Signal Processing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Signal processing is an
Signal processing is an
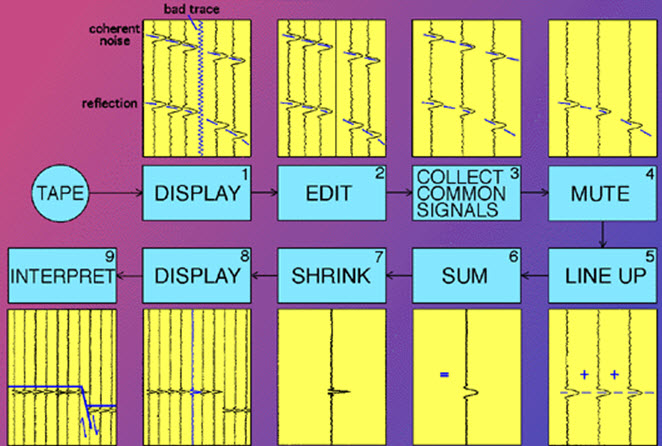 *
*
Statistical Signal Processing lecture notes at the University of Waterloo, Canada. * Ali H. Sayed, Adaptive Filters, Wiley, NJ, 2008, . * Thomas Kailath, Ali H. Sayed, and Babak Hassibi, Linear Estimation, Prentice-Hall, NJ, 2000, .
Signal Processing for Communications
– free online textbook by Paolo Prandoni and Martin Vetterli (2008)
Scientists and Engineers Guide to Digital Signal Processing
– free online textbook by Stephen Smith
Julius O. Smith III: Spectral Audio Signal Processing
– free online textbook
Graph Signal Processing Website
– free online website by Thierry Bouwmans (2025) {{Authority control Mass media technology Telecommunication theory
 Signal processing is an
Signal processing is an electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signal
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology.
In ...
s'', such as sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the br ...
, images, potential fields, seismic signals, altimetry processing, and scientific measurements
In mathematics and empirical science, quantification (or quantitation) is the act of counting and measuring that maps human sense observations and experiences into quantities. Quantification in this sense is fundamental to the scientific method.
...
. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, digital storage
Data storage is the recording (storing) of information (data) in a storage medium. Handwriting, Phonograph record, phonographic recording, magnetic tape, and optical discs are all examples of storage media. Biological molecules such as RNA ...
efficiency, correcting distorted signals, improve subjective video quality
Subjective video quality is video quality as experienced by humans. It is concerned with how video is perceived by a viewer (also called "observer" or "subject") and designates their opinion on a particular video sequence. It is related to the fie ...
, and to detect or pinpoint components of interest in a measured signal.
History
According to Alan V. Oppenheim and Ronald W. Schafer, the principles of signal processing can be found in the classicalnumerical analysis
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation (as opposed to symbolic computation, symbolic manipulations) for the problems of mathematical analysis (as distinguished from discrete mathematics). It is the study of ...
techniques of the 17th century. They further state that the digital refinement of these techniques can be found in the digital control system
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial ...
s of the 1940s and 1950s.
In 1948, Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 – February 24, 2001) was an American mathematician, electrical engineer, computer scientist, cryptographer and inventor known as the "father of information theory" and the man who laid the foundations of th ...
wrote the influential paper "A Mathematical Theory of Communication
"A Mathematical Theory of Communication" is an article by mathematician Claude E. Shannon published in '' Bell System Technical Journal'' in 1948. It was renamed ''The Mathematical Theory of Communication'' in the 1949 book of the same name, a s ...
" which was published in the ''Bell System Technical Journal
The ''Bell Labs Technical Journal'' was the in-house scientific journal for scientists of Bell Labs, published yearly by the IEEE society.
The journal was originally established as ''The Bell System Technical Journal'' (BSTJ) in New York by the Am ...
''. The paper laid the groundwork for later development of information communication systems and the processing of signals for transmission.
Signal processing matured and flourished in the 1960s and 1970s, and digital signal processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a ...
became widely used with specialized digital signal processor
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit chips. ...
chips in the 1980s.
Definition of a signal
A signal is a function , where this function is either * deterministic (then one speaks of a deterministic signal) or * a path , a realization of astochastic process
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables in a probability space, where the index of the family often has the interpretation of time. Sto ...
Categories
Analog
Analog signal processing is for signals that have not been digitized, as in most 20th-centuryradio
Radio is the technology of communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 3 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmitter connec ...
, telephone, and television systems. This involves linear electronic circuits as well as nonlinear ones. The former are, for instance, passive filter
Passivity is a property of engineering systems, most commonly encountered in analog electronics and control systems. Typically, analog designers use ''passivity'' to refer to incrementally passive components and systems, which are incapable of ...
s, active filter
An active filter is a type of analog circuit implementing an electronic filter using active components, typically an amplifier. Amplifiers included in a filter design can be used to improve the cost, performance and predictability of a filter.
...
s, additive mixers, integrator
An integrator in measurement and control applications is an element whose output signal is the time integral of its input signal. It accumulates the input quantity over a defined time to produce a representative output.
Integration is an importan ...
s, and delay lines. Nonlinear circuits include compandors, multipliers (frequency mixer
In electronics, a mixer, or frequency mixer, is an electrical circuit that creates new frequencies from two signals applied to it. In its most common application, two signals are applied to a mixer, and it produces new signals at the sum and di ...
s, voltage-controlled amplifier
A variable-gain (VGA) or voltage-controlled amplifier (VCA) is an electronic amplifier that varies its gain depending on a control voltage (often abbreviated CV).
VCAs have many applications, including audio level compression, synthesizers and ...
s), voltage-controlled filter
A voltage-controlled filter (VCF) is an electronic filter whose operating characteristics (primarily cutoff frequency) can be set by an input control voltage. Voltage-controlled filters are widely used in synthesizers.
A music synthesizer VCF ...
s, voltage-controlled oscillator
A voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is an electronic oscillator whose oscillation frequency is controlled by a voltage input. The applied input voltage determines the instantaneous oscillation frequency. Consequently, a VCO can be used for fre ...
s, and phase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is fixed relative to the phase of an input signal. Keeping the input and output phase in lockstep also implies keeping the input and ou ...
s.
Continuous time
Continuous-time signal processing is for signals that vary with the change of continuous domain (without considering some individual interrupted points). The methods of signal processing includetime domain
In mathematics and signal processing, the time domain is a representation of how a signal, function, or data set varies with time. It is used for the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental ...
, frequency domain
In mathematics, physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency (and possibly phase), rather than time, as in time ser ...
, and complex frequency domain. This technology mainly discusses the modeling of a linear time-invariant continuous system, integral of the system's zero-state response, setting up system function and the continuous time filtering of deterministic signals. For example, in time domain, a continuous-time signal passing through a linear time-invariant filter/system denoted as , can be expressed at the output as
In some contexts, is referred to as the impulse response of the system. The above convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions f and g that produces a third function f*g, as the integral of the product of the two ...
operation is conducted between the input and the system.
Discrete time
Discrete-time signal
In mathematical dynamics, discrete time and continuous time are two alternative frameworks within which variables that evolve over time are modeled.
Discrete time
Discrete time views values of variables as occurring at distinct, separate "poi ...
processing is for sampled signals, defined only at discrete points in time, and as such are quantized in time, but not in magnitude.
''Analog discrete-time signal processing'' is a technology based on electronic devices such as sample and hold
In electronics, a sample and hold (also known as sample and follow) circuit is an analog device that samples (captures, takes) the voltage of a continuously varying analog signal and holds (locks, freezes) its value at a constant level for a ...
circuits, analog time-division multiplexer
In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux; spelled sometimes as multiplexor), also known as a data selector, is a device that selects between several Analog signal, analog or Digital signal (electronics), digital input signals and forwards the sel ...
s, analog delay lines and analog feedback shift register :'' AFSR also stands for the Argonne Fast Source Reacto-- see list of nuclear reactors.''
:'' AFSR was also the abbreviation of the Armed Forces of South Russia.''
An analog feedback shift register (AFSR) is a generalization of the (binary, digit ...
s. This technology was a predecessor of digital signal processing (see below), and is still used in advanced processing of gigahertz signals.
The concept of discrete-time signal processing also refers to a theoretical discipline that establishes a mathematical basis for digital signal processing, without taking quantization error
Quantization, in mathematics and digital signal processing, is the process of mapping input values from a large set (often a continuous set) to output values in a (countable) smaller set, often with a finite number of elements. Rounding and ...
into consideration.
Digital
Digital signal processing is the processing of digitized discrete-time sampled signals. Processing is done by general-purposecomputer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
s or by digital circuits such as ASIC
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-efficien ...
s, field-programmable gate arrays or specialized digital signal processor
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit chips. ...
s. Typical arithmetical operations include fixed-point and floating-point
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic on subsets of real numbers formed by a ''significand'' (a Sign (mathematics), signed sequence of a fixed number of digits in some Radix, base) multiplied by an integer power of that ba ...
, real-valued and complex-valued, multiplication and addition. Other typical operations supported by the hardware are circular buffer
In computer science, a circular buffer, circular queue, cyclic buffer or ring buffer is a data structure that uses a single, fixed-size buffer as if it were connected end-to-end. This structure lends itself easily to buffering data streams. The ...
s and lookup table
In computer science, a lookup table (LUT) is an array data structure, array that replaces runtime (program lifecycle phase), runtime computation of a mathematical function (mathematics), function with a simpler array indexing operation, in a proc ...
s. Examples of algorithms are the fast Fourier transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). A Fourier transform converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in ...
(FFT), finite impulse response
In signal processing, a finite impulse response (FIR) filter is a filter whose impulse response (or response to any finite length input) is of ''finite'' duration, because it settles to zero in finite time. This is in contrast to infinite impuls ...
(FIR) filter, Infinite impulse response
Infinite impulse response (IIR) is a property applying to many linear time-invariant systems that are distinguished by having an impulse response h(t) that does not become exactly zero past a certain point but continues indefinitely. This is in ...
(IIR) filter, and adaptive filter
An adaptive filter is a system with a linear filter that has a transfer function controlled by variable parameters and a means to adjust those parameters according to an optimization algorithm. Because of the complexity of the optimization algorit ...
s such as the Wiener and Kalman filter
In statistics and control theory, Kalman filtering (also known as linear quadratic estimation) is an algorithm that uses a series of measurements observed over time, including statistical noise and other inaccuracies, to produce estimates of unk ...
s.
Nonlinear
Nonlinear signal processing involves the analysis and processing of signals produced fromnonlinear system
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system (or a non-linear system) is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathem ...
s and can be in the time, frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. Frequency is an important parameter used in science and engineering to specify the rate of oscillatory and vibratory phenomena, such as mechanical vibrations, audio ...
, or spatiotemporal domains. Nonlinear systems can produce highly complex behaviors including bifurcations, chaos
Chaos or CHAOS may refer to:
Science, technology, and astronomy
* '' Chaos: Making a New Science'', a 1987 book by James Gleick
* Chaos (company), a Bulgarian rendering and simulation software company
* ''Chaos'' (genus), a genus of amoebae
* ...
, harmonics
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st harm ...
, and subharmonics
In music, the undertone series or subharmonic series is a sequence of Musical note, notes that results from inversion (music), inverting the intervals of the harmonic series (music), overtone series. While overtones naturally occur with the phys ...
which cannot be produced or analyzed using linear methods.
Polynomial signal processing is a type of non-linear signal processing, where polynomial
In mathematics, a polynomial is a Expression (mathematics), mathematical expression consisting of indeterminate (variable), indeterminates (also called variable (mathematics), variables) and coefficients, that involves only the operations of addit ...
systems may be interpreted as conceptually straightforward extensions of linear systems to the nonlinear case.
Statistical
Statistical signal processing is an approach which treats signals asstochastic process
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables in a probability space, where the index of the family often has the interpretation of time. Sto ...
es, utilizing their statistical
Statistics (from German language, German: ', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a s ...
properties to perform signal processing tasks. Statistical techniques are widely used in signal processing applications. For example, one can model the probability distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is a Function (mathematics), function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of possible events for an Experiment (probability theory), experiment. It is a mathematical descri ...
of noise incurred when photographing an image, and construct techniques based on this model to reduce the noise in the resulting image.
Graph
Graph signal processing generalizes signal processing tasks to signals living on non-Euclidean domains whose structure can be captured by a weighted graph. Graph signal processing presents several key points such as sampling signal techniques, recovery techniques and time-varying techiques. Graph signal processing has been applied with success in the field of image processing, computer vision and sound anomaly detection.Application fields
 *
* Audio signal processing
Audio signal processing is a subfield of signal processing that is concerned with the electronic manipulation of audio signals. Audio signals are electronic representations of sound waves—longitudinal waves which travel through air, consisting ...
for electrical signals representing sound, such as speech
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, suc ...
or music
* Image processing
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a pr ...
in digital cameras, computers and various imaging systems
* Video processing In electronics engineering, video processing is a particular case of signal processing, in particular image processing, which often employs filter (video), video filters and where the input and output Signal (electrical engineering), signals are vid ...
for interpreting moving pictures
* Wireless communication
Wireless communication (or just wireless, when the context allows) is the transfer of information (''telecommunication'') between two or more points without the use of an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided med ...
waveform generations, demodulation, filtering, equalization
* Control systems
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial co ...
* Array processing for processing signals from arrays of sensors
* Process control
Industrial process control (IPC) or simply process control is a system used in modern manufacturing which uses the principles of control theory and physical industrial control systems to monitor, control and optimize continuous Industrial processe ...
a variety of signals are used, including the industry standard 4-20 mA current loop
* Seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes (or generally, quakes) and the generation and propagation of elastic ...
* Feature extraction
Feature may refer to:
Computing
* Feature recognition, could be a hole, pocket, or notch
* Feature (computer vision), could be an edge, corner or blob
* Feature (machine learning), in statistics: individual measurable properties of the phenome ...
, such as image understanding
Computer vision tasks include methods for acquiring, processing, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical or symbolic information, e.g. in the form o ...
, semantic audio and speech recognition
Speech recognition is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and computational linguistics that develops methodologies and technologies that enable the recognition and translation of spoken language into text by computers. It is also ...
.
* Quality improvement, such as noise reduction
Noise reduction is the process of removing noise from a signal. Noise reduction techniques exist for audio and images. Noise reduction algorithms may distort the signal to some degree. Noise rejection is the ability of a circuit to isolate an u ...
, image enhancement, and echo cancellation.
* Source coding including audio compression, image compression
Image compression is a type of data compression applied to digital images, to reduce their cost for computer data storage, storage or data transmission, transmission. Algorithms may take advantage of visual perception and the statistical properti ...
, and video compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compression ...
.
* Genomic
Genomics is an interdisciplinary field of molecular biology focusing on the structure, function, evolution, mapping, and editing of genomes. A genome is an organism's complete set of DNA, including all of its genes as well as its hierarchical, ...
signal processing
* In geophysics
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and Physical property, properties of Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. Geophysicists conduct i ...
, signal processing is used to amplify the signal vs the noise within time-series
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. E ...
measurements of geophysical data. Processing is conducted within the time domain
In mathematics and signal processing, the time domain is a representation of how a signal, function, or data set varies with time. It is used for the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental ...
or frequency domain
In mathematics, physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency (and possibly phase), rather than time, as in time ser ...
, or both.
In communication systems, signal processing may occur at:
* OSI layer 1 in the seven-layer OSI model
The Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model is a reference model developed by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) that "provides a common basis for the coordination of standards development for the purpose of systems inter ...
, the physical layer
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer: the layer most closely associated with the physical connection between devices. The physical layer provides an electrical, mechani ...
(modulation
Signal modulation is the process of varying one or more properties of a periodic waveform in electronics and telecommunication for the purpose of transmitting information.
The process encodes information in form of the modulation or message ...
, equalization, multiplexing
In telecommunications and computer networking, multiplexing (sometimes contracted to muxing) is a method by which multiple analog or digital signals are combined into one signal over a shared medium. The aim is to share a scarce resource� ...
, etc.);
* OSI layer 2, the data link layer
The data link layer, or layer 2, is the second layer of the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking. This layer is the protocol layer that transfers data between nodes on a network segment across the physical layer. The data link layer p ...
(forward error correction
In computing, telecommunication, information theory, and coding theory, forward error correction (FEC) or channel coding is a technique used for controlling errors in data transmission over unreliable or noisy communication channels.
The centra ...
);
* OSI layer 6, the presentation layer (source coding, including analog-to-digital conversion
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provide ...
and data compression
In information theory, data compression, source coding, or bit-rate reduction is the process of encoding information using fewer bits than the original representation. Any particular compression is either lossy or lossless. Lossless compressi ...
).
Typical devices
*Filters
Filtration is a physical process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture.
Filter, filtering, filters or filtration may also refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Fil ...
for example analog (passive or active) or digital (FIR
Firs are evergreen coniferous trees belonging to the genus ''Abies'' () in the family Pinaceae. There are approximately 48–65 extant species, found on mountains throughout much of North and Central America, Eurasia, and North Africa. The genu ...
, IIR, frequency domain or stochastic filters, etc.)
* Samplers and analog-to-digital converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a Digital signal (signal processing), digi ...
s for signal acquisition
Data acquisition is the process of Sampling (signal processing), sampling signals that measure real-world physical conditions and converting the resulting samples into Digital data, digital numeric values that can be manipulated by a computer. Dat ...
and reconstruction, which involves measuring a physical signal, storing or transferring it as digital signal, and possibly later rebuilding the original signal or an approximation thereof.
* Digital signal processor
A digital signal processor (DSP) is a specialized microprocessor chip, with its architecture optimized for the operational needs of digital signal processing. DSPs are fabricated on metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit chips. ...
s (DSPs)
Mathematical methods applied
* Differential equations for modeling system behavior, connecting input and output relations in linear time-invariant systems. For instance, a low-pass filter such as anRC circuit
A resistor–capacitor circuit (RC circuit), or RC filter or RC network, is an electric circuit composed of resistors and capacitors. It may be driven by a voltage source, voltage or current source and these will produce different responses. A fi ...
can be modeled as a differential equation in signal processing, which allows one to compute the continuous output signal as a function of the input or initial conditions.
* Recurrence relation
In mathematics, a recurrence relation is an equation according to which the nth term of a sequence of numbers is equal to some combination of the previous terms. Often, only k previous terms of the sequence appear in the equation, for a parameter ...
s
* Transform theory
* Time-frequency analysis for processing non-stationary signals
* Linear canonical transformation
* Spectral estimation for determining the spectral content (i.e., the distribution of power over frequency) of a set of time series
In mathematics, a time series is a series of data points indexed (or listed or graphed) in time order. Most commonly, a time series is a sequence taken at successive equally spaced points in time. Thus it is a sequence of discrete-time data. ...
data points
*Statistical signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing ''signals'', such as sound, images, potential fields, seismic signals, altimetry processing, and scientific measurements. Signal ...
analyzing and extracting information from signals and noise based on their stochastic properties
*Linear time-invariant system
In system analysis, among other fields of study, a linear time-invariant (LTI) system is a system that produces an output signal from any input signal subject to the constraints of Linear system#Definition, linearity and Time-invariant system, ...
theory, and transform theory
* Polynomial signal processing analysis of systems which relate input and output using polynomials
*System identification
The field of system identification uses statistical methods to build mathematical models of dynamical systems from measured data. System identification also includes the optimal design#System identification and stochastic approximation, optimal de ...
and classification
*Calculus
Calculus is the mathematics, mathematical study of continuous change, in the same way that geometry is the study of shape, and algebra is the study of generalizations of arithmetic operations.
Originally called infinitesimal calculus or "the ...
*Coding theory
Coding theory is the study of the properties of codes and their respective fitness for specific applications. Codes are used for data compression, cryptography, error detection and correction, data transmission and computer data storage, data sto ...
*Complex analysis
Complex analysis, traditionally known as the theory of functions of a complex variable, is the branch of mathematical analysis that investigates functions of complex numbers. It is helpful in many branches of mathematics, including algebraic ...
*Vector spaces
In mathematics and physics, a vector space (also called a linear space) is a set whose elements, often called ''vectors'', can be added together and multiplied ("scaled") by numbers called ''scalars''. The operations of vector addition and sc ...
and Linear algebra
Linear algebra is the branch of mathematics concerning linear equations such as
:a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n=b,
linear maps such as
:(x_1, \ldots, x_n) \mapsto a_1x_1+\cdots +a_nx_n,
and their representations in vector spaces and through matrix (mathemat ...
*Functional analysis
Functional analysis is a branch of mathematical analysis, the core of which is formed by the study of vector spaces endowed with some kind of limit-related structure (for example, Inner product space#Definition, inner product, Norm (mathematics ...
*Probability
Probability is a branch of mathematics and statistics concerning events and numerical descriptions of how likely they are to occur. The probability of an event is a number between 0 and 1; the larger the probability, the more likely an e ...
and stochastic processes
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables in a probability space, where the index of the family often has the interpretation of time. Stoc ...
*Detection theory
Detection theory or signal detection theory is a means to measure the ability to differentiate between information-bearing patterns (called stimulus in living organisms, signal in machines) and random patterns that distract from the information (c ...
*Estimation theory
Estimation theory is a branch of statistics that deals with estimating the values of Statistical parameter, parameters based on measured empirical data that has a random component. The parameters describe an underlying physical setting in such ...
*Optimization
Mathematical optimization (alternatively spelled ''optimisation'') or mathematical programming is the selection of a best element, with regard to some criteria, from some set of available alternatives. It is generally divided into two subfiel ...
*Numerical methods
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation (as opposed to symbolic manipulations) for the problems of mathematical analysis (as distinguished from discrete mathematics). It is the study of numerical methods t ...
*Data mining
Data mining is the process of extracting and finding patterns in massive data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. Data mining is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and ...
for statistical analysis of relations between large quantities of variables (in this context representing many physical signals), to extract previously unknown interesting patterns
See also
* Algebraic signal processing *Audio filter
An audio filter is a frequency-dependent circuit, working in the audio frequency range, 0 Hz to 20 kHz. Audio filters can amplify (boost), pass or attenuate (cut) some frequency ranges. Many types of filters exist for different audio ...
* Bounded variation
In mathematical analysis, a function of bounded variation, also known as ' function, is a real number, real-valued function (mathematics), function whose total variation is bounded (finite): the graph of a function having this property is well beh ...
* Digital image processing
Digital image processing is the use of a digital computer to process digital images through an algorithm. As a subcategory or field of digital signal processing, digital image processing has many advantages over analog image processing. It allo ...
* Dynamic range compression
Dynamic range compression (DRC) or simply compression is an audio signal processing operation that reduces the volume of loud sounds or amplifies quiet sounds, thus reducing or ''compressing'' an audio signal's dynamic range. Compression is c ...
, companding
In telecommunications and signal processing, companding (occasionally called compansion) is a method of mitigating the detrimental effects of a channel with limited dynamic range. The name is a portmanteau of the words compressing and expandi ...
, limiting, and noise gating
* Fourier transform
In mathematics, the Fourier transform (FT) is an integral transform that takes a function as input then outputs another function that describes the extent to which various frequencies are present in the original function. The output of the tr ...
* Information theory
Information theory is the mathematical study of the quantification (science), quantification, Data storage, storage, and telecommunications, communication of information. The field was established and formalized by Claude Shannon in the 1940s, ...
* Least-squares spectral analysis
Least-squares spectral analysis (LSSA) is a method of estimating a Spectral density estimation#Overview, frequency spectrum based on a least-squares fit of Sine wave, sinusoids to data samples, similar to Fourier analysis. Fourier analysis, the ...
* Non-local means
Non-local means is an algorithm in image processing for image denoising. Unlike "local mean" filters, which take the mean value of a group of pixels surrounding a target pixel to smooth the image, non-local means filtering takes a mean of all pi ...
* Reverberation
In acoustics, reverberation (commonly shortened to reverb) is a persistence of sound after it is produced. It is often created when a sound is reflection (physics), reflected on surfaces, causing multiple reflections that build up and then de ...
* Sensitivity (electronics)
The sensitivity of an electronic device, such as a communications system receiver, or detection device, such as a PIN diode, is the minimum magnitude of input signal required to produce a specified output signal having a specified signal-to-nois ...
* Similarity (signal processing)
Similarity between two different signals is important in the field of signal processing. Below are some common methods for calculating similarity.
For instance, let's consider two signals represented as x, n/math> and y, n/math>, where m = 0, 1, ...
References
Further reading
* * * * Kainam Thomas WonStatistical Signal Processing lecture notes at the University of Waterloo, Canada. * Ali H. Sayed, Adaptive Filters, Wiley, NJ, 2008, . * Thomas Kailath, Ali H. Sayed, and Babak Hassibi, Linear Estimation, Prentice-Hall, NJ, 2000, .
External links
Signal Processing for Communications
– free online textbook by Paolo Prandoni and Martin Vetterli (2008)
Scientists and Engineers Guide to Digital Signal Processing
– free online textbook by Stephen Smith
Julius O. Smith III: Spectral Audio Signal Processing
– free online textbook
Graph Signal Processing Website
– free online website by Thierry Bouwmans (2025) {{Authority control Mass media technology Telecommunication theory