protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNA
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a functional RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important types of non- ...
s (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples. Less than 2% of the human genome can be transcribed into mRNA ( Human genome#Coding vs. noncoding DNA), while at least 80% of mammalian genomic DNA can be actively transcribed (in one or more types of cells), with the majority of this 80% considered to be ncRNA.
Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main ...
s, which use base pairs of nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecul ...
s as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript.
Transcription proceeds in the following general steps:
# RNA polymerase, together with one or more general transcription factors
General transcription factors (GTFs), also known as basal transcriptional factors, are a class of protein transcription factors that bind to specific sites ( promoter) on DNA to activate transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger ...
, binds to promoter DNA.
# RNA polymerase generates a transcription bubble, which separates the two strands of the DNA helix. This is done by breaking the hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing ...
s between complementary DNA nucleotides.
# RNA polymerase adds RNA nucleotides (which are complementary to the nucleotides of one DNA strand).
# RNA sugar-phosphate backbone forms with assistance from RNA polymerase to form an RNA strand.
# Hydrogen bonds of the RNA–DNA helix break, freeing the newly synthesized RNA strand.
# If the cell has a nucleus, the RNA may be further processed. This may include polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eu ...
, capping
Capping may refer to:
* the creation of five-prime (5') caps in a cell nucleus
** Capping enzyme
* Capping in sport, making an appearance in a game at international level
* Ambulance chasing, the practice of lawyers seeking clients at a disast ...
, and splicing.
# The RNA may remain in the nucleus or exit to the cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. ...
through the nuclear pore
A nuclear pore is a part of a large complex of proteins, known as a nuclear pore complex that spans the nuclear envelope, which is the double membrane surrounding the eukaryotic cell nucleus. There are approximately 1,000 nuclear pore complex ...
complex.
If the stretch of DNA is transcribed into an RNA molecule that encodes a protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
, the RNA is termed messenger RNA (mRNA); the mRNA, in turn, serves as a template for the protein's synthesis through translation
Translation is the communication of the Meaning (linguistic), meaning of a #Source and target languages, source-language text by means of an Dynamic and formal equivalence, equivalent #Source and target languages, target-language text. The ...
. Other stretches of DNA may be transcribed into small non-coding RNA
A non-coding RNA (ncRNA) is a functional RNA molecule that is not translated into a protein. The DNA sequence from which a functional non-coding RNA is transcribed is often called an RNA gene. Abundant and functionally important types of non- ...
s such as microRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. m ...
, transfer RNA
Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes), that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino a ...
(tRNA), small nucleolar RNA (snoRNA), small nuclear RNA (snRNA), or enzymatic RNA molecules called ribozyme
Ribozymes (ribonucleic acid enzymes) are RNA molecules that have the ability to catalyze specific biochemical reactions, including RNA splicing in gene expression, similar to the action of protein enzymes. The 1982 discovery of ribozymes demonst ...
sEldra P. Solomon, Linda R. Berg, Diana W. Martin. ''Biology, 8th Edition, International Student Edition''. Thomson Brooks/Cole. as well as larger non-coding RNAs such as ribosomal RNA
Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal ...
(rRNA), and long non-coding RNA (lncRNA). Overall, RNA helps synthesize, regulate, and process proteins; it therefore plays a fundamental role in performing functions within a cell.
In virology
Virology is the scientific study of biological viruses. It is a subfield of microbiology that focuses on their detection, structure, classification and evolution, their methods of infection and exploitation of host cells for reproduction, th ...
, the term transcription may also be used when referring to mRNA synthesis from an RNA molecule (i.e., equivalent to RNA replication). For instance, the genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
of a negative-sense
A sense is a biological system used by an organism for sensation, the process of gathering information about the world through the detection of stimuli. (For example, in the human body, the brain which is part of the central nervous system rec ...
single-stranded RNA (ssRNA -) virus may be a template for a positive-sense single-stranded RNA (ssRNA +). This is because the positive-sense strand contains the sequence information needed to translate the viral proteins needed for viral replication
Viral replication is the formation of biological viruses during the infection process in the target host cells. Viruses must first get into the cell before viral replication can occur. Through the generation of abundant copies of its genome a ...
. This process is catalyzed by a viral RNA replicase.
Background
A DNA transcription unit encoding for a protein may contain both a ''coding sequence'', which will be translated into the protein, and ''regulatory sequences'', which direct and regulate the synthesis of that protein. The regulatory sequence before (" upstream" from) the coding sequence is called the five prime untranslated region (5'UTR); the sequence after (" downstream" from) the coding sequence is called the three prime untranslated region (3'UTR). As opposed toDNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inherita ...
, transcription results in an RNA complement that includes the nucleotide uracil
Uracil () (symbol U or Ura) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced ...
(U) in all instances where thymine (T) would have occurred in a DNA complement.
Only one of the two DNA strands serve as a template for transcription. The antisense strand of DNA is read by RNA polymerase from the 3' end to the 5' end during transcription (3' → 5'). The complementary RNA is created in the opposite direction, in the 5' → 3' direction, matching the sequence of the sense strand with the exception of switching uracil for thymine. This directionality is because RNA polymerase can only add nucleotides to the 3' end of the growing mRNA chain. This use of only the 3' → 5' DNA strand eliminates the need for the Okazaki fragments that are seen in DNA replication. This also removes the need for an RNA primer to initiate RNA synthesis, as is the case in DNA replication.
The ''non''-template (sense) strand of DNA is called the coding strand, because its sequence is the same as the newly created RNA transcript (except for the substitution of uracil for thymine). This is the strand that is used by convention when presenting a DNA sequence.
Transcription has some proofreading mechanisms, but they are fewer and less effective than the controls for copying DNA. As a result, transcription has a lower copying fidelity than DNA replication.
Major steps
Transcription is divided into ''initiation'', ''promoter escape'', ''elongation,'' and ''termination''.Setting up for transcription
Enhancers, transcription factors, Mediator complex and DNA loops in mammalian transcription
 Setting up for transcription in mammals is regulated by many cis-regulatory elements, including core promoter and promoter-proximal elements that are located near the transcription start sites of genes. Core promoters combined with general transcription factors are sufficient to direct transcription initiation, but generally have low basal activity. Other important cis-regulatory modules are localized in DNA regions that are distant from the transcription start sites. These include enhancers, silencers, insulators and tethering elements. Among this constellation of elements, enhancers and their associated
Setting up for transcription in mammals is regulated by many cis-regulatory elements, including core promoter and promoter-proximal elements that are located near the transcription start sites of genes. Core promoters combined with general transcription factors are sufficient to direct transcription initiation, but generally have low basal activity. Other important cis-regulatory modules are localized in DNA regions that are distant from the transcription start sites. These include enhancers, silencers, insulators and tethering elements. Among this constellation of elements, enhancers and their associated transcription factors
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The f ...
have a leading role in the initiation of gene transcription. An enhancer localized in a DNA region distant from the promoter of a gene can have a very large effect on gene transcription, with some genes undergoing up to 100-fold increased transcription due to an activated enhancer.
Enhancers are regions of the genome that are major gene-regulatory elements. Enhancers control cell-type-specific gene transcription programs, most often by looping through long distances to come in physical proximity with the promoters of their target genes. While there are hundreds of thousands of enhancer DNA regions, for a particular type of tissue only specific enhancers are brought into proximity with the promoters that they regulate. In a study of brain cortical neurons, 24,937 loops were found, bringing enhancers to their target promoters. Multiple enhancers, each often at tens or hundred of thousands of nucleotides distant from their target genes, loop to their target gene promoters and can coordinate with each other to control transcription of their common target gene.
The schematic illustration in this section shows an enhancer looping around to come into close physical proximity with the promoter of a target gene. The loop is stabilized by a dimer of a connector protein (e.g. dimer of CTCF or YY1), with one member of the dimer anchored to its binding motif on the enhancer and the other member anchored to its binding motif on the promoter (represented by the red zigzags in the illustration). Several cell function specific transcription factors (there are about 1,600 transcription factors in a human cell) generally bind to specific motifs on an enhancer and a small combination of these enhancer-bound transcription factors, when brought close to a promoter by a DNA loop, govern level of transcription of the target gene. Mediator (a complex usually consisting of about 26 proteins in an interacting structure) communicates regulatory signals from enhancer DNA-bound transcription factors directly to the RNA polymerase II (pol II) enzyme bound to the promoter.
Enhancers, when active, are generally transcribed from both strands of DNA with RNA polymerases acting in two different directions, producing two enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) as illustrated in the Figure. An inactive enhancer may be bound by an inactive transcription factor. Phosphorylation of the transcription factor may activate it and that activated transcription factor may then activate the enhancer to which it is bound (see small red star representing phosphorylation of transcription factor bound to enhancer in the illustration). An activated enhancer begins transcription of its RNA before activating transcription of messenger RNA from its target gene.
CpG island methylation and demethylation
cytosine
Cytosine () (symbol C or Cyt) is one of the four nucleobases found in DNA and RNA, along with adenine, guanine, and thymine ( uracil in RNA). It is a pyrimidine derivative, with a heterocyclic aromatic ring and two substituents attached ...
(see Figure). 5-mC is an epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are " ...
marker found predominantly within CpG sites. About 28 million CpG dinucleotides occur in the human genome. In most tissues of mammals, on average, 70% to 80% of CpG cytosines are methylated (forming 5-methylCpG or 5-mCpG). Methylated cytosines within 5’cytosine-guanine 3’ sequences often occur in groups, called CpG islands
The CpG sites or CG sites are regions of DNA where a cytosine nucleotide is followed by a guanine nucleotide in the linear sequence of bases along its 5' → 3' direction. CpG sites occur with high frequency in genomic regions called CpG ...
. About 60% of promoter sequences have a CpG island while only about 6% of enhancer sequences have a CpG island. CpG islands constitute regulatory sequences, since if CpG islands are methylated in the promoter of a gene this can reduce or silence gene transcription.
DNA methylation regulates gene transcription through interaction with methyl binding domain (MBD) proteins, such as MeCP2, MBD1 and MBD2. These MBD proteins bind most strongly to highly methylated CpG islands
The CpG sites or CG sites are regions of DNA where a cytosine nucleotide is followed by a guanine nucleotide in the linear sequence of bases along its 5' → 3' direction. CpG sites occur with high frequency in genomic regions called CpG ...
. These MBD proteins have both a methyl-CpG-binding domain as well as a transcription repression domain. They bind to methylated DNA and guide or direct protein complexes with chromatin remodeling and/or histone modifying activity to methylated CpG islands. MBD proteins generally repress local chromatin such as by catalyzing the introduction of repressive histone marks, or creating an overall repressive chromatin environment through nucleosome remodeling and chromatin reorganization.
As noted in the previous section, transcription factors
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The f ...
are proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences in order to regulate the expression of a gene. The binding sequence for a transcription factor in DNA is usually about 10 or 11 nucleotides long. As summarized in 2009, Vaquerizas et al. indicated there are approximately 1,400 different transcription factors encoded in the human genome by genes that constitute about 6% of all human protein encoding genes. About 94% of transcription factor binding sites (TFBSs) that are associated with signal-responsive genes occur in enhancers while only about 6% of such TFBSs occur in promoters.
EGR1 protein is a particular transcription factor that is important for regulation of methylation of CpG islands. An EGR1 transcription factor binding site is frequently located in enhancer or promoter sequences. There are about 12,000 binding sites for EGR1 in the mammalian genome and about half of EGR1 binding sites are located in promoters and half in enhancers. The binding of EGR1 to its target DNA binding site is insensitive to cytosine methylation in the DNA.
While only small amounts of EGR1 transcription factor protein are detectable in cells that are un-stimulated, translation of the ''EGR1'' gene into protein at one hour after stimulation is drastically elevated. Production of EGR1 transcription factor proteins, in various types of cells, can be stimulated by growth factors, neurotransmitters, hormones, stress and injury. In the brain, when neurons are activated, EGR1 proteins are up-regulated and they bind to (recruit) the pre-existing TET1 enzymes that are produced in high amounts in neurons. TET enzymes can catalyse demethylation of 5-methylcytosine. When EGR1 transcription factors bring TET1 enzymes to EGR1 binding sites in promoters, the TET enzymes can demethylate the methylated CpG islands at those promoters. Upon demethylation, these promoters can then initiate transcription of their target genes. Hundreds of genes in neurons are differentially expressed after neuron activation through EGR1 recruitment of TET1 to methylated regulatory sequences in their promoters.
The methylation of promoters is also altered in response to signals. The three mammalian DNA methyltransferasess (DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B) catalyze the addition of methyl groups to cytosines in DNA. While DNMT1 is a “maintenance” methyltransferase, DNMT3A and DNMT3B can carry out new methylations. There are also two splice
Splice may refer to:
Connections
* Rope splicing, joining two pieces of rope or cable by weaving the strands of each into the other
** Eye splice, a method of creating a permanent loop in the end of multi stranded rope by means of rope splicing
* ...
protein isoform
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some iso ...
s produced from the ''DNMT3A'' gene: DNA methyltransferase proteins DNMT3A1 and DNMT3A2.
The splice isoform DNMT3A2 behaves like the product of a classical immediate-early gene and, for instance, it is robustly and transiently produced after neuronal activation. Where the DNA methyltransferase isoform DNMT3A2 binds and adds methyl groups to cytosines appears to be determined by histone post translational modifications.
On the other hand, neural activation causes degradation of DNMT3A1 accompanied by reduced methylation of at least one evaluated targeted promoter.
Initiation
Transcription begins with the binding of RNA polymerase, together with one or moregeneral transcription factors
General transcription factors (GTFs), also known as basal transcriptional factors, are a class of protein transcription factors that bind to specific sites ( promoter) on DNA to activate transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger ...
, to a specific DNA sequence referred to as a " promoter" to form an RNA polymerase-promoter "closed complex". In the "closed complex" the promoter DNA is still fully double-stranded.
RNA polymerase, assisted by one or more general transcription factors, then unwinds approximately 14 base pairs of DNA to form an RNA polymerase-promoter "open complex". In the "open complex" the promoter DNA is partly unwound and single-stranded. The exposed, single-stranded DNA is referred to as the "transcription bubble."
RNA polymerase, assisted by one or more general transcription factors, then selects a transcription start site in the transcription bubble, binds to an initiating NTP and an extending NTP (or a short RNA primer and an extending NTP) complementary to the transcription start site sequence, and catalyzes bond formation to yield an initial RNA product.
In bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were am ...
, RNA polymerase holoenzyme consists of five subunits: 2 α subunits, 1 β subunit, 1 β' subunit, and 1 ω subunit. In bacteria, there is one general RNA transcription factor known as a sigma factor. RNA polymerase core enzyme binds to the bacterial general transcription (sigma) factor to form RNA polymerase holoenzyme and then binds to a promoter.
(RNA polymerase is called a holoenzyme when sigma subunit is attached to the core enzyme which is consist of 2 α subunits, 1 β subunit, 1 β' subunit only). Unlike eukaryotes, the initiating nucleotide of nascent bacterial mRNA is not capped with a modified guanine nucleotide. The initiating nucleotide of bacterial transcripts bears a 5′ triphosphate (5′-PPP), which can be used for genome-wide mapping of transcription initiation sites.
In archaea and eukaryotes
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bact ...
, RNA polymerase contains subunits homologous
Homology may refer to:
Sciences
Biology
*Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor
*Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences
* Homologous chrom ...
to each of the five RNA polymerase subunits in bacteria and also contains additional subunits. In archaea and eukaryotes, the functions of the bacterial general transcription factor sigma are performed by multiple general transcription factors that work together. In archaea, there are three general transcription factors: TBP, TFB, and TFE. In eukaryotes, in RNA polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukary ...
-dependent transcription, there are six general transcription factors: TFIIA, TFIIB (an ortholog of archaeal TFB), TFIID (a multisubunit factor in which the key subunit, TBP, is an ortholog of archaeal TBP), TFIIE (an ortholog of archaeal TFE), TFIIF, and TFIIH. The TFIID is the first component to bind to DNA due to binding of TBP, while TFIIH is the last component to be recruited. In archaea and eukaryotes, the RNA polymerase-promoter closed complex is usually referred to as the " preinitiation complex."
Transcription initiation is regulated by additional proteins, known as activators and repressors, and, in some cases, associated coactivators or corepressors, which modulate formation and function of the transcription initiation complex.
Promoter escape
After the first bond is synthesized, the RNA polymerase must escape the promoter. During this time there is a tendency to release the RNA transcript and produce truncated transcripts. This is called abortive initiation, and is common for both eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Abortive initiation continues to occur until an RNA product of a threshold length of approximately 10 nucleotides is synthesized, at which point promoter escape occurs and a transcription elongation complex is formed. Mechanistically, promoter escape occurs throughDNA scrunching Abortive initiation, also known as abortive transcription, is an early process of genetic transcription in which RNA polymerase binds to a DNA promoter and enters into cycles of synthesis of short mRNA transcripts which are released before the tra ...
, providing the energy needed to break interactions between RNA polymerase holoenzyme and the promoter.
In bacteria, it was historically thought that the sigma factor is definitely released after promoter clearance occurs. This theory had been known as the ''obligate release model.'' However, later data showed that upon and following promoter clearance, the sigma factor is released according to a stochastic model
In probability theory and related fields, a stochastic () or random process is a mathematical object usually defined as a family of random variables. Stochastic processes are widely used as mathematical models of systems and phenomena that appea ...
known as the ''stochastic release model''.
In eukaryotes, at an RNA polymerase II-dependent promoter, upon promoter clearance, TFIIH phosphorylates serine 5 on the carboxy terminal domain of RNA polymerase II, leading to the recruitment of capping enzyme (CE). The exact mechanism of how CE induces promoter clearance in eukaryotes is not yet known.
Elongation
uracil
Uracil () (symbol U or Ura) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced ...
s, and the nucleotides are composed of a ribose (5-carbon) sugar where DNA has deoxyribose (one fewer oxygen atom) in its sugar-phosphate backbone).
mRNA transcription can involve multiple RNA polymerases on a single DNA template and multiple rounds of transcription (amplification of particular mRNA), so many mRNA molecules can be rapidly produced from a single copy of a gene. The characteristic elongation rates in prokaryotes and eukaryotes are about 10–100 nts/sec. In eukaryotes, however, nucleosomes act as major barriers to transcribing polymerases during transcription elongation. In these organisms, the pausing induced by nucleosomes can be regulated by transcription elongation factors such as TFIIS.
Elongation also involves a proofreading mechanism that can replace incorrectly incorporated bases. In eukaryotes, this may correspond with short pauses during transcription that allow appropriate RNA editing factors to bind. These pauses may be intrinsic to the RNA polymerase or due to chromatin structure.
Termination
Bacteria use two different strategies for transcription termination – Rho-independent termination and Rho-dependent termination. In Rho-independent transcription termination, RNA transcription stops when the newly synthesized RNA molecule forms a G-C-richhairpin loop
Stem-loop intramolecular base pairing is a pattern that can occur in single-stranded RNA. The structure is also known as a hairpin or hairpin loop. It occurs when two regions of the same strand, usually complementary in nucleotide sequence whe ...
followed by a run of Us. When the hairpin forms, the mechanical stress breaks the weak rU-dA bonds, now filling the DNA–RNA hybrid. This pulls the poly-U transcript out of the active site of the RNA polymerase, terminating transcription. In the "Rho-dependent" type of termination, a protein factor called "Rho
Rho (uppercase Ρ, lowercase ρ or ; el, ρο or el, ρω, label=none) is the 17th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 100. It is derived from Phoenician letter res . Its uppercase form uses the sa ...
" destabilizes the interaction between the template and the mRNA, thus releasing the newly synthesized mRNA from the elongation complex.
Transcription termination in eukaryotes is less well understood than in bacteria, but involves cleavage of the new transcript followed by template-independent addition of adenines at its new 3' end, in a process called polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eu ...
.
Role of RNA polymerase in post-transcriptional changes in RNA
 RNA polymerase plays a very crucial role in all steps including post-transcriptional changes in RNA.
RNA polymerase plays a very crucial role in all steps including post-transcriptional changes in RNA.
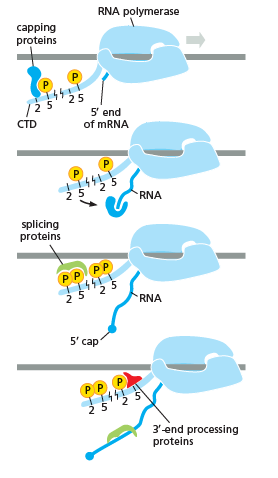 As shown in the image in the right it is evident that the CTD (C Terminal Domain) is a tail that changes its shape; this tail will be used as a carrier of splicing, capping and
As shown in the image in the right it is evident that the CTD (C Terminal Domain) is a tail that changes its shape; this tail will be used as a carrier of splicing, capping and polyadenylation
Polyadenylation is the addition of a poly(A) tail to an RNA transcript, typically a messenger RNA (mRNA). The poly(A) tail consists of multiple adenosine monophosphates; in other words, it is a stretch of RNA that has only adenine bases. In eu ...
, as shown in the image on the left.
Inhibitors
Transcription inhibitors can be used asantibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, ...
s against, for example, pathogenic bacteria (antibacterial
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention ...
s) and fungi
A fungus (plural, : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of Eukaryote, eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and Mold (fungus), molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified ...
( antifungals). An example of such an antibacterial is rifampicin, which inhibits bacterial transcription of DNA into mRNA by inhibiting DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the ...
by binding its beta-subunit, while 8-hydroxyquinoline
8-Hydroxyquinoline (also known as oxine) is a chelating agent which has been used for the quantitative determination of metal ions.
In aqueous solution 8-hydroxyquinoline has a pKa value of ca. 9.9 It reacts with metal ions, losing the proton a ...
is an antifungal transcription inhibitor. The effects of histone methylation may also work to inhibit the action of transcription. Potent, bioactive natural products like triptolide that inhibit mammalian transcription via inhibition of the XPB subunit of the general transcription factor TFIIH has been recently reported as a glucose conjugate for targeting hypoxic cancer cells with increased glucose transporter production.
Endogenous inhibitors
In vertebrates, the majority of gene promoters contain aCpG island
The CpG sites or CG sites are regions of DNA where a cytosine nucleotide is followed by a guanine nucleotide in the linear sequence of bases along its 5' → 3' direction. CpG sites occur with high frequency in genomic regions called CpG isl ...
with numerous CpG sites. When many of a gene's promoter CpG sites are methylated the gene becomes inhibited (silenced). Colorectal cancers typically have 3 to 6 driver mutations and 33 to 66 hitchhiker or passenger mutations. However, transcriptional inhibition (silencing) may be of more importance than mutation in causing progression to cancer. For example, in colorectal cancers about 600 to 800 genes are transcriptionally inhibited by CpG island methylation (see regulation of transcription in cancer). Transcriptional repression in cancer can also occur by other epigenetic
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are " ...
mechanisms, such as altered production of microRNAs. In breast cancer, transcriptional repression of BRCA1 may occur more frequently by over-produced microRNA-182 than by hypermethylation of the BRCA1 promoter (see Low expression of BRCA1 in breast and ovarian cancers).
Transcription factories
Active transcription units are clustered in the nucleus, in discrete sites calledtranscription factories
Transcription factories, in genetics describe the discrete sites where transcription occurs in the cell nucleus, and are an example of a biomolecular condensate. They were first discovered in 1993 and have been found to have structures analogo ...
or euchromatin. Such sites can be visualized by allowing engaged polymerases to extend their transcripts in tagged precursors (Br-UTP or Br-U) and immuno-labeling the tagged nascent RNA. Transcription factories can also be localized using fluorescence in situ hybridization or marked by antibodies directed against polymerases. There are ~10,000 factories in the nucleoplasm of a HeLa cell, among which are ~8,000 polymerase II factories and ~2,000 polymerase III factories. Each polymerase II factory contains ~8 polymerases. As most active transcription units are associated with only one polymerase, each factory usually contains ~8 different transcription units. These units might be associated through promoters and/or enhancers, with loops forming a "cloud" around the factor.
History
A molecule that allows the genetic material to be realized as a protein was first hypothesized by François Jacob andJacques Monod
Jacques Lucien Monod (February 9, 1910 – May 31, 1976) was a French biochemist who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1965, sharing it with François Jacob and André Lwoff "for their discoveries concerning genetic control of ...
. Severo Ochoa won a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine ( sv, Nobelpriset i fysiologi eller medicin) is awarded yearly by the Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute, Nobel Assembly at the Karolinska Institute for outstanding discoveries in physiology or ...
in 1959 for developing a process for synthesizing RNA ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and ...
'' with polynucleotide phosphorylase, which was useful for cracking the genetic code
The genetic code is the set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material ( DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets, or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links ...
. RNA synthesis by RNA polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template.
Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the ...
was established ''in vitro'' by several laboratories by 1965; however, the RNA synthesized by these enzymes had properties that suggested the existence of an additional factor needed to terminate transcription correctly.
In 1972, Walter Fiers became the first person to actually prove the existence of the terminating enzyme.
Roger D. Kornberg won the 2006 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
"for his studies of the molecular basis of eukaryotic transcription".
Measuring and detecting
 Transcription can be measured and detected in a variety of ways:
* G-Less Cassette transcription assay: measures promoter strength
*
Transcription can be measured and detected in a variety of ways:
* G-Less Cassette transcription assay: measures promoter strength
* Run-off transcription
A run-off transcription assay is an assay in molecular biology which is conducted ''in vitro'' to identify the position of the transcription start site (1 base pair upstream) of a specific promoter along with its accuracy and rate of ''in vitro'' ...
assay: identifies transcription start sites (TSS)
* Nuclear run-on A nuclear run-on assay is conducted to identify the genes that are being transcribed at a certain time point. Approximately one million cell nuclei are isolated and incubated with labeled nucleotides, and genes in the process of being transcribe ...
assay: measures the relative abundance of newly formed transcripts
* KAS-seq: measures single-stranded DNA generated by RNA polymerases; can work with 1,000 cells.
* RNase protection assay and ChIP-Chip of RNAP: detect active transcription sites
* RT-PCR: measures the absolute abundance of total or nuclear RNA levels, which may however differ from transcription rates
* DNA microarrays: measures the relative abundance of the global total or nuclear RNA levels; however, these may differ from transcription rates
* In situ hybridization: detects the presence of a transcript
* MS2 tagging
MS2 tagging is a technique based upon the natural interaction of the MS2 bacteriophage coat protein with a stem-loop structure from the phage genome, which is used for biochemical purification of RNA-protein complexes and partnered to GFP for d ...
: by incorporating RNA stem loops, such as MS2, into a gene, these become incorporated into newly synthesized RNA. The stem loops can then be detected using a fusion of GFP and the MS2 coat protein, which has a high affinity, sequence-specific interaction with the MS2 stem loops. The recruitment of GFP to the site of transcription is visualized as a single fluorescent spot. This new approach has revealed that transcription occurs in discontinuous bursts, or pulses (see Transcriptional bursting Transcriptional bursting, also known as transcriptional pulsing, is a fundamental property of genes in which transcription from DNA to RNA can occur in "bursts" or "pulses", which has been observed in diverse organisms, from bacteria to mammals.
...
). With the notable exception of in situ techniques, most other methods provide cell population averages, and are not capable of detecting this fundamental property of genes.
* Northern blot
The northern blot, or RNA blot,Gilbert, S. F. (2000) Developmental Biology, 6th Ed. Sunderland MA, Sinauer Associates. is a technique used in molecular biology research to study gene expression by detection of RNA (or isolated mRNA) in a sample.Ke ...
: the traditional method, and until the advent of RNA-Seq, the most quantitative
* RNA-Seq: applies next-generation sequencing techniques to sequence whole transcriptomes, which allows the measurement of relative abundance of RNA, as well as the detection of additional variations such as fusion genes, post-transcriptional edits and novel splice sites
* Single cell RNA-Seq: amplifies and reads partial transcriptomes from isolated cells, allowing for detailed analyses of RNA in tissues, embryos, and cancers
Reverse transcription
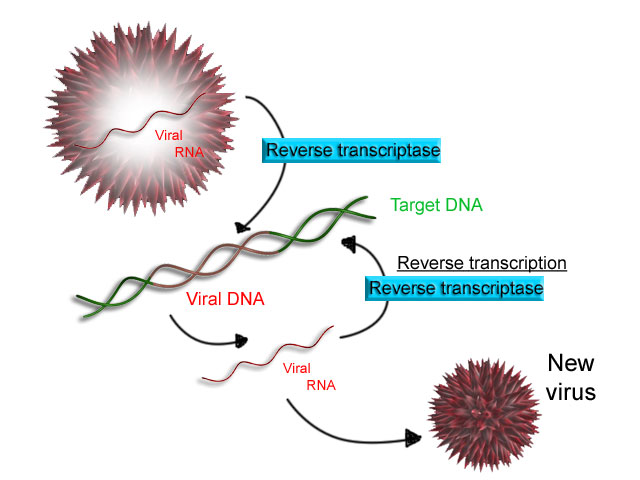 Some
Some viruses
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room ...
(such as HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immu ...
, the cause of AIDS), have the ability to transcribe RNA into DNA. HIV has an RNA genome that is ''reverse transcribed'' into DNA. The resulting DNA can be merged with the DNA genome of the host cell. The main enzyme responsible for synthesis of DNA from an RNA template is called reverse transcriptase.
In the case of HIV, reverse transcriptase is responsible for synthesizing a complementary DNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA synthesized from a single-stranded RNA (e.g., messenger RNA ( mRNA) or microRNA (miRNA)) template in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. cDNA is often used to express a sp ...
strand (cDNA) to the viral RNA genome. The enzyme ribonuclease H
Ribonuclease H (abbreviated RNase H or RNH) is a family of non-sequence-specific endonuclease enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of RNA in an RNA/ DNA substrate via a hydrolytic mechanism. Members of the RNase H family can be found in nearly a ...
then digests the RNA strand, and reverse transcriptase synthesises a complementary strand of DNA to form a double helix DNA structure ("cDNA"). The cDNA is integrated into the host cell's genome by the enzyme integrase
Retroviral integrase (IN) is an enzyme produced by a retrovirus (such as HIV) that integrates—forms covalent links between—its genetic information into that of the host cell it infects. Retroviral INs are not to be confused with phage i ...
, which causes the host cell to generate viral proteins that reassemble into new viral particles. In HIV, subsequent to this, the host cell undergoes programmed cell death, or apoptosis of T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell ...
s. However, in other retroviruses, the host cell remains intact as the virus buds out of the cell.
Some eukaryotic cells contain an enzyme with reverse transcription activity called telomerase
Telomerase, also called terminal transferase, is a ribonucleoprotein that adds a species-dependent telomere repeat sequence to the 3' end of telomeres. A telomere is a region of repetitive sequences at each end of the chromosomes of most e ...
. Telomerase is a reverse transcriptase that lengthens the ends of linear chromosomes. Telomerase carries an RNA template from which it synthesizes a repeating sequence of DNA, or "junk" DNA. This repeated sequence of DNA is called a telomere
A telomere (; ) is a region of repetitive nucleotide sequences associated with specialized proteins at the ends of linear chromosomes. Although there are different architectures, telomeres, in a broad sense, are a widespread genetic feature mo ...
and can be thought of as a "cap" for a chromosome. It is important because every time a linear chromosome is duplicated, it is shortened. With this "junk" DNA or "cap" at the ends of chromosomes, the shortening eliminates some of the non-essential, repeated sequence rather than the protein-encoding DNA sequence, that is farther away from the chromosome end.
Telomerase is often activated in cancer cells to enable cancer cells to duplicate their genomes indefinitely without losing important protein-coding DNA sequence. Activation of telomerase could be part of the process that allows cancer cells to become ''immortal''. The immortalizing factor of cancer via telomere lengthening due to telomerase has been proven to occur in 90% of all carcinogenic tumors ''in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
'' with the remaining 10% using an alternative telomere maintenance route called ALT or Alternative Lengthening of Telomeres.
See also
*Life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for Cell growth, growth, reaction to Stimu ...
* Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients ...
* Cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division usually occurs as part of a larger cell cycle in which the cell grows and replicates its chromosome(s) before dividing. In eukaryotes, there ar ...
* DBTSS DBTSS, the DataBase of Transcriptional
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of ...
* gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
* gene regulation
* gene expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. ...
* Epigenetics
In biology, epigenetics is the study of stable phenotypic changes (known as ''marks'') that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. The Greek prefix '' epi-'' ( "over, outside of, around") in ''epigenetics'' implies features that are " ...
* Genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ...
* Crick's central dogma, in which the product of transcription, mRNA, is translated to form polypeptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides ...
s, and where it is asserted that the reverse processes never occur
* Gene regulation
* Long non-coding RNA
* Missense mRNA
* Splicing – process of removing intron
An intron is any nucleotide sequence within a gene that is not expressed or operative in the final RNA product. The word ''intron'' is derived from the term ''intragenic region'', i.e. a region inside a gene."The notion of the cistron .e., gene ...
s from precursor messenger RNA ( pre-mRNA) to make messenger RNA (mRNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein.
mRNA is created during the ...
)
* Transcriptomics
* Translation (biology)
In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins after the process of transcription of DNA to RNA in the cell's nucleus. The entire proces ...
References
External links
Interactive Java simulation of transcription initiation.
Fro
Center for Models of Life
at the Niels Bohr Institute.
From ttp://cmol.nbi.dk/ Center for Models of Lifeat the Niels Bohr Institute.
Virtual Cell Animation Collection, Introducing Transcription
{{DEFAULTSORT:Transcription (Genetics) Gene expression Molecular biology Cellular processes