Velociraptors on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Velociraptor'' (; ) is a

 Mark J. Powers in his 2020 master thesis fully described MPC-D 100/982, which he concluded to represent a new and third species of ''Velociraptor''. This species, which he named ''"V. vadarostrum"'', was stated to mainly differ from other ''Velociraptor'' species in having a shallow maxilla morphology. Powers and colleagues also in 2020 used
Mark J. Powers in his 2020 master thesis fully described MPC-D 100/982, which he concluded to represent a new and third species of ''Velociraptor''. This species, which he named ''"V. vadarostrum"'', was stated to mainly differ from other ''Velociraptor'' species in having a shallow maxilla morphology. Powers and colleagues also in 2020 used
 ''Velociraptor'' was a small to medium-sized
''Velociraptor'' was a small to medium-sized
 The back or anterior region of the skull was built by the frontal, lacrimal, postorbital, jugal, parietal, quadrate, and quadratojugal bones. The was large element, having a vaguely rectangular shape when seen from above. On its posterior end, this bone was in contact with the , and such elements were the main bodies of the
The back or anterior region of the skull was built by the frontal, lacrimal, postorbital, jugal, parietal, quadrate, and quadratojugal bones. The was large element, having a vaguely rectangular shape when seen from above. On its posterior end, this bone was in contact with the , and such elements were the main bodies of the 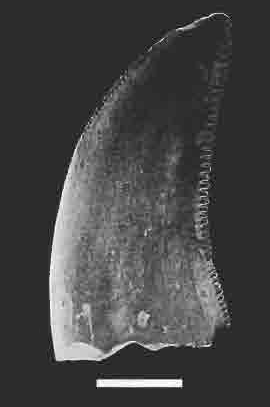 The lower jaw of ''Velociraptor'' comprised mainly the dentary, splenial, angular, surangular, and articular bones. The was a very long, weakly curved, and narrow element that developed several alveoli on its top surface. On its posterior end, it meet the . It had a small hole near its posterior end, called surangular foramen or fenestra. Both bones were the largest elements of the lower jaw of ''Velociraptor'', contributing to virtually its entire length. Below them were the smaller and , closely articulated to each other. The , located on the inner side of the surangular, was a small element that joined the quadrate of the upper skull, enabling the articulation with the lower jaw. An elongated, near oval-shaped hole was developed in the center of the lower jaw (the mandibular fenestra), and it was produced by the joint of the dentary, surangular, and angular bones.
The teeth of ''Velociraptor'' were fairly
The lower jaw of ''Velociraptor'' comprised mainly the dentary, splenial, angular, surangular, and articular bones. The was a very long, weakly curved, and narrow element that developed several alveoli on its top surface. On its posterior end, it meet the . It had a small hole near its posterior end, called surangular foramen or fenestra. Both bones were the largest elements of the lower jaw of ''Velociraptor'', contributing to virtually its entire length. Below them were the smaller and , closely articulated to each other. The , located on the inner side of the surangular, was a small element that joined the quadrate of the upper skull, enabling the articulation with the lower jaw. An elongated, near oval-shaped hole was developed in the center of the lower jaw (the mandibular fenestra), and it was produced by the joint of the dentary, surangular, and angular bones.
The teeth of ''Velociraptor'' were fairly
 The arm of ''Velociraptor'' was formed by the
The arm of ''Velociraptor'' was formed by the  As in other dromaeosaurs, ''Velociraptor'' tails had
As in other dromaeosaurs, ''Velociraptor'' tails had
 Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Material was copied from this source, which is available under
Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License

 Below are the results for the Eudromaeosauria
Below are the results for the Eudromaeosauria
 In 2007 Alan H. Turner and colleagues reported the presence of six
In 2007 Alan H. Turner and colleagues reported the presence of six
 The distinctive claw, on the second digit of dromaeosaurids, has traditionally been depicted as a slashing weapon; its assumed use being to cut and disembowel prey. In the "Fighting Dinosaurs" specimen, the ''Velociraptor'' lies underneath, with one of its sickle claws apparently embedded in the throat of its prey, while the beak of ''Protoceratops'' is clamped down upon the right forelimb of its attacker. This suggests ''Velociraptor'' may have used its sickle claw to pierce vital organs of the throat, such as the jugular vein,
The distinctive claw, on the second digit of dromaeosaurids, has traditionally been depicted as a slashing weapon; its assumed use being to cut and disembowel prey. In the "Fighting Dinosaurs" specimen, the ''Velociraptor'' lies underneath, with one of its sickle claws apparently embedded in the throat of its prey, while the beak of ''Protoceratops'' is clamped down upon the right forelimb of its attacker. This suggests ''Velociraptor'' may have used its sickle claw to pierce vital organs of the throat, such as the jugular vein,  In 2011, Denver Fowler and colleagues suggested a new method by which dromaeosaurs like ''Velociraptor'' and similar dromaeosaurs may have captured and restrained prey. This model, known as the "raptor prey restraint" (RPR) model of predation, proposes that dromaeosaurs killed their prey in a manner very similar to extant
In 2011, Denver Fowler and colleagues suggested a new method by which dromaeosaurs like ''Velociraptor'' and similar dromaeosaurs may have captured and restrained prey. This model, known as the "raptor prey restraint" (RPR) model of predation, proposes that dromaeosaurs killed their prey in a manner very similar to extant
 In both Bayan Mandahu and Djadochta formations many of the same genera were present, though they varied at the species level. These differences in species composition may be due a natural barrier separating the two formations, which are relatively close to each other geographically. However, given the lack of any known barrier which would cause the specific faunal compositions found in these areas, it is more likely that those differences indicate a slight time difference.
''V. osmolskae'' lived alongside the ankylosaurid '' Pinacosaurus mephistocephalus''; alvarezsaurid ''
In both Bayan Mandahu and Djadochta formations many of the same genera were present, though they varied at the species level. These differences in species composition may be due a natural barrier separating the two formations, which are relatively close to each other geographically. However, given the lack of any known barrier which would cause the specific faunal compositions found in these areas, it is more likely that those differences indicate a slight time difference.
''V. osmolskae'' lived alongside the ankylosaurid '' Pinacosaurus mephistocephalus''; alvarezsaurid ''
 Known specimens of ''Velociraptor mongoliensis'' have been recovered from the
Known specimens of ''Velociraptor mongoliensis'' have been recovered from the
Yale’s legacy in ''Jurassic World''
" ''Yale News'', 18-Jun-2015. They portrayed the animals with the size, proportions, and snout shape of ''Deinonychus'' rather than ''Velociraptor''. Production on ''Jurassic Park'' began before the discovery of the large dromaeosaurid ''
3D skull model of ''Velociraptor mongoliensis''
at
Skeletal reconstruction of ''Velociraptor mongoliensis''
at Dr. Scott Hartman's Skeletal Drawing
at
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of small dromaeosaurid
Dromaeosauridae () is a family of feathered theropod dinosaurs. They were generally small to medium-sized feathered carnivores that flourished in the Cretaceous Period. The name Dromaeosauridae means 'running lizards', from Greek ('), meaning ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
that lived in Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
during the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
epoch, about 75 million to 71 million years ago
The abbreviation Myr, "million years", is a unit of a quantity of (i.e. ) years, or 31.556926 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr (million years) is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used with Mya (million years ago). ...
. Two species are currently recognized, although others have been assigned in the past. The type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ...
is ''V. mongoliensis''; fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
s of this species have been discovered in the Djadochta Formation
The Djadochta Formation (sometimes transcribed and also known as Djadokhta, Djadokata, or Dzhadokhtskaya) is a highly fossiliferous geological formation situated in Central Asia, Gobi Desert, dating from the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 milli ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
. A second species, ''V. osmolskae'', was named in 2008 for skull material from the Bayan Mandahu Formation, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
.
Smaller than other dromaeosaurids like '' Deinonychus'' and ''Achillobator
''Achillobator'' ( ; meaning "Achilles hero") is a genus of large dromaeosaurid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous period about 96 million to 89 million years ago in what is now the Bayan Shireh Formation. The genus is curren ...
'', ''Velociraptor'' was about long with a body mass between . It nevertheless shared many of the same anatomical
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having it ...
features. It was a bipedal, feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier ...
ed carnivore with a long tail and an enlarged sickle-shaped claw on each hindfoot, which is thought to have been used to tackle and restrain prey
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the ...
. ''Velociraptor'' can be distinguished from other dromaeosaurids by its long and low skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
, with an upturned snout.
''Velociraptor'' (commonly referred to as "raptor") is one of the dinosaur genera most familiar to the general public due to its prominent role in the ''Jurassic Park
''Jurassic Park'', later also referred to as ''Jurassic World'', is an American science fiction media franchise created by Michael Crichton and centered on a disastrous attempt to create a theme park of cloned dinosaurs. It began in 1990 when ...
'' films. In real life, however, ''Velociraptor'' was roughly the size of a turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, considerably smaller than the approximately tall and reptiles seen in the novels and films (which were based on members of the related genus '' Deinonychus''). Today, ''Velociraptor'' is well known to paleontologists, with over a dozen described fossil skeletons, the most of any dromaeosaurid. One particularly famous specimen preserves a ''Velociraptor'' locked in combat with a ''Protoceratops
''Protoceratops'' (; ) is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 75 to 71 million years ago. The genus ''Protoceratops'' includes two species: ''P. andrewsi'' and the larger ''P. hellenik ...
''.
History of discovery
During anAmerican Museum of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. In Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 26 inter ...
expedition to the Flaming Cliffs (Bayn Dzak or Bayanzag) of the Djadochta Formation
The Djadochta Formation (sometimes transcribed and also known as Djadokhta, Djadokata, or Dzhadokhtskaya) is a highly fossiliferous geological formation situated in Central Asia, Gobi Desert, dating from the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 milli ...
, Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert (Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast an ...
, on 11 August 1923, Peter Kaisen discovered the first ''Velociraptor'' fossil known to science—a crushed but complete skull, associated with one of the raptorial second toe claws ( AMNH 6515). In 1924, museum president Henry Fairfield Osborn designated the skull and claw (which he assumed to come from the hand) as the type specimen
In biology, a type is a particular wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to a ...
of his new genus, ''Velociraptor''. This name is derived from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
words ''velox'' ('swift') and ''raptor'' ('robber' or 'plunderer') and refers to the animal's cursorial
A cursorial organism is one that is adapted specifically to run. An animal can be considered cursorial if it has the ability to run fast (e.g. cheetah) or if it can keep a constant speed for a long distance (high endurance). "Cursorial" is often u ...
nature and carnivorous diet. Osborn named the type species ''V. mongoliensis'' after its country of origin. Earlier that year, Osborn had informally mentioned the animal in a popular press article, under the name "Ovoraptor djadochtari" (not to be confused with the similarly named '' Oviraptor''), eventually changed into ''V. mongoliensis'' during its formal description.
While North American teams were shut out of communist Mongolia
The Mongolian People's Republic ( mn, Бүгд Найрамдах Монгол Ард Улс, БНМАУ; , ''BNMAU''; ) was a socialist state which existed from 1924 to 1992, located in the historical region of Outer Mongolia in East Asia. It ...
during the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, expeditions by Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
scientists, in collaboration with Mongolian colleagues, recovered several more specimens of ''Velociraptor''. The most famous is part of the "Fighting Dinosaurs
The Fighting Dinosaurs is a fossil specimen which was found in the Late Cretaceous Djadokhta Formation of Mongolia. It preserves a ''Protoceratops andrewsi'' and ''Velociraptor mongoliensis'' trapped in combat and provides direct evidence of pre ...
" specimen ( MPC-D 100/25; formerly IGM, GIN, or GI SPS), discovered by a Polish-Mongolian team in 1971. The fossil preserves a ''Velociraptor'' in battle against a ''Protoceratops
''Protoceratops'' (; ) is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 75 to 71 million years ago. The genus ''Protoceratops'' includes two species: ''P. andrewsi'' and the larger ''P. hellenik ...
''. It is considered a national treasure of Mongolia, and in 2000 it was loaned to the American Museum of Natural History in New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
for a temporary exhibition.
Between 1988 and 1990, a joint Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
-Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
team discovered ''Velociraptor'' remains in northern China. American scientists returned to Mongolia in 1990, and a joint Mongolian-American expedition to the Gobi, led by the American Museum of Natural History and the Mongolian Academy of Sciences
The Mongolian Academy of Sciences (, ''Mongol ulsyn Shinjlekh ukhaany Akademi'') is Mongolia's first centre of modern sciences. It came into being in 1921 when the government of newly
independent Mongolia issued a resolution declaring the establi ...
, turned up several well-preserved skeletons. One such specimen, MPC-D 100/980, was nicknamed "Ichabodcraniosaurus" by Norell's team because the fairly complete specimen was found without its skull (an allusion to the Washington Irving
Washington Irving (April 3, 1783 – November 28, 1859) was an American short-story writer, essayist, biographer, historian, and diplomat of the early 19th century. He is best known for his short stories "Rip Van Winkle" (1819) and " The Legen ...
character Ichabod Crane
Ichabod Crane is a fictional character and the protagonist in Washington Irving's short story "The Legend of Sleepy Hollow." Crane is portrayed, in the original work, as well as in most adaptations, as a tall, lanky individual with a scarecro ...
).Novacek, Michael J. (1996). ''Dinosaurs of the Flaming Cliffs''. New York: Anchor Books. . While Norell and Makovicky provisionally considered it a specimen of ''Velociraptor mongoliensis'', it was named as a new species ''Shri devi
''Shri'' (named after Palden Lhamo, a Buddhist deity) is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur discovered in the Barun Goyot Formation in Khulsan, Mongolia. The fossil remains of ''Shri'' date back to the Late Cretaceous period. The type a ...
'' in 2021.
Additional species

Maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
e and a lacrimal (the main tooth-bearing bones of the upper jaw, and the bone that forms the anterior margin of the eye socket, respectively) recovered from the Bayan Mandahu Formation in 1999 by the Sino-Belgian Dinosaur Expeditions were found to pertain to ''Velociraptor'', but not to the type species ''V. mongoliensis''. Pascal Godefroit and colleagues named these bones ''V. osmolskae'' (for Polish paleontologist Halszka Osmólska
Halszka Osmólska (September 15, 1930 – March 31, 2008) was a Polish paleontologist who had specialized in Mongolian dinosaurs.
Biography
She was born in 1930 in Poznań. In 1949, she began to study biology at Faculty of Biology and Earth Scie ...
) in 2008. However, the 2013 study noted that while "the elongate shape of the maxilla in ''V. osmolskae'' is similar to that of ''V. mongoliensis''," phylogenetic analysis found it to be closer to ''Linheraptor
''Linheraptor'' is a genus of dromaeosaurid dinosaur which lived in what is now China in the Late Cretaceous. It was named by Xu Xing and colleagues in 2010, and contains the species ''Linheraptor exquisitus''. This bird-like dinosaur was less ...
'', making the genus paraphyletic
In taxonomy (general), taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's most recent common ancestor, last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few Monophyly, monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be pa ...
; thus, ''V. osmolskae'' might not actually belong to the genus ''Velociraptor'' and requires reassessment.
Paleontologists Mark A. Norell and Peter J. Makovicky in 1997 described new and abundantly preserved specimens of ''V. mongoliensis'', namely MPC-D 100/985 collected from the Tugrik Shireh locality in 1993, and MPC-D 100/986 collected in 1993 from the Chimney Buttes locality. The team briefly mentioned another specimen, MPC-D 100/982, which by the time of this publication remained undescribed. In 1999 Norell and Makovicky provided more insights into the anatomy of ''Velociraptor'' with additional specimens. Among these, MPC-D 100/982 was partially described and figured, and referred to ''V. mongoliensis'' mainly based on cranial similarities with the holotype skull, although they stated that differences were present between the pelvic region of this specimen and other ''Velociraptor'' specimens. This relatively well-preserved specimen including the skull was discovered and collected in 1995 at the Bayn Dzak locality (more especifically at the "Volcano" sub-locality). Martin Kundrát in a 2004 abstract compared the neurocranium of MPC-D 100/982 to another ''Velociraptor'' specimen, MPC-D 100/976. He concluded that the overall morphology of the former was more derived (advanced) than the latter, suggesting that they could represent distinct taxa.
 Mark J. Powers in his 2020 master thesis fully described MPC-D 100/982, which he concluded to represent a new and third species of ''Velociraptor''. This species, which he named ''"V. vadarostrum"'', was stated to mainly differ from other ''Velociraptor'' species in having a shallow maxilla morphology. Powers and colleagues also in 2020 used
Mark J. Powers in his 2020 master thesis fully described MPC-D 100/982, which he concluded to represent a new and third species of ''Velociraptor''. This species, which he named ''"V. vadarostrum"'', was stated to mainly differ from other ''Velociraptor'' species in having a shallow maxilla morphology. Powers and colleagues also in 2020 used morphometric
Morphometrics (from Greek μορϕή ''morphe'', "shape, form", and -μετρία ''metria'', "measurement") or morphometry refers to the quantitative analysis of ''form'', a concept that encompasses size and shape. Morphometric analyses are co ...
analyses to compare several dromaeosaurid maxillae, and found the maxilla of MPC-D 100/982 to strongly differ from specimens referred to ''Velociraptor''. They indicated that this specimen, based on these results, represents a different species. In 2021 Powers with team used Principal Component Analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a popular technique for analyzing large datasets containing a high number of dimensions/features per observation, increasing the interpretability of data while preserving the maximum amount of information, and ...
to separate dromaeosaurid maxillae, most notably finding that MPC-D 100/982 falls outside the instraspecific variability of ''V. mongoliensis'', arguing for a distinct species. They considered that both ''V. mongoliensis'' and this new species were ecologically separated based on their skull anatomy. The team in another 2021 abstract reinforced again the species-level separation, noting that additional differences can be found in the hindlimbs.
Description
 ''Velociraptor'' was a small to medium-sized
''Velociraptor'' was a small to medium-sized dromaeosaurid
Dromaeosauridae () is a family of feathered theropod dinosaurs. They were generally small to medium-sized feathered carnivores that flourished in the Cretaceous Period. The name Dromaeosauridae means 'running lizards', from Greek ('), meaning ...
, with adults measuring between long, approximately high at the hips, and weighing about .
Prominent quill knobs
The pennaceous feather is a type of feather present in most modern birds and in some other species of maniraptoriform dinosaurs.
Description
A pennaceous feather has a stalk or quill. Its basal part, called a ''calamus'', is embedded in the skin ...
—attachment site of "wing
A wing is a type of fin that produces lift while moving through air or some other fluid. Accordingly, wings have streamlined cross-sections that are subject to aerodynamic forces and act as airfoils. A wing's aerodynamic efficiency is expres ...
" feathers and direct indicator of a feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier ...
covering—have been reported from the ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
of a single ''Velociraptor'' specimen (IGM 100/981), which represents an animal of estimated long and in weight. The spacing of 6 preserved knobs suggests that 8 additional knobs may have been present, giving a total of 14 quill knobs that developed large secondaries ("wing" feathers stemming from the forearm). However, the specimen number has been corrected to IGM 100/3503 and its referral to ''Velociraptor'' may require reevaluation, pending further study. Nevertheless, there is strong phylogenetic evidence from other dromaeosaurid relatives that indicates the presence of feathers in ''Velociraptor'', including dromaeosaurids such as ''Microraptor
''Microraptor'' (Greek, μικρός, ''mīkros'': "small"; Latin, ''raptor'': "one who seizes") is a genus of small, four-winged dromaeosaurid dinosaurs. Numerous well-preserved fossil specimens have been recovered from Liaoning, China. They dat ...
'' or '' Zhenyuanlong''.
Skull
The skull of ''Velociraptor'' was rather elongated and grew up to long. It was uniquely up-curved at the snout region, concave on the upper surface, and convex on the lower surface. The snout, which occupied about 60% of the entire skull length, was notably narrow and mainly formed by the nasal, premaxilla, and maxilla bones. The was the anteriormost bone in the skull, and it was longer than taller. While its posterior end joined the nasal, the main body of the premaxilla touched the maxilla. The was nearly triangular in shape and the largest element of the snout. On its center or main body, there was a depression developing a small oval to circular-shaped hole, called maxillary fenestra. Though in front of this fenestra were two small openings, referred to as promaxillary fenestrae. The posterior border of the maxilla formed (predominantly) the antorbital fenestra, one of the several large holes in the skull. Both premaxilla and maxilla had severalalveoli Alveolus (; pl. alveoli, adj. alveolar) is a general anatomical term for a concave cavity or pit.
Uses in anatomy and zoology
* Pulmonary alveolus, an air sac in the lungs
** Alveolar cell or pneumocyte
** Alveolar duct
** Alveolar macrophage
* ...
(tooth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tear ...
sockets) on their bottom surfaces. Above the maxilla and making contact with the premaxilla, there was the bone. It was a thin/narrow and elongated bone contributing to the top surface of the snout. Together, both premaxilla and nasal bones gave form to the naris or narial fenestra (nostril opening), which was relatively large and circular. The posterior end of the nasal was joined by the frontal and lacrimal bones.
 The back or anterior region of the skull was built by the frontal, lacrimal, postorbital, jugal, parietal, quadrate, and quadratojugal bones. The was large element, having a vaguely rectangular shape when seen from above. On its posterior end, this bone was in contact with the , and such elements were the main bodies of the
The back or anterior region of the skull was built by the frontal, lacrimal, postorbital, jugal, parietal, quadrate, and quadratojugal bones. The was large element, having a vaguely rectangular shape when seen from above. On its posterior end, this bone was in contact with the , and such elements were the main bodies of the skull roof
The skull roof, or the roofing bones of the skull, are a set of bones covering the brain, eyes and nostrils in bony fishes and all land-living vertebrates. The bones are derived from dermal bone and are part of the dermatocranium.
In comparati ...
. The was a T-shaped bone and its main body was thin and delicated. Its lower end meet the (often called cheek bone), which was a large, sub-triangular-shaped element. Its lower border was notably straight/horizontal. The was located just above the jugal: a stocky and strongly T-shaped bone. As a whole, the orbit or orbital fenestra (eye socket)—formed by the lacrimal, jugal, frontal, and postorbital—was large and near circular in shape, being longer than taller. When seen from above, a pair of large and markedly rounded holes were present near the rear of the skull (the temporal fenestrae), whose main components were the postorbital and squamosal. Behind the jugal, an inverted T-shaped bone (also seen in other dromaeosaurids), known as the , was developed. While the upper end of the quadratojugal joined the , an irregularly-shaped element, its inner side meet the . The latter was of great importance for the articulation with the lower jaw. The posteriormost bone was the and its projection the occipital condyle: a rounded and bulbous protuberance that meet the first vertebra of the neck.
 The lower jaw of ''Velociraptor'' comprised mainly the dentary, splenial, angular, surangular, and articular bones. The was a very long, weakly curved, and narrow element that developed several alveoli on its top surface. On its posterior end, it meet the . It had a small hole near its posterior end, called surangular foramen or fenestra. Both bones were the largest elements of the lower jaw of ''Velociraptor'', contributing to virtually its entire length. Below them were the smaller and , closely articulated to each other. The , located on the inner side of the surangular, was a small element that joined the quadrate of the upper skull, enabling the articulation with the lower jaw. An elongated, near oval-shaped hole was developed in the center of the lower jaw (the mandibular fenestra), and it was produced by the joint of the dentary, surangular, and angular bones.
The teeth of ''Velociraptor'' were fairly
The lower jaw of ''Velociraptor'' comprised mainly the dentary, splenial, angular, surangular, and articular bones. The was a very long, weakly curved, and narrow element that developed several alveoli on its top surface. On its posterior end, it meet the . It had a small hole near its posterior end, called surangular foramen or fenestra. Both bones were the largest elements of the lower jaw of ''Velociraptor'', contributing to virtually its entire length. Below them were the smaller and , closely articulated to each other. The , located on the inner side of the surangular, was a small element that joined the quadrate of the upper skull, enabling the articulation with the lower jaw. An elongated, near oval-shaped hole was developed in the center of the lower jaw (the mandibular fenestra), and it was produced by the joint of the dentary, surangular, and angular bones.
The teeth of ''Velociraptor'' were fairly homodont
In anatomy, a heterodont (from Greek, meaning 'different teeth') is an animal which possesses more than a single tooth morphology.
In vertebrates, heterodont pertains to animals where teeth are differentiated into different forms. For example ...
(equal in shape) and had several denticles (serrations), each more strongly serrated on the back edge than the front. The premaxilla had 4 alveoli (meaning that 4 teeth were developed), and the maxilla had 11 alveoli. At the dentary, between 14-15 alveoli were present. All teeth present at the premaxilla were poorly curved, and the two first teeth were the longest, with the second having a characteristic large size. The maxillary teeth were more slender, recurved, and most notably, the lower end was strongly more serrated than the upper one.
Postcranial skeleton
 The arm of ''Velociraptor'' was formed by the
The arm of ''Velociraptor'' was formed by the humerus
The humerus (; ) is a long bone in the arm that runs from the shoulder to the elbow. It connects the scapula and the two bones of the lower arm, the radius and ulna, and consists of three sections. The humeral upper extremity consists of a roun ...
(upper arm bone), radius
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the ...
and ulna
The ulna (''pl''. ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the smallest finger, and when in anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. That is, the ulna is on the same side of t ...
(forearm bones), and manus (hand). ''Velociraptor'', like other dromaeosaurids, had a large manus with three elongated digits (fingers), which ended up in strongly curved unguals (claw bones) that were similar in construction and flexibility to the wing bones of modern bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweigh ...
s. The second digit was the longest of the three digits present, while the first was shortest. The structure of the carpal (wrist) bones prevented pronation
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative ...
of the wrist and forced the manus to be held with the palmar
Palmar may refer to:
Anatomy, relating to the palm of the hand
* Palmar aponeurosis, deep fascia connecting and within the muscles of the palm
* Palmar arches (disambiguation), various combinations of arteries in the hand and arm
* Palmar art ...
surface facing inward ( medially), not downward. The pes
Pes (Latin for "foot") or the acronym PES may refer to:
Pes
* Pes (unit), a Roman unit of length measurement roughly corresponding with a foot
* Pes or podatus, a
* Pes (rural locality), several rural localities in Russia
* Pes (river), a river ...
(foot) anatomy of ''Velociraptor'' consisted of the metatarsus—a large element composed of three metatarsals of which the first one was extremely reduced in size—and four digits that developed large unguals. The first digit, as in other theropods, was a small dewclaw. The second digit, for which ''Velociraptor'' is most famous, was highly modified and held retracted off the ground, which caused ''Velociraptor'' and other dromaeosaurids to walk on only their third and fourth digits. It bore a relatively large, sickle-shaped claw, typical of dromaeosaurid and troodontid dinosaurs. This enlarged claw, which could grow to over long around its outer edge, was most likely a predatory device used to restrain struggling prey.
 As in other dromaeosaurs, ''Velociraptor'' tails had
As in other dromaeosaurs, ''Velociraptor'' tails had prezygapophyses
The articular processes or zygapophyses (Greek language, Greek ζυγον = "yoke" (because it links two vertebrae) + απο = "away" + φυσις = "-physis, process") of a vertebra are projections of the vertebra that serve the purpose of fitting ...
(long bony projections) on the upper surfaces of the vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic ...
e, as well as ossified tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
s underneath. The prezygapophyses began on the tenth tail (caudal) vertebra and extended forward to brace four to ten additional vertebrae, depending on position in the tail. These were once thought to fully stiffen the tail, forcing the entire tail to act as a single rod-like unit. However, at least one specimen has preserved a series of intact tail vertebrae curved sideways into an ''S''-shape, suggesting that there was considerably more horizontal flexibility than once thought.
Classification
''Velociraptor'' is a member of the group Eudromaeosauria, aderived
Derive may refer to:
* Derive (computer algebra system), a commercial system made by Texas Instruments
* ''Dérive'' (magazine), an Austrian science magazine on urbanism
*Dérive, a psychogeographical concept
See also
*
*Derivation (disambiguatio ...
sub-group of the larger family Dromaeosauridae. It is often placed within its own subfamily, Velociraptorinae. In phylogenetic taxonomy
Phylogenetic nomenclature is a method of nomenclature for taxa in biology that uses phylogenetic definitions for taxon names as explained below. This contrasts with the traditional approach, in which taxon names are defined by a '' type'', which ...
, Velociraptorinae is usually defined as "all dromaeosaurs more closely related to ''Velociraptor'' than to ''Dromaeosaurus
''Dromaeosaurus'' (, "running lizard") is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur which lived during the Late Cretaceous period (middle late Campanian and Maastrichtian), sometime between 80 and 69 million years ago, in Alberta, Canada and the ...
''." However, dromaeosaurid classification is highly variable. Originally, the subfamily Velociraptorinae was erected solely to contain ''Velociraptor''. Other analyses have often included other genera, usually ''Deinonychus'' and ''Saurornitholestes
''Saurornitholestes'' ("lizard-bird thief") is a genus of carnivorous dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur from the late Cretaceous of Canada (Alberta) and the United States (Montana, New Mexico, Alabama, North Carolina, and South Carolina).
Two spec ...
'', and more recently ''Tsaagan''. Several studies published during the 2010s, including expanded versions of the analyses that found support for Velociraptorinae, have failed to resolve it as a distinct group, but rather have suggested it is a paraphyletic grade which gave rise to the Dromaeosaurinae.
When first described in 1924, ''Velociraptor'' was placed in the family Megalosauridae, as was the case with most carnivorous dinosaurs at the time (Megalosauridae, like '' Megalosaurus'', functioned as a sort of 'wastebin' taxon, where many unrelated species were grouped together). As dinosaur discoveries multiplied, ''Velociraptor'' was later recognized as a dromaeosaurid. All dromaeosaurids have also been referred to the family Archaeopterygidae by at least one author (which would, in effect, make ''Velociraptor'' a flightless bird). In the past, other dromaeosaurid species, including ''Deinonychus antirrhopus'' and ''Saurornitholestes langstoni'', have sometimes been classified in the genus ''Velociraptor''. Since ''Velociraptor'' was the first to be named, these species were renamed ''Velociraptor antirrhopus'' and ''V. langstoni''. As of 2008, the only currently recognized species of ''Velociraptor'' are ''V. mongoliensis'' and ''V. osmolskae''. However, several studies have found "''V.''" ''osmolskae'' to be distantly related to ''V. mongoliensis''. Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License

 Below are the results for the Eudromaeosauria
Below are the results for the Eudromaeosauria phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological spec ...
based on the phylogenetic analysis conducted by James G. Napoli and team in 2021 during the description of ''Kuru
Kuru may refer to:
Anthropology and history
* Kuru (disease), a type of transmissible spongiform encephalopathy associated with the cannibalistic funeral practices of the Fore people
* Kuru (mythology), part of Meithei mythology
* Kuru Kingdom, ...
'', showing the position of ''Velociraptor'':
Paleobiology
Feathers
 In 2007 Alan H. Turner and colleagues reported the presence of six
In 2007 Alan H. Turner and colleagues reported the presence of six quill knobs
The pennaceous feather is a type of feather present in most modern birds and in some other species of maniraptoriform dinosaurs.
Description
A pennaceous feather has a stalk or quill. Its basal part, called a ''calamus'', is embedded in the skin ...
in the ulna of a referred ''Velociraptor'' specimen (IGM 100/981) from the Ukhaa Tolgod locality of the Djadochta Formation
The Djadochta Formation (sometimes transcribed and also known as Djadokhta, Djadokata, or Dzhadokhtskaya) is a highly fossiliferous geological formation situated in Central Asia, Gobi Desert, dating from the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 milli ...
. Turner and colleagues interpreted the presence of feathers on ''Velociraptor'' as evidence against the idea that the larger, flightless maniraptora
Maniraptora is a clade of coelurosaurian dinosaurs which includes the birds and the non-avian dinosaurs that were more closely related to them than to ''Ornithomimus velox''. It contains the major subgroups Avialae, Deinonychosauria, Oviraptoros ...
ns lost their feathers secondarily due to larger body size. Furthermore, they noted that quill knobs are almost never found in flightless bird species today, and that their presence in ''Velociraptor'' (presumed to have been flightless due to its relatively large size and short forelimbs) is evidence that the ancestors of dromaeosaurids could fly, making ''Velociraptor'' and other large members of this family secondarily flightless, though it is possible the large wing feathers inferred in the ancestors of ''Velociraptor'' had a purpose other than flight. The feathers of the flightless ''Velociraptor'' may have been used for display, for covering their nests while brooding, or for added speed and thrust when running up inclined slopes. Because of the presence of another dromaeosaurid in Ukhaa Tolgod, ''Tsaagan
''Tsaagan'' (meaning "white") is a genus of dromaeosaurid dinosaur from the Djadokhta Formation of the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia.
Discovery and naming
The holotype of ''Tsaagan'' was discovered in 1996 and first identified as a specimen of '' ...
'', Napoli and team have noted that the referral of this specimen to ''Velociraptor'' is currently subject to rexamination.
Senses
Examinations of the endocranium of ''Velociraptor'' indicate that it was able to detect and hear a wide range of sound frequencies (2,368–3,965 Hz) and could track prey with ease as a result. The endocranium examinations also further cemented the theory that the dromaeosaur was an agile, swift predator. Fossil evidence suggesting ''Velociraptor'' scavenged also indicates that it was an opportunistic and actively predatory animal, feeding on carrion during times of drought or famine, if in poor health, or depending on the animal's age.Feeding
In 2020, Powers and colleagues re-examined themaxillae
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
of several eudromaeosaur taxa concluding that most Asian and North American eudromaeosaurs were separated by snout morphology and ecological strategies. They found the maxilla to be a reliable reference when inferring the shape of the premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has b ...
and overall snout
A snout is the protruding portion of an animal's face, consisting of its nose, mouth, and jaw. In many animals, the structure is called a muzzle, rostrum, or proboscis. The wet furless surface around the nostrils of the nose of many mammals is c ...
. For instance, most Asian species have elongated snouts based on the maxilla (namely velociraptorines
Velociraptorinae is a subfamily of the theropod group Dromaeosauridae. The earliest velociraptorines are probably ''Nuthetes'' from the United Kingdom, and possibly ''Deinonychus'' from North America. However, several indeterminate velociraptorin ...
), indicating a selective feeding in ''Velociraptor'' and relatives, such as picking up small, fast prey. In contrast, most North American eudromaeosaurs, mostly dromaeosaurines, feature a robust and deep maxillar morphology. However, the large dromaeosurine ''Achillobator'' is a unique exception to Asian taxa with its deep maxilla.
Predatory behavior
The "Fighting Dinosaurs
The Fighting Dinosaurs is a fossil specimen which was found in the Late Cretaceous Djadokhta Formation of Mongolia. It preserves a ''Protoceratops andrewsi'' and ''Velociraptor mongoliensis'' trapped in combat and provides direct evidence of pre ...
" specimen, found in 1971, preserves a ''Velociraptor mongoliensis'' and '' Protoceratops andrewsi'' in combat and provides direct evidence of predatory behavior. When originally reported, it was hypothesized that the two animals drowned. However, as the animals were preserved in ancient sand dune deposits, it is now thought that the animals were buried in sand, either from a collapsing dune or in a sandstorm. Burial must have been extremely fast, judging from the lifelike poses in which the animals were preserved. Parts of the ''Protoceratops'' are missing, which has been seen as evidence of scavenging by other animals. Comparisons between the scleral rings of ''Velociraptor'', ''Protoceratops'', and modern birds and reptiles indicates that ''Velociraptor'' may have been nocturnal
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed sens ...
, while ''Protoceratops'' may have been cathemeral, active throughout the day during short intervals, suggesting that the fight may have occurred at twilight or during low-light conditions.
 The distinctive claw, on the second digit of dromaeosaurids, has traditionally been depicted as a slashing weapon; its assumed use being to cut and disembowel prey. In the "Fighting Dinosaurs" specimen, the ''Velociraptor'' lies underneath, with one of its sickle claws apparently embedded in the throat of its prey, while the beak of ''Protoceratops'' is clamped down upon the right forelimb of its attacker. This suggests ''Velociraptor'' may have used its sickle claw to pierce vital organs of the throat, such as the jugular vein,
The distinctive claw, on the second digit of dromaeosaurids, has traditionally been depicted as a slashing weapon; its assumed use being to cut and disembowel prey. In the "Fighting Dinosaurs" specimen, the ''Velociraptor'' lies underneath, with one of its sickle claws apparently embedded in the throat of its prey, while the beak of ''Protoceratops'' is clamped down upon the right forelimb of its attacker. This suggests ''Velociraptor'' may have used its sickle claw to pierce vital organs of the throat, such as the jugular vein, carotid artery Carotid artery may refer to:
* Common carotid artery, often "carotids" or "carotid", an artery on each side of the neck which divides into the external carotid artery and internal carotid artery
* External carotid artery, an artery on each side of t ...
, or trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a Cartilage, cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends ...
(windpipe), rather than slashing the abdomen. The inside edge of the claw was rounded and not unusually sharp, which may have precluded any sort of cutting or slashing action, although only the bony core of the claw is preserved. The thick abdominal wall of skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
and muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
of large prey species would have been difficult to slash without a specialized cutting surface. The slashing hypothesis
A hypothesis (plural hypotheses) is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon. For a hypothesis to be a scientific hypothesis, the scientific method requires that one can test it. Scientists generally base scientific hypotheses on previous obse ...
was tested during a 2005 BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board ex ...
documentary, ''The Truth About Killer Dinosaurs
''The Truth About Killer Dinosaurs'' is a two-part BBC documentary film, directed by Bill Oddie, in which a group of men test out dinosaur weapons, using studies. The first episode determines the winner of a battle between ''Tyrannosaurus'' and ...
''. The producers of the program created an artificial ''Velociraptor'' leg with a sickle claw and used a pork belly to simulate the dinosaur's prey. Though the sickle claw did penetrate the abdominal wall, it was unable to tear it open, indicating that the claw was not used to disembowel prey.
Remains of '' Deinonychus'', a closely related dromaeosaurid, have commonly been found in aggregations of several individuals. ''Deinonychus'' has also been found in association with the large ornithopod '' Tenontosaurus'', which has been cited as evidence of cooperative (pack) hunting. However, the only solid evidence for social behavior of any kind among dromaeosaurids comes from a Chinese trackway which shows six individuals of a large species moving as a group. Although many isolated fossils of ''Velociraptor'' have been found in Mongolia, none were closely associated with other individuals. Therefore, while ''Velociraptor'' is commonly depicted as a pack hunter, as in ''Jurassic Park'', there is only limited fossil evidence to support this theory for dromaeosaurids in general and none specific to ''Velociraptor'' itself. Dromeosaur footprints in China suggest that a few other raptor genera may have hunted in packs, but there have been no conclusive examples of pack behavior found.
 In 2011, Denver Fowler and colleagues suggested a new method by which dromaeosaurs like ''Velociraptor'' and similar dromaeosaurs may have captured and restrained prey. This model, known as the "raptor prey restraint" (RPR) model of predation, proposes that dromaeosaurs killed their prey in a manner very similar to extant
In 2011, Denver Fowler and colleagues suggested a new method by which dromaeosaurs like ''Velociraptor'' and similar dromaeosaurs may have captured and restrained prey. This model, known as the "raptor prey restraint" (RPR) model of predation, proposes that dromaeosaurs killed their prey in a manner very similar to extant accipitrid
The Accipitridae is one of the three families within the order Accipitriformes, and is a family of small to large birds with strongly hooked bills and variable morphology based on diet. They feed on a range of prey items from insects to medium-si ...
birds of prey: by leaping onto their quarry, pinning it under their body weight, and gripping it tightly with the large, sickle-shaped claws. These researchers proposed that, like accipitrids, the dromaeosaur would then begin to feed on the animal while it was still alive, and prey death would eventually result from blood loss and organ failure. This proposal is based primarily on comparisons between the morphology and proportions of the feet and legs of dromaeosaurs to several groups of extant birds of prey with known predatory behaviors. Fowler found that the feet and legs of dromaeosaurs most closely resemble those of eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just ...
s and hawk
Hawks are bird of prey, birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. They are widely distributed and are found on all continents except Antarctica.
* The subfamily Accipitrinae includes goshawks, sparrowhawks, sharp-shinned hawks and others. Th ...
s, especially in terms of having an enlarged second claw and a similar range of grasping motion. The short metatarsus and foot strength, however, would have been more similar to that of owls. The RPR method of predation would be consistent with other aspects of ''Velociraptor''s anatomy, such as their unusual jaw and arm morphology. The arms, which could exert a lot of force but were likely covered in long feathers, may have been used as flapping stabilizers for balance while atop a struggling prey animal, along with the stiff counterbalancing tail. The jaws, thought by Fowler and colleagues to be comparatively weak, would have been useful for row saw motion bites like the modern day Komodo dragon
The Komodo dragon (''Varanus komodoensis''), also known as the Komodo monitor, is a member of the monitor lizard family Varanidae that is endemic to the Indonesian islands of Komodo, Rinca, Flores, and Gili Motang. It is the largest extant ...
, which also has a weak bite, to finish off its prey if the kicks weren't powerful enough. These predatory adaptations working together may also have implications for the origin of flapping in paravian
Paraves are a widespread group of theropod dinosaurs that originated in the Middle Jurassic period. In addition to the extinct dromaeosaurids, troodontids, anchiornithids, and possibly the scansoriopterygids, the group also contains the aviala ...
s.
Scavenging behavior
In 2010, Hone and colleagues published a paper on their 2008 discovery of shed teeth of what they believed to be a ''Velociraptor'' near a tooth-marked jaw bone of what they believed to be a ''Protoceratops'' in the Bayan Mandahu Formation. The authors concluded that the find represented "late-stage carcass consumption by ''Velociraptor''" as the predator would have eaten other parts of a freshly killed ''Protoceratops'' before biting in the jaw area. The evidence was seen as supporting the inference from the "Fighting Dinosaurs" fossil that ''Protoceratops'' was part of the diet of ''Velociraptor''. In 2012, Hone and colleagues published a paper that described a ''Velociraptor'' specimen with a long bone of an azhdarchidpterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 to ...
in its gut. This was interpreted as showing scavenging behaviour.
Metabolism
''Velociraptor'' waswarm-blooded
Warm-blooded is an informal term referring to animal species which can maintain a body temperature higher than their environment. In particular, homeothermic species maintain a stable body temperature by regulating metabolic processes. The onl ...
to some degree, as it required a significant amount of energy to hunt. Modern animals that possess feathery or furry coats, like ''Velociraptor'' did, tend to be warm-blooded, since these coverings function as insulation. However, bone growth rates in dromaeosaurids and some early birds suggest a more moderate metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cell ...
, compared with most modern warm-blooded mammals and birds. The kiwi
Kiwi most commonly refers to:
* Kiwi (bird), a flightless bird native to New Zealand
* Kiwi (nickname), a nickname for New Zealanders
* Kiwifruit, an edible berry
* Kiwi dollar or New Zealand dollar, a unit of currency
Kiwi or KIWI may also refe ...
is similar to dromaeosaurids in anatomy, feather type, bone structure and even the narrow anatomy of the nasal passages (usually a key indicator of metabolism). The kiwi is a highly active, if specialized, flightless bird, with a stable body temperature and a fairly low resting metabolic rate, making it a good model for the metabolism of primitive birds and dromaeosaurids.
Paleopathology
Norell with colleagues in 1995 reported one ''V. mongoliensis'' skull bearing two parallel rows of small punctures on its frontal bones that, upon closer examination, match the spacing and size of ''Velociraptor'' teeth. They suggested that the wound was likely inflicted by another ''Velociraptor'' during a fight between the species. Because its bone structure shows no sign ofhealing
With physical trauma or disease suffered by an organism, healing involves the repairing of damaged tissue(s), organs and the biological system as a whole and resumption of (normal) functioning. Medicine includes the process by which the cells i ...
near the bite wounds and the overall specimen was not scavenged, this individual was likely killed by this fatal wound. In 2001 Molnar and team noted that this specimen is MPC-D 100/976 hailing from the Tugrik Shireh locality, which has also yielded the Fighting Dinosaurs specimen.
In 2012 David Hone and team reported another injured ''Velociraptor'' specimen (MPC-D 100/54, roughly a sub-adult individual) found with the bones of an azhdarchid pterosaur within its stomach cavity, was carrying or recovering from an injury sustained to one broken rib. From evidence on the pterosaur bones, which were devoid of pitting or deformations from digestion, the ''Velociraptor'' died shortly after, possibly from the earlier injury. Nevertheless, the team noted that this broken ribs shows signs of bone healing.
Paleoenvironment
Bayan Mandahu Formation
 In both Bayan Mandahu and Djadochta formations many of the same genera were present, though they varied at the species level. These differences in species composition may be due a natural barrier separating the two formations, which are relatively close to each other geographically. However, given the lack of any known barrier which would cause the specific faunal compositions found in these areas, it is more likely that those differences indicate a slight time difference.
''V. osmolskae'' lived alongside the ankylosaurid '' Pinacosaurus mephistocephalus''; alvarezsaurid ''
In both Bayan Mandahu and Djadochta formations many of the same genera were present, though they varied at the species level. These differences in species composition may be due a natural barrier separating the two formations, which are relatively close to each other geographically. However, given the lack of any known barrier which would cause the specific faunal compositions found in these areas, it is more likely that those differences indicate a slight time difference.
''V. osmolskae'' lived alongside the ankylosaurid '' Pinacosaurus mephistocephalus''; alvarezsaurid ''Linhenykus
''Linhenykus'' is an extinct genus of alvarezsaurid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Inner Mongolia, China. It is the most basal known member of the Parvicursorinae. The genus gets its name from Linhe, a city near the site where th ...
''; closely related dromaeosaurid ''Linheraptor
''Linheraptor'' is a genus of dromaeosaurid dinosaur which lived in what is now China in the Late Cretaceous. It was named by Xu Xing and colleagues in 2010, and contains the species ''Linheraptor exquisitus''. This bird-like dinosaur was less ...
''; oviraptorids ''Machairasaurus
''Machairasaurus'' is a genus of oviraptorid dinosaur which was found in the Bayan Mandahu Formation, China, dating to the late Cretaceous period.
Discovery
During the Sino-Canadian expeditions of 1988 and 1990 some skeletons of unknown ovirap ...
'' and ''Wulatelong
''Wulatelong'' is an extinct genus of basal oviraptorid dinosaur known from the Late Cretaceous Wulansuhai Formation (Campanian stage) of Bayan Mandahu, Linhe District of Inner Mongolia, northern China. It contains a single species, ''Wulatelong ...
''; protoceratopsids '' Bagaceratops'' and ''Protoceratops hellenikorhinus
''Protoceratops'' (; ) is a genus of small protoceratopsid dinosaurs that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous, around 75 to 71 million years ago. The genus ''Protoceratops'' includes two species: ''P. andrewsi'' and the larger ''P. helleni ...
''; and troodontids ''Linhevenator
''Linhevenator'' is a genus of short-armed troodontid theropod dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous (Campanian) Bayan Mandahu Formation of Bayan Mandahu, Inner Mongolia, China.
Discovery
The type species ''Linhevenator tani'' was named and descri ...
'', ''Papiliovenator
''Papiliovenator'' (meaning "butterfly hunter", after a butterfly-shaped feature on its first two dorsal vertebrae) is a genus of troodontid theropod dinosaur from the Bayan Mandahu Formation of Inner Mongolia, China. The type and only species i ...
'', and ''Philovenator
''Philovenator'' (literally meaning "love hunter") is an extinct genus of troodontid paravian dinosaurs from the Wulansuhai Formation (dated to the Campanian age, sometime between 75 and 71 million years ago) of Inner Mongolia, China. Its specif ...
''. Sediments across the formation indicate a similar depositional environment to that of the Djadochta Formation.
Djadochta Formation
 Known specimens of ''Velociraptor mongoliensis'' have been recovered from the
Known specimens of ''Velociraptor mongoliensis'' have been recovered from the Djadochta Formation
The Djadochta Formation (sometimes transcribed and also known as Djadokhta, Djadokata, or Dzhadokhtskaya) is a highly fossiliferous geological formation situated in Central Asia, Gobi Desert, dating from the Late Cretaceous period, about 75 milli ...
(also spelled Djadokhta), in the Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, ...
n province of Ömnögovi. This geological formation
A geological formation, or simply formation, is a body of rock having a consistent set of physical characteristics ( lithology) that distinguishes it from adjacent bodies of rock, and which occupies a particular position in the layers of rock exp ...
is estimated to date back to the Campanian stage (between 75 million and 71 million years ago) of the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided by ...
. The abundant sediments—sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class of s ...
s, sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) ...
s, or caliche—of the Djadochta Formation were deposited by eolian (wind) processes in arid settings with fields of sand dune
A dune is a landform composed of wind- or water-driven sand. It typically takes the form of a mound, ridge, or hill. An area with dunes is called a dune system or a dune complex. A large dune complex is called a dune field, while broad, f ...
s and only intermittent stream
A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream ...
s, as indicated by very sparse fluvial
In geography and geology, fluvial processes are associated with rivers and streams and the deposits and landforms created by them. When the stream or rivers are associated with glaciers, ice sheets, or ice caps, the term glaciofluvial or fluviog ...
(river-deposited) sedimentation, under a semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
.
The Djadochta Formation is separated into a lower Bayn Dzak Member and upper Turgrugyin Member. ''V. mongoliensis'' is known from both members, represented by numerous specimens. The Bayn Dzak Member (mainly Bayn Dzak locality) has yielded the oviraptorid '' Oviraptor''; ankylosaurid ''Pinacosaurus grangeri
''Pinacosaurus'' (meaning "Plank lizard") is a genus of ankylosaurid thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous (Santonian-Campanian, roughly 75 million to 71 million years ago), mainly in Mongolia and China.
The first ...
''; protoceratopsid '' Protoceratops andrewsi''; and troodontid ''Saurornithoides
''Saurornithoides'' ( ) is a genus of troodontid maniraptoran dinosaur, which lived during the Late Cretaceous period. These creatures were predators, which could run fast on their hind legs and had excellent sight and hearing. The name is deriv ...
''. The younger Turgrugyin Member (mainly Tugriken Shireh locality) has produced the bird ''Elsornis
''Elsornis'' is a genus of enantiornithine bird. Only one species is known, ''Elsornis keni''. It lived during the Late Cretaceous. It is known from a partially articulated fossil skeleton found in the Gobi Desert in Mongolia.
The holotype fo ...
''; dromaeosaurid '' Mahakala'': ornithomimid '' Aepyornithomimus''; and protoceratopsid ''Protoceratops andrewsi''.
''V. mongoliensis'' has been found at many of the most famous and prolific Djadochta localities. The type specimen was discovered at the Flaming Cliffs site (sublocality of the larger Bayn Dzak locality/region), while the "Fighting Dinosaurs" were found at the Tugrik Shire locality (also known as Tugrugeen Shireh and many other spellings). The latter is notorious for its exceptional '' in situ'' fossil preservation. Based on deposits (such as structureless sandstones), it has been concluded that a large number of specimens were buried alive during powerful sand-bearing events, common to the these paleoenvironments.
Cultural significance
''Velociraptor'' is commonly perceived as a vicious and cunning killer thanks to their portrayal in the 1990 novel ''Jurassic Park
''Jurassic Park'', later also referred to as ''Jurassic World'', is an American science fiction media franchise created by Michael Crichton and centered on a disastrous attempt to create a theme park of cloned dinosaurs. It began in 1990 when ...
'' by Michael Crichton
John Michael Crichton (; October 23, 1942 – November 4, 2008) was an American author and filmmaker. His books have sold over 200 million copies worldwide, and over a dozen have been adapted into films. His literary works heavily feature tech ...
and its 1993 film adaptation
A film adaptation is the transfer of a work or story, in whole or in part, to a feature film. Although often considered a type of derivative work, film adaptation has been conceptualized recently by academic scholars such as Robert Stam as a dial ...
, directed by Steven Spielberg
Steven Allan Spielberg (; born December 18, 1946) is an American director, writer, and producer. A major figure of the New Hollywood era and pioneer of the modern blockbuster, he is the most commercially successful director of all time. Spie ...
. The "raptors" portrayed in ''Jurassic Park'' were actually modeled after the closely related dromaeosaurid
Dromaeosauridae () is a family of feathered theropod dinosaurs. They were generally small to medium-sized feathered carnivores that flourished in the Cretaceous Period. The name Dromaeosauridae means 'running lizards', from Greek ('), meaning ...
'' Deinonychus''. Paleontologists in both the novel and film excavate a skeleton in Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
, far from the central Asian range of ''Velociraptor'' but characteristic of the ''Deinonychus'' range. Crichton met with the discoverer of ''Deinonychus'', John Ostrom, several times at Yale University
Yale University is a private research university in New Haven, Connecticut. Established in 1701 as the Collegiate School, it is the third-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and among the most prestigious in the wo ...
to discuss details of the animal's possible range of behaviors and appearance. Crichton at one point apologetically told Ostrom that he had decided to use the name ''Velociraptor'' in place of ''Deinonychus'' because the former name was "more dramatic." According to Ostrom, Crichton stated that the ''Velociraptor'' of the novel was based on ''Deinonychus'' in almost every detail, and that only the name had been changed. The ''Jurassic Park'' film-makers also requested all of Ostrom's published papers on ''Deinonychus'' during production.Cummings, M.Yale’s legacy in ''Jurassic World''
" ''Yale News'', 18-Jun-2015. They portrayed the animals with the size, proportions, and snout shape of ''Deinonychus'' rather than ''Velociraptor''. Production on ''Jurassic Park'' began before the discovery of the large dromaeosaurid ''
Utahraptor
''Utahraptor'' (meaning "Utah's thief") is a genus of large dromaeosaurid dinosaur that lived in North America during the Early Cretaceous period. It was a heavy-built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore. It contains a single species, ''Utahrap ...
'' was made public in 1991, but as Jody Duncan wrote about this discovery: "Later, after we had designed and built the raptor, there was a discovery of a raptor skeleton in Utah, which they labeled 'super-slasher.' They had uncovered the largest Velociraptor to date and it measured five-and-a-half-feet tall, just like ours. So we designed it, we built it, and then they discovered it. That still boggles my mind." Spielberg's name was briefly considered for naming of the new dinosaur in exchange for funding of field work, but no agreement was reached.
''Jurassic Park
''Jurassic Park'', later also referred to as ''Jurassic World'', is an American science fiction media franchise created by Michael Crichton and centered on a disastrous attempt to create a theme park of cloned dinosaurs. It began in 1990 when ...
'' and its sequel '' The Lost World: Jurassic Park'' were released before the discovery that dromaeosaurs had feathers, so the ''Velociraptor'' in both films were depicted as scaled and featherless. For '' Jurassic Park III,'' the male ''Velociraptor'' was given quill-like structures along the back of the head and neck, but these structures do not resemble the feathers that ''Velociraptor'' would have had in reality due to reasons of continuity. The ''Jurassic World
''Jurassic World'' is a 2015 American science fiction action film directed by Colin Trevorrow, who co-wrote the screenplay with Rick Jaffa, Amanda Silver, and Derek Connolly from a story by Jaffa and Silver. It is the first installment in the ...
'' sequel trilogy ignored the feathers of ''Velociraptor'', adhering to the designs from ''Jurassic Park''. However, the dromaeosaur '' Pyroraptor'' was feathered for ''Jurassic World Dominion
''Jurassic World Dominion'' is a 2022 American science fiction action film directed by Colin Trevorrow, who co-wrote the screenplay with Emily Carmichael from a story by Derek Connolly and Trevorrow. The sequel to '' Jurassic World: Fallen ...
'', along with other changes such as stiffening the tail to account for ossified tendons and de-pronating the hands.
See also
* Timeline of dromaeosaurid research *Fighting Dinosaurs
The Fighting Dinosaurs is a fossil specimen which was found in the Late Cretaceous Djadokhta Formation of Mongolia. It preserves a ''Protoceratops andrewsi'' and ''Velociraptor mongoliensis'' trapped in combat and provides direct evidence of pre ...
References
External links
* * * *3D skull model of ''Velociraptor mongoliensis''
at
Sketchfab
Sketchfab is a 3D modeling platform website to publish, share, discover, buy and sell 3D, VR and AR content. It provides a viewer based on the WebGL and WebXR technologies that allows users to display 3D models on the web, to be viewed on a ...
Skeletal reconstruction of ''Velociraptor mongoliensis''
at Dr. Scott Hartman's Skeletal Drawing
at
American Museum of Natural History
The American Museum of Natural History (abbreviated as AMNH) is a natural history museum on the Upper West Side of Manhattan in New York City. In Theodore Roosevelt Park, across the street from Central Park, the museum complex comprises 26 inter ...
(Wayback Machine
The Wayback Machine is a digital archive of the World Wide Web founded by the Internet Archive, a nonprofit based in San Francisco, California. Created in 1996 and launched to the public in 2001, it allows the user to go "back in time" and see ...
)
{{featured article
Campanian genus first appearances
Djadochta fauna
Eudromaeosaurs
Feathered dinosaurs
Fossil taxa described in 1924
Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of Asia
Taxa named by Henry Fairfield Osborn