The United Kingdom European Union membership referendum, commonly referred to as the EU referendum or the Brexit referendum, took place on 23 June 2016 in the United Kingdom (UK) and
Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
to ask the electorate whether the country should remain a member of, or leave, the
European Union (EU). It was organised and facilitated through the
European Union Referendum Act 2015 and the
Political Parties, Elections and Referendums Act 2000. The referendum resulted in 51.9% of the votes cast being in favour of leaving the EU. Although the referendum was legally non-binding, the government of the time promised to implement the result.
Membership of the EU had long been a topic of debate in the United Kingdom. The country joined the
European Communities
The European Communities (EC) were three international organizations that were governed by the same set of institutions. These were the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom), and the ...
(EC), principally the
European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
(EEC) or Common Market, the forerunner to the European Union, in 1973, along with the
European Coal and Steel Community
The European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) was a European organization created after World War II to regulate the coal and steel industries. It was formally established in 1951 by the Treaty of Paris, signed by Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembo ...
(ECSC), and the
European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom).
A referendum on continued membership of the Communities was held in 1975, with 67.2% of the votes cast in favour of Britain remaining a member.
In May 2015, following a Conservative Party manifesto pledge, the legal basis for the EU referendum was established through the
European Union Referendum Act 2015.
Britain Stronger in Europe became the official group campaigning for the UK to remain in the EU, and was endorsed by the Prime Minister
David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron (born 9 October 1966) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2010 to 2016 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2005 to 2016. He previously served as Leader o ...
and
Chancellor
Chancellor ( la, cancellarius) is a title of various official positions in the governments of many nations. The original chancellors were the of Roman courts of justice—ushers, who sat at the or lattice work screens of a basilica or law cou ...
George Osborne.
Vote Leave was the official group campaigning for the UK to leave the EU, and was fronted by Conservative
MPs
MPS, M.P.S., MPs, or mps may refer to:
Science and technology
* Mucopolysaccharidosis, genetic lysosomal storage disorder
* Mononuclear phagocyte system, cells in mammalian biology
* Myofascial pain syndrome
* Metallopanstimulin
* Potassium perox ...
Boris Johnson and
Michael Gove
Michael Andrew Gove (; born Graeme Andrew Logan, 26 August 1967) is a British politician serving as Secretary of State for Levelling Up, Housing and Communities and Minister for Intergovernmental Relations since 2021. He has been Member of Parli ...
along with
Labour
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
MP
Gisela Stuart. Other campaign groups, political parties, businesses, trade unions, newspapers and prominent individuals were also involved, with both sides having supporters from across the
political spectrum. Parties in favour of 'remain' included
Labour
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
, the
Liberal Democrats, the
Scottish National Party
The Scottish National Party (SNP; sco, Scots National Pairty, gd, Pàrtaidh Nàiseanta na h-Alba ) is a Scottish nationalist and social democratic political party in Scotland. The SNP supports and campaigns for Scottish independence from ...
(SNP),
Plaid Cymru and the
Green Party
A green party is a formally organized political party based on the principles of green politics, such as social justice, environmentalism and nonviolence.
Greens believe that these issues are inherently related to one another as a foundation ...
; while the
UK Independence Party (UKIP) campaigned in favour of leaving the European Union; and the
Conservative Party
The Conservative Party is a name used by many political parties around the world. These political parties are generally right-wing though their exact ideologies can range from center-right to far-right.
Political parties called The Conservative P ...
remained neutral. In spite of the official positions of the Conservative Party and Labour, both parties allowed their MPs to publicly campaign for either side of the issue.
Immediately after the result, financial markets reacted negatively worldwide, and Cameron announced that he would resign as
Prime Minister and
Leader of the Conservative Party, having campaigned unsuccessfully to remain in the European Union. It was the first time that a national referendum result had gone against the preferred option of the
UK Government. Cameron was succeeded by
Theresa May on 13 July 2016. Labour leader
Jeremy Corbyn also faced a
leadership challenge as a result of the EU referendum. On 29 March 2017, the
United Kingdom gave formal notice of intent to withdraw from the EU.
Background
The
European Communities
The European Communities (EC) were three international organizations that were governed by the same set of institutions. These were the European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC), the European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom), and the ...
were formed in the 1950s the
European Coal and Steel Community
The European Coal and Steel Community (ECSC) was a European organization created after World War II to regulate the coal and steel industries. It was formally established in 1951 by the Treaty of Paris, signed by Belgium, France, Italy, Luxembo ...
(ECSC) in 1952, and the
European Atomic Energy Community (EAEC or Euratom) and
European Economic Community
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lisb ...
(EEC) in 1957.
The EEC, the more ambitious of the three, came to be known as the "Common Market". The UK first applied to join them in 1961, but this was vetoed by France.
A later application was successful, and the UK joined in 1973; two years later, the
first ever national referendum on continuing membership resulted in 67.2% approval, with a 64.62% turnout.
Political integration gained greater focus when the
Maastricht Treaty established the
European Union (EU) in 1993, which incorporated (and after the
Treaty of Lisbon, succeeded) the European Communities.
Growing pressure for a referendum
Prior to the
2010 general election, the then
Leader of the Conservative Party and Leader of the Opposition
David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron (born 9 October 1966) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2010 to 2016 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2005 to 2016. He previously served as Leader o ...
promised a referendum on the
Lisbon Treaty, which he backtracked on after all EU countries had ratified the treaty before the election.

When they attended the May
2012 NATO summit meeting, UK Prime Minister
David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron (born 9 October 1966) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2010 to 2016 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2005 to 2016. He previously served as Leader o ...
,
Foreign Secretary
The secretary of state for foreign, Commonwealth and development affairs, known as the foreign secretary, is a minister of the Crown of the Government of the United Kingdom and head of the Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office. Seen as ...
William Hague and
Ed Llewellyn discussed the idea of using a European Union referendum as a concession to energise the
Eurosceptic
Euroscepticism, also spelled as Euroskepticism or EU-scepticism, is a political position involving criticism of the European Union (EU) and European integration. It ranges from those who oppose some EU institutions and policies, and seek reform ...
wing of the Conservative Party. In January 2013, Cameron delivered the
Bloomberg speech
The Bloomberg speech was an address on Britain's membership of the European Union, given in January 2013 by the then ( Conservative Party) Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, David Cameron. Although presented while the Conservative-Liberal Dem ...
and promised that, should the Conservatives win a parliamentary majority at the
2015 general election, the
British government
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal Arms
, date_es ...
would negotiate more favourable arrangements for continuing British membership of the EU, before holding a referendum on whether the UK should remain in or leave the EU. The Conservative Party published a draft EU Referendum Bill in May 2013, and outlined its plans for renegotiation followed by an in-out vote (i.e. a referendum giving options only of leaving and of remaining in under the current terms, or under new terms if these had become available), were the party to be re-elected in 2015. The draft Bill stated that the referendum had to be held no later than 31 December 2017.
The draft legislation was taken forward as a
Private member's bill
A private member's bill is a bill (proposed law) introduced into a legislature by a legislator who is not acting on behalf of the executive branch. The designation "private member's bill" is used in most Westminster system jurisdictions, in whi ...
by Conservative MP
James Wharton which was known as the
European Union (Referendum) Bill 2013
The European Union (EU) is a supranational continental political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has ...
. The bill's First Reading in the
House of Commons took place on 19 June 2013. Cameron was said by a spokesperson to be "very pleased" and would ensure the Bill was given "the full support of the Conservative Party".
Regarding the ability of the bill to bind the UK Government in the
2015–20 Parliament (which indirectly, as a result of the referendum itself, proved to last only two years) to holding such a referendum, a parliamentary research paper noted that:
The Bill simply provides for a referendum on continued EU membership by the end of December 2017 and does not otherwise specify the timing, other than requiring the Secretary of State to bring forward orders by the end of 2016. ..If no party obtained a majority at the ext general election due in 2015
Ext, ext or EXT may refer to:
* Ext functor, used in the mathematical field of homological algebra
* Ext (JavaScript library)
Ext JS is a JavaScript application framework for building interactive cross-platform web applications using techniques ...
there might be some uncertainty about the passage of the orders in the next Parliament.
The bill received its Second Reading on 5 July 2013, passing by 304 votes to none after almost all
Labour
Labour or labor may refer to:
* Childbirth, the delivery of a baby
* Labour (human activity), or work
** Manual labour, physical work
** Wage labour, a socioeconomic relationship between a worker and an employer
** Organized labour and the labour ...
MPs and all
Liberal Democrat MPs abstained, cleared the Commons in November 2013, and was then introduced to the
House of Lords in December 2013, where members voted to block the bill.
Conservative MP
Bob Neill
Sir Robert James MacGillivray Neill (born 24 June 1952) is a British barrister and Conservative Party politician. He has served as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Bromley and Chislehurst since a by-election on 29 June 2006, following the ...
then introduced an Alternative Referendum Bill to the Commons. After a debate on 17 October 2014, it passed to the
Public Bills Committee, but because the Commons failed to pass a
money resolution
Money is any item or verifiable record that is generally accepted as payment for goods and services and repayment of debts, such as taxes, in a particular country or socio-economic context. The primary functions which distinguish money are as ...
, the bill was unable to progress further before the
dissolution of parliament on 27 March 2015.
At the
European Parliament election in 2014, the
UK Independence Party (UKIP) secured more votes and more seats than any other party, the first time a party other than the Conservatives or Labour had topped a nationwide poll in 108 years, leaving the Conservatives in third place.
Under
Ed Miliband's leadership between 2010 and 2015, the Labour Party ruled out an in-out referendum unless and until a further transfer of powers from the UK to the EU were to be proposed. In their manifesto for the 2015 general election, the Liberal Democrats pledged to hold an in-out referendum only in the event of there being a change in the EU treaties. The UK Independence Party (UKIP), the
British National Party (BNP), the
Green Party
A green party is a formally organized political party based on the principles of green politics, such as social justice, environmentalism and nonviolence.
Greens believe that these issues are inherently related to one another as a foundation ...
, the
Democratic Unionist Party
The Democratic Unionist Party (DUP) is a unionist, loyalist, and national conservative political party in Northern Ireland. It was founded in 1971 during the Troubles by Ian Paisley, who led the party for the next 37 years. Currently led by J ...
and the
Respect Party all supported the principle of a referendum.
When the Conservative Party won a majority of seats in the House of Commons at the 2015 general election, Cameron reiterated his party's
manifesto
A manifesto is a published declaration of the intentions, motives, or views of the issuer, be it an individual, group, political party or government. A manifesto usually accepts a previously published opinion or public consensus or promotes a ...
commitment to hold an in-out referendum on UK membership of the EU by the end of 2017, but only after "negotiating a new settlement for Britain in the EU".
Renegotiation before the referendum
In early 2014,
David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron (born 9 October 1966) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2010 to 2016 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2005 to 2016. He previously served as Leader o ...
outlined the changes he aimed to bring about in the EU and in the UK's relationship with it.
These were: additional immigration controls, especially for citizens of new EU member states; tougher immigration rules for present EU citizens; new powers for national parliaments collectively to veto proposed EU laws; new free-trade agreements and a reduction in bureaucracy for businesses; a lessening of the influence of the
European Court of Human Rights on British police and courts; more power for individual member states, and less for the central EU; and abandonment of the EU notion of "ever closer union".
He intended to bring these about during a series of negotiations with other EU leaders and then, if re-elected, to announce a referendum.
In November that year, Cameron gave an update on the negotiations and further details of his aims.
The key demands made of the EU were: on economic governance, to recognise officially that
Eurozone laws would not necessarily apply to non-Eurozone EU members and the latter would not have to bail out troubled Eurozone economies; on competitiveness, to expand the single market and to set a target for the reduction of bureaucracy for businesses; on sovereignty, for the UK to be legally exempted from "ever closer union" and for national parliaments to be able collectively to veto proposed EU laws; and, on immigration, for EU citizens going to the UK for work to be unable to claim social housing or in-work benefits until they had worked there for four years, and for them to be unable to send
child benefit payments overseas.
The outcome of the renegotiations was announced in February 2016.
The renegotiated terms were in addition to the United Kingdom's existing
opt-outs in the European Union and the
UK rebate
The UK rebate (or UK correction) was a financial mechanism that reduced the United Kingdom's contribution to the EU budget in effect since 1985. It was a complex calculation which equated to a reduction of approximately 66% of the UK's net contr ...
. The significance of the changes to the EU-UK agreement was contested and speculated upon, with none of the changes considered fundamental, but some considered important to many British people.
Some limits to in-work benefits for EU immigrants were agreed, but these would apply on a sliding scale for four years and would be for new immigrants only; before they could be applied, a country would have to get permission from the
European Council
The European Council (informally EUCO) is a collegiate body that defines the overall political direction and priorities of the European Union. It is composed of the heads of state or government of the EU member states, the President of the E ...
.
Child benefit payments could still be made overseas, but these would be linked to the cost of living in the other country.
On sovereignty, the UK was reassured that it would not be required to participate in "ever closer union"; these reassurances were "in line with existing EU law".
Cameron's demand to allow national parliaments to veto proposed EU laws was modified to allow national parliaments collectively to object to proposed EU laws, in which case the European Council would reconsider the proposal before itself deciding what to do.
On economic governance, anti-discrimination regulations for non-Eurozone members would be reinforced, but they would be unable to veto any legislation.
The final two areas covered were proposals to "exclude from the scope of free movement rights, third country nationals who had no prior lawful residence in a Member State before marrying a Union citizen"
and to make it easier for member states to deport EU nationals for public policy or public security reasons.
The extent to which the various parts of the agreement would be legally binding is complex; no part of the agreement itself changed EU law, but some parts could be enforceable in international law.
The EU had reportedly offered
David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron (born 9 October 1966) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2010 to 2016 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2005 to 2016. He previously served as Leader o ...
a so-called "emergency brake", which would have allowed the UK to withhold social benefits to new immigrants for the first four years after they arrived; this brake could have been applied for a period of seven years. That offer was still on the table at the time of the Brexit referendum, but expired when the vote determined that the UK would leave the EU. Cameron claimed that "he could have avoided Brexit had European leaders let him control migration", according to the ''
Financial Times''. However,
Angela Merkel said that the offer had not been made by the EU. Merkel stated in the German Parliament: "If you wish to have free access to the single market then you have to accept the fundamental European rights as well as obligations that come from it. This is as true for Great Britain as for anybody else."
Legislation
The planned referendum was included in the
Queen's Speech
A speech from the throne, or throne speech, is an event in certain monarchies in which the reigning sovereign, or a representative thereof, reads a prepared speech to members of the nation's legislature when a Legislative session, session is ...
on 27 May 2015. It was suggested at the time that Cameron was planning to hold the referendum in October 2016, but the European Union Referendum Act 2015, which authorised it, went before the House of Commons the following day, just three weeks after the election. On the bill's second reading on 9 June, members of the House of Commons voted by 544 to 53 in favour, endorsing the principle of holding a referendum, with only the
Scottish National Party
The Scottish National Party (SNP; sco, Scots National Pairty, gd, Pàrtaidh Nàiseanta na h-Alba ) is a Scottish nationalist and social democratic political party in Scotland. The SNP supports and campaigns for Scottish independence from ...
voting against. In contrast to the Labour Party's position prior to the 2015 general election under Miliband, acting Labour leader
Harriet Harman committed her party to supporting plans for an EU referendum by 2017.
To enable the referendum to take place, the European Union Referendum Act was passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It extended to include and take legislative effect in
Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
, and received royal assent on 17 December 2015. The Act was, in turn, confirmed, enacted and implemented in Gibraltar by the
European Union (Referendum) Act 2016 (Gibraltar)
The European Union (Referendum) Act 2016 was an Act of the Gibraltar Parliament, which implements the United Kingdom's European Union Referendum Act 2015 in Gibraltar. It was the first time a referendum has been held in Gibraltar on the issue o ...
, which was passed by the
Gibraltar Parliament
The Gibraltar Parliament is the legislature of the British overseas territory of Gibraltar. Between 1969 and 2006, it was called the Gibraltar House of Assembly.
Functions
The House of Assembly, set up under the 1969 constitution, was a uni ...
and entered into law upon receiving the assent of the
Governor of Gibraltar on 28 January 2016.
The European Union Referendum Act required a referendum to be held on the question of the UK's continued membership of the European Union (EU) before the end of 2017. It did not contain any requirement for the UK Government to implement the results of the referendum. Instead, it was designed to gauge the electorate's opinion on EU membership. The referendums held in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland in 1997 and 1998 are examples of this type, where opinion was tested before legislation was introduced.
The UK does not have constitutional provisions which would require the results of a referendum to be implemented, unlike, for example, the
Republic of Ireland, where the circumstances in which a binding referendum should be held are set out in
its constitution. In contrast, the legislation that provided for the referendum held on AV in May 2011 would have implemented the new system of voting without further legislation, provided that the boundary changes also provided for in the
Parliamentary Voting System and Constituencies Act 2011
The Parliamentary Voting System and Constituencies Act 2011 (c. 1) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that made provision for the holding of a referendum on whether to introduce the Alternative Vote system in all future general ele ...
were also implemented. In the event, there was a substantial majority against any change. The 1975 referendum was held after the re-negotiated terms of the UK's EC membership had been agreed by all EC Member States, and the terms set out in a command paper and agreed by both Houses. Following the 2016 referendum, the High Court confirmed that the result was not legally binding, owing to the constitutional principles of parliamentary sovereignty and representative democracy, and the legislation authorising the referendum did not contain clear words to the contrary.
Referendum question

Research by the Electoral Commission confirmed that its recommended question "was clear and straightforward for voters, and was the most neutral wording from the range of options ... considered and tested", citing responses to its consultation by a diverse range of consultees. The proposed question was accepted by the government in September 2015, shortly before the bill's third reading.
The question that appeared on ballot papers in the referendum under the
Act was:
with the responses to the question (to be marked with a single (X)):
and in
Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peop ...
:
with the responses (to be marked with a single (X)):
Administration
Date
Prior to being officially announced, it was widely speculated that a June date for the referendum was a serious possibility. The First Ministers of Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales co-signed a letter to Cameron on 3 February 2016 asking him not to hold the referendum in June, as devolved elections were scheduled to take place the previous month on 5 May. These elections had been postponed for a year to avoid a clash with the 2015 general election, after Westminster had implemented the
Fixed-term Parliament Act. Cameron refused this request, saying people were able to make up their own minds in multiple elections spaced at least six weeks from each other.
In February 2016, Cameron announced that the UK Government would formally recommend to the British people that the UK should remain a member of a reformed European Union and that the referendum would be held on 23 June, marking the official launch of the campaign. He also announced that Parliament would enact secondary legislation on 22 February relating to the European Union Referendum Act 2015. With the official launch, ministers of the UK Government were then free to campaign on either side of the argument in a rare exception to
Cabinet collective responsibility.
Eligibility to vote
The right to vote in the referendum in the United Kingdom is defined by the legislation as limited to residents of the United Kingdom who were either also
Commonwealth citizens
A Commonwealth citizen is a citizen or qualified national of a Commonwealth of Nations member state. Most member countries do not treat citizens of other Commonwealth states any differently from foreign nationals, but some grant limited citizen ...
under the
British Nationality Act 1948 (which include
British citizens and other British nationals), or those who were also
citizens of the Republic of Ireland, or both. Members of the
House of Lords, who could not vote in general elections, were able to vote in the referendum. The electorate of 46,500,001 represented 70.8% of the population of 65,678,000 (
UK and
Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
). Other than the residents of Gibraltar, British Overseas Territories Citizens residing in the British Overseas Territories were unable to vote in the referendum.
Residents of the United Kingdom who were citizens of other EU countries were not allowed to vote unless they were citizens (or were also citizens) of the Republic of Ireland, of
Malta, or of the Republic of
Cyprus.
The
Representation of the People Acts 1983 ''
(1983 c. 2)'' and
1985
The year 1985 was designated as the International Youth Year by the United Nations.
Events January
* January 1
** The Internet's Domain Name System is created.
** Greenland withdraws from the European Economic Community as a result of a ...
''
(1985 c. 50)'', as amended, also permit certain British citizens (but not other British nationals), who had once lived in the United Kingdom, but had since and in the meantime lived outside of the United Kingdom, but for a period of no more than 15 years, to vote.
Voting on the day of the referendum was from 0700 to 2200
BST (
WEST) (0700 to 2200
CEST CEST or cest may refer to:
* Central European Summer Time (UTC+2), daylight saving time observed in the central European time zone
* Cognitive-Experiential Self-Theory
* Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer, a subset of Magnetization transfer in ...
in Gibraltar) in some 41,000 polling stations staffed by over 100,000
poll workers. Each polling station was specified to have no more than 2,500 registered voters. Under the provisions of the
Representation of the People Act 2000
The Representation of the People Act 2000 (c.2) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that changed the British electoral process in four minor amendments to the Representation of the People Act 1983:
* It removed most restrictions on ...
, postal ballots were also permitted in the referendum and were sent out to eligible voters some three weeks ahead of the vote (2 June 2016).
The minimum age for voters in the referendum was set to 18 years, in line with the Representation of the People Act, as amended. A House of Lords amendment proposing to lower the minimum age to 16 years was rejected.
The deadline to register to vote was initially midnight on 7 June 2016; however, this was extended by 48 hours owing to technical problems with the official registration website on 7 June, caused by unusually high web traffic. Some supporters of the Leave campaign, including the Conservative MP
Sir Gerald Howarth
Sir James Gerald Douglas Howarth (born 12 September 1947) is a British Conservative Party politician. He was the Member of Parliament (MP) for Aldershot from 1997 until 2017, having been the MP for Cannock and Burntwood from 1983 to 1992.
He wa ...
, criticised the government's decision to extend the deadline, alleging it gave Remain an advantage because many late registrants were young people who were considered to be more likely to vote for Remain. According to provisional figures from the Electoral Commission, almost 46.5 million people were eligible to vote.
Registration problems
Nottingham City Council emailed a
Vote Leave supporter to say that the council was unable to check whether the nationality that people stated on their voting registration form was true, and hence that they simply had to assume that the information that was submitted was, indeed, correct.
3,462 EU nationals were wrongly sent postal voting cards, due to an IT issue experienced by Xpress, an electoral software supplier to a number of councils. Xpress was initially unable to confirm the exact number of those affected. The matter was resolved by the issuance of a software patch which rendered the wrongly recorded electors ineligible to vote on 23 June.
Crown Dependencies
Residents of the
Crown Dependencies (which are not part of the United Kingdom), namely the
Isle of Man and the Bailiwicks of
Jersey and
Guernsey
Guernsey (; Guernésiais: ''Guernési''; french: Guernesey) is an island in the English Channel off the coast of Normandy that is part of the Bailiwick of Guernsey, a British Crown Dependency.
It is the second largest of the Channel Islands ...
, even if they were British citizens, were excluded from the referendum unless they were also previous residents of the United Kingdom (that is: England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland).
Some residents of the Isle of Man protested that they, as full British citizens under the British Nationality Act 1981 and living within the
British Islands, should also have been given the opportunity to vote in the referendum, as the Isle and the Bailiwicks, although not included as if they were part of the United Kingdom for the purpose of European Union (and
European Economic Area (EEA)) membership (as is the case with Gibraltar), would also have been significantly affected by the outcome and impact of the referendum.
Campaign

In October 2015,
Britain Stronger in Europe, a cross-party group campaigning for Britain to remain a member of the EU, was formed. There were two rival groups promoting British withdrawal from the EU that sought to become the official Leave campaign:
Leave.EU (which was endorsed by most of
UKIP, including
Nigel Farage), and
Vote Leave (endorsed by Conservative Party Eurosceptics). In January 2016,
Nigel Farage and the Leave.EU campaign became part of the
Grassroots Out
Grassroots Out (GO) was an organisation funded by Arron Banks that campaigned in favour of EU withdrawal in the 2016 referendum on EU membership in the United Kingdom. The organisation was formed in January 2016, as a result of infighting bet ...
movement, which was borne out of infighting between Vote Leave and Leave.EU campaigners. In April, the
Electoral Commission announced that Britain Stronger in Europe and Vote Leave were to be designated as the official remain and leave campaigns respectively. This gave them the right to spend up to £7,000,000, a free mailshot, TV broadcasts and £600,000 in public funds. The UK Government's official position was to support the Remain campaign. Nevertheless, Cameron announced that Conservative Ministers and MPs were free to campaign in favour of remaining in the EU or leaving it, according to their conscience. This decision came after mounting pressure for a
free vote for ministers. In an exception to the usual rule of
cabinet collective responsibility, Cameron allowed cabinet ministers to campaign publicly for EU withdrawal. A Government-backed campaign was launched in April. On 16 June, all official national campaigning was suspended until 19 June following the
murder of Jo Cox.
After internal polls suggested that 85% of the UK population wanted more information about the referendum from the government, a leaflet was sent to every household in the UK. It contained details about why the government believed the UK should remain in the EU. This leaflet was criticised by those wanting to leave as giving the remain side an unfair advantage; it was also described as being inaccurate and a waste of taxpayers' money (it cost £9.3m in total).
In the week beginning on 16 May, the
Electoral Commission sent a voting guide regarding the referendum to every household within the UK and Gibraltar to raise awareness of the upcoming referendum. The eight-page guide contained details on how to vote, as well as a sample of the actual ballot paper, and a whole page each was given to the campaign groups Britain Stronger in Europe and Vote Leave to present their case.
The Vote Leave campaign argued that if the UK left the EU, national
sovereignty would be protected, immigration controls could be imposed, and the UK would be able to sign trade deals with the rest of the world. The UK would also be able to stop membership payments to the EU every week. The Britain Stronger in Europe campaign argued that leaving the European Union would damage the UK economy, and that the status of the UK as a world influence was hinged upon its membership.
Responses to the referendum campaign
Party policies

The tables list political parties with representation in the
House of Commons or the
House of Lords, the
European Parliament, the
Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyro ...
, the
Northern Ireland Assembly
sco-ulster, Norlin Airlan Assemblie
, legislature = 7th Northern Ireland Assembly, Seventh Assembly
, coa_pic = File:NI_Assembly.svg
, coa_res = 250px
, house_type = Unicameralism, Unicameral
, hou ...
, the
Welsh Parliament, or the
Gibraltar Parliament
The Gibraltar Parliament is the legislature of the British overseas territory of Gibraltar. Between 1969 and 2006, it was called the Gibraltar House of Assembly.
Functions
The House of Assembly, set up under the 1969 constitution, was a uni ...
at the time of the referendum.
Great Britain
Northern Ireland
Gibraltar
Minor parties
Among minor parties, the
Socialist Labour Party, the
Communist Party of Britain,
Britain First, the
British National Party (BNP),
Éirígí
Éirígí (), officially Éirígí For A New Republic, is a socialist republican political party in Ireland. The party name, , means "Arise" or "Rise Up" in Irish, and is a reference to the slogan "The great only appear great because we are on ...
,
Respect Party,
Trade Unionist and Socialist Coalition
Trade Unionist and Socialist Coalition (TUSC) is a socialist electoral alliance launched in Britain for the 2010 general election.
TUSC's co-founder was the RMT union general secretary Bob Crow. Members of the PCS, NUT, FBU and POA unio ...
(TUSC), the
Social Democratic Party
The name Social Democratic Party or Social Democrats has been used by many political parties in various countries around the world. Such parties are most commonly aligned to social democracy as their political ideology.
Active parties
For ...
,
Liberal Party, and
Independence from Europe
Independence from Europe was a minor, Eurosceptic political party in the United Kingdom. The party was first registered in June 2012 but remained inactive until it was launched in October 2013 by sole party leader Mike Nattrass, a disaffected m ...
, and the
Workers' Party of Ireland, supported leaving the EU. The
Scottish Socialist Party (SSP),
Left Unity and
Mebyon Kernow supported remaining in the EU. The
Socialist Party of Great Britain
The Socialist Party of Great Britain (SPGB) is a socialist political party in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1904 as a split from the Social Democratic Federation (SDF), it advocates using the ballot box for revolutionary purposes and oppos ...
supported neither leave nor remain and the
Women's Equality Party had no official position on the issue.
Cabinet ministers
The
Cabinet of the United Kingdom
The Cabinet of the United Kingdom is the senior decision-making body of His Majesty's Government. A committee of the Privy Council, it is chaired by the prime minister and its members include secretaries of state and other senior ministers.
T ...
is a body responsible for making decisions on policy and organising
governmental departments; it is chaired by the Prime Minister and contains most of the government's ministerial heads. Following the announcement of the referendum in February, 23 of the 30 Cabinet ministers (including attendees) supported the UK staying in the EU.
, in favour of leaving, resigned on 19 March and was replaced by
Stephen Crabb
Stephen Crabb (born 20 January 1973) is a British politician who has served as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Preseli Pembrokeshire since 2005 and Chairman of the Welsh Affairs Select Committee since 2020. A member of the Welsh Conservative ...
who was in favour of remaining.
Crabb was already a cabinet member, as the
Secretary of State for Wales, and his replacement,
Alun Cairns, was in favour of remaining, bringing the total number of pro-remain Cabinet members to 25.
Business
Various UK multinationals have stated that they would not like the UK to leave the EU because of the uncertainty it would cause, such as
Shell,
BT and
Vodafone, with some assessing the
pros and cons of Britain exiting. The banking sector was one of the most vocal advocating to stay in the EU, with the
British Bankers' Association saying: "Businesses don't like that kind of uncertainty".
RBS
RBS may refer to:
Organisations Banking
* The Royal Bank of Scotland, a retail banking subsidiary of NatWest Group
** RBS International, the offshore banking arm of NatWest Group
Education
* Regent's Business School
* Rotterdam Business School
...
warned of potential damage to the economy. Furthermore,
HSBC
HSBC Holdings plc is a British multinational universal bank and financial services holding company. It is the largest bank in Europe by total assets ahead of BNP Paribas, with US$2.953 trillion as of December 2021. In 2021, HSBC had $10.8 tri ...
and foreign-based banks
JP Morgan and
Deutsche Bank claim a Brexit might result in the banks' changing domicile. According to
Goldman Sachs
Goldman Sachs () is an American multinational investment bank and financial services company. Founded in 1869, Goldman Sachs is headquartered at 200 West Street in Lower Manhattan, with regional headquarters in London, Warsaw, Bangalore, H ...
and the
City of London's policy chief, all such factors could impact on the City of London's present status as a European and global market leader in financial services. In February 2016, leaders of 36 of the
FTSE 100 companies, including Shell,
BAE Systems
BAE Systems plc (BAE) is a British multinational arms, security, and aerospace company based in London, England. It is the largest defence contractor in Europe, and ranked the seventh-largest in the world based on applicable 2021 revenues. ...
, BT and
Rio Tinto, officially supported staying in the EU. Moreover, 60% of the
Institute of Directors and the
EEF memberships supported staying.
Many UK-based businesses, including
Sainsbury's, remained steadfastly neutral, concerned that taking sides in the divisive issue could lead to a backlash from customers.
Richard Branson
Sir Richard Charles Nicholas Branson (born 18 July 1950) is a British billionaire, entrepreneur, and business magnate. In the 1970s he founded the Virgin Group, which today controls more than 400 companies in various fields.
Branson expressed ...
stated that he was "very fearful" of the consequences of a UK exit from the EU.
Alan Sugar expressed similar concern.
James Dyson, founder of the
Dyson company, argued in June 2016 that the introduction of tariffs would be less damaging for British exporters than the appreciation of the pound against the Euro, arguing that, because Britain ran a 100 billion pound
trade deficit with the EU, tariffs could represent a significant revenue source for the Treasury.
[Sir James Dyson: 'So if we leave the EU no one will trade with us? Cobblers...']
A. Pearson, ''The Daily Telegraph'' (London), 10 June 2016 Pointing out that languages, plugs and laws differ between EU member states, Dyson said that the 28-country bloc was not a
single market, and argued the fastest growing markets were outside the EU.
Engineering company
Rolls-Royce wrote to employees to say that it did not want the UK to leave the EU.
Surveys of large UK businesses showed a strong majority favoured the UK remaining in the EU.
Small and medium-sized UK businesses were more evenly split.
Polls of foreign businesses found that around half would be less likely to do business in the UK, while 1% would increase their investment in the UK. Two large car manufacturers,
Ford and
BMW, warned in 2013 against Brexit, suggesting it would be "devastating" for the economy. Conversely, in 2015, some other manufacturing executives told Reuters that they would not shut their plants if the UK left the EU, although future investment might be put at risk. The CEO of
Vauxhall
Vauxhall ( ) is a district in South West London, part of the London Borough of Lambeth, England. Vauxhall was part of Surrey until 1889 when the County of London was created. Named after a medieval manor, "Fox Hall", it became well known for ...
stated that a Brexit would not materially affect its business. Foreign-based
Toyota CEO
Akio Toyoda confirmed that, whether or not Britain left the EU, Toyota would carry on manufacturing cars in Britain as they had done before.
Exchange rates and stock markets
In the week following conclusion of the
UK's renegotiation (and especially after
Boris Johnson announced that he would support the UK leaving), the pound fell to a seven-year low against the dollar and economists at
HSBC
HSBC Holdings plc is a British multinational universal bank and financial services holding company. It is the largest bank in Europe by total assets ahead of BNP Paribas, with US$2.953 trillion as of December 2021. In 2021, HSBC had $10.8 tri ...
warned that it could drop even more. At the same time, Daragh Maher, head of HSBC, suggested that if Sterling dropped in value so would the Euro. European banking analysts also cited Brexit concerns as the reason for the Euro's decline. Immediately after a poll in June 2016 showed that the Leave campaign was 10 points ahead, the pound dropped by a further one per cent. In the same month, it was announced that the value of goods exported from the UK in April had shown a month-on-month increase of 11.2%, "the biggest rise since records started in 1998".
Uncertainty over the referendum result, together with several other factors—US interest rates rising, low commodity prices, low Eurozone growth and concerns over emerging markets such as China—contributed to a high level of stock market volatility in January and February 2016. On 14 June, polls showing that a Brexit was more likely led to the FTSE 100 falling by 2%, losing £98 billion in value. After further polls suggested a move back towards Remain, the pound and the FTSE recovered.
On the day of the referendum, sterling hit a 2016 high of $1.5018 for £1 and the FTSE 100 also climbed to a 2016 high, as a new poll suggested a win for the Remain campaign. Initial results suggested a vote for 'Remain' and the value of the pound held its value. However, when the result for
Sunderland
Sunderland () is a port city in Tyne and Wear, England. It is the City of Sunderland's administrative centre and in the Historic counties of England, historic county of County of Durham, Durham. The city is from Newcastle-upon-Tyne and is on t ...
was announced, it indicated an unexpected swing to 'Leave'. Subsequent results appeared to confirm this swing and sterling fell in value to $1.3777, its lowest level since 1985. On the following Monday when the markets opened, £1 sterling fell to a new low of $1.32.
Muhammad Ali Nasir and Jamie Morgan two British economists differentiated and reflected on the weakness of the Sterling due to the weak external position of the UK's economy and the further role played by the uncertainty surrounding Brexit
They reported that during the week of the referendum, up to the declaration of the result, exchange rate depreciation deviated from the long-run trend by approximately 3.5 per cent, but the actual immediate effect on the exchange rate was an 8 per cent depreciation. Furthermore, that over the period from the announcement of the referendum, the exchange rate fluctuated markedly around its trend and one can also identify a larger effect based on the "wrong-footing" of markets at the point when the outcome was announced.
When the
London Stock Exchange opened on the morning of 24 June, the FTSE 100 fell from 6338.10 to 5806.13 in the first ten minutes of trading. It recovered to 6091.27 after a further 90 minutes, before further recovering to 6162.97 by the end of the day's trading. When the markets reopened the following Monday, the FTSE 100 showed a steady decline losing over 2% by mid-afternoon. Upon opening later on the Friday after the referendum, the US
Dow Jones Industrial Average dropped nearly 450 points or about 2½% in less than half an hour. The
Associated Press called the sudden worldwide stock market decline a
stock market crash.
Investors in worldwide stock markets lost more than the equivalent of
US$
The United States dollar (symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official ...
2 trillion on 24 June 2016, making it the worst single-day
loss in history, in absolute terms.
The market losses amounted to US$3 trillion by 27 June.
fell to a 31-year low against the US dollar. The UK's and the EU's sovereign debt
credit ratings were also lowered to AA by
Standard & Poor's
S&P Global Ratings (previously Standard & Poor's and informally known as S&P) is an American credit rating agency (CRA) and a division of S&P Global that publishes financial research and analysis on stocks, bonds, and commodities. S&P is con ...
.
By mid-afternoon on 27 June 2016, sterling was at a 31-year low, having fallen 11% in two trading days, and the FTSE 100 had surrendered £85 billion; however, by 29 June it had recovered all its losses since the markets closed on polling day and the value of the pound had begun to rise.
European responses
The referendum was generally well-accepted by the European far right.
Marine Le Pen
Marion Anne Perrine "Marine" Le Pen (; born 5 August 1968) is a French lawyer and politician who ran for the French presidency in 2012, 2017, and 2022. A member of the National Rally (RN; previously the National Front, FN), she served as its pre ...
, the leader of the French
''Front national'', described the possibility of a Brexit as "like the
fall of the Berlin Wall" and commented that "Brexit would be marvellous – extraordinary – for all European peoples who long for freedom".
A poll in France in April 2016 showed that 59% of the French people were in favour of Britain remaining in the EU.
Dutch politician
Geert Wilders, leader of the
Party for Freedom
The Party for Freedom ( nl, Partij voor de Vrijheid, PVV) is a nationalist, right-wing populist political party in the Netherlands.
Founded in 2006 as the successor to Geert Wilders' one-man faction in the House of Representatives, it won nine ...
, said that the
Netherlands should follow Britain's example: "Like in the 1940s, once again Britain could help liberate Europe from another totalitarian monster, this time called 'Brussels'. Again, we could be saved by the British."
Polish President
Andrzej Duda lent his support for the UK remaining within the EU. Moldovan Prime Minister
Pavel Filip asked all citizens of Moldova living in the UK to speak to their British friends and convince them to vote for the UK to remain in the EU. Spanish foreign minister
José García-Margallo said Spain would demand control of
Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
the "very next day" after a British withdrawal from the EU. Margallo also threatened to close the border with Gibraltar if Britain left the EU.
Swedish foreign minister
Margot Wallström said on 11 June 2016 that if Britain left the EU, other countries would have referendums on whether to leave the EU, and that if Britain stayed in the EU, other countries would negotiate, ask and demand to have special treatment. Czech prime minister
Bohuslav Sobotka suggested in February 2016 that the Czech Republic would start discussions on leaving the EU if the UK voted for an EU exit.
Non-European responses
International Monetary Fund
Christine Lagarde, the managing director of the
International Monetary Fund, warned in February 2016 that the uncertainty over the outcome of the referendum would be bad "in and of itself" for the British economy.
In response, Leave campaigner
Priti Patel
Priti Sushil Patel (born 29 March 1972) is a British politician who served as Home Secretary from 2019 to 2022. A member of the Conservative Party, she was Secretary of State for International Development from 2016 to 2017. Patel has been the Me ...
said a previous warning from the IMF regarding the
coalition government's deficit plan for the UK was proven incorrect and that the IMF "were wrong then and are wrong now".
United States
In October 2015,
United States Trade Representative
The Office of the United States Trade Representative (USTR) is an agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government responsible for developing and promoting Trade policy of the United States, American trade ...
Michael Froman declared that the United States was not keen on pursuing a separate
free-trade agreement (FTA) with Britain if it were to leave the EU, thus, according to ''
The Guardian'' newspaper, undermining a key economic argument of proponents of those who say Britain would prosper on its own and be able to secure bilateral FTAs with trading partners. Also in October 2015, the
United States Ambassador to the United Kingdom Matthew Barzun said that UK participation in NATO and the EU made each group "better and stronger" and that, while the decision to remain or leave is a choice for the British people, it was in the US interest that it remain. In April 2016, eight former
US Secretaries of the Treasury, who had served both
Democratic and
Republican presidents, urged Britain to remain in the EU.
In July 2015, President
Barack Obama confirmed the long-standing US preference for the UK to remain in the EU. Obama said: "Having the UK in the EU gives us much greater confidence about the strength of the transatlantic union, and is part of the cornerstone of the institutions built following
World War II that has made the world safer and more prosperous. We want to make sure that the United Kingdom continues to have that influence." Some Conservative MPs accused U.S. President
Barack Obama of interfering in the Brexit vote, with
Boris Johnson calling the intervention a "piece of outrageous and exorbitant hypocrisy" and UKIP leader
Nigel Farage accusing him of "monstrous interference", saying "You wouldn't expect the British Prime Minister to intervene in your presidential election, you wouldn't expect the Prime Minister to endorse one candidate or another."
Obama's intervention was criticised by Republican Senator
Ted Cruz as "a slap in the face of British self-determination as the president, typically, elevated an international organisation over the rights of a sovereign people", and stated that "Britain will be at the front of the line for a free trade deal with America", were Brexit to occur. More than 100 MPs from the Conservatives, Labour, UKIP and the
DUP wrote a letter to the U.S. ambassador in London asking President Obama not to intervene in the Brexit vote as it had "long been the established practice not to interfere in the domestic political affairs of our allies and we hope that this will continue to be the case." Two years later, one of Obama's former aides recounted that the public intervention was made following a request by Cameron.
Prior to the vote, Republican presidential candidate
Donald Trump anticipated that Britain would leave based on its concerns over migration, while Democratic presidential candidate
Hillary Clinton hoped that Britain would remain in the EU to strengthen transatlantic co-operation.
Other states
In October 2015, Chinese President
Xi Jinping declared his support for Britain remaining in the EU, saying "China hopes to see a prosperous Europe and a united EU, and hopes Britain, as an important member of the EU, can play an even more positive and constructive role in promoting the deepening development of China-EU ties". Chinese diplomats have stated "off the record" that the People's Republic sees the EU as a counterbalance to American economic power, and that an EU without Britain would mean a stronger United States.
In February 2016, the finance ministers from the
G20 major economies warned for the UK to leave the EU would lead to "a shock" in the global economy.
In May 2016, the Australian Prime Minister
Malcolm Turnbull said that Australia would prefer the UK to remain in the EU, but that it was a matter for the British people, and "whatever judgment they make, the relations between Britain and Australia will be very, very close".
Indonesian president
Joko Widodo
Joko Widodo (; born 21 June 1961), popularly known as Jokowi, is an Indonesian politician and businessman who is the 7th and current president of Indonesia. Elected in July 2014, he was the first Indonesian president not to come from an elite ...
stated during a European trip that he was not in favour of Brexit.
Sri Lankan Prime Minister
Ranil Wickremesinghe issued a statement of reasons why he was "very concerned" at the possibility of Brexit.
Russian President
Vladimir Putin said: "I want to say it is none of our business, it is the business of the people of the UK."
Maria Zakharova
Maria Vladimirovna Zakharova (russian: Мария Владимировна Захарова; born 24 December 1975) is the Director of the Information and Press Department of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation (Spokesw ...
, the official Russian foreign ministry spokesperson, said: "Russia has nothing to do with Brexit. We are not involved in this process in any way. We don't have any interest in it."
Economists
In November 2015, the Governor of the
Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the English Government's banker, and still one of the bankers for the Government of ...
Mark Carney said that the Bank of England would do what was necessary to help the UK economy if the British people voted to leave the EU. In March 2016, Carney told MPs that an EU exit was the "biggest domestic risk" to the UK economy, but that remaining a member also carried risks, related to the
European Monetary Union, of which the UK is not a member. In May 2016, Carney said that a "technical recession" was one of the possible risks of the UK leaving the EU. However, Iain Duncan Smith said Carney's comment should be taken with "a pinch of salt", saying "all forecasts in the end are wrong".
In December 2015, the Bank of England published a report about the impact of immigration on wages. The report concluded that immigration put downward pressure on workers' wages, particularly low-skilled workers: a 10 percent point rise in the proportion of migrants working in low-skilled services drove down the average wages of low-skilled workers by about 2 percent.
[The impact of immigration on occupational wages: evidence from Britain]
S. Nickell and J. Saleheen, Staff Working Paper No. 574, Bank of England (2015) The 10 percentage point rise cited in the paper is larger than the entire rise observed since the 2004–06 period in the semi/unskilled services sector, which is about 7 percentage points.
In March 2016, Nobel prize-winning economist
Joseph Stiglitz
Joseph Eugene Stiglitz (; born February 9, 1943) is an American New Keynesian economist, a public policy analyst, and a full professor at Columbia University. He is a recipient of the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences (2001) and the Joh ...
argued that he might reconsider his support for the UK remaining in the EU if the proposed
Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) were to be agreed to.
[EU referendum: UK could be better off leaving if TTIP passes, Joseph Stiglitz says]
H. Sheffield, ''The Independent'', 2 March 2016 Stiglitz warned that under the
investor-state dispute settlement provision in current drafts of the TTIP, governments risked being sued for loss of profits resulting from new regulations, including health and safety regulations to limit the use of
asbestos
Asbestos () is a naturally occurring fibrous silicate mineral. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous crystals, each fibre being composed of many microscopic "fibrils" that can be released into the atmosphere b ...
or tobacco.
The German economist
Clemens Fuest
Clemens Fuest (born 23 August 1968) is a German economist who has been President of the Ifo Institute for Economic Research and director of the Center for Economic Studies at the University of Munich (LMU) since 2016.
Career
Between 2008 and 201 ...
wrote that there was a liberal, free-trade bloc in the EU comprising the UK, the Netherlands, the Czech Republic, Sweden, Denmark, Ireland, Slovakia, Finland, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania, controlling 32% of the votes in the European Council and standing in opposition to the ''
dirigiste
Dirigisme or dirigism () is an economic doctrine in which the state plays a strong directive (policies) role contrary to a merely regulatory interventionist role over a market economy. As an economic doctrine, dirigisme is the opposite of ''lai ...
'', protectionist policies favoured by France and its allies.
Germany with its 'social market' economy stands midway between the French ''dirigiste'' economic model and the British free-market economic model. From the German viewpoint, the existence of the liberal bloc allows Germany to play-off free-market Britain against ''dirigiste'' France, and that if Britain were to leave, the liberal bloc would be severely weakened, thereby allowing the French to take the EU into a much more ''dirigiste'' direction that would be unattractive from the standpoint of Berlin.
A study by Oxford Economics for the
Law Society of England and Wales has suggested that Brexit would have a particularly large negative impact on the UK financial services industry and the law firms that support it, which could cost the law sector as much as £1.7bn per annum by 2030. The Law Society's own report into the possible effects of Brexit notes that leaving the EU would be likely to reduce the role played by the UK as a centre for resolving disputes between foreign firms, whereas a potential loss of "
passporting" rights would require financial services firms to transfer departments responsible for regulatory oversight overseas.
World Pensions Forum director M. Nicolas J. Firzli has argued that the Brexit debate should be viewed within the broader context of
economic analysis of EU law and regulation in relation to
English common law, arguing: "Every year, the British Parliament is forced to pass tens of new statutes reflecting the latest EU directives coming from Brussels – a highly undemocratic process known as '
transposition'... Slowly but surely, these new laws dictated by EU commissars are conquering English common law, imposing upon UK businesses and citizens an ever-growing collection of fastidious regulations in every field".
Thiemo Fetzer, professor of economics from
University of Warwick, analyzed the welfare reforms in the UK since 2000 and suggests that numerous austerity-induced welfare reforms from 2010 onwards have stopped contributing to mitigate income differences through transfer payments. This could be a key activating factor of anti-EU preferences that lie behind the development of economic grievances and the lack of support in a Remain victory.
Michael Jacobs, the current director of the Commission on Economic Justice at the Institute for Public Policy Research and Mariana Mazzucato, a professor in University College London in Economics of Innovation and Public Value have found that the Brexit campaign had the tendency to blame external forces for domestic economic problems and have argued that the problems within the economy wasn't due to 'unstoppable forces of globalisation' but rather the result of active political and business decisions. Instead, they claim that orthodox economic theory has guided poor economic policy such as investment and that has been the cause of problems within the British economy.
Institute for Fiscal Studies
In May 2016, the
Institute for Fiscal Studies said that an EU exit could mean two more years of austerity cuts as the government would have to make up for an estimated loss of £20 billion to £40 billion of tax revenue. The head of the IFS, Paul Johnson, said that the UK "could perfectly reasonably decide that we are willing to pay a bit of a price for leaving the EU and regaining some sovereignty and control over immigration and so on. That there would be some price though, I think is now almost beyond doubt."
Lawyers
A poll of lawyers conducted by a legal recruiter in late May 2016 suggested 57% of lawyers wanted to remain in the EU.
During a Treasury Committee shortly following the vote, economic experts generally agreed that the leave vote would be detrimental to the UK economy.
Michael Dougan, Professor of European Law and
Jean Monnet Chair in EU Law at the
University of Liverpool and a constitutional lawyer, described the Leave campaign as "one of the most dishonest political campaigns this country
he UK
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' in ...
has ever seen", for using arguments based on constitutional law that he said were readily demonstrable as false.
NHS officials
Simon Stevens, head of NHS England, warned in May 2016 that a recession following a Brexit would be "very dangerous" for the National Health Service, saying that "when the British economy sneezes, the NHS catches a cold." Three-quarters of a sample of NHS leaders agreed that leaving the EU would have a negative effect on the NHS as a whole. In particular, eight out of 10 respondents felt that leaving the EU would have a negative impact on trusts' ability to recruit health and social care staff. In April 2016, a group of nearly 200 health professionals and researchers warned that the NHS would be in jeopardy if Britain left the European Union. The leave campaign reacted by saying more money would be available to be spent on the NHS if the UK left the EU.
British health charities
Guidelines by the
Charity Commission for England and Wales
, type = Non-ministerial government department
, seal =
, seal_caption =
, logo = Charity Commission for England and Wales logo.svg
, logo_caption =
, formed =
, preceding1 =
, d ...
that forbid political activity for registered charities have limited UK health organizations' commentary on EU poll, according to anonymous sources consulted by the Lancet.
According to
Simon Wessely
Sir Simon Charles Wessely (born 23 December 1956) is a British psychiatrist. He is Regius Professor of Psychiatry at the Institute of Psychiatry, King's College London and head of its department of psychological medicine, vice dean for academi ...
, head of psychological medicine at the Institute of Psychiatry, King's College London – neither a special revision of the guidelines from 7 March 2016, nor Cameron's encouragement have made health organisations, willing to speak out.
The
Genetic Alliance UK
Genetic Alliance UK is a national charity and an alliance of over 200 patient organisations, supporting those affected by genetic conditions. Genetic Alliance UK's aim is to improve the lives of people affected by genetic conditions, ensuring tha ...
the
Royal College of Midwives
The Royal College of Midwives (RCM) is a British midwives organisation founded in 1881 by Louisa Hubbard and Zepherina Veitch. It has existed under its present name since 1947, and is the United Kingdom's only trade union or professional organis ...
the
and the Chief Executive of the
National Health Service had all stated pro-remain positions by early June 2016.
Fishing industry
A June 2016 survey of British fishermen found that 92% intended to vote to leave the EU.
The EU's
Common Fisheries Policy
The Common Fisheries Policy (CFP) is the fisheries policy of the European Union (EU). It sets quotas for which member states are allowed to catch each type of fish, as well as encouraging the fishing industry by various market interventions. I ...
was mentioned as a central reason for their near-unanimity.
More than three-quarters believed that they would be able to land more fish, and 93% stated that leaving the EU would benefit the fishing industry.
Historians
In May 2016, more than 300 historians wrote in a joint letter to ''The Guardian'' that Britain could play a bigger role in the world as part of the EU. They said: "As historians of Britain and of Europe, we believe that Britain has had in the past, and will have in the future, an irreplaceable role to play in Europe." On the other hand, many historians argued in favour of leaving, seeing it as a return to self-sovereignty.
Exit plan competition
Following
David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron (born 9 October 1966) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2010 to 2016 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2005 to 2016. He previously served as Leader o ...
's announcement of an EU referendum, British
think tank the
Institute of Economic Affairs (IEA) announced in July 2013 a competition to find the best plan for a UK exit from the European Union, declaring that a departure is a "real possibility" following the 2015 general election.
Iain Mansfield, a
Cambridge graduate and
UKTI diplomat, submitted the winning thesis: ''A Blueprint for Britain: Openness not Isolation''.
Mansfield's submission focused on addressing both trade and regulatory issues with
EU member states
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
as well as other
global trading partners.
Opinion polling

Opinion polls from 2010 onwards suggested the British public were relatively evenly divided on the question, with opposition to EU membership peaking in November 2012 at 56% compared with 30% who prefer to remain in, while in June 2015 those in favour of Britain remaining in the EU reached 43% versus those opposed 36%. The largest ever poll (of 20,000 people, in March 2014) showed the public evenly split on the issue, with 41% in favour of withdrawal, 41% in favour of membership, and 18% undecided. However, when asked how they would vote if Britain renegotiated the terms of its membership of the EU, and the UK Government stated that British interests had been satisfactorily protected, more than 50% indicated that they would vote for Britain to stay in.
Analysis of polling suggested that young voters tended to support remaining in the EU, whereas those older tend to support leaving, but there was no gender split in attitudes. In February 2016 YouGov also found that euroscepticism correlated with people of lower income and that "higher social grades are more clearly in favour of remaining in the EU", but noted that euroscepticism also had strongholds in "the more wealthy, Tory shires".
Scotland, Wales and many English urban areas with large student populations were more pro-EU.
[ Big business was broadly behind remaining in the EU, though the situation among smaller companies was less clear-cut. In polls of economists, lawyers, and scientists, clear majorities saw the UK's membership of the EU as beneficial.]Spreadex
Spreadex is a British-based company that offers financial spread betting, sports spread betting, and sports fixed-odds betting.
History
Spreadex commenced trading in 1999 in Dunstable, Bedfordshire. It was founded by former City dealer Jonathan ...
offered a Leave Vote Share spread of 45–46, a Remain Vote Share spread of 53.5-54.5, and a Remain Binary Index spread of 80–84.7, where victory for Remain would makeup to 100 and a defeat 0.
On the day YouGov poll
Shortly after the polls closed at 10 pm on 23 June, the British polling company YouGov released a poll conducted among almost 5,000 people on the day; it suggested a narrow lead for "Remain", which polled 52% with Leave polling 48%. It was later criticised for overestimating the margin of the "Remain" vote, when it became clear a few hours later that the UK had voted 51.9% to 48.1% in favour of leaving the European Union.
Issues
The number of jobs lost or gained by a withdrawal was a dominant issue; the BBC's outline of issues warned that a precise figure was difficult to find. The Leave campaign argued that a reduction in red tape associated with EU regulations would create more jobs and that small to medium-sized companies who trade domestically would be the biggest beneficiaries. Those arguing to remain in the EU, claimed that millions of jobs would be lost. The EU's importance as a trading partner and the outcome of its trade status if it left was a disputed issue. Whereas those wanting to stay cited that most of the UK's trade was made with the EU, those arguing to leave say that its trade was not as important as it used to be. Scenarios of the economic outlook for the country if it left the EU were generally negative. The United Kingdom also paid more into the EU budget than it received.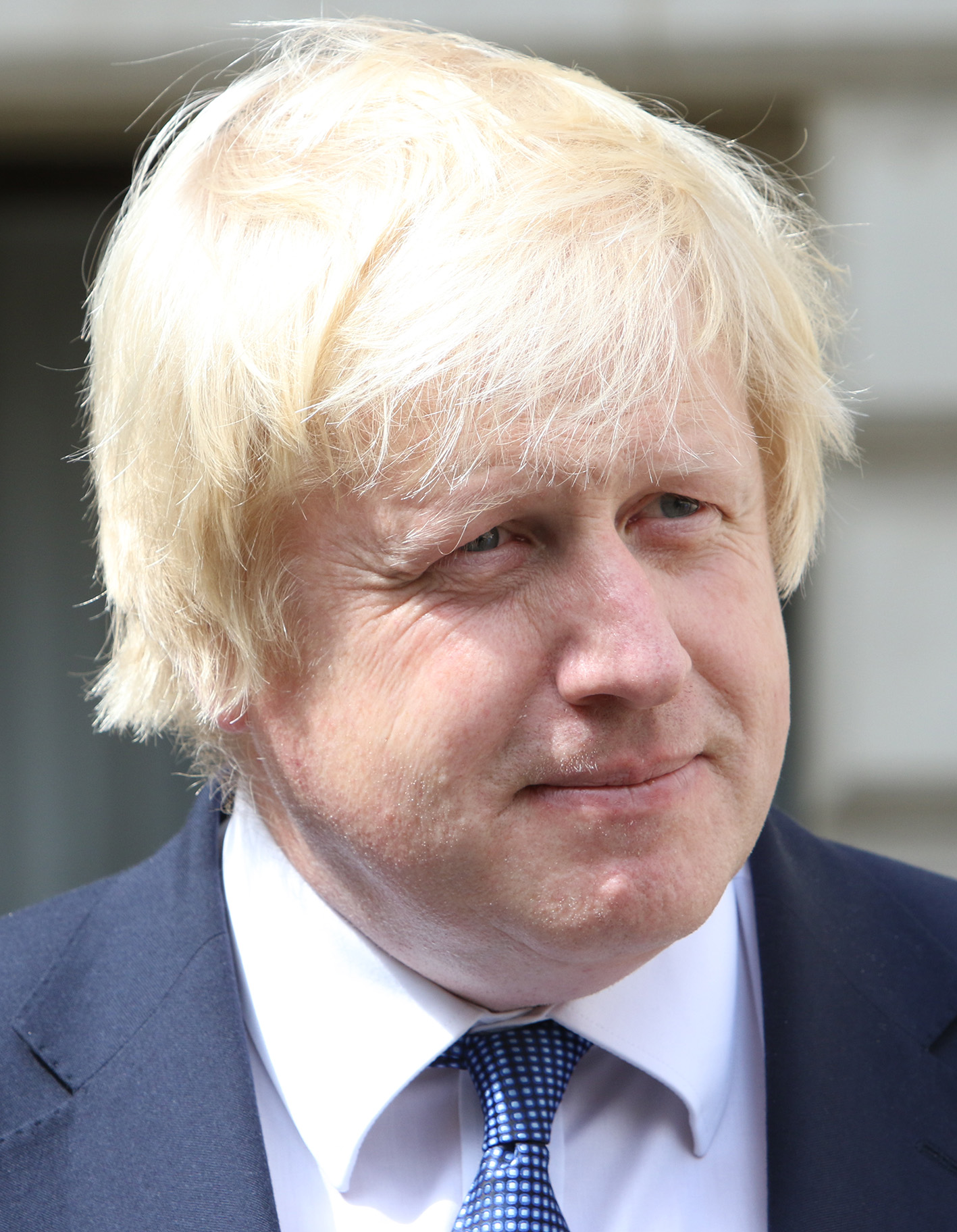 Citizens of EU countries, including the United Kingdom, have the right to travel, live and work within other EU countries, as free movement is one of the four founding principles of the EU. Campaigners for remaining said that EU immigration had positive impacts on the UK's economy, citing that the country's growth forecasts were partly based upon continued high levels of net immigration.
Citizens of EU countries, including the United Kingdom, have the right to travel, live and work within other EU countries, as free movement is one of the four founding principles of the EU. Campaigners for remaining said that EU immigration had positive impacts on the UK's economy, citing that the country's growth forecasts were partly based upon continued high levels of net immigration.[ The Office for Budget Responsibility also claimed that taxes from immigrants boost public funding.][ A recent academic paper suggests that migration from Eastern Europe put pressure on wage growth at the lower end of the wage distribution, while at the same time increasing pressures on public services and housing. The Leave campaign believed reduced immigration would ease pressure in public services such as schools and hospitals, as well as giving British workers more jobs and higher wages.][ According to official Office for National Statistics data, net migration in 2015 was 333,000, which was the second highest level on record, far above David Cameron's target of tens of thousands.][EU Referendum: Record number of migrants arrive in UK without jobs, as Boris Johnson accuses David Cameron of "deeply damaging" faith in democracy]
L. Hughes, ''The Daily Telegraph'' (London), 26 May 2016[Migration Statistics Quarterly Report: May 2016]
ONS, 26 May 2016 Net migration from the EU was 184,000.Daniel Hannan
Daniel John Hannan, Baron Hannan of Kingsclere (born 1 September 1971) is a British writer, journalist and former politician serving as an adviser to the Board of Trade since 2020. He is the founding president of the Initiative for Free Trade ...
, predicted on the BBC programme '' Newsnight'' that the level of immigration would remain high after Brexit. "Frankly, if people watching think that they have voted and there is now going to be zero immigration from the EU, they are going to be disappointed. ... you will look in vain for anything that the Leave campaign said at any point that ever suggested there would ever be any kind of border closure or drawing up of the drawbridge."
The EU had offered David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron (born 9 October 1966) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2010 to 2016 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2005 to 2016. He previously served as Leader o ...
a so-called "emergency brake" which would have allowed the UK to withhold social benefits to new immigrants for the first four years after they arrived; this brake could have been applied for a period of seven years." That offer was still on the table at the time of the Brexit referendum, but expired when the vote determined that the UK would leave the EU.
The possibility that the UK's smaller constituent countries could vote to remain within the EU but find themselves withdrawn from the EU led to discussion about the risk to the unity of the United Kingdom. Scotland's First Minister, Nicola Sturgeon
Nicola Ferguson Sturgeon (born 19 July 1970) is a Scottish politician serving as First Minister of Scotland and Leader of the Scottish National Party (SNP) since 2014. She is the first woman to hold either position. She has been a member of ...
, made it clear that she believed that a second independence referendum would "almost certainly" be demanded by Scots if the UK voted to leave the EU but Scotland did not. The First Minister of Wales
, insignia = First Minister of Wales logo.png
, insigniasize = 120px
, insigniacaption = Logo
, flag = Flag of Wales.svg
, flagsize = 120px
, flagborder = yes
, flagcaption = Flag of Wales
, image = File:Mark Drakeford (cropped).jpg
, ...
, Carwyn Jones, said: "If Wales votes to remain in he EU
He or HE may refer to:
Language
* He (pronoun), an English pronoun
* He (kana), the romanization of the Japanese kana へ
* He (letter), the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets
* He (Cyrillic), a letter of the Cyrillic script called ''He'' ...
but the UK votes to leave, there will be a... constitutional crisis. The UK cannot possibly continue in its present form if England votes to leave and everyone else votes to stay".
There was concern that the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP), a proposed trade agreement between the United States and the EU, would be a threat to the public services of EU member states. Jeremy Corbyn, on the Remain side, said that he pledged to veto TTIP in Government. John Mills, on the Leave side, said that the UK could not veto TTIP because trade pacts were decided by Qualified Majority Voting in the European Council
The European Council (informally EUCO) is a collegiate body that defines the overall political direction and priorities of the European Union. It is composed of the heads of state or government of the EU member states, the President of the E ...
.
There was debate over the extent to which the European Union membership aided security and defence in comparison to the UK's membership of NATO and the United Nations. Security concerns over the union's free movement policy were raised too, because people with EU passports were unlikely to receive detailed checks at border control.
Debates, question and answer sessions, and interviews
A debate was held by '' The Guardian'' on 15 March 2016, featuring the leader of UKIP Nigel Farage, Conservative MP Andrea Leadsom, the leader of Labour's "yes" campaign Alan Johnson and former leader of the Liberal Democrats Nick Clegg.
Earlier in the campaign, on 11 January, a debate took place between Nigel Farage and Carwyn Jones, who was at the time the First Minister of Wales and leader of the Welsh Labour Party. Reluctance to have Conservative Party members argue against one another has seen some debates split, with Leave and Remain candidates interviewed separately.
'' The Spectator'' held a debate hosted by Andrew Neil on 26 April, which featured Nick Clegg, Liz Kendall and Chuka Umunna arguing for a remain vote, and Nigel Farage, Daniel Hannan
Daniel John Hannan, Baron Hannan of Kingsclere (born 1 September 1971) is a British writer, journalist and former politician serving as an adviser to the Board of Trade since 2020. He is the founding president of the Initiative for Free Trade ...
and Labour MP Kate Hoey arguing for a leave vote. The ''Daily Express
The ''Daily Express'' is a national daily United Kingdom middle-market newspaper printed in tabloid format. Published in London, it is the flagship of Express Newspapers, owned by publisher Reach plc. It was first published as a broadsheet i ...
'' held a debate on 3 June, featuring Nigel Farage, Kate Hoey and Conservative MP Jacob Rees-Mogg debating Labour MPs Siobhain McDonagh and Chuka Umunna and businessman Richard Reed
Richard John Reed, (born 13 February 1973) is a British businessman, entrepreneur and public speaker. He is the co-founder of Innocent Drinks (founded in 1999
), an international company producing fresh fruit smoothies and vegetable pots sol ...
, co-founder of Innocent drinks
Innocent Drinks is a company that produces smoothies and juice sold in supermarkets, coffee shops and various other outlets. The company sells more than two million smoothies per week. Innocent is over 90% owned by The Coca-Cola Company.
Histor ...
. Andrew Neil presented four interviews ahead of the referendum. The interviewees were Hilary Benn, George Osborne, Nigel Farage and Iain Duncan Smith on 6, 8, 10 and 17 May, respectively.
The scheduled debates and question sessions included a number of question and answer sessions with various campaigners.Angela Eagle
Dame Angela Eagle DBE (born 17 February 1961) is a British Labour Party politician serving as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Wallasey since 1992. Eagle was born in Yorkshire and studied PPE at the University of Oxford, before working for t ...
, Amber Rudd and Nicola Sturgeon
Nicola Ferguson Sturgeon (born 19 July 1970) is a Scottish politician serving as First Minister of Scotland and Leader of the Scottish National Party (SNP) since 2014. She is the first woman to hold either position. She has been a member of ...
, Boris Johnson, Andrea Leadsom, and Gisela Stuart.Frances O'Grady
Frances Lorraine Maria O'Grady, Baroness O'Grady of Upper Holloway (born 9 November 1959) became the General Secretary of the British Trades Union Congress (TUC) in 2013, the first woman to hold the position. After O'Grady presented her resignat ...
appeared for Remain. Leave was represented by the same trio as the ITV debate on 9 June (Johnson, Leadsom and Stuart). ''Europe: The Final Debate with Jeremy Paxman'' was held the following day on Channel 4.
Voting, voting areas, and counts
 Voting took place from 0700 BST (WEST) until 2200 BST (Same hours CEST in Gibraltar) in 41,000 polling stations across 382 voting areas, with each polling station limited to a maximum of 2,500 voters.
Voting took place from 0700 BST (WEST) until 2200 BST (Same hours CEST in Gibraltar) in 41,000 polling stations across 382 voting areas, with each polling station limited to a maximum of 2,500 voters.[European Referendum Act 2015]
Section 11. The referendum was held across all four countries of the United Kingdom, as well as in Gibraltar, as a single majority vote. The 382 voting areas were grouped into twelve regional counts and there was separate declarations for each of the regional counts.
In England, as happened in the 2011 AV referendum, the 326 districts
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...
were used as the local voting areas and the returns of these then fed into nine English regional counts. In Scotland the local voting areas were the 32 local councils which then fed their results into the Scottish national count, and in Wales the 22 local councils were their local voting areas before the results were then fed into the Welsh national count. Northern Ireland, as was the case in the AV referendum, was a single voting and national count area although local totals by Westminster parliamentary constituency areas were announced.
Gibraltar was a single voting area, but as Gibraltar was to be treated and included as if it were a part of South West England, its results was included together with the South West England regional count.[
The following table shows the breakdown of the voting areas and regional counts that were used for the referendum.][
]
Disturbances
On 16 June 2016, a pro-EU Labour MP, Jo Cox
Helen Joanne Cox ( Leadbeater; 22 June 1974 – 16 June 2016) was a British politician who served as Member of Parliament (MP) for Batley and Spen from May 2015 until her murder in June 2016. She was a member of the Labour Party.
Born in B ...
, was shot and killed in Birstall, West Yorkshire the week before the referendum by a man calling out "death to traitors, freedom for Britain", and a man who intervened was injured. The two rival official campaigns agreed to suspend their activities as a mark of respect to Cox.[ After the referendum, evidence emerged that Leave.EU had continued to put out advertising the day after Jo Cox's murder. ]David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron (born 9 October 1966) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2010 to 2016 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2005 to 2016. He previously served as Leader o ...
cancelled a planned rally in Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
supporting British EU membership. Campaigning resumed on 19 June. Polling officials in the Yorkshire and Humber region also halted counting of the referendum ballots on the evening of 23 June to observe a minute of silence. The Conservative Party
The Conservative Party is a name used by many political parties around the world. These political parties are generally right-wing though their exact ideologies can range from center-right to far-right.
Political parties called The Conservative P ...
, Liberal Democrats, UK Independence Party and the Green Party
A green party is a formally organized political party based on the principles of green politics, such as social justice, environmentalism and nonviolence.
Greens believe that these issues are inherently related to one another as a foundation ...
all announced that they would not contest the ensuing by-election in Cox's constituency
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger State (polity), state (a country, administrative region, ...
as a mark of respect.
On polling day itself two polling stations in Kingston upon Thames were flooded by rain and had to be relocated. In advance of polling day, concern had been expressed that the courtesy pencils provided in polling booths could allow votes to be later altered. Although this was widely dismissed as a conspiracy theory (see: Voting pencil conspiracy theory
The voting pencil conspiracy theory is a conspiracy theory that using the pencils provided in British polling stations allows the result to be changed by MI5. Promoters of the theory urge people to use pen on the basis that it makes it harder for ...
), some Leave campaigners advocated that voters should instead use pens to mark their ballot papers. On polling day in Winchester
Winchester is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs Nation ...
an emergency call was made to police about "threatening behaviour" outside the polling station. After questioning a woman who had been offering to lend her pen to voters, the police decided that no offence was being committed.
Result
 The final result was announced on Friday 24 June 2016 at 07:20 BST by then- Electoral Commission Chairwoman Jenny Watson at
The final result was announced on Friday 24 June 2016 at 07:20 BST by then- Electoral Commission Chairwoman Jenny Watson at Manchester Town Hall
Manchester Town Hall is a Victorian, Neo-gothic municipal building in Manchester, England. It is the ceremonial headquarters of Manchester City Council and houses a number of local government departments. The building faces Albert Square to th ...
after all 382 voting areas and the twelve UK regions had declared their totals. With a national turnout of 72% across the United Kingdom and Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = " Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gib ...
(representing 33,577,342 people), at least 16,788,672 votes were required to win a majority. The electorate voted to "Leave the European Union", with a majority of 1,269,501 votes (3.8%) over those who voted "Remain a member of the European Union". The national turnout of 72% was the highest ever for a UK-wide referendum, and the highest for any national vote since the 1992 general election.
Regional count results
Results by constituent countries & Gibraltar
Voter demographics and trends
Voting figures from local referendum counts and ward-level data (using local demographic information collected in the 2011 census) suggests that Leave votes were strongly correlated with lower qualifications and higher age.[Sascha O Becker, Thiemo Fetzer, Dennis Novy]
"Who voted for Brexit? A comprehensive district-level analysis"
''Economic Policy'', Volume 32, Issue 92, 1 October 2017, pp.601–650. Quotes: "We find that fundamental characteristics of the voting population were key drivers of the Vote Leave share, in particular their education profiles, their historical dependence on manufacturing employment as well as low income and high unemployment. At the much finer level of wards within cities, we find that areas with deprivation in terms of education, income and employment were more likely to vote Leave. ..A larger flow of migrants from Eastern Europe reaching a local authority area with a larger share of unqualified people or a larger share of manufacturing workers is also associated with a larger Vote Leave share". It also tended to be greater where there was a large flow of Eastern European migrants (mainly low-skilled workers) into areas with a large share of native low-skilled workers.["How the United Kingdom voted on Thursday… and why"](_blank)
Lord Ashcroft Polls. 24 June 2016. Immigration is thought to be a particular worry for older people that voted Leave, who consider it a potential threat to national identity and culture. The polling found that the main reasons people had voted Leave were "the principle that decisions about the UK should be taken in the UK", and that leaving "offered the best chance for the UK to regain control over immigration and its own borders". The main reason people voted Remain was that "the risks of voting to leave the EU looked too great when it came to things like the economy, jobs and prices".
Ipsos MORI demographic polling breakdown
On 5 September 2016, the polling company Ipsos MORI estimated the following percentage breakdown of votes in the referendum by different demographic group, as well as the percentage of turnout among registered voters in most of those demographic groups:
All: 48% Remain, 52% Leave (72% turnout)
By Gender:
Men: 45% Remain, 55% Leave (74% turnout)
Women: 51% Remain, 49% Leave (71% turnout)
By Age:
18-24: 75% Remain, 25% Leave (60% turnout)
25-34: 60% Remain, 40% Leave (66% turnout)
35-44: 55% Remain, 45% Leave (71% turnout)
45-54: 44% Remain, 56% Leave (73% turnout)
55-64: 39% Remain, 61% Leave (79% turnout)
65-74: 34% Remain, 66% Leave (82% turnout)
75+: 37% Remain, 63% Leave (73% turnout)
Men by Age:
18-34: 64% Remain, 36% Leave (64% turnout)
35-54: 44% Remain, 56% Leave (74% turnout)
55+: 35% Remain, 65% Leave (80% turnout)
Women by Age:
18-34: 67% Remain, 33% Leave (64% turnout)
35-54: 55% Remain, 45% Leave (70% turnout)
55+: 39% Remain, 61% Leave (76% turnout)
By Social Class
A social class is a grouping of people into a set of Dominance hierarchy, hierarchical social categories, the most common being the Upper class, upper, Middle class, middle and Working class, lower classes. Membership in a social class can for ...
:
AB: 59% Remain, 41% Leave (79% turnout)
C1: 52% Remain, 48% Leave (75% turnout)
C2: 38% Remain, 62% Leave (70% turnout)
DE: 36% Remain, 64% Leave (65% turnout)
Men by Class:
AB: 54% Remain, 46% Leave (81% turnout)
C1: 51% Remain, 49% Leave (75% turnout)
C2: 35% Remain, 65% Leave (70% turnout)
DE: 36% Remain, 64% Leave (67% turnout)
Women by Class:
AB: 65% Remain, 35% Leave (76% turnout)
C1: 54% Remain, 46% Leave (74% turnout)
C2: 41% Remain, 59% Leave (70% turnout)
DE: 37% Remain, 63% Leave (63% turnout)
By Educational Level:
Degree or higher: 68% Remain, 32% Leave (78% turnout)
Qualifications below degree: 44% Remain, 56% Leave (71% turnout)
No qualifications: 30% Remain, 70% Leave (71% turnout)
18-34 Year Olds by Class:
AB: 71% Remain, 29% Leave (71% turnout)
C1: 71% Remain, 29% Leave (67% turnout)
C2: 54% Remain, 46% Leave (58% turnout)
DE: 56% Remain, 44% Leave (54% turnout)
35-54 Year Olds by Class:
AB: 61% Remain, 39% Leave
C1: 53% Remain, 47% Leave
C2: 35% Remain, 65% Leave
DE: 36% Remain, 64% Leave
55+ Year Olds by Class:
AB: 48% Remain, 52% Leave
C1: 37% Remain, 63% Leave
C2: 32% Remain, 68% Leave
DE: 30% Remain, 70% Leave
By Ethnic Group:
White: 46% Remain, 54% Leave (74% turnout)
All Non-White: 69% Remain, 31% Leave (57% turnout)
More breakdown by Ethnic Group:
White: 46% Remain, 54% Leave
Black: 73% Remain, 27% Leave
South Asian: 67% Remain, 33% Leave
Chinese: 70% Remain, 30% Leave
Mixed race: 67% Remain, 33% Leave
Other: 65% Remain, 35% Leave
By Work Status:
Full-time: 53% Remain, 47% Leave
Part-time: 53% Remain, 47% Leave
Unemployed (and claiming UC or JSA): 40% Remain, 60% Leave
Not working - looking after home: 36% Remain, 64% Leave
Student: 80% Remain, 20% Leave
Retired: 36% Remain, 64% Leave
Other: 39% Remain, 61% Leave
By Housing Tenure:
Fully owned: 42% Remain, 58% Leave (79% turnout)
Mortgage: 54% Remain, 46% Leave (75% turnout)
Social renter: 37% Remain, 63% Leave (61% turnout)
Private renter: 56% Remain, 44% Leave (65% turnout)
By Work Sector:
Public sector: 56% Remain, 44% Leave
Private sector: 52% Remain, 48% Leave
By 2015 General Election vote:
Conservative: 41% Remain, 59% Leave (85% turnout)
Labour: 64% Remain, 36% Leave (77% turnout)
Lib Dem: 69% Remain, 31% Leave (81% turnout)
UKIP: 1% Remain, 99% Leave (89% turnout)
Did not vote (but not too young): 42% Remain, 58% Leave (45% turnout)
Reactions to the result

Immediate reaction to the vote
Youth protests and non-inclusion of underage citizens
The referendum was criticised for not granting people younger than 18 years of age a vote. Unlike in the 2014 Scottish independence referendum
A referendum on Scottish independence from the United Kingdom was held in Scotland on 18 September 2014. The referendum question was, "Should Scotland be an independent country?", which voters answered with "Yes" or "No". The "No" side w ...
, the vote was not extended to 16- and 17-year-old citizens. Critics argued that these people would live with the consequences of the referendum for longer than those who were able to vote. Some supporters for the inclusion of these young citizens considered this exclusion a violation of democratic principles and a major shortcoming of the referendum.
Increase of applications for passports of other EU countries
The foreign ministry of Ireland stated on 24 June 2016 that the number of applications from the UK for Irish passports had increased significantly.Irish Embassy in London
The Embassy of Ireland in London is the diplomatic mission of the Republic of Ireland in the United Kingdom. Ireland also maintains a Passport and Visa Office at 114A Cromwell Road, South Kensington.
The London mission is concurrently the non-r ...
reported 4,000 a day immediately after the vote to leave, in comparison with the normal 200 a day.
Abuse and hate crime allegations
There were more than a hundred reports of racist abuse and hate crime in the immediate aftermath of the referendum, with many citing the plan to leave the European Union.Polish Social and Cultural Association
The Polish Social and Cultural Association ( pl, Polski Ośrodek Społeczno-Kulturalny; POSK) is a Polish cultural centre in west London, England. It was funded by public subscription and founded in 1967, on the initiative of Polish engineer R ...
was vandalised with graffiti that was initially characterised as a racist hate crime. However it later emerged that the graffiti, which said, 'F*** you OMP’ may have been directed at OMP, a eurosceptic Polish think tank that had issued a statement congratulating Britain on its Brexit vote.
Petition for a new referendum
Within hours of the result's announcement, a petition, calling for a second referendum to be held in the event that a result was secured with less than 60% of the vote and on a turnout of less than 75%, attracted tens of thousands of new signatures. The petition had actually been initiated by someone favouring an exit from the EU, one William Oliver Healey of the English Democrats on 24 May 2016, when the Remain faction had been leading in the polls, and had received 22 signatures prior to the referendum result being declared.Robin Tilbrook
Robin C. W. Tilbrook (born 1958) is an English solicitor and political leader who chairs the English Democrats, a political party he founded. It advocates a devolved English Parliament, having previously advocated English independence from the ...
suggested those who had signed the petition were experiencing "sour grapes" about the result of the referendum.David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron (born 9 October 1966) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2010 to 2016 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2005 to 2016. He previously served as Leader o ...
's spokesperson stated that holding another vote on Britain's membership of the European Union was "not remotely on the cards".
Political
Conservative Party
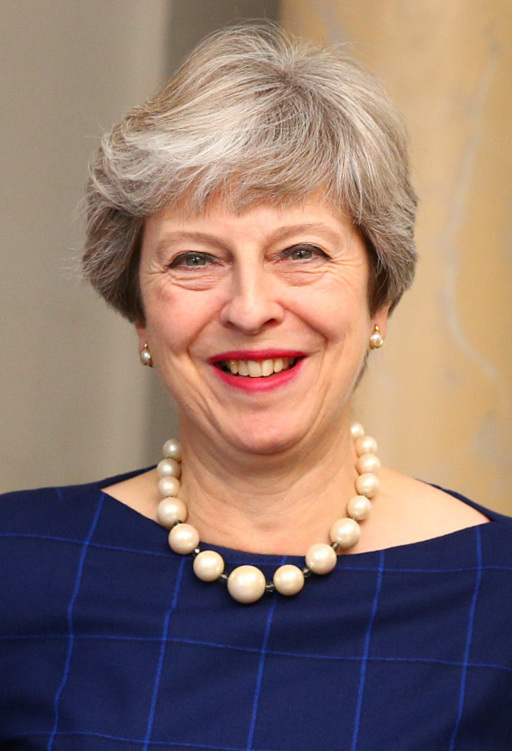
 On 24 June, the Conservative Party leader and Prime Minister
On 24 June, the Conservative Party leader and Prime Minister David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron (born 9 October 1966) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2010 to 2016 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2005 to 2016. He previously served as Leader o ...
announced that he would resign by October because the Leave campaign had been successful in the referendum. The leadership election was scheduled for 9 September. The new leader would be in place before the autumn conference set to begin on 2 October. Unexpectedly, Boris Johnson, who had been a leading figure for Vote Leave, declined to be nominated shortly before the deadline for nominations. On 13 July, almost three weeks after the vote, Theresa May succeeded Cameron as Prime Minister.
Labour Party
The Labour Party leader Jeremy Corbyn faced growing criticism from his party, which had supported remaining within the EU, for poor campaigning. On 26 June 2016, Corbyn sacked Hilary Benn (the shadow foreign secretary) for apparently leading a coup against him. This led to a string of Labour MPs quickly resigning their roles in the party. A no confidence motion was held on 28 June; Corbyn lost the motion with more than 80% (172) of MPs voting against him. Corbyn responded with a statement that the motion had no "constitutional legitimacy" and that he intended to continue as the party's leader. The vote did not require the party to call a leadership election but after Angela Eagle
Dame Angela Eagle DBE (born 17 February 1961) is a British Labour Party politician serving as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Wallasey since 1992. Eagle was born in Yorkshire and studied PPE at the University of Oxford, before working for t ...
and Owen Smith launched leadership challenges to Corbyn, the 2016 Labour Party leadership election was triggered. Corbyn won the contest, with a larger share of the vote than in 2015.
UK Independence Party
On 4 July 2016 Nigel Farage stood down as the leader of UKIP, stating that his "political ambition has been achieved" following the result of the referendum. Following the resignation of the party leader
In a governmental system, a party leader acts as the official representative of their political party, either to a legislature or to the electorate. Depending on the country, the individual colloquially referred to as the "leader" of a political ...
Diane James
Diane Martine James (born 20 November 1959) is a British politician who was a Member of the European Parliament (MEP) for South East England from 2014 to 2019. She was briefly leader-elect of the UK Independence Party (UKIP) from September 2 ...
, Farage became an interim leader on 5 October 2016. He was succeeded by Paul Nuttall
Paul Andrew Nuttall (born 30 November 1976) is a British politician who served as Leader of the UK Independence Party (UKIP) from 2016 to 2017. He was elected to the European Parliament in 2009 as a UK Independence Party (UKIP) candidate, and ...
on 28 November 2016.
Scottish independence
Scottish First Minister Nicola Sturgeon
Nicola Ferguson Sturgeon (born 19 July 1970) is a Scottish politician serving as First Minister of Scotland and Leader of the Scottish National Party (SNP) since 2014. She is the first woman to hold either position. She has been a member of ...
said on 24 June 2016 that it was "clear that the people of Scotland see their future as part of the European Union" and that Scotland had "spoken decisively" with a "strong, unequivocal" vote to remain in the European Union. On the same day, the Scottish Government announced that officials would plan for a "highly likely" second referendum on independence from the United Kingdom and start preparing legislation to that effect.
New political movement
In reaction to the lack of a unified pro-EU voice following the referendum, the Liberal Democrats and others discussed the launch of a new centre-left political movement. This was officially launched on 24 July 2016 as More United
More United is a cross-party political movement in the United Kingdom. It describes itself as a "tech-driven political startup" that supports candidates regardless of party affiliation. The movement advocates public service investment, democra ...
.
Economy
On the morning of 24 June, the pound sterling fell to its lowest level against the US dollar since 1985.Bretton Woods system
The Bretton Woods system of monetary management established the rules for commercial and financial relations among the United States, Canada, Western European countries, Australia, and Japan after the 1944 Bretton Woods Agreement. The Bretto ...
in 1971.
The FTSE 100 initially fell 8%, then recovered to be 3% down by the close of trading on 24 June. The FTSE 100 index fully recovered by 29 June and subsequently rose above its pre-referendum levels.
The referendum result also had an immediate impact on some other countries. The South African rand experienced its largest single-day decline since 2008, dropping over 8% against the United States dollar.Andy Haldane
Andrew G. Haldane, (; born 18 August 1967) is a British economist who worked at the Bank of England between 1989 and 2021 as the chief economist and executive director of monetary analysis and statistics. He resigned from the Bank of England i ...
, chief economist and the executive director of monetary analysis and statistics at the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the English Government's banker, and still one of the bankers for the Government of ...
, admitted that the bank's forecasts (predicting an economic downturn should the referendum favour Brexit) had proved inaccurate given the subsequent strong market performance.
Electoral Reform Society
In August 2016, the Electoral Reform Society published a highly critical report on the referendum and called for a review of how future events are run. Contrasting it very unfavourably with the 'well-informed grassroots' campaign for Scottish independence
Scottish independence ( gd, Neo-eisimeileachd na h-Alba; sco, Scots unthirldom) is the idea of Scotland as a sovereign state, independent from the United Kingdom, and refers to the political movement that is campaigning to bring it about.
S ...
, Katie Ghose described it as "dire" with "glaring democratic deficiencies" which left voters bewildered. Ghose noted a generally negative response to establishment figures with 29% of voters saying David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron (born 9 October 1966) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2010 to 2016 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2005 to 2016. He previously served as Leader o ...
made them more likely to vote leave whereas only 14% said he made them want to vote remain. Looking ahead, the society called for an official organisation to highlight misleading claims and for Office of Communications (Ofcom) to define the role that broadcasters were expected to play.
Television coverage
The BBC, ITV
ITV or iTV may refer to:
ITV
*Independent Television (ITV), a British television network, consisting of:
** ITV (TV network), a free-to-air national commercial television network covering the United Kingdom, the Isle of Man, and the Channel Islan ...
and Sky News
Sky News is a British free-to-air television news channel and organisation. Sky News is distributed via an English-language radio news service, and through online channels. It is owned by Sky Group, a division of Comcast. John Ryley is the hea ...
all provided live coverage of the counts and the reaction to the result. The BBC's coverage, presented by David Dimbleby, Laura Kuenssberg and John Curtice
Sir John Kevin Curtice (born 10 December 1953) is a British political scientist who is currently professor of politics at the University of Strathclyde and senior research fellow at the National Centre for Social Research. He is particularly in ...
, was simulcast domestically on BBC One and the BBC News Channel, and internationally on BBC World News. ITV's coverage was presented by Tom Bradby
Thomas Matthew Bradby (born 13 January 1967) is a British journalist and novelist who currently presents the ''ITV News at Ten''. He was previously political editor for ITV News from 2005 to 2015, and presented '' The Agenda with Tom Bradby'', ...
, Robert Peston and Allegra Stratton
Allegra Elizabeth Jane Stratton (born 10 April 1980) is a British former political aide, journalist, and writer who served as Downing Street Press Secretary under Boris Johnson from November 2020 to April 2021.
Stratton worked for ''The Guardi ...
.
The BBC called the referendum result for Leave with its projected forecast at 04:40 BST on 24 June. David Dimbleby announced it with the words:
(The remark about 1975 was technically incorrect; the UK had joined the Common Market in 1973 and the 1975 referendum was on whether to remain in it.)
Investigations into campaigns
Campaign spending
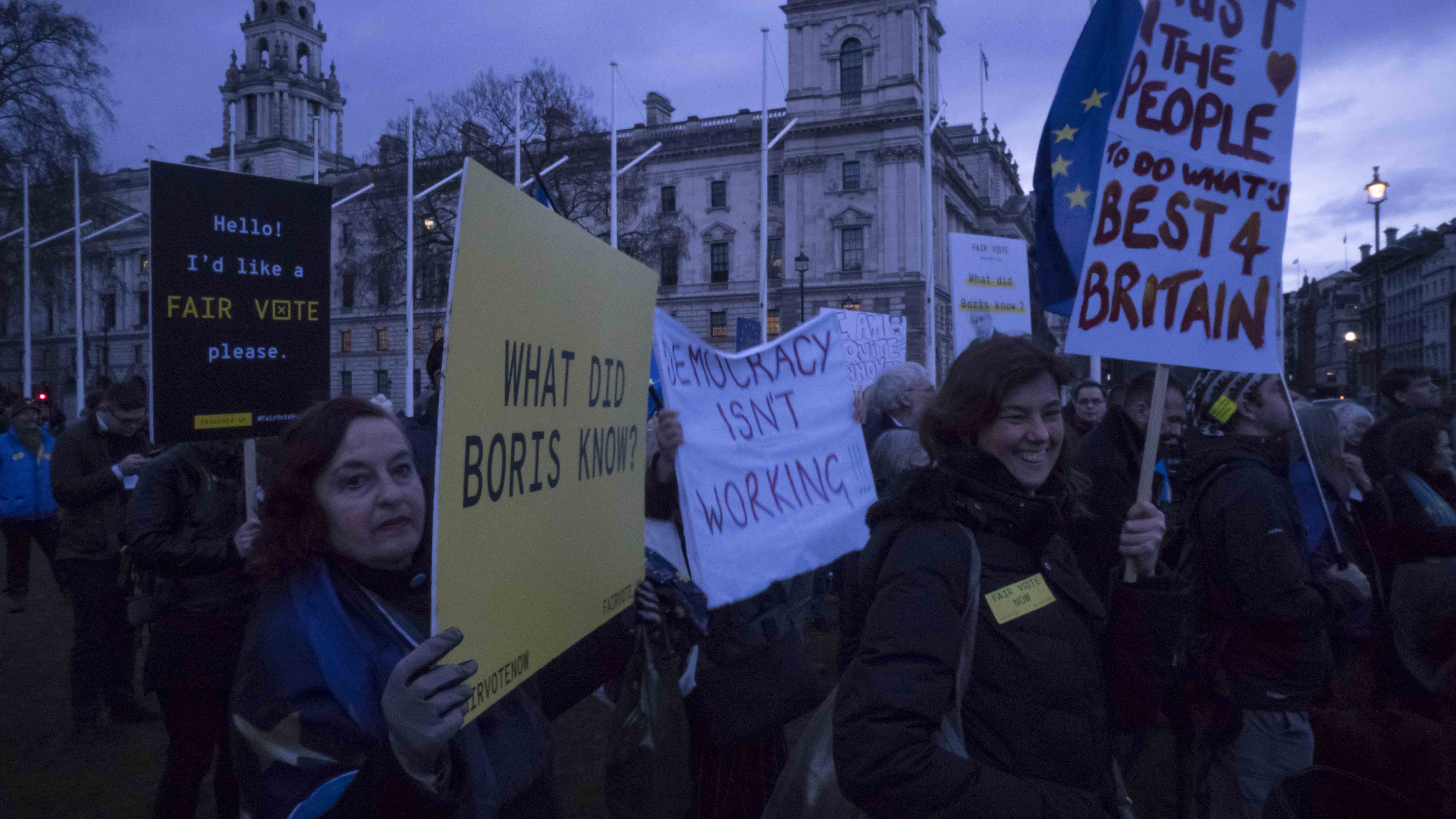 On 9 May 2016, Leave.EU was fined £50,000 by the UK Information Commissioner's Office 'for failing to follow the rules about sending marketing messages': they sent people text messages without having first gained their permission to do so.
In February 2017, the Electoral Commission announced that it was investigating the spending of Stronger in and Vote Leave, along with smaller parties, as they had not submitted all the necessary invoices, receipts, or details to back up their accounts. In April 2017, the Commission specified that 'there were reasonable grounds to suspect that potential offences under the law may have occurred' in relation to Leave.EU.
On 9 May 2016, Leave.EU was fined £50,000 by the UK Information Commissioner's Office 'for failing to follow the rules about sending marketing messages': they sent people text messages without having first gained their permission to do so.
In February 2017, the Electoral Commission announced that it was investigating the spending of Stronger in and Vote Leave, along with smaller parties, as they had not submitted all the necessary invoices, receipts, or details to back up their accounts. In April 2017, the Commission specified that 'there were reasonable grounds to suspect that potential offences under the law may have occurred' in relation to Leave.EU.analytics
Analytics is the systematic computational analysis of data or statistics. It is used for the discovery, interpretation, and communication of meaningful patterns in data. It also entails applying data patterns toward effective decision-making. It ...
, including for political purposes' in relation to the Brexit campaign. It was specified that among the organisations to be investigated was Cambridge Analytica and its relationship with the Leave.EU campaign.[Carole Cadwalladr,]
The great British Brexit robbery: how our democracy was hijacked
, ''The Observer'' (Sunday 7 May 2017).
In May 2017, '' The Irish Times'' reported that £425,622 donated by the Constitutional Research Council to the Democratic Unionist Party
The Democratic Unionist Party (DUP) is a unionist, loyalist, and national conservative political party in Northern Ireland. It was founded in 1971 during the Troubles by Ian Paisley, who led the party for the next 37 years. Currently led by J ...
for spending during the referendum may have originated in Saudi Arabia.
In November 2017, the Electoral Commission said that it was investigating allegations that Arron Banks, an insurance businessman and the largest single financial supporter of Brexit, violated campaign spending laws.[Henry Mance]
Brexit-backer Arron Banks to be investigated over campaign spending
''Financial Times'' (1 November 2017). The commission's investigation focuses on both Banks and Better for the Country Limited, a company of which Banks is a director and majority shareholder. The company donated £2.4 million to groups supporting British withdrawal from the EU.[Henry Mance]
Arron Banks investigated for Brexit campaign spending
''Financial Times'' (1 November 2017). The Commission specifically seeks to determine "whether or not Mr Banks was the true source of loans reported by a referendum campaigner in his name" and "whether or not Better for the Country Limited was the true source of donations made to referendum campaigners in its name, or if it was acting as an agent".[Maidment, Jack (19 December 2017]
"Liberal Democrats fined £18,000 for breaching campaign finance rules relating to EU referendum"
''The Daily Telegraph''. The Liberal Democrats were fined £18,000 and Open Britain (formerly Britain Stronger in Europe) paid £1,250 in fines.
Speculation about Russian interference
In the run-up to the Brexit referendum, Russian President Vladimir Putin refrained from taking a public position on Brexit,Kremlin
The Kremlin ( rus, Московский Кремль, r=Moskovskiy Kreml', p=ˈmɐˈskofskʲɪj krʲemlʲ, t=Moscow Kremlin) is a fortified complex in the center of Moscow founded by the Rurik dynasty, Rurik dynasty. It is the best known of th ...
of secretly backing a "Leave" vote in the referendum.[Steve Rosenberg]
EU referendum: What does Russia gain from Brexit?'
BBC News (26 June 2016). Russian Foreign Ministry spokesperson Maria Zakharova
Maria Vladimirovna Zakharova (russian: Мария Владимировна Захарова; born 24 December 1975) is the Director of the Information and Press Department of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation (Spokesw ...
denied these allegations, saying that "Russia is blamed for everything. Not only in the UK but all over the world. (...) But Russia has nothing to do with Brexit at all. We're not involved in this process."Steve Rosenberg
Steven Barnett Rosenberg (born 5 April 1968) is a British journalist for BBC News. He has been the BBC's Moscow correspondent almost continuously since 2003, except for a stint as Berlin correspondent between 2006 and 2010. In 2022 Rosenberg's r ...
, the Moscow correspondent for BBC News, suggested on 26 June 2016 that the Russian government stood to gain from Brexit in several ways: (1) enabling Russian state media "to contrast post-referendum upheaval and uncertainty abroad with a picture of 'stability' back home and images of a 'strong' President Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin; (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who holds the office of president of Russia. Putin has served continuously as president or prime minister since 1999: as prime min ...
at the helm" in a way that bolstered the ruling United Russia party; (2) to place the value of the British pound
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and t ...
under pressure and thereby exact retaliation for sanctions against Russia Sanctions, economic or international, that have been imposed on Russia include:
* International sanctions during the Russo-Ukrainian War (2014–)
** Countering America's Adversaries Through Sanctions Act, US legislation (2017)
** International sanc ...
imposed after its occupation of Crimea
The Russian occupation of Crimea is an ongoing military occupation within Ukraine by the Russian Federation, which began on 20 February 2014 when the military-political, administrative, economic and social order of Russia was spread to the ...
; (3) to "make the European Union more friendly towards Russia" in the absence of British membership; and (4) to force the resignation of Cameron, who had been critical of Russian actions.Ben Bradshaw
Benjamin Peter James Bradshaw (born 30 August 1960) is a British politician who served as Secretary of State for Culture, Media and Sport from 2009 to 2010. A member of the Labour Party, he has been Member of Parliament (MP) for Exeter since 1 ...
speculated in Parliament that Russia may have interfered in the referendum. In February 2017, he called on the GCHQ intelligence service to reveal the information it had on Russian interference. In April 2017, the House of Commons (PACAC) issued a report suggesting that there were technical indications that a June 2016 crash of the voter-registration website was caused by a distributed denial-of-service attack
In computing, a denial-of-service attack (DoS attack) is a cyber-attack in which the perpetrator seeks to make a machine or network resource unavailable to its intended users by temporarily or indefinitely disrupting services of a host connec ...
using botnets.[Rajeev Syal]
Brexit: foreign states may have interfered in vote, report says
''The Guardian'' (12 April 2017). The Cabinet Office
The Cabinet Office is a department of His Majesty's Government responsible for supporting the prime minister and Cabinet. It is composed of various units that support Cabinet committees and which co-ordinate the delivery of government objecti ...
, in response, stated that it did not believe that "malign intervention" had caused the crash, and instead attributed the crash "to a spike in users just before the registration deadline".Mark Zuckerberg
Mark Elliot Zuckerberg (; born ) is an American business magnate, internet entrepreneur, and philanthropist. He is known for co-founding the social media website Facebook and its parent company Meta Platforms (formerly Facebook, Inc.), o ...
requesting documents relating to possible Russian government manipulation of Facebook during the Brexit referendum and the general election
A general election is a political voting election where generally all or most members of a given political body are chosen. These are usually held for a nation, state, or territory's primary legislative body, and are different from by-elections ( ...
the following year.
In October 2017, a study by researchers at City, University of London was published in the journal '' Social Science Computer Review''. The article identified 13,493 Twitter accounts that posted a total of about 65,000 messages in the last four weeks of the Brexit referendum campaign, the vast majority campaigning for a "Leave" vote; they were deleted shortly after the referendum.[David D. Kirkpatrick]
Parliament Asks Twitter About Russian Meddling in Brexit Vote
''The New York Times'' (3 November 2017).[13,500-strong Twitter bot army disappeared shortly after EU referendum, research reveals](_blank)
City, University of London (20 October 2017). A further 26,538 Twitter accounts suddenly changed their username.[Oliver Wright, Lucy Fisher & Sean O'Neill]
Watchdog starts inquiry into Russia Brexit links
''The Times'' (2 November 2017). The commission was in contact with Facebook and Twitter as part of the inquiry.Dan Sabbagh
Daniel Sabbagh (born 1971) is a British journalist who is the associate editor of ''The Guardian'' (appointed in January 2018), having previously been national news editor. , Luke Harding, Andrew Roth
Russia report reveals UK government failed to investigate Kremlin interference
The Guardian, 21 July 2020.
See also
*
* Causes of the vote in favour of Brexit
* Effect of Brexit on Gibraltar
The effect of Brexit on Gibraltar concerns the status of Gibraltar after withdrawal of the United Kingdom from the European Union. The UK left the EU on 31 January 2020 after having voted to leave in the 2016 referendum and formally notified the ...
* European Union Bill 2004–2005
The European Union Bill 2004–2005 (Bill 45) was a Bill (law), bill of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, United Kingdom Parliament which proposed to ratify the Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe, European Constitution and to inco ...
* European Union law
European Union law is a system of rules operating within the member states of the European Union (EU). Since the founding of the European Coal and Steel Community following World War II, the EU has developed the aim to "promote peace, its valu ...
* European Union (Withdrawal) Act 2018
The European Union (Withdrawal) Act 2018 (also known as the Great Repeal Act) is an Act of Parliament, Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that provides both for repeal of the European Communities Act 1972 (UK), European Communities A ...
* European Union (Withdrawal) Act 2019 ("Cooper–Letwin Act")
* European Union (Withdrawal) (No. 2) Act 2019, Benn Act
* 1982 Greenlandic European Communities membership referendum
* Opinion polling on the United Kingdom's membership of the European Union (2016–2020)
*Opinion polling on the United Kingdom rejoining the European Union (2020–present)
* Proposed referendum on the Brexit withdrawal agreement
* Referendums in the United Kingdom
* Referendums related to the European Union
* Treaty of Accession 1972
* Unlawful campaigning in the 2016 EU referendum
* Withdrawal from the European Union
Notes
References
Further reading
*
*
*
* LSE Library (March 2017),
Collection of campaigning leaflets from the referendum
Brexit and the UN Security Council
External links
House of Commons Briefings: 2016 European Union Referendum
Examples of leaflets used during the referendum campaign
*
Electoral Commission guide to the EU Referendum
BBC News – EU Referendum
BBC Radio 4 ''Why Did People Vote to Leave''
BBC Radio 4 ''How We Voted Brexit''
*[http://theconversation.com/the-un-security-council-in-a-post-brexit-world-france-and-germany-take-the-lead-113078 The UN Security Council in a post-Brexit world: France and Germany take the lead]
{{authority control
2016 United Kingdom European Union membership referendum,
2016 in British politics
2016 in Gibraltar
2016 in the European Union
2016 referendums
Referendums in the United Kingdom
Referendums related to the European Union
United Kingdom and the European Union
June 2016 events in the United Kingdom
 When they attended the May 2012 NATO summit meeting, UK Prime Minister
When they attended the May 2012 NATO summit meeting, UK Prime Minister  In October 2015, Britain Stronger in Europe, a cross-party group campaigning for Britain to remain a member of the EU, was formed. There were two rival groups promoting British withdrawal from the EU that sought to become the official Leave campaign: Leave.EU (which was endorsed by most of UKIP, including Nigel Farage), and Vote Leave (endorsed by Conservative Party Eurosceptics). In January 2016, Nigel Farage and the Leave.EU campaign became part of the
In October 2015, Britain Stronger in Europe, a cross-party group campaigning for Britain to remain a member of the EU, was formed. There were two rival groups promoting British withdrawal from the EU that sought to become the official Leave campaign: Leave.EU (which was endorsed by most of UKIP, including Nigel Farage), and Vote Leave (endorsed by Conservative Party Eurosceptics). In January 2016, Nigel Farage and the Leave.EU campaign became part of the  Citizens of EU countries, including the United Kingdom, have the right to travel, live and work within other EU countries, as free movement is one of the four founding principles of the EU. Campaigners for remaining said that EU immigration had positive impacts on the UK's economy, citing that the country's growth forecasts were partly based upon continued high levels of net immigration. The Office for Budget Responsibility also claimed that taxes from immigrants boost public funding. A recent academic paper suggests that migration from Eastern Europe put pressure on wage growth at the lower end of the wage distribution, while at the same time increasing pressures on public services and housing. The Leave campaign believed reduced immigration would ease pressure in public services such as schools and hospitals, as well as giving British workers more jobs and higher wages. According to official Office for National Statistics data, net migration in 2015 was 333,000, which was the second highest level on record, far above David Cameron's target of tens of thousands.EU Referendum: Record number of migrants arrive in UK without jobs, as Boris Johnson accuses David Cameron of "deeply damaging" faith in democracy
Citizens of EU countries, including the United Kingdom, have the right to travel, live and work within other EU countries, as free movement is one of the four founding principles of the EU. Campaigners for remaining said that EU immigration had positive impacts on the UK's economy, citing that the country's growth forecasts were partly based upon continued high levels of net immigration. The Office for Budget Responsibility also claimed that taxes from immigrants boost public funding. A recent academic paper suggests that migration from Eastern Europe put pressure on wage growth at the lower end of the wage distribution, while at the same time increasing pressures on public services and housing. The Leave campaign believed reduced immigration would ease pressure in public services such as schools and hospitals, as well as giving British workers more jobs and higher wages. According to official Office for National Statistics data, net migration in 2015 was 333,000, which was the second highest level on record, far above David Cameron's target of tens of thousands.EU Referendum: Record number of migrants arrive in UK without jobs, as Boris Johnson accuses David Cameron of "deeply damaging" faith in democracy Voting took place from 0700 BST (WEST) until 2200 BST (Same hours CEST in Gibraltar) in 41,000 polling stations across 382 voting areas, with each polling station limited to a maximum of 2,500 voters.European Referendum Act 2015
Voting took place from 0700 BST (WEST) until 2200 BST (Same hours CEST in Gibraltar) in 41,000 polling stations across 382 voting areas, with each polling station limited to a maximum of 2,500 voters.European Referendum Act 2015

 On 24 June, the Conservative Party leader and Prime Minister
On 24 June, the Conservative Party leader and Prime Minister  On 9 May 2016, Leave.EU was fined £50,000 by the UK Information Commissioner's Office 'for failing to follow the rules about sending marketing messages': they sent people text messages without having first gained their permission to do so.
In February 2017, the Electoral Commission announced that it was investigating the spending of Stronger in and Vote Leave, along with smaller parties, as they had not submitted all the necessary invoices, receipts, or details to back up their accounts. In April 2017, the Commission specified that 'there were reasonable grounds to suspect that potential offences under the law may have occurred' in relation to Leave.EU.
On 4 March 2017, the Information Commissioner's Office also reported that it was 'conducting a wide assessment of the data-protection risks arising from the use of data
On 9 May 2016, Leave.EU was fined £50,000 by the UK Information Commissioner's Office 'for failing to follow the rules about sending marketing messages': they sent people text messages without having first gained their permission to do so.
In February 2017, the Electoral Commission announced that it was investigating the spending of Stronger in and Vote Leave, along with smaller parties, as they had not submitted all the necessary invoices, receipts, or details to back up their accounts. In April 2017, the Commission specified that 'there were reasonable grounds to suspect that potential offences under the law may have occurred' in relation to Leave.EU.
On 4 March 2017, the Information Commissioner's Office also reported that it was 'conducting a wide assessment of the data-protection risks arising from the use of data