Swollen Glands on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a
 Lymph nodes are kidney or oval shaped and range in size from 2 mm to 25 mm on their long axis, with an average of 15 mm.
Each lymph node is surrounded by a fibrous capsule, which extends inside a lymph node to form
Lymph nodes are kidney or oval shaped and range in size from 2 mm to 25 mm on their long axis, with an average of 15 mm.
Each lymph node is surrounded by a fibrous capsule, which extends inside a lymph node to form
 A lymph node is divided into compartments called ''nodules'' (or lobules), each consisting of a region of cortex with combined follicle B cells, a paracortex of T cells, and a part of the nodule in the medulla. The substance of a lymph node is divided into the outer ''cortex'' and the inner ''medulla''. The cortex of a lymph node is the outer portion of the node, underneath the capsule and the subcapsular sinus. It has an outer part and a deeper part known as the ''paracortex''. The outer cortex consists of groups of mainly inactivated B cells called follicles. When activated, these may develop into what is called a
A lymph node is divided into compartments called ''nodules'' (or lobules), each consisting of a region of cortex with combined follicle B cells, a paracortex of T cells, and a part of the nodule in the medulla. The substance of a lymph node is divided into the outer ''cortex'' and the inner ''medulla''. The cortex of a lymph node is the outer portion of the node, underneath the capsule and the subcapsular sinus. It has an outer part and a deeper part known as the ''paracortex''. The outer cortex consists of groups of mainly inactivated B cells called follicles. When activated, these may develop into what is called a

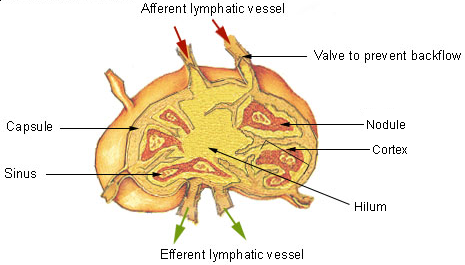 Lymph enters the convex side of a lymph node through multiple afferent lymphatic vessels, which form a network of lymphatic vessels () and from here flows into a space () underneath the capsule called the subcapsular sinus. From here, lymph flows into sinuses within the cortex. After passing through the cortex, lymph then collects in medullary sinuses. All of these sinuses drain into the efferent lymphatic vessels to exit the node at the hilum on the concave side.
These are channels within the node lined by endothelial cells along with fibroblastic reticular cells, allowing for the smooth flow of lymph. The endothelium of the subcapsular sinus is continuous with that of the afferent lymph vessel and also with that of the similar sinuses flanking the trabeculae and within the cortex. These vessels are smaller and don't allow the passage of macrophages so that they remain contained to function within a lymph node. In the course of the lymph, lymphocytes may be activated as part of the adaptive immune response.
There is usually only one efferent vessel though sometimes there may be two. Medullary sinuses contain
Lymph enters the convex side of a lymph node through multiple afferent lymphatic vessels, which form a network of lymphatic vessels () and from here flows into a space () underneath the capsule called the subcapsular sinus. From here, lymph flows into sinuses within the cortex. After passing through the cortex, lymph then collects in medullary sinuses. All of these sinuses drain into the efferent lymphatic vessels to exit the node at the hilum on the concave side.
These are channels within the node lined by endothelial cells along with fibroblastic reticular cells, allowing for the smooth flow of lymph. The endothelium of the subcapsular sinus is continuous with that of the afferent lymph vessel and also with that of the similar sinuses flanking the trabeculae and within the cortex. These vessels are smaller and don't allow the passage of macrophages so that they remain contained to function within a lymph node. In the course of the lymph, lymphocytes may be activated as part of the adaptive immune response.
There is usually only one efferent vessel though sometimes there may be two. Medullary sinuses contain
 Thin
Thin
 The primary function of lymph nodes is the filtering of lymph to identify and fight infection. In order to do this, lymph nodes contain lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, which includes B cells and T cells. These circulate through the bloodstream and enter and reside in lymph nodes. B cells produce antibodies. Each antibody has a single predetermined target, an
The primary function of lymph nodes is the filtering of lymph to identify and fight infection. In order to do this, lymph nodes contain lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, which includes B cells and T cells. These circulate through the bloodstream and enter and reside in lymph nodes. B cells produce antibodies. Each antibody has a single predetermined target, an
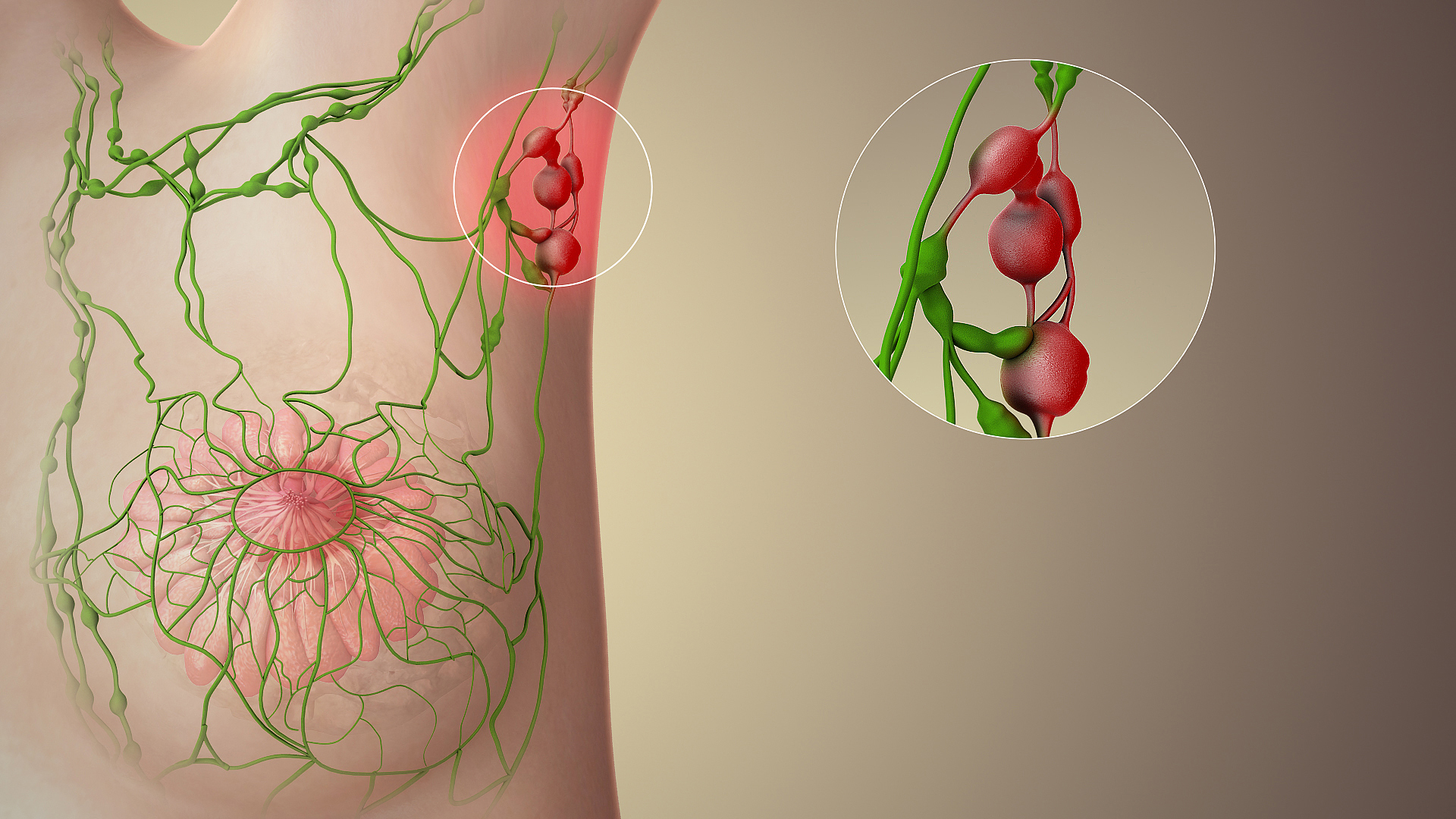 Lymph node enlargement or swelling is known as lymphadenopathy. Swelling may be due to many causes, including
Lymph node enlargement or swelling is known as lymphadenopathy. Swelling may be due to many causes, including
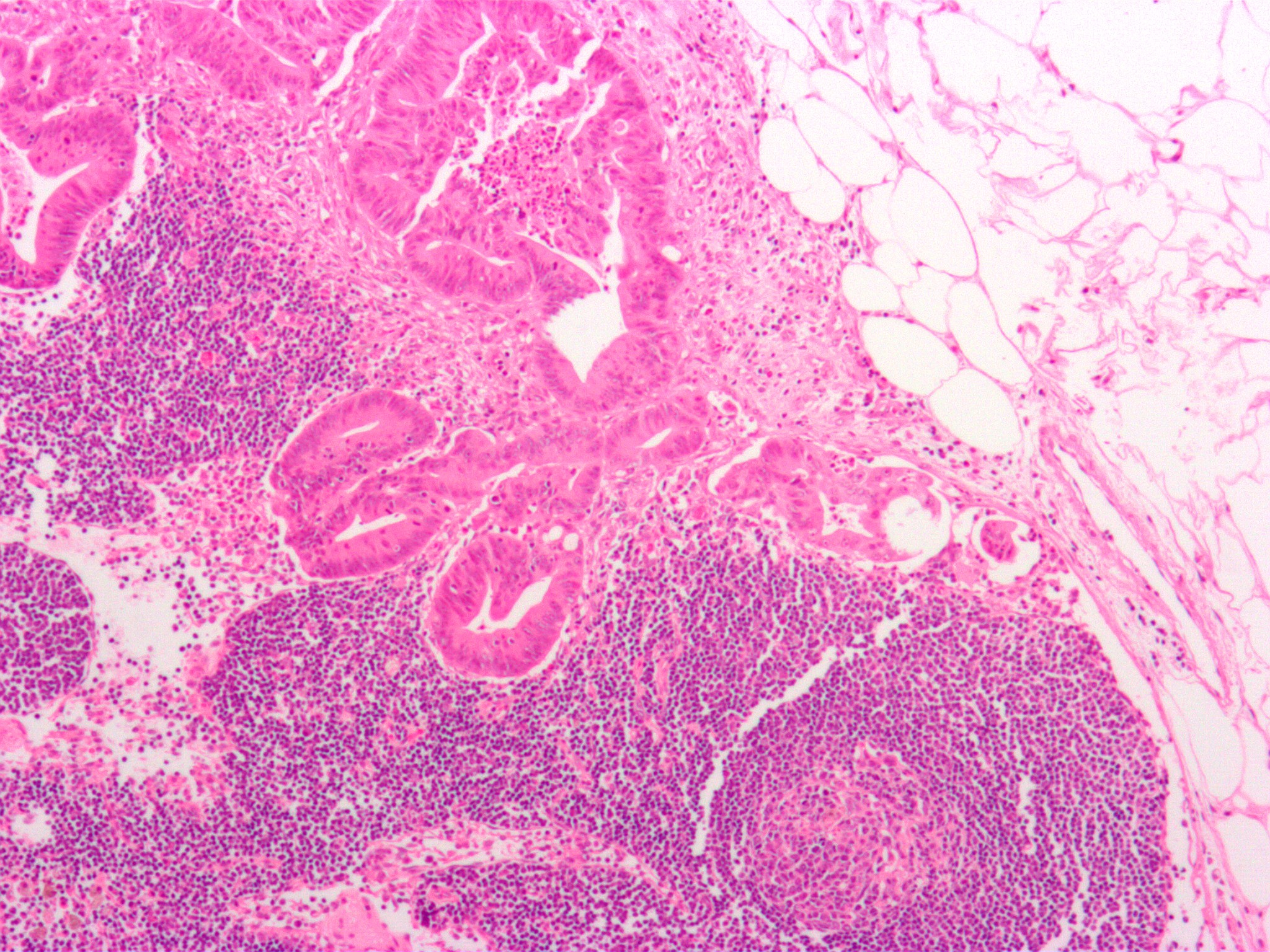 Lymph nodes can be affected by both primary
Lymph nodes can be affected by both primary
Lymph Nodes
Lymph Nodes Drainage
An overview of Normal Lymph Nodes and Swollen lymph nodes and their evaluation
{{Authority control * Immune system Lymphoid organ
kidney
The kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blo ...
-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph ve ...
s. They are major sites of lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic ad ...
s that include B and T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s. Lymph nodes are important for the proper functioning of the immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splint ...
, acting as filters for foreign particles including cancer cell
Cancer cells are cells that divide continually, forming solid tumors or flooding the blood with abnormal cells. Cell division is a normal process used by the body for growth and repair. A parent cell divides to form two daughter cells, and these d ...
s, but have no detoxification
Detoxification or detoxication (detox for short) is the physiological or medicinal removal of toxic substances from a living organism, including the human body, which is mainly carried out by the liver. Additionally, it can refer to the period of ...
function.
In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid ...
. A lymph node is enclosed in a fibrous capsule and is made up of an outer cortex and an inner medulla.
Lymph nodes become inflamed
Inflammation (from la, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecu ...
or enlarged in various diseases, which may range from trivial throat infections to life-threatening cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
s. The condition of lymph nodes is very important in cancer staging
Cancer staging is the process of determining the extent to which a cancer has developed by growing and spreading. Contemporary practice is to assign a number from I to IV to a cancer, with I being an isolated cancer and IV being a cancer that ha ...
, which decides the treatment to be used and determines the prognosis. Lymphadenopathy refers to glands that are enlarged or swollen. When inflamed or enlarged, lymph nodes can be firm or tender.
Structure
 Lymph nodes are kidney or oval shaped and range in size from 2 mm to 25 mm on their long axis, with an average of 15 mm.
Each lymph node is surrounded by a fibrous capsule, which extends inside a lymph node to form
Lymph nodes are kidney or oval shaped and range in size from 2 mm to 25 mm on their long axis, with an average of 15 mm.
Each lymph node is surrounded by a fibrous capsule, which extends inside a lymph node to form trabecula
A trabecula (plural trabeculae, from Latin for "small beam") is a small, often microscopic, tissue element in the form of a small beam, strut or rod that supports or anchors a framework of parts within a body or organ. A trabecula generally ha ...
e. The substance of a lymph node is divided into the outer ''cortex'' and the inner ''medulla''. These are rich with cells. The hilum is an indent on the concave surface of the lymph node where lymphatic vessels leave and blood vessels enter and leave.
Lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues ...
enters the convex side of a lymph node through multiple afferent lymphatic vessels
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph ves ...
and from there flows into a series of sinuses. After entering the lymph node from afferent lymphatic vessels, lymph flows into a space underneath the capsule called the subcapsular sinus, then into cortical sinuses. After passing through the cortex, lymph then collects in medullary sinuses. All of these sinuses drain into the efferent lymph vessels to exit the node at the hilum on the concave side.
Location
Lymph nodes are present throughout the body, are more concentrated near and within the trunk, and are divided into groups. There are about 450 lymph nodes in the adult. Some lymph nodes can be felt when enlarged (and occasionally when not), such as theaxillary lymph nodes
The axillary lymph nodes or armpit lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the human armpit. Between 20 and 49 in number, they drain lymph vessels from the lateral quadrants of the breast, the superficial lymph vessels from thin walls of the chest and th ...
under the arm, the cervical lymph nodes
Cervical lymph nodes are lymph nodes found in the neck. Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the neck. Cervical lymph nodes are subject to a number of different pathological conditions including tumours, infection and inflammati ...
of the head and neck and the inguinal lymph nodes
Inguinal lymph nodes are lymph nodes in the human groin. Located in the femoral triangle of the inguinal region, they are grouped into superficial and deep lymph nodes. The superficial have three divisions: the superomedial, superolateral, and i ...
near the groin crease. Most lymph nodes lie within the trunk adjacent to other major structures in the body - such as the paraaortic lymph nodes
The periaortic lymph nodes (also known as lumbar) are a group of lymph nodes that lie in front of the lumbar vertebrae near the aorta. These lymph nodes receive drainage from the gastrointestinal tract and the abdominal organs.
The periaortic lym ...
and the tracheobronchial lymph nodes
The tracheobronchial lymph nodes are lymph nodes that are located around the division of trachea and main bronchi.
Structure
These lymph nodes form four main groups including paratracheal, tracheobronchial, bronchopulmonary and pulmonary nod ...
. The lymphatic drainage patterns are different from person to person and even asymmetrical on each side of the same body.
There are no lymph nodes in the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
, which is separated from the body by the blood–brain barrier. Lymph from the meningeal lymphatic vessels
The meningeal lymphatic vessels (or meningeal lymphatics) are a network of conventional lymphatic vessels located parallel to the dural venous sinuses and middle meningeal arteries of the mammalian central nervous system (CNS). As a part of the ly ...
in the CNS drains to the deep cervical lymph node
The deep cervical lymph nodes are a group of cervical lymph nodes found near the internal jugular vein in the neck.
Structure
The deep cervical lymph nodes can be divided into upper and lower groups, or superior and inferior groups.
Alternati ...
s.
Size
Subdivisions
 A lymph node is divided into compartments called ''nodules'' (or lobules), each consisting of a region of cortex with combined follicle B cells, a paracortex of T cells, and a part of the nodule in the medulla. The substance of a lymph node is divided into the outer ''cortex'' and the inner ''medulla''. The cortex of a lymph node is the outer portion of the node, underneath the capsule and the subcapsular sinus. It has an outer part and a deeper part known as the ''paracortex''. The outer cortex consists of groups of mainly inactivated B cells called follicles. When activated, these may develop into what is called a
A lymph node is divided into compartments called ''nodules'' (or lobules), each consisting of a region of cortex with combined follicle B cells, a paracortex of T cells, and a part of the nodule in the medulla. The substance of a lymph node is divided into the outer ''cortex'' and the inner ''medulla''. The cortex of a lymph node is the outer portion of the node, underneath the capsule and the subcapsular sinus. It has an outer part and a deeper part known as the ''paracortex''. The outer cortex consists of groups of mainly inactivated B cells called follicles. When activated, these may develop into what is called a germinal centre
Germinal centers or germinal centres (GCs) are transiently formed structures within B cell zone (follicles) in secondary lymphoid organs – lymph nodes, ileal Peyer's patches, and the spleen – where mature B cells are activated, prolifera ...
. The deeper paracortex mainly consists of the T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s. Here the T-cells mainly interact with dendritic cells, and the reticular network is dense.
The medulla contains large blood vessels, sinuses and medullary cords that contain antibody-secreting plasma cells. There are fewer cells in the medulla.
The medullary cords are cords of lymphatic tissue, and include plasma cells, macrophages, and B cells.
Cells
In the lymphatic system a lymph node is asecondary lymphoid organ
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid ...
. Lymph nodes contain lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic ad ...
s, a type of white blood cell, and are primarily made up of B cells and T cells
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell re ...
. B cells are mainly found in the outer cortex where they are clustered together as follicular B cell Within the immune system, Follicular B cells (FO B cells) are a type of B cell that reside in primary and secondary lymphoid follicles (containing germinal centers) of secondary and tertiary lymphoid organs, including spleen and lymph nodes. Antibo ...
s in lymphoid follicles, and T cells and dendritic cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. The ...
are mainly found in the ''paracortex''.
There are fewer cells in the medulla than the cortex. The medulla contains plasma cells, as well as macrophages which are present within the medullary sinuses.
As part of the reticular network, there are follicular dendritic cells
Follicular dendritic cells (FDC) are cells of the immune system found in primary and secondary lymph follicles (lymph nodes) of the B cell areas of the lymphoid tissue. Unlike dendritic cells (DC), FDCs are not derived from the bone-marrow hema ...
in the B cell follicle and fibroblastic reticular cells in the T cell cortex. The reticular network provides structural support and a surface for adhesion of the dendritic cells, macrophages and lymphocytes. It also allows exchange of material with blood through the high endothelial venules High endothelial venules (HEV) are specialized post-capillary venous swellings characterized by plump endothelial cells as opposed to the usual thinner endothelial cells found in regular venules. HEVs enable lymphocytes circulating in the blood to ...
and provides the growth and regulatory factors necessary for activation and maturation of immune cells.
Lymph flow

 Lymph enters the convex side of a lymph node through multiple afferent lymphatic vessels, which form a network of lymphatic vessels () and from here flows into a space () underneath the capsule called the subcapsular sinus. From here, lymph flows into sinuses within the cortex. After passing through the cortex, lymph then collects in medullary sinuses. All of these sinuses drain into the efferent lymphatic vessels to exit the node at the hilum on the concave side.
These are channels within the node lined by endothelial cells along with fibroblastic reticular cells, allowing for the smooth flow of lymph. The endothelium of the subcapsular sinus is continuous with that of the afferent lymph vessel and also with that of the similar sinuses flanking the trabeculae and within the cortex. These vessels are smaller and don't allow the passage of macrophages so that they remain contained to function within a lymph node. In the course of the lymph, lymphocytes may be activated as part of the adaptive immune response.
There is usually only one efferent vessel though sometimes there may be two. Medullary sinuses contain
Lymph enters the convex side of a lymph node through multiple afferent lymphatic vessels, which form a network of lymphatic vessels () and from here flows into a space () underneath the capsule called the subcapsular sinus. From here, lymph flows into sinuses within the cortex. After passing through the cortex, lymph then collects in medullary sinuses. All of these sinuses drain into the efferent lymphatic vessels to exit the node at the hilum on the concave side.
These are channels within the node lined by endothelial cells along with fibroblastic reticular cells, allowing for the smooth flow of lymph. The endothelium of the subcapsular sinus is continuous with that of the afferent lymph vessel and also with that of the similar sinuses flanking the trabeculae and within the cortex. These vessels are smaller and don't allow the passage of macrophages so that they remain contained to function within a lymph node. In the course of the lymph, lymphocytes may be activated as part of the adaptive immune response.
There is usually only one efferent vessel though sometimes there may be two. Medullary sinuses contain histiocyte
A histiocyte is a vertebrate cell that is part of the mononuclear phagocyte system (also known as the reticuloendothelial system or lymphoreticular system). The mononuclear phagocytic system is part of the organism's immune system. The histiocyt ...
s (immobile macrophages) and reticular cells.
A lymph node contains lymphoid tissue, i.e., a meshwork or fibers called ' with white blood cells enmeshed in it. The regions where there are few cells within the meshwork are known as '. It is lined by reticular cells, fibroblasts and fixed macrophages.
Capsule
 Thin
Thin reticular fiber
Reticular fibers, reticular fibres or reticulin is a type of fiber in connective tissue composed of type III collagen secreted by reticular cells. Reticular fibers crosslink to form a fine meshwork (reticulin). This network acts as a supportin ...
s (reticulin) of reticular connective tissue Reticular connective tissue is a type of connective tissue with a network of reticular fibers, made of type III collagen ('' reticulum'' = net or network). Reticular fibers are not unique to reticular connective tissue, but only in this type they ...
form a supporting meshwork inside the node.
The lymph node capsule is composed of dense irregular connective tissue
Dense irregular connective tissue has fibers that are not arranged in parallel bundles as in dense regular connective tissue.
Dense irregular connective tissue consists of mostly collagen fibers. It has less ground substance than loose connec ...
with some plain collagenous fibers
Collagen () is the main structural protein in the extracellular matrix found in the body's various connective tissues. As the main component of connective tissue, it is the most abundant protein in mammals, making up from 25% to 35% of the whole ...
, and a number of membranous processes or trabeculae extend from its internal surface. The trabeculae pass inward, radiating toward the center of the node, for about one-third or one-fourth of the space between the circumference and the center of the node. In some animals they are sufficiently well-marked to divide the peripheral or cortical portion of the node into a number of compartments (nodules), but in humans this arrangement is not obvious. The larger trabeculae springing from the capsule break up into finer bands, and these interlace to form a mesh-work in the central or medullary portion of the node. These trabecular spaces formed by the interlacing trabeculae contain the proper lymph node substance or lymphoid tissue. The node pulp does not, however, completely fill the spaces, but leaves between its outer margin and the enclosing trabeculae a channel or space of uniform width throughout. This is termed the subcapsular sinus (lymph path or lymph sinus). Running across it are a number of finer trabeculae of reticular fibers, mostly covered by ramifying cells.
Function
In the lymphatic system a lymph node is a secondary lymphoid organ.antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune respons ...
, that it can bind to. These circulate throughout the bloodstream and if they find this target, the antibodies bind to it and stimulate an immune response. Each B cell produces different antibodies, and this process is driven in lymph nodes. B cells enter the bloodstream as "naive" cells produced in bone marrow. After entering a lymph node, they then enter a lymphoid follicle, where they multiply and divide, each producing a different antibody. If a cell is stimulated, it will go on to produce more antibodies (a plasma cell) or act as a memory cell to help the body fight future infection. If a cell is not stimulated, it will undergo apoptosis and die.
Antigens are molecules found on bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
l cell walls, chemical substances secreted from bacteria, or sometimes even molecules present in body tissue itself. These are taken up by cells throughout the body called antigen-presenting cells, such as dendritic cells. These antigen presenting cells enter the lymph system and then lymph nodes. They present the antigen to T cells and, if there is a T cell with the appropriate T cell receptor, it will be activated.
B cells acquire antigen directly from the afferent lymph. If a B cell binds its cognate antigen it will be activated. Some B cells will immediately develop into antibody secreting plasma cells, and secrete IgM. Other B cells will internalize the antigen and present it to follicular helper T cells on the B and T cell zone interface. If a cognate FTh cell is found it will upregulate CD40L and promote somatic hypermutation and isotype class switching of the B cell, increasing its antigen binding affinity and changing its effector function. Proliferation of cells within a lymph node will make the node expand.
Lymph is present throughout the body, and circulates through lymphatic vessels
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessel ...
. These drain into and from lymph nodesafferent vessels drain into nodes, and efferent vessels from nodes. When lymph fluid enters a node, it drains into the node just beneath the capsule in a space called the subcapsular sinus. The subcapsular sinus drains into trabecular sinuses and finally into medullary sinuses. The sinus space is criss-crossed by the pseudopod
A pseudopod or pseudopodium (plural: pseudopods or pseudopodia) is a temporary arm-like projection of a eukaryotic cell membrane that is emerged in the direction of movement. Filled with cytoplasm, pseudopodia primarily consist of actin filament ...
s of macrophages, which act to trap foreign particles and filter the lymph. The medullary sinuses converge at the hilum and lymph then leaves the lymph node via the ''efferent lymphatic vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vess ...
'' towards either a more central lymph node or ultimately for drainage into a central venous subclavian blood vessel.
* The B cells migrate to the nodular cortex and medulla.
* The T cells migrate to the deep cortex. This is a region of a lymph node called the paracortex that immediately surrounds the medulla. Because both naive T cells and dendritic cells express CCR7, they are drawn into the paracortex by the same chemotactic factors, increasing the chance of T cell activation. Both B and T lymphocytes enter lymph nodes from circulating blood through specialized high endothelial venules High endothelial venules (HEV) are specialized post-capillary venous swellings characterized by plump endothelial cells as opposed to the usual thinner endothelial cells found in regular venules. HEVs enable lymphocytes circulating in the blood to ...
found in the paracortex.
Clinical significance
Swelling
 Lymph node enlargement or swelling is known as lymphadenopathy. Swelling may be due to many causes, including
Lymph node enlargement or swelling is known as lymphadenopathy. Swelling may be due to many causes, including infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable dis ...
s, tumor
A neoplasm () is a type of abnormal and excessive growth of tissue. The process that occurs to form or produce a neoplasm is called neoplasia. The growth of a neoplasm is uncoordinated with that of the normal surrounding tissue, and persists ...
s, autoimmune disease, drug reactions, diseases such as amyloidosis and sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (also known as ''Besnier-Boeck-Schaumann disease'') is a disease involving abnormal collections of inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly a ...
, or because of lymphoma
Lymphoma is a group of blood and lymph tumors that develop from lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). In current usage the name usually refers to just the cancerous versions rather than all such tumours. Signs and symptoms may include enla ...
or leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
. Depending on the cause, swelling may be painful, particularly if the expansion is rapid and due to an infection or inflammation. Lymph node enlargement may be localised to an area, which might suggest a local source of infection or a tumour in that area that has spread to the lymph node. It may also be generalised, which might suggest infection, connective tissue or autoimmune disease, or a malignancy of blood cells such as a lymphoma or leukaemia. Rarely, depending on location, lymph node enlargement may cause problems such as difficulty breathing, or compression of a blood vessel (for example, superior vena cava obstruction).
Enlarged lymph nodes might be felt as part of a medical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patie ...
, or found on medical imaging. Features of the medical history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is information gained by a physician by asking specific questions, either to the patient or to other peo ...
may point to the cause, such as the speed of onset of swelling, pain, and other constitutional symptoms
Signs and symptoms are the observed or detectable signs, and experienced symptoms of an illness, injury, or condition. A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature than normal, raised or lowered blood pressure or an abnormality showin ...
such as fevers or weight loss. For example, a tumour of the breast may result in swelling of the lymph nodes under the arms and weight loss and night sweat
Night sweats, also referred to as nocturnal hyperhidrosis (Hyperhidrosis - a medical term for excessive sweating + nocturnal - night), is the repeated occurrence of excessive sweating during sleep. The person may or may not also perspire exces ...
s may suggest a malignancy such as lymphoma.
In addition to a medical exam
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient ...
by a medical practitioner, medical test
A medical test is a medical procedure performed to detect, diagnose, or monitor diseases, disease processes, susceptibility, or to determine a course of treatment. Medical tests such as, physical and visual exams, diagnostic imaging, genetic ...
s may include blood tests and scans may be needed to further examine the cause. A biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
of a lymph node may also be needed.
Cancer
 Lymph nodes can be affected by both primary
Lymph nodes can be affected by both primary cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
s of lymph tissue, and secondary cancers affecting other parts of the body. Primary cancers of lymph tissue are called lymphomas and include Hodgkin lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma, in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the patient's lymph nodes. The condition w ...
and non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), also known as non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphomas except Hodgkin lymphomas. Symptoms include enlarged lymph nodes, fever, night sweats, weight loss, and tirednes ...
. Cancer of lymph nodes can cause a wide range of symptoms from painless long-term slowly growing swelling to sudden, rapid enlargement over days or weeks, with symptoms depending on the grade
Grade most commonly refers to:
* Grade (education), a measurement of a student's performance
* Grade, the number of the year a student has reached in a given educational stage
* Grade (slope), the steepness of a slope
Grade or grading may also ref ...
of the tumour. Most lymphomas are tumours of B-cells. Lymphoma is managed by haematologists and oncologists
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ó ...
.
Local cancer in many parts of the body can cause lymph nodes to enlarge because of tumorous cells that have metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then ...
ed into the node. Lymph node involvement is often a key part in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer, acting as " sentinels" of local disease, incorporated into TNM staging
The TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors (TNM) is a globally recognised standard for classifying the extent of spread of cancer. It is a classification system of the anatomical extent of tumor cancers. It has gained wide international acceptance ...
and other cancer staging
Cancer staging is the process of determining the extent to which a cancer has developed by growing and spreading. Contemporary practice is to assign a number from I to IV to a cancer, with I being an isolated cancer and IV being a cancer that ha ...
systems. As part of the investigations or workup for cancer, lymph nodes may be imaged or even surgically removed. If removed, the lymph node will be stained and examined under a microscope by a pathologist
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in t ...
to determine if there is evidence of cells that appear cancerous (i.e. have metastasized into the node). The staging of the cancer, and therefore the treatment approach and prognosis, is predicated on the presence of node metastases.
Lymphedema
Lymphedema
Lymphedema, also known as lymphoedema and lymphatic edema, is a condition of localized swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system. The lymphatic system functions as a critical portion of the body's immune system and returns interstitial fl ...
is the condition of swelling ( edema) of tissue relating to insufficient clearance by the lymphatic system. It can be congenital as a result usually of undeveloped or absent lymph nodes, and is known as primary lymphedema. Lymphedema most commonly arises in the arms or legs, but can also occur in the chest wall, genitals, neck, and abdomen. Secondary lymphedema usually results from the removal of lymph nodes during breast cancer surgery
The breast is one of two prominences located on the upper ventral region of a primate's torso. Both females and males develop breasts from the same embryological tissues.
In females, it serves as the mammary gland, which produces and secre ...
or from other damaging treatments such as radiation. It can also be caused by some parasitic infections. Affected tissues are at a great risk of infection. Management of lymphedema may include advice to lose weight, exercise, keep the affected limb moist, and compress the affected area. Sometimes surgical management is also considered.
Similar lymphoid organs
Thespleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
and the tonsil
The tonsils are a set of lymphoid organs facing into the aerodigestive tract, which is known as Waldeyer's tonsillar ring and consists of the adenoid tonsil, two tubal tonsils, two palatine tonsils, and the lingual tonsils. These organs play ...
s are the larger secondary lymphoid organs that serve somewhat similar functions to lymph nodes, though the spleen filters blood cells rather than lymph. The tonsils are sometimes erroneously referred to as lymph nodes. Although the tonsils and lymph nodes do share certain characteristics, there are also many important differences between them, such as their location, structure and size. Furthermore, the tonsils filter tissue fluid whereas lymph nodes filter lymph.
The appendix contains lymphoid tissue and is therefore believed to play a role not only in the digestive system, but also in the immune system.
See also
*Peyer's patch
Peyer's patches (or aggregated lymphoid nodules) are organized lymphoid follicles, named after the 17th-century Swiss anatomist Johann Conrad Peyer.
* Reprinted as:
* Peyer referred to Peyer's patches as ''plexus'' or ''agmina glandularum'' (c ...
* Lymph sacs
References
Bibliography
* *External links
*Lymph Nodes
Lymph Nodes Drainage
An overview of Normal Lymph Nodes and Swollen lymph nodes and their evaluation
{{Authority control * Immune system Lymphoid organ