|
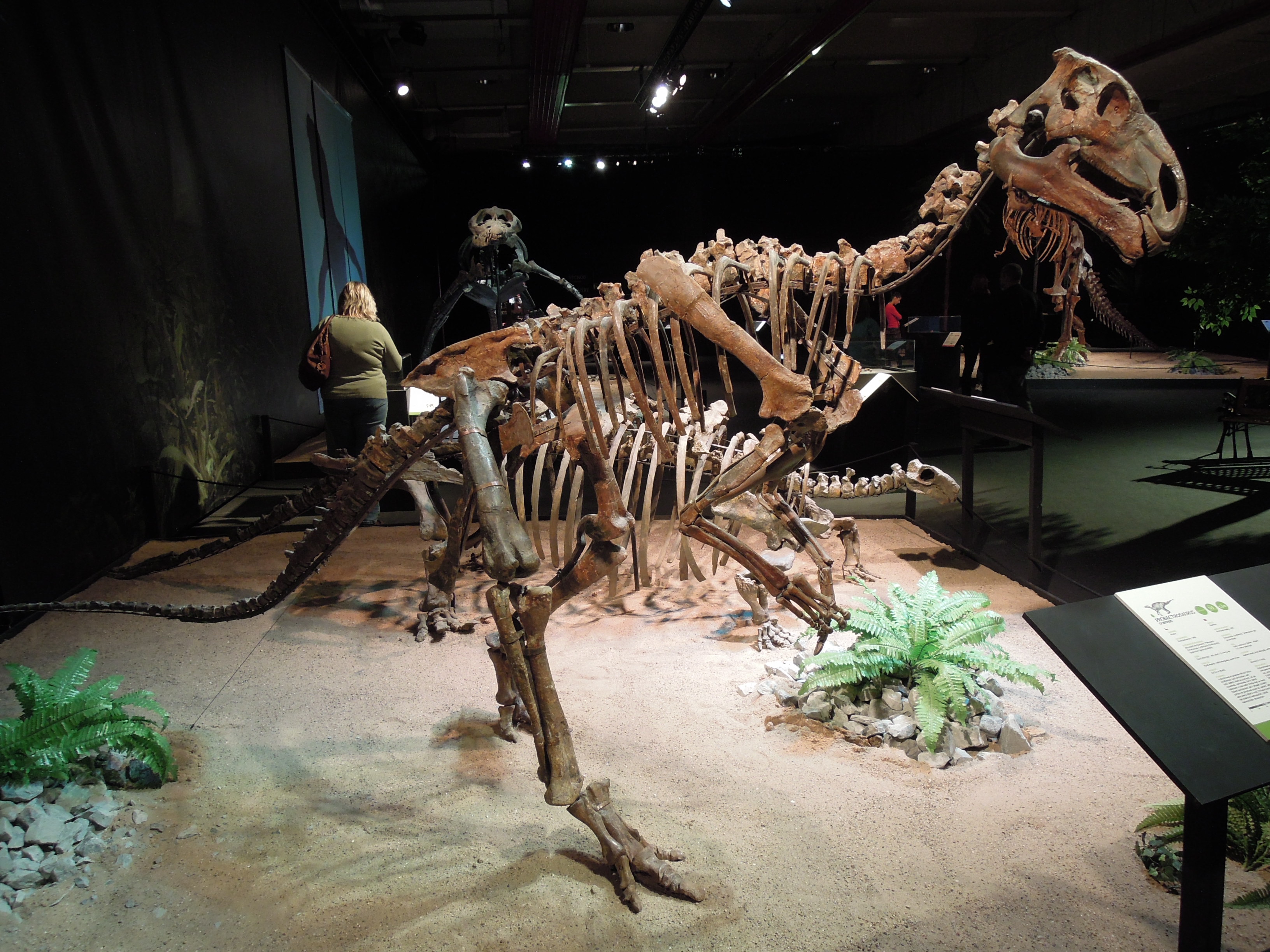
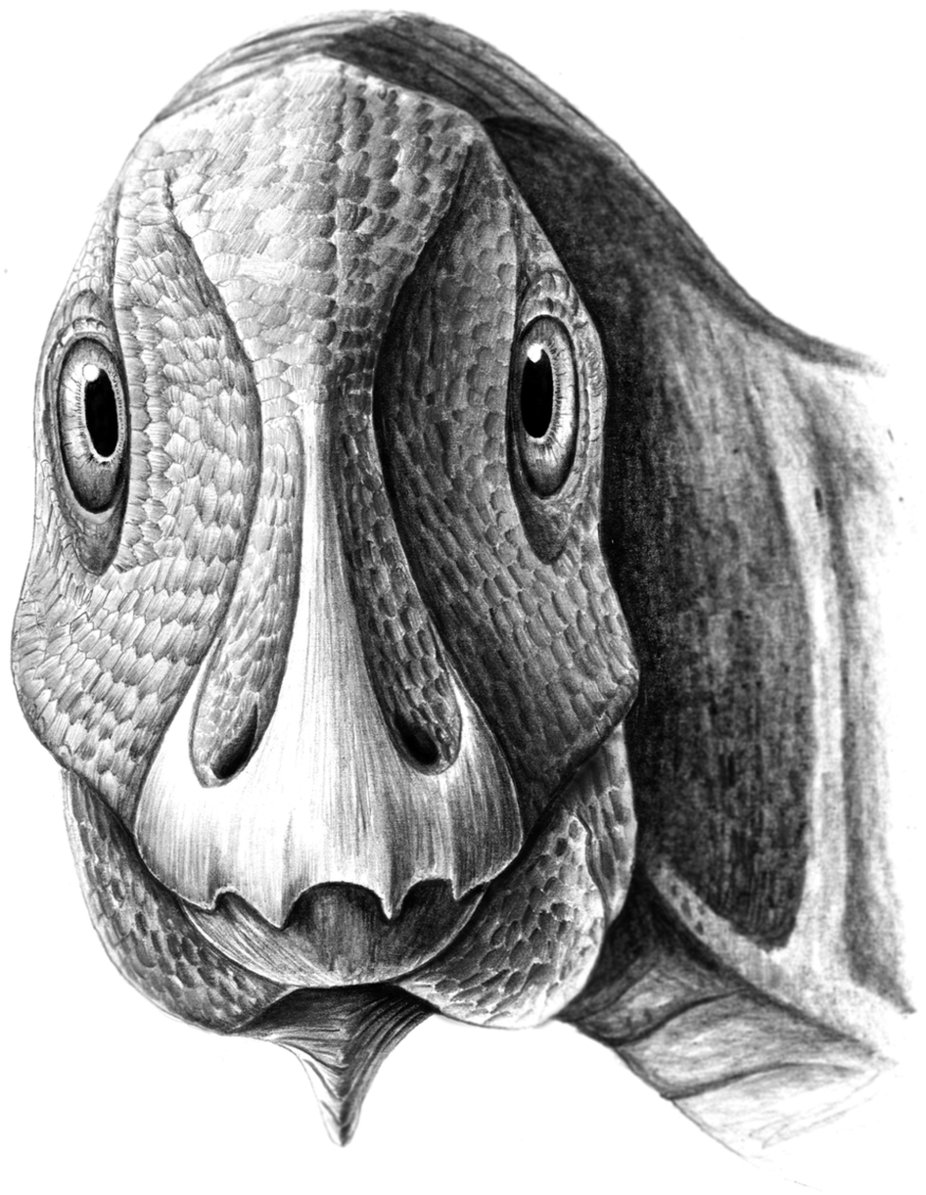
Telmatosaurus
''Telmatosaurus'' (meaning "marsh lizard") is a genus of basal hadrosauromorph dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Romania. It was a relatively small hadrosaur, measuring approximately in length and in body mass, which has been explained as an instance of insular dwarfism. Discovery In 1895 some peasants presented Ilona Nopcsa, the daughter of their lord, with a dinosaur skull they had found at the estate Săcele in the district Hunedoara (then named Hunyad) in Transylvania. Ilona had an elder brother, Ferenc or Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás who was inspired by the find to become a paleontology student at the University of Vienna. In 1899 Nopcsa named the skull ''Limnosaurus transsylvanicus''. The generic name was derived from Greek λιμνή, ''limné'', "swamp", a reference to the presumed swamp-dwelling habits of hadrosaurs. The specific name referred to Transylvania. Later Nopcsa discovered that the name ''Limnosaurus'' had already been used by Othniel Charles Mars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telmatosaurus Scale
''Telmatosaurus'' (meaning "marsh lizard") is a genus of basal hadrosauromorph dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Romania. It was a relatively small hadrosaur, measuring approximately in length and in body mass, which has been explained as an instance of insular dwarfism. Discovery In 1895 some peasants presented Ilona Nopcsa, the daughter of their lord, with a dinosaur skull they had found at the estate Săcele in the district Hunedoara (then named Hunyad) in Transylvania. Ilona had an elder brother, Ferenc or Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás who was inspired by the find to become a paleontology student at the University of Vienna. In 1899 Nopcsa named the skull ''Limnosaurus transsylvanicus''. The generic name was derived from Greek λιμνή, ''limné'', "swamp", a reference to the presumed swamp-dwelling habits of hadrosaurs. The specific name referred to Transylvania. Later Nopcsa discovered that the name ''Limnosaurus'' had already been used by Othniel Charle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telmatosaurus With Pathology
''Telmatosaurus'' (meaning "marsh lizard") is a genus of basal hadrosauromorph dinosaur Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ... from the Late Cretaceous of Romania. It was a relatively small hadrosaur, measuring approximately in length and in body mass, which has been explained as an instance of insular dwarfism. Discovery In 1895 some peasants presented Ilona Nopcsa, the daughter of their lord, with a dinosaur skull they had found at the estate (land), estate Săcele in the district Hunedoara (then named Hunyad) in Transylvania. Ilona had an elder brother, Ferenc or Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás who was inspired by the find to become a paleontology student at the University of Vienna. In 1899 Nopcsa named the skull ''Limnosaurus transsylvanicus''. The generic nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthomerus
''Orthomerus'' (meaning "straight femur") is a genus of dubious hadrosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of the Netherlands. It is today an obscure genus, but in the past was conflated with the much better known ''Telmatosaurus''. Discovery and history The type species ''Orthomerus dolloi'' was in 1883 named by the well-known British paleontologist Harry Govier Seeley. The genus name is derived from the Greek ὀρθός (''orthos''), "straight", and μηρός (''meros''), "thigh". The specific name honours the French/Belgian paleontologist Louis Dollo, who had identified the bones in August 1882, during a visit to London. The type specimen, formed by the syntypes BMNH 42954-57, was probably found in the chalkstone quarries of the Sint-Pietersberg near the city of Maastricht, The Netherlands. It mainly consists of partial juvenile skeletal elements. These remains are from the Maastricht Formation of the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous, about 66 million y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrosauromorph
Hadrosauromorpha is a clade of iguanodontian ornithopods, defined in 2014 by David B. Norman to divide Hadrosauroidea into the basal taxa with compressed manual bones and a pollex, and the derived taxa that lack them. The clade is defined as all the taxa closer to '' Edmontosaurus regalis'' than ''Probactrosaurus gobiensis''. This results in different taxon inclusion depending on the analysis. Classification Hadrosauromorpha was first used in literature by David B. Norman in 2014 in a discussion of phylogenetics of '' Hypselospinus''. In his 2014 paper Norman references another of his publications as the authority for Hadrosauromorpha, a chapter in the book ''Hadrosaurs''. However, the book was in fact published later, in 2015. Following Article 19.4 of the PhyloCode, the authorship of the clade is thus Norman (2015), while the authorship of the definition is Norman (2014). Definition Hadrosauromorpha was defined by Norman (2014 and 2015) as hadrosauroid taxa closer to '' E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1903 In Paleontology
Archosauromorphs Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Sauropterygians * Plesiosaur gastroliths documented.Williston (1903). Sanders, Manley, and Carpenter (2001), "Table 12.1" page 167. Newly named plesiosaurs Synapsids Non-mammalian Eutherians Cetaceans Pholidotes References {{portal, Paleontology * Sanders F, Manley K, Carpenter K. Gastroliths from the Lower Cretaceous sauropod Cedarosaurus weiskopfae. In: Tanke D.H, Carpenter K, editors. Mesozoic vertebrate life: new research inspired by the paleontology of Philip J. Currie. Indiana University Press; Bloomington, IN: 2001. pp. 166–180. * Williston, Samuel Wendel; 1903. North American Plesiosaurs; Field Columbian Museum Publication 73, Geological Series; II(I); Field Columbian Museum, Chicago. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insular Dwarfism
Insular dwarfism, a form of phyletic dwarfism, is the process and condition of large animals evolving or having a reduced body size when their population's range is limited to a small environment, primarily islands. This natural process is distinct from the intentional creation of dwarf breeds, called dwarfing. This process has occurred many times throughout evolutionary history, with examples including dinosaurs, like ''Europasaurus'' and '' Magyarosaurus dacus'', and modern animals such as elephants and their relatives. This process, and other " island genetics" artifacts, can occur not only on islands, but also in other situations where an ecosystem is isolated from external resources and breeding. This can include caves, desert oases, isolated valleys and isolated mountains ("sky islands"). Insular dwarfism is one aspect of the more general "island effect" or "Foster's rule", which posits that when mainland animals colonize islands, small species tend to evolve larger bodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sânpetru Formation
The Sânpetru Formation is an early Maastrichtian geologic formation. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel, et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution." Pp. 517-607. It is located in Romania, near Sânpetru village, part of Sântămăria-Orlea commune. It forms a component of the Hațeg Island fauna. Description The Sânpetru Formation crops out in the central to southern Hațeg Basin along the Bărbat River and comprises sandstones and mudstones deposited in a wet floodplain environment characterized by braided fluvial channels. The formation is correlated with the Densuș-Ciula Formation of the northern section of the same basin, both dating to the Maastrichtian of the Late Cretaceous.Solomon & Codrea, 2015, p.26 Fossil content Amphibians Turtles Squamates Crocodyliformes Ornithischians Sauropods Theropods Pterosaurs Mammals See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from . The Maastrichtian was preceded by the Campanian and succeeded by the Danian (part of the Paleogene and Paleocene). The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event (formerly known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event) occurred at the end of this age. In this mass extinction, many commonly recognized groups such as non-avian dinosaurs, plesiosaurs and mosasaurs, as well as many other lesser-known groups, died out. The cause of the extinction is most commonly linked to an asteroid about wide colliding with Earth, ending the Cretaceous. Stratigraphic definitions Definition The Maastrichtian was introduced into scientific literature by Belgian geologist André Hubert Dumont in 1849, after studying rock strata of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Junior Objective Synonym
The Botanical and Zoological Codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that (now) goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called ''Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank - for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 1758 is a junior synonym of ''Papilio levana'' Linnaeus, 1758, being names for different seasonal forms of the species now referred to as ''Araschnia lev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Archipelago
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to: In general * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe ** Ethnic groups in Europe ** Demographics of Europe ** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe and other Western countries * ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to the European Union ** Citizenship of the European Union ** Demographics of the European Union In publishing * ''The European'' (1953 magazine), a far-right cultural and political magazine published 1953–1959 * ''The European'' (newspaper), a British weekly newspaper published 1990–1998 * ''The European'' (2009 magazine), a German magazine first published in September 2009 *''The European Magazine'', a magazine published in London 1782–1826 *''The New European'', a British weekly pop-up newspaper first published in July 2016 Other uses * * Europeans (band), a British post-punk group, from Bristol See also * * * Europe (disambi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |