Upstate New York on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Upstate New York is a geographic region consisting of the area of
Upstate New York is a geographic region consisting of the area of
 Upstate New York is a geographic region consisting of the area of
Upstate New York is a geographic region consisting of the area of New York State
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. stat ...
that lies north and northwest of the New York City metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the Tri-State area, is the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass, at , and one of the list of most populous metropolitan areas, most populous urban agg ...
. Although the precise boundary is debated, Upstate New York excludes New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
and Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
, and most definitions of the region also exclude all or part of Westchester and Rockland counties, which are typically included in Downstate New York
Downstate New York is a region that generally consists of the southeastern and more densely populated portion of the U.S. state of New York, in contrast to Upstate New York, which comprises a larger geographic area with much sparser population di ...
. Major cities across Upstate New York from east to west include Albany, Utica, Binghamton
Binghamton () is a city in the U.S. state of New York, and serves as the county seat of Broome County. Surrounded by rolling hills, it lies in the state's Southern Tier region near the Pennsylvania border, in a bowl-shaped valley at the conflue ...
, Syracuse, Rochester
Rochester may refer to:
Places Australia
* Rochester, Victoria
Canada
* Rochester, Alberta
United Kingdom
*Rochester, Kent
** City of Rochester-upon-Medway (1982–1998), district council area
** History of Rochester, Kent
** HM Prison ...
, and Buffalo.
Upstate New York is divided into several subregions: the Hudson Valley
The Hudson Valley (also known as the Hudson River Valley) comprises the valley of the Hudson River and its adjacent communities in the U.S. state of New York. The region stretches from the Capital District including Albany and Troy south to ...
(of which the lower part is sometimes debated as to being "upstate"), the Capital District
A capital district, capital region or capital territory is normally a specially designated administrative division where a country's seat of government is located. As such, in a federal model of government, no state or territory has any poli ...
, the Mohawk Valley region
The Mohawk Valley region of the U.S. state of New York is the area surrounding the Mohawk River, sandwiched between the Adirondack Mountains and Catskill Mountains, northwest of the Capital District. As of the 2010 United States Census, th ...
, Central New York
Central New York is the central region of New York State, including the following counties and cities:
With a population of about 773,606 (2009) and an area of , the region includes the Syracuse metropolitan area.
Definitions
The New York ...
, the Southern Tier, the Finger Lakes
The Finger Lakes are a group of eleven long, narrow, roughly north–south lakes located south of Lake Ontario in an area called the ''Finger Lakes region'' in New York, in the United States. This region straddles the northern and transitional ...
region, Western New York
Western New York (WNY) is the westernmost region of the U.S. state of New York. The eastern boundary of the region is not consistently defined by state agencies or those who call themselves "Western New Yorkers". Almost all sources agree WNY i ...
, and the North Country.
Before the European colonization
The historical phenomenon of colonization is one that stretches around the globe and across time. Ancient and medieval colonialism was practiced by the Phoenicians, the Greeks, the Turks, and the Arabs.
Colonialism in the modern sense began ...
of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, Upstate New York was populated by several Native American tribes. It was home to the Iroquois Confederacy
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
, an indigenous confederation of six tribes, known as the Six Nations. Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 16 ...
made the first recorded European exploration of the region in 1609, and the Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
erected Fort Orange
Fort Orange ( nl, Fort Oranje) was the first permanent Dutch settlement in New Netherland; the present-day city of Albany, New York developed at this site. It was built in 1624 as a replacement for Fort Nassau, which had been built on nearb ...
(present-day Albany) in 1624, which was the first permanent European settlement in New York. The region saw many battles during the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, with the Iroquois split between supporters of the loyalists and supporters of the revolutionaries. After the war ended, the 1784 Treaty of Fort Stanwix kicked off a series of treaties and purchases that saw the Iroquois cede the vast majority of their land in Upstate New York to the newly formed United States.
The 1825 opening of the Erie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east-west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, vastly reducing t ...
across Upstate New York transformed the economy of the region and the state. The canal greatly eased the movement of goods from across the upper Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
and the cities along the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
through Upstate New York and to the port of New York City. As a result, Upstate New York became a hotbed for manufacturing during the Second Industrial Revolution
The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, was a phase of rapid scientific discovery, standardization, mass production and industrialization from the late 19th century into the early 20th century. The Fi ...
, giving birth to such firms as General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energ ...
, IBM, Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company (referred to simply as Kodak ) is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in analogue photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorpor ...
, and Xerox
Xerox Holdings Corporation (; also known simply as Xerox) is an American corporation that sells print and electronic document, digital document products and services in more than 160 countries. Xerox is headquartered in Norwalk, Connecticut (ha ...
. The rapid industrialization led to a large influx of immigrants seeking jobs at factories across the region. Since the mid-20th century, American de-industrialization has contributed to economic and population decline, and the region is largely considered part of the Rust Belt
The Rust Belt is a region of the United States that experienced industrial decline starting in the 1950s. The U.S. manufacturing sector as a percentage of the U.S. GDP peaked in 1953 and has been in decline since, impacting certain regions an ...
.
There are a wide variety of land uses in the region, including urban, suburban, forested preserve, and rural landscapes. Due to its vast areas of rural land, Upstate also supports a strong agricultural industry, and is notable for its dairy
A dairy is a business enterprise established for the harvesting or processing (or both) of animal milk – mostly from cows or buffaloes, but also from goats, sheep, horses, or camels – for human consumption. A dairy is typically located on ...
, maple syrup, and fruit production (especially apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
s), as well as winemaking
Winemaking or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over millennia. The science of wine and ...
. Upstate New York includes a number of notable waterways, with the Susquehanna, Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
, and Hudson
Hudson may refer to:
People
* Hudson (given name)
* Hudson (surname)
* Henry Hudson, English explorer
* Hudson (footballer, born 1986), Hudson Fernando Tobias de Carvalho, Brazilian football right-back
* Hudson (footballer, born 1988), Hudso ...
Rivers all originating in the region, and is bordered on its northern and western edges by the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connectin ...
and the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
. As a result, the region is a significant source of hydroelectric power
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined an ...
(going back to the creation of the world's first hydroelectric dam by Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla ( ; ,"Tesla"
''

 There is no clear official boundary between Upstate New York and
There is no clear official boundary between Upstate New York and

 As of 2020, the population of New York State was 20,201,249, with 14,045,410 living in the
As of 2020, the population of New York State was 20,201,249, with 14,045,410 living in the
 The headwaters of the
The headwaters of the  The
The
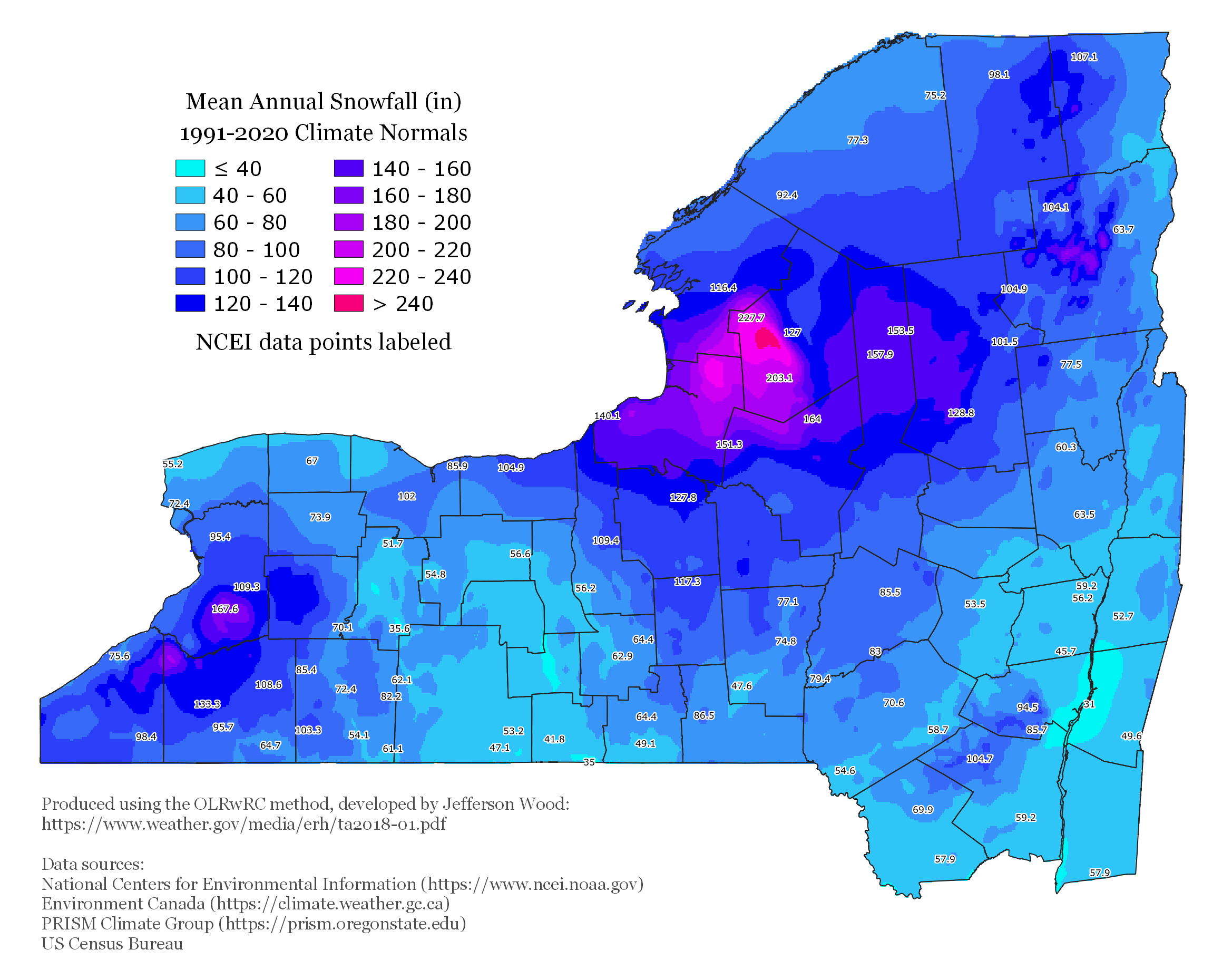 Upstate New York is well known for its cold and snowy winters, particularly in comparison to the more temperate climate of Downstate New York. The snowy reputation is especially true for the cities of Buffalo, Rochester, Oswego and Syracuse, and is largely due to lake-effect snow from Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. The villages of Old Forge and Saranac Lake, both in the Adirondacks, often vie on winter nights with places like International Falls, Minnesota, and Fargo, North Dakota, for the coldest spot in the nation.
Many of the features of Upstate New York landscapes, such as the
Upstate New York is well known for its cold and snowy winters, particularly in comparison to the more temperate climate of Downstate New York. The snowy reputation is especially true for the cities of Buffalo, Rochester, Oswego and Syracuse, and is largely due to lake-effect snow from Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. The villages of Old Forge and Saranac Lake, both in the Adirondacks, often vie on winter nights with places like International Falls, Minnesota, and Fargo, North Dakota, for the coldest spot in the nation.
Many of the features of Upstate New York landscapes, such as the
 Before the arrival of Europeans, the area was long inhabited by
Before the arrival of Europeans, the area was long inhabited by
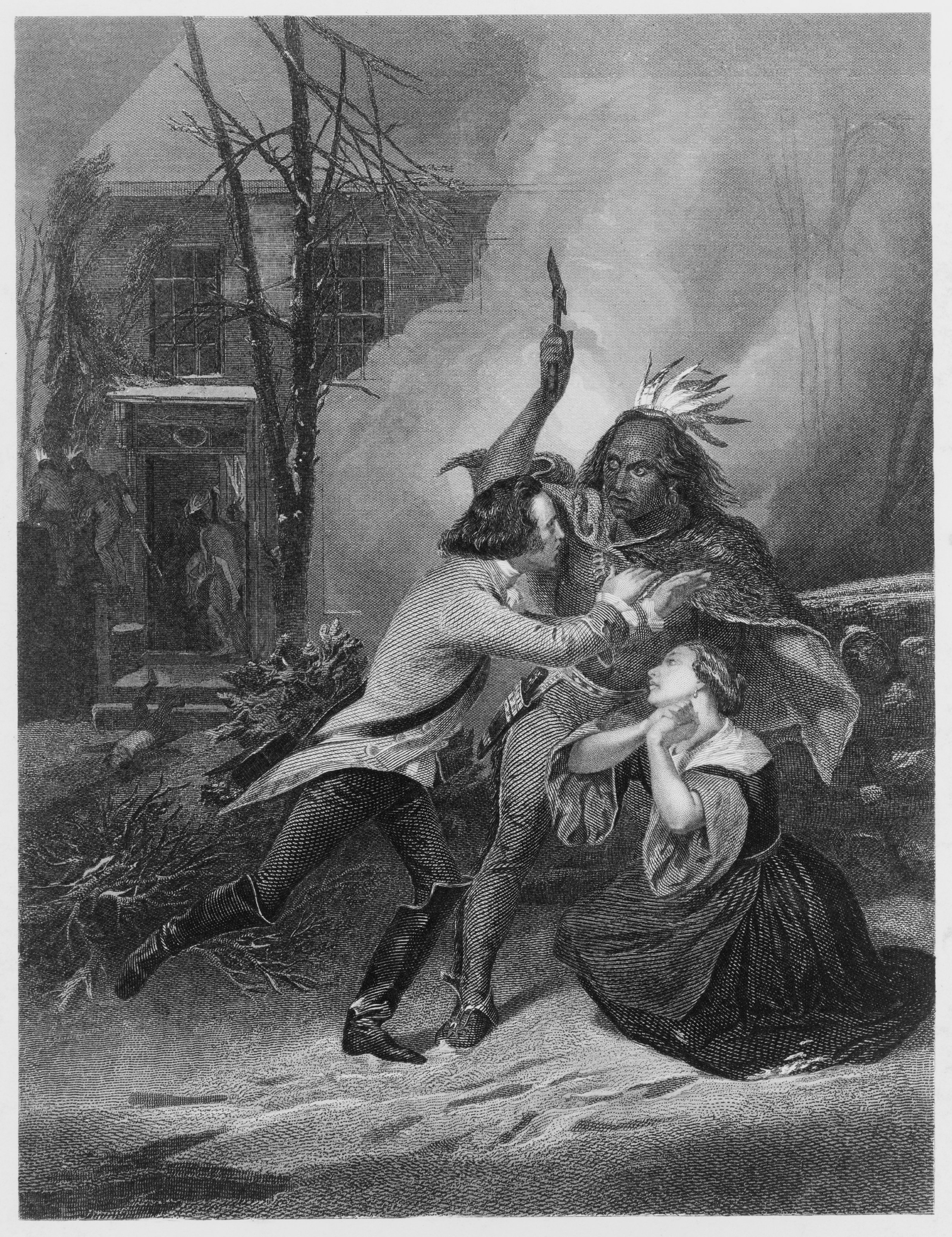 Between 1774 and 1783, deeply divided colonists waged civil war on each other directly and by proxy, through attacks such as the Seneca-led Cherry Valley and the Mohawk-led Cobleskill massacre. In 1779, the
Between 1774 and 1783, deeply divided colonists waged civil war on each other directly and by proxy, through attacks such as the Seneca-led Cherry Valley and the Mohawk-led Cobleskill massacre. In 1779, the
 Battles of the
Battles of the  Although routes for travel on foot and by canoe had existed across the region for hundreds of years, transportation of agricultural goods to market was expensive and slow. Influenced by the canals being built in Britain, leading citizens of New York began to press for the construction of a canal across the state. Governor DeWitt Clinton prevailed upon the legislature to charter and fund construction of a canal from Albany to Buffalo. Construction of the
Although routes for travel on foot and by canoe had existed across the region for hundreds of years, transportation of agricultural goods to market was expensive and slow. Influenced by the canals being built in Britain, leading citizens of New York began to press for the construction of a canal across the state. Governor DeWitt Clinton prevailed upon the legislature to charter and fund construction of a canal from Albany to Buffalo. Construction of the
 During the era immediately following World War II, Upstate reached what was probably its peak influence in the national economy. Major local corporations such as IBM,
During the era immediately following World War II, Upstate reached what was probably its peak influence in the national economy. Major local corporations such as IBM,


 *
*
 *
*
Old Abandoned Buildings of Northern NY
the urban decay of upstate New York, in pictures from the area
Exploring Upstate
travel, culture, and history in Upstate New York
New York History Net
Oral History of Franklin County
history of Franklin County, New York, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries {{Coord missing, New York (state) Upstate New York, Regions of New York (state)
''
Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls () is a group of three waterfalls at the southern end of Niagara Gorge, spanning the border between the province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York in the United States. The largest of the three is Horseshoe Fall ...
) and drinking water (with multiple reservoirs serving New York City). Upstate New York is home to numerous popular tourist and recreational destinations, including Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls () is a group of three waterfalls at the southern end of Niagara Gorge, spanning the border between the province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York in the United States. The largest of the three is Horseshoe Fall ...
, the Adirondack and Catskill Mountains
The Catskill Mountains, also known as the Catskills, are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains, located in southeastern New York. As a cultural and geographic region, the Catskills are generally defined as those areas c ...
, the Thousand Islands
The Thousand Islands (french: Mille-Îles) constitute a North American archipelago of 1,864 islands that straddles the Canada–US border in the Saint Lawrence River as it emerges from the northeast corner of Lake Ontario. They stretch for abo ...
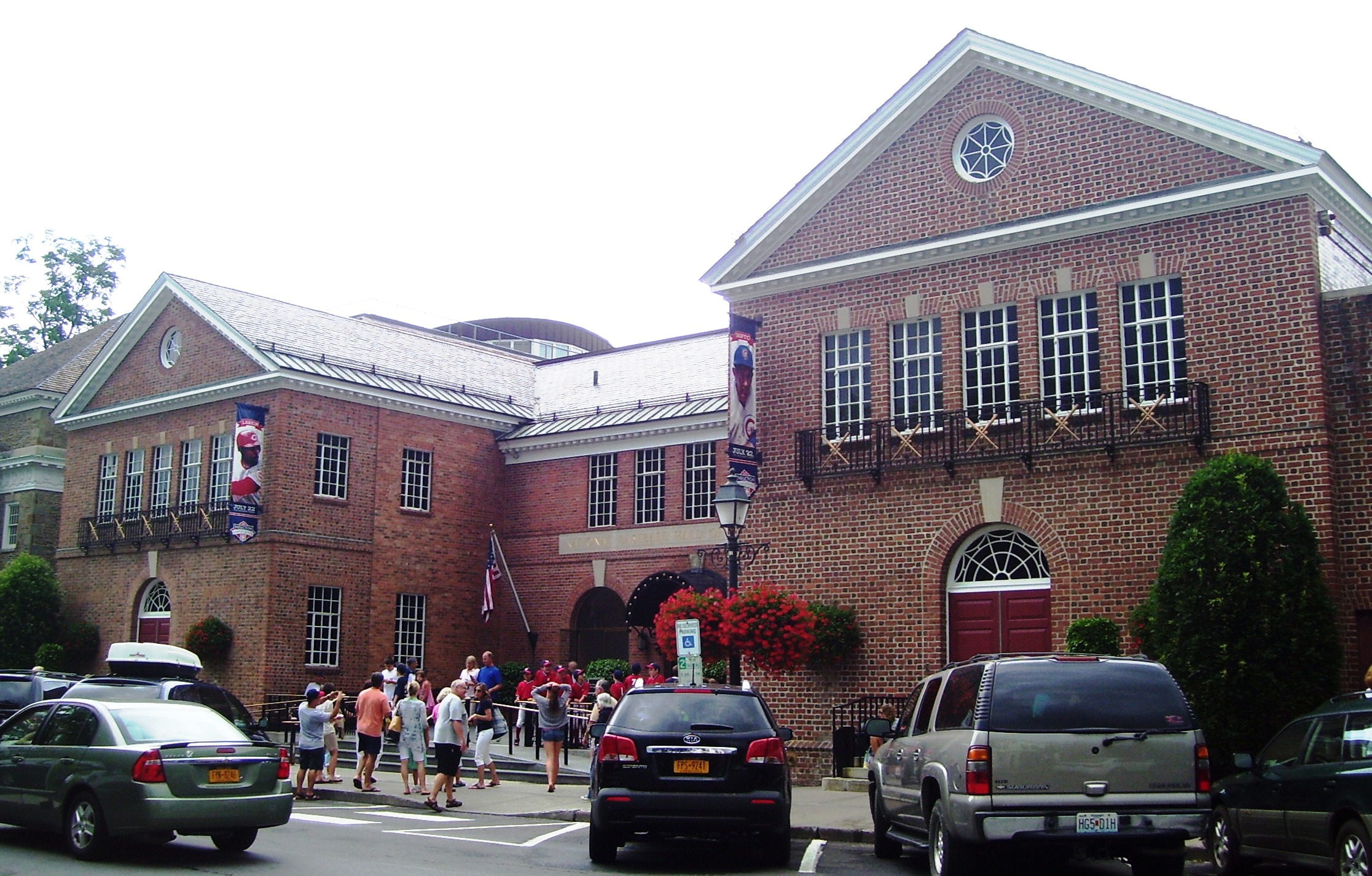
, the National Baseball Hall of Fame, and the Finger Lakes
The Finger Lakes are a group of eleven long, narrow, roughly north–south lakes located south of Lake Ontario in an area called the ''Finger Lakes region'' in New York, in the United States. This region straddles the northern and transitional ...
.
Definition
 There is no clear official boundary between Upstate New York and
There is no clear official boundary between Upstate New York and Downstate New York
Downstate New York is a region that generally consists of the southeastern and more densely populated portion of the U.S. state of New York, in contrast to Upstate New York, which comprises a larger geographic area with much sparser population di ...
. The most expansive definition of the Upstate New York region excludes only New York City and Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
, which are always considered to be part of Downstate New York; this usage is common among New York City residents and significantly less farther north. This definition is used by the Department of Environmental Conservation. A cheeky joke among Manhattanites is that anything north of 14th Street is "upstate".
Another usage locates the Upstate/Downstate boundary farther north, at the point where New York City's suburbs segue into its exurbs, as the exurbs do not generally fall within the Census Bureau-defined New York–Newark Urban Area. This latter boundary places most of the Lower Hudson Valley, or Westchester and Rockland counties and about one-third of Putnam County, Downstate, while putting the northwestern edge of Rockland County as well as the northernmost quarter of Westchester County (including Peekskill
Peekskill is a city in northwestern Westchester County, New York, United States, from New York City. Established as a village in 1816, it was incorporated as a city in 1940. It lies on a bay along the east side of the Hudson River, across fr ...
) Upstate. Conversely, area residents often use Interstate 84 to delineate a boundary between Upstate and Downstate New York.
Yet another usage follows the U.S. Census definition of the New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the Tri-State area, is the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass, at , and one of the list of most populous metropolitan areas, most populous urban agg ...
prior to 2010, which includes all of included Westchester, Rockland, and Putnam counties. This definition was used by the plaintiff
A plaintiff ( Π in legal shorthand) is the party who initiates a lawsuit (also known as an ''action'') before a court. By doing so, the plaintiff seeks a legal remedy. If this search is successful, the court will issue judgment in favor of the p ...
s in the federal redistricting
Redistribution (re-districting in the United States and in the Philippines) is the process by which electoral districts are added, removed, or otherwise changed. Redistribution is a form of boundary delimitation that changes electoral dist ...
case ''Rodriguez v. Pataki''.
In New York state law, the definition of the Upstate boundary also varies: while Westchester is seemingly always considered Downstate under state law, some definitions include Rockland and Putnam counties in the downstate region, and others also include Orange
Orange most often refers to:
*Orange (fruit), the fruit of the tree species '' Citrus'' × ''sinensis''
** Orange blossom, its fragrant flower
*Orange (colour), from the color of an orange, occurs between red and yellow in the visible spectrum
* ...
and Dutchess
Dutchess County is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 295,911. The county seat is the city of Poughkeepsie, New York, Poughkeeps ...
counties; all of these counties are served by Metro-North Railroad lines. Ulster County
Ulster County is a county in the U.S. state of New York. It is situated along the Hudson River. As of the 2020 census, the population was 181,851. The county seat is Kingston. The county is named after the Irish province of Ulster.
History
...
, and, in the largest state-defined extent of Downstate, Columbia County, are also sometimes included. The division line between the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York
The United States District Court for the Southern District of New York (in case citations, S.D.N.Y.) is a federal trial court whose geographic jurisdiction encompasses eight counties of New York State. Two of these are in New York City: New ...
and the United States District Court for the Northern District of New York
The United States District Court for the Northern District of New York (in case citations, N.D.N.Y.) serves one of the 94 judicial districts in the United States and one of four in the state of New York. Appeals from the Northern District of Ne ...
places Sullivan County and Dutchess County in the Southern District, and Ulster and Columbia counties in the Northern District.
Residents of Upstate New York typically prefer to identify with subregions, such as the Hudson Valley
The Hudson Valley (also known as the Hudson River Valley) comprises the valley of the Hudson River and its adjacent communities in the U.S. state of New York. The region stretches from the Capital District including Albany and Troy south to ...
(Middle and Upper), the Capital District
A capital district, capital region or capital territory is normally a specially designated administrative division where a country's seat of government is located. As such, in a federal model of government, no state or territory has any poli ...
, the Mohawk Valley, the North Country, Western New York
Western New York (WNY) is the westernmost region of the U.S. state of New York. The eastern boundary of the region is not consistently defined by state agencies or those who call themselves "Western New Yorkers". Almost all sources agree WNY i ...
or Central New York
Central New York is the central region of New York State, including the following counties and cities:
With a population of about 773,606 (2009) and an area of , the region includes the Syracuse metropolitan area.
Definitions
The New York ...
.
Within New York, surveys have had difficulty determining a consensus. In a 2016 poll of New York voters in which respondents were asked to choose among four definitions of where Upstate begins, three were about equally common, selected by between 25% and 30% of respondents each: north of New York City, north of Westchester County, and north of Poughkeepsie
Poughkeepsie ( ), officially the City of Poughkeepsie, separate from the Town of Poughkeepsie around it) is a city in the U.S. state of New York. It is the county seat of Dutchess County, with a 2020 census population of 31,577. Poughkeepsie ...
in Dutchess County. (The fourth, which also started north of Poughkeepsie but excluded Buffalo as a unique region neither Upstate nor Downstate, drew only 7%.) An informal 2018 poll found the Hudson Valley
The Hudson Valley (also known as the Hudson River Valley) comprises the valley of the Hudson River and its adjacent communities in the U.S. state of New York. The region stretches from the Capital District including Albany and Troy south to ...
region is the most heavily disputed area regarding whether it is Upstate or Downstate.
A number of businesses and institutions in the area have "upstate" as part of their name. Examples of this include the State University of New York Upstate Medical University in Syracuse, the Upstate New York Chapter of the Arthritis Foundation
The Arthritis Foundation is a nonprofit organization that is dedicated to addressing the needs of people living with arthritis in the United States. There are more than 50 million adults and 300,000 children living with arthritis, the nation's ...
serving 31 of New York's 62 counties, and the VA Healthcare Network Upstate New York, which includes all of New York State northward and westward from Kingston in Ulster County
Ulster County is a county in the U.S. state of New York. It is situated along the Hudson River. As of the 2020 census, the population was 181,851. The county seat is Kingston. The county is named after the Irish province of Ulster.
History
...
. Other organizations in New York with "upstate" in their name include the Upstate Collegiate Athletic Association (now known as the Liberty League
The Liberty League is an intercollegiate athletic conference affiliated with the National Collegiate Athletic Association's Division III. Member schools are top institutions that are all located in the state of New York.
History
It was founde ...
), the Upstate Correctional Facility
Upstate Correctional Facility is a maximum security state prison for men in Franklin County, New York, US. The prison, in the Town of Malone, was the first New York State prison built as a supermax.Gonnerman, Jennifer.The Supermax Solution" ' ...
, the Upstate New York Club Hockey League
The Upstate New York Collegiate Hockey League is a college ice hockey league comprising teams from smaller colleges and universities in and near Upstate New York that is affiliated with the Collegiate Hockey Federation (CHF). The league is based i ...
, the Upstate New York Synod, and the Upstate Citizens for Equality.
Culture
The other regions of New York are culturally and economically distinct from the New York City area and in many ways from each other. By area, most of New York is characterized by agricultural and forested rural communities, and by small and medium-sized cities and their surrounding suburbs located along major transportation corridors. The state's major metropolitan areas outside of New York City are Buffalo, Rochester, Syracuse, and Albany-Schenectady-Troy, each of whose population exceeds 500,000. The different regions of New York are influenced by and have affinities with other adjacent regions. Western New York has cultural and economic ties to the other Great Lakes states as well asSouthern Ontario
Southern Ontario is a primary region of the province of Ontario, Canada, the other primary region being Northern Ontario. It is the most densely populated and southernmost region in Canada. The exact northern boundary of Southern Ontario is disp ...
and is effectively, along with Northwestern Pennsylvania, an eastward extension of Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
culture. The Capital District
A capital district, capital region or capital territory is normally a specially designated administrative division where a country's seat of government is located. As such, in a federal model of government, no state or territory has any poli ...
, the Hudson Valley, the Mohawk Valley and the Plattsburgh
Plattsburgh ( moh, Tsi ietsénhtha) is a city in, and the seat of, Clinton County, New York, United States, situated on the north-western shore of Lake Champlain. The population was 19,841 at the 2020 census. The population of the surrounding ...
area have ties to New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
. The North Country, the extreme northern portion of the state, also has strong cultural, economic, linguistic and familial ties to Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
and Eastern Ontario
Eastern Ontario (census population 1,763,186 in 2016) (french: Est de l'Ontario) is a secondary region of Southern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario which lies in a wedge-shaped area between the Ottawa River and St. Lawrence River. It s ...
. Thus, Plattsburgh has close ties to its neighbors in the Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian ...
area as well as Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
. Much of New York receives television and radio broadcasts from Canada, and there are often other cross-border ties, both historical and familial. A similar relationship can be seen in northern New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
.
Linguistically, Upstate New York from Western New York east to Utica is part of the Inland North
Inland Northern (American) English, also known in American linguistics as the Inland North or Great Lakes dialect, is an American English dialect spoken primarily by White Americans in a geographic band reaching from the major urban areas of U ...
region of American English dialectology, a region which includes Midwestern cities as far west as Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
and Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee is ...
. The Hudson and lower Mohawk Valley regions have more in common dialectologically with western New England and New York City. The boundary between the use of the words ''pop'' and ''soda'' to refer to soft drinks falls farther west than the edge of the Inland North, running just to around the city of Rochester. Buffalo and areas west of Rochester use ''pop'', like the rest of the Inland North to the west, whereas areas east of Rochester, like Syracuse and Binghamton, use ''soda'', like New England and New York City. In Ithaca and Elmira, the border is less clear, with some people having grown up with ''pop'' and some with ''soda''; however, current trends see Ithaca, at least, turning to mostly "soda."

Foodways
In social science, foodways are the cultural, social, and economic practices relating to the production and consumption of food. ''Foodways'' often refers to the intersection of food in culture, traditions, and history.
Definition and historical ...
indigenous to regions of Upstate New York include:
* Buffalo wing
A Buffalo wing in American cuisine is an unbreaded chicken wing section ( flat or drumette) that is generally deep-fried and then coated or dipped in a sauce consisting of a vinegar-based cayenne pepper hot sauce and melted butter prior to ser ...
s and beef on weck
A beef on weck is a sandwich found primarily in Western New York State, particularly in the city of Buffalo. It is made with roast beef on a kummelweck roll, a roll that is topped with kosher salt and caraway seeds. The meat on the sandwich i ...
sandwich (Buffalo)
* Cornell chicken barbecue (Ithaca)
* garbage plate
Nick Tahou Hots is a restaurant in Rochester, New York best known for a dish called the Garbage Plate.Mitzewich, John.The Famous Garbage Plate of Rochester, New York. americanfood.about.com. Retrieved on August 31, 2008. The restaurant was fou ...
(Rochester)
* white hot dog
A hot dog (uncommonly spelled hotdog) is a food consisting of a grilled or steamed sausage served in the slit of a partially sliced bun. The term hot dog can refer to the sausage itself. The sausage used is a wiener ( Vienna sausage) or a f ...
s, known as a white hot
The white hot is a variation on the hot dog found primarily in the Rochester, NY area, as well as other parts of Western New York and Central New York. It is composed of a combination of uncured and unsmoked pork, beef, and veal; the lack of smo ...
or Coney (Rochester, Central and Western New York)
* salt potatoes
Salt potatoes are a regional dish of Syracuse, New York, typically served in the summer when the young potatoes are first harvested. They are a staple food at fairs and barbecues in the Central New York region, where they are most popular. Po ...
(Syracuse)
* spiedie
The spiedie is a snack consisting of marinated meat cut into cubes and placed in a long bread roll, local to Binghamton in the central Southern Tier of New York State, and somewhat more broadly known and enjoyed throughout Central New York. A s ...
s (Binghamton)
* chicken riggies
Chicken riggies or Utica riggies is an Italian-American pasta dish native to the Utica-Rome area of New York State. Although many variations exist, it is a pasta-based dish typically consisting of chicken, rigatoni, and hot or sweet peppers in a ...
, tomato pies, Utica greens
Utica greens is an Italian American dish made of escarole sauteed with garlic and olive oil. Most recipes include hot cherry peppers, pecorino cheese, bread crumbs, prosciutto or another cured meat, and sometimes chicken broth.
In the 1980 ...
, and halfmoon cookies (Utica)
* Michigan hot dogs, a variety of the Coney Island hot dog
A Coney Island hot dog, Coney dog, or Coney is a hot dog in a bun topped with a savory meat sauce and sometimes other toppings. It is often offered as part of a menu of classic American "diner" dishes and often at Coney Island restaurants. It is ...
(Plattsburgh)
Although legends lay claim that the potato chip
A potato chip (North American English; often just chip) or crisp (British and Irish English) is a thin slice of potato that has been either deep fried, baked, or air fried until crunchy. They are commonly served as a snack, side dish, or ap ...
was invented in Saratoga Springs, it has achieved such universal popularity that it is no longer identified with the region. Winemaking
Winemaking or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over millennia. The science of wine and ...
is a growing industry in the Finger Lakes
The Finger Lakes are a group of eleven long, narrow, roughly north–south lakes located south of Lake Ontario in an area called the ''Finger Lakes region'' in New York, in the United States. This region straddles the northern and transitional ...
as well as in Chautauqua County, where Welch's
Welch Foods Inc., commonly known as Welch's, is an American company, headquartered in Concord, Massachusetts. It has been owned by the National Grape Cooperative Association, a co-op of grape growers, since 1956.Hays, Constance LHow Too Much P ...
operates one of the oldest extant grape juice factories in the United States. In the center of the Finger Lakes region, Ithaca
Ithaca most commonly refers to:
*Homer's Ithaca, an island featured in Homer's ''Odyssey''
*Ithaca (island), an island in Greece, possibly Homer's Ithaca
*Ithaca, New York, a city, and home of Cornell University and Ithaca College
Ithaca, Ithaka ...
is known for the Bo Burger, a cheeseburger with a fried egg on top.
Two of the most important rock festival
A rock festival is an open-air rock concert featuring many different performers, typically spread over two or three days and having a campsite and other amenities and forms of entertainment provided at the venue. Some festivals are singular even ...
s of the 20th century were held in Upstate New York. In 1969 the Woodstock Festival
Woodstock Music and Art Fair, commonly referred to as Woodstock, was a music festival held during August 15–18, 1969, on Max Yasgur's dairy farm in Bethel, New York, United States, southwest of the town of Woodstock. Billed as "an Aquar ...
was held in Bethel, New York :''This is the article about the Sullivan County, New York town. For the Dutchess County, New York hamlet, see Bethel, Pine Plains''
Bethel is a town in Sullivan County, New York, United States. The population was estimated at 4,255 in 2010. The ...
, while in 1973 another multiday festival was held at the Watkins Glen International Raceway
Watkins Glen International, nicknamed "The Glen", is an automobile race track located in the town of Dix just southwest of the village of Watkins Glen, New York, at the southern tip of Seneca Lake. It was long known around the world as the home ...
.
Some literary, documentary and cinematic depictions of Upstate present a sense of small town, simple lifestyles, such as ''It's a Wonderful Life
''It's a Wonderful Life'' is a 1946 American Christmas fantasy drama film produced and directed by Frank Capra, based on the short story and booklet ''The Greatest Gift'', which Philip Van Doren Stern self-published in 1943 and is in turn loos ...
'', set in a small upstate town (probably based on Seneca Falls) in the 1940s.
Demographics
New York City Metropolitan Area
The New York metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the Tri-State area, is the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass, at , and one of the list of most populous metropolitan areas, most populous urban agg ...
, leaving 6,155,839 for the entire rest of the state. Upstate New York with its larger area has a population density much lower than Downstate. By area, Upstate is typified by farmland and forest, many large lakes, and two (major) mountain ranges, with metro areas dotting the map. Residents of English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
colonial ancestry are common, as well as German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
, Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
, and Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
, with most metropolitan counties having a similar number of residents from each group.
The North Country is heavily French Canadian. Italian Americans are the largest ethnic group in Oneida County and Schenectady County, as well as in some counties in the Hudson Valley
The Hudson Valley (also known as the Hudson River Valley) comprises the valley of the Hudson River and its adjacent communities in the U.S. state of New York. The region stretches from the Capital District including Albany and Troy south to ...
that are closest to New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
. Irish Americans represent the largest ethnic group from the Capital District, Syracuse, Binghamton, and the rest of the Hudson Valley, though the regions also have large Italian American populations. Irish population is consistently above 15% in most of Upstate New York (reaching over 20% in the upper Hudson Valley), compared to less than 8% in most of New York City.
Buffalo and Utica also contain notably large contingent of residents with Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
and other Slavic ancestries. African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, and Americans of African descent, while not as numerous as in New York City, make up at least 25% of the residents in cities such as Buffalo, Rochester, Syracuse, and Albany.
There is also a significant presence of the indigenous Haudenosaunee
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Natio ...
or Six Nations in the region, who retain enclaves of tribal land: the Seneca Nation and Tonawanda Seneca Nation in Western New York, the Onondaga nation
The Onondaga people ( Onondaga: , ''Hill Place people'') are one of the original five constituent nations of the Iroquois (''Haudenosaunee'') Confederacy in northeast North America. Their traditional homeland is in and around present-day Onondaga ...
south of Syracuse and the Oneida nation
The Oneida Nation is a federally recognized tribe of Oneida people in Wisconsin. The tribe's reservation spans parts of two counties west of the Green Bay metropolitan area. The reservation was established by treaty in 1838, and was allotted to ...
of Oneida County in Central New York, and in the North Country, the Mohawk Nation
The Mohawk people ( moh, Kanienʼkehá꞉ka) are the most easterly section of the Haudenosaunee, or Iroquois Confederacy. They are an Iroquoian-speaking Indigenous people of North America, with communities in southeastern Canada and norther ...
caught between Franklin County, Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
, and Québec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is ...
. Members of the Six Nations also live across Upstate New York outside of tribal lands.
Geography
Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent Del ...
, Susquehanna, Mohawk Mohawk may refer to:
Related to Native Americans
* Mohawk people, an indigenous people of North America (Canada and New York)
*Mohawk language, the language spoken by the Mohawk people
* Mohawk hairstyle, from a hairstyle once thought to have been ...
, Hudson, and Allegheny rivers are located in the region. Several regions Upstate are characterized by major mountain ranges, large lakes, and extensive forests.
Allegheny Plateau
The Allegheny Plateau , in the United States, is a large dissected plateau area of the Appalachian Mountains in western and central New York (state), New York, northern and western Pennsylvania, northern and western West Virginia, and eastern Oh ...
extends into west and central New York from the south. The Catskill Mountains
The Catskill Mountains, also known as the Catskills, are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains, located in southeastern New York. As a cultural and geographic region, the Catskills are generally defined as those areas c ...
lie within Lower New York in the southeastern part of the state, closer to New York City. The Catskills and the Allegheny Plateau are part of the Appalachian chain. By contrast, Northern New York contains the Adirondack Mountains
The Adirondack Mountains (; a-də-RÄN-dak) form a massif in northeastern New York with boundaries that correspond roughly to those of Adirondack Park. They cover about 5,000 square miles (13,000 km2). The mountains form a roughly circular ...
, which are sometimes mistaken as part of the Appalachians but are in fact a southern extension of the Canadian Shield.
In the more mountainous eastern parts of Upstate New York, along the valleys of the Hudson River and the Mohawk River
The Mohawk River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed October 3, 2011 river in the U.S. state of New York. It is the largest tributary of the Hudson River. The Mohawk f ...
, have been historically important travel corridors and remain so today. Western New York in the vicinity of Buffalo is very flat, as it was once the bottom of a glacial lake. The only "hills" in Niagara County
Niagara County is in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2020 census, the population was 212,666. The county seat is Lockport. The county name is from the Iroquois word ''Onguiaahra''; meaning ''the strait'' or ''thunder of waters''.
Niaga ...
are the Niagara Escarpment, which formed the Falls.
Upstate New York has a long shared border with the Canadian province of Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
stretching from Western New York across Northern New York. It is primarily divided by water boundaries along Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also h ...
, the Niagara River, Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border sp ...
and the St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
. At the conflux of New York, Québec and Ontario lies the Mohawk Nation of Iroquois. To the east, across the remainder of the North Country region, New York shares a land border with the province of Québec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is ...
.
Upstate counties and towns are generally larger in area and smaller in population, compared with those Downstate, although there are exceptions. The state's smallest county in population ( Hamilton County) and largest county in area ( St. Lawrence County on the state's northern border) are both in Upstate New York, within the North Country and Thousand Islands
The Thousand Islands (french: Mille-Îles) constitute a North American archipelago of 1,864 islands that straddles the Canada–US border in the Saint Lawrence River as it emerges from the northeast corner of Lake Ontario. They stretch for abo ...
regions of northern New York. The counties with the largest in population ( Kings County) and smallest in area (New York County
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
) are both parts of New York City.
Climate
 Upstate New York is well known for its cold and snowy winters, particularly in comparison to the more temperate climate of Downstate New York. The snowy reputation is especially true for the cities of Buffalo, Rochester, Oswego and Syracuse, and is largely due to lake-effect snow from Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. The villages of Old Forge and Saranac Lake, both in the Adirondacks, often vie on winter nights with places like International Falls, Minnesota, and Fargo, North Dakota, for the coldest spot in the nation.
Many of the features of Upstate New York landscapes, such as the
Upstate New York is well known for its cold and snowy winters, particularly in comparison to the more temperate climate of Downstate New York. The snowy reputation is especially true for the cities of Buffalo, Rochester, Oswego and Syracuse, and is largely due to lake-effect snow from Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. The villages of Old Forge and Saranac Lake, both in the Adirondacks, often vie on winter nights with places like International Falls, Minnesota, and Fargo, North Dakota, for the coldest spot in the nation.
Many of the features of Upstate New York landscapes, such as the Finger Lakes
The Finger Lakes are a group of eleven long, narrow, roughly north–south lakes located south of Lake Ontario in an area called the ''Finger Lakes region'' in New York, in the United States. This region straddles the northern and transitional ...
and the drumlin
A drumlin, from the Irish word ''droimnín'' ("littlest ridge"), first recorded in 1833, in the classical sense is an elongated hill in the shape of an inverted spoon or half-buried egg formed by glacial ice acting on underlying unconsolidated ...
s that dot the region, are the result of glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires dis ...
s during the Ice Age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
.
Statistics for selected cities
History
Early history
 Before the arrival of Europeans, the area was long inhabited by
Before the arrival of Europeans, the area was long inhabited by Iroquoian
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.
As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoian ...
-speaking people (mainly west of the Hudson and around the Great Lakes) and Algonquian-speaking people (mainly east of the Hudson). The conflict between the two peoples continued through the period of early European colonization, and the French, Dutch and English tended to ally with their trading partners among the indigenous peoples. The Haudenosaunee or Iroquois confederacy
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
of the Five (later Six) Nations was a powerful force in its home territory.
The Five Nations' territory extended from the Mohawk River Valley through the western part of the state and into current Pennsylvania. From this home base they also controlled at various times large swaths of additional territory throughout what is now the northeastern United States. The Guswhenta (Two Row Wampum Treaty)
The Two Row Wampum Treaty, also known as ''Guswenta'' or ''Kaswentha'' and as the Tawagonshi Agreement of 1613 or the Tawagonshi Treaty, is a mutual treaty agreement, made in 1613 between representatives of the Five Nations of the Haudenosaune ...
, made with the Dutch government in 1613, codified relations between the Haudenosaunee and European colonizers, and formed the basis of subsequent treaties.
In the mid-17th century, during the Beaver Wars
The Beaver Wars ( moh, Tsianì kayonkwere), also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars (french: Guerres franco-iroquoises) were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout t ...
, the Iroquois were victorious and dominated the tribes of Neutral Indians, Wenrohronon
The Wenrohronon or Wenro people were an Iroquoian indigenous nation of North America, originally residing in present-day western New York (and possibly fringe portions of northern & northwestern Pennsylvania), who were conquered by the Confeder ...
and the Erie Indians in western New York. Survivors were mostly assimilated into the Seneca people
The Seneca () ( see, Onödowáʼga:, "Great Hill People") are a group of indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous Iroquoian-speaking people who historically lived south of Lake Ontario, one of the five Great Lakes in North America. Their n ...
of the Iroquois; some are believed to have escaped to South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, where they merged with other Indian tribes.
The region was important from the first days of both French and Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
colonization in the seventeenth century. The New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the East Coast of the United States, east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territor ...
colony encompassed the Hudson Valley from Manhattan island north to the confluence of the Hudson and Mohawk rivers, where Fort Orange
Fort Orange ( nl, Fort Oranje) was the first permanent Dutch settlement in New Netherland; the present-day city of Albany, New York developed at this site. It was built in 1624 as a replacement for Fort Nassau, which had been built on nearb ...
(later Albany) was established in 1624. The fort at Schenectady
Schenectady () is a city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-largest city by population. The city is in eastern New Y ...
was built in 1661. The upper Hudson Valley was the center of much of the colony's fur trade, which was highly lucrative, serving a demand for furs in Europe.
North and west of New Netherland, the French established trading posts along the St. Lawrence River and as far south as the shores of Onondaga Lake
Onondaga Lake is a lake in Central New York, immediately northwest of and adjacent to Syracuse, New York. The southeastern end of the lake and the southwestern shore abut industrial areas and expressways; the northeastern shore and northwestern e ...
. They found both trading and proselytizing difficult among the Haudenosaunee, as Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain (; Fichier OrigineFor a detailed analysis of his baptismal record, see RitchThe baptism act does not contain information about the age of Samuel, neither his birth date nor his place of birth. – 25 December 1635) was a Fre ...
had alienated the Haudenosaunee during military forays from New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spai ...
. In the 1640s, three French Jesuit missionaries to New France—St. René Goupil
René Goupil, S.J. (15 May 1608 – 29 September 1642), was a French Jesuit lay missionary (in French "donné", "given" or "one who offers himself") who became a lay brother of the Society of Jesus shortly before his death. He was the first of ...
, St. Isaac Jogues
Isaac Jogues, S.J. (10 January 1607 – 18 October 1646) was a French missionary and martyr who traveled and worked among the Iroquois, Huron, and other Native populations in North America. He was the first European to name Lake George, call ...
, and St. Jean de Lalande
Jean de Lalande, SJ (died October 19, 1646) was a Jesuit missionary at Sainte-Marie among the Hurons and one of the eight North American Martyrs. He was killed at the Mohawk village of Ossernenon after being captured by warriors.
Life
Jean de ...
—were killed near the Mohawk village of Ossernenon, which was located at the confluence of the Schoharie and Mohawk rivers, where the modern hamlet of Auriesville
Auriesville is a Hamlet (New York), hamlet in the northeastern part of the Town of Glen, New York, Glen in Montgomery County, New York, Montgomery County, New York (state), New York, United States, along the south bank of the Mohawk River and wes ...
was later developed. They are considered to be the first three U.S. saints.
England seized New Netherland by force in 1664, renaming it New York. The Dutch recaptured the colony nine years later, but ceded it to England under the Treaty of Westminster of 1674.
In the eighteenth century, the British consolidated their hold on the region. William Johnson, a Scottish trader, established an estate in the Mohawk Valley, living among the Mohawk, learning their language, and forging an alliance with them. He was appointed as the British Indian agent to the Iroquois. The British also encouraged settlement in the Mohawk Valley by other Europeans, including German Palatines
Palatines (german: Pfälzer), also known as the Palatine Dutch, are the people and princes of Palatinates ( Holy Roman principalities) of the Holy Roman Empire. The Palatine diaspora includes the Pennsylvania Dutch and New York Dutch.
In 1709 ...
beginning in the 1720s.
In what became known as the Albany Congress
The Albany Congress (June 19 – July 11, 1754), also known as the Albany Convention of 1754, was a meeting of representatives sent by the legislatures of seven of the 13 British colonies in British America: Connecticut, Maryland, Massachusetts, ...
in 1754, delegates from seven of the thirteen British North American colonies met at Albany to pursue a treaty with the powerful Mohawk. Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading inte ...
, a Pennsylvania delegate, proposed a plan for uniting the seven colonies that greatly exceeded the scope of the congress. The delegates spent most of their time debating this Albany Plan
The Albany Plan of Union was a rejected plan to create a unified government for the Thirteen Colonies at the Albany Congress on July 10, 1754 in Albany, New York. The plan was suggested by Benjamin Franklin, then a senior leader (age 48) and a del ...
of union, one of the first attempts to form a union of the colonies
In modern parlance, a colony is a territory subject to a form of foreign rule. Though dominated by the foreign colonizers, colonies remain separate from the administration of the original country of the colonizers, the '' metropolitan state'' ...
"under one government as far as might be necessary for defense and other general important purposes". The delegates approved an amended version, but the colonies rejected it.
To counter the French militarily, the British established forts along Lake Ontario and at portages between the Mohawk Valley and the adjacent Lake Champlain and Lake Ontario watersheds. The region became the area for many conflicts of the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
, such as the Battle of Fort Oswego
The Battle of Fort Oswego was one in a series of early French victories in the North American theatre of the Seven Years' War won in spite of New France's military vulnerability. During the week of August 10, 1756, a force of regulars and Can ...
(1756) and the Siege of Fort William Henry
The siege of Fort William Henry (3–9 August 1757, french: Bataille de Fort William Henry) was conducted by a French and Indian force led by Louis-Joseph de Montcalm against the British-held Fort William Henry. The fort, located at the sout ...
(which was later depicted in the work of James Fenimore Cooper), during the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
.
The British conquered New France by 1760 with the fall of Quebec
The Battle of the Plains of Abraham, also known as the Battle of Quebec (french: Bataille des Plaines d'Abraham, Première bataille de Québec), was a pivotal battle in the Seven Years' War (referred to as the French and Indian War to describe ...
. France formally ceded New France to the British in the Treaty of Paris of 1763
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement, after Great Britain and Prussia's victory over France and Spain during the S ...
. The same year, King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
issued the Royal Proclamation of 1763
The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued by King George III on 7 October 1763. It followed the Treaty of Paris (1763), which formally ended the Seven Years' War and transferred French territory in North America to Great Britain. The Procla ...
, which established the western and northern boundary of the Province of New York at the limits of the Hudson, Mohawk and Delaware River watersheds. The area between that boundary and the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence River, including west of the Appalachian Mountains, was to be the "Indian Reserve
In Canada, an Indian reserve (french: réserve indienne) is specified by the '' Indian Act'' as a "tract of land, the legal title to which is vested in Her Majesty,
that has been set apart by Her Majesty for the use and benefit of a band."
Ind ...
."
American Revolution
 Between 1774 and 1783, deeply divided colonists waged civil war on each other directly and by proxy, through attacks such as the Seneca-led Cherry Valley and the Mohawk-led Cobleskill massacre. In 1779, the
Between 1774 and 1783, deeply divided colonists waged civil war on each other directly and by proxy, through attacks such as the Seneca-led Cherry Valley and the Mohawk-led Cobleskill massacre. In 1779, the Sullivan Expedition
The 1779 Sullivan Expedition (also known as the Sullivan-Clinton Expedition, the Sullivan Campaign, and the Sullivan-Clinton Genocide) was a United States military campaign during the American Revolutionary War, lasting from June to October 1779 ...
, a campaign by the Continental Army ordered by General George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of th ...
, drove thousands of the Haudenosaunee from their villages, farms and lands in the region in an effort to both avenge and prevent such attacks.
The region was strategically important to the war plans of both the British and the Continental forces. British efforts to divide the New England colonies from the rest led to battles including the Battle of Valcour Island
The Battle of Valcour Island, also known as the Battle of Valcour Bay, was a naval engagement that took place on October 11, 1776, on Lake Champlain. The main action took place in Valcour Bay, a narrow strait between the New York mainland and ...
and the Battle of Saratoga
The Battles of Saratoga (September 19 and October 7, 1777) marked the climax of the Saratoga campaign, giving a decisive victory to the Americans over the British in the American Revolutionary War. British General John Burgoyne led an invasion ...
, a significant turning point in the war. While New York City remained in the hands of the British during most of the war, the upstate region was eventually dominated by the Colonial forces. At the end of the war, the Continental Army was headquartered in Newburgh. Uncertain that the Continental Congress would pay back wages, some Continental officers threatened an uprising in what became known as the Newburgh Conspiracy
The Newburgh Conspiracy was a failed apparent threat by leaders of the Continental Army in March 1783, at the end of the American Revolutionary War. The Army's commander, George Washington, successfully calmed the soldiers and helped secure back ...
.
Post-revolutionary period
After the American Revolution, theTreaty of Paris Treaty of Paris may refer to one of many treaties signed in Paris, France:
Treaties
1200s and 1300s
* Treaty of Paris (1229), which ended the Albigensian Crusade
* Treaty of Paris (1259), between Henry III of England and Louis IX of France
* Trea ...
established the border between New York and British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English overseas possessions, English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland (island), Newfound ...
. The 45th Parallel became the border with Quebec or Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada (french: province du Bas-Canada) was a British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence (1791–1841). It covered the southern portion of the current Province of Quebec an ...
. The St. Lawrence River, Lake Ontario, the Niagara River and Lake Erie became the border with Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada (french: link=no, province du Haut-Canada) was a part of British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of th ...
. Great Britain continued to occupy military installations along the American shores of the Great Lakes until 1794, including Fort Niagara at the mouth of the Niagara River and Fort Ontario at the mouth of the Oswego River.
The government of the new State of New York seized the property of New Yorkers who had remained loyal to the British crown. Thousands emigrated to colonies that remained under British rule, such as Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
and the newly established Upper Canada (now Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
). Haudenosaunee who had fought with the British also fled. The British Crown granted a large tract of land in Upper Canada to their Haudenosaunee allies, who established the Grand River settlement.
In the federal Treaty of Canandaigua
The Treaty of Canandaigua (or Konondaigua, as spelled in the treaty itself) also known as the Pickering Treaty and the Calico Treaty, is a treaty signed after the American Revolutionary War between the Iroquois#Government, Grand Council of the Si ...
, the new United States recognized the title of the remaining Haudenosaunee to the land north and west of the Proclamation Line of 1763. Nevertheless, New York state officials and private land agents sought through the early 19th century to extinguish Indian title to these lands via non-Federally-sanctioned treaties, such as the Treaty of Big Tree
The Treaty of Big Tree was a formal treaty signed in 1797 between the Seneca Nation and the United States, in which the Seneca relinquished their rights to nearly all of their traditional homeland in New York State—nearly 3.5 million acres. In ...
. The Treaties of Buffalo Creek The Treaties of Buffalo Creek are a series of treaties, named for the Buffalo River in New York, between the United States and Native American peoples:
These include the following:
* First Treaty of Buffalo Creek (1788)
* Second Treaty of Buff ...
were designed to finally remove the last of the native claims in Western New York as part of the federal Indian Removal
Indian removal was the United States government policy of forced displacement of self-governing tribes of Native Americans from their ancestral homelands in the eastern United States to lands west of the Mississippi Riverspecifically, to a de ...
program, but the purchaser failed to buy most of the land in time, and some of the tribes objected to their exclusion. Three of the four reservations remain in the region to this day; one of the reservations leased out their land to form the city of Salamanca
Salamanca () is a city in western Spain and is the capital of the Province of Salamanca in the autonomous community of Castile and León. The city lies on several rolling hills by the Tormes River. Its Old City was declared a UNESCO World Herit ...
, and the coexistence of the predominantly white city and the reservation has been a source of contention since the 1990s.
Both before and after the Revolution, boundary disputes with other colonies and their successor states also complicated American settlement. In conflict with the New York Colony
The Province of New York (1664–1776) was a British proprietary colony and later royal colony on the northeast coast of North America. As one of the Middle Colonies, New York achieved independence and worked with the others to found the Uni ...
's claims west of the Hudson Valley, which placed the entire region in the sprawling Albany County, the Pennsylvania Colony
The Province of Pennsylvania, also known as the Pennsylvania Colony, was a British North American colony founded by William Penn after receiving a land grant from Charles II of England in 1681. The name Pennsylvania ("Penn's Woods") refers to Wi ...
claimed much of the Southern Tier until 1774, while the Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1630–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around the Massachusetts Bay, the northernmost of the several colonies later reorganized as the ...
claimed all of the region west of Massachusetts to the Great Lakes.
The Province of New York also claimed jurisdiction east to the Connecticut River. To pursue this claim north of Connecticut and Massachusetts, New York granted lands to settlers in what is now Vermont at the same time that New Hampshire
New Hampshire is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
made grants of the same lands. When Vermont declared independence in 1777, the new Republic of Vermont
The Vermont Republic (French: ''République du Vermont''), officially known at the time as the State of Vermont (French: ''État du Vermont''), was an independent state in New England that existed from January 15, 1777, to March 4, 1791. The s ...
recognized the New Hampshire grants over those of New York. New Yorkers who lost land in Vermont came to be known as the "Vermont Sufferers" and were granted new lands in 1788 in the town of Bainbridge, New York
Bainbridge is a town in Chenango County, New York, United States. The population was 3,308 at the 2010 census. The town is at the eastern border of Chenango County, halfway between Binghamton and Oneonta.
The Village of Bainbridge is located ...
.
The dispute with Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
over lands to the west of Massachusetts was settled in the 1786 Treaty of Hartford by dividing the rights to the land. The treaty granted sovereignty to the State of New York, but granted to the Commonwealth of Massachusetts the "pre-emptive" right to seek title to the land from the Haudenosaunee. The eastern boundary of the Massachusetts lands was thus known as the Preemption Line
The Preemption Line (also spelled Pre-Emption) divided the aboriginal lands of western New York State awarded to New York from those awarded to Commonwealth of Massachusetts by the Treaty of Hartford of 1786. It was defined as the meridian (north ...
. This line runs from the Pennsylvania line due north to Lake Ontario, passing through Seneca Lake. The line was surveyed a second time due to initial errors. The Commonwealth of Massachusetts sold this land in large tracts, including the Phelps and Gorham Purchase
The Phelps and Gorham Purchase was the purchase in 1788 of of land in what is now western New York State from the Commonwealth of Massachusetts for $1,000,000 ( £300,000), to be paid in three annual installments, and the pre-emptive right to th ...
and the Holland Purchase
The Phelps and Gorham Purchase was the purchase in 1788 of of land in what is now western New York State from the Commonwealth of Massachusetts for $1,000,000 ( £300,000), to be paid in three annual installments, and the pre-emptive right to th ...
.
Many of the settlers of what then became Central and Western New York came from the New England states. The Central New York Military Tract
The Military Tract of Central New York, also called the New Military Tract, consisted of nearly of bounty land set aside in Central New York to compensate New York's soldiers after their participation in the Revolutionary War.
Establishment
T ...
, where many of the townships were given the names of classical military and literary figures by Robert Harpur
Robert Harpur (January 25, 1731 Ballybay, County Monaghan, Ireland - April 15, 1825) was an Irish-American teacher, politician, pioneer, and landowner. He participated in surveying lands within the Central Military Tract in New York State and is ...
, was established to grant land to Revolutionary War veterans. Some of Northern New York was founded by the hundreds of Canadian exiles who had fought in the First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and Second Canadian Regiments of the Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
, who were banished from Canada due to their rebellion against the Crown.
19th century
 Battles of the
Battles of the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
(1812–1815) were fought on the Niagara Frontier
The Niagara Frontier refers to the stretch of land in the United States that is south of Lake Ontario and north of Lake Erie, and extends westward to Cleveland, Ohio. The term dates to the War of 1812, when the northern border was in contention b ...
; in the Champlain Valley
The Champlain Valley is a region of the United States around Lake Champlain in Vermont and New York extending north slightly into Quebec, Canada. It is part of the St. Lawrence River drainage basin, drained northward by the Richelieu River into ...
, including the Battle of Plattsburgh; in the St. Lawrence Valley
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
; and on Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north, west, and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south and east by the U.S. state of New York. The Canada–United States border sp ...
, including the Battle of Sackets Harbor
Sackets Harbor (earlier spelled Sacketts Harbor) is a village in Jefferson County, New York, United States, on Lake Ontario. The population was 1,450 at the 2010 census. The village was named after land developer and owner Augustus Sackett, who ...
. The city of Buffalo was razed by the British as well. After the war, the US government began to construct Fort Montgomery just south of the border at Rouses Point
Rouses Point is a village (New York), village in Clinton County, New York, Clinton County, New York (state), New York, United States, along the 45th parallel north, 45th parallel. The population was 2,209 at the 2010 census. The village is named ...
on Lake Champlain. Subsequently, it was discovered that at that point, the actual 45th parallel was three-quarters of a mile south of the surveyed line, putting the fort, which became known as "Fort Blunder", in Canada. This was not resolved until 1842 with the Webster–Ashburton Treaty
The Webster–Ashburton Treaty, signed August 9, 1842, was a treaty that resolved several border issues between the United States and the British North American colonies (the region that became Canada). Signed under John Tyler's presidency, it r ...
, in which Great Britain and the United States decided to leave the border on the meandering line as surveyed.
Slavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
existed in New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the East Coast of the United States, east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territor ...
and the Province of New York
The Province of New York (1664–1776) was a British proprietary colony and later royal colony on the northeast coast of North America. As one of the Middle Colonies, New York achieved independence and worked with the others to found the Uni ...
. New York was in the 1690s the largest importer of slaves among the American colonies. Slavery did not end with the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolut ...
, although John Jay
John Jay (December 12, 1745 – May 17, 1829) was an American statesman, patriot, diplomat, abolitionist, signatory of the Treaty of Paris, and a Founding Father of the United States. He served as the second governor of New York and the f ...
introduced an emancipation bill into the State Assembly as early as 1777. Sojourner Truth
Sojourner Truth (; born Isabella Baumfree; November 26, 1883) was an American abolitionist of New York Dutch heritage and a women's rights activist. Truth was born into slavery in Swartekill, New York, but escaped with her infant daughter to f ...
was held as a slave in the Hudson Valley
The Hudson Valley (also known as the Hudson River Valley) comprises the valley of the Hudson River and its adjacent communities in the U.S. state of New York. The region stretches from the Capital District including Albany and Troy south to ...
from the time she was born in 1797 until she escaped in 1826. Through efforts of the New York Manumission Society
The New-York Manumission Society was an American organization founded in 1785 by U.S. Founding Father John Jay, among others, to promote the gradual abolition of slavery and manumission of slaves of African descent within the state of New York. ...
and others, New York began to adopt a policy of gradual emancipation in 1799. The law passed in 1817 that would finally emancipate slaves did not take effect for ten years, giving slaveowners an entire decade to sell their slaves away to other states. When the law finally took effect, the last 2,800 slaves in New York State were emancipated on July 4, 1827.
 Although routes for travel on foot and by canoe had existed across the region for hundreds of years, transportation of agricultural goods to market was expensive and slow. Influenced by the canals being built in Britain, leading citizens of New York began to press for the construction of a canal across the state. Governor DeWitt Clinton prevailed upon the legislature to charter and fund construction of a canal from Albany to Buffalo. Construction of the
Although routes for travel on foot and by canoe had existed across the region for hundreds of years, transportation of agricultural goods to market was expensive and slow. Influenced by the canals being built in Britain, leading citizens of New York began to press for the construction of a canal across the state. Governor DeWitt Clinton prevailed upon the legislature to charter and fund construction of a canal from Albany to Buffalo. Construction of the Erie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east-west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, vastly reducing t ...
began in 1817 and was completed in 1825. The canal allowed the area to become an important component of the 19th century industrial expansion in the United States. The canal also promoted trade with British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English overseas possessions, English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland (island), Newfound ...
and settlement of newer states in western territories. Later in the century the New York Central Railroad
The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Mid ...
followed the "water-level route" from New York City to the Great Lakes, contributing to the industrialization of cities along its route.
Several times in the nineteenth century, Upstate New York served as a staging area and refuge for Canadian rebels against Great Britain, as well as Irish-American invaders of Canada, straining British–American relations. In 1837 and 1838, in the aftermath of the Lower Canada Rebellion
The Lower Canada Rebellion (french: rébellion du Bas-Canada), commonly referred to as the Patriots' War () in French, is the name given to the armed conflict in 1837–38 between rebels and the colonial government of Lower Canada (now south ...
, some Québécois rebels escaped south to the North Country, while on the Niagara Frontier
The Niagara Frontier refers to the stretch of land in the United States that is south of Lake Ontario and north of Lake Erie, and extends westward to Cleveland, Ohio. The term dates to the War of 1812, when the northern border was in contention b ...
, events of the Upper Canada Rebellion
The Upper Canada Rebellion was an insurrection against the oligarchic government of the British colony of Upper Canada (present-day Ontario) in December 1837. While public grievances had existed for years, it was the rebellion in Lower Canada (p ...
, also known as the Patriot War
The Patriot War was a conflict along the Canada–United States border in which bands of raiders attacked the British colony of Upper Canada more than a dozen times between December 1837 and December 1838. This so-called war was not a conflic ...
, took place. In the late 1860s, some of the Fenian raids were launched across the Niagara Frontier; Fenian
The word ''Fenian'' () served as an umbrella term for the Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB) and their affiliate in the United States, the Fenian Brotherhood, secret political organisations in the late 19th and early 20th centuries dedicated ...
s also assembled in Malone
Malone is an Irish surname. From the Irish "''Mael Eóin''", the name means a servant or a disciple of Saint John.
People
* Gilla Críst Ua Máel Eóin (died 1127), historian and Abbot of Clonmacnoise, Ó Maoil Eoin
* Adrian Malone (1937–2 ...
.
Although now largely discredited, the report of the 1905–1907 Mills Commission
Abraham Gilbert Mills (March 12, 1844 – August 26, 1929) was the fourth president of the National League of Professional Base Ball Clubs ( 1883–1884), and is best known for heading the "Mills Commission" which controversially credited Civil W ...
, charged with investigating the origins of baseball
The question of the origins of baseball has been the subject of debate and controversy for more than a century. Baseball and the other modern bat, ball, and running games — stoolball, cricket and rounders — were developed from folk games i ...
, named Cooperstown
Cooperstown is a village in and county seat of Otsego County, New York, United States. Most of the village lies within the town of Otsego, but some of the eastern part is in the town of Middlefield. Located at the foot of Otsego Lake in the C ...
as the place where baseball
Baseball is a bat-and-ball sport played between two teams of nine players each, taking turns batting and fielding. The game occurs over the course of several plays, with each play generally beginning when a player on the fielding tea ...
was invented in the 1830s or 1840s by Abner Doubleday
Abner Doubleday (June 26, 1819 – January 26, 1893) was a career United States Army officer and Union major general in the American Civil War. He fired the first shot in defense of Fort Sumter, the opening battle of the war, and had a p ...
. Cooperstown is the home of the National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum
The National Baseball Hall of Fame and Museum is a history museum and hall of fame in Cooperstown, New York, operated by private interests. It serves as the central point of the history of baseball in the United States and displays basebal ...
. (Modern research suggests that the game was actually developed in its modern form in New York City.)
In the pre–Civil War era, Upstate New York became a major center of radical abolitionist
Abolitionism, or the abolitionist movement, is the movement to end slavery. In Western Europe and the Americas, abolitionism was a historic movement that sought to end the Atlantic slave trade and liberate the enslaved people.
The British ...
activity and was an important nexus of the Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clandestine routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early- to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and Canada. ...
. Resistance to the Fugitive Slave Act
A fugitive (or runaway) is a person who is fleeing from custody, whether it be from jail, a government arrest, government or non-government questioning, vigilante violence, or outraged private individuals. A fugitive from justice, also kno ...
was particularly heated in the region, as evidenced by such events as the Jerry Rescue. The American women's rights
Women's rights are the rights and entitlements claimed for women and girls worldwide. They formed the basis for the women's rights movement in the 19th century and the feminist movements during the 20th and 21st centuries. In some countries, ...
movement was also born in Upstate New York at this time. The Seneca Falls Convention
The Seneca Falls Convention was the first women's rights convention. It advertised itself as "a convention to discuss the social, civil, and religious condition and rights of woman".Wellman, 2004, p. 189 Held in the Wesleyan Chapel of the tow ...
, the first women's rights convention, was held at Seneca Falls in 1848. The Rochester Convention, the second such convention, was held two weeks later in Rochester
Rochester may refer to:
Places Australia
* Rochester, Victoria
Canada
* Rochester, Alberta
United Kingdom
*Rochester, Kent
** City of Rochester-upon-Medway (1982–1998), district council area
** History of Rochester, Kent
** HM Prison ...
.
Through the nineteenth century, Upstate New York was a hotbed of religious revivalism. A number of sects, such as the Shakers and the Oneida Community
The Oneida Community was a perfectionist religious communal society founded by John Humphrey Noyes and his followers in 1848 near Oneida, New York. The community believed that Jesus had already returned in AD 70, making it possible for them ...
, established themselves in Upstate New York during that time. This led evangelist Charles Grandison Finney
Charles Grandison Finney (August 29, 1792 – August 16, 1875) was an American Presbyterian minister and leader in the Second Great Awakening in the United States. He has been called the "Father of Old Revivalism." Finney rejected much of trad ...
to coin the term the " Burned-Over District" for the region. Because of the comparative isolation of the region, many of the sects were Nonconformist
Nonconformity or nonconformism may refer to:
Culture and society
* Insubordination, the act of willfully disobeying an order of one's superior
*Dissent, a sentiment or philosophy of non-agreement or opposition to a prevailing idea or entity
** ...
, and because of their non-traditional tenets they had numerous difficulties with government and other local people. The region is considered to be the cradle of Mormonism
Mormonism is the religious tradition and theology of the Latter Day Saint movement of Restorationist Christianity started by Joseph Smith in Western New York in the 1820s and 1830s. As a label, Mormonism has been applied to various aspects of ...
. The Mormons, Seventh-day Adventists
The Seventh-day Adventist Church is an Adventism, Adventist Protestantism, Protestant Christian denomination which is distinguished by its observance of Saturday, the Names of the days of the week#Numbered days of the week, seventh day of the ...
and Spiritualists
Spiritualism is the metaphysics, metaphysical school of thought opposing physicalism and also is the category of all spiritual beliefs/views (in monism and Mind-body dualism, dualism) from ancient to modern. In the long nineteenth century, Spir ...
are the only 21st century survivors of the hundreds of sects created during this time; some more mainstream churches, such as the Wesleyan Church
The Wesleyan Church, also known as the Wesleyan Methodist Church and Wesleyan Holiness Church depending on the region, is a Methodist Christian denomination in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, South Africa, Namibia, Sierra Leone, L ...
and Free Methodist Church
The Free Methodist Church (FMC) is a Methodist Christian denomination within the holiness movement, based in the United States. It is evangelical in nature and is Wesleyan–Arminian in theology.
The Free Methodist Church has members in over 100 ...
(both offshoots of Methodism that originated in political disputes with the mainline Methodist church), also survive.
In the 19th century, extractive industries changed the landscape. Potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form.
was manufactured as the land was cleared for farming. Logging
Logging is the process of cutting, processing, and moving trees to a location for transport. It may include skidding, on-site processing, and loading of trees or logs onto trucks or skeleton cars.
Logging is the beginning of a supply chain ...
was rampant in the Adirondacks. Iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
was mined in the Adirondacks and the North Country. By the 1870s, business leaders, concerned about the effect of deforestation on the water supply necessary to the Erie Canal, advocated for the creation of forest preserves in the Adirondacks and the Catskills. The Adirondack Park
The Adirondack Park is a part of Forest Preserve (New York), New York's Forest Preserve in northeastern New York (state), New York, United States. The park was established in 1892 for “the free use of all the people for their health and pleasur ...
and Catskill Park
The Catskill Park is in the Catskill Mountains in New York in the United States. It consists of of land inside a Blue Line in four counties: Delaware, Greene, Sullivan, and Ulster. As of 2005, or 41 percent of the land within, is owned by ...
were created and strengthened by a series of legislation between 1885 and 1894, when the " forever wild" provision of the New York State Constitution
The Constitution of the State of New York establishes the structure of the government of the State of New York, and enumerates the basic rights of the citizens of New York. Like most state constitutions in the United States, New York's constituti ...
was added.
20th century
 During the era immediately following World War II, Upstate reached what was probably its peak influence in the national economy. Major local corporations such as IBM,
During the era immediately following World War II, Upstate reached what was probably its peak influence in the national economy. Major local corporations such as IBM, General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energ ...
, Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company (referred to simply as Kodak ) is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in analogue photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorpor ...
, Xerox
Xerox Holdings Corporation (; also known simply as Xerox) is an American corporation that sells print and electronic document, digital document products and services in more than 160 countries. Xerox is headquartered in Norwalk, Connecticut (ha ...
and Carrier had national success, producing cutting-edge products for business, government and consumers, and leadership in corporate culture. The opening of the New York State Thruway in the mid-1950s gave the region superior access to other eastern markets. This regional advantage faded as many local firms relocated certain operations to other states, or downsized in the face of foreign competition, similar to events in other areas in the American Rust Belt
The Rust Belt is a region of the United States that experienced industrial decline starting in the 1950s. The U.S. manufacturing sector as a percentage of the U.S. GDP peaked in 1953 and has been in decline since, impacting certain regions an ...
. There have, however, been recent efforts at economic revitalization. In April 2021, GlobalFoundries
GlobalFoundries Inc. (GF or GloFo) is a multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company incorporated in the Cayman Islands and headquartered in Malta, New York. Created by the divestiture of the manufacturing arm of AMD, ...
, a company specializing in the semiconductor industry, moved its headquarters from Silicon Valley, California
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that serves as a global center for high technology and innovation. Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical areas San Mateo Cou ...
to its semiconductor chip manufacturing facility in Malta, New York
Malta is a town in Saratoga County, New York, United States. The town is in the central part of the county and is south of Saratoga Springs. The population was 17,130 as of the 2020 census.
Malta, along with Stillwater, is home to the Luther F ...
.
Since the late 20th century, with the decline of manufacturing and its jobs, the area has generally suffered a net population loss, most heavily in Western New York. By contrast, many Amish
The Amish (; pdc, Amisch; german: link=no, Amische), formally the Old Order Amish, are a group of traditionalist Anabaptist Christian church fellowships with Swiss German and Alsatian origins. They are closely related to Mennonite churc ...
and Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radic ...
families are recent arrivals to the area and have helped revive agriculture as part of the economy. Beginning in 1974, many Mennonite families moved to the Penn Yan area of Yates County from Lancaster County, Pennsylvania
Lancaster County (; Pennsylvania Dutch: Lengeschder Kaundi), sometimes nicknamed the Garden Spot of America or Pennsylvania Dutch Country, is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It is located in the south central part of Pennsylvania. ...
, seeking cheaper farmland. Amish communities have also been established in St. Lawrence, Montgomery, Chautauqua
Chautauqua ( ) was an adult education and social movement in the United States, highly popular in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Chautauqua assemblies expanded and spread throughout rural America until the mid-1920s. The Chautauqua br ...
and Cattaraugus counties, and are making farming profitable.
Artisans are reviving traditional specialty cheeses and developing growing markets for their products, including shipping some items to the New York metropolitan market. A Greek-style yogurt, Chobani
Chobani is an American food company specializing in strained yogurt. The company was founded in 2005 by Hamdi Ulukaya, a Turkish businessman. Chobani sells thick, Greek-style yogurt with a higher protein content than traditional yogurt and is o ...
, is being produced Upstate by a recent immigrant, who has expanded his operation nationally.
Additionally, Upstate New York continues to boast low crime rates, high educational prospects, and readily affordable daily essentials, earning Syracuse, Rochester, Albany, Schenectady
Schenectady () is a city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-largest city by population. The city is in eastern New Y ...
, and Buffalo spots in the ''Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine owned by Integrated Whale Media Investments and the Forbes family. Published eight times a year, it features articles on finance, industry, investing, and marketing topics. ''Forbes'' also re ...
'' magazine list of top ten places to raise a family in the United States.
Five of the six Iroquois nations have filed land claims against New York State (or have sought settlement of pending claims), based on late 18th-century treaties following the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
with the State of New York
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. state ...
(which did not have constitutional authority to treat with American Indian nations) and the United States.
Economy
Politics
Often attributed to the region's semi-rural to rural character, there is moreconservatism
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilizati ...
in culture and politics than found in the more urban downstate area, and the region is the power base of the state's Republican Party. Upstate New York does, however, have several Democratic-dominated counties, including Erie County (Buffalo), Monroe County Monroe County may refer to seventeen counties in the United States, all named for James Monroe:
* Monroe County, Alabama
*Monroe County, Arkansas
* Monroe County, Florida
* Monroe County, Georgia
*Monroe County, Illinois
*Monroe County, Indian ...
(Rochester), Onondaga County
Onondaga County ( ) is a county in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2020 census, the population was 476,516. The county seat is Syracuse.
Onondaga County is the core of the Syracuse, NY MSA.
History
The name ''Onondaga'' derives from ...
(Syracuse), Tompkins County (Ithaca), and Albany County (Albany).
As a whole, Upstate New York is roughly equally divided in federal elections between Democrats and Republicans. In 2004, John Kerry
John Forbes Kerry (born December 11, 1943) is an American attorney, politician and diplomat who currently serves as the first United States special presidential envoy for climate. A member of the Forbes family and the Democratic Party (Unite ...
defeated George W. Bush by fewer than 1,500 votes (1,553,246 votes to 1,551,971) in the Upstate Region.
Relationship with New York City
New York City is dependent on Upstate New York for a variety of services: the latter is the source of the city's water supply via the Delaware Aqueduct and the Catskill Aqueduct; much of the city's electric power supply comes from state-owned Niagara Falls hydroelectric generating plants, hydroelectric plants at Niagara Falls and theSt. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
; and most of the state's prisons are upstate; hence the popular term "being sent up the river" (however, the term originally referred to Sing Sing, which is "up the Hudson River" from New York City, but being in Ossining (town), New York, Ossining in Westchester County is still in the "downstate" region). Conversely, the operation of state facilities providing these services is an important part of the upstate economy.
Historic events
*TheAlbany Congress
The Albany Congress (June 19 – July 11, 1754), also known as the Albany Convention of 1754, was a meeting of representatives sent by the legislatures of seven of the 13 British colonies in British America: Connecticut, Maryland, Massachusetts, ...
, 1754
*Battle of Valcour Island
The Battle of Valcour Island, also known as the Battle of Valcour Bay, was a naval engagement that took place on October 11, 1776, on Lake Champlain. The main action took place in Valcour Bay, a narrow strait between the New York mainland and ...
, 1776
*Battle of Oriskany, 1777
*Battles of Saratoga, turning point of the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, 1777
*Cherry Valley massacre, 1778
*Sullivan Campaign, 1779
*Second Great Awakening in the burned-over district, early 1800s
* Battle of Plattsburgh, 1814
*William Morgan (anti-Mason), The Morgan Affair, 1826
*Publication of the Book of Mormon, 1830
*The Caroline Affair, 1837
*Seneca Falls Convention
The Seneca Falls Convention was the first women's rights convention. It advertised itself as "a convention to discuss the social, civil, and religious condition and rights of woman".Wellman, 2004, p. 189 Held in the Wesleyan Chapel of the tow ...
, the first women's rights
Women's rights are the rights and entitlements claimed for women and girls worldwide. They formed the basis for the women's rights movement in the 19th century and the feminist movements during the 20th and 21st centuries. In some countries, ...
convention held in the United States, 1848
* Jerry Rescue, 1851
*Angola Horror train wreck, 1867
*First execution via the electric chair, in Auburn Prison in 1890
*Assassination of William McKinley, Assassination of President William McKinley in Buffalo, 1901
*Anarchist Leon Czolgosz, McKinley's assassin, convicted at trial and electrocuted in Auburn Prison, 1901
*Split Rock, New York, Split Rock Explosion, 1918
*Remington Rand strike of 1936–1937
*Continental Charters Flight 44-2, 1951
*Allegheny Reservoir construction, 1961–1967
*Northeast blackout of 1965
*Woodstock music festival, 1969
*Attica Prison riot, 1971
*Hurricane Agnes, 1972
*1980 Winter Olympics, Winter Olympics, 1980
*Collapse of New York State Thruway bridge over Schoharie Creek, 1987
*New York State Labor Day derechos, 1998
*Northeast blackout of 2003
*Lake Storm Aphid, 2006
*Continental Airlines Flight 3407, 2009
*Binghamton shooting, 2009
*Hurricane Irene, 2011
*Tropical Storm Lee (2011), Tropical Storm Lee, 2011
*November 13–21, 2014 North American winter storm, Winter Storm Knife, 2014
*Clinton Correctional Facility escape, 2015
Journalists
*Gordon Ackerman *Samuel Hopkins Adams, muckraker, born in Dunkirk, New York, Dunkirk *Wolf Blitzer, raised in Buffalo *Amy Dickinson, ''Chicago Tribune'' advice columnist; grew up on a dairy farm in Freeville, New York, Freeville *Frederick Douglass (1818–1895), editor and publisher of abolitionist newspapers: ''North Star (newspaper), The North Star'', published in Rochester, ''Frederick Douglass Weekly'', ''Frederick Douglass' Paper'', ''Douglass' Monthly'' and ''New National Era'' *Ira Joe Fisher, author and weatherman, born and raised in Little Valley (village), New York, Little Valley *Megyn Kelly, television news anchor and political commentator *Verlyn Klinkenborg, member of the ''New York Times'' editorial board; writer and farmer *Francis Mallison of Rome, New York, Rome; journalist, editor and public servant. Editor of the ''Rome Sentinel'', reporter for the ''Brooklyn Eagle''. He and editor Joseph Howard Jr. organized the "Great Civil War Gold Hoax", for which he was held as a prisoner of war. *Henry Jarvis Raymond, born in Lima (village), New York, Lima, founder of the New York Times. He was the newspaper's editor until his death. *Andy Rooney, radio and television writer and broadcaster *Tim Russert, host of NBC's ''Meet the Press'', born and raised in Buffalo *William James Stillman, author, diplomat, and photographer; born in Schenectady *Dorothy Thompson, journalist and radio broadcaster; born in Lancaster, New York, Lancaster *Tom Toles, political cartoonist; from Buffalo *Scott Wallace (photojournalist), Scott Wallace of Utica, author of ''The Unconquered: In Search of the Amazon's Last Uncontacted Tribes' *James Watson Webb, born in Claverack, New York, Claverack and raised in Cooperstown, New York, Cooperstown; publisher of the New York newspapers the ''Morning Courier'' and the ''New York Enquirer'', which he consolidated as the ''Courier and Enquirer''. He also became a United States diplomat and a New York (state), New York politician in the Whig Party (United States), Whig and Republican Party (United States), Republican parties. *John Zogby of Utica, pollster and blogger'Social, political and religious movements
*Abolitionism in the United States *Anti-Masonic Party *The Anti-Rent War *Ararat, City of Refuge *Brothertown Indians, Brothertown *The Chautauqua Institution *The Frankean Synod *Ganienkeh Territory *The Inspirationalists *Kanatsiohareke *Latter Day Saint movement *Lily Dale *The Millerites *Modern Spiritualism *TheOneida Community
The Oneida Community was a perfectionist religious communal society founded by John Humphrey Noyes and his followers in 1848 near Oneida, New York. The community believed that Jesus had already returned in AD 70, making it possible for them ...
*The Second Great Awakening
*The Shakers
*The Universal Friends
*Women's suffrage
Spiritual and religious figures
*Jehudi Ashmun, religious leader and social reformer born in Champlain (village), New York, Champlain, New York. He was an agent of the American Colonization Society which promoted the settlement of blacks at Monrovia, Liberia, and was effectively governor of the colony from 1824 to 1828. *Antoinette Brown, minister, abolitionist and suffragist. Born in Henrietta, New York, Henrietta, she was the first woman to be ordained a minister in the United States. She served a congregation in Butler, New York, South Butler. *Saint Marianne Cope, Catholic religious sister who ministered to the leper colony in Hawaii without contracting the disease *Avery Dulles, S.J., born in Auburn, New York, Auburn; noted theologian and Cardinal (Catholic Church), cardinal of the Roman Catholic Church *Charles Grandison Finney
Charles Grandison Finney (August 29, 1792 – August 16, 1875) was an American Presbyterian minister and leader in the Second Great Awakening in the United States. He has been called the "Father of Old Revivalism." Finney rejected much of trad ...
*Harry Emerson Fosdick, clergyman; born in Buffalo, and graduated from Colgate University
*George Washington Gale
*Beriah Green
*Handsome Lake
*Mother Ann Lee
*Oren Lyons
*David Marks (preacher), David Marks
*William Miller (preacher), William Miller
*Mordecai Manuel Noah
*John Humphrey Noyes
*The Public Universal Friend
*Walter Rauschenbusch, a Christian theologian, Baptist minister and a key figure in the Social Gospel movement in the United States; born in Rochester
Rochester may refer to:
Places Australia
* Rochester, Victoria
Canada
* Rochester, Alberta
United Kingdom
*Rochester, Kent
** City of Rochester-upon-Medway (1982–1998), district council area
** History of Rochester, Kent
** HM Prison ...
. His father was a preacher who taught at the Rochester Theological Seminary.
*Joseph Smith
*Saint Kateri Tekakwitha
Major highways
*The New York State Thruway *The Adirondack Northway *The Taconic State Parkway *Interstate 81 in New York, Interstate 81 *Interstate 84 in New York, Interstate 84 *Interstate 86 in New York, Interstate 86, incorporating the Southern Tier Expressway and the Quickway *Interstate 87 (New York), Interstate 87 *Interstate 88 (New York), Interstate 88 *Interstate 90 in New York, Interstate 90Major universities and colleges
Public
State University of New York (SUNY) *Alfred State College, SUNY Alfred *University at Albany, The State University of New York, University at Albany *Binghamton University *State University of New York at Brockport, SUNY Brockport *University at Buffalo, The State University of New York, University at Buffalo *Buffalo State College, SUNY College at Buffalo *State University of New York at Canton, SUNY Canton *State University of New York at Cobleskill, SUNY Cobleskill *State University of New York at Cortland, SUNY Cortland *State University of New York at Delhi, SUNY Delhi *Empire State College *College of Environmental Science and Forestry, SUNY ESF *State University of New York at Fredonia, SUNY Fredonia *State University of New York at Geneseo, SUNY Geneseo *State University of New York Polytechnic Institute, SUNY Polytechnic Institute *Morrisville State College *State University of New York at New Paltz, SUNY New Paltz *State University of New York at Oneonta, SUNY Oneonta *State University of New York at Oswego, SUNY Oswego *State University of New York at Plattsburgh, SUNY Plattsburgh *State University of New York at Potsdam, SUNY Potsdam *State University of New York Upstate Medical University, SUNY Upstate Medical University United States Military Academy at West PointPrivate
*Alfred University *Bard College *Canisius College *Cazenovia College *Clarkson University *The College of Saint Rose *Colgate University *Cornell University *D'Youville College *Elmira College *Hamilton College (New York), Hamilton College *Hartwick College *Hobart and William Smith Colleges *Houghton College *Iona College (New York), Iona College *Ithaca College *Keuka College *Le Moyne College *Manhattan College *Marist College *Mount Saint Mary College *Nazareth College (New York), Nazareth College *Niagara University *Paul Smith's College *Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute *Roberts Wesleyan College *University of Rochester *Rochester Institute of Technology *Russell Sage College *St. Bonaventure University *St. John Fisher College *St. Lawrence University *Skidmore College *Siena College *Syracuse University *Union College *Utica College *Vassar College *Wells CollegeMajor tourist attractions and destinations



 *
*Adirondack Mountains
The Adirondack Mountains (; a-də-RÄN-dak) form a massif in northeastern New York with boundaries that correspond roughly to those of Adirondack Park. They cover about 5,000 square miles (13,000 km2). The mountains form a roughly circular ...
*Ausable Chasm
*Baseball Hall of Fame (in Cooperstown, New York, Cooperstown)
*Catskill Mountains
The Catskill Mountains, also known as the Catskills, are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains, located in southeastern New York. As a cultural and geographic region, the Catskills are generally defined as those areas c ...
*Corning Museum of Glass
*Enchanted Forest Water Safari (in Old Forge)
*Erie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east-west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, vastly reducing t ...
*Farmers' Museum (in Cooperstown, New York, Cooperstown)
*Finger Lakes
The Finger Lakes are a group of eleven long, narrow, roughly north–south lakes located south of Lake Ontario in an area called the ''Finger Lakes region'' in New York, in the United States. This region straddles the northern and transitional ...
*Fort Niagara
*Fort Ontario
*Fort Stanwix
*Fort Ticonderoga
*Harness Racing Museum & Hall of Fame (in Goshen (village), New York, Goshen)
*Howe Caverns
*International Boxing Hall of Fame (in Canastota, New York, Canastota)
*Lake George (lake), New York, Lake George
*Lake Placid, New York, Lake Placid
*Letchworth State Park
*National Distance Running Hall of Fame (in Utica)
*National Museum of Dance (in Saratoga Springs, New York, Saratoga Springs)
*National Women's Hall of Fame (in Seneca Falls)
*Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls () is a group of three waterfalls at the southern end of Niagara Gorge, spanning the border between the province of Ontario in Canada and the state of New York in the United States. The largest of the three is Horseshoe Fall ...
*Saratoga Race Course
*Seabreeze Amusement Park (in Irondequoit, New York, Irondequoit)
*Six Flags Darien Lake
*The Great Escape and Hurricane Harbor, Six Flags Great Escape Resort (in Queensbury, New York, Queensbury)
*Sylvan Beach, New York, Sylvan Beach
*Thousand Islands
The Thousand Islands (french: Mille-Îles) constitute a North American archipelago of 1,864 islands that straddles the Canada–US border in the Saint Lawrence River as it emerges from the northeast corner of Lake Ontario. They stretch for abo ...
*Turning Stone Resort Casino (in Verona, New York, Verona)
*Watkins Glen International Raceway
Watkins Glen International, nicknamed "The Glen", is an automobile race track located in the town of Dix just southwest of the village of Watkins Glen, New York, at the southern tip of Seneca Lake. It was long known around the world as the home ...
Geographic divisions
Metropolitan areas and major cities
* Albany (state capital) -Schenectady
Schenectady () is a city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-largest city by population. The city is in eastern New Y ...
- Troy, New York, Troy (Capital District
A capital district, capital region or capital territory is normally a specially designated administrative division where a country's seat of government is located. As such, in a federal model of government, no state or territory has any poli ...
)
* Binghamton
Binghamton () is a city in the U.S. state of New York, and serves as the county seat of Broome County. Surrounded by rolling hills, it lies in the state's Southern Tier region near the Pennsylvania border, in a bowl-shaped valley at the conflue ...
(Triple Cities)
* Buffalo - Cheektowaga, New York, Cheektowaga (largest metropolitan area with the largest city (Buffalo))
* Elmira, New York, Elmira
* Glens Falls, New York, Glens Falls
* Ithaca
Ithaca most commonly refers to:
*Homer's Ithaca, an island featured in Homer's ''Odyssey''
*Ithaca (island), an island in Greece, possibly Homer's Ithaca
*Ithaca, New York, a city, and home of Cornell University and Ithaca College
Ithaca, Ithaka ...
* Kingston
* Poughkeepsie (city), New York, Poughkeepsie - Newburgh - Middletown, Orange County, New York, Middletown
* Rochester
Rochester may refer to:
Places Australia
* Rochester, Victoria
Canada
* Rochester, Alberta
United Kingdom
*Rochester, Kent
** City of Rochester-upon-Medway (1982–1998), district council area
** History of Rochester, Kent
** HM Prison ...
* Syracuse (Central New York
Central New York is the central region of New York State, including the following counties and cities:
With a population of about 773,606 (2009) and an area of , the region includes the Syracuse metropolitan area.
Definitions
The New York ...
)
* Utica - Rome, New York, Rome ( Mohawk Valley)
* Watertown (city), New York, Watertown - Fort Drum
Subregions
Adirondack Mountains
The Adirondack Mountains (; a-də-RÄN-dak) form a massif in northeastern New York with boundaries that correspond roughly to those of Adirondack Park. They cover about 5,000 square miles (13,000 km2). The mountains form a roughly circular ...
* Capital District
A capital district, capital region or capital territory is normally a specially designated administrative division where a country's seat of government is located. As such, in a federal model of government, no state or territory has any poli ...
( Albany and the surrounding area)
* Catskill Mountains
The Catskill Mountains, also known as the Catskills, are a physiographic province of the larger Appalachian Mountains, located in southeastern New York. As a cultural and geographic region, the Catskills are generally defined as those areas c ...
* Central-Leatherstocking Region (includes Cooperstown, New York, Cooperstown)
* Central New York
Central New York is the central region of New York State, including the following counties and cities:
With a population of about 773,606 (2009) and an area of , the region includes the Syracuse metropolitan area.
Definitions
The New York ...
( Syracuse and the surrounding area)
* Finger Lakes
The Finger Lakes are a group of eleven long, narrow, roughly north–south lakes located south of Lake Ontario in an area called the ''Finger Lakes region'' in New York, in the United States. This region straddles the northern and transitional ...
(between Rochester
Rochester may refer to:
Places Australia
* Rochester, Victoria
Canada
* Rochester, Alberta
United Kingdom
*Rochester, Kent
** City of Rochester-upon-Medway (1982–1998), district council area
** History of Rochester, Kent
** HM Prison ...
and Syracuse)
* Holland Purchase
The Phelps and Gorham Purchase was the purchase in 1788 of of land in what is now western New York State from the Commonwealth of Massachusetts for $1,000,000 ( £300,000), to be paid in three annual installments, and the pre-emptive right to th ...
* Hudson Valley
The Hudson Valley (also known as the Hudson River Valley) comprises the valley of the Hudson River and its adjacent communities in the U.S. state of New York. The region stretches from the Capital District including Albany and Troy south to ...
(excluding Rockland and Westchester counties)
* Mohawk Valley (includes Utica and Schenectady
Schenectady () is a city in Schenectady County, New York, United States, of which it is the county seat. As of the 2020 census, the city's population of 67,047 made it the state's ninth-largest city by population. The city is in eastern New Y ...
)
* North Country (northern frontier of New York)
* Shawangunk Ridge
* Ski country (the northern boundary of the Southern Tier, includes Cortland, New York, Cortland, Clymer, New York, Clymer and Ellicottville (town), New York, Ellicottville)
* Southern Tier (just north of Pennsylvania, excluding the Catskills; includes Binghamton
Binghamton () is a city in the U.S. state of New York, and serves as the county seat of Broome County. Surrounded by rolling hills, it lies in the state's Southern Tier region near the Pennsylvania border, in a bowl-shaped valley at the conflue ...
, Corning (city), New York, Corning and Elmira, New York, Elmira)
* Tug Hill
* Western New York
Western New York (WNY) is the westernmost region of the U.S. state of New York. The eastern boundary of the region is not consistently defined by state agencies or those who call themselves "Western New Yorkers". Almost all sources agree WNY i ...
(the westernmost tip; includes Buffalo, Niagara Falls, New York, Niagara Falls, Jamestown, New York, Jamestown, and sometimes Rochester, Monroe County, New York, Rochester)
See also
* Downstate Illinois * Hoaxes and legends of upstate New York * List of people from New York (state) * Northern Michigan * Outline of New York * Sports in upstate New York ** Bills–Jets rivalryExplanatory notes
References
Further reading
* * (Excerpt focused on 1945–1960 in Ithaca, New York)External links
Old Abandoned Buildings of Northern NY
the urban decay of upstate New York, in pictures from the area
Exploring Upstate
travel, culture, and history in Upstate New York
New York History Net
Oral History of Franklin County
history of Franklin County, New York, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries {{Coord missing, New York (state) Upstate New York, Regions of New York (state)