Timeline of Cornish history on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
__NOTOC__
''This



 * Examples of Cornish Stone Age,
* Examples of Cornish Stone Age,
 * 19 AD: Total eclipse in Cornwall.
* 43 AD: Claudian invasion of Britain begins. Roman control of Cornwall comes much later, but at an uncertain date.
*55–60 AD: Construction of Nanstallon Roman fort near Bodmin, one of only a few Roman sites in Cornwall.
*
* 19 AD: Total eclipse in Cornwall.
* 43 AD: Claudian invasion of Britain begins. Roman control of Cornwall comes much later, but at an uncertain date.
*55–60 AD: Construction of Nanstallon Roman fort near Bodmin, one of only a few Roman sites in Cornwall.
*
 *Cornwall's native name (Kernow) appeared on record as early as 400. The
*Cornwall's native name (Kernow) appeared on record as early as 400. The
 *500: The
*500: The
 *825: '' The Battle of Gafulforda'', at an uncertain location, thought to be Galford, near
*825: '' The Battle of Gafulforda'', at an uncertain location, thought to be Galford, near
 * 926: The entry in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' reads....This year fiery lights appeared in the north part of the heavens. And Sihtric perished: and king Aethelstan obtained the kingdom of the North-humbrians. And he ruled all the kings who were in this island: first, Huwal king of the West-Welsh (Cornish or Deheubarth); and Constantine king of the Scots; and Uwen king of the people of Guent; and Ealdred, son of Ealdulf, of Bambrough: and they confirmed the peace by pledge, and by oaths, at the place which is called Eamot, on the 4th of the ides of July
* 926: The entry in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' reads....This year fiery lights appeared in the north part of the heavens. And Sihtric perished: and king Aethelstan obtained the kingdom of the North-humbrians. And he ruled all the kings who were in this island: first, Huwal king of the West-Welsh (Cornish or Deheubarth); and Constantine king of the Scots; and Uwen king of the people of Guent; and Ealdred, son of Ealdulf, of Bambrough: and they confirmed the peace by pledge, and by oaths, at the place which is called Eamot, on the 4th of the ides of July
 *1013: Cornwall's enemy and Anglo-Saxon neighbour,
*1013: Cornwall's enemy and Anglo-Saxon neighbour,
 *1120: Ingulph's Chronicle records Cornwall as a nation distinct from England.
*1154–1214: (effective)/1242 (formal)
*1120: Ingulph's Chronicle records Cornwall as a nation distinct from England.
*1154–1214: (effective)/1242 (formal)
 *1265: Work starts on the Lostwithiel Stannary Palace. It is reputed to be the oldest non-ecclesiastical building in Cornwall and was said to have been built as a replica of the Great Hall of Westminster. Its original function was as a court dealing with the Cornish tin industry.
*1265:
*1265: Work starts on the Lostwithiel Stannary Palace. It is reputed to be the oldest non-ecclesiastical building in Cornwall and was said to have been built as a replica of the Great Hall of Westminster. Its original function was as a court dealing with the Cornish tin industry.
*1265:
 *15th century: the emergence of a popular Cornish literature, centred on the religious-themed
*15th century: the emergence of a popular Cornish literature, centred on the religious-themed

 *1508: By the ' Charter of Pardon', Henry VII confirms that relevant legislation in Cornwall requires the consent of the stannators.
*1509: King Henry VIII's coronation procession includes "nine children of honour" representing "England and France, Gascony,
*1508: By the ' Charter of Pardon', Henry VII confirms that relevant legislation in Cornwall requires the consent of the stannators.
*1509: King Henry VIII's coronation procession includes "nine children of honour" representing "England and France, Gascony,


 *1616:
*1616:
 *1707:
*1707:
* 1747:
 *1801:
*1801:



 *1980s: Split in Cornish language revival, with Modern Cornish and
*1980s: Split in Cornish language revival, with Modern Cornish and


Timeline of Cornish History 400,000 BC – 1066 AD
''
Timeline of Cornish History 1066–1700 AD
''Cornwall County Council webpage''
Timeline of Cornish History 1700 to 1800 AD
''Cornwall County Council webpage''
Timeline of Cornish History 1800 AD to date
''Cornwall County Council webpage'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Timeline Of Cornish History
timeline
A timeline is a display of a list of events in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events.
Timelines can use any suitable scale represen ...
summarizes significant events in the History of Cornwall
The history of Cornwall goes back to the Paleolithic, but in this period Cornwall only had sporadic visits by groups of humans. Continuous occupation started around 10,000 years ago after the end of the last ice age. When recorded history ...
''
Pre-Roman occupation
4000 BC



Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
and Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
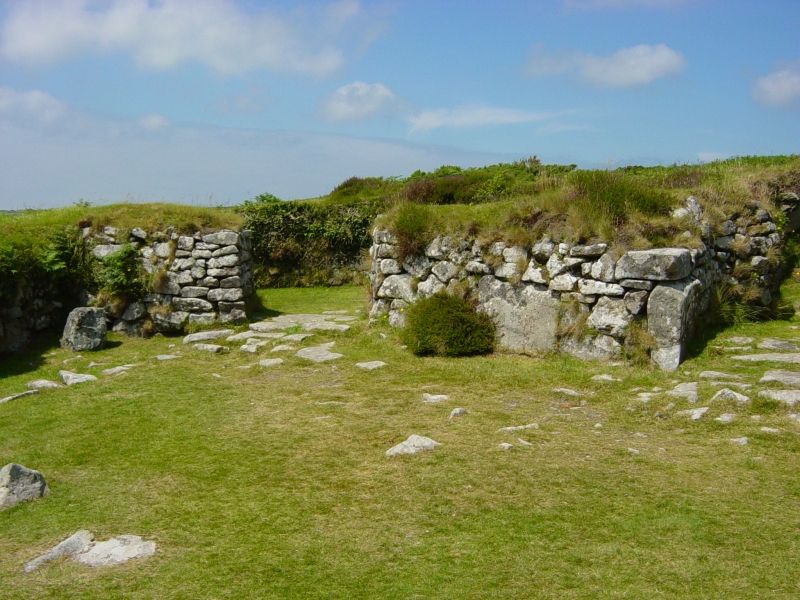
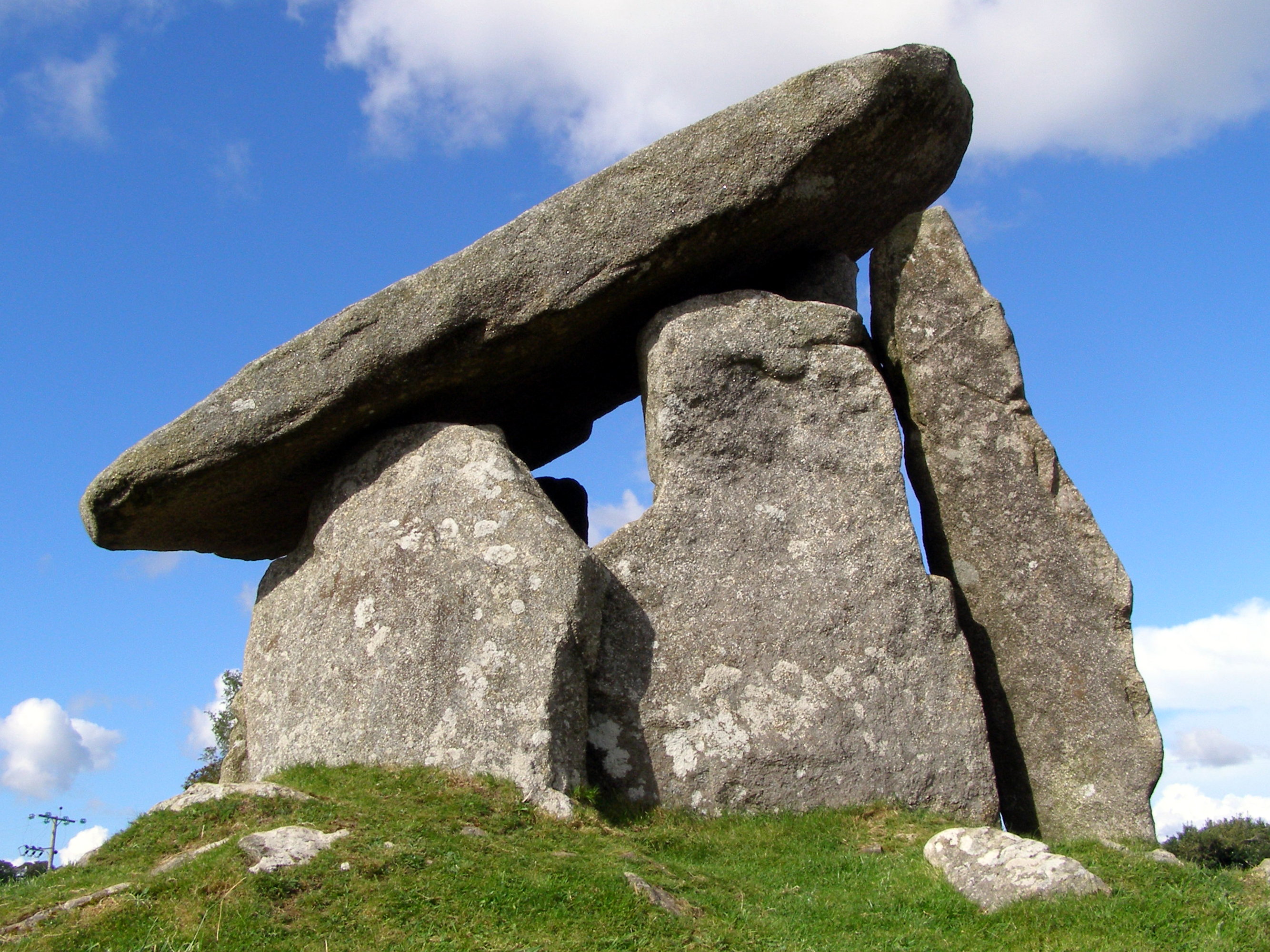
structures are Chûn Quoit
Chûn Quoit is one of the best preserved of all Neolithic quoits (also called dolmens or cromlechs) in western Cornwall, United Kingdom.
Chûn Quoit is located in open moorland near Pendeen and Morvah. Standing on a ridge, near the much later ...
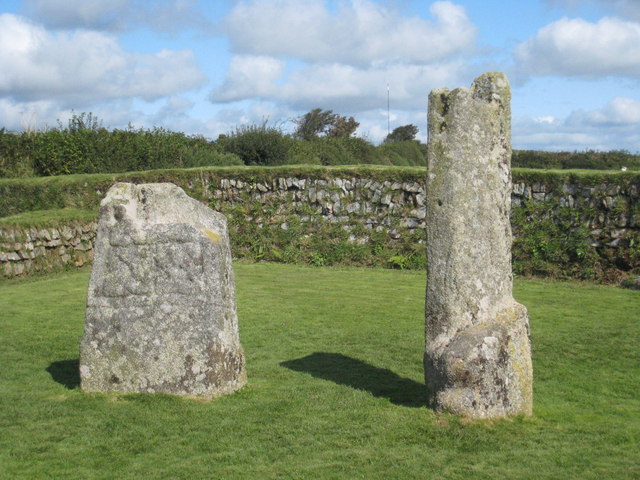
, Boscawen-Un
Boscawen-Ûn () is a Bronze Age stone circle close to St Buryan in Cornwall, UK. It consists of nineteen upright stones in an ellipse with another, leaning, middle stone just south of the centre. There is a west-facing gap in the circle, which ...
and Chysauster Ancient Village. First Cornish hedges.
2000 BC
*Mining in Cornwall
Mining in Cornwall and Devon, in the southwest of England, began in the early Bronze Age, around 2150 BC. Tin, and later copper, were the most commonly extracted metals. Some tin mining continued long after the mining of other metals had be ...
has existed from the early Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
around 2150 BC and it is thought that Cornwall was visited by metal traders from the eastern Mediterranean. It has been suggested that the Cassiterides
The Cassiterides ( el, Κασσιτερίδες, meaning "Tin Islands", from κασσίτερος, ''kassíteros'' "tin") are an ancient geographical name used to refer to a group of islands whose precise location is unknown, but which was believ ...
or "Tin Islands" as recorded by Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
in 445 BC may have referred to the Scilly Islands
The Isles of Scilly (; kw, Syllan, ', or ) is an archipelago off the southwestern tip of Cornwall, England. One of the islands, St Agnes, is the most southerly point in Britain, being over further south than the most southerly point of the ...
and Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
as when first discovered they were both thought to have been islands.
1600 BC
* Cornwall experiences a trade boom driven by the export of tin across Europe.750 BC
* TheIron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostl ...
reaches Cornwall, permitting greater scope of agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people t ...
through the use of new iron ploughs and axes.
330 BC
* Pytheas ofMassilia
Massalia (Greek: Μασσαλία; Latin: Massilia; modern Marseille) was an ancient Greek colony founded ca. 600 BC on the Mediterranean coast of present-day France, east of the river Rhône, by Ionian Greek settlers from Phocaea, in Western An ...
(now Marseilles), a Greek merchant and explorer, circumnavigated the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
between about 330 and 320 BC and produced the first written record of the islands. He described the Cornish as civilised, skilled farmers, usually peaceable, but formidable in war.
100 BC
*60 BC: Greek historian Diodorus Siculus named Cornwall "Belerion" – "The Shining Land", the first recorded place name in theBritish Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, ...
.
*55 BC: First attempted invasion of British mainland by Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
. Over the next century, the Romans come to rule Cornwall, then part of Dumnonia
Dumnonia is the Latinised name for a Brythonic kingdom that existed in Sub-Roman Britain between the late 4th and late 8th centuries CE in the more westerly parts of present-day South West England. It was centred in the area of modern Devon, ...
.
1st millennium
Roman invasion and occupation
 * 19 AD: Total eclipse in Cornwall.
* 43 AD: Claudian invasion of Britain begins. Roman control of Cornwall comes much later, but at an uncertain date.
*55–60 AD: Construction of Nanstallon Roman fort near Bodmin, one of only a few Roman sites in Cornwall.
*
* 19 AD: Total eclipse in Cornwall.
* 43 AD: Claudian invasion of Britain begins. Roman control of Cornwall comes much later, but at an uncertain date.
*55–60 AD: Construction of Nanstallon Roman fort near Bodmin, one of only a few Roman sites in Cornwall.
* Roman villa
A Roman villa was typically a farmhouse or country house built in the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, sometimes reaching extravagant proportions.
Typology and distribution
Pliny the Elder (23–79 AD) distinguished two kinds of villas n ...
at Magor Farm near Camborne occupied.
*360 and after: various Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
came to Roman Britain
Roman Britain was the period in classical antiquity when large parts of the island of Great Britain were under occupation by the Roman Empire. The occupation lasted from AD 43 to AD 410. During that time, the territory conquered wa ...
: raiders, Roman armies recruited from among German tribes, authorized settlers: ref. Ælle of Sussex
Ælle (also Aelle or Ella) is recorded in early sources as the first king of the South Saxons, reigning in what is now called Sussex, England, from 477 to perhaps as late as 514.
According to the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'', Ælle and three of hi ...
5th century
 *Cornwall's native name (Kernow) appeared on record as early as 400. The
*Cornwall's native name (Kernow) appeared on record as early as 400. The Ravenna Cosmography
The ''Ravenna Cosmography'' ( la, Ravennatis Anonymi Cosmographia, "The Cosmography of the Unknown Ravennese") is a list of place-names covering the world from India to Ireland, compiled by an anonymous cleric in Ravenna around 700 AD. Textu ...
, compiled c. 700 from Roman material 300 years older, lists a route running westward into Cornwall and on this route is a place then called Durocornovio (Latinised from British Celtic duno-Cornouio-n – "fortress of the Cornish people"). In Latin, 'V' represented and was pronounced as a 'W' and the fortress name refers to Tintagel
Tintagel () or Trevena ( kw, Tre war Venydh, meaning ''Village on a Mountain'') is a civil parish and village situated on the Atlantic coast of Cornwall, England. The village and nearby Tintagel Castle are associated with the legends surroundin ...
. Payton, Philip (1996). ''Cornwall''. Fowey: Alexander Associates
*410: Emperor Honorius recalls the last legions from Britain. There is some uncertainty: some say that this "rescript" refers not to Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great ...
(= Britain) but to Bruttium 01 or '01 may refer to:
* The year 2001, or any year ending with 01
* The month of January
* 1 (number)
Music
* 01'' (Richard Müller album), 2001
* ''01'' (Son of Dave album), 2000
* ''01'' (Urban Zakapa album), 2011
* ''O1'' (Hiroyuki Sawa ...
in Italy.
*Mid-5th century: first waves of settlers from Cornwall, and Devon, go to Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
*433: The Britons call the Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
to come and help them (as mercenaries) against the Pict
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ear ...
s.
*about 446: The "Groans of the Britons
Paralanguage, also known as vocalics, is a component of meta-communication that may modify meaning, give nuanced meaning, or convey emotion, by using techniques such as prosody, pitch, volume, intonation, etc. It is sometimes defined as relatin ...
" last appeal (possibly to the Consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throu ...
Aetius) for the Roman army to come back to Britain.
*King Mark
Mark of Cornwall ( la, Marcus, kw, Margh, cy, March, br, Marc'h) was a sixth-century King of Kernow (Cornwall), possibly identical with King Conomor. He is best known for his appearance in Arthurian legend as the uncle of Tristan and the husb ...
, of Tristan and Iseult
Tristan and Iseult, also known as Tristan and Isolde and other names, is a medieval chivalric romance told in numerous variations since the 12th century. Based on a Celtic legend and possibly other sources, the tale is a tragedy about the illic ...
fame, probably ruled in the late 5th century. According to Cornish folklore, he held court at Tintagel
Tintagel () or Trevena ( kw, Tre war Venydh, meaning ''Village on a Mountain'') is a civil parish and village situated on the Atlantic coast of Cornwall, England. The village and nearby Tintagel Castle are associated with the legends surroundin ...
. King Salomon, father of Saint Cybi
Saint Cuby (in Cornish) or Saint Cybi (in Welsh) was a 6th-century Cornish bishop, saint and, briefly, king, who worked largely in Cornwall and North Wales: his biography is recorded in two slightly variant medieval 'lives'.
Life in Cornwal ...
, ruled after Mark.
6th century
 *500: The
*500: The Kingdom of Cornwall
The history of Cornwall goes back to the Paleolithic, but in this period Cornwall only had sporadic visits by groups of humans. Continuous occupation started around 10,000 years ago after the end of the last ice age. When recorded history ...
emerged around the 6th century which included the tribes of the Dumnonii
The Dumnonii or Dumnones were a British tribe who inhabited Dumnonia, the area now known as Devon and Cornwall (and some areas of present-day Dorset and Somerset) in the further parts of the South West peninsula of Britain, from at least the Ir ...
and the Cornish Cornovii. The origins of the neighbouring Kingdom of Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
are also in this period.
*490 to 510: likely range of dates for the Battle of Mons Badonicus
The Battle of Badon /ˈbeɪdən/ also known as the Battle of Mons Badonicus ( la, obsessio isBadonici montis, "Blockade/Siege of the Badonic Hill"; ''Bellum in monte Badonis'', "Battle on Badon Hill"; ''Bellum Badonis'', "Battle of Badon"; Old ...
, in which Romano-British Celts defeated an invading Anglo-Saxon army.
*535/6: Extreme weather events of 535–536
The volcanic winter of 536 was the most severe and protracted episode of climatic cooling in the Northern Hemisphere in the last 2,000 years. The volcanic winter was caused by an eruption, with several possible locations proposed in various contin ...
cause European famine.
*After 540s : Plague of Justinian
The plague of Justinian or Justinianic plague (541–549 AD) was the first recorded major outbreak of the first plague pandemic, the first Old World pandemic of plague, the contagious disease caused by the bacterium ''Yersinia pestis''. The dis ...
, which would affect all of Europe.
*577: Battle of Deorham
The Battle of Deorham (or Dyrham) is claimed as a decisive military encounter between the West Saxons and the Britons of the West Country in 577. The battle, which was a major victory for Wessex's forces led by Ceawlin and his son, Cuthwine, ...
Down near Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city in ...
results in the separation of the West Welsh (the Cornish) from the Welsh by the advance of the Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
. The earliest Cornish saints
This is a list of Cornish saints, including saints more loosely associated with Cornwall: many of them will have links to sites elsewhere in regions with significant ancient British history, such as Wales, Brittany or Devon.
List of some o ...
systematically convert Cornwall to Christianity, a considerable period before the conversion of the Anglo-Saxon peoples of England (the territory east of the River Tamar). According to tradition these early monastic foundations were made by Christian preachers or Christian Druids from other Celtic lands, mainly Ireland (as in the cases of Saint Piran
Saint Piran or Pyran ( kw, Peran; la, Piranus), died c. 480,Patrons - The Orthodox Church of Archangel Michael and Holy Piran'' Oecumenical Patriarchate, Archdiocese of Thyateira and Great Britain. Laity Moor, Nr Ponsanooth, Cornwall. TR3 7H ...
and Saint Gwinear
Saint Gwinear was a Celtic martyr, one of only two early Cornish saints whose biographies survived the Reformation. The ''Life of Gwinear'' was written in the early 14th century by a priest named Anselm, and has sometimes been printed among Sa ...
), Wales (as in the case of Saint Petroc
Saint Petroc or Petrock ( lat-med, Petrocus; cy, Pedrog; french: link=no, Perreux; ) was a British prince and Christian saint.
Probably born in South Wales, he primarily ministered to the Britons of Devon (Dewnans) and Cornwall (Kernow) then ...
and the Children of Brychan
Brychan Brycheiniog was a legendary 5th-century king of Brycheiniog (Brecknockshire, alternatively Breconshire) in Mid Wales.
Life
According to Celtic hagiography Brychan was born in Ireland, the son of a Prince Anlach, son of Coronac, and hi ...
), and Brittany (as in the case of Saint Mylor).
7th century
*658Battle of Peonnum
The Battle of Peonnum was fought about AD 660 between the West Saxons under Cenwalh and the Britons of what is now Somerset in England. It was a decisive victory for the Saxons, who gained control of Somerset as far west as the River Parrett. The ...
drives the Britons from the area around Glastonbury abbey down to the River Parret
The River Parrett flows through the counties of Dorset and Somerset in South West England, from its source in the Thorney Mills springs in the hills around Chedington in Dorset. Flowing northwest through Somerset and the Somerset Levels to i ...
.
*664: The Synod of Whitby
In the Synod of Whitby in 664, King Oswiu of Northumbria ruled that his kingdom would calculate Easter and observe the monastic tonsure according to the customs of Rome rather than the customs practiced by Irish monks at Iona and its satellite ins ...
determines that England is again an ecclesiastical province of Rome, with its formal structure of dioceses and parishes. The Celtic Church in Dumnonia is not party to the decision and the Cornish Church remains monastic in nature.
* 682: Centwine, King of Wessex ''drove the Britons of the West at the sword's point as far as the sea''. (ASC) Difficult to place due to the nature of the South-West as a Peninsula but likely to be the North Coast around Bridgewater in Somerset as the border had been set at the River Parret
The River Parrett flows through the counties of Dorset and Somerset in South West England, from its source in the Thorney Mills springs in the hills around Chedington in Dorset. Flowing northwest through Somerset and the Somerset Levels to i ...
by the Battle of Peonnum
The Battle of Peonnum was fought about AD 660 between the West Saxons under Cenwalh and the Britons of what is now Somerset in England. It was a decisive victory for the Saxons, who gained control of Somerset as far west as the River Parrett. The ...
8th century
*710: Battle of Llongborth (probablyLangport
Langport is a small town and civil parish in Somerset, England, west of Somerton in the South Somerset district. The parish, which covers only part of the town, has a population of 1,081. Langport is contiguous with Huish Episcopi, a separate ...
in Somerset) fought to try and prevent further English expansion into Devon. King Geraint of Cornwall's led the fighting and his death is recorded in the Elegy for Geraint in the Black Book of Carmarthen. Tensions possibly exacerbated by Geraints refusal to allow the Celtic church to follow the call of the English church (which was perhaps 300 years younger) to conform to the standards of Rome. The battle was fought against the West Saxon King Ine and his kinsman, Nonna.
*722: ''Battle of Hehil
The Battle of Hehil was a battle won by a force of Britons, probably against the Anglo-Saxons of Wessex around the year 720. The location is unknown, except that it was ''apud Cornuenses'' ("among the Cornish").
Sources
The only direct refere ...
'' – The Cornish Britons together with their friends and allies, push back a West-Saxon offensive at "Hehil", unlocated, but probably somewhere in modern Devon.
*753 Cuthred of Wessex fights 'Against the Welsh (Cornish)' according to the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
*755 Cynewulf fights 'Hard battles against the Welsh (Cornish)'
9th century
*807: Unsuccessful Cornish alliance with Danes. *815: The ''Anglo Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alfr ...
'' states ''"& þy geare gehergade Ecgbryht cyning on West Walas from easteweardum oþ westewearde."''...and in this year king Ecgbryht harried the Cornish from east to west.
 *825: '' The Battle of Gafulforda'', at an uncertain location, thought to be Galford, near
*825: '' The Battle of Gafulforda'', at an uncertain location, thought to be Galford, near Lewdown
Lewtrenchard is a village and civil parish in the West Devon district, in the county of Devon, England. Most of the larger village of Lewdown is in the parish. In the Domesday Book of 1086, a manor of Lew is recorded in this area and two rivers h ...
in West Devon. The ''Anglo Saxon Chronicle'' only states: ''"The Wealas (Cornish) and the Defnas (men of Devon) fought at Gafalforda".''Pearce, Susan M. (1978) ''The Kingdom of Dumnonia: studies in history and tradition in south western Britain, AD 350 – 1150''. Padstow: Lodenek Press
*838: ''Battle of Hingston Down
The Battle of Hingston Down took place in 838, probably at Hingston Down in Cornwall between a combined force of Cornish and Vikings on the one side, and West Saxons led by Ecgberht, King of Wessex on the other. The result was a West Saxon ...
'': the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' reports that the Cornish in alliance with the Danes were defeated by Egbert of Wessex
Ecgberht (770/775 – 839), also spelled Egbert, Ecgbert, Ecgbriht, Ecgbeorht, and Ecbert, was King of Wessex from 802 until his death in 839. His father was King Ealhmund of Kent. In the 780s, Ecgberht was forced into exile to Charlem ...
at "Hengestesdun", generally considered to be Hingston Down
Hingston Down is a hill not far from Gunnislake in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is the subject of an old rhyme, due to the prolific tin mining that formerly took place in the area:
This Hingston Down should not be confused with the ...
in eastern Cornwall.
*850: Settlement at Mawgan Porth occupied. Archaeological excavations revealed a settlement comprising three groups of buildings ('courtyard houses') and a burial ground dating from around 850–1050. Finds included pottery and stone artefacts.
*875: King Dungarth ( Donyarth) of Cerniu ("id est Cornubiae") drowns in what is thought to be the River Fowey.
*880s: the Church in Cornwall is having more Saxon priests appointed to it and they control some church estates like Polltun, Caellwic and Landwithan ( Pawton, in St Breock
St Breock ( kw, Nanssans) is a village and a civil parish in north Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The spelling St Breoke was also formerly in use.
Geography
St Breock village is 1 mile (1.6 km) west of Wadebridge immediately to the sou ...
; perhaps Celliwig Celliwig, Kelliwic or Gelliwic is perhaps the earliest named location for the court of King Arthur. It may be translated as 'forest grove'.
Literary references
It is mentioned in the Welsh tale ''Culhwch and Olwen'' whose manuscript dates from the ...
(Kellywick in Egloshayle
Egloshayle (pronounced "eglos-hale" kw, Eglosheyl – meaning church and ''heyl'' meaning estuary) is a civil parish and village in north Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The village is beside the River Camel, southeast of Wadebridge. Th ...
?); and Lawhitton
Lawhitton ( kw, Nansgwydhenn) is a village in the civil parish of Lawhitton Rural, in east Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The village is situated two miles (3 km) southwest of Launceston and half-a-mile west of Cornwall's border with Dev ...
). Eventually they passed these over to Wessex kings. However, according to Alfred the Great's will the amount of land he owned in Cornwall was very small.
*late 9th century: The earliest known example of written Cornish is a gloss in a late 9th century Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
manuscript of ''De Consolatione Philosophiae
''On the Consolation of Philosophy'' ('' la, De consolatione philosophiae'')'','' often titled as ''The Consolation of Philosophy'' or simply the ''Consolation,'' is a philosophical work by the Roman statesman Boethius. Written in 523 while he ...
'' by Boethius
Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, commonly known as Boethius (; Latin: ''Boetius''; 480 – 524 AD), was a Roman senator, consul, ''magister officiorum'', historian, and philosopher of the Early Middle Ages. He was a central figure in the tr ...
, which used the words ''ud rocashaas''. The phrase means "it (the mind) hated the gloomy places".
10th century
 * 926: The entry in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' reads....This year fiery lights appeared in the north part of the heavens. And Sihtric perished: and king Aethelstan obtained the kingdom of the North-humbrians. And he ruled all the kings who were in this island: first, Huwal king of the West-Welsh (Cornish or Deheubarth); and Constantine king of the Scots; and Uwen king of the people of Guent; and Ealdred, son of Ealdulf, of Bambrough: and they confirmed the peace by pledge, and by oaths, at the place which is called Eamot, on the 4th of the ides of July
* 926: The entry in the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' reads....This year fiery lights appeared in the north part of the heavens. And Sihtric perished: and king Aethelstan obtained the kingdom of the North-humbrians. And he ruled all the kings who were in this island: first, Huwal king of the West-Welsh (Cornish or Deheubarth); and Constantine king of the Scots; and Uwen king of the people of Guent; and Ealdred, son of Ealdulf, of Bambrough: and they confirmed the peace by pledge, and by oaths, at the place which is called Eamot, on the 4th of the ides of July 2 July
Events Pre-1600
* 437 – Emperor Valentinian III begins his reign over the Western Roman Empire. His mother Galla Placidia ends her regency, but continues to exercise political influence at the court in Rome.
* 626 – Li Shimin, the ...
and they renounced all idolatry, and after that submitted to him in peace.''
* 927: William of Malmesbury
William of Malmesbury ( la, Willelmus Malmesbiriensis; ) was the foremost English historian of the 12th century. He has been ranked among the most talented English historians since Bede. Modern historian C. Warren Hollister described him as " ...
, writing around 1120, says that Athelstan evicted the Cornish from Exeter and perhaps the rest of Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devo ...
: "''Exeter was cleansed of its defilement by wiping out that filthy race". Payton, Philip (1996). ''Cornwall: a history''. Fowey: Alexander Associates ''The area inside the city walls still known today as 'Little Britain' is the quarter where most of the Cornish Romano-British aristocracy had their town houses, from which the Cornish were expelled. Under Athelstan's statutes it eventually became unlawful for any Cornishman to own land, and lawful for any Englishman to kill any Cornishman (or woman or child).
* 928: It is thought that the King Huwal, "King of the West Welsh" (Cornwall or Hywel Dda
Hywel Dda, sometimes anglicised as Howel the Good, or Hywel ap Cadell (died 949/950) was a king of Deheubarth who eventually came to rule most of Wales. He became the sole king of Seisyllwg in 920 and shortly thereafter established Deheubart ...
of Deheubarth
Deheubarth (; lit. "Right-hand Part", thus "the South") was a regional name for the realms of south Wales, particularly as opposed to Gwynedd (Latin: ''Venedotia''). It is now used as a shorthand for the various realms united under the House o ...
) was one of several kings who signed a treaty with Aethelstan of Wessex at Egmont Bridge.
* 930: ''Armes Prydein
''Armes Prydein'' (, ''The Prophecy of Britain'') is an early 10th-century Welsh prophetic poem from the '' Book of Taliesin''.
In a rousing style characteristic of Welsh heroic poetry, it describes a future where all of Brythonic peoples are a ...
'', (the Prophecy of Britain), this early Welsh poem mentions 'Cornyw', the Celtic name for Cornwall. It foretells that the Welsh together with Cornwall, Brittany, Ireland and Cumbria would expel the English from Britain. This poem also demonstrates any early allegiance between the Celtic people of Britain.
* 936: Athelstan fixed Cornwall's eastern boundary as the east bank of the Tamar. There is no record of Athelstan taking his campaigns into Cornwall and it seems probable that Huwal, King of the Cornish, agreed to pay tribute thus avoiding further attacks and maintaining a high degree of autonomy. Prior to this the West Saxons had pushed their frontier across the Tamar as far west as the River Lynher, but this was only temporary. It was long enough, however, for Saxon settlement and land charters to influence our modern day inheritance of placenames: between Lynher and Tamar there are today many more English than Cornish place names, as is also the case in that other debatable land between Ottery and Tamar in north Cornwall.
* 944: Athelstan's successor, Edmund I of England
Edmund I or Eadmund I (920/921 – 26 May 946) was King of the English from 27 October 939 until his death in 946. He was the elder son of King Edward the Elder and his third wife, Queen Eadgifu, and a grandson of King Alfred the Great. After ...
, styled himself "''King of the English and ruler of this province of the Britons''"
* 981: The Vikings lay waste "Petroces stow" (probably Padstow
Padstow (; kw, Lannwedhenek) is a town, civil parish and fishing port on the north coast of Cornwall, England. The town is situated on the west bank of the River Camel estuary approximately northwest of Wadebridge, northwest of Bodmin and ...
) according to the Anglo-Saxon Chronicle.
* 986: Olaf Tryggvason
Olaf Tryggvason (960s – 9 September 1000) was King of Norway from 995 to 1000. He was the son of Tryggvi Olafsson, king of Viken ( Vingulmark, and Rånrike), and, according to later sagas, the great-grandson of Harald Fairhair, first King of N ...
allegedly visits the Isles of Scilly
* 997: The Dartmoor town of Lydford
Lydford, sometimes spelled Lidford, is a village, once an important town, in Devon, north of Tavistock on the western fringe of Dartmoor in the West Devon district. There is an electoral ward with the same name which includes Princetown. The p ...
, near the Cornish/Wessex border just east of the Tamar is completely destroyed by an angry mob of Danish Vikings. The surprise attack on Lydford is ordered by the King of Denmark and Viking leader Sweyn Forkbeard (previously, Lydford was believed to be impregnable against Viking attack). However, Cornwall is left alone as Sweyn Forkbeard has no intention of crushing Cornwall—unlike Wessex.
2nd millennium
11th century
Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
is crushed and conquered by a Danish army under the leadership of the Viking leader and King of Denmark Sweyn Forkbeard. Sweyn annexes Wessex to his Viking empire which includes Denmark and Norway. He does not, however, annex Cornwall, Wales and Scotland, allowing these "client nations" self-rule in return for an annual payment of tribute or "danegeld".
*1014–1035: The Kingdom of Cornwall
The history of Cornwall goes back to the Paleolithic, but in this period Cornwall only had sporadic visits by groups of humans. Continuous occupation started around 10,000 years ago after the end of the last ice age. When recorded history ...
, Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
, much of Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a Anglo-Scottish border, border with England to the southeast ...
and Ireland were not included in the territories of King Canute the Great
*1016: Famine throughout Europe.
*1066: Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Con ...
brings many Bretons into Cornwall. The Cornish and Breton languages are mutually intelligible at this point.
*1066: William the Conqueror
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first House of Normandy, Norman List of English monarchs#House of Norman ...
may have granted Cornwall to Brian of Brittany
Brian of Brittany ( 1042 – 14 February, perhaps bef. 1086) was a Breton nobleman who fought in the service of William I of England. A powerful magnate in south-western England, he was the first post-Conquest earl of Cornwall.
Brian was born ...
.
*1067: Harold Godwinson
Harold Godwinson ( – 14 October 1066), also called Harold II, was the last crowned Anglo-Saxon English king. Harold reigned from 6 January 1066 until his death at the Battle of Hastings, fighting the Norman invaders led by William the ...
's sons
A son is a male offspring; a boy or a man in relation to his parents. The female counterpart is a daughter. From a biological perspective, a son constitutes a first degree relative.
Social issues
In pre-industrial societies and some current ...
, who have taken refuge in Ireland, raid Somerset
( en, All The People of Somerset)
, locator_map =
, coordinates =
, region = South West England
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_ ...
, Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devo ...
and Cornwall from the sea.
*1068: The Battle of Exeter – the Cornish attacked the Saxon stronghold of Exeter but were eventually driven back by an Anglo-Norman army sent to mop up pockets of resistance.
*1069: Brian of Brittany, lord of Cornwall, defeats the sons of Harold near the River Taw
The River Taw () rises at Taw Head, a spring on the central northern flanks of Dartmoor, crosses North Devon and at the town of Barnstaple, formerly a significant port, empties into Bideford Bay in the Bristol Channel, having formed a large ...
*1070: (ca.) Robert, Count of Mortain made Earl of Cornwall
The title of Earl of Cornwall was created several times in the Peerage of England before 1337, when it was superseded by the title Duke of Cornwall, which became attached to heirs-apparent to the throne.
Condor of Cornwall
* Condor of Cornwall, ...
.
*1086: Domesday Survey
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
: the major landholders in Cornwall are Robert, Count of Mortain, King William, the Bishop of Exeter, and Tavistock Abbey
*1099: Mount's Bay inundated by the sea making St Michael's Mount an island
12th century
 *1120: Ingulph's Chronicle records Cornwall as a nation distinct from England.
*1154–1214: (effective)/1242 (formal)
*1120: Ingulph's Chronicle records Cornwall as a nation distinct from England.
*1154–1214: (effective)/1242 (formal) Angevin Empire
The Angevin Empire (; french: Empire Plantagenêt) describes the possessions of the House of Plantagenet during the 12th and 13th centuries, when they ruled over an area covering roughly half of France, all of England, and parts of Ireland and W ...
, which includes other Brythonic areas such as Brittany and parts of Wales.
*1173: Reginald de Dunstanville, 1st Earl of Cornwall
{{Infobox noble, type
, name = Reginald de Dunstanville
, title = Earl of Cornwall High Sheriff of Devon
, image =
, caption =
, alt =
, CoA =
, more ...
, grants a charter to his 'free burgesses of Triueru' and he addresses his meetings at Truro
Truro (; kw, Truru) is a cathedral city and civil parish in Cornwall, England. It is Cornwall's county town, sole city and centre for administration, leisure and retail trading. Its population was 18,766 in the 2011 census. People of Truro ...
to: ''"All men both Cornish and English"'' suggesting a continuing differentiation. Subsequently, for Launceston, Reginald's Charter continues that distinction – ''"To all my men, French, English and Cornish".''
*1198: William de Wrotham (Lord Warden of the Stannaries
The Lord Warden of the Stannaries (from la, stannum for Tin, Tin, Sn) used to exercise judicial and military functions in Cornwall, England, and is still the official who, upon the commission of the British monarchy, monarch or Duke of Cornwall ...
) writes of those working tin in Cornwall paying twice the taxation of their Devon counterparts.
13th century
*1214:Battle of Bouvines
The Battle of Bouvines was fought on 27 July 1214 near the town of Bouvines in the County of Flanders. It was the concluding battle of the Anglo-French War of 1213–1214. Although estimates on the number of troops vary considerably among mo ...
confirms the French crown's sovereignty over the Duchy of Normandy
The Duchy of Normandy grew out of the 911 Treaty of Saint-Clair-sur-Epte between King Charles III of West Francia and the Viking leader Rollo. The duchy was named for its inhabitants, the Normans.
From 1066 until 1204, as a result of the Norman c ...
's lands in Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
and Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
, meaning Cornwall and Brittany are once more in separate states.
* 1235–1237: Cornish militia fight against the Scots
 *1265: Work starts on the Lostwithiel Stannary Palace. It is reputed to be the oldest non-ecclesiastical building in Cornwall and was said to have been built as a replica of the Great Hall of Westminster. Its original function was as a court dealing with the Cornish tin industry.
*1265:
*1265: Work starts on the Lostwithiel Stannary Palace. It is reputed to be the oldest non-ecclesiastical building in Cornwall and was said to have been built as a replica of the Great Hall of Westminster. Its original function was as a court dealing with the Cornish tin industry.
*1265: Glasney College
Glasney College ( kw, Kolji Glasneth) was founded in 1265 at Penryn, Cornwall, by Bishop Bronescombe and was a centre of ecclesiastical power in medieval Cornwall and probably the best known and most important of Cornwall's religious institut ...
is founded at Penryn by the Bishop of Exeter.
*c. 1280: The Hereford Mappa Mundi
The Hereford Mappa Mundi is a medieval map of the known world ( la, mappa mundi), of a form deriving from the T and O pattern, dating from c. 1300. Archeological scholars believe the map to have originated from eastern England in either Yor ...
highlights Cornwall.
14th century
*1307: The Tinners Charter is granted by Edward I. *1310–1314: In Europe, climate change leads to theGreat Famine of 1315–1317
The Great Famine of 1315–1317 (occasionally dated 1315–1322) was the first of a series of large-scale crises that struck Europe early in the 14th century. Most of Europe (extending east to Russia and south to Italy) was affected. The famine ...
*1336: Edward, the Black Prince
Edward of Woodstock, known to history as the Black Prince (15 June 1330 – 8 June 1376), was the eldest son of King Edward III of England, and the heir apparent to the English throne. He died before his father and so his son, Richard II, suc ...
is named Duke of Cornwall.
*1338–1339: French raids along the Channel
*1350: the Black Death kills half of the Bodmin population.
15th century
 *15th century: the emergence of a popular Cornish literature, centred on the religious-themed
*15th century: the emergence of a popular Cornish literature, centred on the religious-themed mystery play
Mystery plays and miracle plays (they are distinguished as two different forms although the terms are often used interchangeably) are among the earliest formally developed plays in medieval Europe. Medieval mystery plays focused on the represe ...
s (see Cornish literature).
*1415: Cornish archers present at the Battle of Agincourt
*1455–1487: Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These wars were fought bet ...
, the feud between the Courtenays and Bonvilles in Cornwall and Devon.
*1469–72: Rebuilding of St Petroc's Church, Bodmin
*1473–74: The siege of St Michael's Mount (30 September 1473 – February 1474). The last military threat to Edward IV's rule.
*1480s–1551: Sweating sickness
Sweating sickness, also known as the sweats, English sweating sickness, English sweat or ''sudor anglicus'' in Latin, was a mysterious and contagious disease that struck England and later continental Europe in a series of epidemics beginning ...
*1485: Polydore Vergil
Polydore Vergil or Virgil (Italian: ''Polidoro Virgili''; commonly Latinised as ''Polydorus Vergilius''; – 18 April 1555), widely known as Polydore Vergil of Urbino, was an Italian humanist scholar, historian, priest and diplomat, who spent ...
, an Italian cleric commissioned by King Henry VII to write a history of England, states that "The whole country of Britain is divided into four parts, whereof the one is inhabited by Englishmen, the other of Scots, the third of Welshmen, the fourth of Cornish people ... and which all differ among themselves either in tongue, either in manners, or else in laws and ordinances."
*1497: The Cornish Rebellion of 1497
*1497: Michael An Gof
Michael Joseph (died 27 June 1497), better known as Michael An Gof, was one of the leaders of the Cornish rebellion of 1497, along with Thomas Flamank.
Background
The rebels marched on London to protest against King Henry VII's levy of a ...
, Thomas Flamank
Thomas Flamank (died 27 June 1497) was a lawyer and former MP from Cornwall, who together with Michael An Gof led the Cornish rebellion of 1497, a protest against taxes imposed by Henry VII of England.
Ancestry
He was the eldest son of Richard ...
and James Tuchet, 7th Baron Audley
James Tuchet, 7th Baron Audley (c. 146328 June 1497) was a British nobleman and the only lord to fully join the Cornish rebellion of 1497 opposing the rule of Henry VII of England. He was a leader in the rebel army's march to the edge of Londo ...
the leaders of the rebellion, are executed at Tyburn
Tyburn was a manor (estate) in the county of Middlesex, one of two which were served by the parish of Marylebone.
The parish, probably therefore also the manor, was bounded by Roman roads to the west (modern Edgware Road) and south (modern O ...
.
*1497: Second Cornish Uprising of 1497
The Second Cornish uprising occurred in September 1497 when the pretender to the throne Perkin Warbeck landed at Whitesand Bay, near Land's End, on 7 September with just 120 men in two ships.
Warbeck had seen the potential of the Cornish unrest ...
– the Cornish march on Exeter and Taunton
Taunton () is the county town of Somerset, England, with a 2011 population of 69,570. Its thousand-year history includes a 10th-century monastic foundation, Taunton Castle, which later became a priory. The Normans built a castle owned by the ...
before the pretender to the English throne Perkin Warbeck is captured at Beaulieu Abbey in Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English cities on its south coast, Southampton and Portsmouth, Hampshire ...
.
*1498: Plague
16th century

 *1508: By the ' Charter of Pardon', Henry VII confirms that relevant legislation in Cornwall requires the consent of the stannators.
*1509: King Henry VIII's coronation procession includes "nine children of honour" representing "England and France, Gascony,
*1508: By the ' Charter of Pardon', Henry VII confirms that relevant legislation in Cornwall requires the consent of the stannators.
*1509: King Henry VIII's coronation procession includes "nine children of honour" representing "England and France, Gascony, Guienne
Guyenne or Guienne (, ; oc, Guiana ) was an old French province which corresponded roughly to the Roman province of '' Aquitania Secunda'' and the archdiocese of Bordeaux.
The name "Guyenne" comes from ''Aguyenne'', a popular transformation o ...
, Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
, Anjou Anjou may refer to:
Geography and titles France
* County of Anjou, a historical county in France and predecessor of the Duchy of Anjou
**Count of Anjou, title of nobility
*Duchy of Anjou, a historical duchy and later a province of France
**Duk ...
, Cornwall, Wales and Ireland."
*1509–1510: Plague
*1529: King Henry VIII severs ties with the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
and declares himself head of the church in England.
*1531: From the court of King Henry VIII, the Italian diplomat Lodovico Falier writes in a letter that "The language of the English, Welsh and Cornish men is so different that they do not understand each other". He also claims it is possible to distinguish the members of each group by alleged "national characteristics".
*1533–1540: Henry VIII founds the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Britai ...
and begins the Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
in England.
*1536–1545: Dissolution of the Monasteries including most religious houses in Cornwall
*1538: Writing to his government, the French ambassador in London, Gaspard de Coligny Châtillon, indicates ethnic differences thus: "The kingdom of England is by no means a united whole, for it also contains Wales and Cornwall, natural enemies of the rest of England, and speaking a ifferentlanguage".
*1542: Andrew Borde writes in the ''Boke of the Introduction of Knowledge'', ''"In Cornwall is two speches, the one is naughty Englysshe, and the other is Cornysshe speche. And there be many men and women the which cannot speake one worde of Englysshe, but all Cornyshe."''
*1548: Glasney College
Glasney College ( kw, Kolji Glasneth) was founded in 1265 at Penryn, Cornwall, by Bishop Bronescombe and was a centre of ecclesiastical power in medieval Cornwall and probably the best known and most important of Cornwall's religious institut ...
is closed and much of the cultural heritage held there is destroyed
*1549: The Cornish rise up in the Prayer Book Rebellion
The Prayer Book Rebellion or Western Rising was a popular revolt in Cornwall and Devon in 1549. In that year, the ''Book of Common Prayer (1549), Book of Common Prayer'', presenting the theology of the English Reformation, was introduced. The ...
—some 5,000 "rebels" were killed by mercenary forces. The main confrontations are the siege of Exeter, the battles of Fenny Bridges, Woodbury Common, Clyst St Mary, Clyst Heath (where 900 unarmed Cornish prisoners are killed) and Sampford Courtenay. Following this, Provost Marshal Sir Anthony Kingston
Sir Anthony Kingston (ca. 1508 – 14 April 1556) was an English royal official, holder of various positions under several Tudor monarchs.A.D.K. Hawkyard, 'Kingston, Anthony (by 1512-56), of Cadleigh, Devon and Painswick, Glos.', in S.T. Bind ...
is sent into Cornwall to seek retribution. The Book of Common Prayer
The ''Book of Common Prayer'' (BCP) is the name given to a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion and by other Christian churches historically related to Anglicanism. The original book, published in 1549 in the reign ...
is enforced resulting in a decline in the use of the Cornish language.
*1555: Famine
*1578: Plague in Penzance.Jennings, ''Canon''. ''Notes on the Madron Parish Registers''
*1585–1604: Anglo-Spanish War, intermittent conflict, never declared, many raids on shipping; coastal defences strengthened.
*1585: The Green Book of St Columb has one of the earliest references to Morris dancing
Morris dancing is a form of English folk dance. It is based on rhythmic stepping and the execution of choreographed figures by a group of dancers, usually wearing bell pads on their shins. Implements such as sticks, swords and handkerchiefs may ...
.
*1586: Famine
*1588: Spanish Armada; the first sighting is on July 19, when it appears off St Michael's Mount. Soon afterwards, 55 English ships set out in pursuit from Plymouth under the command of Lord Howard of Effingham
Earl of Effingham, in the County of Surrey, is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom, created in 1837 for Kenneth Howard, 11th Baron Howard of Effingham, named after the village of Effingham, Surrey, where heads of thf family owned ...
, with Sir Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( – 28 January 1596) was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, slave trader, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580 ( ...
as Vice Admiral. There is an inconclusive skirmish off Eddystone Rocks, and the Spanish fleet sails eastwards up the Channel.
*1595: Raid on Mount's Bay
The Raid on Mounts Bay also known as the Spanish attack on Mounts Bay was a Spanish raid on Cornwall, England, that took place between 2 and 4 August 1595 in the context of the Brittany Campaign during the Anglo-Spanish war of 1585-1604. It was ...
. Spanish forces under Don
Don, don or DON and variants may refer to:
Places
*County Donegal, Ireland, Chapman code DON
*Don (river), a river in European Russia
*Don River (disambiguation), several other rivers with the name
*Don, Benin, a town in Benin
*Don, Dang, a vill ...
Carlos de Amesquita
Carlos may refer to:
Places
;Canada
* Carlos, Alberta, a locality
;United States
* Carlos, Indiana, an unincorporated community
* Carlos, Maryland, a place in Allegany County
* Carlos, Minnesota, a small city
* Carlos, West Virginia
;Elsewhe ...
, land in Penzance area raiding and sacking settlements, including Newlyn
Newlyn ( kw, Lulyn: Lu 'fleet', Lynn/Lydn 'pool') is a seaside town and fishing port (the largest fishing port in England) in south-west Cornwall, UK.Ordnance Survey: Landranger map sheet 203 ''Land's End''
Newlyn lies on the shore of Moun ...
*1596: Attack on Cawsand
The Attack on Cawsand was a minor Spanish raid on the coast of Cornwall, England, on the night of 14 March 1596 in the context of the Brittany Campaign during the Anglo-Spanish War.
In August 1595 the area of Mount's Bay in Cornwall had been ...
. A Spanish raid is seen off by local militia at Cawsand
Cawsand (; lit. ''Cow Cove'') and Kingsand ( Cornish: ''Porthruw'') are twin villages in southeast Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The village is situated on the Rame Peninsula and is in the parish of Maker-with-Rame.
Cawsand overlooks Pl ...
before they have sunk two boats and burned several houses.
*1597: 3rd Spanish Armada
The 3rd Spanish Armada, also known as the Spanish Armada of 1597, was a major naval event that took place between October and November 1597 as part of the Anglo–Spanish War.Graham pp. 212–213 The armada, which was the third attempt by Spain ...
. Storms off The Lizard
The Lizard ( kw, An Lysardh) is a peninsula in southern Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The most southerly point of the British mainland is near Lizard Point at SW 701115; Lizard village, also known as The Lizard, is the most southerl ...
put paid to the operation with a number being wrecked. It's possible Spanish soldiers landed near Falmouth in Helford Creek before withdrawing. A number of Spanish ships were captured off the Scilly isles
The Isles of Scilly (; kw, Syllan, ', or ) is an archipelago off the southwestern tip of Cornwall, England. One of the islands, St Agnes, is the most southerly point in Britain, being over further south than the most southerly point of the ...
and St Ives by English ships.
17th century
*1603: Following QueenElizabeth I
Elizabeth I (7 September 153324 March 1603) was List of English monarchs, Queen of England and List of Irish monarchs, Ireland from 17 November 1558 until her death in 1603. Elizabeth was the last of the five House of Tudor monarchs and is ...
's death, the Venetian ambassador writes that the "late queen had ruled over five different 'peoples'--English, Welsh, Cornish, Scottish and Irish".
*1616: Arthur Hopton (ambassador to Madrid) writes that "England is ... divided into three great Provinces, or Countries ... speaking a several and different language, as English, Welsh and Cornish".


 *1616:
*1616: Pocahontas
Pocahontas (, ; born Amonute, known as Matoaka, 1596 – March 1617) was a Native American woman, belonging to the Powhatan people, notable for her association with the colonial settlement at Jamestown, Virginia. She was the daughter of ...
may have visited Indian Queens
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asi ...
, although this is disputed.
*1618–1648: Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was one of the longest and most destructive conflicts in European history, lasting from 1618 to 1648. Fought primarily in Central Europe, an estimated 4.5 to 8 million soldiers and civilians died as a result of battle ...
*1620: The ''Mayflower
''Mayflower'' was an English ship that transported a group of English families, known today as the Pilgrims, from England to the New World in 1620. After a grueling 10 weeks at sea, ''Mayflower'', with 102 passengers and a crew of about 30, r ...
'', en route to America with the Pilgrim Fathers
The Pilgrims, also known as the Pilgrim Fathers, were the English settlers who came to North America on the ''Mayflower'' and established the Plymouth Colony in what is today Plymouth, Massachusetts, named after the final departure port of Plymo ...
, stops off at Newlyn to take on water.
*1640: Charles I Charles I may refer to:
Kings and emperors
* Charlemagne (742–814), numbered Charles I in the lists of Holy Roman Emperors and French kings
* Charles I of Anjou (1226–1285), also king of Albania, Jerusalem, Naples and Sicily
* Charles I of ...
recalls Parliament in order to obtain money to finance his military struggle with Scotland. Parliament agrees to fund Charles, but only on condition he answer their grievances relating to his 11-year "personal rule" or "tyranny". Charles refuses and dissolves Parliament after a mere 3 weeks, hence the name of the " Short Parliament"
*1642: The Cornish play a significant role Civil War
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government policies ...
as Cornwall was a Royalist
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of governm ...
stronghold in the generally Parliamentarian south-west. The reason for this was that Cornwall's rights and privileges were tied up with the royal Duchy and Stannaries
A stannary was an administrative division established under stannary law in the English counties of Cornwall and Devon to manage the collection of tin coinage, which was the duty payable on the metal tin smelted from the ore cassiterite mined ...
and the Cornish saw the Civil War as a fight between England and Cornwall as much as a conflict between King and Parliament.
*1642–1646: The First "English" Civil War
*1642: First Battle of Lostwithiel
The Battle of Lostwithiel took place over a 13-day period from 21 August to 2 September 1644, around the town of Lostwithiel and along the River Fowey valley in Cornwall during the First English Civil War. A Royalist army led by Charles I of E ...
.
*1643 January 19: Cornish Royalist victory at the Battle of Braddock
*1643 May 15: Cornish Royalist victory at the Battle of Stratton.
*1643 autumn: King Charles I issues a letter to the people of Cornwall thanking them for their support for the Royalist campaign which he wrote at Sudeley Castle. (Copies of the letter were made for permanent public display in each Cornish parish church and some are still extant.)
*1644 July 20: Battle of Gunnislake New Bridge
The Battle of Gunnislake New Bridge was a battle that took place on 20 July 1644 on and around Gunnislake New Bridge, a bridge over the River Tamar between Cornwall and Devon, during the First English Civil War.
Background
During the Englis ...
*1644 August 1: King Charles I arrived in Cornwall and spent the night at Trecarrel near Launceston
*1644 August 31: Cornish Royalist victory at the Second Battle of Lostwithiel.
*1645 Cornish Royalist leader Sir Richard Grenville, 1st Baronet
Sir Richard Grenville (26 June 1600 – 21 October 1659) was a professional soldier from Cornwall, who served in the Thirty Years War, and 1638 to 1651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms. He was the younger brother of Sir Bevil Grenville, who died a ...
makes Launceston his base and he stations Cornish troops along the River Tamar
The Tamar (; kw, Dowr Tamar) is a river in south west England, that forms most of the border between Devon (to the east) and Cornwall (to the west). A part of the Tamar Valley is a World Heritage Site due to its historic mining activities.
T ...
and issues them with instructions to keep "all foreign troops out of Cornwall". Grenville tries to use "Cornish particularist sentiment" to muster support for the Royalist cause and puts a plan to the Prince which would, if implemented, have created a semi-independent Cornwall.
*1646: Following the Roundhead victory at the Battle of Naseby
The Battle of Naseby took place on 14 June 1645 during the First English Civil War, near the village of Naseby in Northamptonshire. The Parliamentarian New Model Army, commanded by Sir Thomas Fairfax and Oliver Cromwell, destroyed the main ...
in 1645 they had proceeded towards Cornwall reaching Launceston on 25 February 1646 and Bodmin by 2 March 1646. There were skirmishes but the Cornish were vastly outnumbered. Fairfax offered Hopton terms and the surrender took place at Tresillian Bridge, near Truro
Truro (; kw, Truru) is a cathedral city and civil parish in Cornwall, England. It is Cornwall's county town, sole city and centre for administration, leisure and retail trading. Its population was 18,766 in the 2011 census. People of Truro ...
, on 15 March 1646.
*1646: The siege of Pendennis Castle
Pendennis Castle (Cornish: ''Penn Dinas'', meaning "headland fortification") is an artillery fort constructed by Henry VIII near Falmouth, Cornwall, England between 1540 and 1542. It formed part of the King's Device programme to protect aga ...
began in April 1646 and lasted for five months. Parliamentary forces attacked the castle from both land and sea and it finally surrendered on 17 August 1646.
*1648: The Gear Rout – the last Cornish armed uprising involving some 500 rebels.
*1648–1649: Second English Civil War
The Second English Civil War took place between February to August 1648 in Kingdom of England, England and Wales. It forms part of the series of conflicts known collectively as the 1639-1651 Wars of the Three Kingdoms, which include the 1641� ...
*1649–1651: Third English Civil War
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (disambiguation)
* Third Avenue (disambiguation)
* H ...
* 1651: June: Capture of the Isles of Scilly by Admiral Robert Blake Robert Blake may refer to:
Sportspeople
* Bob Blake (American football) (1885–1962), American football player
* Robbie Blake (born 1976), English footballer
* Bob Blake (ice hockey) (1914–2008), American ice hockey player
* Rob Blake (born 196 ...
*1652: Battle of Plymouth
The Battle of Plymouth was a naval battle in the First Anglo-Dutch War. It took place on 16 August 1652 (26 August 1652 (Gregorian calendar)) and was a short battle, but had the unexpected outcome of a Dutch victory over England. General-at ...
off Cornish coast, part of First Anglo-Dutch War
The First Anglo-Dutch War, or simply the First Dutch War, ( nl, Eerste Engelse (zee-)oorlog, "First English (Sea) War"; 1652–1654) was a conflict fought entirely at sea between the navies of the Commonwealth of England and the United Province ...
*1676: Chesten Marchant
Longevity myths are traditions about long-lived people (generally supercentenarians), either as individuals or groups of people, and practices that have been believed to confer longevity, but for which current scientific evidence does not suppo ...
supposedly the last Cornish monoglot
Monoglottism (Greek μόνος ''monos'', "alone, solitary", + γλῶττα , "tongue, language") or, more commonly, monolingualism or unilingualism, is the condition of being able to speak only a single language, as opposed to multilingualism. ...
, dies.
*1699: Joel Gascoyne's map of Cornwall is published in London.
18th century
* 1702:Sidney Godolphin
Sidney Godolphin is the name of:
* Sidney Godolphin (colonel) (1652–1732), Member of Parliament for fifty years
* Sidney Godolphin (poet) (1610–1643), English poet
* Sidney Godolphin, 1st Earl of Godolphin (c. 1640–1712), leading British poli ...
becomes Lord Treasurer
The post of Lord High Treasurer or Lord Treasurer was an English government position and has been a British government position since the Acts of Union of 1707. A holder of the post would be the third-highest-ranked Great Officer of State i ...
until 1710
 *1707:
*1707: Scilly naval disaster of 1707
The Scilly naval disaster of 1707 was the loss of four warships of a Royal Navy fleet off the Isles of Scilly in severe weather on 22 October 1707. Between 1,400 and 2,000 sailors lost their lives aboard the wrecked vessels, making the incident ...
; Action of 2 May 1707
*1715: Jacobite uprising in Cornwall
The Jacobite uprising in Cornwall of 1715 was the last uprising against the King of Great Britain, British Crown to take place in the county of Cornwall.
Background
On 1 August 1714, Anne, Queen of Great Britain, Queen Anne died, George I of G ...
*1715: Lizard lighthouse built
*1743: John Wesley visits Cornwall for first time. Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's br ...
will become dominant during the next hundred years.* 1747:
Admiral Boscawen
Admiral of the Blue Edward Boscawen, PC (19 August 171110 January 1761) was a British admiral in the Royal Navy and Member of Parliament for the borough of Truro, Cornwall, England. He is known principally for his various naval commands duri ...
wins fame at Cape Finisterre by singly engaging the French fleet until the English fleet arrive
*1755: A tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater exp ...
caused by the Lisbon earthquake strikes the Cornish coast
*1756–1763: Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
*1771: Birth of Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He w ...
*1777: Death of Dolly Pentreath
Dorothy Pentreath (16 May 1692 aptised– 26 December 1777) was a fishwife from Mousehole, Cornwall, England. She is the best-known of the last fluent speakers of the Cornish language. She is also often credited as the last known native spea ...
, commonly known as the last fluent, native speaker of the Cornish language, prior to its revival in 1904
*1778: Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for t ...
born in Penzance
*1779: William Murdoch
William Murdoch (sometimes spelled Murdock) (21 August 1754 – 15 November 1839) was a Scottish engineer and inventor.
Murdoch was employed by the firm of Boulton & Watt and worked for them in Cornwall, as a steam engine erector for ten yea ...
the Scottish inventor moves to Cornwall. Whilst in Cornwall he carried out important work on steam engines and gas-lights.
* 1788: James Ruse
James Ruse (9 August17595 September 1837) was a Cornish farmer who, at age 23, was convicted of burglary and was sentenced to seven years' transportation. He arrived at Sydney Cove, New South Wales, on the First Fleet with 18 months of h ...
, a Cornishman from Launceston, arrives in New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
aboard the transport ''Scarborough'', part of the First Fleet of Australian convict ships.
*1792: Cornwall County Library (public) founded in Truro.
*1792–1802: French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted France against Britain, Austria, Prussia ...
*1796: Earthquake in St Hilary.
19th century

 *1801:
*1801: Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He w ...
builds a full-size steam road carriage.
*1814: Royal Geological Society of Cornwall founded
*1815: The Davy lamp containing a candle is devised by Sir Humphry Davy
Sir Humphry Davy, 1st Baronet, (17 December 177829 May 1829) was a British chemist and inventor who invented the Davy lamp and a very early form of arc lamp. He is also remembered for isolating, by using electricity, several elements for the ...
.
*1818: Royal Institution of Cornwall
The Royal Institution of Cornwall (RIC) is a Learned society in Truro, Cornwall, United Kingdom.
It was founded in Truro on 5 February 1818 as the Cornwall Literary and Philosophical Institution. The Institution was one of the earliest of seve ...
*1832: Royal Cornwall Polytechnic Society
The Royal Cornwall Polytechnic Society (commonly known as The Poly) is an educational, cultural and scientific charity, as well as a local arts and cinema venue, based in Falmouth, Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The Society exists to promot ...
founded in Falmouth.
*1834: Augustus Smith obtains the Isles of Scilly, and evicts the inhabitants of some of the smaller islands.
*1835: Bodmin is made the County Capital of Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
(Previously Launceston) .
*1838: Tin Duties Act 1838
*1846: East Wheal Rose disaster
*1852: Construction of the Cornwall Railway
The Cornwall Railway was a broad gauge railway from Plymouth in Devon to Falmouth in Cornwall, England, built in the second half of the nineteenth century. It was constantly beset with shortage of capital for the construction, and was eventu ...
begins
*1858: The Miners Association
The Miners Association was founded in 1858 by Robert Hunt FRS, and the Royal Cornwall Polytechnic Society.
The Association was formed to create a body that would discuss, develop, address the needs and represent the hard rock mining industry ...
established.
*1858: The Cornish Foreshore Case
The Cornish Foreshore Case was an arbitration case held between 1854 and 1858 to resolve a formal dispute between the British Crown and the Duchy of Cornwall over the rights to minerals and mines under the foreshore of Cornwall
Cornwall (; ...
1854–1858 confirms that the Duke of Cornwall owns the rights to mines and minerals under the Cornish foreshore.
*1859: The Royal Albert Bridge
The Royal Albert Bridge is a railway bridge which spans the River Tamar in England between Plymouth, Devon and Saltash, Cornwall. Its unique design consists of two lenticular iron trusses above the water, with conventional plate-girder app ...
(sometimes called the Brunel Bridge or Saltash Bridge) was opened. Two days later (May 4) the main line of the Cornwall Railway opens giving access to Cornwall from the railways of Devon.
*1860s: Louis Lucien Bonaparte
Louis Lucien Bonaparte (4 January 1813 – 3 November 1891) was a French philologist. The third son of Napoleon's second surviving brother, Lucien Bonaparte, he spent much of his life outside France for political reasons. After a brief politica ...
visits Cornwall.
*1876: Reestablishment of Cornwall as a diocese
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associa ...
, with the see at Truro
*1877: Bishop Benson consecrated the first Bishop of Truro
The Bishop of Truro is the ordinary (diocesan bishop) of the Church of England Diocese of Truro in the Province of Canterbury.
History
There had been between the 9th and 11th centuries a Bishopric of Cornwall until it was merged with Credi ...
*1883: an artists' colony
An art colony, also known as an artists' colony, can be defined two ways. Its most liberal description refers to the organic congregation of Artist, artists in towns, villages and rural areas, often drawn by areas of natural beauty, the prior exi ...
established at Newlyn
Newlyn ( kw, Lulyn: Lu 'fleet', Lynn/Lydn 'pool') is a seaside town and fishing port (the largest fishing port in England) in south-west Cornwall, UK.Ordnance Survey: Landranger map sheet 203 ''Land's End''
Newlyn lies on the shore of Moun ...
*1883: an artists' colony established at Lamorna
Lamorna ( kw, Nansmornow) is a village, valley and cove in west Cornwall, England, UK. It is on the Penwith peninsula approximately south of Penzance. Lamorna became popular with the artists of the Newlyn School, including Alfred Munnings, La ...
*1888: School of Mines
A school of mines (or mining school) is an engineering school, often established in the 18th and 19th centuries, that originally focused on mining engineering and applied science. Most have been integrated within larger constructs such as mine ...
is established.
*1888: Local Government Act
Local Government Act (with its variations) is a stock short title used for legislation in Australia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Ireland and the United Kingdom, relating to local government.
The Bill for an Act with this short title may have been known ...
*1888: an artists' colony established at St Ives
*1890: Bob Fitzsimmons
Robert James Fitzsimmons (26 May 1863 – 22 October 1917) was a British professional boxer who was the sport's first three-division world champion. He also achieved fame for beating Gentleman Jim Corbett (the man who beat John L. Sullivan), ...
of Helston is the first native Briton heavy-weight boxing champion of the world.
*1891: Severe winter weather, including snowdrifts deep.
*1891: John Davey, one of the last people with traditional knowledge of the Cornish language, dies. The Cranken Rhyme
The "Cranken Rhyme" is a Cornish language, Cornish-language song known by farmer John Davey (Cornish speaker), John Davey or Davy (1812–1891), who was one of the last people with some knowledge of the tongue. It was recorded by J. Hobson Matthew ...
, a song he had learnt as a child, is supposed to be one of the last recorded pieces of the Cornish language oral tradition.
*1893: Dolcoath mining disaster
*1896: Stannaries Court (Abolition) Act 1896.
20th century



Pre-WWI
*1904: Cornwall accepted intoCeltic Congress
The International Celtic Congress ( br, Ar C'hendalc'h Keltiek, kw, An Guntelles Keltek, gv, Yn Cohaglym Celtiagh, gd, A' Chòmhdhail Cheilteach, ga, An Chomhdháil Cheilteach, cy, Y Gyngres Geltaidd) is a cultural organisation that seeks to ...
; Henry Jenner
Henry Jenner (8 August 1848 – 8 May 1934) was a British scholar of the Celtic languages, a Cornish cultural activist, and the chief originator of the Cornish language revival.
Jenner was born at St Columb Major on 8 August 1848. He was th ...
's ''Handbook of the Cornish language'' is published.
*1906: 1906 Bodmin by-election
The 1906 Bodmin by-election was a by-election held on 24 July 1906 for the British House of Commons constituency of Bodmin in Cornwall.
Vacancy
The by-election was triggered by the unseating of the town's Liberal Member of Parliament (MP) Thomas ...
*1910: Truro Cathedral completed.
*1914–18: WWI
*1919 Levant Mine disaster. 31 men died.
1920s
*1920: FirstOld Cornwall Society
The Federation of Old Cornwall Societies (FOCS) was formed in 1924, on the initiative of Robert Morton Nance, with the objective of collecting and maintaining "all those ancient things that make the spirit of Cornwall — its traditions, its ol ...
founded in St Ives.
*1921: Cornwall's deepest mine, the 3,500 ft Dolcoath mine
Dolcoath mine ( kw, Bal Dorkoth) was a copper and tin mine in Camborne, Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. Its name derives from the Cornish for 'Old Ground', and it was also affectionately known as ''The Queen of Cornish Mines''. The site is ...
, closes; Railways Act
Railways Act (with its variations) is a stock short title used in India, Malaysia and the United Kingdom for legislation relating to railways.
List India
* The Indian Railways Act, 1890
* The Railways Act, 1989
Malaysia
*The Railways Act 1991
*T ...
*1922: Bodmin by-election
*1928: First Gorseth Kernow
Gorsedh Kernow (Cornish Gorsedd) is a non-political Cornish organisation, based in Cornwall, United Kingdom, which exists to maintain the national Celtic spirit of Cornwall. It is based on the Welsh-based Gorsedd, which was founded by Iolo Morg ...
at Boscawen-un
Boscawen-Ûn () is a Bronze Age stone circle close to St Buryan in Cornwall, UK. It consists of nineteen upright stones in an ellipse with another, leaning, middle stone just south of the centre. There is a west-facing gap in the circle, which ...
, (instituted by Henry Jenner
Henry Jenner (8 August 1848 – 8 May 1934) was a British scholar of the Celtic languages, a Cornish cultural activist, and the chief originator of the Cornish language revival.
Jenner was born at St Columb Major on 8 August 1848. He was th ...
) symbolising the resurgent interest in Cornwall's Celtic cultural and linguistic heritage; Cornwall College
The Cornwall College Group (TCCG; kw, Kolji Kernow) is a further education college situated on eight sites throughout Cornwall and Devon, England, United Kingdom, with its head office in St Austell.
Campuses
There are eight campuses withi ...
founded; 1928 St Ives by-election
The 1928 St Ives by-election was a by-election held on 6 March 1928 for the British House of Commons constituency of St Ives in Cornwall.
Vacancy
The by-election was caused by the resignation of the sitting Unionist Party Member of Parliamen ...
1930s
*1930s:Unified Cornish
Unified Cornish (UC) (''Kernewek Uny '', ''KU'') is a variety of the Cornish language of the Cornish revival. Developed gradually by Robert Morton Nance during and before the 1930s, it derived its name from its standardisation of the variant spe ...
developed
* 1932: 1932 North Cornwall by-election
*1935: Silas Kitto Hocking is the first author to sell a million books in his lifetime.
*1937: 1937 St Ives by-election
*1939: 1939 North Cornwall by-election; WWII
1940s
*1944:Hill 112
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit.
Terminology
The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as ...
in Normandy
Normandy (; french: link=no, Normandie ; nrf, Normaundie, Nouormandie ; from Old French , plural of ''Normant'', originally from the word for "northman" in several Scandinavian languages) is a geographical and cultural region in Northwestern ...
acquired the name "Cornwall Hill" after Cornish soldiers of 5th Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry
The Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry (DCLI) was a light infantry regiment of the British Army in existence from 1881 to 1959.
The regiment was created on 1 July 1881 as part of the Childers Reforms, by the merger of the 32nd (Cornwall Light ...
suffered 320 casualties in the fighting there.
*1945: End of WWII.
*1947: Transport Act nationalises railways in Cornwall.
1950s
*1951: Cornish political party,Mebyon Kernow
Mebyon Kernow – The Party for Cornwall (, MK; Cornish for ''Sons of Cornwall'') is a Cornish nationalist, centre-left political party in Cornwall, in southwestern Britain. It currently has five elected councillors on Cornwall Council, and s ...
, or ("Sons of Cornwall"), is formed.
*1953: Mebyon Kernow
Mebyon Kernow – The Party for Cornwall (, MK; Cornish for ''Sons of Cornwall'') is a Cornish nationalist, centre-left political party in Cornwall, in southwestern Britain. It currently has five elected councillors on Cornwall Council, and s ...
wins first council seat.
*1954: The first of three Formula 1 motor races was held at the Davidstow Circuit
Davidstow Circuit is a disused motor racing circuit and airfield built in Cornwall, in the United Kingdom. The circuit was built on the site of a World War II RAF Coastal Command base, RAF Davidstow Moor, opened in 1942. Davidstow circuit opened ...
1960s
*1961:Celtic League
The Celtic League is a pan-Celtic organisation, founded in 1961, that aims to promote modern Celtic identity and culture in Ireland, Scotland, Wales, Brittany, Cornwall and the Isle of Man – referred to as the Celtic nations; it places part ...
founded at Rhos near Wrexham
Wrexham ( ; cy, Wrecsam; ) is a city and the administrative centre of Wrexham County Borough in Wales. It is located between the Welsh mountains and the lower Dee Valley, near the border with Cheshire in England. Historically in the count ...
, includes Cornish branch; Tamar Road Bridge opens; Westward Television
Westward Television was the first ITV (TV network), ITV franchise-holder for the South West England, South West of England. It held the franchise from 29 April 1961 until 31 December 1981. After a difficult start, Westward Television provided a ...
becomes first ITV franchise in area.
*1962: Goonhilly Receiving Station starts, receives first transatlantic TV broadcast.
*1964: Commercial helicopter service to Isles of Scilly is first in Europe.
*1966: Closure of the railway line
Rail terminology is a form of technical terminology. The difference between the American term ''railroad'' and the international term ''railway'' (used by the International Union of Railways and English-speaking countries outside the United Sta ...
between Halwill Junction and Wadebridge.
*1966: Loss of MV Darlwyne
*1967: Closure of the railway line between Wadebridge and Padstow
*1967: Magical Mystery Tour
''Magical Mystery Tour'' is a record by the English rock band the Beatles that was released as a double EP in the United Kingdom and an LP in the United States. It includes the soundtrack to the 1967 television film of the same name. The EP ...
a British television film
A television film, alternatively known as a television movie, made-for-TV film/movie or TV film/movie, is a feature-length film that is produced and originally distributed by or to a television network, in contrast to theatrical films made for ...
starring the Beatles
The Beatles were an English rock band, formed in Liverpool in 1960, that comprised John Lennon, Paul McCartney, George Harrison and Ringo Starr. They are regarded as the most influential band of all time and were integral to the developmen ...
is partly filmed in Cornwall. Scenes were filmed in Newquay
Newquay ( ; kw, Tewynblustri) is a town on the north coast in Cornwall, in the south west of England. It is a civil parish, seaside resort, regional centre for aerospace industries, spaceport and a fishing port on the North Atlantic coast of ...
and Watergate Bay
Watergate Bay ( kw, Porth Tregoryan, meaning ''cove at Coryan's farmstead/village'') is a long bay or beach flanked by cliffs centred two miles NNE of Newquay below the B3276 Newquay to Padstow road near the hamlet of Tregurrian in Cornwall, Uni ...
*1967: The Torrey Canyon
SS ''Torrey Canyon'' was an LR2 Suezmax class oil tanker with a cargo capacity of of crude oil. She ran aground off the western coast of Cornwall, United Kingdom, on 18 March 1967, causing an environmental disaster. At that time she was the ...
supertanker
An oil tanker, also known as a petroleum tanker, is a ship designed for the bulk transport of oil or its products. There are two basic types of oil tankers: crude tankers and product tankers. Crude tankers move large quantities of unrefined ...
disaster causing severe damage to the nearby sea, coastline and wildlife.
*1969: Cornish National Party founded (not to be confused with Cornish Nationalist Party)
1970s
*1971: The Kilbrandon Report into the British constitution recommends that use of the term Duchy to refer to Cornwall as a whole "on appropriate occasions" would recognise the "special and enduring relationship between Cornwall and the Crown". *1972: Local Government Act 1972: special dispensation for Scilly. *1973: The UK joins the EEC, which was to become the EU. *1975:Cornish Nationalist Party
The Cornish Nationalist Party (CNP; kw, An Parti Kenethlegek Kernow) is a political party, founded by Dr James Whetter, who campaigned for independence for Cornwall.
History
It was formed by people who left Cornwall's main nationalist party Meb ...
founded as split off from Mebyon Kernow.
*1976: Flooding in Polperro
Polperro ( kw, Porthpyra, meaning ''Pyra's cove'') is a large village, civil parish, and fishing harbour within the Polperro Heritage Coastline in south Cornwall, England. Its population is around 1,554.
Polperro, through which runs the River ...
*1978: Peter D. Mitchell
Peter Dennis Mitchell, FRS (29 September 1920 – 10 April 1992) was a British biochemist who was awarded the 1978 Nobel Prize for Chemistry for his discovery of the chemiosmotic mechanism of ATP synthesis.
Education and early life
Mitc ...
, a resident of Cornwall, wins Nobel Prize in Chemistry
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, alt = A golden medallion with an embossed image of a bearded man facing left in profile. To the left of the man is the text "ALFR•" then "NOBEL", and on the right, the text (smaller) "NAT•" then "M ...
*1979: First European Parliament election
Elections to the European Parliament take place every five years by universal adult suffrage; with more than 400 million people eligible to vote, they are considered the second largest democratic elections in the world after India's.
Unti ...
contested in Cornwall and Plymouth (European Parliament constituency)
Cornwall and Plymouth was a European Parliament constituency covering the county of Cornwall and the city of Plymouth in Devon, England.
Prior to its uniform adoption of proportional representation in 1999, the United Kingdom used first-past-t ...
1980s
 *1980s: Split in Cornish language revival, with Modern Cornish and
*1980s: Split in Cornish language revival, with Modern Cornish and Kernewek Kemmyn
Kernewek Kemmyn (Common Cornish or "KK") is a variety of the revived Cornish language.
Kernewek Kemmyn was developed, mainly by Ken George in 1986, based upon George's earlier doctoral thesis on the phonological history of Cornish. It takes muc ...
being developed.
* 1980: William Golding wins Booker Prize.
* 1981: Television South West
Television South West (TSW) was the ITV franchise holder for the South West England region from 1 January 1982 until 31 December 1992, broadcasting from studios at Derry's Cross in Plymouth, Devon.
History
Origins and Launch
On 28 Decembe ...
becomes ITV franchise; Penlee lifeboat disaster Penlee may refer to
* Penlee House - a house and art gallery in Penzance in the UK
* Penlee Point, Mousehole - a promentary near Penzance in the UK
* Penlee Point, Rame - a promentary near Plymouth in the UK
* the Penlee Quarry railway in Newlyn in ...
* 1983: William Golding
Sir William Gerald Golding (19 September 1911 – 19 June 1993) was a British novelist, playwright, and poet. Best known for his debut novel ''Lord of the Flies'' (1954), he published another twelve volumes of fiction in his lifetime. In 1980 ...
wins Nobel Prize for Literature
)
, image = Nobel Prize.png
, caption =
, awarded_for = Outstanding contributions in literature
, presenter = Swedish Academy
, holder = Annie Ernaux (2022)
, location = Stockholm, Sweden
, year = 1901
, ...
; 1983 British Airways Sikorsky S-61 crash
On 16 July 1983 a British Airways Helicopters commercial Sikorsky S-61 helicopter, ''Oscar November'' (G-BEON), crashed in the southern Celtic Sea, in the Atlantic Ocean, while en route from Penzance to St Mary's, Isles of Scilly in poor visibil ...
* 1986: Death of David Penhaligon
David Charles Penhaligon (6 June 1944 – 22 December 1986) was a British politician from Cornwall who was Liberal Member of Parliament for the constituency of Truro from 1974–86. He was a popular figure in all parties and had potential to ...
in a car crash.
* 1987: Cornwall has Britain's first air ambulance
Air medical services is a comprehensive term covering the use of air transportation, aeroplane or helicopter, to move patients to and from healthcare facilities and accident scenes. Personnel provide comprehensive prehospital and emergency and cri ...
service; 1987 Truro by-election
*1988: water pollution incident at Camelford
Camelford ( kw, Reskammel) is a town and civil parish in north Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, situated in the River Camel valley northwest of Bodmin Moor. The town is approximately ten miles (16 km) north of Bodmin and is governed ...
. 20 tonnes of aluminium sulphate
Aluminium sulfate is a salt with the formula Al2 (SO4)3. It is soluble in water and is mainly used as a coagulating agent (promoting particle collision by neutralizing charge) in the purification of drinking water and wastewater treatment plant ...
are accidentally emptied into reservoir, tainting the water supply to 20,000 people, causing brain damage in some cases.
* 1989: Martin Potter of Newquay is world surfing champion.
1990s
* 1990: Storm winds of 177 mph recorded at Falmouth; power loss to 50,000 Cornish residents. * 1991: First windfarm in Cornwall. * 1992:Pirate FM
Pirate FM is an Independent Local Radio station owned and operated by Bauer and based in Cornwall. The station forms part of the Hits Radio network, although its entire output and playlist is locally produced and takes no network programming. ...
launched, the first commercial station in Cornwall.
* 1993: Tate St Ives
Tate St Ives is an art gallery in St Ives, Cornwall, England, exhibiting work by modern British artists with links to the St Ives area. The Tate also took over management of another museum in the town, the Barbara Hepworth Museum and Sculpture ...
art gallery in St Ives, opened
* 1993: The joint Cornwall and Devon bid for Objective One funds fails because of Devon's high GDP.; ITV Westcountry
ITV Westcountry, formerly known as Westcountry Television and Carlton Westcountry, was the ITV franchise holder for the south west of England, covering Cornwall, Devon, Isles of Scilly, southern and western Somerset and western Dorset. The co ...
starts broadcasting.
* 1995: Wreck of the Maria Asumpta, a 19th-century sailing ship.
* 1996: Statistics reveal that out of 56 deprived communities in Cornwall, Devon and Somerset, 51 are in Cornwall.
* 1997: Keskerdh Kernow 500 march to London.
* 1998: South Crofty
South Crofty is a metalliferous tin and copper mine located in the village of Pool, Cornwall, United Kingdom. An ancient mine, it has seen production for over 400 years, and extends almost two and a half miles across and down and has mine ...
tin mine closes in March 1998 when ores began to be produced more cheaply abroad.
* 1999: English China Clays
English China Clays PLC, or ECC, was a mining company involved in the extraction of china clay, based in St Austell, Cornwall. It was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index but in 1999 was acquired by Imetal.
History
English China Clays was i ...
taken over by French owned company, Imerys, in a £756m deal.
* 1999: South West Regional Assembly
The South West Regional Assembly (SWRA) was the regional chamber for South West England, established in 1999. It was wound up in December 2008. Its functions were taken on by the Strategic Leaders' Board, the executive arm of the newly establish ...
established, but is not elected.
3rd millennium
21st century


2000s
*2001: TheEden Project
The Eden Project ( kw, Edenva) is a visitor attraction in Cornwall, England, UK. The project is located in a reclaimed china clay pit, located from the town of St Blazey and from the larger town of St Austell.Ordnance Survey (2005). ''OS ...
opens at St Blazey
*2001: Cornish Assembly
A Cornish Assembly ( kw, Senedh Kernow) is a proposed devolved law-making assembly for Cornwall along the lines of the Scottish Parliament, the Senedd (Welsh Parliament) and the Northern Ireland Assembly in the United Kingdom.
The campaign fo ...
declaration containing the signatures of 50,000 people is handed into 10 Downing Street on Wednesday 12 December 2001.
*2001: The Cornish are allocated the ethnic code of '06' for the 2001 Census – (see Census 2001 Ethnic Codes)
*2002: The Cornish language is officially recognised by the Government.
*2004: Cornwall merged into South West England (European Parliament constituency)
South West was a combined constituency region of the European Parliament, comprising the South West of England and Gibraltar. Seven, later six, Members of the European Parliament using closed party-list proportional representation allocated us ...
; flooding in Boscastle
*2005: British government allocates £80,000 per year for three years of direct central government funding.
* 2007: Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; cy, Swyddfa Ystadegau Gwladol) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible for t ...
announces that a Cornish tick box would be refused on the next 2011 Census because "insufficient requirement for the data had been expressed by Census users" and "national identity and ethnicity questions will contain tick boxes only for the largest groups".
*2008: The Standard Written Form ( kw, Furv Savonek Scrifys) of the Cornish language is formally agreed.
*2009: An election for Cornwall's new unitary council takes place on 4 June 2009. There are now 123 councillors.
2010s
*2010:Wave Hub
The Wave Hub is a floating offshore wind and wave power research project. The project is developed approximately off Hayle, on the north coast of Cornwall, United Kingdom. The hub was installed on the seabed in September 2010,
and is a 'sock ...
installed off the Cornish coast near Hayle
Hayle ( kw, Heyl, "estuary") is a port town and civil parish in west Cornwall, England. It is situated at the mouth of the Hayle River (which discharges into St Ives Bay) and is approximately seven miles (11 km) northeast of Penzance. ...
, the world's largest wave energy site.
*2012: In May 2012, The Olympic torch arrives at Land's End, for the 2012 Summer Olympics torch relay.
*2012: ' Heartlands' opened – 19 acre visitor attraction and World Heritage
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
Site set in Cornwall's former derelict mine land at Robinson's Shaft in the village of Pool
Pool may refer to:
Water pool
* Swimming pool, usually an artificial structure containing a large body of water intended for swimming
* Reflecting pool, a shallow pool designed to reflect a structure and its surroundings
* Tide pool, a rocky po ...
(near Redruth),
*2014: Cornish people
The Cornish people or Cornish ( kw, Kernowyon, ang, Cornƿīelisċ) are an ethnic group native to, or associated with Cornwall: and a recognised national minority in the United Kingdom, which can trace its roots to the ancient Britons ...
recognised and afforded protection by the UK Government under the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities
The Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities (FCNM) is a multilateral treaty of the Council of Europe aimed at protecting the rights of minorities. It came into effect in 1998 and by 2009 it had been ratified by 39 member ...
as a distinct group.
2020s
*2021: The47th G7 summit
The 47th G7 summit was held from 11 to 13 June 2021 in Cornwall, England, during the United Kingdom's tenure of the presidency of the Group of Seven (G7), an inter-governmental political forum of seven advanced nations.
The participants includ ...
is held in Carbis Bay.
See also
* List of years in the Kingdom of England * List of years in Great Britain *History of Cornwall
The history of Cornwall goes back to the Paleolithic, but in this period Cornwall only had sporadic visits by groups of humans. Continuous occupation started around 10,000 years ago after the end of the last ice age. When recorded history ...
*Cornish Bronze Age
The Cornish Bronze Age is an era of the history of Cornwall that spanned the period from 2400 BCE to c. 800 BCE. It was preceded by the Cornish Neolithic, and followed by the Cornish Iron Age. It is characterized by the introduction and wide ...
*Kingdom of Cornwall
The history of Cornwall goes back to the Paleolithic, but in this period Cornwall only had sporadic visits by groups of humans. Continuous occupation started around 10,000 years ago after the end of the last ice age. When recorded history ...
*Miss Susan Gay's Falmouth chronology
A chronology of the town of Falmouth was described by Miss Susan E. Gay in ''Old Falmouth'' (1903), pages 230–238.
Before the eighteenth century
*9th century. Pendennis supposed to have been fortified by the Danes.
*1120 The naming of Gyl ...
References
External links
Timeline of Cornish History 400,000 BC – 1066 AD
''
Cornwall County Council
Cornwall County Council ( kw, Konteth Konsel Kernow) was the county council of the non-metropolitan county of Cornwall in south west England. It came into its powers on 1 April 1889 and was abolished on 1 April 2009.
History
Cornwall County Counc ...
webpage''
Timeline of Cornish History 1066–1700 AD
''Cornwall County Council webpage''
Timeline of Cornish History 1700 to 1800 AD
''Cornwall County Council webpage''
Timeline of Cornish History 1800 AD to date
''Cornwall County Council webpage'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Timeline Of Cornish History
Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
History of Cornwall
Regional timelines
Military history of Cornwall
Cornish history