Tehran Art Center on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Tehran (; fa, تهران ) is the largest city in Tehran Province and the
 In the early 18th century,
In the early 18th century, 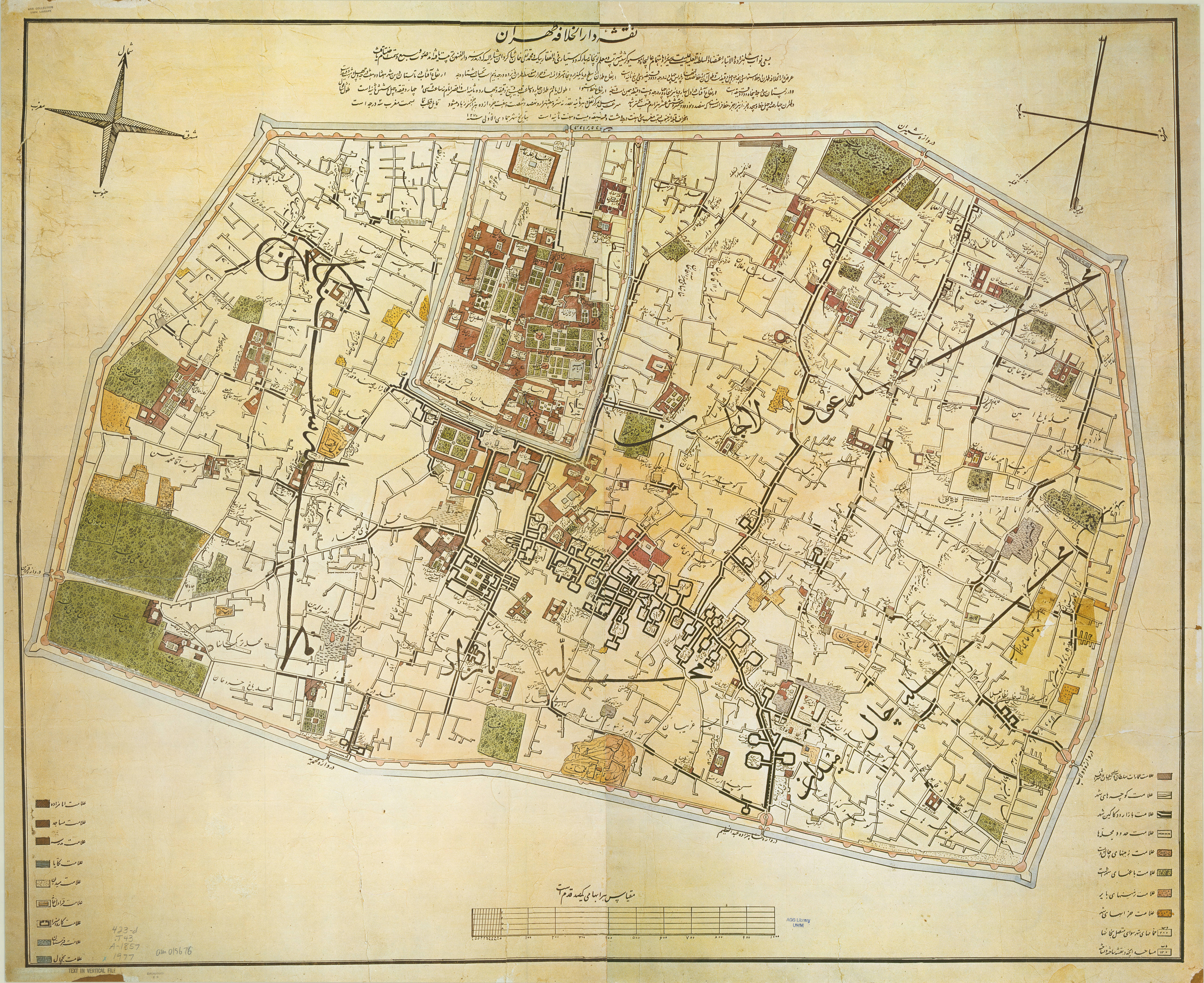 After 50 years of Qajar rule, the city still barely had more than 80,000 inhabitants. Up until the 1870s, Tehran consisted of a walled citadel, a roofed
After 50 years of Qajar rule, the city still barely had more than 80,000 inhabitants. Up until the 1870s, Tehran consisted of a walled citadel, a roofed
 Growing awareness of civil rights resulted in the
Growing awareness of civil rights resulted in the
File:Toopkhooneh ghadeem.jpg, Tupkhane Square in 1911.
File:Tehran1930.jpg, Jalili Square (Khaiyam) street in Tehran in 1930.
File:University of Tehran Faculty of Law 1318.jpg,
The establishment of the planning organization of Iran in 1948 resulted in the first socioeconomic development plan to cover from 1949 to 1955. These plans not only failed to slow the unbalanced growth of Tehran but with the 1962 land reforms that Reza Shah's son and successor  Tehran's most famous landmark, the Azadi Tower, was built by the order of the Shah in 1971. It was designed by Hossein Amanat, an architect whose design won a competition, combining elements of classical Sassanian architecture with post-classical Iranian architecture. Formerly known as the ''Shahyad Tower'', it was built to commemorate the 2,500th anniversary of the Imperial State of Iran.
During the
Tehran's most famous landmark, the Azadi Tower, was built by the order of the Shah in 1971. It was designed by Hossein Amanat, an architect whose design won a competition, combining elements of classical Sassanian architecture with post-classical Iranian architecture. Formerly known as the ''Shahyad Tower'', it was built to commemorate the 2,500th anniversary of the Imperial State of Iran.
During the
 The metropolis of Tehran is divided into 22 municipal districts, each with its own administrative center. Of the 22 municipal districts, 20 are located in
The metropolis of Tehran is divided into 22 municipal districts, each with its own administrative center. Of the 22 municipal districts, 20 are located in
File:Tochal-Tehran.jpg, Tehran and Mount Tochal in the winter of 2006.
File:View of Tehran at Night (25821934418).jpg, View of Tehran at Night from Tajrish.
File:Elahiyeh.jpg,
Northern Tehran is the wealthiest part of the city, consisting of various districts such as
"Tehran: Split Between Liberal, Hard-Line"
.
"Pro-reform Khatami appears victorious after 30 million Iranians cast votes"
''
 The northern area of Tehran has a
The northern area of Tehran has a
. hamshahrionline.ir Other air currents that blow in the area of Tehran are: # Tochal breeze: With the rapid cooling of the Alborz mountain range at night, a local high-pressure center is formed on Mount Tochal, and this cold current flows down the mountain due to its weight and high pressure; Thus, a gentle breeze blows into the city from the north at night. # Southern and southeastern regional winds: these winds blow from the desert plains in the hot months of the year. # Western winds: These winds are among the planetary winds that affect the city of Tehran more or less throughout the year and can be called the prevailing wind. Air currents have a great effect on Tehran's weather. The prevailing wind blowing from the west causes the west of the city to always be exposed to fresh air; Although this wind brings smoke and pollution from the western industrial areas, its strong wind can take the polluted air out of the city of Tehran. In most years, winter provides half of Tehran's total annual rainfall. March is the rainiest month of the year and about one-fifth of the annual rainfall occurs in it. Summer is also the least rainy season and September is the driest month of the year in Tehran. The average annual rainfall of the city is sometimes very different in the north and south regions. There are between 205 and 213 days of clear to partly cloudy weather in Tehran.Climate and air pollution of Tehran (in Persian)
atlas.tehran.ir One of the most intense rains in Tehran happened on April 21, 1962 and this rain lasted for 10 hours. Meteorology also announced that the amount of rainfall on that one day in Tehran was equivalent to six years. Summer is hot and dry with little rain, but
irna.com On February 3, 2014, Tehran received heavy snowfall, specifically in the northern parts of the city, with a depth of . In one week of successive snowfalls, roads were made impassable in some areas, with the temperature ranging from to . On June 3, 2014, a severe thunderstorm with powerful
 A plan to move the capital has been discussed many times in prior years, due mainly to the environmental issues of the region. Tehran is one of the world's most polluted cities and is also located near two major fault lines.
The city suffers from severe air pollution, 80% of it due to cars. The remaining 20% is due to industrial pollution. Other estimates suggest that motorcycles alone account for 30% of air and 50% of
A plan to move the capital has been discussed many times in prior years, due mainly to the environmental issues of the region. Tehran is one of the world's most polluted cities and is also located near two major fault lines.
The city suffers from severe air pollution, 80% of it due to cars. The remaining 20% is due to industrial pollution. Other estimates suggest that motorcycles alone account for 30% of air and 50% of

 The city of Tehran has a population of approximately 10 million in 2016. With its cosmopolitan atmosphere, Tehran is home to diverse ethnic and linguistic groups from all over the country. The present-day dominant language of Tehran is the Tehrani variety of the
The city of Tehran has a population of approximately 10 million in 2016. With its cosmopolitan atmosphere, Tehran is home to diverse ethnic and linguistic groups from all over the country. The present-day dominant language of Tehran is the Tehrani variety of the
File:Mezquita Shah, Teherán, Irán, 2016-09-17, DD 49-51 HDR.jpg, Tehran's Shah Mosque (Tehran), Shah Mosque
File:Greek church of Virgin Mary Tehran.JPG, Tehran's Greek Orthodox Church of Virgin Mary
File:Church of holy mary کلیسای حضرت مریم 1.jpg, Saint Mary Armenian Apostolic Church, Tehran
File:St. Joseph Assyrian Catholic Church, Tehran.jpg, St. Joseph Assyrian Catholic (Chaldean Catholic) Church, Tehran
File:26600-کلیسای آشوری مارگیورگیز.jpg, Assyrian Church of the East of Mar Sarkis, Tehran
File:Yusefabad -5.jpg, Tehran's Yusef Abad Synagogue
File:Adriaan2.jpg, Adrian Fire Temple, Tehran
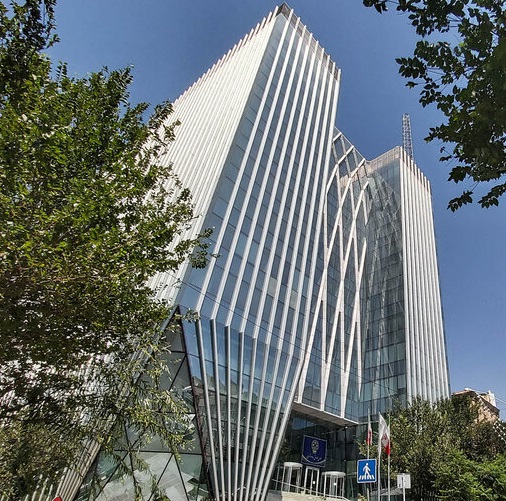 Tehran is the economic centre of Iran. About 30% of Iran's public-sector workforce and 45% of its large industrial firms are located in the city, and almost half of these workers are employed by the government. Most of the remainder of workers are factory workers, shopkeepers, laborers, and transport workers.
Few foreign companies operate in Tehran, due to the government's complex international relations. But prior to the
Tehran is the economic centre of Iran. About 30% of Iran's public-sector workforce and 45% of its large industrial firms are located in the city, and almost half of these workers are employed by the government. Most of the remainder of workers are factory workers, shopkeepers, laborers, and transport workers.
Few foreign companies operate in Tehran, due to the government's complex international relations. But prior to the
File:Iranmall Overview.jpg, Iran Mall
File:Tiraje Mall, Tehran City.JPG, Tiraje Mall in western Tehran
File:فروشگاه زنجیره ای افق کوروش.jpg, Kourosh Mall in Shahid Sattari Expressway
File:Tehran Old Bazaar.jpg, Tehran's Grand Bazaar, Tehran, Old Grand Bazaar
File:OPAL Shopping Center, Sa'adat Abad, Tehran (7).jpg, OPAL Shopping Cente
File:Hyper.star.jpg, Iran Hyper Star, Hyperstar, Tehran's subsidiary of Carrefour
List of modern and most-visited Shopping Malls in Tehran Province:
* Mega Mall
* Bamland Shopping Center
* Palladium Shopping Center
* Sam Center
* Iran Mall
* Kourosh Mall
* Tirajeh Shopping Center
* Modern Elahiyeh Shopping Center
* Donyaye Noor Shopping Centre
* Tandis Shopping Center
* Ava Centre
* Atlas Mall
* Goldis Mall
* OPAL Shopping Center
* Rosha Department Store
* Sivan Center
* Arg Shopping Center
* Nasr Shopping Center
* Galleria Shopping Center
* Charso Mall
* Mirdamad Shopping Center
* Royal Address Complex
* Platin Shopping Center
* Sana Shopping Center
* Sepid Shopping Center Tehran
* Najm Khavar Mianeh
* Parsian Shopping Center
* Artemis Shopping Center
* Heravi Center Shopping Mall
* Tuba shopping center
* Lale Shopping Center
* Andisheh Shopping Center
* Sky Center
* Lotus Mall
* Saba Shopping Mall
* Seven Center Shopping Mall
* Kasa Shopping
* Platin Shopping Center
File:(86-113-8)Seafood_(3).jpg, Tabiat Bridge
File:كاخ گلستان.jpg, Golestan Palace
File:Niavaran palace.jpg, Niavaran Complex
File:Mellat Palace Museum 02.jpg, Sa'dabad Complex
File:Masoodieh.jpg, Masoudieh Mansion, Masoudie, Baharestan (district), Baharestan.
File:Národní muzeum Íránu.jpg, National Museum of Iran
File:Visitors at Tehran Museum of Contemporary Art (25839577818).jpg, Tehran Museum of Contemporary Art, Museum of Contemporary Art
File:Carpet Museum, Tehran.jpg, Carpet Museum of Iran
File:باغ موزه قصر1392.JPG, Museum of the Qasr Prison
File:موزه آبگینه16.jpg, Abgineh Museum of Tehran, Abgineh Museum
Hotel
* Espinas Palace Hotel
* Parsian Azadi Hotel
* Fereshteh Pasargad Hotel
* Laleh International Hotel
* Parsian Enghelab Hotel
* Parsian Esteghlal International Hotel
* Parsian Evin Hotel
* Ibis Hotel
* Espinas International Hotel
* Persian Plaza Hotel
* Hanna Boutique Hotel
* Homa Hotel
* Rexan Hotel
* Tehran Heritage Hostel
* Tehran Grand 1 Hotel
* Iran Cozy Hotel
* Pamchal Hotel
* Amatis Hotel
* Hotel Markazi Iran
* Marlik Hotel
* Ferdowsi Grand Hotel
* Atana Hotel
* Valiasr Hotel
* Taj Mahal Hotel
* Morvarid Hotel
* Hally Hotel
* Howeyzeh hotel
* Atlas Hotel
* Amir Hotel
File:Espinas Palace Hotel 8316.jpg, Espinas Palace Hotel
File:Royal Hilton Hotel, Tehran (1970s).jpg, Parsian Esteghlal International Hotel
File:Ferdowsi International Grand Hotel.jpg, Ferdowsi Grand Hotel
File:Tehranhomahotel.jpg, Homa Hotel
File:Tehran InterContinental Hotel.jpg, Laleh International Hotel
File:Parsian Evin Hotel, Chamran Highway, Tehrān, Teheran, Iran - panoramio (1).jpg, Parsian Azadi Hotel
File:Fresh green ^ Red - panoramio.jpg, Valiasr Street
File:Fajr Bridge Tehran2.jpg, Hemmat Expressway
File:Tehran111.jpg, Modarres Expressway
File:Kordestan-Resalat-Hakim.jpg, Kordestan Expressway interchange with Resalat Expressway, Resalat and Hakim Expressway, Hakim expressways
 A number of streets in Tehran are named after international figures, including:
* Henri Corbin Street, central Tehran
* List of places and things named after Simón Bolivar, Simon Bolivar Boulevard, northwestern Tehran
* Edward Granville Browne, Edward Browne Street, near the University of Tehran
* List of roads named after Mahatma Gandhi#Outside India, Gandhi Street, northern Tehran
* Mohammad Ali Jenah Expressway, western Tehran
* Muhammad Iqbal, Iqbal Lahori Street, eastern Tehran
* Patrice Lumumba Street, western Tehran
* Nelson Mandela Boulevard (Jordan Street) Tehran, Nelson Mandela Boulevard, northern Tehran
* Bobby Sands#Asia, Bobby Sands Street, western side of the Embassy of the United Kingdom, Tehran, British Embassy
A number of streets in Tehran are named after international figures, including:
* Henri Corbin Street, central Tehran
* List of places and things named after Simón Bolivar, Simon Bolivar Boulevard, northwestern Tehran
* Edward Granville Browne, Edward Browne Street, near the University of Tehran
* List of roads named after Mahatma Gandhi#Outside India, Gandhi Street, northern Tehran
* Mohammad Ali Jenah Expressway, western Tehran
* Muhammad Iqbal, Iqbal Lahori Street, eastern Tehran
* Patrice Lumumba Street, western Tehran
* Nelson Mandela Boulevard (Jordan Street) Tehran, Nelson Mandela Boulevard, northern Tehran
* Bobby Sands#Asia, Bobby Sands Street, western side of the Embassy of the United Kingdom, Tehran, British Embassy
 According to the head of Tehran Municipality's Environment and Sustainable Development Office, Tehran was designed to have a capacity of about 300,000 cars, but more than five million cars are on the roads. The automotive industry has recently developed, but international sanctions influence the production processes periodically.
According to local media, Tehran has more than 200,000 taxis plying the roads daily, with several types of taxi available in the city. Airport taxis have a higher cost per kilometer as opposed to regular green and yellow taxis in the city.
According to the head of Tehran Municipality's Environment and Sustainable Development Office, Tehran was designed to have a capacity of about 300,000 cars, but more than five million cars are on the roads. The automotive industry has recently developed, but international sanctions influence the production processes periodically.
According to local media, Tehran has more than 200,000 taxis plying the roads daily, with several types of taxi available in the city. Airport taxis have a higher cost per kilometer as opposed to regular green and yellow taxis in the city.
 Buses have served the city since the 1920s. Tehran's transport system includes conventional buses, trolleybuses, and
Buses have served the city since the 1920s. Tehran's transport system includes conventional buses, trolleybuses, and
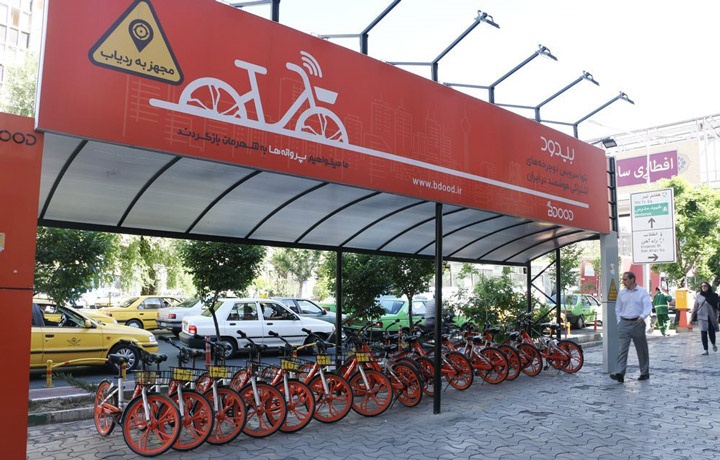 Bdood is a dockless bike-sharing company in
Bdood is a dockless bike-sharing company in

 Tehran has a Tehran Railway Station, central railway station that connects services round the clock to various cities in the country, along with a Tehran–Europe train line also running.
The feasibility study and conceptual planning of the construction of Tehran's subway system were started in the 1970s. The first two of the eight projected metro lines were opened in 2001.
Tehran has a Tehran Railway Station, central railway station that connects services round the clock to various cities in the country, along with a Tehran–Europe train line also running.
The feasibility study and conceptual planning of the construction of Tehran's subway system were started in the 1970s. The first two of the eight projected metro lines were opened in 2001.
 Tehran is served by the international airports of Mehrabad International Airport, Mehrabad and Imam Khomeini International Airport, Imam Khomeini. Mehrabad Airport, an old airport in western Tehran that doubles as a military base, is mainly used for domestic and charter flights. Imam Khomeini Airport, located south of the city, handles the main international flights.
Tehran is served by the international airports of Mehrabad International Airport, Mehrabad and Imam Khomeini International Airport, Imam Khomeini. Mehrabad Airport, an old airport in western Tehran that doubles as a military base, is mainly used for domestic and charter flights. Imam Khomeini Airport, located south of the city, handles the main international flights.
 There are over 2,100 parks within the metropolis of Tehran, with one of the oldest being Jamshidieh Park, Jamshidie Park, which was first established as a private garden for Qajar prince Jamshid Davallu, and was then dedicated to the last empress of Iran, Farah Pahlavi. The total green space within Tehran stretches over 12,600 hectares, covering over 20 percent of the city's area. The Parks and Green Spaces Organization of Tehran was established in 1960, and is responsible for the protection of the urban nature present in the city.
Tehran's Birds Garden is the largest bird park in Iran. There is also Eram Zoo, a zoo located on the Tehran–Karaj Expressway, housing over 290 species within an area of about five hectares.
In 2009, the Ab-o-Atash Park ("Water and Fire park") was founded. Its main features are an open water fountain area for cooling in the hot climate, fire towers, and an amphitheatre.
There are over 2,100 parks within the metropolis of Tehran, with one of the oldest being Jamshidieh Park, Jamshidie Park, which was first established as a private garden for Qajar prince Jamshid Davallu, and was then dedicated to the last empress of Iran, Farah Pahlavi. The total green space within Tehran stretches over 12,600 hectares, covering over 20 percent of the city's area. The Parks and Green Spaces Organization of Tehran was established in 1960, and is responsible for the protection of the urban nature present in the city.
Tehran's Birds Garden is the largest bird park in Iran. There is also Eram Zoo, a zoo located on the Tehran–Karaj Expressway, housing over 290 species within an area of about five hectares.
In 2009, the Ab-o-Atash Park ("Water and Fire park") was founded. Its main features are an open water fountain area for cooling in the hot climate, fire towers, and an amphitheatre.
 Tehran is the largest and most important educational center in Iran. There are a total of nearly 50 major colleges and universities in Greater Tehran.
Since the establishment of Dar ol Fonun by the order of Amir Kabir in the mid-19th century, Tehran has amassed a large number of institutions of higher education. Some of these institutions have played crucial roles in the unfolding of Iranian political events. Samuel M. Jordan, whom Jordan Avenue in Tehran was named after, was one of the founding pioneers of the Alborz High School, American College of Tehran, which was one of the first modern high schools in the Middle East.
Among major educational institutions located in Tehran, Amirkabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic),
Tehran is the largest and most important educational center in Iran. There are a total of nearly 50 major colleges and universities in Greater Tehran.
Since the establishment of Dar ol Fonun by the order of Amir Kabir in the mid-19th century, Tehran has amassed a large number of institutions of higher education. Some of these institutions have played crucial roles in the unfolding of Iranian political events. Samuel M. Jordan, whom Jordan Avenue in Tehran was named after, was one of the founding pioneers of the Alborz High School, American College of Tehran, which was one of the first modern high schools in the Middle East.
Among major educational institutions located in Tehran, Amirkabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic),
File:02 hasan abad Sq..jpg, Hasanabad, Tehran, Hasanabad Square
File:Tehran City Theater 1.jpg, A view of the building of the City Theater of Tehran
File:Ministerstv spravedlnosti 1.jpg, The Courthouse of Tehran
File:Iranian Foreign Affaire Ministry.jpg, Police House,
the National Garden, Tehran, National Garden File:Meydan Mashgh Tehran.jpg, Cossack House,
the National Garden, Tehran, National Garden
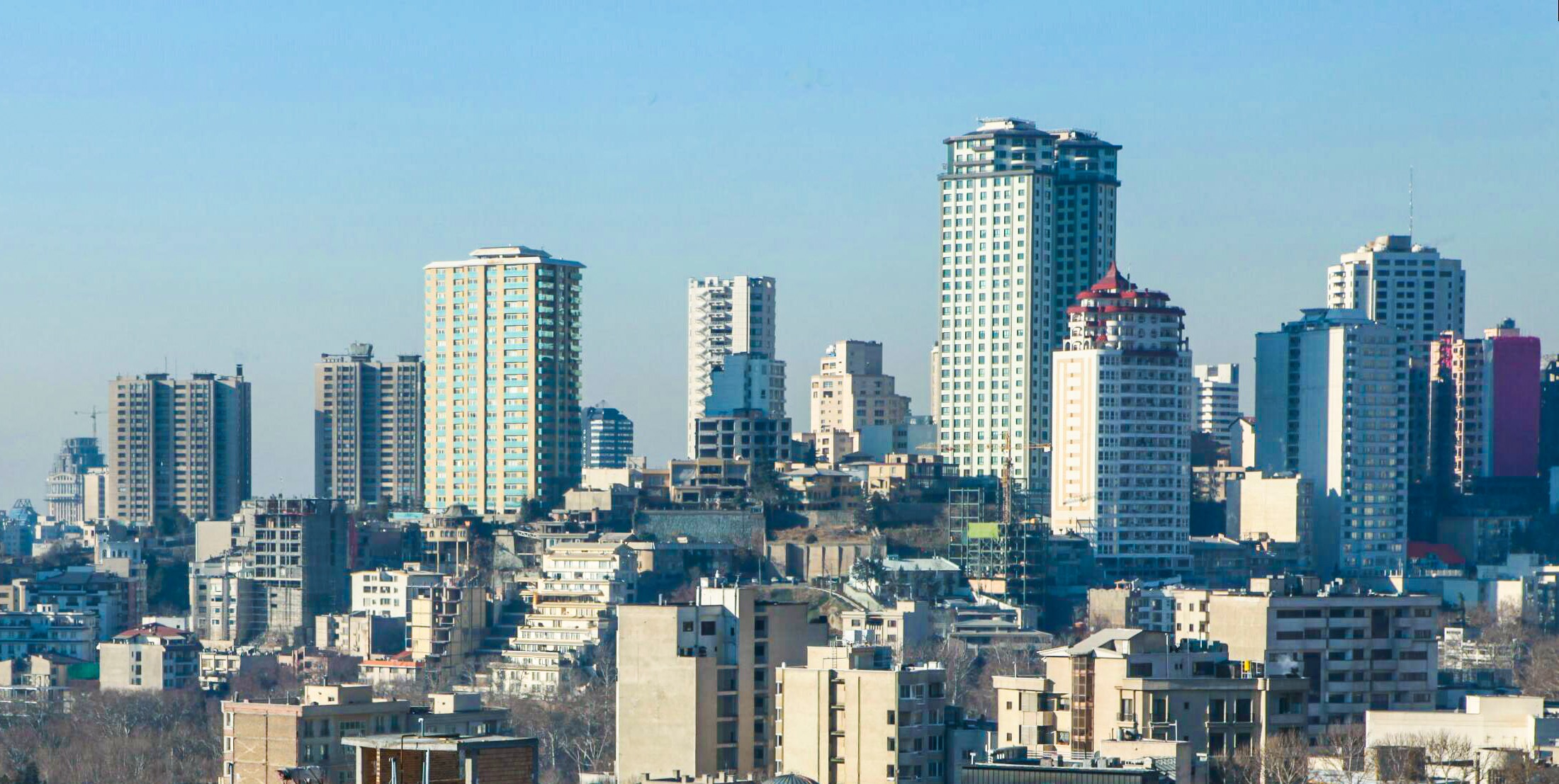 Previously a low-rise city due to seismic activity in the region, modern high-rise developments in Tehran have been built in recent decades in order to service its growing population. There have been no major quakes in Tehran since 1830.
Tehran International Tower is the tallest skyscraper in Iran. It is 54-stories tall and located in the northern district of Yusef Abad.
The Azadi Tower, a memorial built under the reign of the
Previously a low-rise city due to seismic activity in the region, modern high-rise developments in Tehran have been built in recent decades in order to service its growing population. There have been no major quakes in Tehran since 1830.
Tehran International Tower is the tallest skyscraper in Iran. It is 54-stories tall and located in the northern district of Yusef Abad.
The Azadi Tower, a memorial built under the reign of the
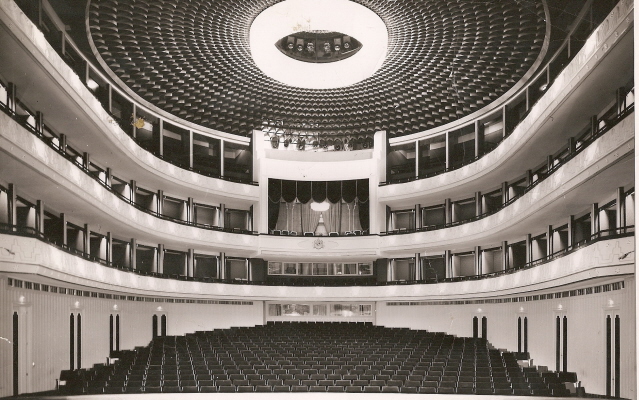 Under the reign of the Qajar dynasty, Qajars, Tehran was home to the royal theatre of Tekye Dowlat, located to the southeast of the Golestan Palace, in which traditional and religious performances were observed. It was eventually demolished and replaced with a bank building in 1947, following the reforms during the reign of Reza Shah.
Before the 1979 Revolution, the Iranian national stage had become the most famous performing scene for known international artists and troupes in the Middle East, with the Roudaki Hall of Tehran constructed to function as the national stage for opera and ballet. The hall was inaugurated in October 1967 and named after prominent Persian poet Rudaki. It is home to the Tehran Symphony Orchestra, the Tehran Opera Orchestra, and the Iranian National Ballet Company.
The City Theater of Tehran, one of Iran's biggest theatre complexes, which contains several performance halls, was opened in 1972. It was built at the initiative and presidency of empress Farah Pahlavi, and was designed by architect Ali Sardar Afkhami, constructed within five years.
The annual events of Fajr International Theater Festival, Fajr Theater Festival and Tehran International Puppet Theatre Festival, Tehran Puppet Theater Festival take place in Tehran.
Under the reign of the Qajar dynasty, Qajars, Tehran was home to the royal theatre of Tekye Dowlat, located to the southeast of the Golestan Palace, in which traditional and religious performances were observed. It was eventually demolished and replaced with a bank building in 1947, following the reforms during the reign of Reza Shah.
Before the 1979 Revolution, the Iranian national stage had become the most famous performing scene for known international artists and troupes in the Middle East, with the Roudaki Hall of Tehran constructed to function as the national stage for opera and ballet. The hall was inaugurated in October 1967 and named after prominent Persian poet Rudaki. It is home to the Tehran Symphony Orchestra, the Tehran Opera Orchestra, and the Iranian National Ballet Company.
The City Theater of Tehran, one of Iran's biggest theatre complexes, which contains several performance halls, was opened in 1972. It was built at the initiative and presidency of empress Farah Pahlavi, and was designed by architect Ali Sardar Afkhami, constructed within five years.
The annual events of Fajr International Theater Festival, Fajr Theater Festival and Tehran International Puppet Theatre Festival, Tehran Puppet Theater Festival take place in Tehran.

 The first movie theater in Tehran was established by Mirza Ebrahim Khan Sahhafbashi, Mirza Ebrahim Khan in 1904. Until the early 1930s, there were 15 theaters in Tehran Province and 11 in other provinces.
In present-day Tehran, most of the movie theatres are located downtown. The complexes of Kourosh Complex, Kourosh Cinema, Mellat Park, Mellat Gallery and Cineplex, Azadi Cinema Complex, Azadi Cinema, and Cinema Farhang are among the most popular cinema complexes in Tehran.
Several film festivals are held in Tehran, including Fajr International Film Festival, Fajr Film Festival, International Film Festival for Children and Youth, Children and Youth Film Festival, House of Cinema Festival, Mobile Film and Photo Festival, Nahal Festival, Roshd International Film Festival, Roshd Film Festival, Tehran Animation Festival, Tehran Short Film Festival, and Urban Film Festival.
The first movie theater in Tehran was established by Mirza Ebrahim Khan Sahhafbashi, Mirza Ebrahim Khan in 1904. Until the early 1930s, there were 15 theaters in Tehran Province and 11 in other provinces.
In present-day Tehran, most of the movie theatres are located downtown. The complexes of Kourosh Complex, Kourosh Cinema, Mellat Park, Mellat Gallery and Cineplex, Azadi Cinema Complex, Azadi Cinema, and Cinema Farhang are among the most popular cinema complexes in Tehran.
Several film festivals are held in Tehran, including Fajr International Film Festival, Fajr Film Festival, International Film Festival for Children and Youth, Children and Youth Film Festival, House of Cinema Festival, Mobile Film and Photo Festival, Nahal Festival, Roshd International Film Festival, Roshd Film Festival, Tehran Animation Festival, Tehran Short Film Festival, and Urban Film Festival.
 Football and volleyball are the city's most popular sports, while wrestling, basketball, and futsal are also major parts of the city's sporting culture.
List of ski areas and resorts in Iran, 12 ski resorts operate in Iran, the most famous being Tochal Complex, Tochal, Dizin, and Shemshak (ski resort), Shemshak, all within one to three hours from the city of Tehran.
Tochal's resort is the world's fifth-highest ski resort at over above sea level at its highest point. It is also the world's nearest ski resort to a capital city. The resort was opened in 1976, shortly before the 1979 Revolution. It is equipped with an gondola lift that covers a huge vertical distance. There are two parallel chair ski lifts in Tochal that reach high near Tochal's peak (at ), rising higher than the gondola's seventh station, which is higher than any of the European ski resorts. From the Tochal peak, there are views of the Alborz range, including the Mount Damavand, a dormant volcano.
Tehran is the site of the Azadi Stadium, national stadium of Azadi, the List of stadiums by capacity, biggest stadium by capacity in West Asia, where many of the top matches of Iran's Premier League are held. The stadium is a part of the Azadi Sport Complex, which was originally built to host the 1974 Asian Games, 7th Asian Games in September 1974. This was the first time the Asian Games were hosted in West Asia. Tehran played host to 3,010 athletes from 25 countries/NOCs, which was at the time the highest number of participants since the inception of the Games. That followed hosting the 1976 AFC Asian Cup, 6th AFC Asian Cup in June 1976, and then the first West Asian Games in November 1997. The success of the games led to the creation of the West Asian Games, West Asian Games Federation (WAGF), and the intention of hosting the games every two years. The city had also hosted the final of the 1968 AFC Asian Cup. Several FIVB Volleyball World League courses have also been hosted in Tehran.
Football and volleyball are the city's most popular sports, while wrestling, basketball, and futsal are also major parts of the city's sporting culture.
List of ski areas and resorts in Iran, 12 ski resorts operate in Iran, the most famous being Tochal Complex, Tochal, Dizin, and Shemshak (ski resort), Shemshak, all within one to three hours from the city of Tehran.
Tochal's resort is the world's fifth-highest ski resort at over above sea level at its highest point. It is also the world's nearest ski resort to a capital city. The resort was opened in 1976, shortly before the 1979 Revolution. It is equipped with an gondola lift that covers a huge vertical distance. There are two parallel chair ski lifts in Tochal that reach high near Tochal's peak (at ), rising higher than the gondola's seventh station, which is higher than any of the European ski resorts. From the Tochal peak, there are views of the Alborz range, including the Mount Damavand, a dormant volcano.
Tehran is the site of the Azadi Stadium, national stadium of Azadi, the List of stadiums by capacity, biggest stadium by capacity in West Asia, where many of the top matches of Iran's Premier League are held. The stadium is a part of the Azadi Sport Complex, which was originally built to host the 1974 Asian Games, 7th Asian Games in September 1974. This was the first time the Asian Games were hosted in West Asia. Tehran played host to 3,010 athletes from 25 countries/NOCs, which was at the time the highest number of participants since the inception of the Games. That followed hosting the 1976 AFC Asian Cup, 6th AFC Asian Cup in June 1976, and then the first West Asian Games in November 1997. The success of the games led to the creation of the West Asian Games, West Asian Games Federation (WAGF), and the intention of hosting the games every two years. The city had also hosted the final of the 1968 AFC Asian Cup. Several FIVB Volleyball World League courses have also been hosted in Tehran.
File:Darband, Teherán, Irán, 2016-09-18, DD 16.jpg, A restaurant in Darband, Tehran, Darband
File:Pizza Capri, Tehran.jpg, A pizzeria in Kamyab Street, Tehran
File:Seryna Jappanese Restaurant 瀬里奈 - panoramio.jpg, A Japanese restaurant in Tehran
File:2008 museum garden cafe Tehran 2789830499.jpg, Shemroon Cafe, in Tehran's Iranian Art Museum
File:139601061250177510379894 خیابان ۳۰ تیر.jpg, 30 Tir food street
 Many styles of graffiti are seen in Tehran. Some are political and revolutionary slogans painted by governmental organizations, and some are works of art by ordinary citizens, representing their views on both social and political issues. However, unsanctioned street art is forbidden in Iran, and such works are usually short-lived.
During the 2009 Iranian presidential election protests, many graffiti works were created by people supporting the Iranian Green Movement, Green Movement. They were removed from the walls by the paramilitary Basij forces.
In recent years, Tehran Municipality has been using graffiti in order to beautify the city. Several graffiti festivals have also taken place in Tehran, including the one organized by the Tehran University of Art in October 2014.
Many styles of graffiti are seen in Tehran. Some are political and revolutionary slogans painted by governmental organizations, and some are works of art by ordinary citizens, representing their views on both social and political issues. However, unsanctioned street art is forbidden in Iran, and such works are usually short-lived.
During the 2009 Iranian presidential election protests, many graffiti works were created by people supporting the Iranian Green Movement, Green Movement. They were removed from the walls by the paramilitary Basij forces.
In recent years, Tehran Municipality has been using graffiti in order to beautify the city. Several graffiti festivals have also taken place in Tehran, including the one organized by the Tehran University of Art in October 2014.
Google Map: Tehran
Tehran Municipality website
Tehran Geographic Information Center
Tehranimages.
A photographic project focusing on neglected pieces of architecture in downtown Tehran, Iran. * https://www.letsvisitpersia.com/must-see-in-tehran/ {{Authority control Tehran, Capitals in Asia Cities in Tehran Province Iranian provincial capitals Populated places along the Silk Road Populated places in Tehran County Articles containing video clips Populated places with period of establishment missing
capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. With a population of around 9 million in the city and around 16 million in the larger metropolitan area of Greater Tehran
Greater Tehran is the urban agglomeration around Tehran that covers the central part of the Tehran Province and eastern part of the Alborz Province, that covers the contiguous cities of Tehran, Ray, Shemirānāt, and other areas.
As of 2012 ...
, Tehran is the most populous city
The United Nations uses three definitions for what constitutes a city, as not all cities in all jurisdictions are classified using the same criteria. Cities may be defined as the city proper, cities proper, the extent of their urban area, or th ...
in Iran and Western Asia
Western Asia, West Asia, or Southwest Asia, is the westernmost subregion of the larger geographical region of Asia, as defined by some academics, UN bodies and other institutions. It is almost entirely a part of the Middle East, and includes Ana ...
, and has the second-largest metropolitan area in the Middle East, after Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo metro ...
. It is ranked 24th in the world by metropolitan area population.
In the Classical era, part of the territory of present-day Tehran was occupied by Rhages
Shahr-e Ray ( fa, شهر ری, ) or simply Ray (Shar e Ray; ) is the capital of Ray County in Tehran Province, Iran. Formerly a distinct city, it has now been absorbed into the metropolitan area of Greater Tehran as the 20th district of munici ...
, a prominent Median
In statistics and probability theory, the median is the value separating the higher half from the lower half of a data sample, a population, or a probability distribution. For a data set, it may be thought of as "the middle" value. The basic fe ...
city destroyed in the medieval Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Turkic
Turkic may refer to:
* anything related to the country of Turkey
* Turkic languages, a language family of at least thirty-five documented languages
** Turkic alphabets (disambiguation)
** Turkish language, the most widely spoken Turkic language
* ...
, and Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of ...
invasions. Modern Ray is an urban area absorbed into the metropolitan area of Greater Tehran.
Tehran was first chosen as the capital of Iran by Agha Mohammad Khan of the Qajar dynasty
The Qajar dynasty (; fa, دودمان قاجار ', az, Qacarlar ) was an IranianAbbas Amanat, ''The Pivot of the Universe: Nasir Al-Din Shah Qajar and the Iranian Monarchy, 1831–1896'', I. B. Tauris, pp 2–3 royal dynasty of Turkic peoples ...
in 1786, because of its proximity to Iran's territories in the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historically ...
, then separated from Iran in the Russo-Iranian Wars, to avoid the vying factions of the previously ruling Iranian dynasties. The capital has been moved several times throughout history, and Tehran is the 32nd national capital of Persia. Large-scale demolition and rebuilding began in the 1920s, and Tehran has been a destination for mass migrations from all over Iran since the 20th century.
Tehran is home to many historical locations, including the royal complexes of Golestan, Sa'dabad, and Niavaran, where the two last dynasties of the former Imperial State of Iran were seated. Tehran's most famous landmarks include the Azadi Tower, a memorial built under the reign of Mohammad Reza Shah
Mohammad Reza Pahlavi ( fa, محمدرضا پهلوی, ; 26 October 1919 – 27 July 1980), also known as Mohammad Reza Shah (), was the last ''Shah'' (King) of the Imperial State of Iran from 16 September 1941 until his overthrow in the Irani ...
of the Pahlavi dynasty
The Pahlavi dynasty ( fa, دودمان پهلوی) was the last Iranian royal dynasty, ruling for almost 54 years between 1925 and 1979. The dynasty was founded by Reza Shah Pahlavi, a non-aristocratic Mazanderani soldier in modern times, who ...
in 1971 to mark the 2,500th anniversary of the founding of the Imperial State of Iran, and the Milad Tower, the world's sixth-tallest self-supporting tower, completed in 2007, and the Tabiat Bridge, completed in 2014.
Most of the population are Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
, and roughly 99% of them understand and speak the Persian language
Persian (), also known by its endonym Farsi (, ', ), is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and ...
, but large populations of other ethnolinguistic groups live in Tehran and speak Persian, as majority of the minorities are Persianized and assimilated.
Tehran has an international airport (Imam Khomeini Airport
Imam Khomeini International Airport is the primary international airport of Tehran, the capital city of Iran, located southwest of Tehran, near the localities of Robat Karim and Eslamshahr and spread over an area of of land. Along with Mehraba ...
), a domestic airport (Mehrabad Airport
Mehrabad International Airport ( fa, فرودگاه بین المللی مهرآباد, ''Foroudgâh-e Beyn Almelali-ye Mehrâbâd'') , is an international airport serving Tehran, the capital city of Iran. Prior to the construction of the larger ...
), a central railway station, a rapid transit
Rapid transit or mass rapid transit (MRT), also known as heavy rail or metro, is a type of high-capacity public transport generally found in urban areas. A rapid transit system that primarily or traditionally runs below the surface may be c ...
system, Tehran Metro, a bus rapid transit
Bus rapid transit (BRT), also called a busway or transitway, is a bus-based public transport system designed to have much more capacity, reliability and other quality features than a conventional bus system. Typically, a BRT system includes ...
system, trolleybuses
A trolleybus (also known as trolley bus, trolley coach, trackless trolley, trackless tramin the 1910s and 1920sJoyce, J.; King, J. S.; and Newman, A. G. (1986). ''British Trolleybus Systems'', pp. 9, 12. London: Ian Allan Publishing. .or troll ...
, and a large network of highways.
Plans to relocate Iran's capital from Tehran to another area, due to air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different types ...
and earthquakes, have so far not yet received approval. A 2016 survey of 230 cities across the globe by consultant Mercer
Mercer may refer to:
Business
* Mercer (car), a defunct American automobile manufacturer (1909–1925)
* Mercer (consulting firm), a large human resources consulting firm headquartered in New York City
* Mercer (occupation), a merchant or trader ...
ranked Tehran 203rd for quality of life
Quality of life (QOL) is defined by the World Health Organization as "an individual's perception of their position in life in the context of the culture and value systems in which they live and in relation to their goals, expectations, standards ...
. According to the Global Destinations Cities Index in 2016, Tehran is among the top ten fastest growing destinations.
The City Council declared October 6 Tehran Day in 2016, celebrating the day in 1907 when the city officially became the capital of Iran.
Etymology
Various theories on the origin of the name Tehran have been put forward. Iranian linguist Ahmad Kasravi, in an article "Shemiran-Tehran", suggested that Tehran and Kehran mean "the warm place", and "Shemiran" means "the cool place". He listed cities with the same base and suffix and studied the components of the word in ancientIranian languages
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau.
The Iranian languages are grouped ...
, and came to the conclusion that Tehran and Kehran meant the same thing in different Iranian language families, as the constant "t" and "k" are close to each other in such languages. He also provided evidence that cities named "Shemiran" were colder than those named "Tehran" or "Kehran". He considered other theories not considering the ancient history of Iranian languages such as "Tirgan" theory and "Tahran" theory folk etymology
Folk etymology (also known as popular etymology, analogical reformation, reanalysis, morphological reanalysis or etymological reinterpretation) is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a more famili ...
.
Another theory is that "Tehran" derives from Tiran/Tirgan, "the abode of Tir", the Zoroastrian
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheistic on ...
equivalent of Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travellers, thieves, merchants, and orato ...
). The ancient Parthian Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
town of Tiran had a neighbour, Mehran ("abode of Mehr/Mithra", the Zoroastrian sun/justice angel). Both of these were mere villages in the suburbs of the great city of Ray/Rhages. Mehran still exists as a residential district in Greater Tehran, as well as Ray, which forms the southern suburbs of Tehran.
The official City of Tehran website says that "Tehran" comes from the Persian words "Tah" meaning "end", or "bottom", and "Ran" meaning " ountainslope"—literally, the bottom of the mountain (ته کوه). Given Tehran's position at the foot of the Alborz mountains, this seems plausible.
In English, it was formerly spelt "Teheran".
History
Archaeological remains from the ancient city of Ray suggest that settlement in Tehran dates back over 8,000 years.Classical era
Tehran is in the historical Media region of ( peo, 𐎶𐎠𐎭 ) in northwestern Iran. By the time of theMedian Empire
The Medes (Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, the ...
, part of present-day Tehran was a suburb of the prominent Median city of Rhages ( peo, 𐎼𐎥𐎠 ). In the Avesta's '' Videvdat'' (i, 15), Rhages is mentioned as the 12th sacred place created by Ohrmazd
Ahura Mazda (; ae, , translit=Ahura Mazdā; ), also known as Oromasdes, Ohrmazd, Ahuramazda, Hoormazd, Hormazd, Hormaz and Hurmuz, is the creator deity in Zoroastrianism. He is the first and most frequently invoked spirit in the ''Yasna''. ...
. In Old Persian
Old Persian is one of the two directly attested Old Iranian languages (the other being Avestan language, Avestan) and is the ancestor of Middle Persian (the language of Sasanian Empire). Like other Old Iranian languages, it was known to its native ...
inscriptions, Rhages appears as a province ( Bistun 2, 10–18). From Rhages, Darius I
Darius I ( peo, 𐎭𐎠𐎼𐎹𐎺𐎢𐏁 ; grc-gre, Δαρεῖος ; – 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his ...
sent reinforcements to his father Hystaspes Vishtaspa ( ae, wiktionary:𐬬𐬌𐬱𐬙𐬁𐬯𐬞𐬀, 𐬬𐬌𐬱𐬙𐬁𐬯𐬞𐬀 ; peo, wikt:𐎻𐏁𐎫𐎠𐎿𐎱, 𐎻𐏁𐎫𐎠𐎿𐎱, ), Hellenization, hellenized as Hystáspes (, ), may refer to:
* Vishtaspa (floruit, fl. ...
, who was putting down a rebellion in Parthia
Parthia ( peo, 𐎱𐎼𐎰𐎺 ''Parθava''; xpr, 𐭐𐭓𐭕𐭅 ''Parθaw''; pal, 𐭯𐭫𐭮𐭥𐭡𐭥 ''Pahlaw'') is a historical region located in northeastern Greater Iran. It was conquered and subjugated by the empire of the Med ...
(Bistun 3, 1–10). Some Middle Persian
Middle Persian or Pahlavi, also known by its endonym Pārsīk or Pārsīg () in its later form, is a Western Middle Iranian language which became the literary language of the Sasanian Empire. For some time after the Sasanian collapse, Middle Per ...
texts give Rhages as the birthplace of Zoroaster
Zoroaster,; fa, زرتشت, Zartosht, label=New Persian, Modern Persian; ku, زەردەشت, Zerdeşt also known as Zarathustra,, . Also known as Zarathushtra Spitama, or Ashu Zarathushtra is regarded as the spiritual founder of Zoroastria ...
, although modern historians generally place the birth of Zoroaster in Khorasan Province.
Mount Damavand, the highest peak of Iran, which is located near Tehran, is an important location in Ferdowsi
Abul-Qâsem Ferdowsi Tusi ( fa, ; 940 – 1019/1025 CE), also Firdawsi or Ferdowsi (), was a Persians, Persian poet and the author of ''Shahnameh'' ("Book of Kings"), which is one of the world's longest epic poetry, epic poems created by a sin ...
's '' Šāhnāme'',A. Tafazolli, "In Iranian Mythology" in Encyclopædia Iranica an Iranian epic poem based on the ancient legends of Iran. It appears in the epics as the homeland of the protoplast
Protoplast (), is a biological term coined by Hanstein in 1880 to refer to the entire cell, excluding the cell wall. Protoplasts can be generated by stripping the cell wall from plant, bacterial, or fungal cells by mechanical, chemical or enzy ...
Keyumars
Keyumars or Kiomars ( fa, کیومرث) was the name of the first king (shah) of the Pishdadian dynasty of Iran according to the ''Shahnameh''.
The name appears in Avestan in the form of ''𐬔𐬀𐬌𐬌𐬊 𐬨𐬆𐬭𐬆𐬙𐬀𐬥 Gai ...
, the birthplace of King Manuchehr, the place where King Fereydun bound the dragon fiend Aždahāk (Bivarasp), and the place where Arash
Arash the Archer ( fa, آرش کمانگیر ''Āraš-e Kamāngīr'') is a heroic archer-figure of Iranian mythology.
According to Iranian folklore, the boundary between Iran and Turan was set by an arrow launched by Arash, after he put his own ...
shot his arrow.
Medieval period
In 641, during the reign of theSasanian Empire
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the History of Iran, last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th cen ...
, Yazdgerd III issued his last appeal to the nation from Rhages, before fleeing to Khorasan. Rhages was dominated by the Parthian Parthian may be:
Historical
* A demonym "of Parthia", a region of north-eastern of Greater Iran
* Parthian Empire (247 BC – 224 AD)
* Parthian language, a now-extinct Middle Iranian language
* Parthian shot, an archery skill famously employed by ...
House of Mihran, and Siyavakhsh Siyavakhsh (also spelled Siyavash) was an Iranian aristocrat from the House of Mihran who was descended from Bahram Chobin, the famous ''spahbed'' of the Sasanian Empire.
Biography
Siyavakhsh was the son Mihran Bahram-i Chubin, whose father was ...
—the son of Mehran, the son of Bahram Chobin—who resisted the seventh-century Muslim invasion of Iran. Because of this resistance, when the Arabs captured Rhages, they ordered the town destroyed and rebuilt anew by traitor aristocrat Farrukhzad.
In the ninth century, Tehran was a well-known village, but less so than the city of Rhages, flourishing nearby. Rhages was described in detail by tenth-century Muslim geographers. Despite the interest that Arabian Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
displayed in Rhages, the number of Arabs in the city remained insignificant and the population mainly consisted of Iranians of all classes.
The Oghuz Turks
The Oghuz or Ghuzz Turks (Middle Turkic languages, Middle Turkic: ٱغُز, ''Oγuz'', ota, اوغوز, Oġuz) were a western Turkic people that spoke the Oghuz languages, Oghuz branch of the Turkic languages, Turkic language family. In th ...
invaded Rhages in 1035 and again in 1042, but the city was recovered under the Seljuks and the Khwarezmians. Medieval writer Najm od Din Razi declared the population of Rhages about 500,000 before the Mongol invasion
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire ( 1206- 1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastati ...
. In the 13th century, the Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
invaded Rhages, laid the city to ruins, and massacred many of its inhabitants. Others escaped to Tehran.
In July 1404, Castilian ambassador Ruy González de Clavijo
Ruy González de Clavijo (died 2 April 1412) was a Castilian traveler and writer. In 1403-05 Clavijo was the ambassador of Henry III of Castile to the court of Timur, founder and ruler of the Timurid Empire. A diary of the journey, perhaps based ...
visited Tehran on a journey to Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
, the capital of Turco-Mongol conqueror Timur
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617–19 February 1405), later Timūr Gurkānī ( chg, ''Temür Kür ...
, the ruler of Iran at the time. He described it in his diary as an unwalled region.
Early modern era
Italian travelerPietro della Valle
Pietro Della Valle ( la, Petrus a Valle; 2 April 1586 – 21 April 1652), also written Pietro della Valle, was an Italian composer, musicologist, and author who travelled throughout Asia during the Renaissance period. His travels took him to the ...
passed through Tehran overnight in 1618, and in his memoirs called the city ''Taheran''. English traveler Thomas Herbert entered Tehran in 1627, and mentioned it as ''Tyroan''. Herbert stated that the city had about 3,000 houses.
 In the early 18th century,
In the early 18th century, Karim Khan
Mohammad Karim Khan Zand ( fa, محمدکریم خان زند, Mohammad Karīm Khân-e Zand; ) was the founder of the Zand Dynasty, ruling from 1751 to 1779. He ruled all of Iran (Name of Iran, Persia) except for Khorasan Province, Khorasan. He ...
of the Zand dynasty ordered a palace and a government office built in Tehran, possibly to declare the city his capital; but he later moved his government to Shiraz
Shiraz (; fa, شیراز, Širâz ) is the List of largest cities of Iran, fifth-most-populous city of Iran and the capital of Fars province, Fars Province, which has been historically known as Pars (Sasanian province), Pars () and Persis. As o ...
. Eventually, Qajar king Agha Mohammad Khan chose Tehran as the capital of Iran in 1786.
Agha Mohammad Khan's choice of his capital was based on a similar concern for the control of both northern and southern Iran. He was aware of the loyalties of the inhabitants of former capitals Isfahan
Isfahan ( fa, اصفهان, Esfahân ), from its Achaemenid empire, ancient designation ''Aspadana'' and, later, ''Spahan'' in Sassanian Empire, middle Persian, rendered in English as ''Ispahan'', is a major city in the Greater Isfahan Regio ...
and Shiraz to the Safavid
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often conside ...
and Zand dynasties respectively, and was wary of the power of the local notables in these cities. Thus, he probably viewed Tehran's lack of a substantial urban structure as a blessing, because it minimized the chances of resistance to his rule by the notables and by the general public. Moreover, he had to remain within close reach of Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of th ...
and Iran's integral northern
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United States
* Northern Province, Sri Lanka
* Northern Range, a ra ...
and southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
Caucasian territories—at that time not yet irrevocably lost per the treaties of Golestan and Turkmenchay to the neighboring Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
—which would follow in the course of the 19th century.
 After 50 years of Qajar rule, the city still barely had more than 80,000 inhabitants. Up until the 1870s, Tehran consisted of a walled citadel, a roofed
After 50 years of Qajar rule, the city still barely had more than 80,000 inhabitants. Up until the 1870s, Tehran consisted of a walled citadel, a roofed bazaar
A bazaar () or souk (; also transliterated as souq) is a marketplace consisting of multiple small Market stall, stalls or shops, especially in the Middle East, the Balkans, North Africa and India. However, temporary open markets elsewhere, suc ...
, and the three main neighborhoods of Udlajan, Chale-Meydan, and Sangelaj, where the majority resided.
The first development plan of Tehran in 1855 emphasized traditional spatial structure. The second, under the supervision of Dar ol Fonun in 1878, included new city walls, in the form of a perfect octagon with an area of 19 square kilometers, mimicking the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
cities of Europe. Tehran was 19.79 square kilometers, and had expanded more than fourfold.
Late modern era
 Growing awareness of civil rights resulted in the
Growing awareness of civil rights resulted in the Constitutional Revolution
The Persian Constitutional Revolution ( fa, مشروطیت, Mashrūtiyyat, or ''Enghelāb-e Mashrūteh''), also known as the Constitutional Revolution of Iran, took place between 1905 and 1911. The revolution led to the establishment of a par ...
and the first constitution of Iran in 1906. On June 2, 1907, the parliament passed a law on local governance known as the ''Baladie'' (municipal law
Municipal law is the national, domestic, or internal law of a sovereign state and is defined in opposition to international law. Municipal law includes many levels of law: not only national law but also state, provincial, territorial, regional, ...
), providing a detailed outline of issues such as the role of councils within the city, the members' qualifications, the election process, and the requirements to be entitled to vote. The then-Qajar monarch Mohammad Ali Shah
Mohammad Ali Shah Qajar ( fa, محمدعلی شاه قاجار; 21 June 1872 – 5 April 1925, San Remo, Italy), Shah of Iran from 8 January 1907 to 16 July 1909. He was the sixth shah of the Qajar dynasty.
Biography
Mohammad Ali Shah Qajar ...
abolished the constitution and bombarded the parliament with the help of the Russian-controlled Cossack Brigade on June 23, 1908. That was followed by the capture of the city by the revolutionary forces of Ali-Qoli Khan (Sardar Asad II) and Mohammad Vali Khan (Sepahsalar e Tonekaboni) on July 13, 1909. As a result, the monarch was exiled and replaced with his son Ahmad
Ahmad ( ar, أحمد, ʾAḥmad) is an Arabic male given name common in most parts of the Muslim world. Other spellings of the name include Ahmed and Ahmet.
Etymology
The word derives from the root (ḥ-m-d), from the Arabic (), from the ve ...
, and the parliament was re-established.
After World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, the constituent assembly
A constituent assembly (also known as a constitutional convention, constitutional congress, or constitutional assembly) is a body assembled for the purpose of drafting or revising a constitution. Members of a constituent assembly may be elected b ...
elected Reza Shah of the Pahlavi dynasty
The Pahlavi dynasty ( fa, دودمان پهلوی) was the last Iranian royal dynasty, ruling for almost 54 years between 1925 and 1979. The dynasty was founded by Reza Shah Pahlavi, a non-aristocratic Mazanderani soldier in modern times, who ...
as the new monarch, who immediately suspended the Baladie law of 1907, replacing the decentralized and autonomous city councils with centralist approaches to governance
Governance is the process of interactions through the laws, social norm, norms, power (social and political), power or language of an organized society over a social system (family, tribe, formal organization, formal or informal organization, a ...
and planning.
From the 1920s to the 1930s, under the rule of Reza Shah, the city was essentially rebuilt from scratch. Several old buildings, including parts of the Golestan Palace, Tekye Dowlat, and Tupkhane Square, were replaced with modern buildings influenced by classical Iranian architecture, particularly the buildings of the National Bank, the police headquarters, the telegraph office, and the military academy.
Changes to the urban fabric began with the street-widening act of 1933, which served as a framework for changes in all other cities. The Grand Bazaar was divided in half and many historic buildings were demolished and replaced by wide straight avenues, and the traditional texture of the city was replaced with intersecting cruciform streets that created large roundabouts in major public spaces such as the bazaar.
As an attempt to create a network for easy transportation within the city, the old citadel and city walls were demolished in 1937, replaced by wide streets cutting through the urban fabric. The new city map of Tehran in 1937 was heavily influenced by modernist planning patterns of zoning and gridiron networks.
During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Soviet and British troops entered the city. In 1943, Tehran was the site of the Tehran Conference
The Tehran Conference (codenamed Eureka) was a strategy meeting of Joseph Stalin, Franklin Roosevelt, and Winston Churchill from 28 November to 1 December 1943, after the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran. It was held in the Soviet Union's embassy i ...
, attended by U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
, Soviet Premier Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
, and British Prime Minister Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
.
University of Tehran
The University of Tehran (Tehran University or UT, fa, دانشگاه تهران) is the most prominent university located in Tehran, Iran. Based on its historical, socio-cultural, and political pedigree, as well as its research and teaching pro ...
's Faculty of Law in 1939.
File:Bank Melli Sabze Meydan.JPG, National Bank of Iran, Sabze-Meydan, in the 1940s.
File:Teheran conference-1943.jpg, The Tehran Conference in 1943.
File:MajIes1956.JPG, The former Parliament Building in 1956.
File:Ferdowsi-Ave-1960.jpg, Ferdowsi Avenue in 1960.
File:Elizabeth (Keshavarz) Blvd-Tehran-1970s.jpg, Keshavarz Boulevard
Keshavarz Boulevard (Blvd.) ( fa, بلوار کشاورز ''Bolvār e Keshāvarz'') or simply ''Bolvār'' (the Boulevard) is a central Boulevard in Tehran, Iran. It is a 2.2 km long, East-West boulevard which connects Valiasr Street and Val ...
in 1970.
File:Karimkhan Vila 1977jpg.jpg, Karimkhan Street in 1977.
Mohammad Reza Shah
Mohammad Reza Pahlavi ( fa, محمدرضا پهلوی, ; 26 October 1919 – 27 July 1980), also known as Mohammad Reza Shah (), was the last ''Shah'' (King) of the Imperial State of Iran from 16 September 1941 until his overthrow in the Irani ...
named the '' White Revolution'', Tehran's chaotic growth was further accentuated.
Throughout the 1960s and 1970s, Tehran developed rapidly under Mohammad Reza Shah. Modern buildings altered the face of Tehran and ambitious projects were planned for the following decades. To resolve the problem of social exclusion
Social exclusion or social marginalisation is the social disadvantage and relegation to the fringe of society. It is a term that has been used widely in Europe and was first used in France in the late 20th century. It is used across discipline ...
, the first comprehensive plan was approved in 1968. The consortium of Iranian architect Abd-ol-Aziz Farmanfarmaian and the American firm of Victor Gruen Associates identified the main problems blighting the city as high-density suburbs, air and water pollution, inefficient infrastructure, unemployment, and rural-urban migration. Eventually, the whole plan was marginalized by the 1979 Revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynas ...
and the subsequent Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. It began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for almost eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations Security Council ...
.
 Tehran's most famous landmark, the Azadi Tower, was built by the order of the Shah in 1971. It was designed by Hossein Amanat, an architect whose design won a competition, combining elements of classical Sassanian architecture with post-classical Iranian architecture. Formerly known as the ''Shahyad Tower'', it was built to commemorate the 2,500th anniversary of the Imperial State of Iran.
During the
Tehran's most famous landmark, the Azadi Tower, was built by the order of the Shah in 1971. It was designed by Hossein Amanat, an architect whose design won a competition, combining elements of classical Sassanian architecture with post-classical Iranian architecture. Formerly known as the ''Shahyad Tower'', it was built to commemorate the 2,500th anniversary of the Imperial State of Iran.
During the Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. It began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for almost eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations Security Council ...
in 1980 to 1988, Tehran was repeatedly targeted by airstrikes and Scud
A Scud missile is one of a series of tactical ballistic missiles developed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. It was exported widely to both Second World, Second and Third World, Third World countries. The term comes from the NATO reporti ...
missile attacks.
The 435-meter-high Milad Tower, one of the proposed development projects of pre-revolutionary Iran, was completed in 2007, and has become a famous landmark of Tehran. Tabiat Bridge a 270-meter pedestrian overpass
A footbridge (also a pedestrian bridge, pedestrian overpass, or pedestrian overcrossing) is a bridge designed solely for pedestrians.''Oxford English Dictionary'' While the primary meaning for a bridge is a structure which links "two points at a ...
, designed by award-winning architect Leila Araghian
Leila Araghian ( fa, لیلا عراقیان; born 1983), is an Iranian architect. She has a Master degree of Architecture from the University of British Columbia, where she won the UBC Architecture Alumni Henry Elder Prize. She previously studied ...
, was completed in 2014.
Geography
Location and subdivisions
Tehran County
Tehran County ( fa, شهرستان تهران) is located in Tehran province, Iran. The capital of the county is Tehran. At the 2006 census, the county's population (including those portions of the county later split off to form Pardis County) ...
's Central District, while districts 1 and 20 are respectively located in the counties of Shemiranat and Ray
Ray may refer to:
Fish
* Ray (fish), any cartilaginous fish of the superorder Batoidea
* Ray (fish fin anatomy), a bony or horny spine on a fin
Science and mathematics
* Ray (geometry), half of a line proceeding from an initial point
* Ray (g ...
. Although administratively separate, the cities of Ray and Shemiran
Shemirān ( fa, شمیران, , also Romanized as Shemīrān or Šemirân), also known as Shemirānāt ( fa, شمیرانات ) is the capital of Shemiranat County, Tehran Province, Iran, but is actually located just north of the borders of Teh ...
are often considered part of Greater Tehran.
Elahieh
Elahieh (also spelt Elahiyeh; fa, الهیه) is an affluent and upper-class district in northern Tehran. The area is a residential and commercial locale and is filled with the homes and businesses of many politicians, diplomats, expatriates, ...
, an upper-class residential and commercial district in northern Tehran.
File:Ekhtiarieh, Tehran, Tehran, Iran - panoramio.jpg, Ekhtiarieh
Ekhtiyariyeh ( fa, اختیاریه; also Romanized as ''Ekhtiyāriyeh'' or ''Extiyāriye(h)'') is a neighborhood in the district of Shemiran in northern Tehran, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called ...
, an old residential area in northern Tehran.
File:Tehran from Qeytariyeh.jpg, Tehran from Gheytarieh.
File:Boukhares Ave., Tehran - panoramio.jpg, Bucharest Street in Abbas Abad, north-central Tehran.
File:Resalat Tunnel in Tehran.jpg, Resalat Tunnel in Tehran.
File:Sattarkhan, Tehran, Tehran Province, Iran - panoramio.jpg, Sattarkhan street in Tehran.
File:Sabet Pasal Palace-01.jpg, Jordan view.
File:Tehran - Kamranieh 2.jpg, Kamranieh alley
File:2008-11-26 Teheran Velenjak 02 (cropped).jpg, Velenjak northwestern Tehran.
File:Pasdaran Street Tehran.jpg, Pasdaran Street.
Zafaraniyeh
Zafaraniyeh (main street: Shahid Sarlashkar Fallahi) is an affluent neighbourhood in the north of Tehran, Iran. The name's origin lies in the fact that it was the residence of many saffron traders long ago, thus the name Zafaraniyeh (the Persia ...
, Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
, Elahiyeh
Elahieh (also spelt Elahiyeh; fa, الهیه) is an affluent and upper-class district in northern Tehran. The area is a residential and commercial locale and is filled with the homes and businesses of many politicians, diplomats, expatriates, ...
, Pasdaran
, meaning "Guards") can refer to:
* Pasdaran (district) in Tehran
* Informal name for the Army of the Guardians of the Islamic Revolution (Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps
The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC; fa, سپاه پاسدا� ...
, Kamranieh, Ajodanieh, Farmanieh, Darrous
Darrous is a neighborhood in Shemiran, northern Tehran, Iran. It is considered one of the most affluent areas in the city, as many modern and fashionable families reside there. Darrous is bounded by Pasdaran, Gholhak, Doulat, and Ekhtiyarieh.
...
, Niavaran, Jamaran
Jamaran( fa, جماران) is a neighbourhood located north of the city of Tehran in Iran.
Jamaran was once an independent village; it is now a part of the North Tehran region. It is best known for being the home of Ayatollah Khomeini. Khomeini' ...
, Aghdasieh
Aghdasieh ( fa, اقدسیه, also spelled Aghdassieh) is a neighborhood in the north of Tehran, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by ...
, Mahmoodieh
Mahmoudyeh, Mahmoodieh or Mahmoodiyeh is an affluent residential area in Tehran, located south of Zaferaniyeh, bordering Valiasr Avenue on the east side, Velenjak on the west, and Chamran expressway to the south. The area is in close proximity to ...
, Velenjak
Velenjak ( fa, ولنجک) is an affluent neighbourhood in the northwest of Tehran, Iran. Velenjak (Also Called Roof of Tehran) is located in the Shemiran area in the northernmost part of Tehran, on the slopes of the Alborz mountain range. It is k ...
, Qeytarieh, Ozgol and Ekhtiarieh
Ekhtiyariyeh ( fa, اختیاریه; also Romanized as ''Ekhtiyāriyeh'' or ''Extiyāriye(h)'') is a neighborhood in the district of Shemiran in northern Tehran, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called ...
.Buzbee, Sally"Tehran: Split Between Liberal, Hard-Line"
.
Associated Press
The Associated Press (AP) is an American non-profit news agency headquartered in New York City. Founded in 1846, it operates as a cooperative, unincorporated association. It produces news reports that are distributed to its members, U.S. newspa ...
via ''The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large nati ...
''. Thursday 4 October 2007.Hundley, Tom"Pro-reform Khatami appears victorious after 30 million Iranians cast votes"
''
Chicago Tribune
The ''Chicago Tribune'' is a daily newspaper based in Chicago, Illinois, United States, owned by Tribune Publishing. Founded in 1847, and formerly self-styled as the "World's Greatest Newspaper" (a slogan for which WGN radio and television ar ...
''. 8 June 2001. While the center of the city houses government ministries and headquarters, commercial centers are located further north.
Climate
 The northern area of Tehran has a
The northern area of Tehran has a Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
: ''Csa''), with a cold semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
(''BSk'') elsewhere, with hot dry summers and cool rainy winters. Tehran's climate is largely defined by its geographic location, with the towering Alborz mountains to its north and the country's central desert to the south. It can be generally described as mild in spring and autumn, hot and dry in summer, and cold and wet in winter.
As the city has a large area, with significant differences in elevation among various districts, the weather is often cooler in the hilly north than in the flat southern part of Tehran. For instance, the Valiasr Street runs from Tehran's railway station at elevation above sea level in the south of the city to Tajrish Square
Tajrish ( fa, تجريش, , also romanized as Tajrīš) is a neighbourhood of Tehran, capital of Iran. Administratively it is in Shemiranat County, Tehran Province. It used to be a village and later was absorbed into the city of Tehran.
The Tajri ...
at 1712.6 m (5612.3 ft) elevation above sea level in the north. However, the elevation can even rise up to at the end of Velenjak
Velenjak ( fa, ولنجک) is an affluent neighbourhood in the northwest of Tehran, Iran. Velenjak (Also Called Roof of Tehran) is located in the Shemiran area in the northernmost part of Tehran, on the slopes of the Alborz mountain range. It is k ...
in northern Tehran. The sparse texture, the existence of old gardens, orchards, green spaces along the highways and the lack of industrial activities in the north of the city have helped the air in the northern areas to be 2 to 3 degrees Celsius cooler than the southern areas of the city.
The main direction of the prevailing wind in Tehran is northwest to southeast.lake (in Persian). hamshahrionline.ir Other air currents that blow in the area of Tehran are: # Tochal breeze: With the rapid cooling of the Alborz mountain range at night, a local high-pressure center is formed on Mount Tochal, and this cold current flows down the mountain due to its weight and high pressure; Thus, a gentle breeze blows into the city from the north at night. # Southern and southeastern regional winds: these winds blow from the desert plains in the hot months of the year. # Western winds: These winds are among the planetary winds that affect the city of Tehran more or less throughout the year and can be called the prevailing wind. Air currents have a great effect on Tehran's weather. The prevailing wind blowing from the west causes the west of the city to always be exposed to fresh air; Although this wind brings smoke and pollution from the western industrial areas, its strong wind can take the polluted air out of the city of Tehran. In most years, winter provides half of Tehran's total annual rainfall. March is the rainiest month of the year and about one-fifth of the annual rainfall occurs in it. Summer is also the least rainy season and September is the driest month of the year in Tehran. The average annual rainfall of the city is sometimes very different in the north and south regions. There are between 205 and 213 days of clear to partly cloudy weather in Tehran.Climate and air pollution of Tehran (in Persian)
atlas.tehran.ir One of the most intense rains in Tehran happened on April 21, 1962 and this rain lasted for 10 hours. Meteorology also announced that the amount of rainfall on that one day in Tehran was equivalent to six years. Summer is hot and dry with little rain, but
relative humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depe ...
is generally low, making the heat tolerable. Average high temperatures are between and during summer months, and it can sometimes rise up to during heat waves. Average low temperatures in summer are between and , and it can occasionally drop to below in the mountainous north of the city at night.
Winter is cold and occasionally snowy, with an average of 12.3 snow days annually in central Tehran and more than 23.7 snow days annually in northern Tehran. During the winter months, average high temperatures are between and and average low temperatures are between and , and it can occasionally drop to below during cold waves
A cold wave (known in some regions as a cold snap, cold spell or Arctic Snap) is a weather phenomenon that is distinguished by a cooling of the air. Specifically, as used by the U.S. National Weather Service, a cold wave is a rapid fall in tem ...
.
Most of the annual precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
occurs from late autumn to mid-spring. March is the wettest month with an average precipitation of . The hottest month is July, with a mean minimum temperature of and a mean maximum temperature of , and the coldest is January, with a mean minimum temperature of and a mean maximum temperature of .
The highest recorded temperature was on 3 July 1958 and the lowest recorded temperature was on 8 January 1969.
In February 2005, heavy snow covered all parts of the city. Snow depth was recorded as in the southern part of the city and in the northern part of city. One newspaper reported that it had been the worst weather in 34 years. Ten thousand bulldozers and 13,000 municipal workers were deployed to keep the main roads open.
On January 5 and 6, 2008, a wave of heavy snow and low temperatures covered the city in a thick layer of snow and ice, forcing the Council of Ministers to officially declare a state of emergency
A state of emergency is a situation in which a government is empowered to be able to put through policies that it would normally not be permitted to do, for the safety and protection of its citizens. A government can declare such a state du ...
and close down the capital from January 6 through January 7.Heavy Snowfall in Tehran (in Persian)irna.com On February 3, 2014, Tehran received heavy snowfall, specifically in the northern parts of the city, with a depth of . In one week of successive snowfalls, roads were made impassable in some areas, with the temperature ranging from to . On June 3, 2014, a severe thunderstorm with powerful
microbursts
In meteorology, a downburst is a strong downward and outward gushing wind system that emanates from a point source above and blows Rotational symmetry, radially, that is, in straight lines in all directions from the area of impact at surface l ...
created a haboob
A haboob ( ar, هَبوب, lit=blasting/drifting, translit=habūb) is a type of intense dust storm carried on an atmospheric gravity current, also known as a weather front. Haboobs occur regularly in dry land area regions throughout the world.
...
, engulfing the city in sand and dust and causing five deaths, with more than 57 injured. This event also knocked down numerous trees and power lines. It struck between 5:00 and 6:00 p.m., dropping temperatures from to within an hour. The dramatic temperature drop was accompanied by wind gusts reaching nearly .
Environmental issues
 A plan to move the capital has been discussed many times in prior years, due mainly to the environmental issues of the region. Tehran is one of the world's most polluted cities and is also located near two major fault lines.
The city suffers from severe air pollution, 80% of it due to cars. The remaining 20% is due to industrial pollution. Other estimates suggest that motorcycles alone account for 30% of air and 50% of
A plan to move the capital has been discussed many times in prior years, due mainly to the environmental issues of the region. Tehran is one of the world's most polluted cities and is also located near two major fault lines.
The city suffers from severe air pollution, 80% of it due to cars. The remaining 20% is due to industrial pollution. Other estimates suggest that motorcycles alone account for 30% of air and 50% of noise pollution
Noise pollution, also known as environmental noise or sound pollution, is the propagation of noise with ranging impacts on the activity of human or animal life, most of them are harmful to a degree. The source of outdoor noise worldwide is main ...
in Tehran. Tehran is also considered one of the strongest sources of greenhouse gas emissions in the Middle East. Enhanced concentration of carbon dioxide over the city (that are likely originated from the anthropogenic urban sources in the city) is easily detectable from satellite observations throughout the year.
In 2010, the government announced that "for security and administrative reasons, the plan to move the capital from Tehran has been finalized." There are plans to relocate 163 state firms and several universities
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, t ...
from Tehran to avoid damages from a potential earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
.
The officials are engaged in a battle to reduce air pollution. It has, for instance, encouraged taxis and buses to convert from petrol engines to engines that run on compressed natural gas
Compressed natural gas (CNG) is a fuel gas mainly composed of methane (CH4), compressed to less than 1% of the volume it occupies at standard atmospheric pressure. It is stored and distributed in hard containers at a pressure of , usually in cy ...
. Furthermore, the government has set up a "Traffic Zone" covering the city centre during peak traffic hours. Entering and driving inside this zone is only allowed with a special permit.
There have also been plans to raise people's awareness of the hazards of pollution. One method that is being employed is the installation of Pollution Indicator Boards all around the city to monitor the level of particulate matter
Particulates – also known as atmospheric aerosol particles, atmospheric particulate matter, particulate matter (PM) or suspended particulate matter (SPM) – are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The ter ...
(PM10), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), ozone (O3), sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activ ...
(SO2), and carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
(CO).
Demographics

 The city of Tehran has a population of approximately 10 million in 2016. With its cosmopolitan atmosphere, Tehran is home to diverse ethnic and linguistic groups from all over the country. The present-day dominant language of Tehran is the Tehrani variety of the
The city of Tehran has a population of approximately 10 million in 2016. With its cosmopolitan atmosphere, Tehran is home to diverse ethnic and linguistic groups from all over the country. The present-day dominant language of Tehran is the Tehrani variety of the Persian language
Persian (), also known by its endonym Farsi (, ', ), is a Western Iranian language belonging to the Iranian branch of the Indo-Iranian subdivision of the Indo-European languages. Persian is a pluricentric language predominantly spoken and ...
, and the majority of people in Tehran identify themselves as Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
. However, before, the native language of the Tehran–Ray region was not Persian, which is linguistically Southwest Iranian and originates in Fars, but a now extinct Northwestern Iranian language.
Iranian Azeris
Iranian Azerbaijanis (; az, ایران آذربایجانلیلاری, italics=no ), also known as Iranian Azeris, Iranian Turks, Persian Turks or Persian Azerbaijanis, are Iranians of Azerbaijani ethnicity who may speak the Azerbaijani lang ...
form the second-largest ethnic group of the city, comprising about 10-15% of the total population, while ethnic Mazanderanis
The Mazanderani people ( mzn, مازرونیون or mzn, تبریون) or Tabari people ( mzn, تپورون, links=no) are an Iranian peopleAcademic American Encyclopedia By Grolier Incorporated, page 294 who are indigenous to the Caspian sea ...
are the third-largest, comprising about 5% of the total population. Tehran's other ethnic communities include Kurds ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Iran, northern Ir ...
, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
, Georgians
The Georgians, or Kartvelians (; ka, ქართველები, tr, ), are a nation and indigenous Caucasian ethnic group native to Georgia and the South Caucasus. Georgian diaspora communities are also present throughout Russia, Turkey, G ...
, Bakhtyaris, Talysh Talysh may refer to:
*Talysh people
*History of Talysh
*Talysh language
*Talysh Khanate, in existence from 1747 to 1828
*Talysh-Mughan Autonomous Republic, a self-declared autonomy, which existed briefly in the south of Azerbaijan in 1993
*Talysh M ...
, Baloch
Baloch, also spelled Baloch, Beluch and in other ways, may refer to:
* Baloch people, an ethnic group of Pakistan, Iran and Afghanistan
* Baluch, a small itinerant community of Afghanistan
* Balouch, Azad Kashmir, a town in Pakistan
* Baloch (s ...
, Assyrians
Assyrian may refer to:
* Assyrian people, the indigenous ethnic group of Mesopotamia.
* Assyria, a major Mesopotamian kingdom and empire.
** Early Assyrian Period
** Old Assyrian Period
** Middle Assyrian Empire
** Neo-Assyrian Empire
* Assyrian ...
, Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Wester ...
, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, and Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia in ...
.
According to a 2010 census conducted by the Sociology Department of the University of Tehran
The University of Tehran (Tehran University or UT, fa, دانشگاه تهران) is the most prominent university located in Tehran, Iran. Based on its historical, socio-cultural, and political pedigree, as well as its research and teaching pro ...
, in many districts of Tehran across various socio-economic classes in proportion to population sizes of each district and socio-economic class, 63% of the people were born in Tehran, 98% knew Persian, 75% identified themselves as ethnic Persian, and 13% had some degree of proficiency in a European language.
Tehran saw a drastic change in its ethnic-social composition in the early 1980s. After the political, social, and economic consequences of the 1979 Revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynas ...
and the years that followed, a number of Iranian citizens, mostly Tehranis, left Iran. The majority of Iranian emigrations have left for the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
, and Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
.
With the start of the Iran–Iraq War
The Iran–Iraq War was an armed conflict between Iran and Iraq that lasted from September 1980 to August 1988. It began with the Iraqi invasion of Iran and lasted for almost eight years, until the acceptance of United Nations Security Council ...
(1980–1988), the second wave of inhabitants fled the city, especially during the Iraqi air offensives on the capital. With most major powers backing Iraq at the time, economic isolation gave yet more reason for many inhabitants to leave the city (and the country). Having left all they had and have struggled to adapt to a new country and build a life, most of them never came back when the war was over. During the war, Tehran also received a great number of migrants from the west and the southwest of the country bordering Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
.
The unstable situation and the war in neighbouring Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
and Iraq prompted a rush of refugees into the country who arrived in their millions, with Tehran being a magnet for much seeking work, who subsequently helped the city to recover from war wounds, working for far less pay than local construction workers. Many of these refugees are being repatriated with the assistance of the UNHCR
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a United Nations agency mandated to aid and protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people, and to assist in their voluntary repatriation, local integrati ...
, but there are still sizable groups of Afghan and Iraqi refugees in Tehran who are reluctant to leave, being pessimistic about the situation in their own countries. Afghan refugees are mostly Dari
Dari (, , ), also known as Dari Persian (, ), is the variety of the Persian language spoken in Afghanistan. Dari is the term officially recognised and promoted since 1964 by the Afghan government for the Persian language,Lazard, G.Darī � ...
-speaking Tajik
Tajik, Tadjik, Tadzhik or Tajikistani may refer to:
* Someone or something related to Tajikistan
* Tajiks, an ethnic group in Tajikistan, Afghanistan and Uzbekistan
* Tajik language, the official language of Tajikistan
* Tajik (surname)
* Tajik cu ...
and Hazara
Hazara may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* The Hazaras, a Persian-speaking people of Afghanistan and Pakistan
* Aimaq Hazara, Aimaq's subtribe of Hazara origin
* Hazarawals, a Hindko-speaking people of the Hazara region of northern Pakistan
* Hazar ...
, speaking a variety of Persian, and Iraqi refugees are mainly Mesopotamian Arabic
Mesopotamian Arabic, ( ar, لهجة بلاد ما بين النهرين) also known as Iraqi Arabic ( ar, اللهجة العراقية), or Gilit Mesopotamian Arabic (as opposed to Qeltu Mesopotamian Arabic) is a continuum of mutually intelligib ...
-speakers who are often of Iranian and Persian ethnic heritage.
Religion
The majority of Tehranis are officiallyTwelver Shia
Twelver Shīʿīsm ( ar, ٱثْنَا عَشَرِيَّة; '), also known as Imāmīyyah ( ar, إِمَامِيَّة), is the largest branch of Shīʿa Islam, comprising about 85 percent of all Shīʿa Muslims. The term ''Twelver'' refers t ...
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraha ...
, which has also been the state religion since the 16th-century Safavid conversion. Other religious communities in the city include followers of the Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a disagr ...
and Mystic branches of Islam, various Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
denominations, Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
, Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion and one of the world's History of religion, oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian peoples, Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a Dualism in cosmology, du ...
, and the Baháʼí Faith
The Baháʼí Faith is a religion founded in the 19th century that teaches the Baháʼí Faith and the unity of religion, essential worth of all religions and Baháʼí Faith and the unity of humanity, the unity of all people. Established by ...
.
There are many religious centres scattered around the city, from old to newly built centres, including mosques
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, i ...
, churches, synagogues, and Zoroastrian fire temples. The city also has a very small third-generation Indian Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
community with a local gurdwara
A gurdwara (sometimes written as gurudwara) (Gurmukhi: ਗੁਰਦੁਆਰਾ ''guradu'ārā'', meaning "Door to the Guru") is a place of assembly and worship for Sikhs. Sikhs also refer to gurdwaras as ''Gurdwara Sahib''. People from all faiths ...
that was visited by the Indian Prime Minister in 2012.
Economy
 Tehran is the economic centre of Iran. About 30% of Iran's public-sector workforce and 45% of its large industrial firms are located in the city, and almost half of these workers are employed by the government. Most of the remainder of workers are factory workers, shopkeepers, laborers, and transport workers.
Few foreign companies operate in Tehran, due to the government's complex international relations. But prior to the
Tehran is the economic centre of Iran. About 30% of Iran's public-sector workforce and 45% of its large industrial firms are located in the city, and almost half of these workers are employed by the government. Most of the remainder of workers are factory workers, shopkeepers, laborers, and transport workers.
Few foreign companies operate in Tehran, due to the government's complex international relations. But prior to the 1979 Revolution
The Iranian Revolution ( fa, انقلاب ایران, Enqelâb-e Irân, ), also known as the Islamic Revolution ( fa, انقلاب اسلامی, Enqelâb-e Eslâmī), was a series of events that culminated in the overthrow of the Pahlavi dynas ...
, many foreign companies were active in Iran. Tehran's present-day modern industries include the manufacturing of automobiles, electronics and electrical equipment, weaponry, textiles, sugar, cement, and chemical products. It is also a leading centre for the sale of carpets and furniture. The oil refining companies of Pars Oil, Sepahan Oil Company, Speedy, and Behran Oil Company, Behran are based in Tehran.
Tehran relies heavily on private cars, buses, motorcycles, and taxis, and is one of the most car-dependent cities in the world. The Tehran Stock Exchange, which is a full member of the World Federation of Exchanges (WFE) and a founding member of the Federation of Euro-Asian Stock Exchanges, has been one of the world's best-performing stock exchanges in recent years.
Shopping
Tehran has a wide range of shopping centers, and is home to over 60 modern shopping malls. The city has a number of commercial districts, including those located at Valiasr Street, Valiasr, Davoodiyeh, Davudie, and Zafaraniyeh, Zaferanie. The largest oldbazaar
A bazaar () or souk (; also transliterated as souq) is a marketplace consisting of multiple small Market stall, stalls or shops, especially in the Middle East, the Balkans, North Africa and India. However, temporary open markets elsewhere, suc ...
s of Tehran are the Grand Bazaar and the Tajrish, Bazaar of Tajrish. Iran Mall is the largest mall in the world in area.
Most of the international branded stores and upper-class shops are in the northern and western parts of the city. Tehran's retail business is growing with several newly built malls and shopping centres.
Tourism
Tehran, as one of the main tourist destinations in Iran, has a wealth of cultural attractions. It is home to royal complexes of Golestan, Sa'dabad Complex, Saadabad and Niavaran, which were built under the reign of the country's last two monarchies. There are several historic, artistic, and scientific museums in Tehran, including the *National Museum of Iran, National Museum *Malik National Museum of Iran, Malek Museum *Cinema Museum at Ferdows Garden *Abgineh Museum of Tehran, Abgineh Museum *Museum of the Qasr Prison *The Carpet Museum of Iran, Carpet Museum *Reverse Glass Painting Museum (vitray art) *Safir Office Machines Museum Also the Tehran Museum of Contemporary Art, Museum of Contemporary Art, which hosts works of famous artists such as Van Gogh, Pablo Picasso, and Andy Warhol. The Iranian Crown Jewels, Iranian Imperial Crown Jewels, one of the largest jewel collections in the world, are also on display at Tehran's National Jewelry Museum. A number of cultural and trade exhibitions take place in Tehran, which are mainly operated by the country's Iran International Exhibitions Company, International Exhibitions Company. Tehran's annual Tehran International Book Fair, International Book Fair is known to the international publishing world as one of the most important publishing events in Asia.Infrastructure
Highways and streets
Following the Iranian Revolution, Islamic Revolution in 1979, the political system changed from constitutional monarchy to Islamic republic. Then the construction of political power in the country needed to change so that new spectrums of political power decision-making centers emerged in Iran. Motives, desires and actions of these new political power decision-making centers in Iran, made them rename streets and public places throughout the country, especially Tehran. For example Shahyad square changed to Azadi Square, Azadi square and Pahlavi street changed to Valiasr Street, Valiasr street. The metropolis of Tehran is equipped with a large network of highways and interchanges. A number of streets in Tehran are named after international figures, including:
* Henri Corbin Street, central Tehran
* List of places and things named after Simón Bolivar, Simon Bolivar Boulevard, northwestern Tehran
* Edward Granville Browne, Edward Browne Street, near the University of Tehran
* List of roads named after Mahatma Gandhi#Outside India, Gandhi Street, northern Tehran
* Mohammad Ali Jenah Expressway, western Tehran
* Muhammad Iqbal, Iqbal Lahori Street, eastern Tehran
* Patrice Lumumba Street, western Tehran
* Nelson Mandela Boulevard (Jordan Street) Tehran, Nelson Mandela Boulevard, northern Tehran
* Bobby Sands#Asia, Bobby Sands Street, western side of the Embassy of the United Kingdom, Tehran, British Embassy
A number of streets in Tehran are named after international figures, including:
* Henri Corbin Street, central Tehran
* List of places and things named after Simón Bolivar, Simon Bolivar Boulevard, northwestern Tehran
* Edward Granville Browne, Edward Browne Street, near the University of Tehran
* List of roads named after Mahatma Gandhi#Outside India, Gandhi Street, northern Tehran
* Mohammad Ali Jenah Expressway, western Tehran
* Muhammad Iqbal, Iqbal Lahori Street, eastern Tehran
* Patrice Lumumba Street, western Tehran
* Nelson Mandela Boulevard (Jordan Street) Tehran, Nelson Mandela Boulevard, northern Tehran
* Bobby Sands#Asia, Bobby Sands Street, western side of the Embassy of the United Kingdom, Tehran, British Embassy
Cars
 According to the head of Tehran Municipality's Environment and Sustainable Development Office, Tehran was designed to have a capacity of about 300,000 cars, but more than five million cars are on the roads. The automotive industry has recently developed, but international sanctions influence the production processes periodically.
According to local media, Tehran has more than 200,000 taxis plying the roads daily, with several types of taxi available in the city. Airport taxis have a higher cost per kilometer as opposed to regular green and yellow taxis in the city.
According to the head of Tehran Municipality's Environment and Sustainable Development Office, Tehran was designed to have a capacity of about 300,000 cars, but more than five million cars are on the roads. The automotive industry has recently developed, but international sanctions influence the production processes periodically.
According to local media, Tehran has more than 200,000 taxis plying the roads daily, with several types of taxi available in the city. Airport taxis have a higher cost per kilometer as opposed to regular green and yellow taxis in the city.
Buses
 Buses have served the city since the 1920s. Tehran's transport system includes conventional buses, trolleybuses, and
Buses have served the city since the 1920s. Tehran's transport system includes conventional buses, trolleybuses, and bus rapid transit
Bus rapid transit (BRT), also called a busway or transitway, is a bus-based public transport system designed to have much more capacity, reliability and other quality features than a conventional bus system. Typically, a BRT system includes ...
(BRT). The city's four major bus stations include the South Terminal, the East Terminal, the West Terminal, and the northcentral Beyhaghi Terminal.
The trolleybus system was opened in 1992, using a fleet of 65 articulated bus, articulated trolleybuses built by Czech Republic's Škoda Works, Škoda.Murray, Alan (2000). ''World Trolleybus Encyclopaedia'', pp. 57 and 99. Yateley, Hampshire, UK: Trolleybooks. . This was the first trolleybus system in Iran. In 2005, trolleybuses were operating on five routes, all starting at Imam Hossein Square.''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 265 (January–February 2006), pp. 16–17. National Trolleybus Association (UK). . Two routes running northeastwards operate almost entirely in a segregated Bus Rapid Transit, busway located in the middle of the wide carriageway along Damavand Street, stopping only at purpose-built stops located about every 500 metres along the routes, effectively making these routes trolleybus-BRT (but they are not called such). The other three trolley bus routes run south and operate in mixed traffic. Both route sections are served by limited-stop services and local (making all stops) services. A 3.2-kilometer extension from Shoosh Square to Rah Ahan Square was opened in March 2010.''Trolleybus Magazine'' No. 298 (July–August 2011), pp. 89–90. National Trolleybus Association (UK).
Tehran Bus Rapid Transit, Tehran's bus rapid transit (BRT) was officially inaugurated in 2008. It has 10 lines with some 215 stations in different areas of the city. , the BRT system had a network of , transporting 1.8 million passengers on a daily basis.
Bicycle
 Bdood is a dockless bike-sharing company in
Bdood is a dockless bike-sharing company in Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. Founded in 2017, it is available in the central and northwest regions of the capital city of Tehran. The company has plans to expand across the city in the future.
In the first phase, the application covers the flat areas of Tehran and they would be out of use in poor weather conditions.
Riders can use 29 parking lots for the bikes across Enqelab Street, Enqelab Avenue, Keshavarz Boulevard
Keshavarz Boulevard (Blvd.) ( fa, بلوار کشاورز ''Bolvār e Keshāvarz'') or simply ''Bolvār'' (the Boulevard) is a central Boulevard in Tehran, Iran. It is a 2.2 km long, East-West boulevard which connects Valiasr Street and Val ...
, Beheshti Street and Motahhari Avenue in which the bikes are available 24/7 for riders.
Railway and subway

 Tehran has a Tehran Railway Station, central railway station that connects services round the clock to various cities in the country, along with a Tehran–Europe train line also running.
The feasibility study and conceptual planning of the construction of Tehran's subway system were started in the 1970s. The first two of the eight projected metro lines were opened in 2001.
Tehran has a Tehran Railway Station, central railway station that connects services round the clock to various cities in the country, along with a Tehran–Europe train line also running.
The feasibility study and conceptual planning of the construction of Tehran's subway system were started in the 1970s. The first two of the eight projected metro lines were opened in 2001.
Airport
 Tehran is served by the international airports of Mehrabad International Airport, Mehrabad and Imam Khomeini International Airport, Imam Khomeini. Mehrabad Airport, an old airport in western Tehran that doubles as a military base, is mainly used for domestic and charter flights. Imam Khomeini Airport, located south of the city, handles the main international flights.
Tehran is served by the international airports of Mehrabad International Airport, Mehrabad and Imam Khomeini International Airport, Imam Khomeini. Mehrabad Airport, an old airport in western Tehran that doubles as a military base, is mainly used for domestic and charter flights. Imam Khomeini Airport, located south of the city, handles the main international flights.
Parks and green spaces
 There are over 2,100 parks within the metropolis of Tehran, with one of the oldest being Jamshidieh Park, Jamshidie Park, which was first established as a private garden for Qajar prince Jamshid Davallu, and was then dedicated to the last empress of Iran, Farah Pahlavi. The total green space within Tehran stretches over 12,600 hectares, covering over 20 percent of the city's area. The Parks and Green Spaces Organization of Tehran was established in 1960, and is responsible for the protection of the urban nature present in the city.
Tehran's Birds Garden is the largest bird park in Iran. There is also Eram Zoo, a zoo located on the Tehran–Karaj Expressway, housing over 290 species within an area of about five hectares.
In 2009, the Ab-o-Atash Park ("Water and Fire park") was founded. Its main features are an open water fountain area for cooling in the hot climate, fire towers, and an amphitheatre.
There are over 2,100 parks within the metropolis of Tehran, with one of the oldest being Jamshidieh Park, Jamshidie Park, which was first established as a private garden for Qajar prince Jamshid Davallu, and was then dedicated to the last empress of Iran, Farah Pahlavi. The total green space within Tehran stretches over 12,600 hectares, covering over 20 percent of the city's area. The Parks and Green Spaces Organization of Tehran was established in 1960, and is responsible for the protection of the urban nature present in the city.
Tehran's Birds Garden is the largest bird park in Iran. There is also Eram Zoo, a zoo located on the Tehran–Karaj Expressway, housing over 290 species within an area of about five hectares.
In 2009, the Ab-o-Atash Park ("Water and Fire park") was founded. Its main features are an open water fountain area for cooling in the hot climate, fire towers, and an amphitheatre.
Energy
Water
Greater Tehran
Greater Tehran is the urban agglomeration around Tehran that covers the central part of the Tehran Province and eastern part of the Alborz Province, that covers the contiguous cities of Tehran, Ray, Shemirānāt, and other areas.
As of 2012 ...
with its population of more than 13 million is supplied by surface water from the Lar Dam, Lar dam on the Lar River in the Northeast of the city, the Latyan Dam, Latyan dam on the Jajrood River in the North, the Karaj River in the Northwest, as well as by groundwater in the vicinity of the city.
Solar Energy
Solar panels have been installed in Tehran's Pardisan Park for green electricity production, said Masoumeh Ebtekar, head of the Department of Environment. According to the national energy roadmap, the government plans to promote green technology to increase the nominal capacity of power plants from 74 gigawatts to over 120 gigawatts by the end of 2025.Education
 Tehran is the largest and most important educational center in Iran. There are a total of nearly 50 major colleges and universities in Greater Tehran.
Since the establishment of Dar ol Fonun by the order of Amir Kabir in the mid-19th century, Tehran has amassed a large number of institutions of higher education. Some of these institutions have played crucial roles in the unfolding of Iranian political events. Samuel M. Jordan, whom Jordan Avenue in Tehran was named after, was one of the founding pioneers of the Alborz High School, American College of Tehran, which was one of the first modern high schools in the Middle East.
Among major educational institutions located in Tehran, Amirkabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic),
Tehran is the largest and most important educational center in Iran. There are a total of nearly 50 major colleges and universities in Greater Tehran.
Since the establishment of Dar ol Fonun by the order of Amir Kabir in the mid-19th century, Tehran has amassed a large number of institutions of higher education. Some of these institutions have played crucial roles in the unfolding of Iranian political events. Samuel M. Jordan, whom Jordan Avenue in Tehran was named after, was one of the founding pioneers of the Alborz High School, American College of Tehran, which was one of the first modern high schools in the Middle East.
Among major educational institutions located in Tehran, Amirkabir University of Technology (Tehran Polytechnic), University of Tehran
The University of Tehran (Tehran University or UT, fa, دانشگاه تهران) is the most prominent university located in Tehran, Iran. Based on its historical, socio-cultural, and political pedigree, as well as its research and teaching pro ...
, Sharif University of Technology, and Tehran University of Medical Sciences are the most prestigious. Other major universities located in Tehran include Tehran University of Art, Allameh Tabatabaei University, K. N. Toosi University of Technology, Shahid Beheshti University (Melli University), Kharazmi University, Iran University of Science and Technology, Iran University of Medical Sciences, Islamic Azad University, International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology, Iran's Polymer and Petrochemical Institute, Shahed University, and Tarbiat Modarres University. Sharif University of Technology, Amirkabir University of Technology, and Iran University of Science and Technology also located in Tehran are nationally well known for taking in the top undergraduate Engineering and Science students; and internationally recognized for training competent under graduate students. It has probably the highest percentage of graduates who seek higher education abroad.
Tehran is also home to Iran's largest military academy, and several religious schools and seminaries.
Culture
Architecture
The oldest surviving architectural monuments of Tehran are from the Qajar dynasty, Qajar and Pahlavi dynasty, Pahlavi eras. In Greater Tehran, monuments dating back to the Seljuk Empire, Seljuk era remain as well; notably the Tughrul Tower, Toqrol Tower in Ray. Rashkan Castle, dating back to the ancient Parthian Empire, of which some artifacts are housed at the National Museum of Iran, National Museum; and the Bahram fire temple, which remains since the Sasanian Empire, Sassanian Empire. Tehran only had a small population until the late 18th century but began to take a more considerable role in Iranian society after it was chosen as the capital city. Despite the regular occurrence of earthquakes during the Qajar period and after, some historic buildings remain from that era. Tehran is Iran's primate city, and is considered to have the most modernized infrastructure in the country. However, the gentrification of old neighbourhoods and the demolition of buildings of cultural significance have caused concerns.the National Garden, Tehran, National Garden File:Meydan Mashgh Tehran.jpg, Cossack House,
the National Garden, Tehran, National Garden
 Previously a low-rise city due to seismic activity in the region, modern high-rise developments in Tehran have been built in recent decades in order to service its growing population. There have been no major quakes in Tehran since 1830.
Tehran International Tower is the tallest skyscraper in Iran. It is 54-stories tall and located in the northern district of Yusef Abad.
The Azadi Tower, a memorial built under the reign of the
Previously a low-rise city due to seismic activity in the region, modern high-rise developments in Tehran have been built in recent decades in order to service its growing population. There have been no major quakes in Tehran since 1830.
Tehran International Tower is the tallest skyscraper in Iran. It is 54-stories tall and located in the northern district of Yusef Abad.
The Azadi Tower, a memorial built under the reign of the Pahlavi dynasty
The Pahlavi dynasty ( fa, دودمان پهلوی) was the last Iranian royal dynasty, ruling for almost 54 years between 1925 and 1979. The dynasty was founded by Reza Shah Pahlavi, a non-aristocratic Mazanderani soldier in modern times, who ...
, has long been the most famous symbol of Tehran. Originally constructed in commemoration of the 2,500-year celebration of the Persian Empire, 2,500th year of the foundation of the Imperial State of Iran, it combines elements of the architecture of the Achaemenid architecture, Achaemenid and Sassanid architecture, Sassanid eras with post-classical Iranian architecture. The Milad Tower, which is the List of towers, sixth tallest tower and the List of tallest buildings and structures#Tallest structures, freestanding structures, and buildings, 24th-tallest freestanding structure in the world, is the city's other famous landmark tower. Leila Araghian
Leila Araghian ( fa, لیلا عراقیان; born 1983), is an Iranian architect. She has a Master degree of Architecture from the University of British Columbia, where she won the UBC Architecture Alumni Henry Elder Prize. She previously studied ...
's Tabiat Bridge, the largest pedestrian overpass in Tehran, was completed in 2014 and is also considered a landmark.
Theater
 Under the reign of the Qajar dynasty, Qajars, Tehran was home to the royal theatre of Tekye Dowlat, located to the southeast of the Golestan Palace, in which traditional and religious performances were observed. It was eventually demolished and replaced with a bank building in 1947, following the reforms during the reign of Reza Shah.
Before the 1979 Revolution, the Iranian national stage had become the most famous performing scene for known international artists and troupes in the Middle East, with the Roudaki Hall of Tehran constructed to function as the national stage for opera and ballet. The hall was inaugurated in October 1967 and named after prominent Persian poet Rudaki. It is home to the Tehran Symphony Orchestra, the Tehran Opera Orchestra, and the Iranian National Ballet Company.
The City Theater of Tehran, one of Iran's biggest theatre complexes, which contains several performance halls, was opened in 1972. It was built at the initiative and presidency of empress Farah Pahlavi, and was designed by architect Ali Sardar Afkhami, constructed within five years.
The annual events of Fajr International Theater Festival, Fajr Theater Festival and Tehran International Puppet Theatre Festival, Tehran Puppet Theater Festival take place in Tehran.
Under the reign of the Qajar dynasty, Qajars, Tehran was home to the royal theatre of Tekye Dowlat, located to the southeast of the Golestan Palace, in which traditional and religious performances were observed. It was eventually demolished and replaced with a bank building in 1947, following the reforms during the reign of Reza Shah.
Before the 1979 Revolution, the Iranian national stage had become the most famous performing scene for known international artists and troupes in the Middle East, with the Roudaki Hall of Tehran constructed to function as the national stage for opera and ballet. The hall was inaugurated in October 1967 and named after prominent Persian poet Rudaki. It is home to the Tehran Symphony Orchestra, the Tehran Opera Orchestra, and the Iranian National Ballet Company.
The City Theater of Tehran, one of Iran's biggest theatre complexes, which contains several performance halls, was opened in 1972. It was built at the initiative and presidency of empress Farah Pahlavi, and was designed by architect Ali Sardar Afkhami, constructed within five years.
The annual events of Fajr International Theater Festival, Fajr Theater Festival and Tehran International Puppet Theatre Festival, Tehran Puppet Theater Festival take place in Tehran.
Cinema

 The first movie theater in Tehran was established by Mirza Ebrahim Khan Sahhafbashi, Mirza Ebrahim Khan in 1904. Until the early 1930s, there were 15 theaters in Tehran Province and 11 in other provinces.
In present-day Tehran, most of the movie theatres are located downtown. The complexes of Kourosh Complex, Kourosh Cinema, Mellat Park, Mellat Gallery and Cineplex, Azadi Cinema Complex, Azadi Cinema, and Cinema Farhang are among the most popular cinema complexes in Tehran.
Several film festivals are held in Tehran, including Fajr International Film Festival, Fajr Film Festival, International Film Festival for Children and Youth, Children and Youth Film Festival, House of Cinema Festival, Mobile Film and Photo Festival, Nahal Festival, Roshd International Film Festival, Roshd Film Festival, Tehran Animation Festival, Tehran Short Film Festival, and Urban Film Festival.
The first movie theater in Tehran was established by Mirza Ebrahim Khan Sahhafbashi, Mirza Ebrahim Khan in 1904. Until the early 1930s, there were 15 theaters in Tehran Province and 11 in other provinces.
In present-day Tehran, most of the movie theatres are located downtown. The complexes of Kourosh Complex, Kourosh Cinema, Mellat Park, Mellat Gallery and Cineplex, Azadi Cinema Complex, Azadi Cinema, and Cinema Farhang are among the most popular cinema complexes in Tehran.
Several film festivals are held in Tehran, including Fajr International Film Festival, Fajr Film Festival, International Film Festival for Children and Youth, Children and Youth Film Festival, House of Cinema Festival, Mobile Film and Photo Festival, Nahal Festival, Roshd International Film Festival, Roshd Film Festival, Tehran Animation Festival, Tehran Short Film Festival, and Urban Film Festival.
Concerts
There are a variety of concert halls in Tehran. An organization like the Roudaki Culture and Art Foundation has five different venues where more than 500 concerts take place this year. Vahdat Hall, Roudaki Hall, Ferdowsi Hall, Hafez Hall and Azadi Theater are the top five venues in Tehran, where classical, pop, traditional, rock or solo concerts take place.Sports
 Football and volleyball are the city's most popular sports, while wrestling, basketball, and futsal are also major parts of the city's sporting culture.
List of ski areas and resorts in Iran, 12 ski resorts operate in Iran, the most famous being Tochal Complex, Tochal, Dizin, and Shemshak (ski resort), Shemshak, all within one to three hours from the city of Tehran.
Tochal's resort is the world's fifth-highest ski resort at over above sea level at its highest point. It is also the world's nearest ski resort to a capital city. The resort was opened in 1976, shortly before the 1979 Revolution. It is equipped with an gondola lift that covers a huge vertical distance. There are two parallel chair ski lifts in Tochal that reach high near Tochal's peak (at ), rising higher than the gondola's seventh station, which is higher than any of the European ski resorts. From the Tochal peak, there are views of the Alborz range, including the Mount Damavand, a dormant volcano.
Tehran is the site of the Azadi Stadium, national stadium of Azadi, the List of stadiums by capacity, biggest stadium by capacity in West Asia, where many of the top matches of Iran's Premier League are held. The stadium is a part of the Azadi Sport Complex, which was originally built to host the 1974 Asian Games, 7th Asian Games in September 1974. This was the first time the Asian Games were hosted in West Asia. Tehran played host to 3,010 athletes from 25 countries/NOCs, which was at the time the highest number of participants since the inception of the Games. That followed hosting the 1976 AFC Asian Cup, 6th AFC Asian Cup in June 1976, and then the first West Asian Games in November 1997. The success of the games led to the creation of the West Asian Games, West Asian Games Federation (WAGF), and the intention of hosting the games every two years. The city had also hosted the final of the 1968 AFC Asian Cup. Several FIVB Volleyball World League courses have also been hosted in Tehran.
Football and volleyball are the city's most popular sports, while wrestling, basketball, and futsal are also major parts of the city's sporting culture.
List of ski areas and resorts in Iran, 12 ski resorts operate in Iran, the most famous being Tochal Complex, Tochal, Dizin, and Shemshak (ski resort), Shemshak, all within one to three hours from the city of Tehran.
Tochal's resort is the world's fifth-highest ski resort at over above sea level at its highest point. It is also the world's nearest ski resort to a capital city. The resort was opened in 1976, shortly before the 1979 Revolution. It is equipped with an gondola lift that covers a huge vertical distance. There are two parallel chair ski lifts in Tochal that reach high near Tochal's peak (at ), rising higher than the gondola's seventh station, which is higher than any of the European ski resorts. From the Tochal peak, there are views of the Alborz range, including the Mount Damavand, a dormant volcano.
Tehran is the site of the Azadi Stadium, national stadium of Azadi, the List of stadiums by capacity, biggest stadium by capacity in West Asia, where many of the top matches of Iran's Premier League are held. The stadium is a part of the Azadi Sport Complex, which was originally built to host the 1974 Asian Games, 7th Asian Games in September 1974. This was the first time the Asian Games were hosted in West Asia. Tehran played host to 3,010 athletes from 25 countries/NOCs, which was at the time the highest number of participants since the inception of the Games. That followed hosting the 1976 AFC Asian Cup, 6th AFC Asian Cup in June 1976, and then the first West Asian Games in November 1997. The success of the games led to the creation of the West Asian Games, West Asian Games Federation (WAGF), and the intention of hosting the games every two years. The city had also hosted the final of the 1968 AFC Asian Cup. Several FIVB Volleyball World League courses have also been hosted in Tehran.
Football clubs
The first football club of Tehran, ''Iran Club'', was founded in 1920 and dissolved within two years in 1923. Today, Tehran's oldest existing football club is Rah Ahan Yazdan F.C., Rah Ahan, which was founded in 1937. Persepolis F.C., Persepolis and Esteghlal F.C., Esteghlal, which are the city's biggest clubs and two of the biggest clubs in Asia, compete in the Tehran derby. Tehran is also home to the F.C. Ararat Tehran, a popular Iranian Armenians, Armenian football team based at the Ararat Stadium. The following table lists Tehran's six major football clubs. Smaller clubs based in Tehran are listed below.Food
There are many restaurants and cafes in Tehran, both modern and classic, serving both Iranian and cosmopolitan cuisine. Pizzerias, sandwich bars, and kebab shops make up the majority of food shops in Tehran.Graffiti
 Many styles of graffiti are seen in Tehran. Some are political and revolutionary slogans painted by governmental organizations, and some are works of art by ordinary citizens, representing their views on both social and political issues. However, unsanctioned street art is forbidden in Iran, and such works are usually short-lived.
During the 2009 Iranian presidential election protests, many graffiti works were created by people supporting the Iranian Green Movement, Green Movement. They were removed from the walls by the paramilitary Basij forces.
In recent years, Tehran Municipality has been using graffiti in order to beautify the city. Several graffiti festivals have also taken place in Tehran, including the one organized by the Tehran University of Art in October 2014.
Many styles of graffiti are seen in Tehran. Some are political and revolutionary slogans painted by governmental organizations, and some are works of art by ordinary citizens, representing their views on both social and political issues. However, unsanctioned street art is forbidden in Iran, and such works are usually short-lived.
During the 2009 Iranian presidential election protests, many graffiti works were created by people supporting the Iranian Green Movement, Green Movement. They were removed from the walls by the paramilitary Basij forces.
In recent years, Tehran Municipality has been using graffiti in order to beautify the city. Several graffiti festivals have also taken place in Tehran, including the one organized by the Tehran University of Art in October 2014.
Twin towns – sister cities
Tehran is Sister city, twinned with: * Ankara, Turkey *Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
, Iraq
* Beijing, China
* Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan
* Brasília, Brazil
* Budapest, Hungary
* Caracas, Venezuela
* Dushanbe, Tajikistan
* East Jerusalem, Palestine
* Havana, Cuba
* Kabul, Afghanistan
* Khartoum, Sudan
* London, England, United Kingdom
* Los Angeles, United States
* New York City, United States
* Manila, Philippines
* Minsk, Belarus
* Moscow, Russia
* Pretoria, South Africa
* Sanaa, Yemen
* Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
* Tbilisi, Georgia
Cooperation agreements
Tehran cooperates with: * Istanbul, Turkey * Paris, France * Seoul, South KoreaPanoramic views
See also
* Iran International Exhibitions Company * Islamic City Council of Tehran * List of people from Tehran * Tehran City Council (1968–1979)References
Bibliography
* Emerson, Charles. ''1913: In Search of the World Before the Great War'' (2013) compares Tehran to 20 major world cities; pp 309–24.External links
Google Map: Tehran
Tehran Municipality website
Tehran Geographic Information Center
Tehranimages.
A photographic project focusing on neglected pieces of architecture in downtown Tehran, Iran. * https://www.letsvisitpersia.com/must-see-in-tehran/ {{Authority control Tehran, Capitals in Asia Cities in Tehran Province Iranian provincial capitals Populated places along the Silk Road Populated places in Tehran County Articles containing video clips Populated places with period of establishment missing