Ultrasound Of Human Fetus, 8 Weeks And 1 Day on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


 Ultrasound is
Ultrasound is
 Ultrasound is defined by the
Ultrasound is defined by the


 Bats use a variety of ultrasonic ranging ( echolocation) techniques to detect their prey. They can detect frequencies beyond 100 kHz, possibly up to 200 kHz.
Many insects have good ultrasonic hearing, and most of these are
Bats use a variety of ultrasonic ranging ( echolocation) techniques to detect their prey. They can detect frequencies beyond 100 kHz, possibly up to 200 kHz.
Many insects have good ultrasonic hearing, and most of these are


 Ultrasound is
Ultrasound is sound wave
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave, through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the ...
s with frequencies
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from ''angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is eq ...
higher than the upper audible limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is not different from "normal" (audible) sound in its physical properties, except that humans cannot hear it. This limit varies from person to person and is approximately 20 kilohertz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one h ...
(20,000 hertz) in healthy young adults. Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20 kHz up to several gigahertz.
Ultrasound is used in many different fields. Ultrasonic devices are used to detect objects and measure distances. Ultrasound imaging or sonography is often used in medicine. In the nondestructive testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage.
The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), n ...
of products and structures, ultrasound is used to detect invisible flaws. Industrially, ultrasound is used for cleaning, mixing, and accelerating chemical processes. Animals such as bats and porpoise
Porpoises are a group of fully aquatic marine mammals, all of which are classified under the family Phocoenidae, parvorder Odontoceti (toothed whales). Although similar in appearance to dolphins, they are more closely related to narwhals an ...
s use ultrasound for locating prey and obstacles.
History

Acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician ...
, the science of sound, starts as far back as Pythagoras in the 6th century BC, who wrote on the mathematical properties of stringed instruments. Echolocation in bats was discovered by Lazzaro Spallanzani in 1794, when he demonstrated that bats hunted and navigated by inaudible sound, not vision. Francis Galton
Sir Francis Galton, FRS FRAI (; 16 February 1822 – 17 January 1911), was an English Victorian era polymath: a statistician, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, proto- ...
in 1893 invented the Galton whistle, an adjustable whistle that produced ultrasound, which he used to measure the hearing range of humans and other animals, demonstrating that many animals could hear sounds above the hearing range of humans. The first technological application of ultrasound was an attempt to detect submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
s by Paul Langevin in 1917. The piezoelectric effect, discovered by Jacques and Pierre Curie in 1880, was useful in transducers to generate and detect ultrasonic waves in air and water.
Definition
American National Standards Institute
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organi ...
as " sound at frequencies greater than 20 kHz". In air at atmospheric pressure, ultrasonic waves have wavelengths of 1.9 cm or less.
Perception

Humans
The upper frequency limit in humans (approximately 20 kHz) is due to limitations of the middle ear.Auditory sensation
Auditory means of or relating to the process of hearing:
* Auditory system, the neurological structures and pathways of sound perception
** Auditory bulla, part of auditory system found in mammals other than primates
** Auditory nerve, also known ...
can occur if high‐intensity ultrasound is fed directly into the human skull and reaches the cochlea through bone conduction, without passing through the middle ear.
Children can hear some high-pitched sounds that older adults cannot hear, because in humans the upper limit pitch of hearing tends to decrease with age. An American cell phone
A mobile phone, cellular phone, cell phone, cellphone, handphone, hand phone or pocket phone, sometimes shortened to simply mobile, cell, or just phone, is a portable telephone that can make and receive calls over a radio frequency link whil ...
company has used this to create ring signals that supposedly are only audible to younger humans, but many older people can hear the signals, which may be because of the considerable variation of age-related deterioration in the upper hearing threshold. The Mosquito is an electronic device that uses a high pitched frequency to deter loitering by young people.
Animals

nocturnal
Nocturnality is an animal behavior characterized by being active during the night and sleeping during the day. The common adjective is "nocturnal", versus diurnal meaning the opposite.
Nocturnal creatures generally have highly developed sens ...
insects listening for echolocating bats. These include many groups of moths, beetles
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 describ ...
, praying mantises and lacewings. Upon hearing a bat, some insects will make evasive manoeuvres to escape being caught. Ultrasonic frequencies trigger a reflex action in the noctuid moth that causes it to drop slightly in its flight to evade attack. Tiger moth
The de Havilland DH.82 Tiger Moth is a 1930s British biplane designed by Geoffrey de Havilland and built by the de Havilland Aircraft Company. It was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and other operators as a primary trainer aircraft. ...
s also emit clicks which may disturb bats' echolocation, and in other cases may advertise the fact that they are poison
Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broa ...
ous by emitting sound.
Dogs and cats' hearing range extends into the ultrasound; the top end of a dog's hearing range is about 45 kHz, while a cat's is 64 kHz. The wild ancestors of cats and dogs evolved this higher hearing range to hear high-frequency sounds made by their preferred prey, small rodents. A dog whistle is a whistle that emits ultrasound, used for training and calling dogs. The frequency of most dog whistles is within the range of 23 to 54 kHz.
Toothed whales, including dolphins, can hear ultrasound and use such sounds in their navigational system ( biosonar) to orient and to capture prey. Porpoises
Porpoises are a group of fully aquatic marine mammals, all of which are classified under the family Phocoenidae, parvorder Odontoceti (toothed whales). Although similar in appearance to dolphins, they are more closely related to narwhals an ...
have the highest known upper hearing limit at around 160 kHz. Several types of fish can detect ultrasound. In the order Clupeiformes, members of the subfamily Alosinae
The Alosinae, or the shads,Alosinae
(
(
shad
The Alosinae, or the shads,Alosinae
) have been shown to be able to detect sounds up to 180 kHz, while the other subfamilies (e.g.
 Ultrasonic testing is a type of
Ultrasonic testing is a type of 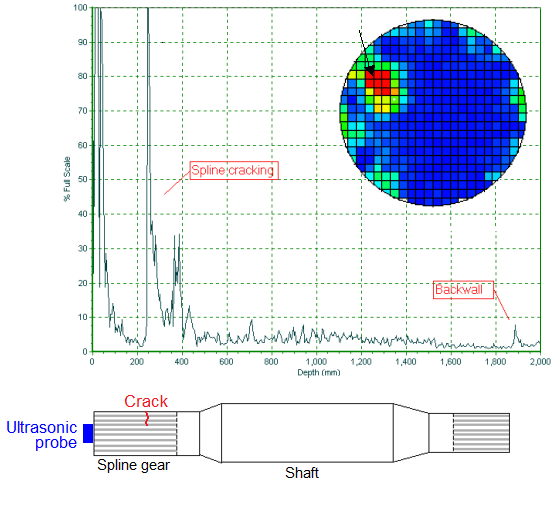 Ultrasonic thickness measurement is one technique used to monitor quality of welds.
Ultrasonic thickness measurement is one technique used to monitor quality of welds.
 A common use of ultrasound is in underwater range finding; this use is also called Sonar. An ultrasonic pulse is generated in a particular direction. If there is an object in the path of this pulse, part or all of the pulse will be reflected back to the transmitter as an echo and can be detected through the receiver path. By measuring the difference in time between the pulse being transmitted and the echo being received, it is possible to determine the distance.
The measured travel time of Sonar pulses in water is strongly dependent on the temperature and the salinity of the water. Ultrasonic ranging is also applied for measurement in air and for short distances. For example, hand-held ultrasonic measuring tools can rapidly measure the layout of rooms.
Although range finding underwater is performed at both sub-audible and audible frequencies for great distances (1 to several kilometers), ultrasonic range finding is used when distances are shorter and the accuracy of the distance measurement is desired to be finer. Ultrasonic measurements may be limited through barrier layers with large salinity, temperature or vortex differentials. Ranging in water varies from about hundreds to thousands of meters, but can be performed with centimeters to meters accuracy
A common use of ultrasound is in underwater range finding; this use is also called Sonar. An ultrasonic pulse is generated in a particular direction. If there is an object in the path of this pulse, part or all of the pulse will be reflected back to the transmitter as an echo and can be detected through the receiver path. By measuring the difference in time between the pulse being transmitted and the echo being received, it is possible to determine the distance.
The measured travel time of Sonar pulses in water is strongly dependent on the temperature and the salinity of the water. Ultrasonic ranging is also applied for measurement in air and for short distances. For example, hand-held ultrasonic measuring tools can rapidly measure the layout of rooms.
Although range finding underwater is performed at both sub-audible and audible frequencies for great distances (1 to several kilometers), ultrasonic range finding is used when distances are shorter and the accuracy of the distance measurement is desired to be finer. Ultrasonic measurements may be limited through barrier layers with large salinity, temperature or vortex differentials. Ranging in water varies from about hundreds to thousands of meters, but can be performed with centimeters to meters accuracy
 The potential for ultrasonic imaging of objects, with a 3 GHz sound wave producing resolution comparable to an optical image, was recognized by Sokolov in 1939, but techniques of the time produced relatively low-contrast images with poor sensitivity.
Ultrasonic imaging uses frequencies of 2 megahertz and higher; the shorter wavelength allows resolution of small internal details in structures and tissues. The power density is generally less than 1 watt per square centimetre to avoid heating and cavitation effects in the object under examination. High and ultra high ultrasound waves are used in
The potential for ultrasonic imaging of objects, with a 3 GHz sound wave producing resolution comparable to an optical image, was recognized by Sokolov in 1939, but techniques of the time produced relatively low-contrast images with poor sensitivity.
Ultrasonic imaging uses frequencies of 2 megahertz and higher; the shorter wavelength allows resolution of small internal details in structures and tissues. The power density is generally less than 1 watt per square centimetre to avoid heating and cavitation effects in the object under examination. High and ultra high ultrasound waves are used in
 Substantial ultrasonic intensity and high ultrasonic vibration amplitudes are required for many processing applications, such as nano-crystallization, nano-emulsification, deagglomeration, extraction, cell disruption, as well as many others. Commonly, a process is first tested on a laboratory scale to prove feasibility and establish some of the required ultrasonic exposure parameters. After this phase is complete, the process is transferred to a pilot (bench) scale for flow-through pre-production optimization and then to an industrial scale for continuous production. During these scale-up steps, it is essential to make sure that all local exposure conditions (ultrasonic amplitude,
Substantial ultrasonic intensity and high ultrasonic vibration amplitudes are required for many processing applications, such as nano-crystallization, nano-emulsification, deagglomeration, extraction, cell disruption, as well as many others. Commonly, a process is first tested on a laboratory scale to prove feasibility and establish some of the required ultrasonic exposure parameters. After this phase is complete, the process is transferred to a pilot (bench) scale for flow-through pre-production optimization and then to an industrial scale for continuous production. During these scale-up steps, it is essential to make sure that all local exposure conditions (ultrasonic amplitude,
Guidelines for the Safe Use of Ultrasound
valuable insight on the boundary conditions tending towards abuse of ultrasound {{Authority control Acoustics Sound
) have been shown to be able to detect sounds up to 180 kHz, while the other subfamilies (e.g.
herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, i ...
s) can hear only up to 4 kHz.
Contrary to popular belief, birds cannot hear ultrasonic sound.
Ultrasound generator/speaker systems are sold as electronic pest control devices, which are claimed to frighten away rodents and insects, but there is no scientific evidence that the devices work.
Detection and ranging
Non-contact sensor
An ultrasonic level or sensing system requires no contact with the target. For many processes in the medical, pharmaceutical, military and general industries this is an advantage over inline sensors that may contaminate the liquids inside a vessel or tube or that may be clogged by the product. Both continuous wave and pulsed systems are used. The principle behind a pulsed-ultrasonic technology is that the transmit signal consists of short bursts of ultrasonic energy. After each burst, the electronics looks for a return signal within a small window of time corresponding to the time it takes for the energy to pass through the vessel. Only a signal received during this window will qualify for additional signal processing. A popular consumer application of ultrasonic ranging was the Polaroid SX-70 camera, which included a lightweight transducer system to focus the camera automatically. Polaroid later licensed this ultrasound technology and it became the basis of a variety of ultrasonic products.Motion sensors and flow measurement
A common ultrasound application is an automatic door opener, where an ultrasonic sensor detects a person's approach and opens the door. Ultrasonic sensors are also used to detect intruders; the ultrasound can cover a wide area from a single point. The flow in pipes or open channels can be measured by ultrasonic flowmeters, which measure the average velocity of flowing liquid. In rheology, an acoustic rheometer relies on the principle of ultrasound. In fluid mechanics, fluid flow can be measured using an ultrasonic flow meter.Nondestructive testing
nondestructive testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage.
The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), n ...
commonly used to find flaws in materials and to measure the thickness of objects. Frequencies of 2 to 10 MHz are common, but for special purposes other frequencies are used. Inspection may be manual or automated and is an essential part of modern manufacturing processes. Most metals can be inspected as well as plastics
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or semi-synthetic materials that use polymers as a main ingredient. Their Plasticity (physics), plasticity makes it possible for plastics to be Injection moulding, moulded, Extrusion, e ...
and aerospace composites. Lower frequency ultrasound (50–500 kHz) can also be used to inspect less dense materials such as wood, concrete and cement.
Ultrasound inspection of welded joints has been an alternative to radiography for nondestructive testing
Nondestructive testing (NDT) is any of a wide group of analysis techniques used in science and technology industry to evaluate the properties of a material, component or system without causing damage.
The terms nondestructive examination (NDE), n ...
since the 1960s. Ultrasonic inspection eliminates the use of ionizing radiation, with safety and cost benefits. Ultrasound can also provide additional information such as the depth of flaws in a welded joint. Ultrasonic inspection has progressed from manual methods to computerized systems that automate much of the process. An ultrasonic test of a joint can identify the existence of flaws, measure their size, and identify their location. Not all welded materials are equally amenable to ultrasonic inspection; some materials have a large grain size that produces a high level of background noise in measurements.
 Ultrasonic thickness measurement is one technique used to monitor quality of welds.
Ultrasonic thickness measurement is one technique used to monitor quality of welds.
Ultrasonic range finding
Ultrasound Identification (USID)
Ultrasound Identification (USID) is aReal-Time Locating System
Real-time locating systems (RTLS), also known as real-time tracking systems, are used to automatically identify and track the location of objects or people in real time, usually within a building or other contained area. Wireless RTLS tags are ...
(RTLS) or Indoor Positioning System (IPS) technology used to automatically track and identify the location of objects in real time using simple, inexpensive nodes (badges/tags) attached to or embedded in objects and devices, which then transmit an ultrasound signal to communicate their location to microphone sensors.
Imaging
 The potential for ultrasonic imaging of objects, with a 3 GHz sound wave producing resolution comparable to an optical image, was recognized by Sokolov in 1939, but techniques of the time produced relatively low-contrast images with poor sensitivity.
Ultrasonic imaging uses frequencies of 2 megahertz and higher; the shorter wavelength allows resolution of small internal details in structures and tissues. The power density is generally less than 1 watt per square centimetre to avoid heating and cavitation effects in the object under examination. High and ultra high ultrasound waves are used in
The potential for ultrasonic imaging of objects, with a 3 GHz sound wave producing resolution comparable to an optical image, was recognized by Sokolov in 1939, but techniques of the time produced relatively low-contrast images with poor sensitivity.
Ultrasonic imaging uses frequencies of 2 megahertz and higher; the shorter wavelength allows resolution of small internal details in structures and tissues. The power density is generally less than 1 watt per square centimetre to avoid heating and cavitation effects in the object under examination. High and ultra high ultrasound waves are used in acoustic microscopy
Acoustic microscopy is microscopy that employs very high or ultra high frequency ultrasound. Acoustic microscopes operate non-destructively and penetrate most solid materials to make visible images of internal features, including defects such as c ...
, with frequencies up to 4 gigahertz. Ultrasonic imaging applications include industrial nondestructive testing, quality control and medical uses.
Acoustic microscopy
Acoustic microscopy
Acoustic microscopy is microscopy that employs very high or ultra high frequency ultrasound. Acoustic microscopes operate non-destructively and penetrate most solid materials to make visible images of internal features, including defects such as c ...
is the technique of using sound waves to visualize structures too small to be resolved by the human eye. Frequencies up to several gigahertz are used in acoustic microscopes. The reflection and diffraction of sound waves from microscopic structures can yield information not available with light.
Human medicine
Medical ultrasound is an ultrasound-based diagnosticmedical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
technique used to visualize muscles, tendons, and many internal organs to capture their size, structure and any pathological lesions with real time tomographic images. Ultrasound has been used by radiologists and sonographers to image the human body for at least 50 years and has become a widely used diagnostic tool. The technology is relatively inexpensive and portable, especially when compared with other techniques, such as magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio wave ...
(MRI) and computed tomography
A computed tomography scan (CT scan; formerly called computed axial tomography scan or CAT scan) is a medical imaging technique used to obtain detailed internal images of the body. The personnel that perform CT scans are called radiographers ...
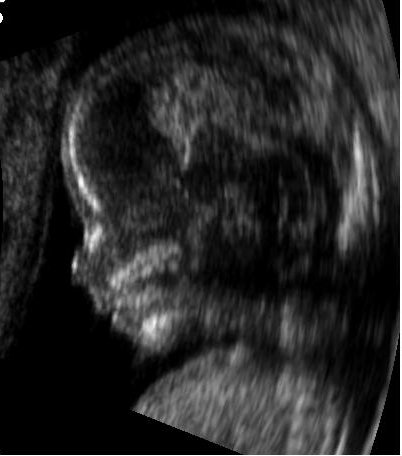
(CT). Ultrasound is also used to visualize fetuses during routine and emergency prenatal care. Such diagnostic applications used during pregnancy are referred to as obstetric sonography. As currently applied in the medical field, properly performed ultrasound poses no known risks to the patient. Sonography does not use ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation (or ionising radiation), including nuclear radiation, consists of subatomic particles or electromagnetic waves that have sufficient energy to ionize atoms or molecules by detaching electrons from them. Some particles can travel ...
, and the power levels used for imaging are too low to cause adverse heating or pressure effects in tissue. Although the long-term effects due to ultrasound exposure at diagnostic intensity are still unknown, currently most doctors feel that the benefits to patients outweigh the risks. The ALARA (As Low As Reasonably Achievable) principle has been advocated for an ultrasound examination that is, keeping the scanning time and power settings as low as possible but consistent with diagnostic imaging and that by that principle nonmedical uses, which by definition are not necessary, are actively discouraged.
Ultrasound is also increasingly being used in trauma and first aid cases, with emergency ultrasound
Emergency ultrasound employing point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is the application of ultrasound at the point of care to make immediate patient-care decisions. It is performed by the health care professional caring for the injured or ill persons. T ...
becoming a staple of most EMT response teams. Furthermore, ultrasound is used in remote diagnosis cases where teleconsultation is required, such as scientific experiments in space or mobile sports team diagnosis.
According to RadiologyInfo, ultrasounds are useful in the detection of pelvic abnormalities and can involve techniques known as abdominal (transabdominal) ultrasound, vaginal (transvaginal or endovaginal) ultrasound in women, and also rectal (transrectal) ultrasound in men.
Veterinary medicine
Diagnostic ultrasound is used externally in horses for evaluation of soft tissue and tendon injuries, and internally in particular for reproductive workevaluation of the reproductive tract of the mare and pregnancy detection. It may also be used in an external manner in stallions for evaluation of testicular condition and diameter as well as internally for reproductive evaluation (deferent duct etc.). By 2005, ultrasound technology began to be used by the beef cattle industry to improve animal health and the yield of cattle operations. Ultrasound is used to evaluate fat thickness, rib eye area, and intramuscular fat in living animals. It is also used to evaluate the health and characteristics of unborn calves. Ultrasound technology provides a means for cattle producers to obtain information that can be used to improve the breeding and husbandry of cattle. The technology can be expensive, and it requires a substantial time commitment for continuous data collection and operator training. Nevertheless, this technology has proven useful in managing and running a cattle breeding operation.Processing and power
High-power applications of ultrasound often use frequencies between 20 kHz and a few hundred kHz. Intensities can be very high; above 10 watts per square centimeter, cavitation can be inducted in liquid media, and some applications use up to 1000 watts per square centimeter. Such high intensities can induce chemical changes or produce significant effects by direct mechanical action, and can inactivate harmful microorganisms.Physical therapy
Ultrasound has been used since the 1940s by physical and occupational therapists for treatingconnective tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tiss ...
: ligament
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the:
* Peritoneal li ...
s, tendons, and fascia
A fascia (; plural fasciae or fascias; adjective fascial; from Latin: "band") is a band or sheet of connective tissue, primarily collagen, beneath the skin that attaches to, stabilizes, encloses, and separates muscles and other internal organs. ...
(and also scar tissue). Conditions for which ultrasound may be used for treatment include the follow examples: ligament sprain
A sprain, also known as a torn ligament, is an acute soft tissue injury of the ligaments within a joint, often caused by a sudden movement abruptly forcing the joint to exceed its functional range of motion. Ligaments are tough, inelastic fibers ...
s, muscle strains, tendonitis, joint inflammation, plantar fasciitis, metatarsalgia, facet irritation, impingement syndrome, bursitis
Bursitis is the inflammation of one or more bursae (fluid filled sacs) of synovial fluid in the body. They are lined with a synovial membrane that secretes a lubricating synovial fluid. There are more than 150 bursae in the human body. The bursa ...
, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and scar tissue adhesion.
Biomedical applications
Ultrasound has diagnostic and therapeutic applications, which can be highly beneficial when used with dosage precautions. Relatively high power ultrasound can break up stony deposits or tissue, accelerate the effect of drugs in a targeted area, assist in the measurement of the elastic properties of tissue, and can be used to sort cells or small particles for research.Ultrasonic impact treatment
Ultrasonic impact treatment (UIT) uses ultrasound to enhance the mechanical and physical properties of metals. It is a metallurgical processing technique in which ultrasonic energy is applied to a metal object. Ultrasonic treatment can result in controlled residual compressive stress, grain refinement and grain size reduction. Low and high cycle fatigue are enhanced and have been documented to provide increases up to ten times greater than non-UIT specimens. Additionally, UIT has proven effective in addressingstress corrosion cracking
Stress corrosion cracking (SCC) is the growth of crack formation in a corrosive environment. It can lead to unexpected and sudden failure of normally ductile metal alloys subjected to a tensile stress, especially at elevated temperature. SCC ...
, corrosion fatigue and related issues.
When the UIT tool, made up of the ultrasonic transducer, pins and other components, comes into contact with the work piece it acoustically couples with the work piece, creating harmonic resonance. This harmonic resonance is performed at a carefully calibrated frequency, to which metals respond very favorably.
Depending on the desired effects of treatment a combination of different frequencies and displacement amplitude is applied. These frequencies range between 25 and 55 kHz, with the displacement amplitude of the resonant body of between 22 and 50 µm (0.00087 and 0.0020 in).
UIT devices rely on magnetostrictive transducers.
Processing
Ultrasonication offers great potential in the processing of liquids and slurries, by improving the mixing and chemical reactions in various applications and industries. Ultrasonication generates alternating low-pressure and high-pressure waves in liquids, leading to the formation and violent collapse of small vacuum bubbles. This phenomenon is termedcavitation
Cavitation is a phenomenon in which the static pressure of a liquid reduces to below the liquid's vapour pressure, leading to the formation of small vapor-filled cavities in the liquid. When subjected to higher pressure, these cavities, cal ...
and causes high speed impinging liquid jets and strong hydrodynamic shear-forces. These effects are used for the deagglomeration and milling of micrometre and nanometre-size materials as well as for the disintegration of cells or the mixing of reactants. In this aspect, ultrasonication is an alternative to high-speed mixers and agitator bead mills. Ultrasonic foils under the moving wire in a paper machine will use the shock waves from the imploding bubbles to distribute the cellulose fibres more uniformly in the produced paper web, which will make a stronger paper with more even surfaces. Furthermore, chemical reactions benefit from the free radicals created by the cavitation as well as from the energy input and the material transfer through boundary layers. For many processes, this sonochemical (see sonochemistry) effect leads to a substantial reduction in the reaction time, like in the transesterification of oil into biodiesel.
 Substantial ultrasonic intensity and high ultrasonic vibration amplitudes are required for many processing applications, such as nano-crystallization, nano-emulsification, deagglomeration, extraction, cell disruption, as well as many others. Commonly, a process is first tested on a laboratory scale to prove feasibility and establish some of the required ultrasonic exposure parameters. After this phase is complete, the process is transferred to a pilot (bench) scale for flow-through pre-production optimization and then to an industrial scale for continuous production. During these scale-up steps, it is essential to make sure that all local exposure conditions (ultrasonic amplitude,
Substantial ultrasonic intensity and high ultrasonic vibration amplitudes are required for many processing applications, such as nano-crystallization, nano-emulsification, deagglomeration, extraction, cell disruption, as well as many others. Commonly, a process is first tested on a laboratory scale to prove feasibility and establish some of the required ultrasonic exposure parameters. After this phase is complete, the process is transferred to a pilot (bench) scale for flow-through pre-production optimization and then to an industrial scale for continuous production. During these scale-up steps, it is essential to make sure that all local exposure conditions (ultrasonic amplitude, cavitation
Cavitation is a phenomenon in which the static pressure of a liquid reduces to below the liquid's vapour pressure, leading to the formation of small vapor-filled cavities in the liquid. When subjected to higher pressure, these cavities, cal ...
intensity, time spent in the active cavitation zone, etc.) stay the same. If this condition is met, the quality of the final product remains at the optimized level, while the productivity is increased by a predictable "scale-up factor". The productivity increase results from the fact that laboratory, bench and industrial-scale ultrasonic processor systems incorporate progressively larger ultrasonic horns, able to generate progressively larger high-intensity cavitation
Cavitation is a phenomenon in which the static pressure of a liquid reduces to below the liquid's vapour pressure, leading to the formation of small vapor-filled cavities in the liquid. When subjected to higher pressure, these cavities, cal ...
zones and, therefore, to process more material per unit of time. This is called "direct scalability". It is important to point out that increasing the power of the ultrasonic processor alone does ''not'' result in direct scalability, since it may be (and frequently is) accompanied by a reduction in the ultrasonic amplitude and cavitation intensity. During direct scale-up, all processing conditions must be maintained, while the power rating of the equipment is increased in order to enable the operation of a larger ultrasonic horn.
Ultrasonic manipulation and characterization of particles
A researcher at the Industrial Materials Research Institute, Alessandro Malutta, devised an experiment that demonstrated the trapping action of ultrasonic standing waves on wood pulp fibers diluted in water and their parallel orienting into the equidistant pressure planes. The time to orient the fibers in equidistant planes is measured with a laser and an electro-optical sensor. This could provide the paper industry a quick on-line fiber size measurement system. A somewhat different implementation was demonstrated at Pennsylvania State University using a microchip which generated a pair of perpendicular standing surface acoustic waves allowing to position particles equidistant to each other on a grid. This experiment, called acoustic tweezers, can be used for applications in material sciences, biology, physics, chemistry and nanotechnology.Ultrasonic cleaning
Ultrasonic cleaner
Ultrasonic cleaning is a process that uses ultrasound (usually from 20 to 40 kHz) to agitate a fluid, with a cleaning effect. Ultrasonic cleaners come in a variety of sizes, from small desktop units with an internal volume of less than , to larg ...
s, sometimes mistakenly called ''supersonic
Supersonic speed is the speed of an object that exceeds the speed of sound ( Mach 1). For objects traveling in dry air of a temperature of 20 °C (68 °F) at sea level, this speed is approximately . Speeds greater than five times ...
cleaners'', are used at frequencies from 20 to 40 kHz for jewellery, lenses
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements ...
and other optical parts, watches, dental instrument
Dental instruments are tools that dental professionals use to provide dental treatment. They include tools to examine, manipulate, treat, restore, and remove teeth and surrounding oral structures.
Examination instruments
These tools allow denta ...
s, surgical instruments, diving regulators and industrial parts. An ultrasonic cleaner works mostly by energy released from the collapse of millions of microscopic cavitation
Cavitation is a phenomenon in which the static pressure of a liquid reduces to below the liquid's vapour pressure, leading to the formation of small vapor-filled cavities in the liquid. When subjected to higher pressure, these cavities, cal ...
s near the dirty surface. The bubbles made by cavitation collapse form tiny shockwaves that break up and disperse contaminants on the object's surface.
Ultrasonic disintegration
Similar to ultrasonic cleaning, biological cells including bacteria can be disintegrated. High power ultrasound producescavitation
Cavitation is a phenomenon in which the static pressure of a liquid reduces to below the liquid's vapour pressure, leading to the formation of small vapor-filled cavities in the liquid. When subjected to higher pressure, these cavities, cal ...
that facilitates particle disintegration or reactions. This has uses in biological science for analytical or chemical purposes ( sonication and sonoporation) and in killing bacteria in sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged from residenc ...
. High power ultrasound can disintegrate corn slurry and enhance liquefaction and saccharification for higher ethanol yield in dry corn milling plants.
Ultrasonic humidifier
The ultrasonic humidifier, one type of nebulizer (a device that creates a very fine spray), is a popular type of humidifier. It works by vibrating a metal plate at ultrasonic frequencies to nebulize (sometimes incorrectly called "atomize") the water. Because the water is not heated for evaporation, it produces a cool mist. The ultrasonic pressure waves nebulize not only the water but also materials in the water including calcium, other minerals, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and other impurities. Illness caused by impurities that reside in a humidifier's reservoir fall under the heading of "Humidifier Fever". Ultrasonic humidifiers are frequently used in aeroponics, where they are generally referred to as foggers.Ultrasonic welding
In ultrasonic welding of plastics, high frequency (15 kHz to 40 kHz) low amplitude vibration is used to create heat by way of friction between the materials to be joined. The interface of the two parts is specially designed to concentrate the energy for maximum weld strength.Sonochemistry
Power ultrasound in the 20–100 kHz range is used inchemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ...
. The ultrasound does not interact directly with molecules to induce the chemical change, as its typical wavelength (in the millimeter range) is too long compared to the molecules. Instead, the energy causes cavitation
Cavitation is a phenomenon in which the static pressure of a liquid reduces to below the liquid's vapour pressure, leading to the formation of small vapor-filled cavities in the liquid. When subjected to higher pressure, these cavities, cal ...
which generates extremes of temperature and pressure in the liquid where the reaction happens. Ultrasound also breaks up solids and removes passivating layers of inert
Inert may refer to:
* Chemically inert, not chemically reactive
** Inert gas
** Noble gas, historically called inert gas
* Inert knowledge, information which one can express but not use
* Inert waste, waste which is neither chemically nor biol ...
material to give a larger surface area
The surface area of a solid object is a measure of the total area that the surface of the object occupies. The mathematical definition of surface area in the presence of curved surfaces is considerably more involved than the definition of arc ...
for the reaction to occur over. Both of these effects make the reaction faster. In 2008, Atul Kumar reported synthesis of Hantzsch esters and polyhydroquinoline derivatives via multi-component reaction protocol in aqueous micelles using ultrasound.
Ultrasound is used in extraction Extraction may refer to:
Science and technology
Biology and medicine
* Comedo extraction, a method of acne treatment
* Dental extraction, the surgical removal of a tooth from the mouth
Computing and information science
* Data extraction, the pro ...
, using different frequencies.
Wireless communication
In July 2015, '' The Economist'' reported that researchers at the University of California, Berkeley have conducted ultrasound studies using graphene diaphragms. The thinness and low weight of graphene combined with its strength make it an effective material to use in ultrasound communications. One suggested application of the technology would be underwater communications, where radio waves typically do not travel well. Ultrasonic signals have been used in "audio beacons" for cross-device tracking of Internet users.Other uses
Ultrasound when applied in specific configurations can produce short bursts of light in an exotic phenomenon known as sonoluminescence. This phenomenon is being investigated partly because of the possibility ofbubble fusion
Bubble fusion is the non-technical name for a nuclear fusion reaction hypothesized to occur inside extraordinarily large collapsing gas bubbles created in a liquid during Sonic cavitation, acoustic cavitation. The more technical name is sonofusion ...
(a nuclear fusion reaction hypothesized to occur during sonoluminescence).
Ultrasound is used when characterizing particulates through the technique of ultrasound attenuation spectroscopy or by observing electroacoustic phenomena or by transcranial pulsed ultrasound.
Audio can be propagated by modulated ultrasound.
A formerly popular consumer application of ultrasound was in television remote controls for adjusting volume and changing channels. Introduced by Zenith in the late 1950s, the system used a hand-held remote control containing short rod resonators struck by small hammers, and a microphone on the set. Filters and detectors discriminated between the various operations. The principal advantages were that no battery was needed in the hand-held control box and, unlike radio waves, the ultrasound was unlikely to affect neighboring sets. Ultrasound remained in use until displaced by infrared systems starting in the late 1980s.
Safety
Occupational exposure to ultrasound in excess of 120 dB may lead to hearing loss. Exposure in excess of 155 dB may produce heating effects that are harmful to the human body, and it has been calculated that exposures above 180 dB may lead to death. The UK's independent Advisory Group on Non-ionising Radiation (AGNIR) produced a report in 2010, which was published by the UK Health Protection Agency (HPA). This report recommended an exposure limit for the general public to airborne ultrasound sound pressure levels (SPL) of 70 dB (at 20 kHz), and 100 dB (at 25 kHz and above).See also
* Acoustic droplet ejection *Acoustic emission Acoustic emission (AE) is the phenomenon of radiation of acoustic (elastic) waves in solids that occurs when a material undergoes irreversible changes in its internal structure, for example as a result of crack formation or plastic deformation due t ...
* Bat detector
* Delay-line memory
* Infrasound — sound at extremely low frequencies
* Isochoic
* Laser ultrasonics Laser-ultrasonics uses lasers to generate and detect ultrasonic waves.C.B. Scruby and L.E. Drain, Laser Ultrasonics, (Adam Hilger: Bristol), 1990. It is a non-contact technique used to measure materials thickness, detect flaws and carry out material ...
* Phased array ultrasonics
* Picosecond ultrasonics
* Sonomicrometry
* Sound from ultrasound (also known as hypersonic sound)
* Surface acoustic wave
* Ultrasonic motor
* Ultrasonic attenuation
In physics, attenuation (in some contexts, extinction) is the gradual loss of flux intensity through a medium. For instance, dark glasses attenuate sunlight, lead attenuates X-rays, and water and air attenuate both light and sound at variable a ...
* Ultrasound attenuation spectroscopy
References
Further reading
* *External links
Guidelines for the Safe Use of Ultrasound
valuable insight on the boundary conditions tending towards abuse of ultrasound {{Authority control Acoustics Sound