|
Multiplexer
In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux; spelled sometimes as multiplexor), also known as a data selector, is a device that selects between several Analog signal, analog or Digital signal (electronics), digital input signals and forwards the selected input to a single output line. The selection is directed by a separate set of digital inputs known as select lines. A multiplexer of 2^n inputs has n select lines, which are used to select which input line to send to the output. A multiplexer makes it possible for several input signals to share one device or resource, for example, one analog-to-digital converter or one communications transmission medium, instead of having one device per input signal. Multiplexers can also be used to implement Boolean algebra, Boolean functions of multiple variables. Conversely, a demultiplexer (or demux) is a device that takes a single input signal and selectively forwards it to one of several output lines. A multiplexer is often used with a complem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demultiplexer
In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux; spelled sometimes as multiplexor), also known as a data selector, is a device that selects between several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input to a single output line. The selection is directed by a separate set of digital inputs known as select lines. A multiplexer of 2^n inputs has n select lines, which are used to select which input line to send to the output. A multiplexer makes it possible for several input signals to share one device or resource, for example, one analog-to-digital converter or one communications transmission medium, instead of having one device per input signal. Multiplexers can also be used to implement Boolean functions of multiple variables. Conversely, a demultiplexer (or demux) is a device that takes a single input signal and selectively forwards it to one of several output lines. A multiplexer is often used with a complementary demultiplexer on the receiving end. An electronic mul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield of physics and electrical engineering which uses Passivity (engineering), active devices such as transistors, diodes, and integrated circuits to control and amplify the flow of electric current and to convert it from one form to another, such as from alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) or from analog signal, analog signals to digital signal, digital signals. Electronic devices have significantly influenced the development of many aspects of modern society, such as telecommunications, entertainment, education, health care, industry, and security. The main driving force behind the advancement of electronics is the semiconductor industry, which continually produces ever-more sophisticated electronic devices and circuits in respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Decoder
In digital electronics, a binary decoder is a combinational logic circuit that converts binary information from the n coded inputs to a maximum of 2n unique outputs. They are used in a wide variety of applications, including instruction decoding, data multiplexing and data demultiplexing, seven segment displays, and as address decoders for memory and port-mapped I/O. There are several types of binary decoders, but in all cases a decoder is an electronic circuit with multiple input and multiple output signals, which converts every unique combination of input states to a specific combination of output states. In addition to integer data inputs, some decoders also have one or more "enable" inputs. When the enable input is negated (disabled), all decoder outputs are forced to their inactive states. Depending on its function, a binary decoder will convert binary information from n input signals to as many as 2n unique output signals. Some decoders have less than 2n output lines; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Truth Table
A truth table is a mathematical table used in logic—specifically in connection with Boolean algebra, Boolean functions, and propositional calculus—which sets out the functional values of logical expressions on each of their functional arguments, that is, for each combination of values taken by their logical variables. In particular, truth tables can be used to show whether a propositional expression is true for all legitimate input values, that is, logically valid. A truth table has one column for each input variable (for example, A and B), and one final column showing all of the possible results of the logical operation that the table represents (for example, A XOR B). Each row of the truth table contains one possible configuration of the input variables (for instance, A=true, B=false), and the result of the operation for those values. A proposition's truth table is a graphical representation of its truth function. The truth function can be more useful for mathema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Collector
Open collector, open drain, open emitter, and open source refer to integrated circuit (IC) output pin configurations that process the IC's internal function through a transistor with an exposed terminal that is internally unconnected (i.e. "open"). One of the IC's internal high or low voltage rails typically connects to another terminal of that transistor. When the transistor is off, the output is internally disconnected from any internal power rail, a state called "high-impedance" ( Hi-Z). Open outputs configurations thus differ from push–pull outputs, which use a pair of transistors to output a specific voltage or current. These open outputs configurations are often used for digital applications when the transistor acts as a switch, to allow for logic-level conversion, wired-logic connections, and line sharing. External pull-up/down resistors are typically required to set the output during the Hi-Z state to a specific voltage. Analog applications include analog weighting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
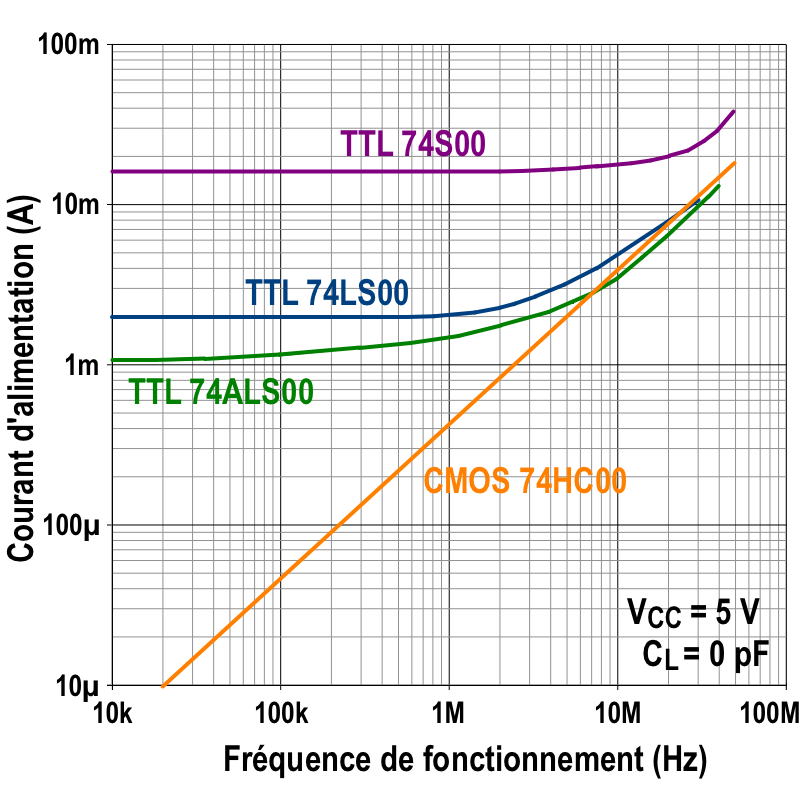
7400 Series
The 7400 series is a popular logic family of transistor–transistor logic (TTL) integrated circuits (ICs). In 1964, Texas Instruments introduced the SN5400 series of logic chips, in a ceramic semiconductor package. A low-cost plastic package SN7400 series was introduced in 1966 which quickly gained over 50% of the logic chip market, and eventually becoming ''de facto'' standardized electronic components. Since the introduction of the original bipolar-transistor TTL parts, Pin-compatibility, pin-compatible parts were introduced with such features as low power CMOS technology and LVCMOS, lower supply voltages. Surface-mount technology, Surface mount packages exist for several popular logic family functions. Overview The 7400 series contains hundreds of devices that provide everything from basic logic gates, flip-flop (electronics), flip-flops, and counters, to special purpose bus transceivers and arithmetic logic units (ALU). Specific functions are described in a list of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |