February 1796 – 17 February 1874) was a Belgian astronomer, mathematician, statistician and sociologist who founded and directed the Brussels Observatory and was influential in introduc ...
discovered that its extremely wide applicability in his analysis of vast amounts of statistics of human physical characteristics such as height and other traits such as criminality and alcoholism. Quetelet derived the concept of the "average man" from his studies. Sir
Francis Galton
Sir Francis Galton, FRS FRAI (; 16 February 1822 – 17 January 1911), was an English Victorian era polymath: a statistician, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto- ...
employed Quetelet's ideas in his research on mathematical biology. In his experiments with sweet peas in the 1870s, Galton discovered that the spread of the distributions of a particular trait did not change over the generations. He invented what he called the "
quincunx" to demonstrate why mixtures of normal distributions were normal. Galton noticed that the means of a particular trait in the offspring generation differed from those of the parent generation, a phenomenon now known as
regression to the mean. He found that the slopes of the regression lines of two given variables were the same if the two data sets were scaled by units of probable error and introduced the notion of the correlation coefficient, but noted that
correlation does not imply causation
The phrase "correlation does not imply causation" refers to the inability to legitimately deduce a cause-and-effect relationship between two events or variables solely on the basis of an observed association or correlation between them. The id ...
.
During the late nineteenth century, British statisticians introduced a number of methods to relate and draw conclusions from statistical quantities.
Francis Edgeworth developed a test for
statistical significance
In statistical hypothesis testing, a result has statistical significance when it is very unlikely to have occurred given the null hypothesis (simply by chance alone). More precisely, a study's defined significance level, denoted by \alpha, is the p ...
that estimated the "fluctuations"—twice the variance in modern language—from two given means. By modern standards, however, he was extremely conservative when it comes to drawing conclusions about the significance of an observation. For Edgeworth, an observation was significant if it was at the level of 0.005, which is much stricter than the requirement of 0.05 to 0.01 commonly used today. Pearson defined the
standard deviation
In statistics, the standard deviation is a measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. A low standard deviation indicates that the values tend to be close to the mean (also called the expected value) of the set, while ...
and introduced the
-statistic (
chi-squared). Pearson's student,
George Udney Yule, demonstrated that one could compute the regression equation of a given data set using the
method of least squares.
In 1828, miller and autodidactic mathematician
George Green published ''
'', making use of the mathematics of potential theory developed by Continental mathematicians. But this paper fell on deaf ears until William Thomson read it, realised its significance, and had it re-printed in 1850. Green's work became a source of inspiration for the Cambridge school of mathematical physicists, which included Thomson himself, George Gabriel Stokes, and James Clerk Maxwell. Green's ''Essay'' contained what became known as
Green's theorem
In vector calculus, Green's theorem relates a line integral around a simple closed curve to a double integral over the plane region bounded by . It is the two-dimensional special case of Stokes' theorem.
Theorem
Let be a positively orient ...
, a basic result in vector calculus,
Green's identities
In mathematics, Green's identities are a set of three identities in vector calculus relating the bulk with the boundary of a region on which differential operators act. They are named after the mathematician George Green, who discovered Green's ...
, and the notion of
Green's functions, which appears in the study of differential equations.
Thomson went on to prove
Stokes' theorem
Stokes's theorem, also known as the Kelvin–Stokes theorem Nagayoshi Iwahori, et al.:"Bi-Bun-Seki-Bun-Gaku" Sho-Ka-Bou(jp) 1983/12Written in Japanese)Atsuo Fujimoto;"Vector-Kai-Seki Gendai su-gaku rekucha zu. C(1)" :ja:培風館, Bai-Fu-Kan( ...
, which earned that name after Stokes asked students to prove in the
Smith's Prize
The Smith's Prize was the name of each of two prizes awarded annually to two research students in mathematics and theoretical physics at the University of Cambridge from 1769. Following the reorganization in 1998, they are now awarded under the n ...
exam in 1854. Stokes learned it from Thomson in a letter in 1850. Stokes' theorem generalises Green's theorem, which itself is a higher-dimensional version of the
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
The fundamental theorem of calculus is a theorem that links the concept of differentiating a function (calculating its slopes, or rate of change at each time) with the concept of integrating a function (calculating the area under its graph, or ...
.
Research in physics—in particular elasticity, heat conduction, hydrodynamics, and electromagnetism—motivated the development of vector calculus in the nineteenth century.
Arthur Cayley
Arthur Cayley (; 16 August 1821 – 26 January 1895) was a prolific United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, British mathematician who worked mostly on algebra. He helped found the modern British school of pure mathematics.
As a child, C ...
is credited with the creation of the theory of
matrices—rectangular arrays of numbers—as distinct objects from
determinant
In mathematics, the determinant is a scalar value that is a function of the entries of a square matrix. It characterizes some properties of the matrix and the linear map represented by the matrix. In particular, the determinant is nonzero if and ...
s, studied since the mid-eighteenth century. The term ''matrix'' was coined by
James Joseph Sylvester
James Joseph Sylvester (3 September 1814 – 15 March 1897) was an English mathematician. He made fundamental contributions to matrix theory, invariant theory, number theory, partition theory, and combinatorics. He played a leadership ro ...
, a major contributor to the theory of determinants. It is difficult to overestimate the value of matrix theory to modern theoretical physics. Peter Tait wrote, prophetically, that Cayley was "forging the weapons for future generations of physicists."
Theoretical mechanics and optics
Early contributions study of elasticity—how objects behave under stresses, pressures, and loads— employed ''ad hoc'' hypotheses to solve specific problems. It was during the nineteenth century that scientists began to work out a thorough theory. In 1821, using an analogy with elastic bodies, French professor of mechanics
Claude-Louis Navier arrived at the basic equations of motion for viscous fluids.
George Gabriel Stokes re-derived them in 1845 using continuum mechanics in a paper titled "On the Theories of Internal Friction of Fluids in Motion." In it, Stokes sought to develop a mathematical description for all known fluids that take into account
viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
, or internal friction. These are now referred to as the
Navier–Stokes equations.
In 1852, Stokes showed that light
polarisation can be described in terms of what are now known as the
Stokes parameters. The Stokes parameters for a given wave may be viewed as a vector.
Founded in the eighteenth century, the
calculus of variations
The calculus of variations (or Variational Calculus) is a field of mathematical analysis that uses variations, which are small changes in functions
and functionals, to find maxima and minima of functionals: mappings from a set of functions t ...
grew into a much favored mathematical tool among physicists. Scientific problems thus became the impetus for the development of the subject.
William Rowan Hamilton
Sir William Rowan Hamilton Doctor of Law, LL.D, Doctor of Civil Law, DCL, Royal Irish Academy, MRIA, Royal Astronomical Society#Fellow, FRAS (3/4 August 1805 – 2 September 1865) was an Irish mathematician, astronomer, and physicist. He was the ...
advanced it in his course to construct a deductive framework for
optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behaviour of visible, ultraviole ...
; he then applied the same ideas to
mechanics
Mechanics (from Ancient Greek: μηχανική, ''mēkhanikḗ'', "of machines") is the area of mathematics and physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among physical objects. Forces applied to objects r ...
.
With an appropriate
variational principle, one could deduce the equations of motion for a given mechanical or optical system. Soon, scientists worked out the variational principles for the theory of elasticity, electromagnetism, and fluid mechanics (and, in the future, relativity and quantum theory). Whilst variational principles did not necessarily provide a simpler way to solve problems, they were of interest for philosophical or aesthetic reasons, though scientists at this time were not as motivated by religion in their work as their predecessors.
Hamilton's work in physics was great achievement; he was able to provide a unifying mathematical framework for wave propagation and particle motion.
In light of this description, it becomes clear why the wave and corpuscle theories of light were equally able to account for the phenomena of reflection and refraction. Hamilton's equations also proved useful in calculating planetary orbits.
In 1845,
John James Waterson submitted to the Royal Society a paper on the
kinetic theory of gases
Kinetic (Ancient Greek: κίνησις “kinesis”, movement or to move) may refer to:
* Kinetic theory, describing a gas as particles in random motion
* Kinetic energy, the energy of an object that it possesses due to its motion
Art and enter ...
that included a statement of the
equipartition theorem and a calculation of the ratio of the specific heats of gases. Although the paper was read before the Society and its abstract published, Waterson's paper faced antipathy. At this time, the kinetic theory of gases was considered highly speculative as it was based on the then not-accepted atomic hypothesis.
But by the mid-1850s, interest was revived. In the 1860s, James Clerk Maxwell published a series of papers on the subject. Unlike those of his predecessors, who were only using averages, Maxwell's papers were explicitly statistical in nature. He proposed that the speeds of molecules in a gas followed a distribution. Although the speeds would cluster around the average, some molecules were moving faster or slower than this average. He showed that this distribution is a function of temperature and mathematically described various properties of gases, such as diffusion and viscosity. He predicted, surprisingly, that the viscosity of a gas is independent of its density. This was verified at once by a series of experiments Maxwell conducted with his wife, Katherine. Experimental verification of the
Maxwell distribution
Maxwell may refer to:
People
* Maxwell (surname), including a list of people and fictional characters with the name
** James Clerk Maxwell, mathematician and physicist
* Justice Maxwell (disambiguation)
* Maxwell baronets, in the Baronetage of ...
was not obtained till 60 years later, however. In the meantime, the Austrian
Ludwig Boltzmann developed Maxwell's statistics further and
proved, in 1872, using the "
-function," that the Maxwellian distribution is stable and any non-Maxwellian distribution would morph into it.
In his ''Dynamics of Rigid Bodies'' (1877),
Edward John Routh noted the importance of what he called "absent coordinates," also known as cyclic coordinates or
ignorable coordinates (following the terminology of E. T. Whittaker). Such coordinates are associated with conserved momenta and as such are useful in problem solving. Routh also devised a new method for solving problems in mechanics. Although
Routh's procedure does not add any new insights, it allows for more systematic and convenient analysis, especially in problems with many degrees of freedom and at least some cyclic coordinates.
In 1899, at the request the British Association for the Advancement of Science from the year before,
Edmund Taylor Whittaker
Sir Edmund Taylor Whittaker (24 October 1873 – 24 March 1956) was a British mathematician, physicist, and historian of science. Whittaker was a leading mathematical scholar of the early 20th-century who contributed widely to applied mathema ...
submitted his ''Report on the Progress of Solution to the Problem of Three Bodies''. At that time, classical mechanics in general and the
three-body problem in particular captured the imagination of many talented mathematicians, whose contributions Whittaker covered in his ''Report''. Whittaker later incorporated the ''Report'' into his textbook titled ''
Analytical Dynamics of Particles and Rigid Bodies
''A Treatise on the Analytical Dynamics of Particles and Rigid Bodies'' is a treatise and textbook on analytical dynamics by British mathematician Sir Edmund Taylor Whittaker. Initially published in 1904 by the Cambridge University Press, the ...
'' (first edition 1907). It helped provide the scientific basis for the aerospace industry in the twentieth century. Despite its age, it remains in print in the early twenty-first century.
Thermodynamics, heat engines, and refrigerators

During the 1830s and 1840s, traditional caloric theory of heat began losing favour to "dynamical" alternatives, which posit that heat is a kind of motion. Brewer and amateur scientist
James Prescott Joule was one of the proponents of the latter. Joule's intricate experiments—the most successful of which involved heating water with paddle wheels—making full use of his skill in temperature control as a brewer, demonstrated decisively the reality of the "mechanical equivalent of heat." What would later become known as the "conservation of energy" was pursued by many other workers approaching the subject from a variety of backgrounds, from medicine and physiology to physics and engineering. Another notable contributor to this development was the German researcher
Hermann von Helmholtz
Hermann Ludwig Ferdinand von Helmholtz (31 August 1821 – 8 September 1894) was a German physicist and physician who made significant contributions in several scientific fields, particularly hydrodynamic stability. The Helmholtz Association, ...
, who gave an essentially Newtonian, that is, mechanical, account.
William Thomson (later Lord Kelvin) received the works of Joule and Helmholtz positively, embracing them as providing support for the emerging "science of energy."
In the late 1840s to the 1850s, Kelvin, his friend
William John Macquorn Rankine
William John Macquorn Rankine (; 5 July 1820 – 24 December 1872) was a Scottish mechanical engineer who also contributed to civil engineering, physics and mathematics. He was a founding contributor, with Rudolf Clausius and William Thomson ( ...
, and the German
Rudolf Clausius
Rudolf Julius Emanuel Clausius (; 2 January 1822 – 24 August 1888) was a German physicist and mathematician and is considered one of the central founding fathers of the science of thermodynamics. By his restatement of Sadi Carnot's principle ...
published a steady stream of papers concerning heat engines and an absolute temperature scale. Indeed, the commercial value of new science had already become apparent by this time; some businessmen were quite willing to offer generous financial support for researchers. Rankine spoke confidently of the new science of ''thermodynamics'', a term Kelvin coined in 1854, whose fundamental principles came to be known as the
First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and
Second Laws and whose core concepts were "energy" and "entropy."
Kelvin and
Peter Guthrie Tait's ''
Treatise on Natural Philosophy
''Treatise on Natural Philosophy'' was an 1867 text book by William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, William Thomson (later Lord Kelvin) and Peter Guthrie Tait, published by Oxford University Press.
The ''Treatise'' was often referred to as T and ''T^ ...
'' (1867) was an attempt to reformulate physics in terms of energy. Here, Kelvin and Tait introduced the phrase ''
kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its accele ...
'' (instead of 'actual'), now in standard usage. The phrase ''
potential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy held by an object because of its position relative to other objects, stresses within itself, its electric charge, or other factors.
Common types of potential energy include the gravitational potentia ...
'' was promoted by Rankine.
On the practical side, the food-preserving effect of low temperatures had long been recognised. Natural ice was vigorously traded in the early nineteenth century, but it was inevitably in short supply, especially in Australia. During the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, there was considerable commercial incentive to develop ever more effective
refrigerator
A refrigerator, colloquially fridge, is a commercial and home appliance consisting of a thermally insulated compartment and a heat pump (mechanical, electronic or chemical) that transfers heat from its inside to its external environment so th ...
s thanks to the expansion of agriculture in the Americas, Australia, and New Zealand and rapid urbanization in Western Europe. From the 1830s onward, refrigerators relied on the expansion of compressed air or the evaporation of a volatile liquid; evaporation became the basis of all modern refrigerator designs. Long-distance shipping of perishable foods, such as meat, boomed in the late 1800s.
On the theoretical side, new refrigeration techniques were also of great value. From his
absolute temperature scale, Lord Kelvin deduced the existence of absolute zero occurring at −273.15 °C. Scientists began trying to reach ever lower temperatures and to liquefy every gas they encountered. This paved the way for the development of
low-temperature physics
In physics, cryogenics is the production and behaviour of materials at very low temperatures.
The 13th IIR International Congress of Refrigeration (held in Washington DC in 1971) endorsed a universal definition of “cryogenics” and “cr ...
and the
Third Law of Thermodynamics
The third law of thermodynamics states, regarding the properties of closed systems in thermodynamic equilibrium: This constant value cannot depend on any other parameters characterizing the closed system, such as pressure or applied magnetic fiel ...
.
Natural history
This study of natural history was most powerfully advanced by
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
and his theory of
evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
first published in his book ''
On the Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
'' in 1859.
Research in geology and evolutionary biology naturally led to the question of how old the Earth was. Indeed, between the mid-1700s to the mid-1800s, this was the topic of increasingly sophisticated intellectual discussions. With the advent of thermodynamics, it became clear that the Earth and the Sun must have an old but finite age. Whatever the energy source of the Sun, it must be finite, and since it is constantly dissipating, there must be a day when the Sun runs out of energy. Lord Kelvin wrote in 1852, "...within a finite period of time past the earth must have been, and within a finite period of time to come the earth must again be, unfit for the habitation of man as at present constituted, unless operations have been, or are to be performed, which are impossible under the laws to which the known operations going on are subject." In the 1860s, Kelvin employed a mathematical model by von Helmholtz suggesting that the energy of the Sun is released via gravitational collapse to calculate the age of the Sun to be between 50 and 500 million years. He reached comparable figures for the Earth. The missing ingredient here was radioactivity, which was not known to science till the end of the nineteenth century.
Electricity, magnetism, and electrification

After the Dane
Hans Christian Ørsted
Hans Christian Ørsted ( , ; often rendered Oersted in English; 14 August 17779 March 1851) was a Danish physicist and chemist who discovered that electric currents create magnetic fields, which was the first connection found between electricity ...
demonstrated that it was possible to deflect a magnetic needle by closing or opening an electric circuit nearby, a deluge of papers attempting explain the phenomenon was published.
Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English scientist who contributed to the study of electromagnetism and electrochemistry. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic inducti ...
set himself to the task of clarifying the nature of electricity and magnetism by experiments. In doing so, he devised what could be described as the first
electric motor
An electric motor is an Electric machine, electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a Electromagneti ...
(though it does not resemble a modern one), a
transformer
A transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer' ...
(now used to step up the voltage and step down the current or vice versa), and a
dynamo (which contains the basics of all electric turbine generators).
The practical value of Faraday's research on electricity and magnetism was nothing short of revolutionary. A dynamo converts mechanical energy into an electrical current whilst a motor does the reverse. The world's first power plants entered service in 1883, and by the following year, people realized the possibility of using electricity to power a variety of household appliances. Inventors and engineers soon raced to develop such items, starting with affordable and durable incandescent light bulbs, perhaps the most important of the early applications of electricity.
As the foremost expert on electricity and magnetism at the time, Lord Kelvin oversaw the laying of the trans-Atlantic telegraphic cable, which became successful in 1866.
Drawing on the work of his predecessors, especially the experimental research of Michael Faraday, the analogy with heat flow by Lord Kelvin, and the mathematical analysis of George Green,
James Clerk Maxwell
James Clerk Maxwell (13 June 1831 – 5 November 1879) was a Scottish mathematician and scientist responsible for the classical theory of electromagnetic radiation, which was the first theory to describe electricity, magnetism and ligh ...
synthesized all that was known about electricity and magnetism into a single mathematical framework,
Maxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits.
...
.
Maxwell used his equations to predict the existence of electromagnetic waves, which travel at the speed of light. In other words, light is but one kind of electromagnetic wave. Maxwell's theory predicted there ought to be other types, with different frequencies. After some ingenious experiments, Maxwell's prediction was confirmed by German physicist
Heinrich Hertz
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz ( ; ; 22 February 1857 – 1 January 1894) was a German physicist who first conclusively proved the existence of the electromagnetic waves predicted by James Clerk Maxwell's Maxwell's equations, equations of electrom ...
. In the process, Hertz generated and detected what are now called radio waves and built crude radio antennas and the predecessors of satellite dishes.
Dutch physicist
Hendrik Lorentz
Hendrik Antoon Lorentz (; 18 July 1853 – 4 February 1928) was a Dutch physicist who shared the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Pieter Zeeman for the discovery and theoretical explanation of the Zeeman effect. He also derived the Lorentz t ...
derived, using suitable boundary conditions,
Fresnel's equations
The Fresnel equations (or Fresnel coefficients) describe the reflection and transmission of light (or electromagnetic radiation in general) when incident on an interface between different optical media. They were deduced by Augustin-Jean Fresne ...
for the reflection and transmission of light in different media from Maxwell's equations. He also showed that Maxwell's theory succeeded in illuminating the phenomenon of light dispersion where other models failed. John William Strutt, 3rd Baron Rayleigh, John William Strutt (Lord Rayleigh) and the American Josiah Willard Gibbs then proved that the optical equations derived from Maxwell's theory are the only self-consistent description of the reflection, refraction, and dispersion of light consistent with experimental results. Optics thus found a new foundation in electromagnetism.
But it was Oliver Heaviside, an enthusiastic supporter of Maxwell's electromagnetic theory, who deserves most of the credit for shaping how people understood and applied Maxwell's work for decades to come.
Maxwell originally wrote down a grand total of 20 equations for the electromagnetic field, which he later reduced to eight. Heaviside rewrote them in the form commonly used today, just four expressions. In addition, Heaviside was responsible for considerable progress in electrical telegraphy, telephony, and the study of the propagation of electromagnetic waves. Independent of Gibbs, Heaviside assembled a set of mathematical tools known as vector calculus to replace the quaternions, which were in vogue at the time but which Heaviside dismissed as "antiphysical and unnatural."
Faraday also investigated how electrical currents affected chemical solutions. His experiments led him to the two laws of electrochemistry. Together with Whewell, Faraday introduced the basic vocabulary for the subject, the words ''electrode'', ''anode'', ''cathode'', ''electrolysis'', ''electrolyte'', ''ion'', ''anion'', and ''cation''. They remain in standard usage. But Faraday's work was of value to more than just chemists. In his Faraday Memorial Lecture in 1881, the German Hermann von Helmholtz asserted that Faraday's laws of electrolysis, Faraday's laws of electrochemistry hinted at the atomic structure of matter. If the chemical elements were distinguishable from one another by simple ratios of mass, and if the same amounts of electricity deposited amounts of these elements upon the poles in ratios, then electricity must also come in as discrete units, later named electrons.
In the late nineteenth century, the nature of the energy emitted by the discharge between high-voltage electrodes inside an evacuated tube—cathode rays—attracted the attention of many physicists. While the Germans thought cathode rays were waves, the British and the French believed they were particles. Working at the Cavendish Laboratory, established by Maxwell, J. J. Thomson directed a dedicate experiment demonstrating that cathode rays were in fact negatively charged particles, now called electrons. The experiment enabled Thompson to calculate the ratio between the magnitude of the charge and the mass of the particle (
). In addition, because the ratio was the same regardless of the metal used, Thompson concluded that electrons must be a constituent of all atoms. Although the atoms of each chemical elements have different numbers of electrons, all electrons are identical.
Computer science and logic
Inspired by the explorations in abstract algebra of George Peacock (mathematician), George Peacock and Augustus De Morgan, Augustus de Morgan, George Boole published a book titled ''An Investigation of the Laws of Thought'' (1854), in which he brought the study of logic from philosophy and metaphysics to mathematics. His stated goal was to "investigate the fundamental laws of those operations of the mind by which reasoning is performed; to give expression to them in the symbolical language of a Calculus, and upon this foundation to establish the science of logical and construct its methods." Although ignored at first, Boolean algebra, as it is now known, became central to the design of circuits and computers in the following century.
The desire to construct calculating machines is not new. In fact, it can be traced all the way back to the Hellenistic Civilization. While people have devised such machines over the centuries, mathematicians continued to perform calculations by hand, as machines offered little advantage in speed. For complicated calculations, they employed tables, especially of logarithmic and trigonometric functions, which were computed by hand. But right in the middle of the Industrial Revolution in England, Charles Babbage thought of using the all-important steam engine to power a mechanical computer, the Difference Engine. Unfortunately, whilst Babbage managed to secure government funds for the construction of the machine, the government subsequently lost interest and Babbage faced considerable troubles developing the necessary machine components. He abandoned the project to pursue a new one, his Analytical Engine. By 1838, he had worked out the basic design. Like a modern computer, it consisted of two basic parts, one that stores the numbers to be processed (the store), and one that performed the operations (the mill). Babbage adopted the concept of punch cards from the French engineer Joseph Jacquard, who had used it to automate the textile industry in France, to control the operations of his Analytical Engine. Unfortunately, he again lacked the financial resources to build it, and so it remained a theoretical construct. But he did leave behind detailed notes and engineering drawings, from which modern experts conclude that the technology of the time was advanced enough to actually build it, even if he never had enough money to do so.
In 1840, Babbage went to Turin to give lectures on his work designing the Analytical Engine to Italian scientists. Ada Lovelace translated the notes published by one of the attendees into English and heavily annotated it. She wrote down the very first computer program, in her case one for computing the Bernoulli numbers. She employed what modern computer programmers would recognise as Loop (computing), loops and decision steps, and gave a detailed diagram, possibly the first flowchart ever created.
She noted that a calculating machine could perform not just arithmetic operations but also symbolic manipulations. On the limitations and implications of the computer, she wrote,
Communication and transportation
Steam ships

Steam ships were one of the keys to Britain's prosperity in the nineteenth century. This technology, which predates the Victorian era, had a long a rich history. Starting in the late 1700s, people had begun building steam-powered ships with ever increasing size, operational range, and speed, first to cross the English Channel and then the Atlantic and finally to reach places as far away as India and Australia without having to refuel mid-route. International trade and travel boosted demand, and there was intense competition among the shipping companies.
Steam ships such as the SS Great Britain, SS ''Great Britain'' and SS Great Western, SS ''Great Western'' made international travel more common but also advanced trade, so that in Britain it was not just the luxury goods of earlier times that were imported into the country but essentials and raw materials such as corn and cotton from the United States and meat and wool from Australia.
At 693 feet long, 120 feet wide and weighing over 18,900 tons, the SS Great Eastern, SS ''Great Eastern'' was the largest ship built at the time, capable of transporting 4,000 passengers from Britain to Australia without having to refuel along the way. Even when she was finally broken up for scraps in 1888, she was still the largest ship in the world. Her record was not broken till the Edwardian era with super liners like the ''Lusitania'' in 1907, the ''Titanic'' in 1912. Yet despite being a remarkable feat of engineering, the ''Great Eastern'' became more and more of a white elephant as smaller and faster ships were in greater demand. Nevertheless, she gained a new lease of life when she was chartered to lay telegraphic cables across the Atlantic, and then to India. Her size and range made her ideally suited for the task.
The British government had long realised that national prosperity depended on trade. For that reason, it deployed the Royal Navy to protect maritime trade routes and financed the construction of many steam ships.
Telegraphy, telephony, the wireless, and photography
File:James Pollard - The Louth-London Royal Mail Travelling by Train from Peterborough East, Northamptonshire - Google Art Project.jpg, ''The Louth-London Royal Mail Travelling by Train from Peterborough East, Northamptonshire'' (1845) by James Pollard.
File:All Red Line.jpg, The British Empire's All Red Line, submarine telegraphic cable network eventually connected all of its major possessions.
Although the idea of transmitting messages via electrical signals dated back to the eighteenth century, it was not until the 1820s that advances in the study of electricity and magnetism made that a practical reality. In 1837, William Fothergill Cooke and Charles Wheatstone invented a telegraphic system that used electrical currents to deflect magnetic needles, thus transmitting coded messages. This Cooke and Wheatstone telegraph, design soon made its way all across Britain, appearing in every town and post office. By the mid-1800s, a telegraphic cable was laid across the English Channel, the Irish Sea, and the North Sea. In 1866, the SS ''Great Eastern'' successfully laid the Transatlantic telegraph cable, transatlantic telegraphic cable. A global network boomed towards the end of the century.
In 1876, Alexander Graham Bell patented the telephone. Like the telegraph, the telephone enabled rapid personal communication. A little over a decade later, 26,000 telephones were in service in Britain (and 150,000 in America). Multiple switchboards were installed in every major town and city.
Hertz's experimental work in electromagnetism stimulated interest in the possibility of wireless communication, which did not require long and expensive cables and was faster than even the telegraph. Receiving little support in his native Italy, Guglielmo Marconi moved to England and adapted Hertz's equipment for this purpose in the 1890s. He achieved the first international wireless transmission between England and France in 1900 and by the following year, he succeeded in sending messages in Morse code across the Atlantic. Seeing its value, the shipping industry adopted this technology at once. Radio broadcasting became extremely popular in the twentieth century and remains in common use in the early twenty-first.
In fact, the global communications network of the twenty-first century has its roots in the Victorian era.
Photography was realised in 1839 by Louis Daguerre in France and William Fox Talbot in Britain. By 1889, hand-held cameras were available.
Another important innovation in communications was the Penny Black, the first postage stamp, which standardised postage to a flat price regardless of distance sent.
Railways
A central development during the Victorian era was the rise of rail transport. The new railways all allowed goods, raw materials, and people to be moved about, rapidly facilitating trade and industry. The financing of railways became an important specialty of London's financiers. They retained an ownership share even while turning over management to locals; that ownership was largely liquidated in 1914–1916 to pay for the World War. Railroads originated in England because industrialists had already discovered the need for inexpensive transportation to haul coal for the new steam engines, to supply parts to specialized factories, and to take products to market. The existing system of canals was inexpensive but was too slow and too limited in geography. The railway system led to a reorganisation of society more generally, with "railway time" being the standard by which clocks were set throughout Britain; the complex railway system setting the standard for technological advances and efficiency.
The engineers and businessmen needed to create and finance a railway system were available; they knew how to invent, to build, and to finance a large complex system. The first quarter of the 19th century involved numerous experiments with locomotives and rail technology. By 1825 railways were commercially feasible, as demonstrated by George Stephenson (1791–1848) when he built the Stockton and Darlington. On his first run, his locomotive pulled 38 freight and passenger cars at speeds as high as 12 miles per hour. Stephenson went on to design many more railways and is best known for standardizing designs, such as the "standard gauge" of rail spacing, at 4 feet 8 inches.
Thomas Brassey (1805–70) was even more prominent, operating construction crews that at one point in the 1840s totalled 75,000 men throughout Europe, the British Empire, and Latin America. Brassey took thousands of British engineers and mechanics across the globe to build new lines. They invented and improved thousands of mechanical devices, and developed the science of civil engineering to build roadways, tunnels and bridges. Britain had a superior financial system based in London that funded both the railways in Britain and also in many other parts of the world, including the United States, up until 1914. The boom years were 1836 and 1845–47 when Parliament authorised 8,000 miles of lines at a projected cost of £200 million, which was about the same value as the country's annual Gross Domestic Product (GDP) at that time. A new railway needed a charter, which typically cost over £200,000 (about $1 million) to obtain from Parliament, but opposition could effectively prevent its construction. The canal companies, unable or unwilling to upgrade their facilities to compete with railways, used political power to try to stop them. The railways responded by purchasing about a fourth of the canal system, in part to get the right of way, and in part to buy off critics. Once a charter was obtained, there was little government regulation, as laissez-faire and private ownership had become accepted practices.
The different lines typically had exclusive territory, but given the compact size of Britain, this meant that multiple competing lines could provide service between major cities. George Hudson (1800–1871) became the "railway king" of Britain. He merged various independent lines and set up a "Clearing House" in 1842 which rationalized interconnections by establishing uniform paperwork and standard methods for transferring passengers and freight between lines, and rates when one system used freight cars owned by another. By 1850, rates had fallen to a penny a ton mile for coal, at speeds of up to fifty miles an hour. Britain now had had the model for the world in a well integrated, well-engineered system that allowed fast, cheap movement of freight and people, and which could be replicated in other major nations.
The railways directly or indirectly employed tens of thousands of engineers, mechanics, repairmen and technicians, as well as statisticians and financial planners. They developed new and more efficient and less expensive techniques. Most important, they created a mindset of how technology could be used in many different forms of business. Railways had a major impact on industrialization. By lowering transportation costs, they reduced costs for all industries moving supplies and finished goods, and they increased demand for the production of all the inputs needed for the railroad system itself. By 1880, there were 13,500 locomotives which each carried 97,800 passengers a year, or 31,500 tons of freight.
Member of Parliament and Solicitor to the City of London Charles Pearson campaigned for an underground rail service in London. Parts of the first such railway, the Metropolitan line, Metropolitan Line, opened to the public in 1863, thereby becoming the first subway line in the world. Trains were originally steam-powered, but in 1890, the first electric trains entered service. That same year, the whole system became officially known as the Tube after the shape of the rail tunnels. (It was not until 1908 that the name London Underground was introduced.)
India provides an example of the London-based financiers pouring money and expertise into a very well built system designed for military reasons (after the Mutiny of 1857), and with the hope that it would stimulate industry. The system was overbuilt and much too elaborate and expensive for the small amount of freight traffic it carried. However, it did capture the imagination of the Indians, who saw their railways as the symbol of an industrial modernity—but one that was not realised until a century or so later.
Public safety, health and medicine
A Coal gas, gas Cross-link, network for Gas lighting, lighting and Gas heater, heating was introduced in the 1880s.
[Anthony S. Wohl, ''Endangered lives: public health in Victorian Britain'' (JM Dent and Sons, 1983)] The model town of Saltaire was founded, along with others, as a planned environment with good sanitation and many civic, educational and recreational facilities, although it lacked a pub, which was regarded as a focus of dissent. Although initially developed in the early years of the 19th century, gas lighting became widespread during the Victorian era in industry, homes, public buildings and the Street light, streets. The invention of the Incandescence, incandescent gas mantle in the 1890s greatly improved light output and ensured its survival as late as the 1960s. Hundreds of gasworks were constructed in cities and towns across the country. In 1882, incandescent electric lights were introduced to London streets, although it took many years before they were installed everywhere.
Medicine progressed during Queen Victoria's reign. In fact, medicine at the start of the nineteenth century was little different from that in the medieval era whereas by the end of the century, it became a lot closer to twenty-first century practice thanks to advances in science, especially microbiology, paving the way for the germ theory of disease. This was during the height of the Industrial Revolution, and urbanisation occurred at a frantic pace. As the population density of the cities grew, epidemics of cholera, smallpox, tuberculosis, and typhus were commonplace.
After studying previous outbreaks, physician John Snow drew the conclusion that cholera was a water-borne disease. When the 1854 broke out, Snow mapped the locations of the cases in Soho, London, and found that they centered around a well he deemed contaminated. He asked that the pump's handle be replaced, after which the epidemic petered out. Snow also discovered that households whose water supplies came from companies that used the Thames downstream, after many sewers had flown into the river, were fourteen times more likely to die from cholera. He thus recommended boiling water before use.
Sanitation reforms, prompted by the Public Health Acts Public Health Act 1848, 1848 and 1869, were made in the crowded, dirty streets of the existing cities, and soap was the main product shown in the relatively new phenomenon of advertising. A great engineering feat in the Victorian Era was the London sewerage system, sewage system in London. It was designed by Joseph Bazalgette in 1858. He proposed to build of sewer system linked with over of street sewers. Many problems were encountered but the sewers were completed. After this, Bazalgette designed the Thames Embankment which housed sewers, water pipes and the London Underground. During the same period, London's water supply network was expanded and improved.
John Simon (pathologist), John Simon, as chief medical officer of the General Board of Health, secured funds for research into various common infectious diseases at the time, including cholera, diphtheria, smallpox, and typhus. Using his political influence, he garnered support for the Public Health Act 1875, Public Health Act of 1875, which focused on preventative measures in housing, the water supply, sewage and drainage, providing Britain with an extensive public health system.

By mid-century, the stethoscope became an oft-used device and designs of the microscope had advanced enough for scientists to closely examine pathogens. The pioneering work of French microbiologist Louis Pasteur from the 1850s earned widespread acceptance for the germ theory of disease.
It led to the introduction antiseptics by Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister in 1867 in the form of carbolic acid (phenol).
He instructed the hospital staff to wear gloves and wash their hands, instruments, and dressings with a phenol solution and in 1869, he invented a machine that would spray carbolic acid in the operating theatre during surgery.
Infection-related deaths fell noticeably as a result.
As the British Empire expanded, Britons found themselves facing novel climates and contagions; there was active research into tropical diseases. In 1898, Ronald Ross proved that the mosquito was responsible for spreading malaria.
Although nitrous oxide, or laughing gas, had been proposed as an anaesthetic as far back as 1799 by
Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for t ...
, it was not until 1846 when an American dentist named William T.G. Morton, William Morton started using diethyl ether, ether on his patients that anaesthetics became common in the medical profession.
In 1847 chloroform was introduced as an anaesthetic by James Young Simpson.
Chloroform was favoured by doctors and hospital staff because it is much less flammable than ether, but critics complained that it could cause the patient to have a heart attack.
Chloroform gained in popularity in England and Germany after John Snow gave Queen Victoria chloroform for the birth of her eighth child (Prince Leopold).
By 1920, chloroform was used in 80 to 95% of all narcoses performed in the UK and German-speaking countries.
A combination of antiseptics and anaesthetics helped surgeons operate more carefully and comfortably on their patients.
Anaesthetics made painless dentistry possible. At the same time sugar consumption in the British diet increased, greatly increasing instances of tooth decay.
As a result, more and more people were having teeth extracted and needing dentures. This gave rise to "Waterloo Teeth", which were real human teeth set into hand-carved pieces of ivory from hippopotamus or walrus jaws.
The teeth were obtained from executed criminals, victims of battlefields, from grave-robbers, and were even bought directly from the desperately impoverished.
The increase in tooth decay also brought the first prominent recommendation for fluoride as a nutrient, particularly in pregnancy and childhood, in 1892.
News of the discovery of X-rays in 1895 spread like wildfire. Its medical value was realised immediately, and within a year, doctors were prescribing X-rays for diagnosis, in particular to locate bone fractures and foreign objects inside the patient's body. Radioactivity was discovered 1896, and was later to used to treat cancer.
During the second half of the nineteenth century, British medical doctors became increasingly specialised, following the footsteps of their German counterparts, and more hospitals were built. Surgeons began wearing gowns in the operating room and doctors white coats and stethoscopes, sights that are common in the early twenty-first century.
Yet despite all the aforementioned medical advances, the mortality rate fell only marginally, from 20.8 per thousand in 1850 to 18.2 by the end of the century. Urbanisation aided the spread of diseases and squalid living conditions in many places exacerbated the problem. Moreover, while some diseases, such as cholera, were being driven out, others, such as Sexually transmitted infection, sexually transmitted diseases, made themselves felt.
Moral standards
Victorian morality was a surprising new reality. The changes in moral standards and actual behaviour across the British were profound. Historian Harold Perkin wrote:
Between 1780 and 1850 the English ceased to be one of the most aggressive, brutal, rowdy, outspoken, riotous, cruel and bloodthirsty nations in the world and became one of the most inhibited, polite, orderly, tender-minded, prudish and hypocritical.
Historians continue to debate the various causes of this dramatic change.
Asa Briggs
Asa Briggs, Baron Briggs (7 May 1921 – 15 March 2016) was an English historian. He was a leading specialist on the Victorian era, and the foremost historian of broadcasting in Britain. Briggs achieved international recognition during his lon ...
emphasizes the strong reaction against the French Revolution, and the need to focus British efforts on its defeat and not be diverged by pleasurable sins. Briggs also stresses the powerful role of the evangelical movement among the Nonconformists, as well as the evangelical faction inside the established Church of England. The religious and political reformers set up organizations that monitored behaviour, and pushed for government action.
Among the higher social classes, there was a marked decline in gambling, horse races, and obscene theatres; there was much less heavy gambling or patronage of upscale houses of prostitution. The highly visible debauchery characteristic of aristocratic England in the early 19th century simply disappeared.
Historians agree that the middle classes not only professed high personal moral standards, but actually followed them. There is a debate whether the working classes followed suit. Moralists in the late 19th century such as Henry Mayhew decried the slums for their supposed high levels of cohabitation without marriage and illegitimate births. However new research using computerized matching of data files shows that the rates of cohabitation were quite low—under 5%—for the working class and the poor. By contrast, in 21st-century Britain nearly half of all children are born outside marriage, and nine in ten newlyweds have been cohabitating.
Crime, police and prisons
Crime was getting exponentially worse. There were 4,065 arrests for criminal offenses in 1805, tripling to 14,437 in 1835 and doubling to 31,309 in 1842 in England and Wales.
18th-century British criminology had emphasized severe punishment. Slowly capital punishment was replaced by transportation, first to the American colonies and then to Australia, and, especially, by long-term incarceration in newly built prisons. As one historian points out, "Public and violent punishment which attacked the body by branding, whipping, and hanging was giving way to reformation of the mind of the criminal by breaking his spirit, and encouraging him to reflect on his shame, before labour and religion transformed his character." Crime rates went up, leading to calls for harsher measures to stop the 'flood of criminals' released under the penal servitude system. The reaction from the committee set up under the commissioner of prisons, Colonel Edmund Frederick du Cane, was to increase minimum sentences for many offences with deterrent principles of 'hard labour, hard fare, and a hard bed'. As the prisons grew more numerous, they became more depraved. Historian S. G. Checkland says, "It was sunk in promiscuity and squalor, jailers' tyranny and greed, and administrative confusion." In 1877 du Cane encouraged Benjamin Disraeli, Disraeli's government to remove all prisons from local government; he held a firm grip on the prison system till his forced retirement in 1895. By the 1890s, the prison population was over 20,000.
By the Victorian era, penal transportation to Australia was falling out of use since it did not reduce crime rates. The British penal system underwent a transition from harsh punishment to reform, education, and training for post-prison livelihoods. The reforms were controversial and contested. In 1877–1914 era a series of major legislative reforms enabled significant improvement in the penal system. In 1877, the previously localized prisons were nationalized in the Home Office under a Prison Commission. The Prison Act of 1898 enabled the Home Secretary to impose multiple reforms on his own initiative, without going through the politicized process of Parliament. The Probation of Offenders Act of 1907 introduced a new probation system that drastically cut down the prison population, while providing a mechanism for transition back to normal life. The Criminal Justice Administration Act of 1914 required courts to allow a reasonable time before imprisonment was ordered for people who did not pay their fines. Previously tens of thousands of prisoners had been sentenced solely for that reason. The Borstal system after 1908 was organized to reclaim young offenders, and the Children Act of 1908 prohibited imprisonment under age 14, and strictly limited that of ages 14 to 16. The principal reformer was Sir Evelyn Ruggles-Brise, the chair of the Prison Commission.
The infamous Whitechapel murders, purportedly composed by serial killer Jack the Ripper, were committed in London in 1888, during the mid-to-late chapter of the Victorian era.
Prostitution
During Victorian England, prostitution was seen as a "great social evil" by clergymen and major news organizations, but many feminists viewed prostitution as a means of economic independence for women. Estimates of the number of prostitutes in London in the 1850s vary widely, but in his landmark study, ''Prostitution'', William Acton (doctor), William Acton reported an estimation of 8,600 prostitutes in London alone in 1857.
The differing views on prostitution have made it difficult to understand its history.
Judith Walkowitz has multiple works focusing on the feminist point of view on the topic of prostitution. Many sources blame economic disparities as leading factors in the rise of prostitution, and Walkowitz writes that the demographic within prostitution varied greatly. However, women who struggled financially were much more likely to be prostitutes than those with a secure source of income. Orphaned or half-orphaned women were more likely to turn to prostitution as a means of income.
While overcrowding in urban cities and the amount of job opportunities for females were limited, Walkowitz argues that there were other variables that lead women to prostitution. Walkowitz acknowledges that prostitution allowed for women to feel a sense of independence and self-respect.
Although many assume that pimps controlled and exploited these prostitutes, some women managed their own clientele and pricing. It is evident that women were exploited by this system, yet Walkowitz says that prostitution was often their opportunity to gain social and economic independence.
Prostitution at this time was regarded by women in the profession to be a short-term position, and once they earned enough money, there were hopes that they would move on to a different profession.
As previously stated, the arguments for and against prostitution varied greatly from it being perceived as a mortal sin or desperate decision to an independent choice. While there were plenty of people publicly denouncing prostitution in England, there were also others who took opposition to them. One event that sparked a lot of controversy was the implementation of the Contagious Diseases Acts. This was a series of three acts in 1864, 1866 and 1869 that allowed police officers to stop women whom they believed to be prostitutes and force them to be examined.
If the suspected woman was found with a venereal disease, they placed the woman into a Lock Hospital. Arguments made against the acts claimed that the regulations were unconstitutional and that they only targeted women.
In 1869, a National Association in opposition of the acts was created. Because women were excluded from the first National Association, the Ladies National Association was formed. The leader of that organization was Josephine Butler.
Butler was an outspoken feminist during this time who fought for many social reforms. Her book ''Personal Reminiscences of a Great Crusade'' describes her oppositions to the C.D. acts. Along with the publication of her book, she also went on tours condemning the C.D. acts throughout the 1870s.
Other supporters of reforming the acts included Quakers, Methodists and many doctors.
Eventually the acts were fully repealed in 1886.
The book ''Prostitution-Action'' by Dr. William Acton (doctor), William Acton included detailed reports on his observations of prostitutes and the hospitals they would be placed in if they were found with a venereal disease.
Acton believed that prostitution was a poor institution but it is a result of the supply and demand for it. He wrote that men had sexual desires and they sought to relieve them, and for many, prostitution was the way to do it.
While he referred to prostitutes as wretched women, he did note how the acts unfairly criminalized women and ignored the men involved.
Events
;1832: Passage of the first Reform Act.
[Swisher, Clarice, ed. ''Victorian England''. San Diego: Greenhaven Press, 2000. pp. 248–250]
;1833: The first Tract for the Times is written by
John Henry Newman
John Henry Newman (21 February 1801 – 11 August 1890) was an English theologian, academic, intellectual, philosopher, polymath, historian, writer, scholar and poet, first as an Anglican ministry, Anglican priest and later as a Catholi ...
, starting the Oxford Movement in the Church of England.
;1837: Ascension of Queen Victoria to the throne.
;1838: Publication of The People's Charter, a working-class manifesto, launches the Chartism movement for political reform. The Treaty of Balta Liman (Great Britain trade alliance with the Ottoman Empire).
;1839:
First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
(1839–42) fought between Britain and China.
;1840:
Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until Death and state funeral of Queen Victoria, her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 21 ...
marries
Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfield
Prince Albert of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha (Franz August Karl Albert Emanuel; 26 August 1819 – 14 December 1861) was the consort of Queen Victoria from their marriage on 10 February 1840 until his death in 1861.
Albert was born in the Saxon duch ...
. He had been naturalisation, naturalised and granted the British style of ''Royal Highness'' beforehand. For the next 17 years, he was known as ''HRH'' Prince Albert.
;1840: New Zealand becomes a British colony, through the
Treaty of Waitangi and no longer part of New South Wales
;1842: Chartism reaches a second climax with the presentation of 3 million signatures on its second Petition; Chartism launches a general strike across the northern and midland industrial districts. The
Treaty of Nanking gives British traders dominance in Chinese port cities. The Massacre of Elphinstone's Army by the Afghans results in the death or incarceration of 16,500 soldiers and civilians. The Mines Act of 1842 banned women/children from working in coal, iron, lead and tin mining.
''The Illustrated London News'' was first published.
;1845: The Great Famine (Ireland), Irish famine begins. Within five years it would become the UK's List of disasters of the United Kingdom and preceding states, worst human disaster, with starvation and emigration reducing the population of Ireland itself by over 50%. The famine permanently changed Ireland's and Scotland's demographics and became a rallying point for nationalist sentiment that pervaded British politics for much of the following century.
;1846: Repeal of the
Corn Laws opens era of free trade.
;1848: Death of 2,000 people a week in a cholera epidemic.
;1850: Restoration of the Roman Catholicism in the United Kingdom, Roman Catholic hierarchy in England and Wales. (Scotland Restoration of the Scottish hierarchy, followed in 1878.)
;1851:
The Great Exhibition
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary structure in which it was held), was an international exhibition which took pl ...
(the first World's Fair) is held at the Crystal Palace, with great success and international attention. The Victorian gold rush. In ten years the Australian population nearly tripled.
;1854:
Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the de ...
: Britain, France and Turkey declare limited war on Russia. Russia loses, but very high British casualties makes the work of the nurses led by
Florence Nightingale
Florence Nightingale (; 12 May 1820 – 13 August 1910) was an English Reform movement, social reformer, statistician and the founder of modern nursing. Nightingale came to prominence while serving as a manager and trainer of nurses during t ...
famous.
;1857: The Indian Rebellion of 1857, Indian Mutiny, a concentrated revolt in northern India against the rule of East India Company, the privately owned British East India Company, is sparked by ''
sepoy
''Sepoy'' () was the Persian-derived designation originally given to a professional Indian infantryman, traditionally armed with a musket, in the armies of the Mughal Empire.
In the 18th century, the French East India Company and its oth ...
s'' (native Indian soldiers) in the company's army. The rebellion, involving not just sepoys but many sectors of the Indian population as well, is largely quashed within a year. The East India Company is replaced by the British government beginning the period of the British Raj.
;1858: The Prime Minister, Lord Palmerston, responds to the Orsini affair, Orsini plot against French Emperor Napoleon III of France, Napoleon III, the bombs for which were purchased in Birmingham, by attempting to make such acts a felony; the resulting uproar forces him to resign.
;1859:
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin ( ; 12 February 1809 – 19 April 1882) was an English naturalist, geologist, and biologist, widely known for his contributions to evolutionary biology. His proposition that all species of life have descended fr ...
publishes ''
On the Origin of Species
''On the Origin of Species'' (or, more completely, ''On the Origin of Species by Means of Natural Selection, or the Preservation of Favoured Races in the Struggle for Life''),The book's full original title was ''On the Origin of Species by Me ...
'', which leads to Reaction to Darwin's theory, various reactions.
Victoria and Albert's first grandchild, Prince Wilhelm of Prussia, is born – he later became William II, German Emperor.
John Stuart Mill
John Stuart Mill (20 May 1806 – 7 May 1873) was an English philosopher, political economist, Member of Parliament (MP) and civil servant. One of the most influential thinkers in the history of classical liberalism, he contributed widely to ...
publishes ''On Liberty'', a defence of the famous harm principle.
;1861: Death of Albert, Prince Consort, Prince Albert;
Queen Victoria refuses to go out in public for many years, and when she did she wore a widow's Bonnet (headgear), bonnet instead of the crown.
;1865:
Lewis Carroll
Charles Lutwidge Dodgson (; 27 January 1832 – 14 January 1898), better known by his pen name Lewis Carroll, was an English author, poet and mathematician. His most notable works are ''Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' (1865) and its sequel ...
's ''
Alice's Adventures in Wonderland'' is published.
;1866: An angry crowd in London, protesting against John Russell, 1st Earl Russell, John Russell's resignation as Prime Minister, is barred from Hyde Park, London, Hyde Park by the Law enforcement in the United Kingdom, police; they tear down iron guard rail, railings and trample on garden, flower beds. Disturbances like this convince Derby and Disraeli of the need for further parliamentary reform.
;1867: The Constitution Act, 1867 passes and British North America becomes Dominion of Canada.
;1870-1899: A series of educational reforms leads to the introduction of compulsory education for 5- to 12-year-olds (13-year-olds in Scotland) and universal access to free State school, state primary education in Great Britain.
;1875: Britain purchased Egypt's shares in the Suez Canal
as the African nation was forced to raise money to pay off its Isma'il Pasha#Suez Canal, debts.
;1876: Scottish-born inventor Alexander Graham Bell patents the telephone.
;1878: Treaty of Berlin (1878), Treaty of Berlin. Cyprus becomes a Crown colony.
;1879: The Battle of Isandlwana is the first major encounter in the Anglo-Zulu War.
;1881: The British suffer defeat at the Battle of Majuba Hill, leading to the signing of a peace treaty and later the Pretoria Convention, between the British and the reinstated South African Republic, ending the
First Boer War. Sometimes claimed to mark the beginning of the decline of the
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
.
;1882: British Army, British troops begin the British occupation of Egypt, occupation of Egypt by taking the Suez Canal, to secure the vital trade route and passage to India, and the country becomes a protectorate.
;1884: The Fabian Society is founded in London by a group of middle-class intellectuals, including Religious Society of Friends, Quaker Edward R. Pease, Havelock Ellis and E. Nesbit, to promote socialism.
Prince Leopold, Duke of Albany dies.
;1885: Blackpool Electric Tramway Company starts the first electric tram service in the United Kingdom.
;1886: Prime Minister
William Ewart Gladstone
William Ewart Gladstone ( ; 29 December 1809 – 19 May 1898) was a British statesman and Liberal politician. In a career lasting over 60 years, he served for 12 years as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, spread over four non-conse ...
and the Liberal Party tries passing the First Irish Home Rule Bill, but the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons rejects it.
;1888: The serial killer known as Jack the Ripper murders and mutilates five (and possibly more) women on the streets of London.
;1889: Emily Williamson founds the Royal Society for the Protection of Birds.
;1889-1890: Russian flu Pandemic.
;1898: British and Egyptian troops led by Horatio Kitchener, 1st Earl Kitchener of Khartoum, Horatio Kitchener defeat the Mahdist forces at the battle of Omdurman, thus establishing British dominance in the Sudan. Winston Churchill takes part in the British cavalry charge at Omdurman.
;1899: The
Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the Sout ...
is fought between the British Empire and the two independent Boer Republics, Boer republics. The Boers finally surrendered and the British annexed the Boer republics.
;1901: The death of Victoria sees the end of this era. The ascension of her eldest son, Edward, begins the Edwardian era.
See also
Citations
Further reading
General
* Adams, James Eli, ed. ''Encyclopedia of the Victorian Era'' (4 Vol. 2004), short essays on a wide range of topics by experts
* Bailey, Peter. ''Leisure and class in Victorian England: Rational recreation and the contest for control, 1830–1885'' (Routledge, 2014).
* Best, Geoffrey. ''Mid-Victorian Britain, 1851-1875'' (Weidenfeld & Nicolson, 1971)
* Bourne, Kenneth. ''The foreign policy of Victorian England, 1830-1902'' (1970
online survey plus primary documents
* Briggs, Asa. ''The Age of Improvement 1783–1867'' (1979), Wide-ranging older survey emphasizing the reforms
online* Cevasco, G. A. ed. ''The 1890s: An Encyclopedia of British Literature, Art, and Culture'' (1993) 736pp; short articles by experts
* Chadwick, Owen. ''The Victorian Church'' (2 vol 1966), covers all denomination
online* Clark, G. Kitson ''The making of Victorian England'' (1963)
online* Ensor, R. C. K. ''England, 1870–1914'' (1936) https://archive.org/details/in.ernet.dli.2015.49856 online] influential scholarly survey
* Gregg, Pauline. ''A Social and Economic History of Britain: 1760–1950'' (1950
online* Harrison, J.F.C. ''Early Victorian Britain 1832–1851'' (Fontana, 1979).
* Harrison, J.F.C. ''Late Victorian Britain 1875–1901'' (Routledge, 2013).
* Heffer, Simon. ''High Minds: The Victorians and the Birth of Modern Britain'' (2014), survey to 1880.
* Heffer, Simon. ''The Age of Decadence: Britain 1880 to 1914'' (2017), wide-ranging scholarly survey.
* Heilmann, Ann, and Mark Llewellyn, eds. ''Neo-Victorianism: The Victorians in the Twenty-First Century, 1999–2009'' (Palgrave Macmillan; 2011) 323 pages; looks at recent literary & cinematic, interest in the Victorian era, including magic, sexuality, theme parks, and the postcolonial
* Hilton, Boyd. ''A Mad, Bad, and Dangerous People?: England 1783–1846'' (New Oxford History of England. 2006); in-depth scholarly survey, 784pp.
*
* McCord, Norman and Bill Purdue. ''British History, 1815–1914'' (2nd ed. 2007), 612 p
online university textbook
* Paul, Herbert. ''History of Modern England'', 1904-6 (5 vols
online free* Perkin, Harold. ''The Origins of Modern English Society: 1780–1880'' (1969
online* Hoppen, K. Theodore. ''The Mid-Victorian Generation 1846–1886'' (New Oxford History of England) (2000), comprehensive scholarly histor
excerpt and text search* Roberts, Clayton and David F. Roberts. ''A History of England, Volume 2: 1688 to the present'' (2013) university textbook; iarchive:historyofengland00robe, 1985 edition online
* Somervell, D. C. ''English thought in the nineteenth century'' (1929) iarchive:englishthoughtin030312mbp, online
* Steinbach, Susie L. ''Understanding the Victorians: Politics, Culture and Society in Nineteenth-Century Britain'' (2012
excerpt and text search* Swisher, Clarice, ed. ''Victorian England'' (2000) 20 excerpts from leading primary and secondary sources regarding literary, cultural, technical, political, and social themes. iarchive:victorianengland00swis, online free
Daily life and culture
* Aston, Jennifer, Amanda Capern, and Briony McDonagh. "More than bricks and mortar: female property ownership as economic strategy in mid-nineteenth-century urban England." Urban History 46.4 (2019): 695–721
online* Flanders, Judith. ''Inside the Victorian Home: A Portrait of Domestic Life in Victorian England''. W.W. Norton & Company: 2004. .
*
* Mitchell, Sally. ''Daily Life in Victorian England''. Greenwood Press: 1996. .
* O'Gorman, Francis, ed. ''The Cambridge companion to Victorian culture'' (2010)
* Roberts, Adam Charles, ed. ''Victorian culture and society: the essential glossary'' (2003).
* Thompson, F. M. L. '' Rise of Respectable Society: A Social History of Victorian Britain, 1830–1900 (1988) Strong on family, marriage, childhood, houses, and play.''
* Weiler, Peter. ''The New Liberalism: Liberal Social Theory in Great Britain, 1889–1914'' (Routledge, 2016).
*A. N. Wilson, Wilson, A. N. ''The Victorians''. Arrow Books: 2002.
* Young, Gerard Mackworth, ed. ''Early Victorian England 1830-1865'' (2 vol 1934) scholarly surveys of cultural history
vol 2 online
Literature
* Richard Altick, Altick, Richard Daniel. ''Victorian People and Ideas: A Companion for the Modern Reader of Victorian Literature''. (1974) iarchive:victorianpeoplei00alti, online free
* Felluga, Dino Franco, et al. ''The Encyclopedia of Victorian Literature'' (2015).
* Flint, Kay. ''The Cambridge History of Victorian Literature'' (2014).
* Horsman, Alan. ''The Victorian Novel'' (Oxford History of English Literature, 1991)
Politics
* Aydelotte, William O. “Parties and Issues in Early Victorian England.” ''Journal of British Studies,'' 5#2 1966, pp. 95–114
online* Bourne, Kenneth. ''The foreign policy of Victorian England, 1830–1902'' (Oxford UP, 1970), contains a short narrative history and 147 "Selected documents" on pp 195–504.
* Boyd, Kelly and Rohan McWilliam, eds. ''The Victorian Studies Reader'' (2007) 467pp; articles and excerpts by scholar
excerpts and text search* Bright, J. Franck. ''A History of England. Period 4: Growth of Democracy: Victoria 1837–1880'' (1902
online608pp; highly detailed older political narrative
**''A History of England: Period V. Imperial Reaction, Victoria, 1880‒1901'' (1904) iarchive:historyofengland05brig/page/n5, online
* Brock, M. G. "Politics at the Accession of Queen Victoria" ''History Today'' (1953) 3#5 pp 329–338 online.
* Brown, David, Robert Crowcroft, and Gordon Pentland, eds. ''The Oxford Handbook of Modern British Political History, 1800–2000'' (2018
excerpt*Antoinette Burton, Burton, Antoinette, ed. ''Politics and Empire in Victorian Britain: A Reader''. Palgrave Macmillan: 2001.
*Marriott, J. A. R. ''England Since Waterloo'' (1913); focus on politics and diplomacy
online* Martin, Howard.''Britain in the 19th Century'' (Challenging History series, 2000) 409pp; textbook; emphasizing politics, diplomacy and use of primary sources
* Trevelyan, G. M. ''British History in the Nineteenth Century and After (1782–1901)'' (1922). iarchive:in.ernet.dli.2015.226562, online very well written scholarly survey
* Walpole, Spencer. ''A History of England from the Conclusion of the Great War in 1815'' (6 vol. 1878–86), very well written political narrative to 1855
online**Walpole, Spencer. ''History of Twenty-Five Years'' (4 vol. 1904–1908) covers 1856–1880
online* Woodward, E. L. ''The Age of Reform: 1815–1870'' (1954) comprehensive survey iarchive:in.ernet.dli.2015.179823, online
* Young, G. M. "Mid-Victorianism" ''History Today'' (1951) 1#1 pp 11–17, online.
Crime and punishment
*
* Bailey, Victor. ''Policing and punishment in nineteenth century Britain'' (2015).
* Churchill, David. ''Crime Control and Everyday Life in the Victorian City'' (Oxford UP, 2018)
* Emsley, Clive. ''Crime and society in England: 1750–1900'' (2013).
* Emsley, Clive. "Crime in 19th Century Britain." ''History Today'' 38 (1988): 40+
* Emsley, Clive. ''The English Police: A Political and Social History'' (2nd ed. 1996) also published as ''The Great British Bobby: A History of British Policing from the 18th Century to the Present'' (201
excerpt*
* Gatrell, V. A. C. "Crime, authority and the policeman-state." in E.M.L. Thompson, ed., ''The Cambridge social history of Britain 1750-1950: Volume 3'' (1990). 3:243-310
* Hay, Douglas. "Crime and justice in eighteenth-and nineteenth-century England." ''Crime and Justice'' 2 (1980): 45–84
online* Kilday, Anne-Marie. "Women and crime." ''Women's History, Britain 1700–1850'' ed. Hannah Barker and Elaine Chalus, (Routledge, 2004) pp. 186–205.
* May, Margaret. "Innocence and experience: the evolution of the concept of juvenile delinquency in the mid-nineteenth century." ''Victorian Studies'' 17.1 (1973): 7–29
online* Radzinowicz, Leon. '' A History of English Criminal Law and Its Administration from 1750'' (5 vol. 1948–1976)
* Radzinowicz, Leon and Roger Hood ''The Emergence of Penal Policy in Victorian and Edwardian England'' (1990)
*
* Shore, Heather. "Crime, policing and punishment." in Chris Williams, ed., ''A companion to nineteenth-century Britain'' (2007): 381–395
excerpt*
*
* Tobias, J. J. ''Crime and Industrial Society in the Nineteenth Century'' (1967) .
* Tobias, J.J. ed, ''Nineteenth-century crime: prevention and punishment'' (1972) primary sources.
* Taylor, Howard. "Rationing crime: the political economy of criminal statistics since the 1850s." ''Economic history review'' (1998) 51#3 569–590
online
Historiography
*
* Elton, G. R. ''Modern Historians on British History 1485–1945: A Critical Bibliography 1945–1969'' (1969), annotated guide to 1000 history books on every major topic, plus book reviews and major scholarly articles
online*
*
* Homans, Margaret, and Adrienne Munich, eds. ''Remaking Queen Victoria'' (Cambridge University Press, 1997)
*
*
* Moore, D. C. "In Search of a New Past: 1820 – 1870," in Richard Schlatter, ed., ''Recent Views on British History: Essays on Historical Writing since 1966'' (Rutgers UP, 1984), pp 255–298
*
*
* Stansky, Peter. "British History: 1870 – 1914," in Richard Schlatter, ed., ''Recent Views on British History: Essays on Historical Writing since 1966'' (Rutgers UP, 1984), pp. 299–326
*
*
* Webb, R. K. ''Modern England: from the 18th century to the present'' (1968) online widely recommended university textbook
Primary sources
* Black, E.C. ed. ''British politics in the nineteenth century'' (1969
online* Bourne, Kenneth. ''The foreign policy of Victorian England, 1830–1902'' (Oxford UP, 1970.) pp 195–504 are 147 selected documents
* Hicks, Geoff, et al. eds. ''Documents on Conservative Foreign Policy, 1852–1878'' (2013), 550 document
excerpt* Temperley, Harold and L.M. Penson, eds. ''Foundations of British Foreign Policy: From Pitt (1792) to Salisbury (1902)'' (1938), 608pp of primary source
online
External links
Free online books on the Victorian eraVictorians
British Library website exploring the Victorian period.
Victorians.co.uk
Victorian Era History Guide.
Mostly-Victorian.com
A collection of primary-source documents drawn from Victorian periodicals.
The Victorian DictionaryThe Victorian Web
British Library history resources about the Victorian era, featuring collection material and text by Liza Picard.
Timelines: Sources from history – British Library interactiveCollection: "Victorian Studies" from the University of Michigan Museum of Art"What Happened During the Victorian Era?" resources from the Royal Museums GreenwichVictorian mate choice
by evolutionary psychologist Geoffrey Miller (psychologist), Geoffrey Miller
{{DEFAULTSORT:Victorian Era
Victorian era,
Historical eras
History of the United Kingdom by period
History of England by period
19th century in England
19th century in the United Kingdom, .
 In 1840, Queen Victoria married her German cousin
In 1840, Queen Victoria married her German cousin  Her diary entries suggest the Queen had contemplated the possibility of a union of her North American colonies as early as February 1865. She wrote, "...we must struggle for it, and far the best it would be to let it go as an Independent Kingdom, under an English Prince!" She also mentioned how her late husband Prince Albert had hoped that one day, their sons would rule over the British colonies. In February 1867, the Queen received a copy of the British North America Act (also known as the
Her diary entries suggest the Queen had contemplated the possibility of a union of her North American colonies as early as February 1865. She wrote, "...we must struggle for it, and far the best it would be to let it go as an Independent Kingdom, under an English Prince!" She also mentioned how her late husband Prince Albert had hoped that one day, their sons would rule over the British colonies. In February 1867, the Queen received a copy of the British North America Act (also known as the  Key leaders included Conservatives
Key leaders included Conservatives  After weeks of illness, Queen Victoria died on 22 January 1901. By her bedside were her son and heir
After weeks of illness, Queen Victoria died on 22 January 1901. By her bedside were her son and heir  Religion was a battleground during this era, with the Nonconformists fighting bitterly against the established status of the Church of England, especially regarding education and access to universities and public office. Penalties on Roman Catholics were mostly removed. The Vatican restored the English Catholic bishoprics in 1850 and numbers grew through conversions and immigration from Ireland. The
Religion was a battleground during this era, with the Nonconformists fighting bitterly against the established status of the Church of England, especially regarding education and access to universities and public office. Penalties on Roman Catholics were mostly removed. The Vatican restored the English Catholic bishoprics in 1850 and numbers grew through conversions and immigration from Ireland. The  The abstract theological or philosophical doctrine of agnosticism, whereby it is theoretically impossible to prove whether or not God exists, suddenly became a popular issue around 1869, when
The abstract theological or philosophical doctrine of agnosticism, whereby it is theoretically impossible to prove whether or not God exists, suddenly became a popular issue around 1869, when 
 The centrality of the family was a dominant feature for all classes. Worriers repeatedly detected threats that had to be dealt with: working wives, overpaid youths, harsh factory conditions, bad housing, poor sanitation, excessive drinking, and religious decline. The licentiousness so characteristic of the upper class of the late 18th and early 19th centuries dissipated. The home became a refuge from the harsh world; middle-class wives sheltered their husbands from the tedium of domestic affairs. The number of children shrank, allowing much more attention to be paid to each child. Extended families were less common, as the nuclear family became both the ideal and the reality.
In Great Britain, elsewhere in Europe, and in the United States, the notion that marriage should be based on
The centrality of the family was a dominant feature for all classes. Worriers repeatedly detected threats that had to be dealt with: working wives, overpaid youths, harsh factory conditions, bad housing, poor sanitation, excessive drinking, and religious decline. The licentiousness so characteristic of the upper class of the late 18th and early 19th centuries dissipated. The home became a refuge from the harsh world; middle-class wives sheltered their husbands from the tedium of domestic affairs. The number of children shrank, allowing much more attention to be paid to each child. Extended families were less common, as the nuclear family became both the ideal and the reality.
In Great Britain, elsewhere in Europe, and in the United States, the notion that marriage should be based on  The emerging middle-class norm for women was separate spheres, whereby women avoid the public sphere – the domain of politics, paid work, commerce, and public speaking. Instead, they should dominate in the realm of domestic life, focused on the care of the family, the husband, the children, the household, religion, and moral behaviour. Religiosity was in the female sphere, and the Nonconformist churches offered new roles that women eagerly entered. They taught in Sunday schools, visited the poor and sick, distributed tracts, engaged in fundraising, supported missionaries, led Methodist class meetings, prayed with other women, and a few were allowed to preach to mixed audiences.
The long 1854 poem ''
The emerging middle-class norm for women was separate spheres, whereby women avoid the public sphere – the domain of politics, paid work, commerce, and public speaking. Instead, they should dominate in the realm of domestic life, focused on the care of the family, the husband, the children, the household, religion, and moral behaviour. Religiosity was in the female sphere, and the Nonconformist churches offered new roles that women eagerly entered. They taught in Sunday schools, visited the poor and sick, distributed tracts, engaged in fundraising, supported missionaries, led Methodist class meetings, prayed with other women, and a few were allowed to preach to mixed audiences.
The long 1854 poem '' A key component of the curriculum at Cambridge since the mid-eighteenth century had been the "
A key component of the curriculum at Cambridge since the mid-eighteenth century had been the " Popular forms of entertainment varied by social class. Victorian Britain, like the periods before it, was interested in literature, theatre and
Popular forms of entertainment varied by social class. Victorian Britain, like the periods before it, was interested in literature, theatre and  Another form of entertainment involved "spectacles" where paranormal events, such as
Another form of entertainment involved "spectacles" where paranormal events, such as  The Victorian era saw the introduction and development of many modern sports. Often originating in the public schools, they exemplified new ideals of manliness.
The Victorian era saw the introduction and development of many modern sports. Often originating in the public schools, they exemplified new ideals of manliness. 
 According to historians David Brandon and Alan Brooke, the new system of railways after 1830 brought into being our modern world:
:They stimulated demand for building materials, coal, iron and, later, steel. Excelling in the bulk movement of coal, they provided the fuel for the furnaces of industry and for domestic fireplaces. Millions of people were able to travel who had scarcely ever travelled before. Railways enabled mail, newspapers, periodicals and cheap literature to be distributed easily, quickly and cheaply allowing a much wider and faster dissemination of ideas and information. They had a significant impact on improving diet.... nd enableda proportionately smaller agricultural industry was able to feed a much larger urban population....They employed huge quantities of labour both directly and indirectly. They helped Britain to become the ‘Workshop of the World’ by reducing transport costs not only of raw materials but of finished goods, large amounts of which were exported.... day’s global corporations originated with the great limited liability railway companies....By the third quarter of the nineteenth century, there was scarcely any person living in Britain whose life had not been altered in some way by the coming of the railways. Railways contributed to the transformation of Britain from a rural to a predominantly urban society.
Historians have characterised the mid-Victorian era (1850–1870) as Britain's "Golden Years". It was not till the two to three decades following the Second World War that substantial economic growth was seen again. In the long-term view, the mid-Victorian boom was one upswing in the Kondratiev cycle (see figure). There was prosperity, as the national income per person grew by half. Much of the prosperity was due to the increasing industrialisation, especially in textiles and machinery, as well as to the worldwide network of exports that produced profits for British merchants. British entrepreneurs built railways in India and many independent nations. There was peace abroad (apart from the short Crimean War, 1854–56), and social peace at home. Opposition to the new order melted away, says Porter. The Chartist movement peaked as a democratic movement among the working class in 1848; its leaders moved to other pursuits, such as trade unions and cooperative societies. The working class ignored foreign agitators like Karl Marx in their midst, and joined in celebrating the new prosperity. Employers typically were paternalistic and generally recognised the trade unions. Companies provided their employees with welfare services ranging from housing, schools and churches, to libraries, baths, and gymnasia. Middle-class reformers did their best to assist the working classes' aspirations to middle-class norms of "respectability".
There was a spirit of libertarianism, says Porter, as people felt they were free. Taxes were very low, and government restrictions were minimal. There were still problem areas, such as occasional riots, especially those motivated by anti-Catholicism. Society was still ruled by the aristocracy and the gentry, who controlled high government offices, both houses of Parliament, the church, and the military. Becoming a rich businessman was not as prestigious as inheriting a title and owning a landed estate. Literature was doing well, but the fine arts languished as the Great Exhibition of 1851 showcased Britain's industrial prowess rather than its sculpture, painting or music. The educational system was mediocre; the main universities (outside Scotland) were likewise mediocre.
Historian Llewellyn Woodward has concluded:
: For leisure or work, for getting or for spending, England was a better country in 1879 than in 1815. The scales were less weighted against the weak, against women and children, and against the poor. There was greater movement, and less of the fatalism of an earlier age. The public conscience was more instructed, and the content of liberty was being widened to include something more than freedom from political constraint ... Yet England in 1871 was by no means an earthly paradise. The housing and conditions of life of the working class in town & country were still a disgrace to an age of plenty.
In December 1844,
According to historians David Brandon and Alan Brooke, the new system of railways after 1830 brought into being our modern world:
:They stimulated demand for building materials, coal, iron and, later, steel. Excelling in the bulk movement of coal, they provided the fuel for the furnaces of industry and for domestic fireplaces. Millions of people were able to travel who had scarcely ever travelled before. Railways enabled mail, newspapers, periodicals and cheap literature to be distributed easily, quickly and cheaply allowing a much wider and faster dissemination of ideas and information. They had a significant impact on improving diet.... nd enableda proportionately smaller agricultural industry was able to feed a much larger urban population....They employed huge quantities of labour both directly and indirectly. They helped Britain to become the ‘Workshop of the World’ by reducing transport costs not only of raw materials but of finished goods, large amounts of which were exported.... day’s global corporations originated with the great limited liability railway companies....By the third quarter of the nineteenth century, there was scarcely any person living in Britain whose life had not been altered in some way by the coming of the railways. Railways contributed to the transformation of Britain from a rural to a predominantly urban society.
Historians have characterised the mid-Victorian era (1850–1870) as Britain's "Golden Years". It was not till the two to three decades following the Second World War that substantial economic growth was seen again. In the long-term view, the mid-Victorian boom was one upswing in the Kondratiev cycle (see figure). There was prosperity, as the national income per person grew by half. Much of the prosperity was due to the increasing industrialisation, especially in textiles and machinery, as well as to the worldwide network of exports that produced profits for British merchants. British entrepreneurs built railways in India and many independent nations. There was peace abroad (apart from the short Crimean War, 1854–56), and social peace at home. Opposition to the new order melted away, says Porter. The Chartist movement peaked as a democratic movement among the working class in 1848; its leaders moved to other pursuits, such as trade unions and cooperative societies. The working class ignored foreign agitators like Karl Marx in their midst, and joined in celebrating the new prosperity. Employers typically were paternalistic and generally recognised the trade unions. Companies provided their employees with welfare services ranging from housing, schools and churches, to libraries, baths, and gymnasia. Middle-class reformers did their best to assist the working classes' aspirations to middle-class norms of "respectability".
There was a spirit of libertarianism, says Porter, as people felt they were free. Taxes were very low, and government restrictions were minimal. There were still problem areas, such as occasional riots, especially those motivated by anti-Catholicism. Society was still ruled by the aristocracy and the gentry, who controlled high government offices, both houses of Parliament, the church, and the military. Becoming a rich businessman was not as prestigious as inheriting a title and owning a landed estate. Literature was doing well, but the fine arts languished as the Great Exhibition of 1851 showcased Britain's industrial prowess rather than its sculpture, painting or music. The educational system was mediocre; the main universities (outside Scotland) were likewise mediocre.
Historian Llewellyn Woodward has concluded:
: For leisure or work, for getting or for spending, England was a better country in 1879 than in 1815. The scales were less weighted against the weak, against women and children, and against the poor. There was greater movement, and less of the fatalism of an earlier age. The public conscience was more instructed, and the content of liberty was being widened to include something more than freedom from political constraint ... Yet England in 1871 was by no means an earthly paradise. The housing and conditions of life of the working class in town & country were still a disgrace to an age of plenty.
In December 1844,  Founded in 1799 with the stated purpose of "diffusing the Knowledge, and facilitating the general Introduction, of Useful Mechanical Inventions and Improvements; and for teaching, by Courses of Philosophical Lectures and Experiments, the application of Science to the common Purposes of Life," the
Founded in 1799 with the stated purpose of "diffusing the Knowledge, and facilitating the general Introduction, of Useful Mechanical Inventions and Improvements; and for teaching, by Courses of Philosophical Lectures and Experiments, the application of Science to the common Purposes of Life," the  In the field of statistics, the nineteenth century saw significant innovations in data visualisation. William Playfair, who created charts of all sorts, justified it thus, "a man who has carefully investigated a printed table, finds, when done, that he has only a very faint and partial idea of what he has read; and that like a figure imprinted on sand, is soon totally erased and defaced." For example, in a chart showing the relationship between population and government revenue of some European nations, he used the areas of circles to represent the geographical sizes of those nations. In the same graph he used the slopes of lines to indicate the tax burden of a given population. While serving as nurse during the Crimean War,
In the field of statistics, the nineteenth century saw significant innovations in data visualisation. William Playfair, who created charts of all sorts, justified it thus, "a man who has carefully investigated a printed table, finds, when done, that he has only a very faint and partial idea of what he has read; and that like a figure imprinted on sand, is soon totally erased and defaced." For example, in a chart showing the relationship between population and government revenue of some European nations, he used the areas of circles to represent the geographical sizes of those nations. In the same graph he used the slopes of lines to indicate the tax burden of a given population. While serving as nurse during the Crimean War,  During the 1830s and 1840s, traditional caloric theory of heat began losing favour to "dynamical" alternatives, which posit that heat is a kind of motion. Brewer and amateur scientist James Prescott Joule was one of the proponents of the latter. Joule's intricate experiments—the most successful of which involved heating water with paddle wheels—making full use of his skill in temperature control as a brewer, demonstrated decisively the reality of the "mechanical equivalent of heat." What would later become known as the "conservation of energy" was pursued by many other workers approaching the subject from a variety of backgrounds, from medicine and physiology to physics and engineering. Another notable contributor to this development was the German researcher
During the 1830s and 1840s, traditional caloric theory of heat began losing favour to "dynamical" alternatives, which posit that heat is a kind of motion. Brewer and amateur scientist James Prescott Joule was one of the proponents of the latter. Joule's intricate experiments—the most successful of which involved heating water with paddle wheels—making full use of his skill in temperature control as a brewer, demonstrated decisively the reality of the "mechanical equivalent of heat." What would later become known as the "conservation of energy" was pursued by many other workers approaching the subject from a variety of backgrounds, from medicine and physiology to physics and engineering. Another notable contributor to this development was the German researcher  After the Dane
After the Dane  Steam ships were one of the keys to Britain's prosperity in the nineteenth century. This technology, which predates the Victorian era, had a long a rich history. Starting in the late 1700s, people had begun building steam-powered ships with ever increasing size, operational range, and speed, first to cross the English Channel and then the Atlantic and finally to reach places as far away as India and Australia without having to refuel mid-route. International trade and travel boosted demand, and there was intense competition among the shipping companies. Steam ships such as the SS Great Britain, SS ''Great Britain'' and SS Great Western, SS ''Great Western'' made international travel more common but also advanced trade, so that in Britain it was not just the luxury goods of earlier times that were imported into the country but essentials and raw materials such as corn and cotton from the United States and meat and wool from Australia.
At 693 feet long, 120 feet wide and weighing over 18,900 tons, the SS Great Eastern, SS ''Great Eastern'' was the largest ship built at the time, capable of transporting 4,000 passengers from Britain to Australia without having to refuel along the way. Even when she was finally broken up for scraps in 1888, she was still the largest ship in the world. Her record was not broken till the Edwardian era with super liners like the ''Lusitania'' in 1907, the ''Titanic'' in 1912. Yet despite being a remarkable feat of engineering, the ''Great Eastern'' became more and more of a white elephant as smaller and faster ships were in greater demand. Nevertheless, she gained a new lease of life when she was chartered to lay telegraphic cables across the Atlantic, and then to India. Her size and range made her ideally suited for the task.
The British government had long realised that national prosperity depended on trade. For that reason, it deployed the Royal Navy to protect maritime trade routes and financed the construction of many steam ships.
Steam ships were one of the keys to Britain's prosperity in the nineteenth century. This technology, which predates the Victorian era, had a long a rich history. Starting in the late 1700s, people had begun building steam-powered ships with ever increasing size, operational range, and speed, first to cross the English Channel and then the Atlantic and finally to reach places as far away as India and Australia without having to refuel mid-route. International trade and travel boosted demand, and there was intense competition among the shipping companies. Steam ships such as the SS Great Britain, SS ''Great Britain'' and SS Great Western, SS ''Great Western'' made international travel more common but also advanced trade, so that in Britain it was not just the luxury goods of earlier times that were imported into the country but essentials and raw materials such as corn and cotton from the United States and meat and wool from Australia.
At 693 feet long, 120 feet wide and weighing over 18,900 tons, the SS Great Eastern, SS ''Great Eastern'' was the largest ship built at the time, capable of transporting 4,000 passengers from Britain to Australia without having to refuel along the way. Even when she was finally broken up for scraps in 1888, she was still the largest ship in the world. Her record was not broken till the Edwardian era with super liners like the ''Lusitania'' in 1907, the ''Titanic'' in 1912. Yet despite being a remarkable feat of engineering, the ''Great Eastern'' became more and more of a white elephant as smaller and faster ships were in greater demand. Nevertheless, she gained a new lease of life when she was chartered to lay telegraphic cables across the Atlantic, and then to India. Her size and range made her ideally suited for the task.
The British government had long realised that national prosperity depended on trade. For that reason, it deployed the Royal Navy to protect maritime trade routes and financed the construction of many steam ships.
 By mid-century, the stethoscope became an oft-used device and designs of the microscope had advanced enough for scientists to closely examine pathogens. The pioneering work of French microbiologist Louis Pasteur from the 1850s earned widespread acceptance for the germ theory of disease. It led to the introduction antiseptics by Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister in 1867 in the form of carbolic acid (phenol). He instructed the hospital staff to wear gloves and wash their hands, instruments, and dressings with a phenol solution and in 1869, he invented a machine that would spray carbolic acid in the operating theatre during surgery. Infection-related deaths fell noticeably as a result.
As the British Empire expanded, Britons found themselves facing novel climates and contagions; there was active research into tropical diseases. In 1898, Ronald Ross proved that the mosquito was responsible for spreading malaria.
Although nitrous oxide, or laughing gas, had been proposed as an anaesthetic as far back as 1799 by
By mid-century, the stethoscope became an oft-used device and designs of the microscope had advanced enough for scientists to closely examine pathogens. The pioneering work of French microbiologist Louis Pasteur from the 1850s earned widespread acceptance for the germ theory of disease. It led to the introduction antiseptics by Joseph Lister, 1st Baron Lister, Joseph Lister in 1867 in the form of carbolic acid (phenol). He instructed the hospital staff to wear gloves and wash their hands, instruments, and dressings with a phenol solution and in 1869, he invented a machine that would spray carbolic acid in the operating theatre during surgery. Infection-related deaths fell noticeably as a result.
As the British Empire expanded, Britons found themselves facing novel climates and contagions; there was active research into tropical diseases. In 1898, Ronald Ross proved that the mosquito was responsible for spreading malaria.
Although nitrous oxide, or laughing gas, had been proposed as an anaesthetic as far back as 1799 by