|
Stannary Courts And Parliaments
Stannary law (derived from the la, stannum for tin) is the body of English law that governs tin mining in Devon and Cornwall; although no longer of much practical relevance, the stannary law remains part of the law of the United Kingdom and is arguably the oldest law incorporated into the English legal system. The stannary law's complexity and comprehensive reach into the lives of tin miners necessitated the existence of the legislative Stannary Convocations of Devon and Cornwall, the judicial Courts of the Vice-Warden of the Stannaries, and the executive Lord Warden of the Stannaries. The separate and powerful government institutions available to the tin miners reflected the enormous importance of the tin industry to the English economy during the Middle Ages. Special laws for tin miners pre-date written legal codes in Britain, and ancient traditions exempted everyone connected with tin mining in Cornwall and Devon from any jurisdiction other than the stannary courts in all b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plympton
Plympton is a suburb of the city of Plymouth in Devon, England. It is in origin an ancient stannary town. It was an important trading centre for locally mined tin, and a seaport before the River Plym silted up and trade moved down river to Plymouth and was the seat of Plympton Priory the most significant local landholder for many centuries. Plympton is an amalgamation of several villages, including St Mary's, St Maurice, Colebrook, Woodford, Newnham, and Chaddlewood. Fore Street, the town's main street, is lined with mediaeval buildings, around thirty of which are either Grade II* or Grade II listed. The Grade II* buildings are The Old Rectory, the Guildhall and Tudor Lodge. Toponymy Although the name of the town appears to be derived from its location on the River Plym (compare, for instance, Otterton or Yealmpton), this is not considered to be the case. As J. Brooking Rowe pointed out in 1906, the town is not and never was sited on the river – rather it is sited on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luxulyan
Luxulyan (; kw, Logsulyan), also spelt Luxullian or Luxulian, is a village and civil parish in mid Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The village lies four miles (6.5 km) northeast of St Austell and six miles (10 km) south of Bodmin. The population of the parish was 1,371 in the 2001 census.GENUKI website Luxulyan. Retrieved April 2010 This had risen to 1,381 at the 2011 census. Geography and geology Luxulyan parish lies in an area of on the St Austell |
Hensbarrow Beacon
Hensbarrow Beacon is a hill in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated a mile north-west of Stenalees village at . It is the highest natural point of the Hensbarrow uplands, a natural region and national character area. The natural summit of Hensbarrow Beacon is 312m high and is marked by a trig point.Ordnance Survey 1:50,000 ''Landranger'' map series. The trig point sits atop a 5.4m tall round cairn that was later used as a beacon, it is a scheduled monument. It can be reached by a short walk from the road to the west. However, the summit is overtopped by several large spoil heaps from the nearby china clay workings, the highest of which rises to 355 m, therefore creating an 'artificial' summit 43 metres higher than the natural one. Geographically, the hill is also the highest point of the St Austell Downs, a large region of downland to the north-west of St Austell. The large degree of separation between it and Bodmin Moor to the north-east gives it enough relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Launceston, Cornwall
Launceston ( or , locally or , kw, Lannstevan; rarely spelled Lanson as a local abbreviation) is a town, ancient borough, and civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is west of the middle stage of the River Tamar, which constitutes almost the entire border between Cornwall and Devon. The landscape of the town is generally steep particularly at a sharp south-western knoll topped by Launceston Castle. These gradients fall down to the River Kensey and smaller tributaries. The town centre itself is bypassed and is no longer physically a main thoroughfare. The A388 still runs through the town close to the centre. The town remains figuratively the "gateway to Cornwall", due to having the A30, one of the two dual carriageways into the county, pass directly next to the town. The other dual carriageway and alternative main point of entry is the A38 at Saltash over the Tamar Bridge and was completed in 1962. There are smaller points of entry to Cornwall on minor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hensbarrow Downs
Hensbarrow Beacon is a hill in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated a mile north-west of Stenalees village at . It is the highest natural point of the Hensbarrow uplands, a natural region and national character area. The natural summit of Hensbarrow Beacon is 312m high and is marked by a trig point.Ordnance Survey 1:50,000 ''Landranger'' map series. The trig point sits atop a 5.4m tall round cairn that was later used as a beacon, it is a scheduled monument. It can be reached by a short walk from the road to the west. However, the summit is overtopped by several large spoil heaps from the nearby china clay workings, the highest of which rises to 355 m, therefore creating an 'artificial' summit 43 metres higher than the natural one. Geographically, the hill is also the highest point of the St Austell Downs, a large region of downland to the north-west of St Austell. The large degree of separation between it and Bodmin Moor to the north-east gives it enough relative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lostwithiel
Lostwithiel (; kw, Lostwydhyel) is a civil parish and small town in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom at the head of the estuary of the River Fowey. According to the 2001 census it had a population of 2,739, increasing to 2,899 at the 2011 census. The Lostwithiel electoral ward had a population of 4,639 at the 2011 census. The name Lostwithiel comes from the Cornish "lostwydhyel" which means "tail of a wooded area". Origin of the name The origin of the name Lostwithiel is a subject much debated. In the 16th century it was thought that the name came from the Roman name ''Uzella'', translated as ''Les Uchel'' in Cornish. In the 17th century popular opinion was that the name came from a translation of ''Lost'' (a tail) and ''Withiel'' (a lion), the lion in question being the lord who lived in the castle. Current thinking is that the name comes from the Old Cornish ''Lost Gwydhyel'' meaning "tail-end of the woodland". The view from Restormel Castle looking towards the town sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
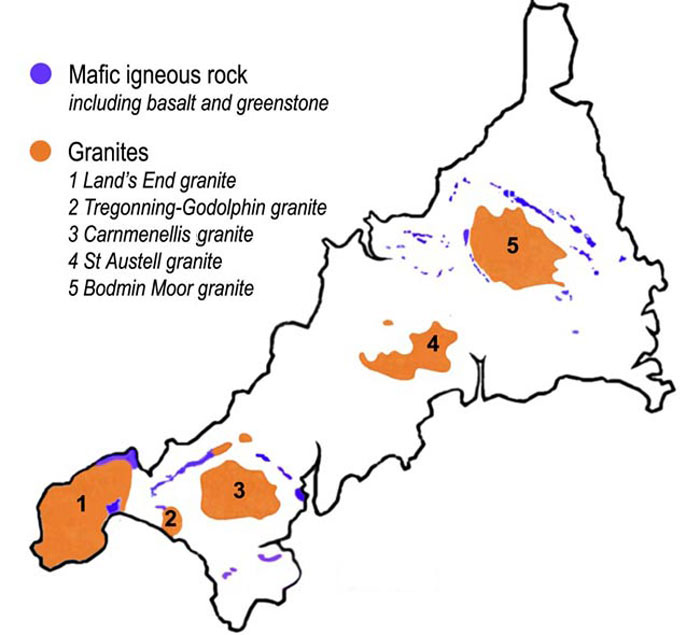
Bodmin Moor
Bodmin Moor ( kw, Goon Brenn) is a granite moorland in north-eastern Cornwall, England. It is in size, and dates from the Carboniferous period of geological history. It includes Brown Willy, the highest point in Cornwall, and Rough Tor, a slightly lower peak. Many of Cornwall's rivers have their sources here. It has been inhabited since at least the Neolithic era, when primitive farmers started clearing trees and farming the land. They left their megalithic monuments, hut circles and cairns, and the Bronze Age culture that followed left further cairns, and more stone circles and stone rows. By medieval and modern times, nearly all the forest was gone and livestock rearing predominated. The name Bodmin Moor is relatively recent. An early mention is in the ''Royal Cornwall Gazette'' of 28 November 1812. The upland area was formerly known as Fowey Moor after the River Fowey, which rises within it. Geology Bodmin Moor is one of five granite plutons in Cornwall that make up pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charter Of Pardon, 1508
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the recipient admits a limited (or inferior) status within the relationship, and it is within that sense that charters were historically granted, and it is that sense which is retained in modern usage of the term. The word entered the English language from the Old French ''charte'', via Latin ''charta'', and ultimately from Greek χάρτης (''khartes'', meaning "layer of papyrus"). It has come to be synonymous with a document that sets out a grant of rights or privileges. Other usages The term is used for a special case (or as an exception) of an institutional charter. A charter school, for example, is one that has different rules, regulations, and statutes from a state school. Charter can be used as a synonym for "hire" or "lease", as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pound Sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and the word "pound" is also used to refer to the British currency generally, often qualified in international contexts as the British pound or the pound sterling. Sterling is the world's oldest currency that is still in use and that has been in continuous use since its inception. It is currently the fourth most-traded currency in the foreign exchange market, after the United States dollar, the euro, and the Japanese yen. Together with those three currencies and Renminbi, it forms the basket of currencies which calculate the value of IMF special drawing rights. As of mid-2021, sterling is also the fourth most-held reserve currency in global reserves. The Bank of England is the central bank for sterling, issuing its own banknotes, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry VII Of England
Henry VII (28 January 1457 – 21 April 1509) was King of England and Lord of Ireland from his seizure of the crown on 22 August 1485 until his death in 1509. He was the first monarch of the House of Tudor. Henry's mother, Margaret Beaufort, was a descendant of the Lancastrian branch of the House of Plantagenet. Henry's father, Edmund Tudor, 1st Earl of Richmond, a half-brother of Henry VI of England and a member of the Welsh Tudors of Penmynydd, died three months before his son Henry was born. During Henry's early years, his uncle Henry VI was fighting against Edward IV, a member of the Yorkist Plantagenet branch. After Edward retook the throne in 1471, Henry Tudor spent 14 years in exile in Brittany. He attained the throne when his forces, supported by France, Scotland, and Wales, defeated Edward IV's brother Richard III at the Battle of Bosworth Field, the culmination of the Wars of the Roses. He was the last king of England to win his throne on the field of battle. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

