Time Partition Testing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
TPT (time partition testing) is a systematic
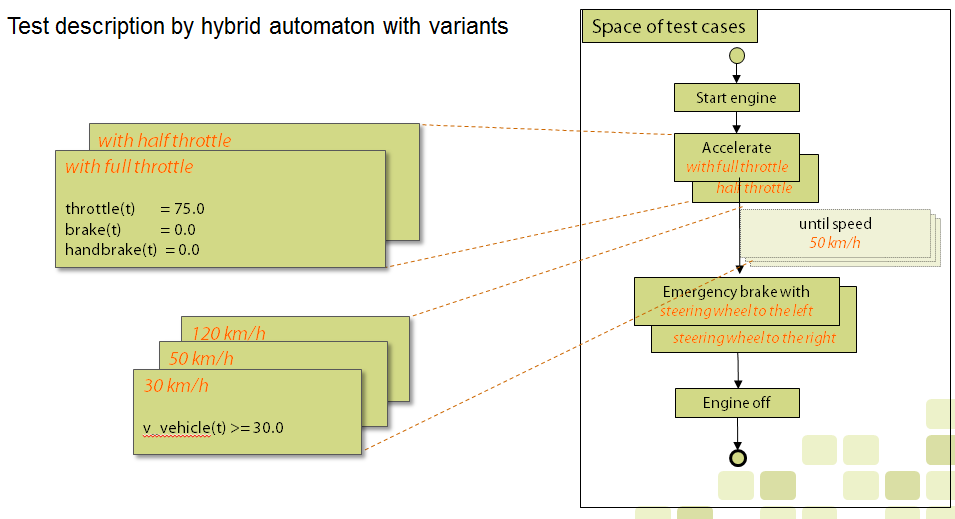 In TPT tests are modelled graphically with the aid of special state machines and time partitioning. All test cases for one system under test can be modelled using one hybrid automaton. Tests often consist of a sequence of logical phases. The
In TPT tests are modelled graphically with the aid of special state machines and time partitioning. All test cases for one system under test can be modelled using one hybrid automaton. Tests often consist of a sequence of logical phases. The

 * test cases from equivalence classes
* test cases for the coverage of
* test cases from equivalence classes
* test cases for the coverage of
Hauser Automotive Website. Retrieved 16 March 2015
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tpt (Software) Software testing tools Unit testing
test
Test(s), testing, or TEST may refer to:
* Test (assessment), an educational assessment intended to measure the respondents' knowledge or other abilities
Arts and entertainment
* ''Test'' (2013 film), an American film
* ''Test'' (2014 film) ...
methodology
In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for bri ...
for the automated
Automation describes a wide range of technologies that reduce human intervention in processes, mainly by predetermining decision criteria, subprocess relationships, and related actions, as well as embodying those predeterminations in machine ...
software test
Software testing is the act of checking whether software satisfies expectations.
Software testing can provide objective, independent information about the quality of software and the risk of its failure to a user or sponsor.
Software testing ...
and verification of embedded control systems, cyber-physical systems, and dataflow programs. TPT is specialised on testing and validation of embedded systems whose inputs and outputs can be represented as signals
A signal is both the process and the result of Signal transmission, transmission of data over some transmission media, media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processin ...
and is a dedicated method for testing continuous behaviour of system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
s. Most control system
A control system manages, commands, directs, or regulates the behavior of other devices or systems using control loops. It can range from a single home heating controller using a thermostat controlling a domestic boiler to large industrial ...
s belong to this system class. The outstanding characteristic of control systems is the fact that they interact closely interlinked with a real world environment. Controllers need to observe their environment and react correspondingly to its behaviour. The system works in an interactional cycle with its environment and is subject to temporal constraints. Testing these systems is to stimulate and to check the timing behaviour. Traditional functional testing methods use scripts – TPT uses model-based testing
Model-based testing is an application of model-based design for designing and optionally also executing artifacts to perform software testing or system testing. Models can be used to represent the desired behavior of a system under test (SUT), or ...
.
TPT combines a systematic and graphic modelling technique for test cases with a fully automated test execution in different environments and automatic test evaluation. TPT covers the following four test activities:
* test case modelling
* test execution in different environments (automated)
* test result analysis (test assessment (automated))
* test documentation (automated)
* test management
Test management most commonly refers to the activity of managing a testing process. A test management tool is software used to manage tests (automated or manual) that have been previously specified by a test procedure. It is often associated with ...
Graphic test cases
 In TPT tests are modelled graphically with the aid of special state machines and time partitioning. All test cases for one system under test can be modelled using one hybrid automaton. Tests often consist of a sequence of logical phases. The
In TPT tests are modelled graphically with the aid of special state machines and time partitioning. All test cases for one system under test can be modelled using one hybrid automaton. Tests often consist of a sequence of logical phases. The states
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
of the finite-state machine
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: ''automata''), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number o ...
represent the logical passes of a test which are similar for all tests. Trigger conditions model the transitions between the test phases. Each state and transition of the automaton may have different variants. The combination of the variants model the individual test cases.
Natural language
A natural language or ordinary language is a language that occurs naturally in a human community by a process of use, repetition, and change. It can take different forms, typically either a spoken language or a sign language. Natural languages ...
texts become part of the graphics, supporting the simple and demonstrative readability even for non-programmers. Substantial techniques such as parallel and hierarchical branching state machines
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
, conditional branching, reactivity, signal description, measured signals as well as lists of simple test steps allow an intuitive and graphic modelling even of complex test cases.
The test's complexity is hidden behind graphics. The lowest level signal description consists of either test step lists or so called direct definitions.
Modelling simple sequences: Test-Step List
Through the use of the Test-Step List, one can model simple sequences of test steps that do not need to execute in parallel, such as setting signals (Set channel), ramping signals (Ramp channel), setting parameters (Set parameter), and waiting (Wait). Requests for the expected test results can be made within the test sequence to evaluate the system under test as it runs. It is also possible to place subautomatons in the Test-Step List, which in turn contain automatons and sequences, resulting in hierarchical Test-Step Lists. The test sequences can also be combined with other modelling methods, allowing for a great deal of complexity (or simplicity) in one's test. Test sequences can also be combined and parallelised with other modelling methods.
Direct signal definition: Direct Definition
Within the Test-Step-List it is possible to implement so-called "Direct Definitions". Using this type of modelling, one can define signals as a function of time, past variables/test events, and other signals. It is also possible to define these signals by writing " C-Style" code as well as importing measurement data and using a manual signal editor.Functions
It is possible to define functions that can act as aclient
Client(s) or The Client may refer to:
* Client (business)
* Client (computing), hardware or software that accesses a remote service on another computer
* Customer or client, a recipient of goods or services in return for monetary or other valuable ...
s or server
Server may refer to:
Computing
*Server (computing), a computer program or a device that provides requested information for other programs or devices, called clients.
Role
* Waiting staff, those who work at a restaurant or a bar attending custome ...
s. Client functions are called from TPT in the system under test, where server functions implemented in TPT can be called as "stub
Stub or Stubb may refer to:
Shortened objects and entities
* Stub, a tree cut and allowed to regrow from the trunk; see pollarding
* Pay stub, a receipt or record that the employer has paid an employee
* Stub period, period of time over which i ...
functions" from the system under test. TPT itself may also call the server functions.
Systematic test cases
TPT was developed specifically for testing of continuous and reactive behaviour of embedded systems. TPT can be seen as the extension of theClassification Tree Method
The Classification Tree Method is a method for test design, as it is used in different areas of software development.
It was developed by Grimm and Grochtmann in 1993.
Classification Trees in terms of the Classification Tree Method must not be co ...
in terms of timing behaviour. Because of its systematic approach in test case
In software engineering, a test case is a specification of the inputs, execution conditions, testing procedure, and expected results that define a single test to be executed to achieve a particular software testing objective, such as to exercise ...
generation, TPT even keeps track of very complex systems whose thorough testing requires a large number of test cases thus making it possible to find failures in the system under test with an ideal number of test cases.
The underlying idea of TPT's systematic is the separation of similarities and differences among the test cases: most test cases are very similar in their structural process and can "only" be differentiated in a few, but crucial details. TPT makes use of this fact by jointly modelling and using joint structures. On the one hand, redundancies are thus avoided. On the other hand, it is made very clear what the test cases actually differ in – i.e. which specific aspect they respectively test. The comparability of test cases and thus the overview is improved in this approach and the attention of the tester is focused on the essential – the differentiating features of the test cases.
The hierarchical structure of the test cases makes it possible to break complex test problems down into sub-problems thus also improving the clarity and – as a result – the quality of the test.
These modelling techniques support the tester in finding the actually relevant cases, avoiding redundancies and keeping track of even large numbers of test cases.
Automatic test case generation
TPT comprises several possibilities to automatically generate test cases: * test cases from equivalence classes
* test cases for the coverage of
* test cases from equivalence classes
* test cases for the coverage of Simulink
Simulink is a MATLAB-based graphical programming environment for modeling, simulating and analyzing multidomain dynamical systems. Its primary interface is a graphical block diagramming tool and a customizable set of block libraries. It offe ...
models by using static analysis and a search-based method
* test cases by building sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is cal ...
from variants of states and transitions of a test model
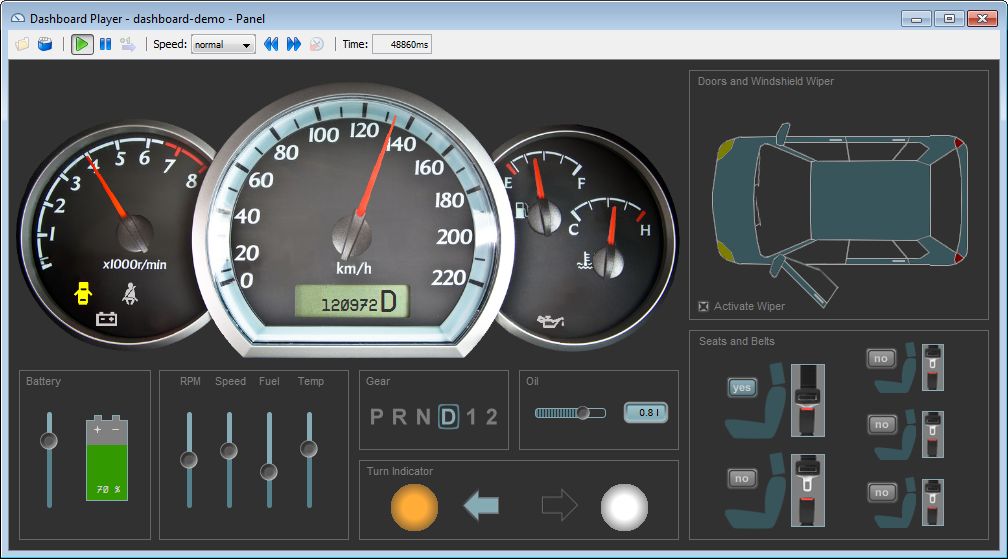
* test cases by transforming recordings of user interactions with the system under test via a graphical user interface (Dashboard)
Reactive tests
With TPT, each test case can specifically react to the system's behaviour during the testing process in real time – for instance to react on the system exactly when a certain system-state occurs or a sensor signal exceeds a certain threshold. If, for example, a sensor failure for an engine controller is to be simulated when the engine idling speed is exceeded, it has to be possible to react to the event "engine idling speed exceeded" in the description of the test case.Test execution
TPT test cases are made independent of its execution. The test cases can be executed in almost any environment due to the so-calledvirtual machine
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulator, emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve ...
(VM) concept also in real time environments. Examples are MATLAB
MATLAB (an abbreviation of "MATrix LABoratory") is a proprietary multi-paradigm programming language and numeric computing environment developed by MathWorks. MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementat ...
/Simulink
Simulink is a MATLAB-based graphical programming environment for modeling, simulating and analyzing multidomain dynamical systems. Its primary interface is a graphical block diagramming tool and a customizable set of block libraries. It offe ...
, TargetLink, ASCET, C-code, CAN, AUTOSAR
AUTOSAR (AUTomotive Open System ARchitecture) is a global development partnership founded in 2003 by automotive manufacturers, suppliers and other companies from the electronics, semiconductor and software industries. Its purpose is to develop ...
, SystemDesk, DaVinci CT, LABCAR, INCA, Software-in-the-Loop (SiL) and HiL. Thus TPT is an integrated tool to be used in all testing phases of the development like unit testing
Unit testing, component or module testing, is a form of software testing by which isolated source code is tested to validate expected behavior.
Unit testing describes tests that are run at the unit-level to contrast testing at the Integration ...
, integration testing
Integration testing is a form of software testing in which multiple software components, modules, or services are tested together to verify they work as expected when combined. The focus is on testing the interactions and data exchange between i ...
, system testing
System testing, a.k.a. end-to-end (E2E) testing, is testing conducted on a complete software system.
System testing describes testing at the system level to contrast to testing at the system integration, integration or unit level.
System t ...
and regression testing
Regression testing (rarely, ''non-regression testing'') is re-running functional and non-functional tests to ensure that previously developed and tested software still performs as expected after a change. If not, that would be called a '' regr ...
.
For analysis and measurement of code coverage
In software engineering, code coverage, also called test coverage, is a percentage measure of the degree to which the source code of a program is executed when a particular test suite is run. A program with high code coverage has more of its ...
, TPT can interact with coverage tools like Testwell CTC++ for C-code.
A configurable graphical user interface (Dashboard), based on GUI widgets, can be used to interact with tests.
TPT virtual machine
The modelled test cases in TPT are compiled and during test execution interpreted by the so-calledvirtual machine
In computing, a virtual machine (VM) is the virtualization or emulator, emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architectures and provide the functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve ...
(VM). The VM is the same for all platforms and all tests. Only a platform adapter
An adapter or adaptor is a device that converts attributes of one electrical device or system to those of an otherwise incompatible device or system. Some modify power or signal attributes, while others merely adapt the physical form of one co ...
realises the signal mapping for the individual application. The TPT-VM is implemented in ANSI C
ANSI C, ISO C, and Standard C are successive standards for the C programming language published by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 22/WG 14 of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the ...
and requires a memory of just a few kilobytes and can completely do without a dynamic memory allocation, allowing it to be applied in minimalist and environments with few resources too. There are also API
An application programming interface (API) is a connection between computers or between computer programs. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how to build ...
s for C and .NET
The .NET platform (pronounced as "''dot net"'') is a free and open-source, managed code, managed computer software framework for Microsoft Windows, Windows, Linux, and macOS operating systems. The project is mainly developed by Microsoft emplo ...
.
TPT's Virtual Machine is able to process tests in real time with defined response behaviour. The response times of TPT test cases are normally given within micro seconds – depending on the complexity and test hardware.
Programmed test assessment
The expected system behaviour for individual test cases should also be automatically tested to assure efficient test processes. TPT offers the possibility to compute the properties for the expected behaviour online (during test execution) and offline (after test execution). While online evaluation uses the same modelling techniques as test modelling, offline evaluation offers decidedly more far-reaching possibilities for more complex evaluations, including operations such as comparisons with external reference data, limit-value monitoring, signal filters, analyses of state sequences and time conditions. The offline evaluation is, technically speaking, based on thePython
Python may refer to:
Snakes
* Pythonidae, a family of nonvenomous snakes found in Africa, Asia, and Australia
** ''Python'' (genus), a genus of Pythonidae found in Africa and Asia
* Python (mythology), a mythical serpent
Computing
* Python (prog ...
script language, which has been extended by specific syntactic language elements and a specialised evaluation library to give optimal support to the test evaluation. The use of a script language ensures a high degree of flexibility in the test evaluation: access to reference data, communication with other tools and development of one's own domain-specific libraries for test evaluation is supported. Besides of the script based test result evaluation user interfaces provide simple access to the test assessments and help non-programmers to avoid scripting.
Measurement data from other sources like '' TargetLink'' and ''Simulink
Simulink is a MATLAB-based graphical programming environment for modeling, simulating and analyzing multidomain dynamical systems. Its primary interface is a graphical block diagramming tool and a customizable set of block libraries. It offe ...
'' signal logging or MCD-3 measurement data can be assessed automatically. This data can be independent from the test execution.
Test documentation
TPT test documentation according to IEEE 829 presents the result of the test evaluation to the tester in a HTML, report, in which not only the pure information "success", "failed" or "unknown" can be depicted as the test result for each test case, but also details such as characteristic parameters or signals that have been observed in the test execution or computed in the test evaluation. Since the test assessment returns proper information about the timing and the checked behaviour this information can be made available in the report. The content of the test documentation as well as the structure of the document can be freely configured with the help of a template.Test management
TPT supportstest management
Test management most commonly refers to the activity of managing a testing process. A test management tool is software used to manage tests (automated or manual) that have been previously specified by a test procedure. It is often associated with ...
of TPT test projects with the following activities:
* Test case development in a test project
* Test planning through test set configuration and test execution configuration
* Automatic test execution and evaluation (assessment) in a Test campaign
* Test reporting (detailed for an individual test run)
* Test summary reporting over different release cycles and
* Traceability of requirements, tests, test runs, test results
Requirements tracing
Industry norms such asIEC 61508
IEC 61508 is an international standard published by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) consisting of methods on how to apply, design, deploy and maintain automatic protection systems called safety-related systems. It is titled '' ...
, DO-178B
DO-178B, Software Considerations in Airborne Systems and Equipment Certification is a guideline dealing with the safety of safety-critical software used in certain airborne systems. It was jointly developed by the safety-critical working group R ...
, EN 50128 and ISO 26262
ISO 26262, titled "Road vehicles – Functional safety", is an international standard for functional safety of electrical and/or electronic systems that are installed in serial production road vehicles (excluding mopeds), defined by the Intern ...
require traceability of requirements and tests. TPT offers an interface to requirement
In engineering, a requirement is a condition that must be satisfied for the output of a work effort to be acceptable. It is an explicit, objective, clear and often quantitative description of a condition to be satisfied by a material, design, pro ...
s tools like Telelogic DOORS to support these activities.
Application
TPT is amodel-based testing
Model-based testing is an application of model-based design for designing and optionally also executing artifacts to perform software testing or system testing. Models can be used to represent the desired behavior of a system under test (SUT), or ...
tool
A tool is an Physical object, object that can extend an individual's ability to modify features of the surrounding environment or help them accomplish a particular task. Although many Tool use by animals, animals use simple tools, only human bei ...
and is applied mainly in the automotive controller development and has originally been developed within Daimler AG
Mercedes-Benz Group AG (formerly Daimler-Benz, DaimlerChrysler, and Daimler) is a German multinational automotive company headquartered in Stuttgart, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. It is one of the world's leading car manufacturers. Daimler-B ...
for their own development. Daimler coordinated the development of the testing tool for years. Since 2007 PikeTec continues the development of the tool. TPT is used by many different other car manufacturers like BMW
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG, trading as BMW Group (commonly abbreviated to BMW (), sometimes anglicised as Bavarian Motor Works), is a German multinational manufacturer of vehicles and motorcycles headquartered in Munich, Bavaria, Germany. Th ...
, Volkswagen
Volkswagen (VW; )English: , . is a German automotive industry, automobile manufacturer based in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Established in 1937 by German Labour Front, The German Labour Front, it was revitalized into the global brand it ...
, Audi
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. A subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
The origins of the compa ...
, Porsche
Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG, usually shortened to Porsche (; see below), is a German automobile manufacturer specializing in luxury, high-performance sports cars, SUVs and sedans, headquartered in Stuttgart, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Th ...
and General Motors
General Motors Company (GM) is an American Multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automotive manufacturing company headquartered in Detroit, Michigan, United States. The company is most known for owning and manufacturing f ...
as well as suppliers like Robert Bosch GmbH
Robert Bosch GmbH (; ), commonly known as Bosch (styled BOSCH), is a German multinational engineering and technology company headquartered in Gerlingen, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The company was founded by Robert Bosch in Stuttgart in 188 ...
, Continental
Continental may refer to:
Places
* Continental, Arizona, a small community in Pima County, Arizona, US
* Continental, Ohio, a small town in Putnam County, US
Arts and entertainment
* ''Continental'' (album), an album by Saint Etienne
* Continen ...
and Hella.References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Tpt (Software) Software testing tools Unit testing