Tethys Ocean on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Tethys Ocean ( ; ), also called the Tethys Sea or the Neo-Tethys, was a prehistoric ocean during much of the Mesozoic Era and early-mid Cenozoic Era. It was the predecessor to the modern
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), ...
, the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
, and the Eurasian inland marine basins (primarily represented today by the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
and Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
).
During the early Mesozoic, as Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea ( ) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous period approximately 335 mi ...
broke up, the Tethys Ocean was defined as the ocean located between the ancient continents of Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zea ...
and Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pa ...
. After the opening of the Indian and Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for se ...
oceans during the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
Period and the breakup of these continents over the same period, it came to be defined as the ocean bordered by the continents of Africa, Eurasia, India, and Australasia. During the early-mid Cenozoic, the Indian, African, Australian and Arabian plates moved north and collided with the Eurasian plate, which created new borders to the ocean, a land barrier to the flow of currents between the Indian and Mediterranean basins, and the orogenies of the Alpide belt (including the Alps
The Alps () are some of the highest and most extensive mountain ranges in Europe, stretching approximately across eight Alpine countries (from west to east): Monaco, France, Switzerland, Italy, Liechtenstein, Germany, Austria and Slovenia.
...
, Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
, Zagros
The Zagros Mountains are a mountain range in Iran, northern Iraq, and southeastern Turkey. The mountain range has a total length of . The Zagros range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border while covering much of s ...
, and Caucasus Mountains). All of these geological events, in addition to a drop in sea level rise from Antarctic glaciation, brought an end to the Tethys as it previously existed, fragmenting it into the Indian Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Paratethys.
It was preceded by the Paleo-Tethys Ocean, which lasted between the Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
and the Early Triassic
The Early Triassic is the first of three epochs of the Triassic Period of the geologic timescale. It spans the time between 251.9 Ma and Ma (million years ago). Rocks from this epoch are collectively known as the Lower Triassic Series, which ...
, while the Neotethys formed during the Late Triassic
The Late Triassic is the third and final epoch (geology), epoch of the Triassic geologic time scale, Period in the geologic time scale, spanning the time between annum, Ma and Ma (million years ago). It is preceded by the Middle Triassic Epoch a ...
and lasted in some form up to the Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that defin ...
–Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
boundary (about 24–21 million years ago) when it completely closed. A portion known as the Paratethys was isolated during the Oligocene (34 million years ago) and lasted up to the Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch (geology), epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.33 to 2.58

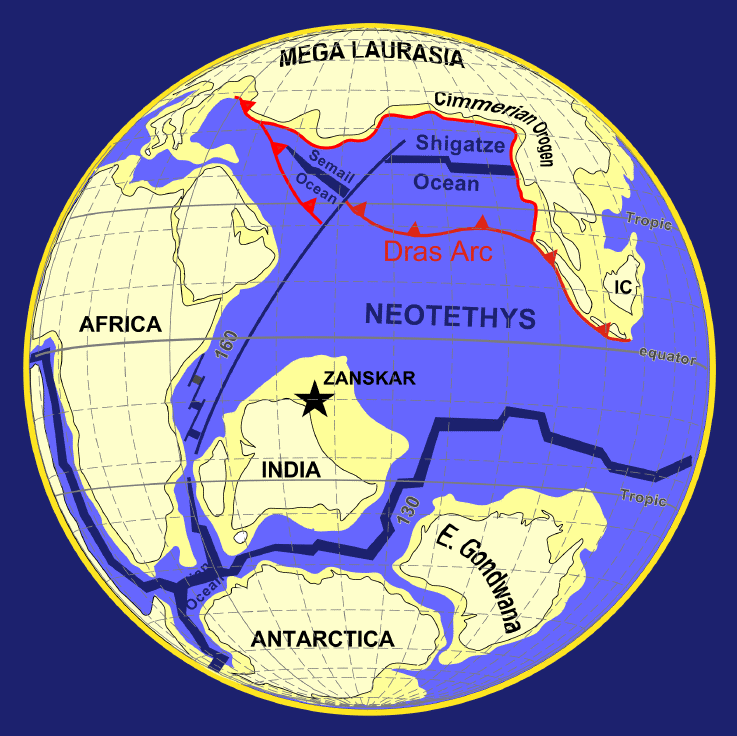 Between the Jurassic and the
Between the Jurassic and the
 Throughout the
Throughout the
 In 1885, the Austrian palaeontologist Melchior Neumayr deduced the existence of the Tethys Ocean from Mesozoic marine sediments and their distribution, calling his concept () and described it as a Jurassic seaway, which extended from the Caribbean to the Himalayas.
In 1893, the Austrian geologist
In 1885, the Austrian palaeontologist Melchior Neumayr deduced the existence of the Tethys Ocean from Mesozoic marine sediments and their distribution, calling his concept () and described it as a Jurassic seaway, which extended from the Caribbean to the Himalayas.
In 1893, the Austrian geologist
Etymology
The sea is named after Tethys, who, in ancient Greek mythology, is a water goddess, a sister and consort ofOceanus
In Greek mythology, Oceanus ( ; , also , , or ) was a Titans, Titan son of Uranus (mythology), Uranus and Gaia, the husband of his sister the Titan Tethys (mythology), Tethys, and the father of the River gods (Greek mythology), river gods ...
, mother of the Oceanid sea nymphs and of the world's great rivers, lakes and fountains.
Terminology and subdivisions
The eastern part of the Tethys Ocean is sometimes referred to as Eastern Tethys. The western part of the Tethys Ocean is called Tethys Sea, Western Tethys Ocean, or Paratethys or Alpine Tethys Ocean. TheBlack
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
, Caspian, and Aral seas are thought to be its crustal remains, though the Black Sea may, in fact, be a remnant of the older Paleo-Tethys Ocean.
The Western Tethys was not simply a single open ocean. It covered many small plates, Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
island arc
Island arcs are long archipelago, chains of active volcanoes with intense earthquake, seismic activity found along convergent boundary, convergent plate tectonics, tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have re ...
s, and microcontinents. Many small oceanic basin
In hydrology, an oceanic basin (or ocean basin) is anywhere on Earth that is covered by seawater. Geologically, most of the ocean basins are large Structural basin, geologic basins that are below sea level.
Most commonly the ocea ...
s ( Valais Ocean, Piemont-Liguria Ocean, Meliata Ocean) were separated from each other by continental terranes on the Alboran, Iberian, and Apulian plates. The high sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an mean, average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal Body of water, bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical ...
in the Mesozoic flooded most of these continental domains, forming shallow seas.
During the early Cenozoic, the Tethys Ocean could be divided into three sections: the Mediterranean Tethys (the direct predecessor to the Mediterranean Sea), the Peri-Tethys (a vast inland sea that covered much of eastern Europe and central Asia, and the direct predecessor to the Paratethys Sea), and the Indian Tethys (the direct predecessor to the Indian Ocean). The Turgai Strait extended out of the Peri-Tethys, connecting the Tethys with the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
.
As theories have improved, scientists have extended the "Tethys" name to refer to three similar oceans that preceded it, separating the continental terranes: in Asia, the Paleo-Tethys (Devonian–Triassic), Meso-Tethys (late Early Permian 01 or 01 may refer to:
* The year 2001, or any year ending with 01
* The month of January
* 1 (number)
Music
* '01 (Richard Müller album), ''01'' (Richard Müller album), 2001
* 01 (Urban Zakapa album), ''01'' (Urban Zakapa album), 2011
* ''01011 ...
–Late Cretaceous), and Ceno-Tethys (Late-Triassic–Cenozoic) are recognized. None of the Tethys oceans should be confused with the Rheic Ocean, which existed to the west of them in the Silurian Period. To the north of the Tethys, the then-land mass is called Angaraland and to the south of it, it is called Gondwanaland.
Modern theory
From theEdiacaran
The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last ...
(600 ) into the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
(360 ), the Proto-Tethys Ocean existed and was situated between Baltica
Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains.
The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, i ...
and Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American craton is a large continental craton that forms the Geology of North America, ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of ...
to the north and Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zea ...
to the south.
From the Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
(440 ) through the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
periods, the Paleo-Tethys Ocean existed between the Hunic terranes and Gondwana. Over a period of 400 million years, continental terranes intermittently separated from Gondwana in the Southern Hemisphere to migrate northward to form Asia in the Northern Hemisphere.
Triassic Period
About 250 Mya, during theTriassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is t ...
, a new ocean began forming in the southern end of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. A rift formed along the northern continental shelf of Southern Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea ( ) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous period approximately 335 mi ...
(Gondwana). Over the next 60 million years, that piece of shelf, known as Cimmeria, traveled north, pushing the floor of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean under the eastern end of northern Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea ( ) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous period approximately 335 mi ...
(early / proto- Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pa ...
). The Neo-Tethys Ocean formed between Cimmeria and Gondwana, directly over where the Paleo-Tethys formerly rested.
Jurassic Period
During theJurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
period about 150 Mya, Cimmeria finally collided with Laurasia and stalled, so the ocean floor behind it buckled under, forming the Tethys Trench. Water levels rose, and the western Tethys shallowly covered significant portions of Europe, forming the first Tethys Sea. Around the same time, Laurasia and Gondwana began drifting apart, opening an extension of the Tethys Sea between them which today is the part of the Atlantic Ocean between the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
and the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
. As North and South America were still attached to the rest of Laurasia and Gondwana, respectively, the Tethys Ocean in its widest extension was part of a continuous oceanic belt running around the Earth between about latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
30°N and the Equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
. Thus, ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, sh ...
s at the time around the Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous (geochronology, geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphy, chronostratigraphic name) is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 143.1 ...
ran very differently from the way they do today.
Late Cretaceous
 Between the Jurassic and the
Between the Jurassic and the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''cre ...
, which started about 100 Mya, Gondwana began breaking up, pushing Africa and India north across the Tethys and opening up the Indian Ocean. During the Late Cretaceous the Tethys sea was home to many different animals, including marine reptiles, bony fish
Osteichthyes ( ; ), also known as osteichthyans or commonly referred to as the bony fish, is a Biodiversity, diverse clade of vertebrate animals that have endoskeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondricht ...
, cartilaginous fish
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class of jawed fish that contains the cartilaginous fish or chondrichthyans, which all have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fish'', which have skeleto ...
and cephalopods
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan Taxonomic rank, class Cephalopoda (Greek language, Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral symm ...
. The islands
This is a list of the lists of islands in the world grouped by country, by continent, by body of water, and by other classifications. For rank-order lists, see the #Other lists of islands, other lists of islands below.
Lists of islands by count ...
that were located in the northern parts of the Tethys sea (Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
) created biodiverse ecosystems
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
that had animals that went through insular dwarfism
Insular dwarfism, a form of phyletic dwarfism, is the process and condition of large animals evolving or having a reduced body size when their population's range is limited to a small environment, primarily islands. This natural process is disti ...
and insular gigantism. The insular dwarfism process happened mostly to the dinosaurs
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic Geological period, period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the #Evolutio ...
that lived on the islands, like the sauropods
Sauropoda (), whose members are known as sauropods (; from '' sauro-'' + '' -pod'', 'lizard-footed'), is a clade of saurischian ('lizard-hipped') dinosaurs. Sauropods had very long necks, long tails, small heads (relative to the rest of their b ...
and the hadrosaurs. Telmatosaurus is a good representation of the insular dwarfism process. While the insular dwarfism process happened to the dinosaurs, the pterosaurs
Pterosaurs are an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the Order (biology), order Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 million to 66 million years ago). Pterosau ...
that lived on the islands went through the process known as insular gigantism. Hatzegopteryx was a huge azhdarchid pterosaur that lived on the islands of the Tethys sea. This giant pterosaur would have filled its ecological niche
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of Resource (biology), resources an ...
as an apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator or superpredator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the hig ...
. During the Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian ( ) is, in the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS) geologic timescale, the latest age (geology), age (uppermost stage (stratigraphy), stage) of the Late Cretaceous epoch (geology), Epoch or Upper Cretaceous series (s ...
, the Tethys sea had many different large mosasaurs that lived in the same geographical area and would have competed with each other. Europe had large mosasaurs like Prognathodon giganteus, Prognathodon saturator, Prognathodon sectorius, Mosasaurus hoffmannii and Mosasaurus lemonnieri. North Africa
North Africa (sometimes Northern Africa) is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region. However, it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of t ...
would have also had large mosasaurs like Prognathodon giganteus, Prognathodon currii, Thalassotitan atrox, Hainosaurus boubker and Mosasaurus beaugei. The competition between many different apex predators is something we don't only see in the Tethys sea, but also in the Western Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway (also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, the North American Inland Sea, or the Western Interior Sea) was a large inland sea (geology), inland sea that existed roughly over the present-day Great Plains of ...
.
Cenozoic
 Throughout the
Throughout the Cenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three g ...
(66 million to the dawn of the Neogene, 23 Mya), the connections between the Atlantic and Indian Oceans across the Tethys were eventually closed off in what is now the Middle East during the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
, as a consequence of the northern migration of Africa/Arabia and global sea levels falling due to the concurrent formation of the Antarctic Ice Sheet. This decoupling occurred in two steps, first around 20 Mya and another around 14 Mya. The complete closure of the Tethys led to a global reorganization of currents, and is what is thought to have allowed for upwelling
Upwelling is an physical oceanography, oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted sur ...
in the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea () is a region of sea in the northern Indian Ocean, bounded on the west by the Arabian Peninsula, Gulf of Aden and Guardafui Channel, on the northwest by Gulf of Oman and Iran, on the north by Pakistan, on the east by India, and ...
and led to the establishment of the modern South Asian Monsoon. It also caused major modifications to the functioning of the AMOC and ACC.
During the Oligocene
The Oligocene ( ) is a geologic epoch (geology), epoch of the Paleogene Geologic time scale, Period that extends from about 33.9 million to 23 million years before the present ( to ). As with other older geologic periods, the rock beds that defin ...
(33.9 to 23 Mya), large parts of central and eastern Europe were covered by a northern branch of the Tethys Ocean, called the Paratethys. The Paratethys was separated from the Tethys with the formation of the Alps, Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe and Southeast Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains ...
, Dinarides, Taurus, and Elburz mountains during the Alpine orogeny. During the late Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
, the Paratethys gradually disappeared, and became an isolated inland sea. Separation from the wider Tethys during the early Miocene initially led to a boost in primary productivity
Primary or primaries may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and labels
* Primary (band), from Australia
* Primary (musician), hip hop musician and record producer from South Korea
* Primary Music, Israeli record label
Works
* ...
for the Paratethys, but this gave way to a total ecosystem collapse during the late Miocene as a result of rapid dissolution of carbonate
A carbonate is a salt of carbonic acid, (), characterized by the presence of the carbonate ion, a polyatomic ion with the formula . The word "carbonate" may also refer to a carbonate ester, an organic compound containing the carbonate group ...
.
Historical theory
In Chapter 13 of his 1845 book, Roderick Murchison described a distinctive formation extending from theBlack Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ...
to the Aral Sea in which the creatures differed from those of the purely marine period that preceded them. The Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
deposits of Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukrain ...
and Taman (south of the Sea of Azov
The Sea of Azov is an inland Continental shelf#Shelf seas, shelf sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch, and sometimes regarded as a northern extension of the Black Sea. The sea is bounded by Ru ...
) are identical with formations surrounding the present Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, ...
, in which the univalves of freshwater origin are associated with forms of Cardiacae and Mytili that are common to partially saline or brackish waters. This distinctive fauna has been found throughout all the enormously developed Tertiary formations of the southern and south-eastern steppes.
On the accompanying map, Murchison shows the Aralo-Caspian Formation extending from close to the Danube delta across Crimea, up the east side of the Volga river
The Volga (, ) is the longest river in Europe and the longest endorheic basin river in the world. Situated in Russia, it flows through Central Russia to Southern Russia and into the Caspian Sea. The Volga has a length of , and a catchment ...
to Samara, then south of the Urals to beyond the Aral Sea. Brackish and upper freshwater components (OSM) of the Miocene are now known to extend through the North Alpine foreland basin and onto the Swabian Jura with thickness of up to ; these were deposited in the Paratethys when the Alpine front was still farther south.
 In 1885, the Austrian palaeontologist Melchior Neumayr deduced the existence of the Tethys Ocean from Mesozoic marine sediments and their distribution, calling his concept () and described it as a Jurassic seaway, which extended from the Caribbean to the Himalayas.
In 1893, the Austrian geologist
In 1885, the Austrian palaeontologist Melchior Neumayr deduced the existence of the Tethys Ocean from Mesozoic marine sediments and their distribution, calling his concept () and described it as a Jurassic seaway, which extended from the Caribbean to the Himalayas.
In 1893, the Austrian geologist Eduard Suess
Eduard Suess (; 20 August 1831 – 26 April 1914) was an Austrian geologist and an expert on the geography of the Alps. He is responsible for hypothesising two major former geographical features, the supercontinent Gondwana (proposed in 1861) and ...
proposed the hypothesis that an ancient and extinct inland sea had once existed between Laurasia and the continents which formed Gondwana
Gondwana ( ; ) was a large landmass, sometimes referred to as a supercontinent. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America, Africa, Antarctica, Australia (continent), Australia, Zea ...
II. He named it the Tethys Sea after the Greek sea goddess Tethys. He provided evidence for his theory using fossil records from the Alps and Africa. He proposed the concept of ''Tethys'' in his four-volume work (''The Face of the Earth'').
In the following decades during the 20th century, " mobilist" geologists such as Uhlig (1911), Diener (1925), and Daque (1926) regarded Tethys as a large trough between two supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", ...
s which lasted from the late Palaeozoic until continental fragments derived from Gondwana obliterated it.
After World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, Tethys was described as a triangular ocean with a wide eastern end.
From 1920s to the 1960s, "fixist" geologists, however, regarded Tethys as a composite trough, which evolved through a series of orogenic cycles. They used the terms 'Paleotethys', 'Mesotethys', and 'Neotethys' for the Caledonian, Variscan, and Alpine orogenies, respectively. In the 1970s and 1980s, these terms and 'Proto-Tethys', were used in different senses by various authors, but the concept of a single ocean wedging into Pangea from the east, roughly where Suess first proposed it, remained.
In the 1960s, the theory of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed durin ...
became established, and Suess's "sea" could clearly be seen to have been an ocean. Plate tectonics provided an explanation for the mechanism by which the former ocean disappeared: oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramaf ...
can subduct under continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as '' continental shelves''. This layer is sometimes called '' si ...
.
Tethys was considered an oceanic plate by Smith (1971); Dewey, Pitman, Ryan and Bonnin (1973); Laubscher and Bernoulli (1973); and Bijou-Duval, Dercourt and Pichon (1977).
See also
* * * * * * * *References
Notes
Sources
* * * * * * * *External links
* {{Authority control Historical oceans Mesozoic paleogeography Paleogene paleogeography Permian paleogeography Plate tectonics