|
Onondaga County, New York
Onondaga County ( ) is a county in the U.S. state of New York. As of the 2020 census, the population was 476,516. The county seat is Syracuse. Onondaga County is the core of the Syracuse, NY MSA. History The name ''Onondaga'' derives from the name of the Native American tribe who lived in this area at the time of European contact, one of the original Five Nations of the ''Haudenosaunee''. They called themselves (autonym) ''Onoda'gega'', sometimes spelled ''Onontakeka.'' The word means "People of the Hills." Sometimes the term was ''Onondagaono'' ("The People of the Hills"). The federally recognized Onondaga Nation has a reservation within the county, on which they have self-government. When counties were established in New York in 1683, the present Onondaga County was part of Albany County. This enormous county included the northern part of New York State as well as all of the present State of Vermont and, in theory, extended westward to the Pacific Ocean. It was re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Counties In New York
There are 62 counties in the state of New York. The first 12 were created immediately after the British took over the Dutch colony of New Amsterdam; two of these counties were later abolished, their land going to Massachusetts. The newest is Bronx County, created in 1914 from the portions of New York City that had been annexed from Westchester County in the late 19th century and added to New York County. New York's counties are named for a variety of Native American words; British provinces, counties, cities, and royalty; early American statesmen and military personnel; and New York State politicians. The FIPS county code is the five-digit Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) code which uniquely identifies counties and county equivalents in the United States. The three-digit number is unique to each individual county within a state, but to be unique within the entire United States, it must be prefixed by the state code. This means that, for example, while Albany C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
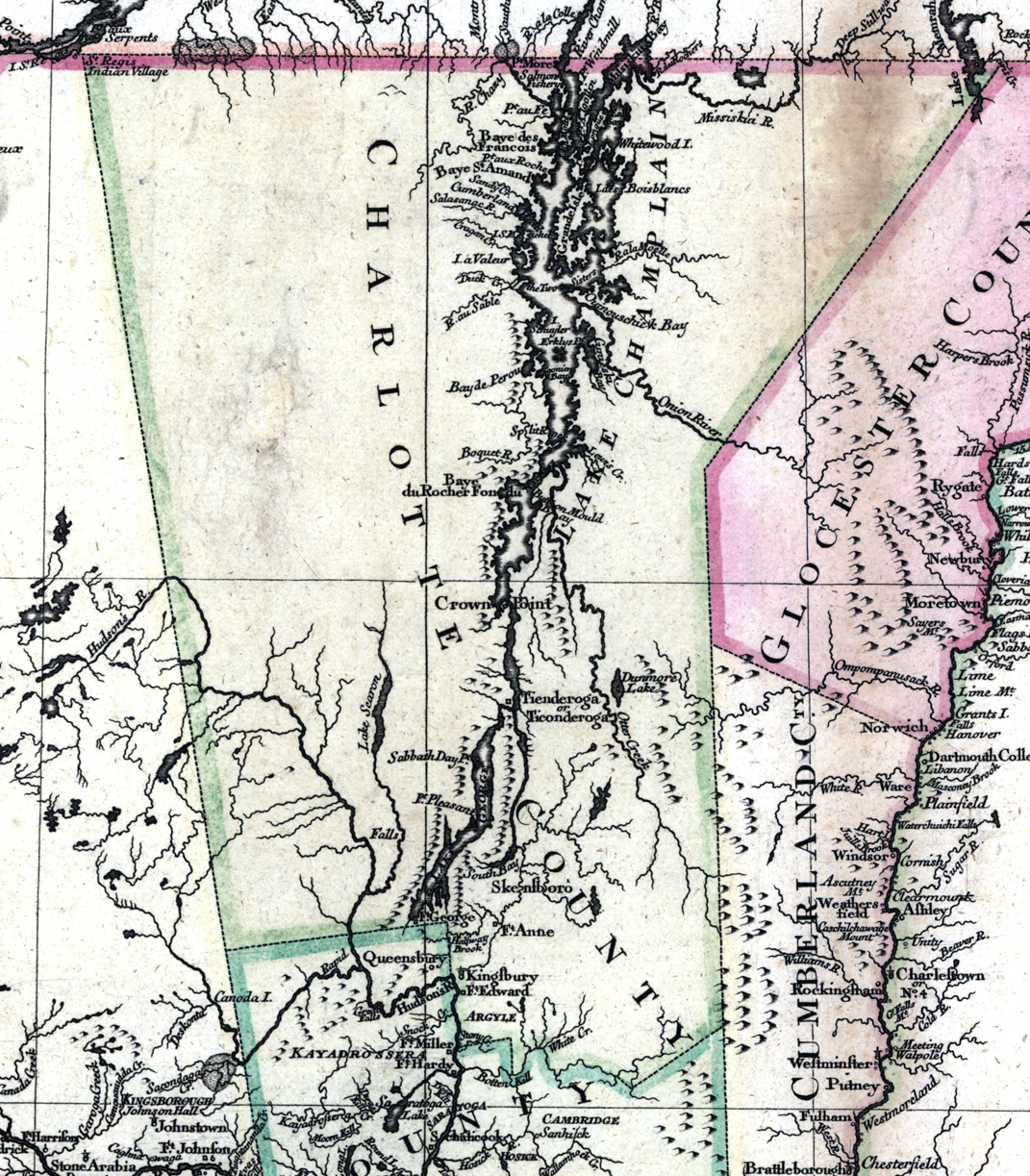
Cumberland County, New York
Cumberland County, New York was a county in the Province of New York that became part of the state of Vermont. It was divided out of Albany County in New York in 1766, but eventually became a part of Vermont in 1777. At that time, Vermont was holding itself out as the Republic of Vermont and was not admitted to the Union until 1791. Located south of Gloucester County and east of Charlotte County (Anderson, p. 6, incorporated from Albany County (see map from 1777 Charlotte County, Province of New York), Cumberland County was fused with Gloucester County, New York to become Cumberland County, Vermont, which, along with Bennington County, comprised the only two counties in that state. The Vermont Cumberland County was abolished by being partitioned into several new counties in Vermont and one in New Hampshire. See also *List of former United States counties *List of counties in Vermont There are fourteen counties in the U.S. state of Vermont. These counties together contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Name
A name is a term used for identification by an external observer. They can identify a class or category of things, or a single thing, either uniquely, or within a given context. The entity identified by a name is called its referent. A personal name identifies, not necessarily uniquely, a ''specific'' individual human. The name of a specific entity is sometimes called a proper name (although that term has a philosophical meaning as well) and is, when consisting of only one word, a proper noun. Other nouns are sometimes called "common names" or (obsolete) "general names". A name can be given to a person, place, or thing; for example, parents can give their child a name or a scientist can give an element a name. Etymology The word ''name'' comes from Old English ''nama''; cognate with Old High German (OHG) ''namo'', Sanskrit (''nāman''), Latin ''Roman naming conventions, nomen'', Greek language, Greek (''onoma''), and Persian language, Persian (''nâm''), from the Proto-Indo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of the United States, fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. Established by royal charter in the 17th and 18th centuries, the American colonies were largely autonomous in domestic affairs and commercially prosperous, trading with Britain and its Caribbean colonies, as well as other European powers via their Caribbean entrepôts. After British victory over the French in the Seven Years' War in 1763, tensions between the motherland and he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
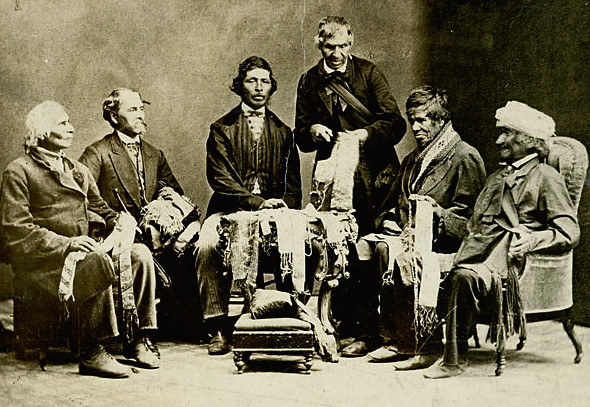
Six Nations Of The Grand River First Nation
Six Nations (or Six Nations of the Grand River, french: Réserve des Six Nations, see, Ye:i’ Níónöëdzage:h) is demographically the largest First Nations reserve in Canada. As of the end of 2017, it has a total of 27,276 members, 12,848 of whom live on the reserve. It is the only reserve in North America that has representatives of all six Haudenosaunee nations living together. These nations are the Mohawk, Cayuga, Onondaga, Oneida, Seneca and Tuscarora. Some Lenape (formerly known as Delaware) also live in the territory. The Six Nations reserve is bordered by the County of Brant, Norfolk County, and Haldimand County, with a subsection reservation, the New Credit Reserve, located within its boundaries. The acreage at present covers some near the city of Brantford, Ontario. This represents approximately 5% of the original of land granted to the Six Nations by the 1784 Haldimand Treaty. History Many of the Haudenosaunee people allied with the British during the Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Brant
Thayendanegea or Joseph Brant (March 1743 – November 24, 1807) was a Mohawk people, Mohawk military and political leader, based in present-day New York (state), New York, who was closely associated with Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain during and after the American Revolution. Perhaps the Native Americans in the United States, Native American of his generation best known to the Americans and British, he met many of the most significant Anglo-American people of the age, including both George Washington and George III of the United Kingdom, King George III. While not born into a hereditary leadership role within the Iroquois, Iroquois League, Brant rose to prominence due to his education, abilities, and connections to British officials. His sister, Molly Brant, was the wife of Sir William Johnson, 1st Baronet, Sir William Johnson, the influential British Superintendent of Indian Affairs in the province of New York. During the American Revolutionary War, Brant led Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loyalists
Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Crown, notably with the loyalists opponents of the American Revolution, and United Empire Loyalists who moved to other colonies in British North America after the revolution. Historical loyalism 18th century North America In North America, the term ''loyalist'' characterised colonists who rejected the American Revolution in favour of remaining loyal to the king. American loyalists included royal officials, Anglican clergymen, wealthy merchants with ties to London, demobilised British soldiers, and recent arrivals (especially from Scotland), as well as many ordinary colonists who were conservative by nature and/or felt that the protection of Britain was needed. Colonists with loyalist sympathies accounted for an estimated 15 per cent to 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oneida Lake Seen From Yacht Club In Cicero New York
Oneida may refer to: Native American/First Nations * Oneida people, a Native American/First Nations people and one of the five founding nations of the Iroquois Confederacy * Oneida language * Oneida Indian Nation, based in New York * Oneida Nation of the Thames, also known as "Onyota'a:ka First Nation" * Oneida Nation of Wisconsin Places * Oneida County (other) * Oneida Township (other) Canada * Oneida 41, Ontario, also known as the "Oneida Settlement" * Oneida Township, Ontario, a historic township of Haldimand County United States * Oneida, former name of Martell, California * Oneida, Illinois * Oneida, Kansas * Oneida, Kentucky * Oneida, New York * Oneida, Ohio * Oneida, Pennsylvania * Oneida Falls, one of 24 named waterfalls in Ricketts Glen State Park in Pennsylvania * Oneida, Tennessee * Oneida (town), Wisconsin in Outagamie County * Oneida, Wisconsin, unincorporated community in both Outagamie and Brown Counties * Oneida Castle, New York, a vill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Tryon
Lieutenant-General William Tryon (8 June 172927 January 1788) was a British Army officer and colonial administrator who served as governor of North Carolina from 1764 to 1771 and the governor of New York from 1771 to 1777. He also served during the Seven Years' War, the Regulator Movement and the American War of Independence. Early life and career William Tryon was born on 8 June 1729 at the Tryon family's seat at Norbury Park, Surrey, the son of Charles Tryon and Lady Mary Shirley. His maternal grandfather was Robert Shirley, 1st Earl Ferrers. In 1751, Tryon enlisted the British Army as a lieutenant in the 1st Regiment of Foot Guards and was promoted to the rank of captain later that year. In 1758, Tryon was promoted to lieutenant-colonel. Seven Years' War During the Seven Years' War, Tryon and his regiment were involved in the British raid on Cherbourg. They landed at Cherbourg and destroyed all military facilities. In September, they reembarked for St Malo, where the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of New York (state), New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware, before emptying into Delaware Bay. It is the longest free-flowing river in the Eastern United States. The river has been recognized by the National Wildlife Federation as one of the country's Great Waters. The river's drainage basin, watershed drains an area of and provides drinking water for 17 million people. The river has two branches that rise in the Catskill Mountains of New York: the West Branch Delaware River, West Branch at Mount Jefferson (New York), Mount Jefferson in Jefferson, New York, Jefferson, Schoharie County, New York, Schoharie County, and the East Branch Delaware River, East Branch at Grand Gorge, New York, Grand Gorge, Delaware County, New York, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adirondack Mountains
The Adirondack Mountains (; a-də-RÄN-dak) form a massif in northeastern New York with boundaries that correspond roughly to those of Adirondack Park. They cover about 5,000 square miles (13,000 km2). The mountains form a roughly circular dome, about in diameter and about high. The current relief owes much to glaciation. There are more than 200 lakes around the mountains, including Lake George, Lake Placid, and Lake Tear of the Clouds, which is the source of the Hudson River. The Adirondack Region is also home to hundreds of mountain summits, with some reaching heights of or more. Etymology The word Adirondack is thought to come from the Mohawk word ''ha-de-ron-dah'' meaning "eaters of trees". The earliest written use of the name was in 1635 by Harmen Meyndertsz Van Den Bogaert in his Mohawk to Dutch glossary, found in his ''Journey into Mohawk Country''. He spelled it Adirondakx and said that it stood for Frenchmen, meaning the Algonquians who allied with the Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |