|
Bone Conduction
Bone conduction is the conduction of sound to the inner ear primarily through the bones of the skull, allowing the hearer to perceive audio content without blocking the ear canal. Bone conduction transmission occurs constantly as sound waves vibrate bone, specifically the bones in the skull, although it is hard for the average individual to distinguish sound being conveyed through the bone as opposed to the sound being conveyed through the air via the ear canal. Intentional transmission of sound through bone can be used with individuals with normal hearing — as with bone-conduction headphones — or as a treatment option for certain types of hearing impairment. Bone generally conveys lower-frequency sounds better than higher frequency sounds. Overview Bone conduction is one reason why a person's voice sounds different to them when it is recorded and played back. Because the skull conducts lower frequencies better than air, people perceive their own voices to be lower an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conduction
Conductor or conduction may refer to: Music * Conductor (music), a person who leads a musical ensemble, such as an orchestra. * Conductor (album), ''Conductor'' (album), an album by indie rock band The Comas * Conduction, a type of structured free improvisation in music notably practiced by Butch Morris#"Conduction", Butch Morris Mathematics * Conductor (ring theory), an ideal of a ring that measures how far it is from being integrally closed * Conductor of an abelian variety, a description of its bad reduction * Dirichlet character, Conductor of a Dirichlet character, the natural (smallest) modulus for a character * Conductor (class field theory), a modulus describing the ramification in an abelian extension of local or global fields * Artin conductor, an ideal or number associated to a representation of a Galois group of a local or global field * Conductor of a numerical semigroup, the smallest integer in the semigroup such that all subsequent integers are likewise in the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gothenburg
Gothenburg (; abbreviated Gbg; sv, Göteborg ) is the second-largest city in Sweden, fifth-largest in the Nordic countries, and capital of the Västra Götaland County. It is situated by the Kattegat, on the west coast of Sweden, and has a population of approximately 590,000 in the city proper and about 1.1 million inhabitants in the metropolitan area. Gothenburg was founded as a heavily fortified, primarily Dutch, trading colony, by royal charter in 1621 by King Gustavus Adolphus. In addition to the generous privileges (e.g. tax relaxation) given to his Dutch allies from the ongoing Thirty Years' War, the king also attracted significant numbers of his German and Scottish allies to populate his only town on the western coast. At a key strategic location at the mouth of the Göta älv, where Scandinavia's largest drainage basin enters the sea, the Port of Gothenburg is now the largest port in the Nordic countries. Gothenburg is home to many students, as the city inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal Processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, digital storage efficiency, correcting distorted signals, subjective video quality and to also detect or pinpoint components of interest in a measured signal. History According to Alan V. Oppenheim and Ronald W. Schafer, the principles of signal processing can be found in the classical numerical analysis techniques of the 17th century. They further state that the digital refinement of these techniques can be found in the digital control systems of the 1940s and 1950s. In 1948, Claude Shannon wrote the influential paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication" which was published in the Bell System Technical Journal. The paper laid the groundwork for later development of information communication systems and the processing of signals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microphone
A microphone, colloquially called a mic or mike (), is a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signal. Microphones are used in many applications such as telephones, hearing aids, public address systems for concert halls and public events, motion picture production, live and recorded audio engineering, sound recording, two-way radios, megaphones, and radio and television broadcasting. They are also used in computers for recording voice, speech recognition, VoIP, and for other purposes such as ultrasonic sensors or knock sensors. Several types of microphone are used today, which employ different methods to convert the air pressure variations of a sound wave to an electrical signal. The most common are the dynamic microphone, which uses a coil of wire suspended in a magnetic field; the condenser microphone, which uses the vibrating diaphragm as a capacitor plate; and the contact microphone, which uses a crystal of piezoelectric material. Microphones typi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unilateral Hearing Loss
Unilateral hearing loss (UHL) is a type of hearing impairment where there is normal hearing in one ear and impaired hearing in the other ear. Signs and symptoms Patients with unilateral hearing loss have difficulty: * Hearing conversation on their impaired side * Localizing sound * Understanding speech in the presence of background noise * In interpersonal interaction in social settings * Focusing on individual sound sources in large, open environments * Heavy impairment of the auditory Figure–ground perception In quiet conditions, speech discrimination is no worse than normal hearing in those with partial deafness; however, in noisy environments speech discrimination is almost always severe. The prevalence is 3–8.3% of the population. Individuals who are diagnosed with Single Sided Deafness have difficulties with sound localization and speech in noise discrimination. Children with SSD are more likely to experience developmental delays- school, speech, behavioral problems. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treacher Collins Syndrome
Treacher Collins syndrome (TCS) is a genetic disorder characterized by deformities of the ears, eyes, cheekbones, and chin. The degree to which a person is affected, however, may vary from mild to severe. Complications may include breathing problems, problems seeing, cleft palate, and hearing loss. Those affected generally have normal intelligence. TCS is usually autosomal dominant. More than half the time it occurs as a result of a new mutation rather than being inherited from a person's parents. The involved genes may include '' TCOF1'', ''POLR1C'', or '' POLR1D''. Diagnosis is generally suspected based on symptoms and X-rays, and potentially confirmation by genetic testing. Treacher Collins syndrome is not curable. Symptoms may be managed with reconstructive surgery, hearing aids, speech therapy, and other assistive devices. Life expectancy is generally normal. TCS occurs in about one in 50,000 people. The syndrome is named after Edward Treacher Collins, an English surgeon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
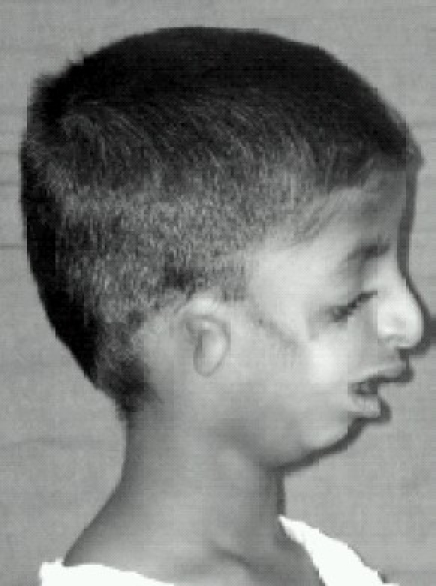
Goldenhar Syndrome
Goldenhar syndrome is a rare congenital defect characterized by incomplete development of the ear, nose, soft palate, lip and mandible on usually one side of the body. Common clinical manifestations include limbal dermoids, preauricular skin tags and strabismus. It is associated with anomalous development of the first branchial arch and second branchial arch. The term is sometimes used interchangeably with hemifacial microsomia, although this definition is usually reserved for cases without internal organ and vertebrae disruption. It affects between 1 in 3,500 and 1 in 5,600 live births, with a male-to-female ratio of 3:2. Signs and symptoms Chief markers of Goldenhar syndrome are incomplete development of the ear, nose, soft palate, lip, and mandible on usually one side of the body. Additionally, some patients will have growing issues with internal organs, especially heart, kidneys and lungs. Typically, the organ will either not be present on one side or will be underdevel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microtia
Microtia is a congenital deformity where the auricle (external ear) is underdeveloped. A completely undeveloped pinna is referred to as anotia. Because microtia and anotia have the same origin, it can be referred to as microtia-anotia. Microtia can be unilateral (one side only) or bilateral (affecting both sides). Microtia occurs in 1 out of about 8,000–10,000 births. In unilateral microtia, the right ear is most commonly affected. It may occur as a complication of taking Accutane (isotretinoin) during pregnancy. Classification According to the Altman-classification, there are four grades of microtia: *Grade I: A less than complete development of the external ear with identifiable structures and a small but present external ear canal *Grade II: A partially developed ear (usually the top portion is underdeveloped) with a closed stenotic external ear canal producing a conductive hearing loss. *Grade III: Absence of the external ear with a small peanut-like vestige structure a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atresia
Atresia is a condition in which an orifice or passage in the body is (usually abnormally) closed or absent. Examples of atresia include: *Aural atresia, a congenital deformity where the ear canal is underdeveloped. * Biliary atresia, a condition in newborns in which the common bile duct between the liver and the small intestine is blocked or absent. * Congenital bronchial atresia, a rare congenital abnormality * Choanal atresia, blockage of the back of the nasal passage, usually by abnormal bony or soft tissue. * Esophageal atresia, which affects the alimentary tract and causes the esophagus to end before connecting normally to the stomach. *Follicular atresia, degeneration and resorption of the ovarian follicles. * Imperforate anus, malformation of the opening between the rectum and anus. * Intestinal atresia, malformation of the intestine, usually resulting from a vascular accident in utero. * Microtia, absence of the ear canal or failure of the canal to be tubular or fully fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outer Ear
The outer ear, external ear, or auris externa is the external part of the ear, which consists of the auricle (also pinna) and the ear canal. It gathers sound energy and focuses it on the eardrum (tympanic membrane). Structure Auricle The visible part is called the auricle, also known as the pinna, especially in other animals. It is composed of a thin plate of yellow elastic cartilage, covered with integument, and connected to the surrounding parts by ligaments and muscles; and to the commencement of the ear canal by fibrous tissue. Many mammals can move the pinna (with the auriculares muscles) in order to focus their hearing in a certain direction in much the same way that they can turn their eyes. Most humans do not have this ability. Ear canal From the pinna, the sound waves move into the ear canal (also known as the ''external acoustic meatus'') a simple tube running through to the middle ear. This tube leads inward from the bottom of the auricula and conducts t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochlea
The cochlea is the part of the inner ear involved in hearing. It is a spiral-shaped cavity in the bony labyrinth, in humans making 2.75 turns around its axis, the modiolus. A core component of the cochlea is the Organ of Corti, the sensory organ of hearing, which is distributed along the partition separating the fluid chambers in the coiled tapered tube of the cochlea. The name cochlea derives . Structure The cochlea (plural is cochleae) is a spiraled, hollow, conical chamber of bone, in which waves propagate from the base (near the middle ear and the oval window) to the apex (the top or center of the spiral). The spiral canal of the cochlea is a section of the bony labyrinth of the inner ear that is approximately 30 mm long and makes 2 turns about the modiolus. The cochlear structures include: * Three ''scalae'' or chambers: ** the vestibular duct or ''scala vestibuli'' (containing perilymph), which lies superior to the cochlear duct and abuts the oval window ** the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mixed Hearing Loss , a person who is of multiple races
*
*
{{disambiguation ...
Mixed is the past tense of ''mix''. Mixed may refer to: * Mixed (United Kingdom ethnicity category), an ethnicity category that has been used by the United Kingdom's Office for National Statistics since the 1991 Census * ''Mixed'' (album), a compilation album of two avant-garde jazz sessions featuring performances by the Cecil Taylor Unit and the Roswell Rudd Sextet See also * Mix (other) * Mixed breed, an animal whose parents are from different breeds or species * Mixed ethnicity Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-eth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)