|
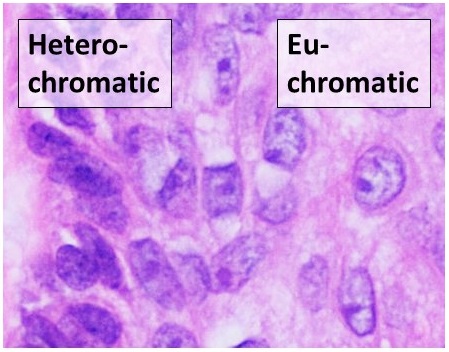
Euchromatin
Euchromatin (also called "open chromatin") is a lightly packed form of chromatin ( DNA, RNA, and protein) that is enriched in genes, and is often (but not always) under active transcription. Euchromatin stands in contrast to heterochromatin, which is tightly packed and less accessible for transcription. 92% of the human genome is euchromatic. In eukaryotes, euchromatin comprises the most active portion of the genome within the cell nucleus. In prokaryotes, euchromatin is the ''only'' form of chromatin present; this indicates that the heterochromatin structure evolved later along with the nucleus, possibly as a mechanism to handle increasing genome size. Structure Euchromatin is composed of repeating subunits known as nucleosomes, reminiscent of an unfolded set of beads on a string, that are approximately 11 nm in diameter. At the core of these nucleosomes are a set of four histone protein pairs: H3, H4, H2A, and H2B. Each core histone protein possesses a 'tail' str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterochromatin
Heterochromatin is a tightly packed form of DNA or '' condensed DNA'', which comes in multiple varieties. These varieties lie on a continue between the two extremes of constitutive heterochromatin and facultative heterochromatin. Both play a role in the expression of genes. Because it is tightly packed, it was thought to be inaccessible to polymerases and therefore not transcribed; however, according to Volpe et al. (2002), and many other papers since, much of this DNA is in fact transcribed, but it is continuously turned over via RNA-induced transcriptional silencing (RITS). Recent studies with electron microscopy and OsO4 staining reveal that the dense packing is not due to the chromatin. Constitutive heterochromatin can affect the genes near itself (e.g. position-effect variegation). It is usually repetitive and forms structural functions such as centromeres or telomeres, in addition to acting as an attractor for other gene-expression or repression signals. Facultative hete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins are the histones. These proteins, aided by chaperone proteins, bind to and condense the DNA molecule to maintain its integrity. These chromosomes display a complex three-dimensional structure, which plays a significant role in transcriptional regulation. Chromosomes are normally visible under a light microscope only during the metaphase of cell division (where all chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell in their condensed form). Before this happens, each chromosome is duplicated ( S phase), and both copies are joined by a centromere, resulting either in an X-shaped structure (pictured above), if the centromere is located equatorially, or a two-arm structure, if the centromere is located distally. The joined copies are now called si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromatin
Chromatin is a complex of DNA and protein found in eukaryotic cells. The primary function is to package long DNA molecules into more compact, denser structures. This prevents the strands from becoming tangled and also plays important roles in reinforcing the DNA during cell division, preventing DNA damage, and regulating gene expression and DNA replication. During mitosis and meiosis, chromatin facilitates proper segregation of the chromosomes in anaphase; the characteristic shapes of chromosomes visible during this stage are the result of DNA being coiled into highly condensed chromatin. The primary protein components of chromatin are histones. An octamer of two sets of four histone cores (Histone H2A, Histone H2B, Histone H3, and Histone H4) bind to DNA and function as "anchors" around which the strands are wound.Maeshima, K., Ide, S., & Babokhov, M. (2019). Dynamic chromatin organization without the 30-nm fiber. ''Current opinion in cell biology, 58,'' 95–104. https://doi.o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karyotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of metaphase chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is discerned by determining the chromosome complement of an individual, including the number of chromosomes and any abnormalities. A karyogram or idiogram is a graphical depiction of a karyotype, wherein chromosomes are organized in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size. Karyotyping generally combines light microscopy and photography, and results in a photomicrographic (or simply micrographic) karyogram. In contrast, a schematic karyogram is a designed graphic representation of a karyotype. In schematic karyograms, just one of the sister chromatids of each chromosome is generally shown for brevity, and in reality they are generally so close together that they look as one on photomicrographs as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone H2A
Histone H2A is one of the five main histone proteins involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryotic cells. The other histone proteins are: H1, H2B, H3 and H4. Background Histones are proteins that package DNA into nucleosomes. Histones are responsible for maintaining the shape and structure of a nucleosome. One chromatin molecule is composed of at least one of each core histones per 100 base pairs of DNA. There are five families of histones known to date; these histones are termed H1/H5, H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. H2A is considered a core histone, along with H2B, H3 and H4. Core formation first occurs through the interaction of two H2A molecules. Then, H2A forms a dimer with H2B; the core molecule is complete when H3-H4 also attaches to form a tetramer. Sequence variants Histone H2A is composed of non-allelic variants. The term "Histone H2A" is intentionally non-specific and refers to a variety of closely related proteins that vary often by only a few amino acids. Apart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histone H4
Histone H4 is one of the five main histone proteins involved in the structure of chromatin in eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. Featuring a main globular domain and a long N-terminus, N-terminal tail, H4 is involved with the structure of the nucleosome of the 'beads on a string' organization. Histone proteins are highly post-translationally modified. Covalently bonded modifications include acetylation and methylation of the N-terminal tails. These modifications may alter Gene expression, expression of genes located on DNA associated with its parent histone octamer. Histone H4 is an important protein in the structure and function of chromatin, where its sequence variants and variable modification states are thought to play a role in the dynamic and long term regulation of genes. Genetics Histone H4 is encoded in multiple genes at different loci including: HIST1H4A, HIST1H4B, HIST1H4C, HIST1H4D, HIST1H4E, HIST1H4F, HIST1H4G, HIST1H4H, HIST1H4I, HIST1H4J, HIST1H4K, HIST1H4L, HIST2H4A, H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleosome
A nucleosome is the basic structural unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes. The structure of a nucleosome consists of a segment of DNA wound around eight histone proteins and resembles thread wrapped around a spool. The nucleosome is the fundamental subunit of chromatin. Each nucleosome is composed of a little less than two turns of DNA wrapped around a set of eight proteins called histones, which are known as a histone octamer. Each histone octamer is composed of two copies each of the histone proteins H2A, H2B, H3, and H4. DNA must be compacted into nucleosomes to fit within the cell nucleus. In addition to nucleosome wrapping, eukaryotic chromatin is further compacted by being folded into a series of more complex structures, eventually forming a chromosome. Each human cell contains about 30 million nucleosomes. Nucleosomes are thought to carry epigenetically inherited information in the form of covalent modifications of their core histones. Nucleosome positions in the gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples. Less than 2% of the human genome can be transcribed into mRNA ( Human genome#Coding vs. noncoding DNA), while at least 80% of mammalian genomic DNA can be actively transcribed (in one or more types of cells), with the majority of this 80% considered to be ncRNA. Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. Transcription proceeds in the following general steps: # RNA polymerase, together with one or more general transcription factors, binds to promoter DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (biology)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples. Less than 2% of the human genome can be transcribed into mRNA ( Human genome#Coding vs. noncoding DNA), while at least 80% of mammalian genomic DNA can be actively transcribed (in one or more types of cells), with the majority of this 80% considered to be ncRNA. Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. Transcription proceeds in the following general steps: # RNA polymerase, together with one or more general transcription factors, binds to promoter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytogenetics
Cytogenetics is essentially a branch of genetics, but is also a part of cell biology/cytology (a subdivision of human anatomy), that is concerned with how the chromosomes relate to cell behaviour, particularly to their behaviour during mitosis and meiosis. Techniques used include karyotyping, analysis of G-banded chromosomes, other cytogenetic banding techniques, as well as molecular cytogenetics such as fluorescent ''in situ'' hybridization (FISH) and comparative genomic hybridization (CGH). History Beginnings Chromosomes were first observed in plant cells by Carl Nägeli in 1842. Their behavior in animal (salamander) cells was described by Walther Flemming, the discoverer of mitosis, in 1882. The name was coined by another German anatomist, von Waldeyer in 1888. The next stage took place after the development of genetics in the early 20th century, when it was appreciated that the set of chromosomes (the karyotype) was the carrier of the genes. Levitsky seems to have been t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linker DNA
In molecular biology, linker DNA is double-stranded DNA (38-53 base pairs long) in between two nucleosome cores that, in association with histone H1, holds the cores together. Linker DNA is seen as the string in the "beads and string model", which is made by using an ionic solution on the chromatin. Linker DNA connects to histone H1 and histone H1 sits on the nucleosome core. Nucleosome is technically the consolidation of a nucleosome core and one adjacent linker DNA; however, the term nucleosome is used freely for solely the core. Linker DNA may be degraded by endonucleases.Molecular Biology of The Cell, Fifth Edition, Alberts et al., Garland Science, 2008 The linkers are short double stranded DNA segments which are formed of oligonucleotides. These contain target sites for the action of one or more restriction enzymes. The linkers can be synthesized chemically and can be ligated to the blunt end of foreign DNA or vector DNA In molecular cloning, a vector is any particle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |