Transnistria Stamp Of 1993 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Transnistria, officially the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (PMR), is an unrecognised breakaway state that is internationally recognised as a part of Moldova. Transnistria controls most of the narrow strip of land between the Dniester river and the Moldovan–Ukrainian border, as well as some land on the other side of the river's bank. Its
 In 1924, the Moldavian ASSR was proclaimed within the Ukrainian SSR; the ASSR included today's Transnistria () and an area () to the northeast around the city of
In 1924, the Moldavian ASSR was proclaimed within the Ukrainian SSR; the ASSR included today's Transnistria () and an area () to the northeast around the city of
 In the 1980s,
In the 1980s,
Stuart J. Kaufman, Cornell University Press, 2001, , pp. 143 In the interest of preserving a unified Moldavian SSR within the USSR and preventing the situation escalating further, then
 The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is trying to facilitate a negotiated settlement. Under OSCE auspices, on 8 May 1997, Moldovan President Petru Lucinschi and Transnistrian president Igor Smirnov, signed the "Memorandum on the principles of normalization of the relations between the Republic of Moldova and Transnistria", also known as the "Primakov Memorandum", sustaining the establishment of legal and state relations, although the memorandum's provisions were interpreted differently by the governments of Moldova and Transnistria.
In November 2003, Dmitry Kozak, a counselor of Russian president Vladimir Putin, proposed a memorandum on the creation of an asymmetric federal Moldovan state, with Moldova holding a majority and Transnistria being a minority part of the federation. Known as "the
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is trying to facilitate a negotiated settlement. Under OSCE auspices, on 8 May 1997, Moldovan President Petru Lucinschi and Transnistrian president Igor Smirnov, signed the "Memorandum on the principles of normalization of the relations between the Republic of Moldova and Transnistria", also known as the "Primakov Memorandum", sustaining the establishment of legal and state relations, although the memorandum's provisions were interpreted differently by the governments of Moldova and Transnistria.
In November 2003, Dmitry Kozak, a counselor of Russian president Vladimir Putin, proposed a memorandum on the creation of an asymmetric federal Moldovan state, with Moldova holding a majority and Transnistria being a minority part of the federation. Known as "the
 Transnistria is
Transnistria is
 Transnistria is subdivided into five districts ('' raions'') and one municipality, the city of Tiraspol (which is entirely surrounded by but administratively distinct from Slobozia District), listed below from north to south (Russian names and transliterations are appended in parentheses). In addition, another municipality, the City of Bender, situated on the western bank of the Dniester, in Bessarabia, and geographically outside Transnistria, is not part of the territorial unit of Transnistria as defined by the Moldovan central authorities, but it is controlled by the PMR authorities, which consider it part of PMR's administrative organisation:
},
Transnistria is subdivided into five districts ('' raions'') and one municipality, the city of Tiraspol (which is entirely surrounded by but administratively distinct from Slobozia District), listed below from north to south (Russian names and transliterations are appended in parentheses). In addition, another municipality, the City of Bender, situated on the western bank of the Dniester, in Bessarabia, and geographically outside Transnistria, is not part of the territorial unit of Transnistria as defined by the Moldovan central authorities, but it is controlled by the PMR authorities, which consider it part of PMR's administrative organisation:
}, 
 All
All
 Nina Shtanski served as Transnistria's Minister of Foreign Affairs from 2012 to 2015; succeeded her as minister.
Nina Shtanski served as Transnistria's Minister of Foreign Affairs from 2012 to 2015; succeeded her as minister.
Herd, Graeme P., The opposition Narodovlastie party and Power to the People movement were outlawed at the beginning of 2000 and eventually dissolved.
A list published by the European Union bans travel to the EU for some members of the Transnistrian leadership.
In 2007, the registration of a Social Democratic Party was allowed. This party, led by a former separatist leader and member of the PMR government Andrey Safonov, allegedly favours a union with Moldova.
In September 2007, the leader of the
The opposition Narodovlastie party and Power to the People movement were outlawed at the beginning of 2000 and eventually dissolved.
A list published by the European Union bans travel to the EU for some members of the Transnistrian leadership.
In 2007, the registration of a Social Democratic Party was allowed. This party, led by a former separatist leader and member of the PMR government Andrey Safonov, allegedly favours a union with Moldova.
In September 2007, the leader of the

"Russian troops in Transnistria – a threat to the security of the Republic of Moldova", Institute of Political and Military Studies, Chișinău, Moldova
Russia continues to 'sustain the Dniestr region as a quasi-independent entity through direct and indirect means' however, Russia insists that it has already fulfilled those obligations. It states the remaining troops are serving as peacekeepers authorised under the 1992 ceasefire, are not in violation of the Istanbul accords and will remain until the conflict is fully resolved. On the other hand, Moldova believes that fewer than 500 soldiers are authorised pursuant to the ceasefire and, in 2015, began to arrest and deport Russian soldiers who are part of the excess forces and attempt to use Moldovan airports. In a NATO resolution on 18 November 2008, Russia was urged to withdraw its military presence from the "Transdnestrian region of Moldova".
In 2011, US Senator
In a NATO resolution on 18 November 2008, Russia was urged to withdraw its military presence from the "Transdnestrian region of Moldova".
In 2011, US Senator
 , the armed forces and the paramilitary of Transnistria were composed of around 4,500–7,500 soldiers, divided into four motorised infantry brigades in Tiraspol, Bender,
, the armed forces and the paramilitary of Transnistria were composed of around 4,500–7,500 soldiers, divided into four motorised infantry brigades in Tiraspol, Bender,
 Transnistria has its own central bank, the
Transnistria has its own central bank, the
Stuart Hensel, Economist Intelligence Unit. The largest company in the textile industry is

, SEESAC 1 July 2007, Their report stated that the evidence for the illicit production and
Moldova & The Dniestr Region: Contested Past, Frozen Present, Speculative Futures?
Graeme P. Herd. In 2010, Viktor Kryzhanivsky, Ukraine's special envoy on Transnistria, stated that there was no ongoing
online
* Blakkisrud, Helge, and Pål Kolstø. "From secessionist conflict toward a functioning state: processes of state-and nation-building in Transnistria." ''Post-Soviet Affairs'' 27.2 (2011): 178–21
online
* Cojocaru, Natalia. "Nationalism and identity in Transnistria." ''Innovation'' 19.3–4 (2006): 261–27
online
* Lynch, Dov. ''Russian peacekeeping strategies in the CIS: the case of Moldova, Georgia and Tajikistan'' (Springer, 1999). * Maclean, Rory ''Pravda Ha Ha: Truth, Lies and the End of Europe'' (Bloomsbury, 2020) ISBN 978-1-4088-9651-
* Protsyk, Oleh. "Representation and democracy in Eurasia's unrecognized states: The case of Transnistria." ''Post-Soviet Affairs'' 25.3 (2009): 257–28
online
* RAND, ''Russia's Hostile Measures: Combating Russian Gray Zone Aggression Against NATO in the Contact, Blunt, and Surge Layers of Competition'' (2020
online
on Transnistria
Profile of Trans-Dniester
BBC News.
The black hole that ate Moldova
'' The Economist''.
Transdniester Conflict Was Long In The Making
Radio Free Europe.
"Moldova, Transnistria, and European Democracy Polices"
Jos Boonstra
FRIDE
February 2007. * Matsuzato, Kimitaka: "Canonization, Obedience, and Defiance: Strategies for Survival of the Orthodox Communities in Transnistria, Abkhazia, and South Ossetia" in th
Caucasus Analytical Digest No. 20
*
PMR Presidential website
*
Website of the Supreme Council (Parliament) of PMR
*
Website MFA of Pridnestrovie
*
Pridnestrovian News – Website of the official information agency of Pridnestrovie
*
Transnistria Guide
*
Transnistria.md News and interviews. Moldova administration
*
Radio PMR. Radio-News. Pridnestrovie administration
*
First Pridnestrovian TV Channel – State television of Pridnestrovie
*
On-line TV PMR. Video, news and interviews. Pridnestrovie administration
{{coord, 46, 50, N, 29, 37, E, display=title Disputed territories in Europe Post-Soviet states Romanian-speaking countries and territories Russian-speaking countries and territories Ukrainian-speaking countries and territories History of Eastern Europe Landlocked countries Regions of Europe with multiple official languages Eastern European countries States and territories established in 1990 1990 establishments in the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic 1990 establishments in Europe Neo-Sovietism Russian irredentism States with limited recognition Frozen conflict zones
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and largest city is Tiraspol. Transnistria has been recognised only by three other unrecognised or partially recognised breakaway states: Abkhazia
Abkhazia, ka, აფხაზეთი, tr, , xmf, აბჟუა, abzhua, or ( or ), officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, recognised by most countries as part of Georgia, which vi ...
, Artsakh and South Ossetia. Transnistria is officially designated by the Republic of Moldova as the Administrative-Territorial Units of the Left Bank of the Dniester
The Administrative-Territorial Units of the Left Bank of the Dniester (Transnistria); russian: Административно-территориальные единицы левобережья Днестра (Приднестровья); uk, ...
( ro, Unitățile Administrativ-Teritoriale din stînga Nistrului) or as ("Left Bank of the Dniester"). The Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
considers the territory to be under military occupation by Russia.
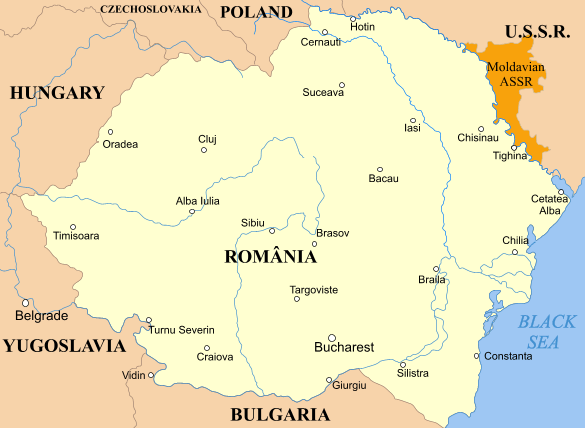
The region's origins can be traced to the Moldavian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic, which was formed in 1924 within the Ukrainian SSR. During World War II, the Soviet Union took parts of the Moldavian ASSR, which was dissolved, and of the Kingdom of Romania's Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Be ...
to form the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic in 1940. The present history of the region dates to 1990, during the dissolution of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
, when the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic was established in hopes that it would remain within the Soviet Union should Moldova seek unification with Romania or independence, the latter occurring in August 1991. Shortly afterwards, a military conflict between the two parties started in March 1992 and concluded with a ceasefire in July that year.
As part of the ceasefire agreement, a three-party (Russia, Moldova, Transnistria) Joint Control Commission supervises the security arrangements in the demilitarised zone, comprising 20 localities on both sides of the river. Although the ceasefire has held, the territory's political status remains unresolved: Transnistria is an unrecognised but '' de facto'' independent presidential republic with its own government, parliament, military, police, postal system, currency, and vehicle registration. Its authorities have adopted a constitution, flag
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design empl ...
, national anthem, and coat of arms. After a 2005 agreement between Moldova and Ukraine, all Transnistrian companies that seek to export goods through the Ukrainian border must be registered with the Moldovan authorities. This agreement was implemented after the European Union Border Assistance Mission to Moldova and Ukraine
The European Union Border Assistance Mission to Moldova and Ukraine (EUBAM Moldova and Ukraine) was launched in 2005. It promotes border control, customs, and trade norms and practices that meet European Union standards and serve the needs of its ...
(EUBAM) took force in 2005. Most Transnistrians have Moldovan citizenship, but many also have Russian, Romanian, or Ukrainian citizenship. The main ethnic groups are Russians, Moldovans/Romanians, and Ukrainians.
Transnistria, along with Abkhazia, South Ossetia, and Artsakh, is a post-Soviet " frozen conflict" zone. These four partially recognised or unrecognised states maintain friendly relations with each other and form the Community for Democracy and Rights of Nations
The Community for Democracy and Rights of Nations (russian: Сообщество за демократию и права народов), also commonly and colloquially known as the Commonwealth of Unrecognized States, rarely as CIS-2 (), is a ...
.
Names
The region can also be referred to in English as ''Trans-Dniester'' or ''Transdniestria''. These names are adaptations of the Romanian colloquial name of the region, ''Transnistria'', meaning "beyond the Dniester River". The term ''Transnistria'' was used in relation to eastern Moldova for the first time in 1989, in the election slogan of the deputy and member of the Popular Front of MoldovaLeonida Lari
Leonida Lari (26 October 1949 – 11 December 2011) was a Moldovan poet, journalist, and politician who advocated for the reunion of Bessarabia with Romania. She published 24 volumes of poetry and prose and was a prolific translator of key works ...
:
The documents of the government of Moldova refer to the region as (in full, ) meaning "Left Bank of the Dniester" (in full, "Administrative-territorial unit(s) of the Left Bank of the Dniester").
According to the Transnistrian authorities, the name of the state is the "Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic" (PMR) (russian: Приднестро́вская Молда́вская Респу́блика, ПМР, ; ro, Republica Moldovenească Nistreană, RMN, Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet: ; uk, Придністро́вська Молда́вська Респу́бліка, ПМР, ). The short form is (russian: Приднестровье; ro, Nistrenia, Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet: ; uk, Придністров'я, ), meaning "and
or AND may refer to:
Logic, grammar, and computing
* Conjunction (grammar), connecting two words, phrases, or clauses
* Logical conjunction in mathematical logic, notated as "∧", "⋅", "&", or simple juxtaposition
* Bitwise AND, a boole ...
by the Dniester".
History
Soviet and Romanian administration
 In 1924, the Moldavian ASSR was proclaimed within the Ukrainian SSR; the ASSR included today's Transnistria () and an area () to the northeast around the city of
In 1924, the Moldavian ASSR was proclaimed within the Ukrainian SSR; the ASSR included today's Transnistria () and an area () to the northeast around the city of Balta
Balta may refer to:
People
* Balta (footballer) (born 1962), Spanish footballer and manager
* Balta (surname)
Places
* Balta (crater), on Mars
* Balta, Mehedinți, Romania
*Bâlta, a village in Filiași, Dolj County, Romania
*Bâlta, a village ...
, but nothing from Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Be ...
, which at the time formed part of Romania. One of the reasons for the creation of the Moldavian ASSR was the desire of the Soviet Union at the time to eventually incorporate Bessarabia. On 28 June 1940, the USSR annexed part of Bessarabia from Romania under the terms of the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, and on 2 August 1940 the Supreme Soviet of the USSR created the Moldavian SSR by combining the annexed territory with a part of the former Moldavian ASSR roughly equivalent to present-day Transnistria.
In 1941, after Axis forces invaded the Soviet Union during the Second World War, they defeated the Soviet troops in the region and occupied it. Romania controlled the entire region between Dniester and Southern Bug
, ''Pivdennyi Buh''
, name_etymology =
, image = Sunset S Bug Vinnitsa 2007 G1.jpg
, image_size = 270
, image_caption = Southern Bug River in the vicinity of Vinnytsia, Ukraine
, map = PietinisBug ...
rivers, including the city of Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrativ ...
as local capital. The Romanian-administered territory, known as the Transnistria Governorate, with an area of and a population of 2.3 million inhabitants, was divided into 13 counties: Ananiev, Balta, Berzovca, Dubasari, Golta, Jugastru, Movilau, Oceacov, Odessa, Ovidiopol, Rîbnița, Tiraspol, and Tulcin. This enlarged Transnistria was home to nearly 200,000 Romanian-speaking residents. The Romanian administration of Transnistria attempted to stabilise the situation in the area under Romanian control, implementing a process of Romanianization
Romanianization is the series of policies aimed toward ethnic assimilation implemented by the Romanian authorities during the 20th and 21st century. The most noteworthy policies were those aimed at the Hungarian minority in Romania, Jews and as ...
. During the Romanian occupation of 1941–44, between 150,000 and 250,000 Ukrainian and Romanian Jews were deported to Transnistria; the majority were executed or died from other causes in ghettos and concentration camps of the Governorate.
After the Red Army advanced into the area in 1944, Soviet authorities executed, exiled or imprisoned hundreds of inhabitants of the Moldavian SSR in the following months on charges of collaboration with the Romanian occupiers. A later campaign was directed against the rich peasant families, who were deported to Kazakhstan and Siberia. Over the course of two days, 6–7 July 1949, a plan named "Operation South" saw the deportation of over 11,342 families by order of the Moldavian Minister of State Security, Iosif Mordovets.
Secession
 In the 1980s,
In the 1980s, Mikhail Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet politician who served as the 8th and final leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to dissolution of the Soviet Union, the country's dissolution in 1991. He served a ...
's policies of perestroika
''Perestroika'' (; russian: links=no, перестройка, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈstrojkə, a=ru-perestroika.ogg) was a political movement for reform within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) during the late 1980s widely associated wit ...
and glasnost
''Glasnost'' (; russian: link=no, гласность, ) has several general and specific meanings – a policy of maximum openness in the activities of state institutions and freedom of information, the inadmissibility of hushing up problems, ...
in the Soviet Union allowed political liberalisation at a regional level. This led to the creation of various informal movements all over the country, and to a rise of nationalism within most Soviet republics. In the Moldavian SSR in particular, there was a significant resurgence of pro-Romanian nationalism among Moldovans. The most prominent of these movements was the Popular Front of Moldova. In early 1988, PFM demanded that the Soviet authorities declare Moldovan the only state language, return to the use of the Latin alphabet, and recognise the shared ethnic identity of Moldovans and Romanians. The more radical factions of the Popular Front espoused extreme anti-minority, ethnocentric and chauvinist positions, calling for minority populations, particularly the Slavs (mainly Russians and Ukrainians) and Gagauz, to leave or be expelled from Moldova.
On 31 August 1989, the Supreme Soviet of the Moldavian SSR adopted Moldovan as the official language with Russian retained only for secondary purposes, returned Moldovan to the Latin alphabet, and declared a shared Moldovan-Romanian linguistic identity. As plans for major cultural changes in Moldova were made public, tensions rose further. Ethnic minorities felt threatened by the prospects of removing Russian as the official language, which served as the medium of interethnic communication, and by the possible future reunification of Moldova and Romania, as well as the ethnocentric rhetoric of the Popular Front. The Yedinstvo (Unity) Movement, established by the Slavic population of Moldova, pressed for equal status to be given to both Russian and Moldovan. Transnistria's ethnic and linguistic composition differed significantly from most of the rest of Moldova. The share of ethnic Russians and Ukrainians was especially high and an overall majority of the population, some of them Moldovans, spoke Russian as a mother tongue.
The nationalist Popular Front won the first free parliamentary elections in the Moldavian SSR in early 1990, and its agenda started slowly to be implemented. On 2 September 1990, the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic (PMSSR) was proclaimed as a Soviet republic by an '' ad hoc'' assembly, the Second Congress of the Peoples' Representatives of Transnistria, following a successful referendum. Violence escalated when in October 1990 the Popular Front called for volunteers to form armed militias to stop an autonomy referendum in Gagauzia
Gagauzia or Gagauz-Yeri, or ; ro, Găgăuzia; russian: Гагаузия, Gagauziya officially the Autonomous Territorial Unit of Gagauzia; ro, Unitatea Teritorială Autonomă Găgăuzia, ''UTAG''; russian: Автономное территор ...
, which had an even higher share of ethnic minorities. In response, volunteer militias were formed in Transnistria. In April 1990, nationalist mobs attacked ethnic Russian members of parliament, while the Moldovan police refused to intervene or restore order.''Modern Hatreds: The Symbolic Politics of Ethnic War''Stuart J. Kaufman, Cornell University Press, 2001, , pp. 143 In the interest of preserving a unified Moldavian SSR within the USSR and preventing the situation escalating further, then
Soviet President
The president of the Soviet Union (russian: Президент Советского Союза, Prezident Sovetskogo Soyuza), officially the president of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (), abbreviated as president of the USSR (), was ...
Mikhail Gorbachev, while citing the restriction of civil rights of ethnic minorities by Moldova as the cause of the dispute, declared the Transnistria proclamation to be lacking legal basis and annulled it by presidential decree on 22 December 1990. Nevertheless, no significant action was taken against Transnistria and the new authorities were slowly able to establish control of the region.
Following the 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt
The 1991 Soviet coup d'état attempt, also known as the August Coup,, "August Putsch". was a failed attempt by hardliners of the Soviet Union's Communist Party to forcibly seize control of the country from Mikhail Gorbachev, who was Soviet ...
, the Pridnestrovian Moldavian SSR declared its independence from the Soviet Union; on 5 November 1991 Transnistria abandoned its socialist ideology and was renamed "Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic".
Transnistria War
The Transnistria War followed armed clashes on a limited scale that broke out between Transnistrian separatists and Moldova as early as November 1990 atDubăsari
Dubăsari ( ro, Dubăsari , Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet: Дубэсарь) or Dubossary (russian: Дубоссары; yi, דובאסאר; uk, Дубоcсари) is a city in Transnistria, with a population of 23,650. Claimed by both the Republic ...
. Volunteers, including Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
, came from Russia to help the separatist
Separatism is the advocacy of cultural, ethnic, tribal, religious, racial, governmental or gender separation from the larger group. As with secession, separatism conventionally refers to full political separation. Groups simply seeking greate ...
side. In mid-April 1992, under the agreements on the split of the military equipment of the former Soviet Union negotiated between the former 15 republics in the previous months, Moldova created its own Defence Ministry. According to the decree of its creation, most of the 14th Guards Army
The 14th Guards Army () was a field army of the Red Army, the Soviet Ground Forces, and the Russian Ground Forces, active from 1956 to 1995. According to sources within the 14th Army, the majority of its troops came from the Pridnestrovian Moldavia ...
's military equipment was to be retained by Moldova. Starting from 2 March 1992, there was concerted military action between Moldova and Transnistria. The fighting intensified throughout early 1992. The former Soviet 14th Guards Army entered the conflict in its final stage, opening fire against Moldovan forces; approximately 700 people were killed. Moldova has since then exercised no effective control or influence on Transnistrian authorities. A ceasefire agreement, signed on 21 July 1992, has held to the present day.
Further negotiations
 The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is trying to facilitate a negotiated settlement. Under OSCE auspices, on 8 May 1997, Moldovan President Petru Lucinschi and Transnistrian president Igor Smirnov, signed the "Memorandum on the principles of normalization of the relations between the Republic of Moldova and Transnistria", also known as the "Primakov Memorandum", sustaining the establishment of legal and state relations, although the memorandum's provisions were interpreted differently by the governments of Moldova and Transnistria.
In November 2003, Dmitry Kozak, a counselor of Russian president Vladimir Putin, proposed a memorandum on the creation of an asymmetric federal Moldovan state, with Moldova holding a majority and Transnistria being a minority part of the federation. Known as "the
The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) is trying to facilitate a negotiated settlement. Under OSCE auspices, on 8 May 1997, Moldovan President Petru Lucinschi and Transnistrian president Igor Smirnov, signed the "Memorandum on the principles of normalization of the relations between the Republic of Moldova and Transnistria", also known as the "Primakov Memorandum", sustaining the establishment of legal and state relations, although the memorandum's provisions were interpreted differently by the governments of Moldova and Transnistria.
In November 2003, Dmitry Kozak, a counselor of Russian president Vladimir Putin, proposed a memorandum on the creation of an asymmetric federal Moldovan state, with Moldova holding a majority and Transnistria being a minority part of the federation. Known as "the Kozak memorandum
The Kozak memorandum, officially Russian Draft Memorandum on the Basic Principles of the State Structure of a United State in Moldova, was a 2003 proposal aimed at a final settlement of relations between Moldova and Transnistria and a solving of ...
", it did not coincide with the Transnistrian position, which sought equal status between Transnistria and Moldova, but gave Transnistria veto powers over future constitutional changes; this encouraged Transnistria to sign it. Moldovan President Vladimir Voronin was initially supportive of the plan, but refused to sign it after internal opposition and international pressure from the OSCE and US, and after Russia had endorsed the Transnistrian demand to maintain a Russian military presence for the next 20 years as a guarantee for the intended federation.
The 5+2 format
5 (five) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number, and cardinal number, following 4 and preceding 6, and is a prime number. It has attained significance throughout history in part because typical humans have five digits on eac ...
(or 5+2 talks; composed by Transnistria, Moldova, Ukraine, Russia and the OSCE, plus the United States and the EU as external observers) for negotiation was started in 2005 to deal with the problems, but without results for many years as it was suspended. In February 2011, it was started again in Vienna.
After the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation
In February and March 2014, Russia invaded and subsequently annexed the Crimean Peninsula from Ukraine. This event took place in the aftermath of the Revolution of Dignity and is part of the wider Russo-Ukrainian War.
The events in Kyiv th ...
in March 2014, the head of the Transnistrian parliament asked to join Russia.
Geography

landlocked
A landlocked country is a country that does not have territory connected to an ocean or whose coastlines lie on endorheic basins. There are currently 44 landlocked countries and 4 landlocked de facto states. Kazakhstan is the world's largest ...
and borders Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Be ...
(the region the Republic of Moldova is based on, for 411 km, 255 miles) to the west, and Ukraine (for 405 km, 250 miles) to the east. It is a narrow valley stretching north–south along the bank of the Dniester river
The Dniester, ; rus, Дне́стр, links=1, Dnéstr, ˈdⁿʲestr; ro, Nistru; grc, Τύρᾱς, Tyrās, ; la, Tyrās, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and th ...
, which forms a natural boundary along most of the ''de facto'' border with Moldova.
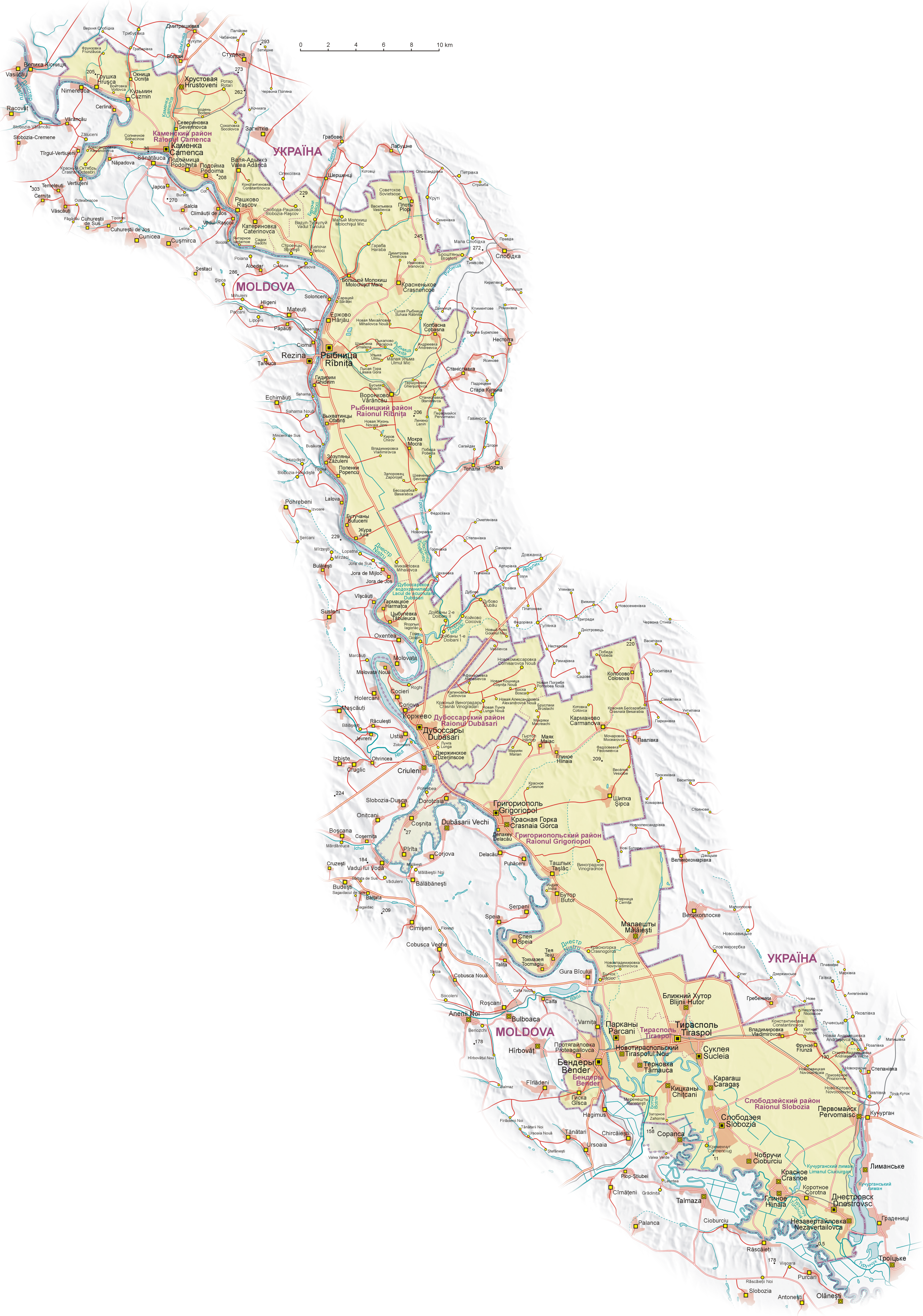
The territory controlled by the PMR is mostly, but not completely, coincident with the left (eastern) bank of Dniester. It includes ten cities and towns, and 69 communes, with a total of 147 localities (counting the unincorporated ones as well). Six communes on the left bank (Cocieri
Cocieri is a commune in the Republic of Moldova, and the administrative center of Dubăsari District. It is located on the eastern bank of the Dniester River, consisting of two villages, ''Cocieri'' and ''Vasilievca''.
During 1992 War of Transni ...
, Molovata Nouă
Molovata Nouă is a commune located in Dubăsari District of the Republic of Moldova, on the eastern bank of the River Dniester. It consists of two villages, ''Molovata Nouă'' and ''Roghi''.
During the 1992 War of Transnistria, the commune was ...
, Corjova, Pîrîta
Pîrîta is a village in Dubăsari District, Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukra ...
, Coșnița
Coșnița is a commune located in Dubăsari District of the Republic of Moldova, on the eastern bank of the River Dniester. It consists of two villages, ''Coșnița'' and ''Pohrebea'' ( ro, Pohrebea; russian: Погребя, ''Pogrebya'').
Durin ...
, and Doroțcaia
Doroțcaia is a village in the Dubăsari District, Republic of Moldova, situated on the eastern bank of the River Dniester.
The village was a place of fighting during 1992 War of Transnistria. It is now under the control of the central authoriti ...
) remained under the control of the Moldovan government after the War of Transnistria in 1992, as part of the Dubăsari District. They are situated north and south of the city of Dubăsari
Dubăsari ( ro, Dubăsari , Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet: Дубэсарь) or Dubossary (russian: Дубоссары; yi, דובאסאר; uk, Дубоcсари) is a city in Transnistria, with a population of 23,650. Claimed by both the Republic ...
, which itself is under PMR control. The village of Roghi of Molovata Nouă Commune is also controlled by the PMR (Moldova controls the other nine of the 10 villages of the six communes).
On the west bank, in Bessarabia, the city of Bender (Tighina) and four communes (containing six villages) to its east, south-east, and south, on the opposite bank of the river Dniester from the city of Tiraspol (Proteagailovca
Proteagailovca is a village in the municipality of Bender (Tighina), Moldova. It had a population of 3,142 at the 2004 Census. The locality, although situated on the right (western) bank of the river Dniester, is under the control of the breakawa ...
, Gîsca
Gîsca (meaning " hegoose" in Romanian language, Romanian; russian: Гиска) is a village near in Căușeni District, Moldova, composed of a single village with the same name, population 4,841 at the 2004 Census in Transnistria, 2004 Census ...
, Chițcani, and Cremenciug) are controlled by the PMR.
The localities controlled by Moldova on the eastern bank, the village of Roghi, and the city of Dubăsari (situated on the eastern bank and controlled by the PMR) form a security zone along with the six villages and one city controlled by the PMR on the western bank, as well as two ( Varnița and Copanca
Copanca is a village in Căușeni District, Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukrai ...
) on the same west bank under Moldovan control. The security situation inside it is subject to the Joint Control Commission rulings.
The main transportation route in Transnistria is the road from Tiraspol to Rîbnița through Dubăsari. North and south of Dubăsari it passes through the lands of the villages controlled by Moldova (Doroțcaia
Doroțcaia is a village in the Dubăsari District, Republic of Moldova, situated on the eastern bank of the River Dniester.
The village was a place of fighting during 1992 War of Transnistria. It is now under the control of the central authoriti ...
, Cocieri
Cocieri is a commune in the Republic of Moldova, and the administrative center of Dubăsari District. It is located on the eastern bank of the Dniester River, consisting of two villages, ''Cocieri'' and ''Vasilievca''.
During 1992 War of Transni ...
, Roghi, while Vasilievca is entirely situated east of the road). Conflict erupted on several occasions when the PMR prevented the villagers from reaching their farmland east of the road.
Transnistrians are able to travel (normally without difficulty) in and out of the territory under PMR control to neighbouring Moldovan-controlled territory, to Ukraine, and on to Russia, by road or (when service is not interrupted by political tensions) on two international trains, the year-round Moscow-Chișinău, and the seasonal Saratov
Saratov (, ; rus, Сара́тов, a=Ru-Saratov.ogg, p=sɐˈratəf) is the largest city and administrative center of Saratov Oblast, Russia, and a major port on the Volga River upstream (north) of Volgograd. Saratov had a population of 901,36 ...
-Varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city in Bulgaria
**Varna Province
**Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
**Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
*Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
*Varniai, a city in Lithuania
* Varna (Šaba ...
. International air travellers rely on the airport in Chișinău
Chișinău ( , , ), also known as Kishinev (russian: Кишинёв, r=Kishinjóv ), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the Republic of Moldova. The city is Moldova's main industrial and commercial center, and is located in the ...
, the Moldovan capital, or the airport in Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrativ ...
, in Ukraine.
The climate is humid continental with subtropical characteristics. Transnistria has warm summers and cool to cold winters. Precipitation is equal year round although with a slight increase in the summer months.
Administrative divisions
 Transnistria is subdivided into five districts ('' raions'') and one municipality, the city of Tiraspol (which is entirely surrounded by but administratively distinct from Slobozia District), listed below from north to south (Russian names and transliterations are appended in parentheses). In addition, another municipality, the City of Bender, situated on the western bank of the Dniester, in Bessarabia, and geographically outside Transnistria, is not part of the territorial unit of Transnistria as defined by the Moldovan central authorities, but it is controlled by the PMR authorities, which consider it part of PMR's administrative organisation:
},
Transnistria is subdivided into five districts ('' raions'') and one municipality, the city of Tiraspol (which is entirely surrounded by but administratively distinct from Slobozia District), listed below from north to south (Russian names and transliterations are appended in parentheses). In addition, another municipality, the City of Bender, situated on the western bank of the Dniester, in Bessarabia, and geographically outside Transnistria, is not part of the territorial unit of Transnistria as defined by the Moldovan central authorities, but it is controlled by the PMR authorities, which consider it part of PMR's administrative organisation:
}, Moldovan Cyrillic
The Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet is a Cyrillic alphabet designed for the Romanian language spoken in the Soviet Union ( Moldovan) and was in official use from 1924 to 1932 and 1938 to 1989 (and still in use today in the breakaway Moldovan regio ...
: )
, style="text-align:right;", , , style="text-align:right;", 21,000, , 47.82% Moldovans, 42.55% Ukrainians, 6.89% Russians, 2.74% others
, -
! scope="row" , Rîbnița District
The Rîbnița District ( ro, Raionul Rîbnița; russian: Рыбницкий район; uk, Рибницький район) is an administrative district of Transnistria (''de facto'') in Moldova (''de jure''). Its seat is the city of Rîbnița ...
( ro, Rîbnița, Moldovan Cyrillic
The Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet is a Cyrillic alphabet designed for the Romanian language spoken in the Soviet Union ( Moldovan) and was in official use from 1924 to 1932 and 1938 to 1989 (and still in use today in the breakaway Moldovan regio ...
: )
, style="text-align:right;", , , style="text-align:right;", 69,000, , 29.90% Moldovans, 45.41% Ukrainians, 17.22% Russians, 7.47% others
, -
! scope="row" , Dubăsari District ( ro, Dubăsari, Moldovan Cyrillic
The Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet is a Cyrillic alphabet designed for the Romanian language spoken in the Soviet Union ( Moldovan) and was in official use from 1924 to 1932 and 1938 to 1989 (and still in use today in the breakaway Moldovan regio ...
: )
, style="text-align:right;", , , style="text-align:right;", 31,000, , 50.15% Moldovans, 28.29% Ukrainians, 19.03% Russians, 2.53% others
, -
! scope="row" , Grigoriopol District
Grigoriopol District ( ro, Raionul Grigoriopol; russian: Григориопольский район; uk, Григоріопольський район) is an administrative district of Transnistria (''de facto'') in Moldova (''de jure''). It is ...
( ro, Grigoriopol, Moldovan Cyrillic
The Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet is a Cyrillic alphabet designed for the Romanian language spoken in the Soviet Union ( Moldovan) and was in official use from 1924 to 1932 and 1938 to 1989 (and still in use today in the breakaway Moldovan regio ...
: )
, style="text-align:right;", , , style="text-align:right;", 40,000, , 64.83% Moldovans, 15.28% Ukrainians, 17.36% Russians, 2.26% others
, -
! scope="row" , Slobozia District ( ro, Slobozia, Moldovan Cyrillic
The Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet is a Cyrillic alphabet designed for the Romanian language spoken in the Soviet Union ( Moldovan) and was in official use from 1924 to 1932 and 1938 to 1989 (and still in use today in the breakaway Moldovan regio ...
: )
, style="text-align:right;", , , style="text-align:right;", 84,000, , 41.51% Moldovans, 21.71% Ukrainians, 26.51% Russians, 10.27% others
, -
! scope="row" , City of Tiraspol ( ro, Tiraspol, Moldovan Cyrillic
The Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet is a Cyrillic alphabet designed for the Romanian language spoken in the Soviet Union ( Moldovan) and was in official use from 1924 to 1932 and 1938 to 1989 (and still in use today in the breakaway Moldovan regio ...
: )
, style="text-align:right;", , , style="text-align:right;", 129,000, , 18.41% Moldovans, 32.31% Ukrainians, 41.44% Russians, 7.84% others
, -
! scope="row" , City of Bender ( ro, Tighina, Moldovan Cyrillic
The Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet is a Cyrillic alphabet designed for the Romanian language spoken in the Soviet Union ( Moldovan) and was in official use from 1924 to 1932 and 1938 to 1989 (and still in use today in the breakaway Moldovan regio ...
: )
, style="text-align:right;", , , style="text-align:right;", 91,000, , 25.03% Moldovans, 17.98% Ukrainians, 43.35% Russians, 13.64% others
Each of the districts is further divided into cities and communes.
Political status
UN member states
The United Nations member states are the sovereign states that are members of the United Nations (UN) and have equal representation in the United Nations General Assembly, UN General Assembly. The UN is the world's largest international o ...
consider Transnistria a legal part of the Republic of Moldova. Only the partially recognised or unrecognised states of South Ossetia, Artsakh, and Abkhazia
Abkhazia, ka, აფხაზეთი, tr, , xmf, აბჟუა, abzhua, or ( or ), officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, recognised by most countries as part of Georgia, which vi ...
have recognised Transnistria as a sovereign entity after it declared independence from Moldova in 1990 with Tiraspol as its declared capital.
Between 1929 and 1940, Tiraspol functioned as the capital of the Moldavian ASSR, an autonomous republic that existed from 1924 to 1940 within the Ukrainian SSR.
Although exercising no direct control over the territory of Transnistria, the Moldovan government passed the "Law on Basic Provisions of the Special Legal Status of Localities from the Left Bank of the Dniester" on 22 July 2005, which established part of Transnistria (territory of Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic without Bender and without territories, which are under control of Moldova) as an autonomous territorial unit within the Republic of Moldova.
the population of Transnistria comprised about 555,000 people. Ninety per cent of the population of Transnistria are citizens of Transnistria. Transnistrians may have dual, triple or even quadruple citizenship of internationally recognised countries, including:
* Citizens of Moldova: around 300,000 people (including dual citizens of Moldova and Russia, around 20,000) or of Moldova and the EU states (around 80%) of Romania, Bulgaria, or the Czech Republic
* Citizens of Romania: unknown number
* Citizens of Russia: around 150,000 people (including around 15,000 dual citizens of Belarus, Israel, Turkey); excluding those holding dual citizenship of Russia and of Moldova (around 20,000)
* Citizens of Ukraine: around 100,000 people There are around 20,000–30,000 people with dual citizenship (Moldova and Ukraine, or Russia and Ukraine) or triple citizenship (Moldova, Russia and Ukraine). They are included in the number of Ukrainian citizens.
* Persons without citizenship: around 20,000–30,000 people
There are unsettled border issues
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political bo ...
between Transnistria and Moldova. Fifteen villages from the 11 communes of Dubăsari District, including Cocieri
Cocieri is a commune in the Republic of Moldova, and the administrative center of Dubăsari District. It is located on the eastern bank of the Dniester River, consisting of two villages, ''Cocieri'' and ''Vasilievca''.
During 1992 War of Transni ...
and Doroțcaia
Doroțcaia is a village in the Dubăsari District, Republic of Moldova, situated on the eastern bank of the River Dniester.
The village was a place of fighting during 1992 War of Transnistria. It is now under the control of the central authoriti ...
that geographically belong to Transnistria, have been under the control of the central government of Moldova after the involvement of local inhabitants on the side of Moldovan forces during the War of Transnistria. These villages, along with Varnița and Copanca
Copanca is a village in Căușeni District, Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a Landlocked country, landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukrai ...
, near Bender and Tiraspol, are claimed by the PMR. One city (Bender) and six villages on the west bank are controlled by the PMR, but are considered by Moldova as a separate municipality (Bender and village of Proteagailovca
Proteagailovca is a village in the municipality of Bender (Tighina), Moldova. It had a population of 3,142 at the 2004 Census. The locality, although situated on the right (western) bank of the river Dniester, is under the control of the breakawa ...
) or part of the Căușeni District (five villages in three communes).
Tense situations have periodically surfaced due to these territorial disputes, such as in 2005, when Transnistrian forces entered Vasilievca, in 2006 around Varnița, and in 2007 in the Dubăsari-Cocieri area, when a confrontation between Moldovan and Transnistrian forces occurred, though without any casualties.
June 2010 surveys indicated that 13% of Transnistria's population desired the area's reintegration into Moldova in the condition of territorial autonomy, while 46% wanted Transnistria to be part of the Russian Federation.
International relations
 Nina Shtanski served as Transnistria's Minister of Foreign Affairs from 2012 to 2015; succeeded her as minister.
Nina Shtanski served as Transnistria's Minister of Foreign Affairs from 2012 to 2015; succeeded her as minister.
Government and politics
Transnistria is apresidential
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
* President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese fu ...
republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
. The president is directly elected for a maximum of two consecutive five-year terms. The current President is Vadim Krasnoselsky.
The Supreme Council is a unicameral legislature. It has 43 members who are elected for 5-year terms. Elections take place within a multi-party system. The majority in the Parliament of Transnistria belongs to the Renewal movement that defeated the Republic
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
party affiliated with Igor Smirnov in 2005 and performed even better in the 2010
File:2010 Events Collage New.png, From top left, clockwise: The 2010 Chile earthquake was one of the strongest recorded in history; The Eruption of Eyjafjallajökull in Iceland disrupts air travel in Europe; A scene from the opening ceremony of ...
and 2015
File:2015 Events Collage new.png, From top left, clockwise: Civil service in remembrance of November 2015 Paris attacks; Germanwings Flight 9525 was purposely crashed into the French Alps; the rubble of residences in Kathmandu following the Apri ...
elections. Elections in Transnistria are not recognised by international bodies such as the European Union, as well as numerous individual countries, who called them a source of increased tensions.
There is disagreement over whether elections in Transnistria are free and fair. The political regime has been described as one of "super- presidentialism".Moldova and the Dniestr Region: Contest Past, Frozen Present, Speculative Futures?Herd, Graeme P.,
Conflict Studies Research Centre
The Conflict Studies Research Centre (CSRC), was a component of the Defence Academy of the United Kingdom, based at Shrivenham, Oxfordshire. It specialised in potential causes of conflict in a wide area ranging from the Baltics to Central Asia.
...
, 2005. Accessed 25 May 2007. During the 2006 presidential election, the registration of opposition candidate Andrey Safonov was delayed until a few days before the vote, so that he had little time to conduct an election campaign. Some sources consider election results suspect. In 2001, in one region it was reported that Igor Smirnov collected 103.6% of the votes. The PMR government said "the government of Moldova launched a campaign aimed at convincing international observers not to attend" an election held on 11 December 2005but monitors from the Russian-led Commonwealth of Independent States election monitors ignored that and declared the ballot democratic.
 The opposition Narodovlastie party and Power to the People movement were outlawed at the beginning of 2000 and eventually dissolved.
A list published by the European Union bans travel to the EU for some members of the Transnistrian leadership.
In 2007, the registration of a Social Democratic Party was allowed. This party, led by a former separatist leader and member of the PMR government Andrey Safonov, allegedly favours a union with Moldova.
In September 2007, the leader of the
The opposition Narodovlastie party and Power to the People movement were outlawed at the beginning of 2000 and eventually dissolved.
A list published by the European Union bans travel to the EU for some members of the Transnistrian leadership.
In 2007, the registration of a Social Democratic Party was allowed. This party, led by a former separatist leader and member of the PMR government Andrey Safonov, allegedly favours a union with Moldova.
In September 2007, the leader of the Pridnestrovie Communist Party
The Pridnestrovie Communist Party (PCP), Moldovan Cyrillic: , uk, Придністровська комуністична партія is a communist party in the unrecognized state of Transnistria. The party was led by Oleg Khorzhan until his ...
, Oleg Khorzhan, was sentenced to a suspended sentence of 1½ years' imprisonment for organising unsanctioned actions of protest.
According to the 2006 referendum, carried out by the PMR government, 97.2% of the population voted in favour of "independence from Moldova and free association with Russia". EU and several other countries refused to recognise the referendum results.
Transnistria border customs dispute
On 3 March 2006, Ukraine introduced new customs regulations on its border with Transnistria. Ukraine declared that it would import goods from Transnistria only with documents processed by Moldovancustoms
Customs is an authority or agency in a country responsible for collecting tariffs and for controlling the flow of goods, including animals, transports, personal effects, and hazardous items, into and out of a country. Traditionally, customs ...
offices as part of the implementation of the joint customs protocol agreed between Ukraine and Moldova on 30 December 2005. Transnistria and Russia termed the act an "economic blockade".
The United States, the European Union, and the OSCE approved the Ukrainian move, while Russia saw it as a means of political pressure. On 4 March, Transnistria responded by blocking the Moldovan and Ukrainian transport at the borders of Transnistria. The Transnistrian block was lifted after two weeks. However, the Moldovan/Ukrainian block remains in place and holds up progress in status settlement negotiations between the sides. In the months after the regulations, exports from Transnistria declined drastically. Transnistria declared a "humanitarian catastrophe" in the region, while Moldova called the declaration "deliberate misinformation". Cargoes of humanitarian aid were sent from Russia in response.

Russian military presence in Transnistria
The 1992 cease-fire agreement between Moldova and Transnistria established a Russian peace-keeper presence in Transnistria and a 1,200-member Russian military contingent is present in Transnistria. Russian troops stationed in parts of Moldova except Transnistria since the time of the USSR were fully withdrawn to Russia by January 1993. In April 1995, the Soviet14th Guards Army
The 14th Guards Army () was a field army of the Red Army, the Soviet Ground Forces, and the Russian Ground Forces, active from 1956 to 1995. According to sources within the 14th Army, the majority of its troops came from the Pridnestrovian Moldavia ...
became the Operational Group of Russian Forces, which by the 2010s had shrunk to two battalions and no more than 1,500 troops.
On 21 October 1994, Russia and Moldova signed an agreement that committed Russia to the withdrawal of the troops in three years from the date of entry into force of the agreement; this did not come into effect, however, because the Russian Duma did not ratify it. The Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE) included a paragraph about the removal of Russian troops from Moldova's territory and was introduced into the text of the OSCE Summit Declaration of Istanbul (1999) in which Russia had committed itself to pulling out its troops from Transnistria by the end of 2002. However, even after 2002, the Russian parliament did not ratify the Istanbul accords. On 19 July 2004, after it finally passed through parliament President Vladimir Putin signed the Law on the ratification of the CFE Treaty in Europe, which committed Russia to remove the heavy armaments limited by this Treaty. During 2000–2001, although the CFE Treaty was not fully ratified, to comply with it, Moscow withdrew 125 pieces of Treaty Limited Equipment (TLE) and 60 railway wagons containing ammunition from the Transnistrian region of Moldova. In 2002, Russia withdrew three trainloads (118 railway wagons) of military equipment and two (43 wagons) of ammunition from the Transnistrian region of Moldova, and in 2003, 11 rail convoys transporting military equipment and 31 transporting ammunition. According to the OSCE Mission to Moldova, of a total of 42,000 tons of ammunition stored in Transnistria, 1,153 tons (3%) was transported back to Russia in 2001, 2,405 tons (6%) in 2002 and 16,573 tons (39%) in 2003.
Andrei Stratan
Andrei Stratan (born September 3, 1966) is a Moldovan politician.
He was the Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs and European Integration in the Vasile Tarlev Cabinet and the Zinaida Greceanîi Cabinets.Minister of Foreign Affairs of Moldova
The Ministry of Foreign Affairs () is one of the fourteen ministries of the Government of Moldova.
Pre-history
The ministry was established on 1 February 1944, as the People's Commissariat of Foreign Affairs of the Moldavian SSR. It would late ...
, stated in his speech during the 12th OSCE Ministerial Council Meeting in Sofia on 6–7 December 2004 that "The presence of Russian troops on the territory of the Republic of Moldova is against the political will of Moldovan constitutional authorities and defies the unanimously recognized international norms and principles, being qualified by Moldovan authorities as a foreign military occupation illegally deployed on the territory of the state".Mihai Gribincea"Russian troops in Transnistria – a threat to the security of the Republic of Moldova", Institute of Political and Military Studies, Chișinău, Moldova
Russia continues to 'sustain the Dniestr region as a quasi-independent entity through direct and indirect means' however, Russia insists that it has already fulfilled those obligations. It states the remaining troops are serving as peacekeepers authorised under the 1992 ceasefire, are not in violation of the Istanbul accords and will remain until the conflict is fully resolved. On the other hand, Moldova believes that fewer than 500 soldiers are authorised pursuant to the ceasefire and, in 2015, began to arrest and deport Russian soldiers who are part of the excess forces and attempt to use Moldovan airports.
 In a NATO resolution on 18 November 2008, Russia was urged to withdraw its military presence from the "Transdnestrian region of Moldova".
In 2011, US Senator
In a NATO resolution on 18 November 2008, Russia was urged to withdraw its military presence from the "Transdnestrian region of Moldova".
In 2011, US Senator John McCain
John Sidney McCain III (August 29, 1936 – August 25, 2018) was an American politician and United States Navy officer who served as a United States senator from Arizona from 1987 until his death in 2018. He previously served two terms ...
claimed in a visit to Moldova that Moscow is violating the territorial integrity of Moldova and Georgia and one of the "fundamental norms" of "international behavior". On 21 May 2015, the Ukrainian parliament passed a law terminating five co-operation agreements with Russia. This law effectively terminates the "Agreement on transit of Russian military units temporarily located on the territory of the Republic of Moldova through the territory of Ukraine" dated 4 December 1998.
One point of access for Russian soldiers travelling to Transnistria remains Chișinău International Airport and the short overland journey from there to Tiraspol. Over the years, Moldova has largely permitted Russian officers and soldiers to transit the airport on their way to Transnistria, though occasionally it blocked those that were not clearly identified as international peacekeepers or who failed to give sufficient advance notice. Chișinău Airport would likely only ever agree to the possibility of moving employees, officers, and soldiers of the peacekeeping forces. The passage of soldiers of the 14th Guards Army
The 14th Guards Army () was a field army of the Red Army, the Soviet Ground Forces, and the Russian Ground Forces, active from 1956 to 1995. According to sources within the 14th Army, the majority of its troops came from the Pridnestrovian Moldavia ...
would be illegal.
On 27 June 2016, a new law entered in force in Transnistria, punishing actions or public statements, including through the usage of mass media, networks of information and telecommunications or the Internet, criticising the peace-keeping mission of the Russian Army in the Transnistrian Moldovan Republic, or presenting interpretations perceived to be "false" by the Transnistrian government of the Russian Army's peacekeeping mission. The punishment is up to three years of jail for ordinary people or up to seven years of jail if the crime was committed by a person of responsibility or a group of persons by prior agreement.
Russian invasion of Ukraine
After the2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. An ...
, Transnistria declared it would maintain its neutrality in the situation and denied claims that it would assist in the attack on Ukraine.
During the prelude to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
In March and April 2021, the Russian Armed Forces began massing thousands of personnel and military equipment near Russia's border with Ukraine and in Crimea, representing the largest mobilization since the illegal annexation of Crimea ...
, Ukrainian military intelligence stated on 14 January 2022 that they had evidence that the Russian government was covertly planning false flag
A false flag operation is an act committed with the intent of disguising the actual source of responsibility and pinning blame on another party. The term "false flag" originated in the 16th century as an expression meaning an intentional misr ...
"provocations" against Russian soldiers stationed in Transnistria, which would be used to justify a Russian invasion of Ukraine. The Russian government denied the claims. In that prelude, similar unattributed clashes happened in Donbas
The Donbas or Donbass (, ; uk, Донба́с ; russian: Донба́сс ) is a historical, cultural, and economic region in eastern Ukraine. Parts of the Donbas are controlled by Russian separatist groups as a result of the Russo-Ukrai ...
in February 2022: Ukraine denied being involved in those incidents and called them a false flag operation as well.
On 15 March 2022, the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe recognised Transnistria as a Moldovan territory occupied by Russia.
On 14 April 2022, one of Ukraine's deputy defence ministers
A defence minister or minister of defence is a Cabinet (government), cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from coun ...
, Hanna Maliar, stated that Russia was massing its troops along the borders with Transnistria but the Transnistrian authorities denied it. According to the Transnistrian authorities, on April 25 there was an attack on the premises of the Ministry for State Security and on the next day two transmitting antennas broadcasting Russian radio programs at Grigoriopol transmitter
The Grigoriopol transmitter, officially the Transnistrian Radio and Television Center, is a very large broadcasting facility situated near Maiac, an urban settlement 11 km (7 miles) northeast of Grigoriopol, Transnistria (Moldova).
History
At th ...
near the Ukrainian border were blown up. The Moldovan authorities called these events a provocation aimed at destabilising the situation in the region. The Russian army has a military base, a large ammunition dump and about 1,500 soldiers stationed in breakaway Transnistria, stating that they are there as "peacekeepers".
Military
 , the armed forces and the paramilitary of Transnistria were composed of around 4,500–7,500 soldiers, divided into four motorised infantry brigades in Tiraspol, Bender,
, the armed forces and the paramilitary of Transnistria were composed of around 4,500–7,500 soldiers, divided into four motorised infantry brigades in Tiraspol, Bender, Rîbnița
Rîbnița or Rybnitsa ( ro, Rîbnița or , Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet: Рыбница; russian: Ры́бница, ''Rybnitsa''; uk, Ри́бниця, ''Rybnytsia''; yi, ריבניצע, ''Ribnitse'') is a town in Transnistria (''de facto'') in M ...
, and Dubăsari
Dubăsari ( ro, Dubăsari , Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet: Дубэсарь) or Dubossary (russian: Дубоссары; yi, דובאסאר; uk, Дубоcсари) is a city in Transnistria, with a population of 23,650. Claimed by both the Republic ...
. They have 18 tanks, 107 armoured personnel carrier
An armoured personnel carrier (APC) is a broad type of armoured military vehicle designed to transport personnel and equipment in combat zones. Since World War I, APCs have become a very common piece of military equipment around the world.
Acc ...
s, 73 field guns, 46 anti-aircraft installations, and 173 tank destroyer units. The airforce is composed of 9 Mi-8T
The Mil Mi-8 (russian: Ми-8, NATO reporting name: Hip) is a medium twin-turbine helicopter, originally designed by the Soviet Union in the 1960s and introduced into the Soviet Air Force in 1968.
It is now produced by Russia.
In addition to ...
helicopters, 6 Mi-24
The Mil Mi-24 (russian: Миль Ми-24; NATO reporting name: Hind) is a large helicopter gunship, attack helicopter and low-capacity troop transport with room for eight passengers. It is produced by Mil Moscow Helicopter Plant and has been o ...
helicopters, 2 Mi-2 helicopters, and several fixed-wing aircraft, including, An-2
The Antonov An-2 ("kukuruznik"—corn crop duster; USAF/DoD reporting name Type 22, NATO reporting name Colt) is a Soviet mass-produced single-engine biplane utility/agricultural aircraft designed and manufactured by the Antonov Design Bureau ...
, An-26 and Yak-18 types.
Demographics

2015 census
In October 2015, Transnistrian authorities organised another separate census from the 2014 Moldovan census. According to the 2015 census, the population of the region was 475,373, a 14.5% decrease from the figure recorded in the 2004 census. The urbanisation rate was 69.9%. By ethnic composition, the population of Transnistria was distributed as follows: Russians – 29.1%, Moldovans – 28.6%, Ukrainians – 22.9%, Bulgarians – 2.4%, Gagauzians – 1.1%, Belarusians – 0.5%, Transnistrian – 0.2%, other nationalities – 1.4%. About 14% of the population did not declare their nationality. Also, for the first time, the population had the option to identify as "Transnistrian". According to another source, the largest ethnic groups in 2015 were 161,300 Russians (34%), 156,600 Moldovans (33%), and 126,700 Ukrainians (26.7%). Bulgarians comprised 13,300 (2.8%), Gagauz 5,700 (1.2%) andBelarusians
, native_name_lang = be
, pop = 9.5–10 million
, image =
, caption =
, popplace = 7.99 million
, region1 =
, pop1 = 600,000–768,000
, region2 =
, pop2 ...
2,800 (0.6%). Germans accounted for 1,400 or 0.3% and Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
for 1,000 or 0.2%. Others accounted for 5,700 people or 1.2%.
2004 census
In 2004, Transnistrian authorities organised a separate census from the2004 Moldovan Census
The 2004 Moldovan census was carried out between October 5 and October 12, 2004. The breakaway Transnistria failed to come into an agreement with the central government in Chişinău, and carried out its own census between November 11 and Novemb ...
. As per 2004 census, in the areas controlled by the PMR government, there were 555,347 people, including 177,785 Moldovans (32.1%) 168,678 Russians (30.4%) 160,069 Ukrainians (28.8%) 13,858 Bulgarians (2.5%) 4,096 Gagauzians (0.7%), 1,791 Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
(0.3%), 1,259 Jews (0.2%), 507 Roma
Roma or ROMA may refer to:
Places Australia
* Roma, Queensland, a town
** Roma Airport
** Roma Courthouse
** Electoral district of Roma, defunct
** Town of Roma, defunct town, now part of the Maranoa Regional Council
*Roma Street, Brisbane, a ...
(0.1%) and 27,454 others (4.9%).
Of these, 439,243 lived in Transnistria itself, and 116,104 lived in localities controlled by the PMR government, but formally belonging to other districts of Moldova: the city of Bender (Tighina), the communes of Proteagailovca
Proteagailovca is a village in the municipality of Bender (Tighina), Moldova. It had a population of 3,142 at the 2004 Census. The locality, although situated on the right (western) bank of the river Dniester, is under the control of the breakawa ...
, Gîsca
Gîsca (meaning " hegoose" in Romanian language, Romanian; russian: Гиска) is a village near in Căușeni District, Moldova, composed of a single village with the same name, population 4,841 at the 2004 Census in Transnistria, 2004 Census ...
, Chițcani, Cremenciug, and the village of ''Roghi'' of commune Molovata Nouă
Molovata Nouă is a commune located in Dubăsari District of the Republic of Moldova, on the eastern bank of the River Dniester. It consists of two villages, ''Molovata Nouă'' and ''Roghi''.
During the 1992 War of Transnistria, the commune was ...
.
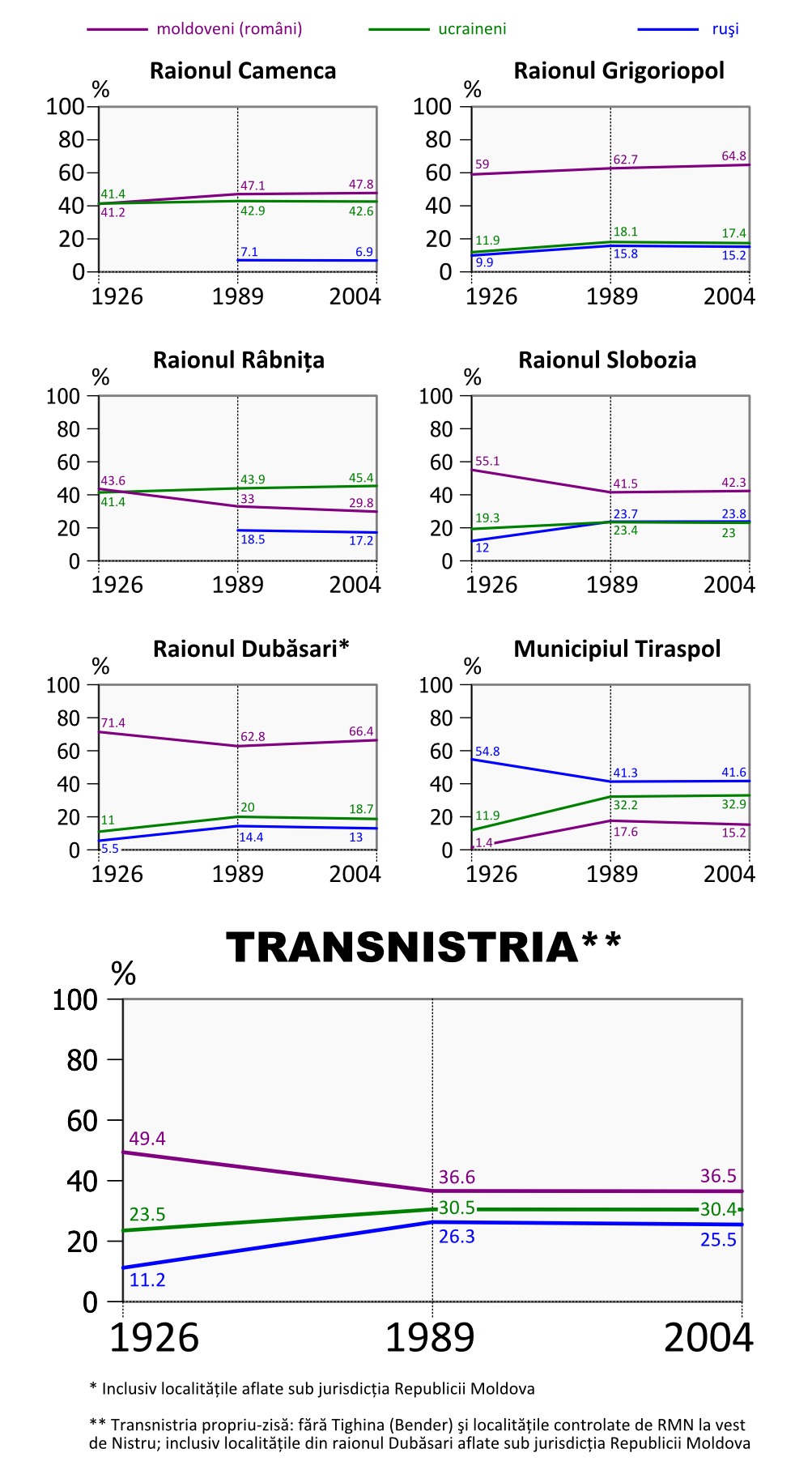
Moldovans were the largest ethnic group, representing an overall majority in the two districts in the central Transnistria ( Dubăsari District, 50.2%, and Grigoriopol District
Grigoriopol District ( ro, Raionul Grigoriopol; russian: Григориопольский район; uk, Григоріопольський район) is an administrative district of Transnistria (''de facto'') in Moldova (''de jure''). It is ...
, 64.8%) a 47.8% relative majority in the northern Camenca District, and a 41.5% relative majority in the southern ( Slobozia District). In Rîbnița District they were a 29.9% minority, and in the city of Tiraspol, they constituted a 15.2% minority of the population.
As per last census, Russians were the second largest ethnic group, representing a 41.6% relative majority in the city of Tiraspol, a 24.1% minority in Slobozia, a 19.0% minority in Dubăsari, a 17.2% minority in Râbnița, a 15.3% minority in Grigoriopol, and a 6.9% minority in Camenca.
Ukrainians were the third largest ethnic group, representing a 45.41% relative majority in the northern Rîbnița District
The Rîbnița District ( ro, Raionul Rîbnița; russian: Рыбницкий район; uk, Рибницький район) is an administrative district of Transnistria (''de facto'') in Moldova (''de jure''). Its seat is the city of Rîbnița ...
, a 42.6% minority in Camenca, a 33.0% minority in Tiraspol, a 28.3% minority in Dubăsari, a 23.4% minority in Slobozia, and a 17.4% minority in Grigoriopol. A substantial number of Poles clustered in northern Transnistria were Ukrainianised during Soviet rule.
Bulgarians were the fourth largest ethnic group in Transnistria, albeit much less numerous than the three larger ethnicities. Most Bulgarians in Transnistria are Bessarabian Bulgarians, descendants of expatriates who settled in Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Be ...
in the 18th–19th century. The major centre of Bulgarians in Transnistria is the large village of Parcani Parcani may refer to:
* Parcani, Prozor, a village in Bosnia and Herzegovina
* Parcani, Şoldăneşti, a commune in Moldova
* Parcani, Soroca, a commune in Moldova
*Parcani, Transnistria, a commune in Moldova
*Parcani, a village in Răciula Commune ...
(situated between the cities of Tiraspol and Bender), which had an absolute Bulgarian majority and a total population of around 10,000.
In Bender (Tighina) and the other non- Transnistria localities under PMR control, ethnic Russians represented a 43.4% relative majority, followed by Moldovans at 26.2%, Ukrainians at 17.1%, Bulgarians at 2.9%, Gagauzians at 1.0%, Jews at 0.3%, Poles at 0.2%, Roma at 0.1%, and others at 7.8%.
1989 census
At the census of 1989, the population was 679,000 (including all the localities in the security zone, even those under Moldovan control). The ethnic composition of the region has been unstable in recent history, with the most notable change being the decreasing share of Moldovan and Jewish population segments and increase of the Russian. For example, the percentage of Russians grew from 13.7% in 1926 to 25.5% in 1989 and further to 30.4% in 2004, while the Moldovan population decreased from 44.1% in 1926 to 39.9% in 1989 and 31.9% in 2004. Only the proportion of Ukrainians remained reasonably stable27.2% in 1926, 28.3% in 1989 and 28.8% in 2004.Religion
PMR official statistics show that 91% of the Transnistrian population adhere toEastern Orthodox Christianity
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
, with 4% adhering to Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
. Roman Catholics are mainly located in northern Transnistria, where a notable Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
minority lives.
Transnistria's government has supported the restoration and construction of new Orthodox churches. It affirms that the republic has freedom of religion and states that 114 religious beliefs and congregations are officially registered. However, as recently as 2005, registration hurdles were met with by some religious groups, notably the Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved in ...
. In 2007, the US-based Christian Broadcasting Network denounced the persecution of Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
in Transnistria.
Economy
Transnistria has a mixed economy. Following a large scaleprivatisation
Privatization (also privatisation in British English) can mean several different things, most commonly referring to moving something from the public sector into the private sector. It is also sometimes used as a synonym for deregulation when ...
process in the late 1990s, most of the companies in Transnistria are now privately owned. The economy is based on a mix of heavy industry (steel production), electricity production, and manufacturing (textile production), which together account for about 80% of the total industrial output.
 Transnistria has its own central bank, the
Transnistria has its own central bank, the Transnistrian Republican Bank
The Transnistrian Republican Bank (russian: Приднестровский республиканский банк, Pridnestrovskiy respublikanskiy bank) is the central bank of Transnistria. It issues its own currency, the Transnistrian rubla and ...
, which issues its national currency, the Transnistrian rubla
The rubla ( ro, рублэ, rublă, , plural ruble; russian: wikt:рубль, рубль) is the currency of Transnistria and is divided into 100 ''kopecks''. It is also known as the rouble in Commonwealth English or ruble in American English. Si ...
. It is convertible at a freely floating exchange rate but only in Transnistria.
Transnistria's economy is frequently described as dependent on contraband
Contraband (from Medieval French ''contrebande'' "smuggling") refers to any item that, relating to its nature, is illegal to be possessed or sold. It is used for goods that by their nature are considered too dangerous or offensive in the eyes o ...
and gunrunning
Arms trafficking or gunrunning is the illicit trade of contraband small arms and ammunition, which constitutes part of a broad range of illegal activities often associated with transnational criminal organizations. The illegal trade of small arm ...
. Some commentators, including Zbigniew Brzezinski, have even labelled it a mafia state. These allegations are denied by the Transnistrian government, and sometimes downplayed by the officials of Russia and Ukraine.
Economic history
After World War II, Transnistria was heavily industrialised, to the point that, in 1990, it was responsible for 40% of Moldova's GDP and 90% of its electricity, although it accounted for only 17% of Moldova's population. After the collapse of the Soviet Union, Transnistria wanted to return to a "Brezhnev-styleplanned economy
A planned economy is a type of economic system where investment, production and the allocation of capital goods takes place according to economy-wide economic plans and production plans. A planned economy may use centralized, decentralized, part ...
". However, several years later, it decided to head toward a market economy
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers ...
.
Macroeconomics
According to the government of Transnistria, the 2007 GDP was 6789 mln ruble (appx US$799 million) and the GDP per capita was about US$1,500. The GDP increased by 11.1% and inflation rate was 19.3% with the GDP per capita now being $2,140, higher than Moldova's GDP per capita that is $2,040. Transnistria's government budget for 2007 was US$246 million, with an estimated deficit of about US$100 million that the government planned to cover with income from privatisations. The budget for 2008 is US$331 million, with an estimated deficit of about US$80 million. In 2004, Transnistria had debts of US$1.2 billion (two-thirds are with Russia) that was per capita about six times higher than in Moldova (without Transnistria). In March 2007 the debt toGazprom
PJSC Gazprom ( rus, Газпром, , ɡɐzˈprom) is a Russian majority state-owned multinational energy corporation headquartered in the Lakhta Center in Saint Petersburg. As of 2019, with sales over $120 billion, it was ranked as the larges ...
for the acquisition of natural gas increased to US$1.3 billion. On 22 March 2007 Gazprom sold Transnistria's gas debt to the Russian businessman Alisher Usmanov, who controls Moldova Steel Works
Moldova Steel Works ( ro, Uzina Metalurgică Moldovenească; russian: Молдавский металлургический завод) is a steel-producing company in Rîbnița, Transnistria. It accounts more than half of Transnistrian industrial ...
, the largest enterprise in Transnistria. Transnistria's president Igor Smirnov has announced that Transnistria will not pay its gas debt because "Transnistria has no legal debt to Gazprom". In November 2007, the total debt of Transnistria's public sector was up to US$1.64 billion.
According to a 2007 interview with Yevgeny Shevchuk, the then-speaker of the Transnistrian Supreme Council
The Supreme Council of the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic ( ro, Sovietul Suprem al Republicii Moldovenești Nistrene, Moldovan Cyrillic: Советул Супрем ал Републичий Молдовенешть Нистрене; russian ...
, Transnistria is in a difficult economic situation. Despite a 30% tax increase in 2007, the pension fund is still lacking money and emergency measures must be taken. However, Shevchuk mentioned that the situation is not hopeless and it cannot be considered a crisis, as a crisis means three-month delays in payment of pensions and salaries.
External trade
In 2020, the Transnistrian Customs reported exports of US$633.1 million and imports of US$1,052.7 million. In the early 2000s over 50% of the export went to theCIS
Cis or cis- may refer to:
Places
* Cis, Trentino, in Italy
* In Poland:
** Cis, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, south-central
** Cis, Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, north
Math, science and biology
* cis (mathematics) (cis(''θ'')), a trigonome ...
, mainly to Russia, but also to Belarus, Ukraine, and Moldova (which Transnistrian authorities consider foreign). Main non-CIS markets for the Transnistrian goods were Italy, Egypt, Greece, Romania, and Germany. The CIS accounted for over 60% of the imports, while the share of the EU was about 23%. The main imports were non-precious metals, food products, and electricity.
After Moldova signed the Association Agreement with the EU in 2014, Transnistriabeing claimed as part of Moldovaenjoyed the tariff-free exports to the EU. As a result, in 2015, 27% of Transnistria's US$189 million exports went to the EU, while exports to Russia went down to 7.7%. This shift towards the EU market continued to grow in 2016.
Economic sectors
The leading industry is steel, due to theMoldova Steel Works
Moldova Steel Works ( ro, Uzina Metalurgică Moldovenească; russian: Молдавский металлургический завод) is a steel-producing company in Rîbnița, Transnistria. It accounts more than half of Transnistrian industrial ...
(part of the Russian Metalloinvest
Metalloinvest Management Company LLC (russian: link=no, Металлоинвест) is a Russian mining and metallurgy company specializing in the manufacture of steel. It was founded in 1999 and is composed of a mining division (Lebedinsky GO ...
holding) in Rîbnița
Rîbnița or Rybnitsa ( ro, Rîbnița or , Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet: Рыбница; russian: Ры́бница, ''Rybnitsa''; uk, Ри́бниця, ''Rybnytsia''; yi, ריבניצע, ''Ribnitse'') is a town in Transnistria (''de facto'') in M ...
, which accounts for about 60% of the budget revenue of Transnistria.Moldova Strategic Conflict Assessment (SCA)Stuart Hensel, Economist Intelligence Unit. The largest company in the textile industry is
Tirotex
Tirotex (russian: Тиротекс) is a Transnistrian textile company producing clothing and other textile products. It is located in (and gets its name from) Tiraspol. The company was established in 1972 with the construction of its factory, wh ...
, which claims to be the second largest textile company in Europe. The energy sector is dominated by Russian companies. The largest power company Moldavskaya GRES (Cuciurgan power station
The Cuciurgan power station ( ro, Termocentrala de la Cuciurgan, russian: Молдавская ГРЭС, translit=Moldavskaya GRES) is the largest power station of Moldova, located in Dnestrovsc, Transnistria, on the shores of the Cuciurgan Rese ...
) is in Dnestrovsc
Dnestrovsc ( ro, Nistrovsc; russian: Днестрóвск, Dnestrovsk; uk, Дністровськ, Dnistrovs'k) is a town in southern Moldova, near the border with Ukraine. It is at the shores of the Cuciurgan Reservoir and is home to the Cuciur ...
and owned by Inter RAO UES, and the gas transmission and distribution company Tiraspoltransgas is probably controlled by Gazprom
PJSC Gazprom ( rus, Газпром, , ɡɐzˈprom) is a Russian majority state-owned multinational energy corporation headquartered in the Lakhta Center in Saint Petersburg. As of 2019, with sales over $120 billion, it was ranked as the larges ...
, although Gazprom has not confirmed the ownership officially. The banking sector of Transnistria consists of 8 commercial banks, including Gazprombank. The oldest alcohol producer KVINT
KVINT (acronym for ''Kon’iaki, vina i napitki Tiraspol’ia'' ("cognacs, wines, and beverages of Tiraspol")) is a winery and distillery based in Tiraspol, the administrative center of Transnistria. Kvint products are certified 'Made in Moldova' ...
, located in Tiraspol, produces and exports brandy, wines and vodka.
Human rights
The human rights record of Transnistria has been criticised by several governments and international organisations. The 2007 '' Freedom in the World'' report, published by the U.S.-basedFreedom House
Freedom House is a non-profit, majority U.S. government funded organization in Washington, D.C., that conducts research and advocacy on democracy, political freedom, and human rights. Freedom House was founded in October 1941, and Wendell Wil ...
, described Transnistria as a "non-free" territory, having an equally bad situation in both political rights and civil liberties.
According to a 2006 U.S. Department of State
The United States Department of State (DOS), or State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the Federal government of the United States, U.S. federal government responsible for the country's fore ...
report:
Media
There is a regular mix of modern news media in Transnistria with a number of television stations, newspapers, and radio stations. According to the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) the media climate in Transnistria is restrictive and the authorities continue a long-standing campaign to silence independent opposition voices and groups. According to a US Department of State report for 2006, "Both of the region's major newspapers were controlled by the authorities. There was one independent weekly newspaper in Bender and another in the northern city of Rîbnița... Separatist authorities harassed independent newspapers for critical reporting of the Transnistrian regime... Most television and radio stations and print publication were controlled by Transnistrian authorities, which largely dictated their editorial policies and finance operations. Some broadcast networks, such as the TSV television station and the INTER-FM radio station, were owned by Transnistria's largest monopoly,Sheriff
A sheriff is a government official, with varying duties, existing in some countries with historical ties to England where the office originated. There is an analogous, although independently developed, office in Iceland that is commonly transla ...
, which also holds a majority in the region's legislature... In July 2005 the Transnistrian Supreme Council amended the election code to prohibit media controlled by the Transnistrian authorities from publishing results of polls and forecasts related to elections." United States Department of State report for 2006
Romanian-language schools
Public education
State schools (in England, Wales, Australia and New Zealand) or public schools (Scottish English and North American English) are generally primary or secondary schools that educate all students without charge. They are funded in whole or in pa ...
in the Romanian language (officially called Moldovan language in Transnistria) is done using the Soviet-originated Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet. The usage of the Latin script was restricted to only six schools. Four of these schools were forcibly closed by the authorities, who claimed this was due to the refusal of the schools to apply for official accreditation. These schools were later registered as private schools and reopened, which may have been accelerated by pressure from the European Union.
The OSCE mission to Moldova has urged local authorities in the Transnistrian city of Rîbnița
Rîbnița or Rybnitsa ( ro, Rîbnița or , Moldovan Cyrillic alphabet: Рыбница; russian: Ры́бница, ''Rybnitsa''; uk, Ри́бниця, ''Rybnytsia''; yi, ריבניצע, ''Ribnitse'') is a town in Transnistria (''de facto'') in M ...
to return a confiscated building to the Moldovan Latin script school in the city. The unfinished building was nearing completion in 2004 when Transnistria took control of it during that year's school crisis.
In November 2005 Ion Iovcev
Ion Iovcev is a teacher for the Republic of Moldova. Since 1992, he has been the principal of a Romanian language school in Tiraspol and active advocate for human rights as well as a critic of the Transnistrian leadership. Ion Iovcev was decorated ...
, the principal of a Romanian-language school in Transnistria and active advocate for human rights as well as a critic of the Transnistrian leadership, received threatening calls that he attributed to his criticism of the separatist regime.
In August 2021, the Transnistrian government refused to register the Lucian Blaga Theoretical Lyceum at Tiraspol and forced it to cease its activities for three months, which will affect the school year of the students of the school and constitutes a violation of several articles of the Convention on the Rights of the Child.
Arms control and disarmament
Following the collapse of the former Soviet Union, the Russian 14th Army left 40,000 tons of weaponry and ammunition in Transnistria. In later years there were concerns that the Transnistrian authorities would try to sell these stocks internationally, and intense pressure was applied to have these removed by Russia. In 2000 and 2001, Russia withdrew by rail 141 self-propelled artillery pieces and other armoured vehicles and destroyed locally, 108 T-64 tanks and 139 other pieces of military equipment limited by the Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE). During 2002 and 2003 Russian military officials destroyed a further 51 armoured vehicles, all of which were types not limited by the CFE Treaty. The OSCE also observed and verified the withdrawal of 48 trains with military equipment and ammunition in 2003. However, no further withdrawal activities have taken place since March 2004 and a further 20,000 tons of ammunition, as well as some remaining military equipment, are still to be removed. In the autumn of 2006, the Transnistrian leadership agreed to let an OSCE inspectorate examine the munitions and further access was agreed moving forward. Recent weapons inspections were permitted by Transnistria and conducted by the OSCE. The onus of responsibility rests on Russia to remove the rest of the supplies. Transnistrian authorities declared that they are not involved in the manufacture or export of weapons. OSCE and European Union officials stated in 2005 that there is no evidence that Transnistria "has ever trafficked arms or nuclear material" and much of the alarm is due to the Moldovan government's attempts to pressure Transnistria. In 2007, foreign experts working on behalf of the United Nations said that the historically low levels of transparency and continued denial of full investigations to international monitors have reinforced negative perceptions of the Transnistrian government, although recent co-operation by Transnistrian authorities may have reflected a shift in the attitude of Transnistria.UNDP: 2006 Small arms and light weapons survey of Moldova, SEESAC 1 July 2007, Their report stated that the evidence for the illicit production and
trafficking of weapons
Arms trafficking or gunrunning is the illicit trade of contraband small arms and ammunition, which constitutes part of a broad range of illegal activities often associated with transnational criminal organizations. The illegal trade of small arm ...
into and from Transnistria, has in the past been exaggerated, although the trafficking of light weapons is likely to have occurred before 2001 (the last year when export data showed US$900,000 worth of 'weapons, munitions, their parts and accessories' exported from Transnistria). The report also states that the same holds true for the production of such weapons, which is likely to have been carried out in the 1990s, primarily to equip Transnistrian forces.
The OSCE mission spokesman Claus Neukirch spoke about this situation: "There is often talk about sale of armaments from Transnistria, but there is no convincing evidence."Conflict Studies Research CentreMoldova & The Dniestr Region: Contested Past, Frozen Present, Speculative Futures?
Graeme P. Herd. In 2010, Viktor Kryzhanivsky, Ukraine's special envoy on Transnistria, stated that there was no ongoing
arms
Arms or ARMS may refer to:
*Arm or arms, the upper limbs of the body
Arm, Arms, or ARMS may also refer to:
People
* Ida A. T. Arms (1856–1931), American missionary-educator, temperance leader
Coat of arms or weapons
*Armaments or weapons
**Fi ...
or drug trafficking
A drug is any chemical substance that causes a change in an organism's physiology or psychology when consumed. Drugs are typically distinguished from food and substances that provide nutritional support. Consumption of drugs can be via insuffla ...
through the Transnistrian section of the Ukrainian-Moldovan border at the time.
See also
*Abkhazia
Abkhazia, ka, აფხაზეთი, tr, , xmf, აბჟუა, abzhua, or ( or ), officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, recognised by most countries as part of Georgia, which vi ...
* Community for Democracy and Rights of Nations
The Community for Democracy and Rights of Nations (russian: Сообщество за демократию и права народов), also commonly and colloquially known as the Commonwealth of Unrecognized States, rarely as CIS-2 (), is a ...
* Gagauz Republic
* List of active separatist movements in Europe
* Northern Cyprus
Northern Cyprus ( tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs), officially the Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus (TRNC; tr, Kuzey Kıbrıs Türk Cumhuriyeti, ''KKTC''), is a ''de facto'' state that comprises the northeastern portion of the Geography of Cyprus, isl ...
* Republic of Artsakh
* South Ossetia
* Transnistrian Railway
Transnistrian Railway is the operator of railways in Transnistria.
History
The first railway line on the territory of Transnistria was built in 1867 from Kuchurgan station to station Tiraspol, and in 1871 to Chisinau.
In early November 1877, t ...
* Poles in Moldova
The history of Poles in Moldova has to be examined keeping in mind the traditional borderline along the Dniester river which separates Bessarabia from Transnistria in Moldova. While the regions on both sides of the river were socially and cultura ...
* Women in Transnistria
Women in Transnistria are women who live in or are from Transnistria (may also be spelled as Transdniestria; and also known as the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic, abbreviated as PMR).
Population
Based on the census conducted in 2004, 54% of ...
* FC Sheriff Tiraspol
Fotbal Club Sheriff (russian: ФК Шериф Тирасполь), commonly known as Sheriff Tiraspol or simply Sheriff, is a Moldovan professional football club based in Tiraspol, a city located in the unrecognised breakaway state of Transnist ...
Notes
References
Further reading
* Beyer, John, and Stefan Wolff. "Linkage and leverage effects on Moldova's Transnistria problem." ''East European Politics'' 32.3 (2016): 335–35online
* Blakkisrud, Helge, and Pål Kolstø. "From secessionist conflict toward a functioning state: processes of state-and nation-building in Transnistria." ''Post-Soviet Affairs'' 27.2 (2011): 178–21
online
* Cojocaru, Natalia. "Nationalism and identity in Transnistria." ''Innovation'' 19.3–4 (2006): 261–27
online
* Lynch, Dov. ''Russian peacekeeping strategies in the CIS: the case of Moldova, Georgia and Tajikistan'' (Springer, 1999). * Maclean, Rory ''Pravda Ha Ha: Truth, Lies and the End of Europe'' (Bloomsbury, 2020) ISBN 978-1-4088-9651-
* Protsyk, Oleh. "Representation and democracy in Eurasia's unrecognized states: The case of Transnistria." ''Post-Soviet Affairs'' 25.3 (2009): 257–28
online
* RAND, ''Russia's Hostile Measures: Combating Russian Gray Zone Aggression Against NATO in the Contact, Blunt, and Surge Layers of Competition'' (2020
online
on Transnistria
External links
*Profile of Trans-Dniester
BBC News.
The black hole that ate Moldova
'' The Economist''.
Transdniester Conflict Was Long In The Making
Radio Free Europe.
"Moldova, Transnistria, and European Democracy Polices"
Jos Boonstra
FRIDE
February 2007. * Matsuzato, Kimitaka: "Canonization, Obedience, and Defiance: Strategies for Survival of the Orthodox Communities in Transnistria, Abkhazia, and South Ossetia" in th
Caucasus Analytical Digest No. 20
*
PMR Presidential website
*
Website of the Supreme Council (Parliament) of PMR
*
Website MFA of Pridnestrovie
*
Pridnestrovian News – Website of the official information agency of Pridnestrovie
*
Transnistria Guide
*
Transnistria.md News and interviews. Moldova administration
*
Radio PMR. Radio-News. Pridnestrovie administration
*
First Pridnestrovian TV Channel – State television of Pridnestrovie
*
On-line TV PMR. Video, news and interviews. Pridnestrovie administration
{{coord, 46, 50, N, 29, 37, E, display=title Disputed territories in Europe Post-Soviet states Romanian-speaking countries and territories Russian-speaking countries and territories Ukrainian-speaking countries and territories History of Eastern Europe Landlocked countries Regions of Europe with multiple official languages Eastern European countries States and territories established in 1990 1990 establishments in the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic 1990 establishments in Europe Neo-Sovietism Russian irredentism States with limited recognition Frozen conflict zones