Star Model Z45 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A star is an
 Historically, stars have been important to
Historically, stars have been important to
Medieval Islamic astronomers gave Arabic names to many stars that are still used today and they invented numerous With the exception of rare events such as supernovae and
With the exception of rare events such as supernovae and
 Stars condense from regions of
Stars condense from regions of
 The time a star spends on the main sequence depends primarily on the amount of fuel it has and the rate at which it fuses it. The Sun is expected to live 10 billion (1010) years. Massive stars consume their fuel very rapidly and are short-lived. Low mass stars consume their fuel very slowly. Stars less massive than 0.25 , called
The time a star spends on the main sequence depends primarily on the amount of fuel it has and the rate at which it fuses it. The Sun is expected to live 10 billion (1010) years. Massive stars consume their fuel very rapidly and are short-lived. Low mass stars consume their fuel very slowly. Stars less massive than 0.25 , called
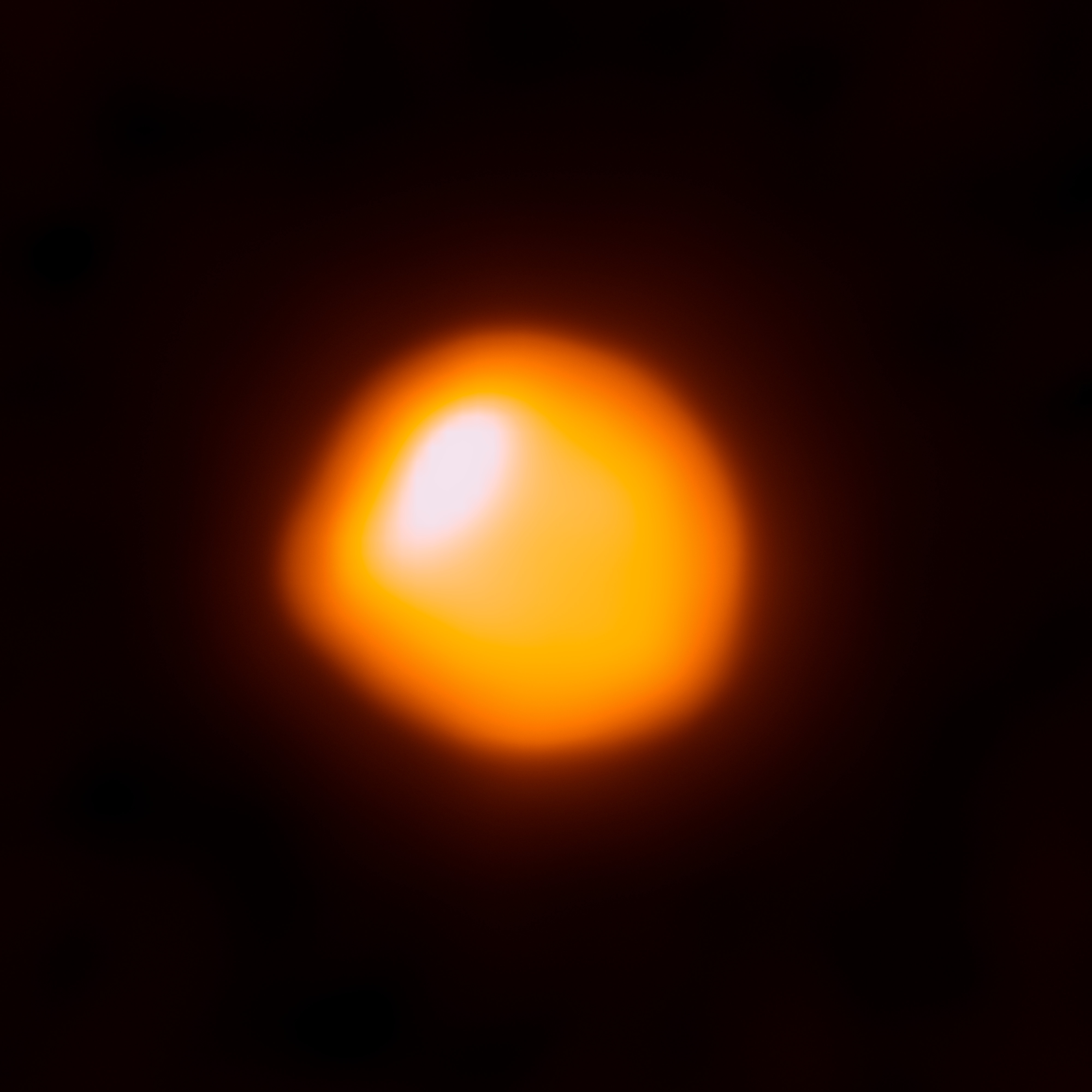 As stars of at least 0.4 exhaust the supply of hydrogen at their core, they start to fuse hydrogen in a shell surrounding the helium core. The outer layers of the star expand and cool greatly as they transition into a
As stars of at least 0.4 exhaust the supply of hydrogen at their core, they start to fuse hydrogen in a shell surrounding the helium core. The outer layers of the star expand and cool greatly as they transition into a
 During their helium-burning phase, a star of more than 9 solar masses expands to form first a
During their helium-burning phase, a star of more than 9 solar masses expands to form first a
 In massive stars, fusion continues until the iron core has grown so large (more than 1.4 ) that it can no longer support its own mass. This core will suddenly collapse as its electrons are driven into its protons, forming neutrons,
In massive stars, fusion continues until the iron core has grown so large (more than 1.4 ) that it can no longer support its own mass. This core will suddenly collapse as its electrons are driven into its protons, forming neutrons,
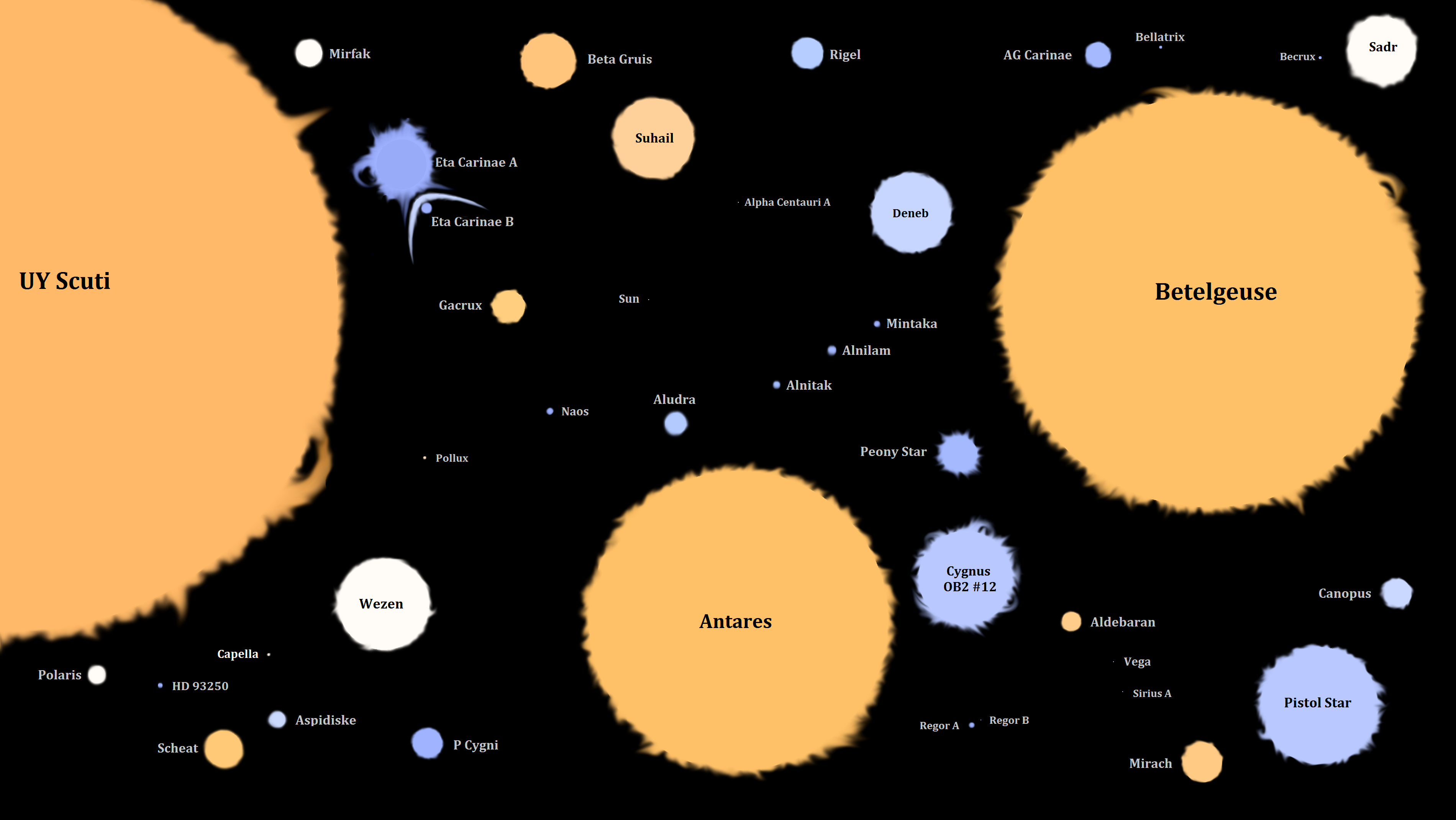
 Stars are not spread uniformly across the universe, but are normally grouped into galaxies along with interstellar gas and dust. A typical large galaxy like the Milky Way contains hundreds of billions of stars. There are more than 2 trillion (1012) galaxies, though most are less than 10% the mass of the Milky Way. Overall, there are likely to be between and stars (more stars than all the grains of sand on planet
Stars are not spread uniformly across the universe, but are normally grouped into galaxies along with interstellar gas and dust. A typical large galaxy like the Milky Way contains hundreds of billions of stars. There are more than 2 trillion (1012) galaxies, though most are less than 10% the mass of the Milky Way. Overall, there are likely to be between and stars (more stars than all the grains of sand on planet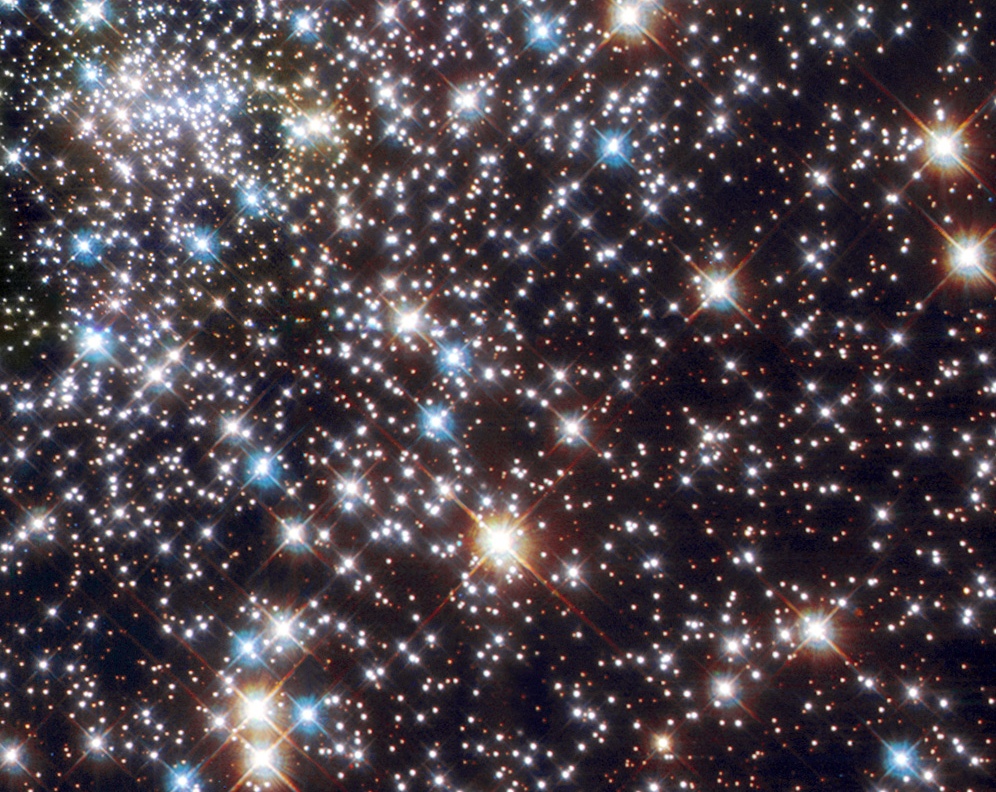  The nearest star to the Earth, apart from the Sun, is
The nearest star to the Earth, apart from the Sun, is
 Due to their great distance from the Earth, all stars except the Sun appear to the unaided eye as shining points in the night sky that
Due to their great distance from the Earth, all stars except the Sun appear to the unaided eye as shining points in the night sky that
 The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding galaxy. The components of motion of a star consist of the
The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding galaxy. The components of motion of a star consist of the
 The
The
 The first stars to form after the Big Bang may have been larger, up to 300 , due
to the complete absence of elements heavier than
The first stars to form after the Big Bang may have been larger, up to 300 , due
to the complete absence of elements heavier than
 Variable stars have periodic or random changes in luminosity because of intrinsic or extrinsic properties. Of the intrinsically variable stars, the primary types can be subdivided into three principal groups.
During their stellar evolution, some stars pass through phases where they can become pulsating variables. Pulsating variable stars vary in radius and luminosity over time, expanding and contracting with periods ranging from minutes to years, depending on the size of the star. This category includes Cepheid and Cepheid-like stars, and long-period variables such as
Variable stars have periodic or random changes in luminosity because of intrinsic or extrinsic properties. Of the intrinsically variable stars, the primary types can be subdivided into three principal groups.
During their stellar evolution, some stars pass through phases where they can become pulsating variables. Pulsating variable stars vary in radius and luminosity over time, expanding and contracting with periods ranging from minutes to years, depending on the size of the star. This category includes Cepheid and Cepheid-like stars, and long-period variables such as
 The photosphere is that portion of a star that is visible to an observer. This is the layer at which the plasma of the star becomes transparent to photons of light. From here, the energy generated at the core becomes free to propagate into space. It is within the photosphere that
The photosphere is that portion of a star that is visible to an observer. This is the layer at which the plasma of the star becomes transparent to photons of light. From here, the energy generated at the core becomes free to propagate into space. It is within the photosphere that
 :34He → 12C + γ + 7.2 MeV
In massive stars, heavier elements can be burned in a contracting core through the
:34He → 12C + γ + 7.2 MeV
In massive stars, heavier elements can be burned in a contracting core through the
astronomical object
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often us ...
comprising a luminous spheroid
A spheroid, also known as an ellipsoid of revolution or rotational ellipsoid, is a quadric surface obtained by rotating an ellipse about one of its principal axes; in other words, an ellipsoid with two equal semi-diameters. A spheroid has ...
of plasma held together by its gravity
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the str ...
. The nearest star to Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
is the Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared rad ...
. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night
Night (also described as night time, unconventionally spelled as "nite") is the period of ambient darkness from sunset
Sunset, also known as sundown, is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon due to Earth's rotation. As view ...
, but their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light. The most prominent stars have been categorised into constellations and asterisms, and many of the brightest stars have proper name
A proper noun is a noun that identifies a single entity and is used to refer to that entity (''Africa'', ''Jupiter'', ''Sarah'', ''Microsoft)'' as distinguished from a common noun, which is a noun that refers to a class of entities (''continent, ...
s. Astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies – in either o ...
s have assembled star catalogue
A star catalogue is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years ...
s that identify the known stars and provide standardized stellar designation In astronomy, stars have a variety of different stellar designations and names, including catalogue designations, current and historical proper names, and foreign language names.
Only a tiny minority of known stars have proper names; all others h ...
s. The observable universe
The observable universe is a ball-shaped region of the universe comprising all matter that can be observed from Earth or its space-based telescopes and exploratory probes at the present time, because the electromagnetic radiation from these obj ...
contains an estimated to stars. Only about 4,000 of these stars are visible to the naked eye, all within the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked ey ...
galaxy
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar Sys ...
.
A star's life begins with the gravitational collapse
Gravitational collapse is the contraction of an astronomical object due to the influence of its own gravity, which tends to draw matter inward toward the center of gravity. Gravitational collapse is a fundamental mechanism for structure formatio ...
of a gaseous nebula
A nebula ('cloud' or 'fog' in Latin; pl. nebulae, nebulæ or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regio ...
of material composed primarily of hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
, along with helium and trace amounts of heavier elements. Its total mass is the main factor determining its evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
and eventual fate. A star shines for most of its active life due to the thermonuclear fusion
Thermonuclear fusion is the process of atomic nuclei combining or “fusing” using high temperatures to drive them close enough together for this to become possible. There are two forms of thermonuclear fusion: ''uncontrolled'', in which the re ...
of hydrogen into helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
in its core. This process releases energy that traverses the star's interior and radiates
Radiata or Radiates is a historical taxonomic rank that was used to classify animals with radially symmetric body plans. The term Radiata is no longer accepted, as it united several different groupings of animals that do not form a monophyleti ...
into outer space
Outer space, commonly shortened to space, is the expanse that exists beyond Earth and its atmosphere and between celestial bodies. Outer space is not completely empty—it is a near-perfect vacuum containing a low density of particles, pred ...
. At the end of a star's lifetime, its core becomes a stellar remnant
In astronomy, the term compact star (or compact object) refers collectively to white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes. It would grow to include exotic stars if such hypothetical, dense bodies are confirmed to exist. All compact object ...
: a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
, a neutron star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. w ...
, or—if it is sufficiently massive—a black hole
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can defo ...
.
Stellar nucleosynthesis
Stellar nucleosynthesis is the creation (nucleosynthesis) of chemical elements by nuclear fusion reactions within stars. Stellar nucleosynthesis has occurred since the original creation of hydrogen, helium and lithium during the Big Bang. As a ...
in stars or their remnants creates almost all naturally occurring chemical element
A chemical element is a species of atoms that have a given number of protons in their nuclei, including the pure substance consisting only of that species. Unlike chemical compounds, chemical elements cannot be broken down into simpler sub ...
s heavier than lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid ...
. Stellar mass loss Stellar mass loss is a phenomenon observed in stars. All stars lose some mass over their lives at widely varying rates. Triggering events can cause the sudden ejection of a large portion of the star's mass. Stellar mass loss can also occur when a s ...
or supernova explosions return chemically enriched material to the interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
. These elements are then recycled into new stars. Astronomers can determine stellar properties—including mass, age, metallicity
In astronomy, metallicity is the abundance of elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal physical matter in the Universe is either hydrogen or helium, and astronomers use the word ''"metals"'' as ...
(chemical composition), variability, distance
Distance is a numerical or occasionally qualitative measurement of how far apart objects or points are. In physics or everyday usage, distance may refer to a physical length or an estimation based on other criteria (e.g. "two counties over"). ...
, and motion through space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually con ...
—by carrying out observations of a star's apparent brightness
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's lig ...
, spectrum
A spectrum (plural ''spectra'' or ''spectrums'') is a condition that is not limited to a specific set of values but can vary, without gaps, across a continuum. The word was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of color ...
, and changes in its position in the sky over time.
Stars can form orbital systems with other astronomical objects, as in the case of planetary system
A planetary system is a set of gravitationally bound non-stellar objects in or out of orbit around a star or star system. Generally speaking, systems with one or more planets constitute a planetary system, although such systems may also consis ...
s and star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a '' star cluster'' or ''galaxy'', although, broadly speakin ...
s with two
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many culture ...
or more
More or Mores may refer to:
Computing
* MORE (application), outline software for Mac OS
* more (command), a shell command
* MORE protocol, a routing protocol
* Missouri Research and Education Network
Music Albums
* ''More!'' (album), by Booka ...
stars. When two such stars have a relatively close orbit, their gravitational interaction can significantly impact their evolution. Stars can form part of a much larger gravitationally bound structure, such as a star cluster
Star clusters are large groups of stars. Two main types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of ten thousand to millions of old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters are more loosely clus ...
or a galaxy.
Etymology
The word "star" ultimately derives from theProto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo- ...
root "h₂stḗr" also meaning star, but further analyzable as h₂eh₁s- ("to burn", also the source of the word "ash") + -tēr (agentive suffix). Compare Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
stella, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
aster, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
Stern. Some scholars believe the word is a borrowing from Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform, early writing system
* Akkadian myt ...
"istar" (venus), however some doubt that suggestion. Star is cognate (shares the same root) with the following words: asterisk
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often vo ...
, asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the Solar System#Inner solar system, inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic o ...
, astral
Astral may refer to:
Concepts of the non-physical
* Astral body, a subtle body posited by many religious philosophers
* Astral journey (or ''astral trip''), the same as having an ''out-of-body experience''
* Astral plane (AKA astral world), a p ...
, constellation, Esther
Esther is the eponymous heroine of the Book of Esther. In the Achaemenid Empire, the Persian king Ahasuerus seeks a new wife after his queen, Vashti, is deposed for disobeying him. Hadassah, a Jewess who goes by the name of Esther, is chose ...
.
Observation history
 Historically, stars have been important to
Historically, stars have been important to civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
C ...
s throughout the world. They have been part of religious practices, used for celestial navigation
Celestial navigation, also known as astronavigation, is the practice of position fixing using stars and other celestial bodies that enables a navigator to accurately determine their actual current physical position in space (or on the surface ...
and orientation, to mark the passage of seasons, and to define calendars.
Early astronomers recognized a difference between "fixed stars
In astronomy, fixed stars ( la, stellae fixae) is a term to name the full set of glowing points, astronomical objects actually and mainly stars, that appear not to move relative to one another against the darkness of the night sky in the backgro ...
", whose position on the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
does not change, and "wandering stars" (planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a ...
s), which move noticeably relative to the fixed stars over days or weeks. Many ancient astronomers believed that the stars were permanently affixed to a heavenly sphere
The celestial spheres, or celestial orbs, were the fundamental entities of the cosmological models developed by Plato, Eudoxus, Aristotle, Ptolemy, Copernicus, and others. In these celestial models, the apparent motions of the fixed stars a ...
and that they were immutable. By convention, astronomers grouped prominent stars into asterisms and constellations and used them to track the motions of the planets and the inferred position of the Sun. The motion of the Sun against the background stars (and the horizon) was used to create calendars
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physi ...
, which could be used to regulate agricultural practices. The Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It was introduced in October 1582 by Pope Gregory XIII as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian calendar. The principal change was to space leap years di ...
, currently used nearly everywhere in the world, is a solar calendar based on the angle of the Earth's rotational axis relative to its local star, the Sun.
The oldest accurately dated star chart
A star chart is a celestial map of the night sky with astronomical objects laid out on a grid system. They are used to identify and locate constellations, stars, nebulae, galaxies, and planets. They have been used for human navigation since ...
was the result of ancient Egyptian astronomy
Egyptian astronomy began in prehistoric times, in the Predynastic Period. In the 5th millennium BCE, the stone circles at Nabta Playa may have made use of astronomical alignments. By the time the historical Dynastic Period began in the 3rd m ...
in 1534 BC. The earliest known star catalogues were compiled by the ancient Babylonian astronomers
Babylonian astronomy was the study or recording of celestial objects during the early history of Mesopotamia.
Babylonian astronomy seemed to have focused on a select group of stars and constellations known as Ziqpu stars. These constellations ...
of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
in the late 2nd millennium BC, during the Kassite Period
The Kassites () were people of the ancient Near East, who controlled Babylonia after the fall of the Old Babylonian Empire c. 1531 BC and until c. 1155 BC (short chronology).
They gained control of Babylonia after the Hittite sack of Babylo ...
(c. 1531 BC–1155 BC).
The first star catalogue
A star catalogue is an astronomical catalogue that lists stars. In astronomy, many stars are referred to simply by catalogue numbers. There are a great many different star catalogues which have been produced for different purposes over the years ...
in Greek astronomy
Greek astronomy is astronomy written in the Greek language in classical antiquity. Greek astronomy is understood to include the Ancient Greek, Hellenistic, Greco-Roman, and Late Antiquity eras. It is not limited geographically to Greece or to e ...
was created by Aristillus
Aristyllus ( el, Ἀρίστυλλος; fl. c. 261 BC) was a Greek astronomer, presumably of the school of Timocharis (c. 300 BC). He was among the earliest meridian-astronomy observers. Six of his stellar declinations are preserved at ...
in approximately 300 BC, with the help of Timocharis Timocharis of Alexandria ( grc-gre, Τιμόχαρις or Τιμοχάρης, ''gen.'' Τιμοχάρους; c. 320–260 BC) was a Greek astronomer and philosopher. Likely born in Alexandria, he was a contemporary of Euclid.
Work
What little is k ...
. The star catalog of Hipparchus
Hipparchus (; el, Ἵππαρχος, ''Hipparkhos''; BC) was a Greek astronomer, geographer, and mathematician. He is considered the founder of trigonometry, but is most famous for his incidental discovery of the precession of the equ ...
(2nd century BC) included 1,020 stars, and was used to assemble Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of import ...
's star catalogue. Hipparchus is known for the discovery of the first recorded ''nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramati ...
'' (new star). Many of the constellations and star names in use today derive from Greek astronomy.
In spite of the apparent immutability of the heavens, Chinese astronomers
Astronomy in China has a long history stretching from the Shang dynasty, being refined over a period of more than 3,000 years. The Ancient China, ancient Chinese people have identified stars from 1300 BCE, as Chinese star names later categoriz ...
were aware that new stars could appear. In 185 AD, they were the first to observe and write about a supernova, now known as SN 185
SN 185 was a transient astronomical event observed in the year AD 185, likely a supernova. The transient occurred in the direction of Alpha Centauri, between the constellations Circinus and Centaurus, centered at RA Dec , in Circinus. This ...
. The brightest stellar event in recorded history was the SN 1006 supernova, which was observed in 1006 and written about by the Egyptian astronomer Ali ibn Ridwan
Abu'l Hassan Ali ibn Ridwan Al-Misri () (c. 988 - c. 1061) was an Arab of Egyptian origin who was a physician, astrologer and astronomer, born in Giza.
He was a commentator on ancient Greek medicine, and in particular on Galen; his commentary o ...
and several Chinese astronomers. The SN 1054
SN 1054 is a supernova that was first observed on 1054, and remained visible until 1056.
The event was recorded in contemporary Chinese astronomy, and references to it are also found in a later (13th-century) Japanese document, and in a doc ...
supernova, which gave birth to the Crab Nebula
The Crab Nebula (catalogue designations Messier object, M1, New General Catalogue, NGC 1952, Taurus (constellation), Taurus A) is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus (constellation), Taurus. The common name ...
, was also observed by Chinese and Islamic astronomers.Medieval Islamic astronomers gave Arabic names to many stars that are still used today and they invented numerous
astronomical instruments
Astronomical instruments include:
*Alidade
*Armillary sphere
* Astrarium
*Astrolabe
*Astronomical clock
*the Antikythera mechanism, an astronomical clock
*Blink comparator
*Bolometer
*the Canterbury Astrolabe Quadrant
*Celatone
*Celestial sphere
...
that could compute the positions of the stars. They built the first large observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysical, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. H ...
research institutes, mainly for the purpose of producing ''Zij
A zij ( fa, زيج, zīj) is an Islamic astronomical book that tabulates parameters used for astronomical calculations of the positions of the Sun, Moon, stars, and planets.
Etymology
The name ''zij'' is derived from the Middle Persian term '' ...
'' star catalogues. Among these, the ''Book of Fixed Stars
The ''Book of Fixed Stars'' ( ar, كتاب صور الكواكب ', literally ''The Book of the Shapes of Stars'') is an astronomical text written by Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi (Azophi) around 964. Following the translation movement in the 9th centu ...
'' (964) was written by the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi
ʿAbd al-Rahman al-Sufi ( fa, عبدالرحمن صوفی; December 7, 903 – May 25, 986) was an iranianRobert Harry van Gent. Biography of al-Sūfī'. "The Persian astronomer Abū al-Husayn ‘Abd al-Rahmān ibn ‘Umar al-Sūfī was born i ...
, who observed a number of stars, star cluster
Star clusters are large groups of stars. Two main types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of ten thousand to millions of old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters are more loosely clus ...
s (including the Omicron Velorum
Omicron Velorum (ο Vel, ο Velorum) is a star in the constellation Vela. It is the brightest member of the loose naked eye open cluster IC 2391, also known as the ο Velorum Cluster.
Omicron Velorum is a blue-white B-type star with a ...
and Brocchi's Cluster
Brocchi's Cluster (also known as Collinder 399, Cr 399 or Al Sufi's Cluster) is a asterism of six stars in an apparent row, across 1.3° of the night sky and four others, in the south of the constellation Vulpecula, thus near Sagitta. Its nick ...
s) and galaxies
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System. ...
(including the Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy (IPA: ), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224 and originally the Andromeda Nebula, is a barred spiral galaxy with the diameter of about approximately from Earth and the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. The gal ...
). According to A. Zahoor, in the 11th century, the Persian polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
scholar Abu Rayhan Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Co ...
described the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked ey ...
galaxy as a multitude of fragments having the properties of nebulous
''Nebulous'' is a post-apocalyptic science fiction comedy radio show written by Graham Duff and produced by Ted Dowd from Baby Cow Productions; it is directed by Nicholas Briggs. The series premiered in the United Kingdom on BBC Radio 4. Se ...
stars, and gave the latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north po ...
s of various stars during a lunar eclipse
A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. Such alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six months, during the full moon phase, when the Moon's orbital plane is closest to the plane of the Eart ...
in 1019.
According to Josep Puig, the Andalusian astronomer Ibn Bajjah
Abū Bakr Muḥammad ibn Yaḥyà ibn aṣ-Ṣā’igh at-Tūjībī ibn Bājja ( ar, أبو بكر محمد بن يحيى بن الصائغ التجيبي بن باجة), best known by his Latinised name Avempace (; – 1138), was an A ...
proposed that the Milky Way was made up of many stars that almost touched one another and appeared to be a continuous image due to the effect of refraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomen ...
from sublunary material, citing his observation of the conjunction
Conjunction may refer to:
* Conjunction (grammar), a part of speech
* Logical conjunction, a mathematical operator
** Conjunction introduction, a rule of inference of propositional logic
* Conjunction (astronomy), in which two astronomical bodies ...
of Jupiter and Mars on 500 AH (1106/1107 AD) as evidence.
Early European astronomers such as Tycho Brahe
Tycho Brahe ( ; born Tyge Ottesen Brahe; generally called Tycho (14 December 154624 October 1601) was a Danish astronomer, known for his comprehensive astronomical observations, generally considered to be the most accurate of his time. He was ...
identified new stars in the night sky
The night sky is the nighttime appearance of celestial objects like stars, planets, and the Moon, which are visible in a clear sky between sunset and sunrise, when the Sun is below the horizon.
Natural light sources in a night sky inc ...
(later termed ''novae''), suggesting that the heavens were not immutable. In 1584, Giordano Bruno
Giordano Bruno (; ; la, Iordanus Brunus Nolanus; born Filippo Bruno, January or February 1548 – 17 February 1600) was an Italian philosopher, mathematician, poet, cosmological theorist, and Hermetic occultist. He is known for his cosmolo ...
suggested that the stars were like the Sun, and may have other planets, possibly even Earth-like, in orbit around them, an idea that had been suggested earlier by the ancient Greek philosophers
Ancient Greek philosophy arose in the 6th century BC, marking the end of the Greek Dark Ages. Greek philosophy continued throughout the Hellenistic period and the period in which Greece and most Greek-inhabited lands were part of the Roman Empire ...
, Democritus
Democritus (; el, Δημόκριτος, ''Dēmókritos'', meaning "chosen of the people"; – ) was an Ancient Greek pre-Socratic philosopher from Abdera, primarily remembered today for his formulation of an atomic theory of the universe. ...
and Epicurus, and by medieval Islamic cosmologists such as Fakhr al-Din al-Razi. By the following century, the idea of the stars being the same as the Sun was reaching a consensus among astronomers. To explain why these stars exerted no net gravitational pull on the Solar System, Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a " natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the g ...
suggested that the stars were equally distributed in every direction, an idea prompted by the theologian Richard Bentley
Richard Bentley FRS (; 27 January 1662 – 14 July 1742) was an English classical scholar, critic, and theologian. Considered the "founder of historical philology", Bentley is widely credited with establishing the English school of Helle ...
.
The Italian astronomer Geminiano Montanari
Geminiano Montanari (1 June 1633 – 13 October 1687) was an Italian astronomer, lens-maker, and proponent of the experimental approach to science. He was a member of various learned academies, notably the Accademia dei Gelati. Montanari's famous s ...
recorded observing variations in luminosity of the star Algol
ALGOL (; short for "Algorithmic Language") is a family of imperative computer programming languages originally developed in 1958. ALGOL heavily influenced many other languages and was the standard method for algorithm description used by th ...
in 1667. Edmond Halley
Edmond (or Edmund) Halley (; – ) was an English astronomer, mathematician and physicist. He was the second Astronomer Royal in Britain, succeeding John Flamsteed in 1720.
From an observatory he constructed on Saint Helena in 1676–77, Hal ...
published the first measurements of the proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of the observed changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects in the sky, as seen from the center of mass of the Solar System, compared to the abstract background of the more dista ...
of a pair of nearby "fixed" stars, demonstrating that they had changed positions since the time of the ancient Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
astronomers Ptolemy and Hipparchus.
William Herschel
Frederick William Herschel (; german: Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-born British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Carolin ...
was the first astronomer to attempt to determine the distribution of stars in the sky. During the 1780s, he established a series of gauges in 600 directions and counted the stars observed along each line of sight. From this he deduced that the number of stars steadily increased toward one side of the sky, in the direction of the Milky Way core
Core or cores may refer to:
Science and technology
* Core (anatomy), everything except the appendages
* Core (manufacturing), used in casting and molding
* Core (optical fiber), the signal-carrying portion of an optical fiber
* Core, the centra ...
. His son John Herschel
Sir John Frederick William Herschel, 1st Baronet (; 7 March 1792 – 11 May 1871) was an English polymath active as a mathematician, astronomer, chemist, inventor, experimental photographer who invented the blueprint and did botanic ...
repeated this study in the southern hemisphere and found a corresponding increase in the same direction. In addition to his other accomplishments, William Herschel is noted for his discovery that some stars do not merely lie along the same line of sight, but are physical companions that form binary star systems.
The science of stellar spectroscopy was pioneered by Joseph von Fraunhofer
Joseph Ritter von Fraunhofer (; ; 6 March 1787 – 7 June 1826) was a German physicist and optical lens manufacturer. He made optical glass, an achromatic telescope, and objective lenses. He also invented the spectroscope and developed diffr ...
and Angelo Secchi
Angelo Secchi (; 28 June 1818 – 26 February 1878) was an Italian Catholic priest, astronomer from the Italian region of Emilia. He was director of the observatory at the Pontifical Gregorian University (then called the Roman College) for ...
. By comparing the spectra of stars such as Sirius
Sirius is the brightest star in the night sky. Its name is derived from the Greek word , or , meaning 'glowing' or 'scorching'. The star is designated α Canis Majoris, Latinized to Alpha Canis Majoris, and abbreviated Alpha CMa ...
to the Sun, they found differences in the strength and number of their absorption lines
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to identif ...
—the dark lines in stellar spectra caused by the atmosphere's absorption of specific frequencies. In 1865, Secchi began classifying stars into spectral types. The modern version of the stellar classification scheme was developed by Annie J. Cannon during the early 1900s.
The first direct measurement of the distance to a star (61 Cygni
61 Cygni is a binary star system in the constellation Cygnus, consisting of a pair of K-type dwarf stars that orbit each other in a period of about 659 years. Of apparent magnitude 5.20 and 6.05, respectively, they can be seen ...
at 11.4 light-years
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 trillion miles ().One trillion here is taken to be 101 ...
) was made in 1838 by Friedrich Bessel
Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel (; 22 July 1784 – 17 March 1846) was a German astronomer, mathematician, physicist, and geodesist. He was the first astronomer who determined reliable values for the distance from the sun to another star by the met ...
using the parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different lines of sight and is measured by the angle or semi-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to foreshortening, nearby object ...
technique. Parallax measurements demonstrated the vast separation of the stars in the heavens. Observation of double stars gained increasing importance during the 19th century. In 1834, Friedrich Bessel observed changes in the proper motion of the star Sirius and inferred a hidden companion. Edward Pickering discovered the first spectroscopic binary in 1899 when he observed the periodic splitting of the spectral lines of the star Mizar
Mizar is a second- magnitude star in the handle of the Big Dipper asterism in the constellation of Ursa Major. It has the Bayer designation ζ Ursae Majoris ( Latinised as Zeta Ursae Majoris). It forms a well-known naked eye ...
in a 104-day period. Detailed observations of many binary star systems were collected by astronomers such as Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve
Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve (russian: link=no, Василий Яковлевич Струве, trans. ''Vasily Yakovlevich Struve''; 15 April 1793 – ) was a Baltic German astronomer and geodesist from the famous Struve family. He is be ...
and S. W. Burnham
Sherburne Wesley Burnham (December 12, 1838 – March 11, 1921) was an American astronomer.
For more than 50 years Burnham spent all his free time observing the heavens, mainly concerning himself with binary stars.
Biography
Sherburne ...
, allowing the masses of stars to be determined from computation of orbital elements
Orbital elements are the parameters required to uniquely identify a specific orbit. In celestial mechanics these elements are considered in two-body systems using a Kepler orbit. There are many different ways to mathematically describe the same ...
. The first solution to the problem of deriving an orbit of binary stars from telescope observations was made by Felix Savary in 1827.
The twentieth century saw increasingly rapid advances in the scientific study of stars. The photograph
A photograph (also known as a photo, image, or picture) is an image created by light falling on a photosensitive surface, usually photographic film or an electronic image sensor, such as a CCD or a CMOS chip. Most photographs are now creat ...
became a valuable astronomical tool. Karl Schwarzschild
Karl Schwarzschild (; 9 October 1873 – 11 May 1916) was a German physicist and astronomer.
Schwarzschild provided the first exact solution to the Einstein field equations of general relativity, for the limited case of a single spherical non-r ...
discovered that the color of a star and, hence, its temperature, could be determined by comparing the visual magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's lig ...
against the photographic magnitude
Photographic magnitude ( or ) is a measure of the relative brightness of a star or other astronomical object as imaged on a photographic film emulsion with a camera attached to a telescope. An object's apparent photographic magnitude depends on i ...
. The development of the photoelectric
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, and solid sta ...
photometer
A photometer is an instrument that measures the strength of electromagnetic radiation in the range from ultraviolet to infrared and including the visible spectrum. Most photometers convert light into an electric current using a photoresistor, ...
allowed precise measurements of magnitude at multiple wavelength intervals. In 1921 Albert A. Michelson
Albert Abraham Michelson FFRS HFRSE (surname pronunciation anglicized as "Michael-son", December 19, 1852 – May 9, 1931) was a German-born American physicist of Polish/Jewish origin, known for his work on measuring the speed of light and espe ...
made the first measurements of a stellar diameter using an interferometer
Interferometry is a technique which uses the '' interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber o ...
on the Hooker telescope
The Mount Wilson Observatory (MWO) is an astronomical observatory in Los Angeles County, California, United States. The MWO is located on Mount Wilson, a peak in the San Gabriel Mountains near Pasadena, northeast of Los Angeles.
The observato ...
at Mount Wilson Observatory
The Mount Wilson Observatory (MWO) is an astronomical observatory in Los Angeles County, California, United States. The MWO is located on Mount Wilson, a peak in the San Gabriel Mountains near Pasadena, northeast of Los Angeles.
The observ ...
.
Important theoretical work on the physical structure of stars occurred during the first decades of the twentieth century. In 1913, the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram was developed, propelling the astrophysical study of stars. Successful models were developed to explain the interiors of stars and stellar evolution. Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin
Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin (born Cecilia Helena Payne; – ) was a British-born American astronomer and astrophysicist who proposed in her 1925 doctoral thesis that stars were composed primarily of hydrogen and helium. Her groundbreaking con ...
first proposed that stars were made primarily of hydrogen and helium in her 1925 PhD thesis. The spectra of stars were further understood through advances in quantum physics
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental theory in physics that provides a description of the physical properties of nature at the scale of atoms and subatomic particles. It is the foundation of all quantum physics including quantum chemistry, q ...
. This allowed the chemical composition of the stellar atmosphere to be determined.
 With the exception of rare events such as supernovae and
With the exception of rare events such as supernovae and supernova imposter
Supernova impostors are stellar explosions that appear at first to be a supernova but do not destroy their progenitor stars. As such, they are a class of extra-powerful novae. They are also known as Type V supernovae, Eta Carinae analogs, and gia ...
s, individual stars have primarily been observed in the Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way.
It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of .
It consists of two collections of galaxies in a "dumbbell" shape: the Milky Way and its satellites form ...
, and especially in the visible part of the Milky Way (as demonstrated by the detailed star catalogues available for the Milky Way galaxy) and its satellites. Individual stars such as Cepheid variables have been observed in the M87 and M100 M100 or M-100 may refer to:
* M-100 (Michigan highway), a north–south state trunkline highway in the U.S. state of Michigan
* M100 (Cape Town), a metropolitan route near Cape Town, South Africa
* M-100 (rocket), a two-stage Soviet sounding rock ...
galaxies of the Virgo Cluster
The Virgo Cluster is a large cluster of galaxies whose center is 53.8 ± 0.3 Mly (16.5 ± 0.1 Mpc) away in the constellation Virgo. Comprising approximately 1,300 (and possibly up to 2,000) member galaxies, the cluster forms the heart of the l ...
, as well as luminous stars in some other relatively nearby galaxies. With the aid of gravitational lensing
A gravitational lens is a distribution of matter (such as a cluster of galaxies) between a distant light source and an observer that is capable of bending the light from the source as the light travels toward the observer. This effect is known ...
, a single star (named Icarus
In Greek mythology, Icarus (; grc, Ἴκαρος, Íkaros, ) was the son of the master craftsman Daedalus, the architect of the labyrinth of Crete. After Theseus, king of Athens and enemy of Minos, escaped from the labyrinth, King Minos sus ...
) has been observed at 9 billion light-years away.
Designations
The concept of a constellation was known to exist during the Babylonian period. Ancient sky watchers imagined that prominent arrangements of stars formed patterns, and they associated these with particular aspects of nature or their myths. Twelve of these formations lay along the band of theecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic agai ...
and these became the basis of astrology
Astrology is a range of divinatory practices, recognized as pseudoscientific since the 18th century, that claim to discern information about human affairs and terrestrial events by studying the apparent positions of celestial objects. Di ...
. Many of the more prominent individual stars were given names, particularly with Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walte ...
or Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
designations.
As well as certain constellations and the Sun itself, individual stars have their own myths
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not objectively true, the identification of a narrati ...
. To the Ancient Greeks
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
, some "stars", known as planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a ...
s (Greek πλανήτης (planētēs), meaning "wanderer"), represented various important deities, from which the names of the planets Mercury, Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
, Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmos ...
, Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousandt ...
and Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; ...
were taken. (Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus (Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars), grandfather of Zeus (Jupiter) and father of Cronu ...
and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 time ...
were Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and Roman gods
The Roman deities most widely known today are those the Romans identified with Greek counterparts (see '' interpretatio graeca''), integrating Greek myths, iconography, and sometimes religious practices into Roman culture, including Latin lit ...
, but neither planet was known in Antiquity because of their low brightness. Their names were assigned by later astronomers.)
Circa 1600, the names of the constellations were used to name the stars in the corresponding regions of the sky. The German astronomer Johann Bayer
Johann Bayer (1572 – 7 March 1625) was a German lawyer and uranographer (celestial cartographer). He was born in Rain, Lower Bavaria, in 1572. At twenty, in 1592 he began his study of philosophy and law at the University of Ingolstadt, ...
created a series of star maps and applied Greek letters as designations to the stars in each constellation. Later a numbering system based on the star's right ascension
Right ascension (abbreviated RA; symbol ) is the angular distance of a particular point measured eastward along the celestial equator from the Sun at the March equinox to the ( hour circle of the) point in question above the earth.
When pai ...
was invented and added to John Flamsteed
John Flamsteed (19 August 1646 – 31 December 1719) was an English astronomer and the first Astronomer Royal. His main achievements were the preparation of a 3,000-star catalogue, ''Catalogus Britannicus'', and a star atlas called '' Atlas C ...
's star catalogue in his book ''"Historia coelestis Britannica"'' (the 1712 edition), whereby this numbering system came to be called ''Flamsteed designation
A Flamsteed designation is a combination of a number and constellation name that uniquely identifies most naked eye stars in the modern constellations visible from southern England. They are named for John Flamsteed who first used them while c ...
'' or ''Flamsteed numbering''.
The internationally recognized authority for naming celestial bodies is the International Astronomical Union
The International Astronomical Union (IAU; french: link=yes, Union astronomique internationale, UAI) is a nongovernmental organisation with the objective of advancing astronomy in all aspects, including promoting astronomical research, outreach ...
(IAU). The International Astronomical Union maintains the Working Group on Star Names
The International Astronomical Union (IAU) established a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN) in May 2016 to catalog and standardize List of proper names of stars, proper names for stars for the international astronomical community. It operates under ...
(WGSN) which catalogs and standardizes proper names for stars. A number of private companies sell names of stars which are not recognized by the IAU, professional astronomers, or the amateur astronomy community. The British Library
The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom and is one of the largest libraries in the world. It is estimated to contain between 170 and 200 million items from many countries. As a legal deposit library, the Briti ...
calls this an unregulated commercial enterprise
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for pr ...
, and the New York City Department of Consumer and Worker Protection
The New York City Department of Consumer and Worker Protection (DCWP), formerly the Department of Consumer Affairs (DCA), is an agency of the Government of New York City.
History
The duties were performed by the Commissioner of Public Markets un ...
issued a violation against one such star-naming company for engaging in a deceptive trade practice.
Units of measurement
Although stellar parameters can be expressed inSI units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. E ...
or Gaussian units
Gaussian units constitute a metric system of physical units. This system is the most common of the several electromagnetic unit systems based on cgs (centimetre–gram–second) units. It is also called the Gaussian unit system, Gaussian-cgs uni ...
, it is often most convenient to express mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different element ...
, luminosity
Luminosity is an absolute measure of radiated electromagnetic power (light), the radiant power emitted by a light-emitting object over time. In astronomy, luminosity is the total amount of electromagnetic energy emitted per unit of time by a s ...
, and radii
In classical geometry, a radius ( : radii) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The name comes from the latin ''radius'', meaning ray but also the ...
in solar units, based on the characteristics of the Sun. In 2015, the IAU defined a set of ''nominal'' solar values (defined as SI constants, without uncertainties) which can be used for quoting stellar parameters:
:
The solar mass
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass o ...
M⊙ was not explicitly defined by the IAU due to the large relative uncertainty (10−4) of the Newtonian gravitational constant G. Since the product of the Newtonian gravitational constant and solar mass
together (GM⊙) has been determined to much greater precision, the IAU defined the ''nominal'' solar mass parameter to be:
:
The nominal solar mass parameter can be combined with the most recent (2014) CODATA estimate of the Newtonian gravitational constant G to derive the solar mass to be approximately 1.9885 × 1030 kg. Although the exact values for the luminosity, radius, mass parameter, and mass may vary slightly in the future due to observational uncertainties, the 2015 IAU nominal constants will remain the same SI values as they remain useful measures for quoting stellar parameters.
Large lengths, such as the radius of a giant star or the semi-major axis
In geometry, the major axis of an ellipse is its longest diameter: a line segment that runs through the center and both foci, with ends at the two most widely separated points of the perimeter. The semi-major axis (major semiaxis) is the lo ...
of a binary star system, are often expressed in terms of the astronomical unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au, or or AU) is a unit of length, roughly the distance from Earth to the Sun and approximately equal to or 8.3 light-minutes. The actual distance from Earth to the Sun varies by about 3% as Earth orbi ...
—approximately equal to the mean distance between the Earth and the Sun (150 million km or approximately 93 million miles). In 2012, the IAU defined the astronomical constant An astronomical constant is any of several physical constants used in astronomy. Formal sets of constants, along with recommended values, have been defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) several times: in 1964Resolution No.4 of thXIIt ...
to be an exact length in meters: 149,597,870,700 m.
Formation and evolution
space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually con ...
of higher matter density, yet those regions are less dense than within a vacuum chamber
A vacuum chamber is a rigid enclosure from which air and other gases are removed by a vacuum pump. This results in a low-pressure environment within the chamber, commonly referred to as a vacuum. A vacuum environment allows researchers to con ...
. These regions—known as ''molecular cloud
A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydroge ...
s''—consist mostly of hydrogen, with about 23 to 28 percent helium and a few percent heavier elements. One example of such a star-forming region is the Orion Nebula
The Orion Nebula (also known as Messier 42, M42, or NGC 1976) is a diffuse nebula situated in the Milky Way, being south of Orion's Belt in the Orion (constellation), constellation of Orion. It is one of the brightest nebulae and is visible to t ...
. Most stars form in groups of dozens to hundreds of thousands of stars.
Massive stars
This is a list of the most massive stars that have been discovered, in solar masses ().
Uncertainties and caveats
Most of the masses listed below are contested and, being the subject of current research, remain under review and subject to consta ...
in these groups may powerfully illuminate those clouds, ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conven ...
izing the hydrogen, and creating H II region
An H II region or HII region is a region of interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized. It is typically in a molecular cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place, with a size ranging from one to hundre ...
s. Such feedback effects, from star formation, may ultimately disrupt the cloud and prevent further star formation.
All stars spend the majority of their existence as ''main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Her ...
stars'', fueled primarily by the nuclear fusion of hydrogen into helium within their cores. However, stars of different masses have markedly different properties at various stages of their development. The ultimate fate of more massive stars differs from that of less massive stars, as do their luminosities and the impact they have on their environment. Accordingly, astronomers often group stars by their mass:
* ''Very low mass stars'', with masses below 0.5 , are fully convective and distribute helium
Helium (from el, ἥλιος, helios, lit=sun) is a chemical element with the symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. ...
evenly throughout the whole star while on the main sequence. Therefore, they never undergo shell burning and never become red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around or ...
s. After exhausting their hydrogen they become helium white dwarfs and slowly cool. As the lifetime of stars is longer than the age of the universe
In physical cosmology, the age of the universe is the time elapsed since the Big Bang. Astronomers have derived two different measurements of the age of the universe:
a measurement based on direct observations of an early state of the universe, ...
, no such star has yet reached the white dwarf stage.
* ''Low mass stars'' (including the Sun), with a mass between and ~ depending on composition, do become red giants as their core hydrogen is depleted and they begin to burn helium in core in a helium flash
A helium flash is a very brief thermal runaway nuclear fusion of large quantities of helium into carbon through the triple-alpha process in the core of low mass stars (between 0.8 solar masses () and 2.0 ) during their red giant phase (the Sun i ...
; they develop a degenerate carbon-oxygen core later on the asymptotic giant branch
The asymptotic giant branch (AGB) is a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram populated by evolved cool luminous stars. This is a period of stellar evolution undertaken by all low- to intermediate-mass stars (about 0.5 to 8 solar masses) lat ...
; they finally blow off their outer shell as a planetary nebula
A planetary nebula (PN, plural PNe) is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelate ...
and leave behind their core in the form of a white dwarf.
* ''Intermediate-mass stars'', between ~ and ~, pass through evolutionary stages similar to low mass stars, but after a relatively short period on the red-giant branch
The red-giant branch (RGB), sometimes called the first giant branch, is the portion of the giant branch before helium ignition occurs in the course of stellar evolution. It is a stage that follows the main sequence for low- to intermediate-mass sta ...
they ignite helium without a flash and spend an extended period in the red clump
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a seconda ...
before forming a degenerate carbon-oxygen core.
* ''Massive stars'' generally have a minimum mass of ~. After exhausting the hydrogen at the core these stars become supergiant
Supergiants are among the most massive and most luminous stars. Supergiant stars occupy the top region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram with absolute visual magnitudes between about −3 and −8. The temperature range of supergiant stars s ...
s and go on to fuse
Fuse or FUSE may refer to:
Devices
* Fuse (electrical), a device used in electrical systems to protect against excessive current
** Fuse (automotive), a class of fuses for vehicles
* Fuse (hydraulic), a device used in hydraulic systems to prote ...
elements heavier than helium. They end their lives when their cores collapse and they explode as supernovae.
Star formation
The formation of a star begins with gravitational instability within a molecular cloud, caused by regions of higher density—often triggered by compression of clouds by radiation from massive stars, expanding bubbles in the interstellar medium, the collision of different molecular clouds, or the collision of galaxies (as in astarburst galaxy
A starburst galaxy is one undergoing an exceptionally high rate of star formation, as compared to the long-term average rate of star formation in the galaxy or the star formation rate observed in most other galaxies. For example, the star formatio ...
). When a region reaches a sufficient density of matter to satisfy the criteria for Jeans instability
In stellar physics, the Jeans instability causes the collapse of interstellar gas clouds and subsequent star formation, named after James Jeans. It occurs when the internal gas pressure is not strong enough to prevent gravitational collapse of ...
, it begins to collapse under its own gravitational force.
As the cloud collapses, individual conglomerations of dense dust and gas form "Bok globule
In astronomy, Bok globules are isolated and relatively small dark nebulae, containing dense cosmic dust and gas from which star formation may take place. Bok globules are found within H II regions, and typically have a mass of about 2 to 50 so ...
s". As a globule collapses and the density increases, the gravitational energy converts into heat and the temperature rises. When the protostellar cloud has approximately reached the stable condition of hydrostatic equilibrium
In fluid mechanics, hydrostatic equilibrium (hydrostatic balance, hydrostasy) is the condition of a fluid or plastic solid at rest, which occurs when external forces, such as gravity, are balanced by a pressure-gradient force. In the planetar ...
, a protostar
A protostar is a very young star that is still gathering mass from its parent molecular cloud. The protostellar phase is the earliest one in the process of stellar evolution. For a low-mass star (i.e. that of the Sun or lower), it lasts about ...
forms at the core. These pre-main-sequence star
A pre-main-sequence star (also known as a PMS star and PMS object) is a star in the stage when it has not yet reached the main sequence. Earlier in its life, the object is a protostar that grows by acquiring mass from its surrounding envelope o ...
s are often surrounded by a protoplanetary disk
A protoplanetary disk is a rotating circumstellar disc of dense gas and dust surrounding a young newly formed star, a T Tauri star, or Herbig Ae/Be star. The protoplanetary disk may also be considered an accretion disk for the star itself, ...
and powered mainly by the conversion of gravitational energy. The period of gravitational contraction lasts about 10 million years for a star like the sun, up to 100 million years for a red dwarf.
Early stars of less than 2 are called T Tauri star
T Tauri stars (TTS) are a class of variable stars that are less than about ten million years old. This class is named after the prototype, T Tauri, a young star in the Taurus star-forming region. They are found near molecular clouds and ide ...
s, while those with greater mass are Herbig Ae/Be star
A Herbig Ae/Be star (HAeBe) is a pre-main-sequence star – a young () star of spectral types A or B. These stars are still embedded in gas-dust envelopes and are sometimes accompanied by circumstellar disks. Hydrogen and calcium emission lines a ...
s. These newly formed stars emit jets of gas along their axis of rotation, which may reduce the angular momentum
In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed sy ...
of the collapsing star and result in small patches of nebulosity known as Herbig–Haro object
Herbig–Haro (HH) objects are bright patches of nebulosity associated with newborn stars. They are formed when narrow jets of partially ionised gas ejected by stars collide with nearby clouds of gas and dust at several hundred kilometres per s ...
s.
These jets, in combination with radiation from nearby massive stars, may help to drive away the surrounding cloud from which the star was formed.
Early in their development, T Tauri stars follow the Hayashi track
The Hayashi track is a luminosity–temperature relationship obeyed by infant stars of less than in the pre-main-sequence phase (PMS phase) of stellar evolution. It is named after Japanese astrophysicist Chushiro Hayashi. On the Hertzsprung– ...
—they contract and decrease in luminosity while remaining at roughly the same temperature. Less massive T Tauri stars follow this track to the main sequence, while more massive stars turn onto the Henyey track
The Henyey track is a path taken by pre-main-sequence stars with masses greater than 0.5 solar masses in the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram after the end of the Hayashi track. The astronomer Louis G. Henyey and his colleagues in the 1950s show ...
.
Most stars are observed to be members of binary star systems, and the properties of those binaries are the result of the conditions in which they formed. A gas cloud must lose its angular momentum in order to collapse and form a star. The fragmentation of the cloud into multiple stars distributes some of that angular momentum. The primordial binaries transfer some angular momentum by gravitational interactions during close encounters with other stars in young stellar clusters. These interactions tend to split apart more widely separated (soft) binaries while causing hard binaries to become more tightly bound. This produces the separation of binaries into their two observed populations distributions.
Main sequence
Stars spend about 90% of their existence fusing hydrogen into helium in high-temperature and high-pressure reactions in the core region. Such stars are said to be on the main sequence, and are called dwarf stars. Starting at zero-age main sequence, the proportion of helium in a star's core will steadily increase, the rate of nuclear fusion at the core will slowly increase, as will the star's temperature and luminosity. The Sun, for example, is estimated to have increased in luminosity by about 40% since it reached the main sequence 4.6 billion (4.6 × 109) years ago. Every star generates astellar wind
A stellar wind is a flow of gas ejected from the upper atmosphere of a star. It is distinguished from the bipolar outflows characteristic of young stars by being less collimated, although stellar winds are not generally spherically symmetric. ...
of particles that causes a continual outflow of gas into space. For most stars, the mass lost is negligible. The Sun loses 10−14 every year, or about 0.01% of its total mass over its entire lifespan. However, very massive stars can lose 10−7 to 10−5 each year, significantly affecting their evolution. Stars that begin with more than 50 can lose over half their total mass while on the main sequence.
 The time a star spends on the main sequence depends primarily on the amount of fuel it has and the rate at which it fuses it. The Sun is expected to live 10 billion (1010) years. Massive stars consume their fuel very rapidly and are short-lived. Low mass stars consume their fuel very slowly. Stars less massive than 0.25 , called
The time a star spends on the main sequence depends primarily on the amount of fuel it has and the rate at which it fuses it. The Sun is expected to live 10 billion (1010) years. Massive stars consume their fuel very rapidly and are short-lived. Low mass stars consume their fuel very slowly. Stars less massive than 0.25 , called red dwarf
''Red Dwarf'' is a British science fiction comedy franchise created by Rob Grant and Doug Naylor, which primarily consists of a television sitcom that aired on BBC Two between 1988 and 1999, and on Dave (TV channel), Dave since 2009, gaining a ...
s, are able to fuse nearly all of their mass while stars of about 1 can only fuse about 10% of their mass. The combination of their slow fuel-consumption and relatively large usable fuel supply allows low mass stars to last about one trillion (1012) years; the most extreme of 0.08 will last for about 12 trillion years. Red dwarfs become hotter and more luminous as they accumulate helium. When they eventually run out of hydrogen, they contract into a white dwarf and decline in temperature.
Since the lifespan of such stars is greater than the current age of the universe (13.8 billion years), no stars under about 0.85
are expected to have moved off the main sequence.
Besides mass, the elements heavier than helium can play a significant role in the evolution of stars. Astronomers label all elements heavier than helium "metals", and call the chemical concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', '' number concentration'' ...
of these elements in a star, its metallicity
In astronomy, metallicity is the abundance of elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal physical matter in the Universe is either hydrogen or helium, and astronomers use the word ''"metals"'' as ...
. A star's metallicity can influence the time the star takes to burn its fuel, and controls the formation of its magnetic fields, which affects the strength of its stellar wind. Older, population II
During 1944, Walter Baade categorized groups of stars within the Milky Way into stellar populations.
In the abstract of the article by Baade, he recognizes that Jan Oort originally conceived this type of classification in 1926:
Baade noticed th ...
stars have substantially less metallicity than the younger, population I stars due to the composition of the molecular clouds from which they formed. Over time, such clouds become increasingly enriched in heavier elements as older stars die and shed portions of their atmospheres
The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as Pa. It is sometimes used as a ''reference pressure'' or ''standard pressure''. It is approximately equal to Earth's average atmospheric pressure at sea level.
History
The s ...
.
Post–main sequence
 As stars of at least 0.4 exhaust the supply of hydrogen at their core, they start to fuse hydrogen in a shell surrounding the helium core. The outer layers of the star expand and cool greatly as they transition into a
As stars of at least 0.4 exhaust the supply of hydrogen at their core, they start to fuse hydrogen in a shell surrounding the helium core. The outer layers of the star expand and cool greatly as they transition into a red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around or ...
. In some cases, they will fuse heavier elements
Element or elements may refer to:
Science
* Chemical element, a pure substance of one type of atom
* Heating element, a device that generates heat by electrical resistance
* Orbital elements, parameters required to identify a specific orbit of ...
at the core or in shells around the core. As the stars expand, they throw part of their mass, enriched with those heavier elements, into the interstellar environment, to be recycled later as new stars. In about 5 billion years, when the Sun enters the helium burning phase, it will expand to a maximum radius of roughly , 250 times its present size, and lose 30% of its current mass.
See also
As the hydrogen-burning shell produces more helium, the core increases in mass and temperature. In a red giant of up to 2.25 , the mass of the helium core becomes degenerate prior to helium fusion
The triple-alpha process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions by which three helium-4 nuclei (alpha particles) are transformed into carbon.
Triple-alpha process in stars
Helium accumulates in the cores of stars as a result of the proton–pr ...
. Finally, when the temperature increases sufficiently, core helium fusion begins explosively in what is called a helium flash
A helium flash is a very brief thermal runaway nuclear fusion of large quantities of helium into carbon through the triple-alpha process in the core of low mass stars (between 0.8 solar masses () and 2.0 ) during their red giant phase (the Sun i ...
, and the star rapidly shrinks in radius, increases its surface temperature, and moves to the horizontal branch
The horizontal branch (HB) is a stage of stellar evolution that immediately follows the red-giant branch in stars whose masses are similar to the Sun's. Horizontal-branch stars are powered by helium fusion in the core (via the triple-alpha proce ...
of the HR diagram. For more massive stars, helium core fusion starts before the core becomes degenerate, and the star spends some time in the red clump
Red is the color at the long wavelength end of the visible spectrum of light, next to orange and opposite violet. It has a dominant wavelength of approximately 625–740 nanometres. It is a primary color in the RGB color model and a seconda ...
, slowly burning helium, before the outer convective envelope collapses and the star then moves to the horizontal branch.
After a star has fused the helium of its core, it begins fusing helium along a shell surrounding the hot carbon core. The star then follows an evolutionary path called the asymptotic giant branch
The asymptotic giant branch (AGB) is a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram populated by evolved cool luminous stars. This is a period of stellar evolution undertaken by all low- to intermediate-mass stars (about 0.5 to 8 solar masses) lat ...
(AGB) that parallels the other described red-giant phase, but with a higher luminosity. The more massive AGB stars may undergo a brief period of carbon fusion before the core becomes degenerate. During the AGB phase, stars undergo thermal pulse
The asymptotic giant branch (AGB) is a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram populated by evolved cool luminous stars. This is a period of stellar evolution undertaken by all low- to intermediate-mass stars (about 0.5 to 8 solar masses) late ...
s due to instabilities in the core of the star. In these thermal pulses, the luminosity of the star varies and matter is ejected from the star's atmosphere, ultimately forming a planetary nebula. As much as 50 to 70% of a star's mass can be ejected in this mass loss Stellar mass loss is a phenomenon observed in stars. All stars lose some mass over their lives at widely varying rates. Triggering events can cause the sudden ejection of a large portion of the star's mass. Stellar mass loss can also occur when a st ...
process. Because energy transport in an AGB star is primarily by convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the c ...
, this ejected material is enriched with the fusion products dredged up from the core. Therefore, the planetary nebula is enriched with elements like carbon and oxygen. Ultimately, the planetary nebula disperses, enriching the general interstellar medium. Therefore, future generations of stars are made of the "star stuff" from past stars.
Massive stars
 During their helium-burning phase, a star of more than 9 solar masses expands to form first a
During their helium-burning phase, a star of more than 9 solar masses expands to form first a blue
Blue is one of the three primary colours in the RYB colour model (traditional colour theory), as well as in the RGB (additive) colour model. It lies between violet and cyan on the spectrum of visible light. The eye perceives blue when ...
and then a red supergiant
Red supergiants (RSGs) are stars with a supergiant luminosity class ( Yerkes class I) of spectral type K or M. They are the largest stars in the universe in terms of volume, although they are not the most massive or luminous. Betelgeuse and Antar ...
. Particularly massive stars may evolve to a Wolf-Rayet star, characterised by spectra dominated by emission lines of elements heavier than hydrogen, which have reached the surface due to strong convection and intense mass loss, or from stripping of the outer layers.
When helium is exhausted at the core of a massive star, the core contracts and the temperature and pressure rises enough to fuse carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes ...
(see Carbon-burning process
The carbon-burning process or carbon fusion is a set of nuclear fusion reactions that take place in the cores of massive stars (at least 8 \beginM_\odot\end at birth) that combines carbon into other elements. It requires high temperatures (> 5&t ...
). This process continues, with the successive stages being fueled by neon
Neon is a chemical element with the symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is a noble gas. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with about two-thirds the density of air. It was discovered (along with krypt ...
(see neon-burning process
The neon-burning process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions that take place in evolved massive stars with at least 8 Solar masses. Neon burning requires high temperatures and densities (around 1.2×109 K or 100 keV and 4×109 kg/m3).
At suc ...
), oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
(see oxygen-burning process
The oxygen-burning process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions that take place in massive stars that have used up the lighter elements in their cores. Oxygen-burning is preceded by the neon-burning process and succeeded by the silicon-burning pr ...
), and silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ...
(see silicon-burning process
In astrophysics, silicon burning is a very brief sequence of nuclear fusion reactions that occur in massive stars with a minimum of about 8–11 solar masses. Silicon burning is the final stage of fusion for massive stars that have run out of the f ...
). Near the end of the star's life, fusion continues along a series of onion-layer shells within a massive star. Each shell fuses a different element, with the outermost shell fusing hydrogen; the next shell fusing helium, and so forth.
The final stage occurs when a massive star begins producing iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
. Since iron nuclei are more tightly bound than any heavier nuclei, any fusion beyond iron does not produce a net release of energy.
Collapse
As a star's core shrinks, the intensity of radiation from that surface increases, creating suchradiation pressure
Radiation pressure is the mechanical pressure exerted upon any surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of any wavelength that is a ...
on the outer shell of gas that it will push those layers away, forming a planetary nebula. If what remains after the outer atmosphere has been shed is less than roughly 1.4 , it shrinks to a relatively tiny object about the size of Earth, known as a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
. White dwarfs lack the mass for further gravitational compression to take place. The electron-degenerate matter
Degenerate matter is a highly dense state of fermionic matter in which the Pauli exclusion principle exerts significant pressure in addition to, or in lieu of, thermal pressure. The description applies to matter composed of electrons, protons, ...
inside a white dwarf is no longer a plasma. Eventually, white dwarfs fade into black dwarf
A black dwarf is a theoretical stellar remnant, specifically a white dwarf that has cooled sufficiently to no longer emit significant heat or light. Because the time required for a white dwarf to reach this state is calculated to be longer than ...
s over a very long period of time.
 In massive stars, fusion continues until the iron core has grown so large (more than 1.4 ) that it can no longer support its own mass. This core will suddenly collapse as its electrons are driven into its protons, forming neutrons,
In massive stars, fusion continues until the iron core has grown so large (more than 1.4 ) that it can no longer support its own mass. This core will suddenly collapse as its electrons are driven into its protons, forming neutrons, neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is a fermion (an elementary particle with spin of ) that interacts only via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass ...
s, and gamma rays in a burst of electron capture
Electron capture (K-electron capture, also K-capture, or L-electron capture, L-capture) is a process in which the proton-rich nucleus of an electrically neutral atom absorbs an inner atomic electron, usually from the K or L electron shells. T ...
and inverse beta decay
Inverse beta decay, commonly abbreviated to IBD, is a nuclear reaction involving an electron antineutrino scattering off a proton, creating a positron and a neutron. This process is commonly used in the detection of electron antineutrinos in neu ...
. The shockwave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a me ...
formed by this sudden collapse causes the rest of the star to explode in a supernova. Supernovae become so bright that they may briefly outshine the star's entire home galaxy. When they occur within the Milky Way, supernovae have historically been observed by naked-eye observers as "new stars" where none seemingly existed before.
A supernova explosion blows away the star's outer layers, leaving a remnant
Remnant or remnants may refer to:
Religion
* Remnant (Bible), a recurring theme in the Bible
* Remnant (Seventh-day Adventist belief), the remnant theme in the Seventh-day Adventist Church
* ''The Remnant'' (newspaper), a traditional Catholic ...
such as the Crab Nebula. The core is compressed into a neutron star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. w ...
, which sometimes manifests itself as a pulsar
A pulsar (from ''pulsating radio source'') is a highly magnetized rotating neutron star that emits beams of electromagnetic radiation out of its magnetic poles. This radiation can be observed only when a beam of emission is pointing toward E ...
or X-ray burster
X-ray bursters are one class of X-ray binary stars exhibiting X-ray bursts, periodic and rapid increases in luminosity (typically a factor of 10 or greater) that peak in the X-ray region of the electromagnetic spectrum. These astrophysical syst ...
. In the case of the largest stars, the remnant is a black hole greater than 4 . In a neutron star the matter is in a state known as neutron-degenerate matter
Degenerate matter is a highly dense state of fermionic matter in which the Pauli exclusion principle exerts significant pressure in addition to, or in lieu of, thermal pressure. The description applies to matter composed of electrons, protons, ne ...
, with a more exotic form of degenerate matter, QCD matter
Quark matter or QCD matter (quantum chromodynamic) refers to any of a number of hypothetical phases of matter whose degrees of freedom include quarks and gluons, of which the prominent example is quark-gluon plasma. Several series of conferences ...
, possibly present in the core.
The blown-off outer layers of dying stars include heavy elements, which may be recycled during the formation of new stars. These heavy elements allow the formation of rocky planets. The outflow from supernovae and the stellar wind of large stars play an important part in shaping the interstellar medium.
Binary stars
The evolution of binary stars may be significantly different from the evolution of single stars of the same mass. If stars in a binary system are sufficiently close, when one of the stars expands to become a red giant it may overflow itsRoche lobe
In astronomy, the Roche lobe is the region around a star in a binary system within which orbiting material is gravitationally bound to that star. It is an approximately teardrop-shaped region bounded by a critical gravitational equipotential, ...
, the region around a star where material is gravitationally bound to that star, leading to transfer of material to the other. When the Roche lobe is overflowed, a variety of phenomena can result, including contact binaries
In astronomy, a contact binary is a binary star system whose component stars are so close that they touch each other or have merged to share their gaseous envelopes. A binary system whose stars share an envelope may also be called an overcontac ...
, common-envelope binaries, cataclysmic variables
In astronomy, cataclysmic variable stars (CVs) are stars which irregularly increase in brightness by a large factor, then drop back down to a quiescent state. They were initially called novae (), since ones with an outburst brightness visible to ...
, blue stragglers
A blue straggler is a main-sequence star in an open or globular cluster that is more luminous and bluer than stars at the main sequence turnoff point for the cluster. Blue stragglers were first discovered by Allan Sandage in 1953 while performing ...
, and type Ia supernova
A Type Ia supernova (read: "type one-A") is a type of supernova that occurs in binary systems (two stars orbiting one another) in which one of the stars is a white dwarf. The other star can be anything from a giant star to an even smaller whit ...
e. Mass transfer leads to cases such as the Algol paradox, where the most-evolved star in a system is the least massive.
The evolution of binary and higher-order star system
A star system or stellar system is a small number of stars that orbit each other, bound by gravitational attraction. A large group of stars bound by gravitation is generally called a '' star cluster'' or ''galaxy'', although, broadly speakin ...
s is intensely researched since so many stars have been found to be members of binary systems. Around half of Sun-like stars, and an even higher proportion of more massive stars, form in multiple systems and this may greatly influence such phenomena as novae and supernovae, the formation of certain types of star, and the enrichment of space with nucleosynthesis products.
The influence of binary star evolution on the formation of evolved massive stars such as luminous blue variable
Luminous blue variables (LBVs) are massive evolved stars that show unpredictable and sometimes dramatic variations in their spectra and brightness. They are also known as S Doradus variables after S Doradus, one of the brightest stars of the Larg ...
s, Wolf-Rayet stars, and the progenitors of certain classes of core collapse supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when ...
is still disputed. Single massive stars may be unable to expel their outer layers fast enough to form the types and numbers of evolved stars that are observed, or to produce progenitors that would explode as the supernovae that are observed. Mass transfer through gravitational stripping in binary systems is seen by some astronomers as the solution to that problem.
Distribution
 Stars are not spread uniformly across the universe, but are normally grouped into galaxies along with interstellar gas and dust. A typical large galaxy like the Milky Way contains hundreds of billions of stars. There are more than 2 trillion (1012) galaxies, though most are less than 10% the mass of the Milky Way. Overall, there are likely to be between and stars (more stars than all the grains of sand on planet
Stars are not spread uniformly across the universe, but are normally grouped into galaxies along with interstellar gas and dust. A typical large galaxy like the Milky Way contains hundreds of billions of stars. There are more than 2 trillion (1012) galaxies, though most are less than 10% the mass of the Milky Way. Overall, there are likely to be between and stars (more stars than all the grains of sand on planet Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
). Most stars are within galaxies, but between 10 and 50% of the starlight in large galaxy cluster
A galaxy cluster, or a cluster of galaxies, is a structure that consists of anywhere from hundreds to thousands of galaxies that are bound together by gravity, with typical masses ranging from 1014 to 1015 solar masses. They are the second-la ...
s may come from stars outside of any galaxy.
A multi-star system consists of two or more gravitationally bound stars that orbit each other. The simplest and most common multi-star system is a binary star, but systems of three or more stars exist. For reasons of orbital stability, such multi-star systems are often organized into hierarchical sets of binary stars. Larger groups are called star clusters. These range from loose stellar associations
A stellar association is a very loose star cluster, looser than both open clusters and globular clusters. Stellar associations will normally contain from 10 to 100 or more stars. The stars share a common origin, but have become gravitationally u ...
with only a few stars to open cluster
An open cluster is a type of star cluster made of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way galaxy, and ...
s with dozens to thousands of stars, up to enormous globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars. Globular clusters are bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards their centers. They can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of memb ...
s with hundreds of thousands of stars. Such systems orbit their host galaxy. The stars in an open or globular cluster all formed from the same giant molecular cloud
A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydrogen, ...
, so all members normally have similar ages and compositions.
Many stars are observed and most or all may have originally formed in gravitationally bound, multiple-star systems. This is particularly true for very massive O and B class stars, 80% of which are believed to be part of multiple-star systems. The proportion of single star systems increases with decreasing star mass, so that only 25% of red dwarfs are known to have stellar companions. As 85% of all stars are red dwarfs, more than two thirds of stars in the Milky Way are likely single red dwarfs.
In a 2017 study of the Perseus molecular cloud
The Perseus molecular cloud (Per MCld) is a nearby (~1000 ly) giant molecular cloud in the constellation of Perseus and contains over 10,000 solar masses of gas and dust covering an area of 6 by 2 degrees. Unlike the Orion molecular cloud it is ...
, astronomers found that most of the newly formed stars are in binary systems. In the model that best explained the data, all stars initially formed as binaries, though some binaries later split up and leave single stars behind.
 The nearest star to the Earth, apart from the Sun, is
The nearest star to the Earth, apart from the Sun, is Proxima Centauri
Proxima Centauri is a small, low-mass star located away from the Sun in the southern constellation of Centaurus. Its Latin name means the 'nearest tarof Centaurus'. It was discovered in 1915 by Robert Innes and is the nearest- ...
, away. Travelling at the orbital speed of the Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
, , it would take about 150,000 years to arrive. This is typical of stellar separations in galactic discs. Stars can be much closer to each other in the centres of galaxies and in globular clusters, or much farther apart in galactic halos.
Due to the relatively vast distances between stars outside the galactic nucleus, collisions between stars are thought to be rare. In denser regions such as the core of globular clusters or the galactic center, collisions can be more common. Such collisions can produce what are known as blue straggler
A blue straggler is a main-sequence star in an open or globular cluster that is more luminous and bluer than stars at the main sequence turnoff point for the cluster. Blue stragglers were first discovered by Allan Sandage in 1953 while performin ...
s. These abnormal stars have a higher surface temperature and thus are bluer than stars at the main sequence turnoff
The turnoff point for a star refers to the point on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram where it leaves the main sequence after its main fuel is exhaustedthe main sequence turnoff.
By plotting the turnoff points of individual stars in a star cluster ...
in the cluster to which they belong; in standard stellar evolution, blue stragglers would already have evolved off the main sequence and thus would not be seen in the cluster.
Characteristics
Almost everything about a star is determined by its initial mass, including such characteristics as luminosity, size, evolution, lifespan, and its eventual fate.Age
Most stars are between 1 billion and 10 billion years old. Some stars may even be close to 13.8 billion years old—the observedage of the universe
In physical cosmology, the age of the universe is the time elapsed since the Big Bang. Astronomers have derived two different measurements of the age of the universe:
a measurement based on direct observations of an early state of the universe, ...
. The oldest star yet discovered, HD 140283
HD 140283 (also known as the Methuselah star) is a metal-poor subgiant star about 190 light years away from the Earth in the constellation Libra, near the boundary with Ophiuchus in the Milky Way Galaxy. Its apparent magnitude is ...
, nicknamed Methuselah star, is an estimated 14.46 ± 0.8 billion years old. (Due to the uncertainty in the value, this age for the star does not conflict with the age of the universe, determined by the Planck satellite
''Planck'' was a space observatory operated by the European Space Agency (ESA) from 2009 to 2013, which mapped the anisotropies of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) at microwave and infrared frequencies, with high sensitivity and small ang ...
as 13.799 ± 0.021).
The more massive the star, the shorter its lifespan, primarily because massive stars have greater pressure on their cores, causing them to burn hydrogen more rapidly. The most massive stars last an average of a few million years, while stars of minimum mass (red dwarfs) burn their fuel very slowly and can last tens to hundreds of billions of years.
Chemical composition
When stars form in the present Milky Way galaxy, they are composed of about 71% hydrogen and 27% helium, as measured by mass, with a small fraction of heavier elements. Typically the portion of heavy elements is measured in terms of the iron content of the stellar atmosphere, as iron is a common element and its absorption lines are relatively easy to measure. The portion of heavier elements may be an indicator of the likelihood that the star has a planetary system. The star with the lowest iron content ever measured is the dwarf HE1327-2326, with only 1/200,000th the iron content of the Sun. By contrast, the super-metal-rich star μ Leonis has nearly double the abundance of iron as the Sun, while the planet-bearing star14 Herculis
14 Herculis or 14 Her is the Flamsteed designation of a K-type main-sequence star approximately 58.5 light-years away in the constellation Hercules. Because of its apparent magnitude, the star cannot be seen with the naked eye. As ...
has nearly triple the iron. Chemically peculiar star
In astrophysics, chemically peculiar stars (CP stars) are stars with distinctly unusual metal abundances, at least in their surface layers.
Classification
Chemically peculiar stars are common among hot main-sequence (hydrogen-burning) stars. Thes ...
s show unusual abundances of certain elements in their spectrum; especially chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and h ...
and rare earth element
The rare-earth elements (REE), also called the rare-earth metals or (in context) rare-earth oxides or sometimes the lanthanides ( yttrium and scandium are usually included as rare earths), are a set of 17 nearly-indistinguishable lustrous si ...
s. Stars with cooler outer atmospheres, including the Sun, can form various diatomic and polyatomic molecules.
Diameter
 Due to their great distance from the Earth, all stars except the Sun appear to the unaided eye as shining points in the night sky that
Due to their great distance from the Earth, all stars except the Sun appear to the unaided eye as shining points in the night sky that twinkle
Twinkle may refer to:
* Twinkling, the variation of brightness of distant objects
People
* Twinkle (singer) (1948–2015), born Lynn Annette Ripley, English singer-songwriter
* Twinkle Khanna, Indian movie actress
* Twinkle Bajpai, female conte ...
because of the effect of the Earth's atmosphere. The Sun is close enough to the Earth to appear as a disk instead, and to provide daylight. Other than the Sun, the star with the largest apparent size is R Doradus
R Doradus (HD 29712 or P Doradus) is a red giant variable star in the far-southern constellation Dorado. Its distance from Earth is . Having a uniform disk diameter of , it is thought to be the extrasolar star with the largest apparen ...
, with an angular diameter
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular distance describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the visual angle, and in optics, it i ...
of only 0.057 arcsecond
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The na ...
s.
The disks of most stars are much too small in angular size
The angular diameter, angular size, apparent diameter, or apparent size is an angular distance describing how large a sphere or circle appears from a given point of view. In the vision sciences, it is called the visual angle, and in optics, it i ...
to be observed with current ground-based optical telescopes, and so interferometer
Interferometry is a technique which uses the '' interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber o ...
telescopes are required to produce images of these objects. Another technique for measuring the angular size of stars is through occultation
An occultation is an event that occurs when one object is hidden from the observer by another object that passes between them. The term is often used in astronomy, but can also refer to any situation in which an object in the foreground blocks ...
. By precisely measuring the drop in brightness of a star as it is occulted by the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width ...
(or the rise in brightness when it reappears), the star's angular diameter can be computed.
Stars range in size from neutron stars, which vary anywhere from 20 to in diameter, to supergiant
Supergiants are among the most massive and most luminous stars. Supergiant stars occupy the top region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram with absolute visual magnitudes between about −3 and −8. The temperature range of supergiant stars s ...
s like Betelgeuse
Betelgeuse is a red supergiant of spectral type M1-2 and one of the largest stars visible to the naked eye. It is usually the tenth-brightest star in the night sky and, after Rigel, the second-brightest in the constellation of Orio ...
in the Orion constellation
Orion is a prominent constellation located on the celestial equator and visible throughout the world. It is one of the most conspicuous and recognizable constellations in the night sky. It is named after Orion, a hunter in Greek mythology. It ...
, which has a diameter about 1,000 times that of the Sun with a much lower density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematicall ...
.
Kinematics
 The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding galaxy. The components of motion of a star consist of the
The motion of a star relative to the Sun can provide useful information about the origin and age of a star, as well as the structure and evolution of the surrounding galaxy. The components of motion of a star consist of the radial velocity
The radial velocity or line-of-sight velocity, also known as radial speed or range rate, of a target with respect to an observer is the rate of change of the distance or range between the two points. It is equivalent to the vector projection ...
toward or away from the Sun, and the traverse angular movement, which is called its proper motion.
Radial velocity is measured by the doppler shift
The Doppler effect or Doppler shift (or simply Doppler, when in context) is the change in frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the wave source. It is named after the Austrian physicist Christian Doppler, who ...
of the star's spectral lines and is given in units of km/ s. The proper motion of a star, its parallax, is determined by precise astrometric measurements in units of milli-arc second
A minute of arc, arcminute (arcmin), arc minute, or minute arc, denoted by the symbol , is a unit of angular measurement equal to of one degree. Since one degree is of a turn (or complete rotation), one minute of arc is of a turn. The nau ...
s (mas) per year. With knowledge of the star's parallax and its distance, the proper motion velocity can be calculated. Together with the radial velocity, the total velocity can be calculated. Stars with high rates of proper motion are likely to be relatively close to the Sun, making them good candidates for parallax measurements.
When both rates of movement are known, the space velocity of the star relative to the Sun or the galaxy can be computed. Among nearby stars, it has been found that younger population I stars have generally lower velocities than older, population II stars. The latter have elliptical orbits that are inclined to the plane of the galaxy. A comparison of the kinematics of nearby stars has allowed astronomers to trace their origin to common points in giant molecular clouds, and are referred to as stellar association
A stellar association is a very loose star cluster, looser than both open clusters and globular clusters. Stellar associations will normally contain from 10 to 100 or more stars. The stars share a common origin, but have become gravitationally ...
s.
Magnetic field
 The
The magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and t ...
of a star is generated within regions of the interior where convective circulation occurs. This movement of conductive plasma functions like a dynamo
"Dynamo Electric Machine" (end view, partly section, )
A dynamo is an electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator. Dynamos were the first electrical generators capable of delivering power for industry, and the foundat ...
, wherein the movement of electrical charges induce magnetic fields, as does a mechanical dynamo. Those magnetic fields have a great range that extend throughout and beyond the star. The strength of the magnetic field varies with the mass and composition of the star, and the amount of magnetic surface activity depends upon the star's rate of rotation. This surface activity produces starspot
Starspots are stellar phenomena, so-named by analogy with sunspots.
Spots as small as sunspots have not been detected on other stars, as they would cause undetectably small fluctuations in brightness. The commonly observed starspots are in gen ...
s, which are regions of strong magnetic fields and lower than normal surface temperatures. Coronal loop
In solar physics, a coronal loop is a well-defined arch-like structure in the Sun's atmosphere made up of relatively dense plasma confined and isolated from the surrounding medium by magnetic flux tubes. Coronal loops begin and end at two f ...
s are arching magnetic field flux lines that rise from a star's surface into the star's outer atmosphere, its corona. The coronal loops can be seen due to the plasma they conduct along their length. Stellar flare
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , ''asteriskos'', "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often vo ...
s are bursts of high-energy particles that are emitted due to the same magnetic activity.
Young, rapidly rotating stars tend to have high levels of surface activity because of their magnetic field. The magnetic field can act upon a star's stellar wind, functioning as a brake to gradually slow the rate of rotation with time. Thus, older stars such as the Sun have a much slower rate of rotation and a lower level of surface activity. The activity levels of slowly rotating stars tend to vary in a cyclical manner and can shut down altogether for periods of time. During
the Maunder Minimum, for example, the Sun underwent a
70-year period with almost no sunspot activity.
Mass
One of the most massive stars known isEta Carinae
Eta Carinae (η Carinae, abbreviated to η Car), formerly known as Eta Argus, is a stellar system containing at least two stars with a combined luminosity greater than five million times that of the Sun, located around distant in th ...
, which,
with 100–150 times as much mass as the Sun, will have a lifespan of only several million years. Studies of the most massive open clusters suggests as a rough upper limit for stars in the current era of the universe. This
represents an empirical value for the theoretical limit on the mass of forming stars due to increasing radiation pressure on the accreting gas cloud. Several stars in the R136
R136 (formerly known as RMC 136 from the Radcliffe Observatory Magellanic Clouds catalogue) is the central concentration of stars in the NGC 2070 star cluster, which lies at the centre of the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Wh ...
cluster in the Large Magellanic Cloud
The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), or Nubecula Major, is a satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. At a distance of around 50 kiloparsecs (≈160,000 light-years), the LMC is the second- or third-closest galaxy to the Milky Way, after the ...
have been measured with larger masses, but
it has been determined that they could have been created through the collision and merger of massive stars in close binary systems, sidestepping the 150 limit on massive star formation.
 The first stars to form after the Big Bang may have been larger, up to 300 , due
to the complete absence of elements heavier than
The first stars to form after the Big Bang may have been larger, up to 300 , due
to the complete absence of elements heavier than lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid ...
in their composition. This generation of supermassive population III stars
During 1944, Walter Baade categorized groups of stars within the Milky Way into stellar populations.
In the abstract of the article by Baade, he recognizes that Jan Oort originally conceived this type of classification in 1926:
Baade noticed th ...
is likely to have existed in the very early universe (i.e., they are observed to have a high redshift), and may have started the production of chemical elements heavier than hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
that are needed for the later formation of planets and life
Life is a quality that distinguishes matter that has biological processes, such as Cell signaling, signaling and self-sustaining processes, from that which does not, and is defined by the capacity for Cell growth, growth, reaction to Stimu ...
. In June 2015, astronomers reported evidence for Population III stars in the Cosmos Redshift 7 galaxy at .
With a mass only 80 times that of Jupiter (), 2MASS J0523-1403
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different elementa ...
is the smallest known star undergoing nuclear fusion in its core. For
stars with metallicity similar to the Sun, the theoretical minimum mass the star can have and still undergo fusion at the core, is estimated to be about 75 . When the metallicity is very low, the minimum star size seems to be about 8.3% of the solar mass, or about 87 . Smaller bodies called brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs (also called failed stars) are substellar objects that are not massive enough to sustain nuclear fusion of ordinary hydrogen (hydrogen-1, 1H) into helium in their cores, unlike a main sequence, main-sequence star. Instead, they have ...
s, occupy a poorly defined grey area between stars and gas giant
A gas giant is a giant planet composed mainly of hydrogen and helium. Gas giants are also called failed stars because they contain the same basic elements as a star. Jupiter and Saturn are the gas giants of the Solar System. The term "gas giant" ...
s.
The combination of the radius and the mass of a star determines its surface gravity. Giant stars have a much lower surface gravity than do main sequence stars, while the opposite is the case for degenerate, compact stars such as white dwarfs. The surface gravity can influence the appearance of a star's spectrum, with higher gravity causing a broadening of the absorption line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to ident ...
s.
Rotation
The rotation rate of stars can be determined through spectroscopic measurement, or more exactly determined by tracking theirstarspot
Starspots are stellar phenomena, so-named by analogy with sunspots.
Spots as small as sunspots have not been detected on other stars, as they would cause undetectably small fluctuations in brightness. The commonly observed starspots are in gen ...
s. Young stars can have a rotation greater than 100 km/s at the equator. The B-class star Achernar
Achernar is the brightest star in the constellation of Eridanus, and the ninth-brightest in the night sky. It has the Bayer designation Alpha Eridani, which is Latinized from α Eridani and abbreviated Alpha Eri or α Eri. The name ...
, for example, has an equatorial velocity of about 225 km/s or greater, causing its equator to bulge outward and giving it an equatorial diameter that is more than 50% greater than between the poles. This rate of rotation is just below the critical velocity of 300 km/s at which speed the star would break apart. By contrast, the Sun rotates once every 25–35 days depending on latitude, with an equatorial velocity of 1.93 km/s. A main sequence star's magnetic field and the stellar wind serve to slow its rotation by a significant amount as it evolves on the main sequence.
Degenerate star
In astronomy, the term compact star (or compact object) refers collectively to white dwarfs, neutron stars, and black holes. It would grow to include exotic stars if such hypothetical, dense bodies are confirmed to exist. All compact objects h ...
s have contracted into a compact mass, resulting in a rapid rate of rotation. However they have relatively low rates of rotation compared to what would be expected by conservation of angular momentum—the tendency of a rotating body to compensate for a contraction in size by increasing its rate of spin. A large portion of the star's angular momentum is dissipated as a result of mass loss through the stellar wind. In spite of this, the rate of rotation for a pulsar can be very rapid. The pulsar at the heart of the Crab nebula
The Crab Nebula (catalogue designations Messier object, M1, New General Catalogue, NGC 1952, Taurus (constellation), Taurus A) is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus (constellation), Taurus. The common name ...
, for example, rotates 30 times per second. The rotation rate of the pulsar will gradually slow due to the emission of radiation.
Temperature
The surface temperature of a main sequence star is determined by the rate of energy production of its core and by its radius, and is often estimated from the star'scolor index
In astronomy, the color index is a simple numerical expression that determines the color of an object, which in the case of a star gives its temperature. The lower the color index, the more blue (or hotter) the object is. Conversely, the larg ...
. The temperature is normally given in terms of an effective temperature
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature of a black body that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's surface temperature ...
, which is the temperature of an idealized black body that radiates its energy at the same luminosity per surface area as the star. The effective temperature is only representative of the surface, as the temperature increases toward the core. The temperature in the core region of a star is several million kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and ph ...
s.
The stellar temperature will determine the rate of ionization of various elements, resulting in characteristic absorption lines in the spectrum. The surface temperature of a star, along with its visual absolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude () is a measure of the luminosity of a celestial object on an inverse logarithmic astronomical magnitude scale. An object's absolute magnitude is defined to be equal to the apparent magnitude that the object would have if it we ...
and absorption features, is used to classify a star (see classification below).
Massive main sequence stars can have surface temperatures of 50,000 K. Smaller stars such as the Sun have surface temperatures of a few thousand K. Red giants have relatively low surface temperatures of about 3,600 K; but they have a high luminosity due to their large exterior surface area.
Radiation
The energy produced by stars, a product of nuclear fusion, radiates to space as bothelectromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible ...
and particle radiation
Particle radiation is the radiation of energy by means of fast-moving subatomic particles. Particle radiation is referred to as a particle beam if the particles are all moving in the same direction, similar to a light beam.
Due to the wave–pa ...
. The particle radiation emitted by a star is manifested as the stellar wind, which
streams from the outer layers as electrically charged protons and alpha and beta particle
A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation (symbol β), is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus during the process of beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β� ...
s. A steady stream of almost massless neutrinos emanate directly from the star's core.
The production of energy at the core is the reason stars shine so brightly: every time two or more atomic nuclei fuse together to form a single atomic nucleus
The atomic nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom, discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden experiments, Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After th ...
of a new heavier element, gamma ray
A gamma ray, also known as gamma radiation (symbol γ or \gamma), is a penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nucleus, atomic nuclei. It consists of the shortest wavelength electromagnetic wav ...
photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are Massless particle, massless ...
s are released from the nuclear fusion product. This energy is converted to other forms of electromagnetic energy
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions o ...
of lower frequency, such as visible light, by the time it reaches the star's outer layers.
The color of a star, as determined by the most intense frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit of time. It is also occasionally referred to as ''temporal frequency'' for clarity, and is distinct from '' angular frequency''. Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) which is ...
of the visible light, depends on the temperature of the star's outer layers, including its photosphere
The photosphere is a star's outer shell from which light is radiated.
The term itself is derived from Ancient Greek roots, φῶς, φωτός/''phos, photos'' meaning "light" and σφαῖρα/''sphaira'' meaning "sphere", in reference to it ...
. Besides visible light, stars emit forms of electromagnetic radiation that are invisible to the human eye. In fact, stellar electromagnetic radiation spans the entire electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.
The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from ...
, from the longest wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tr ...
s of radio waves
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz ( GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (s ...
through infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from aroun ...
, visible light, ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiati ...
, to the shortest of X-ray
X-rays (or rarely, ''X-radiation'') are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. In many languages, it is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it in 1895 and named it ' ...
s, and gamma rays. From the standpoint of total energy emitted by a star, not all components of stellar electromagnetic radiation are significant, but all frequencies provide insight into the star's physics.
Using the stellar spectrum
Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, ultraviolet, X-ray, infrared and radio waves that radiate from stars and other ...
, astronomers can determine the surface temperature, surface gravity
The surface gravity, ''g'', of an astronomical object is the gravitational acceleration experienced at its surface at the equator, including the effects of rotation. The surface gravity may be thought of as the acceleration due to gravity experien ...
, metallicity and rotation
Rotation, or spin, is the circular movement of an object around a '' central axis''. A two-dimensional rotating object has only one possible central axis and can rotate in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction. A three-dimensional ...
al velocity of a star. If the distance of the star is found, such as by measuring the parallax, then the luminosity of the star can be derived. The mass, radius, surface gravity, and rotation period can then be estimated based on stellar models. (Mass can be calculated for stars in binary systems by measuring their orbital velocities and distances. Gravitational microlensing
Gravitational microlensing is an astronomical phenomenon due to the gravitational lens effect. It can be used to detect objects that range from the mass of a planet to the mass of a star, regardless of the light they emit. Typically, astronomers ...
has been used to measure the mass of a single star.) With these parameters, astronomers can estimate the age of the star.
Luminosity
The luminosity of a star is the amount of light and other forms ofradiant energy
Radiant may refer to:
Computers, software, and video games
* Radiant (software), a content management system
* GtkRadiant, a level editor created by id Software for their games
* Radiant AI, a technology developed by Bethesda Softworks for '' ...
it radiates per unit of time. It has units of power
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may ...
. The luminosity of a star is determined by its radius and surface temperature. Many stars do not radiate uniformly across their entire surface. The rapidly rotating star Vega
Vega is the brightest star in the northern
Northern may refer to the following:
Geography
* North, a point in direction
* Northern Europe, the northern part or region of Europe
* Northern Highland, a region of Wisconsin, United Sta ...
, for example, has a higher energy flux Energy flux is the rate of transfer of energy through a surface. The quantity is defined in two different ways, depending on the context:
# Total rate of energy transfer (not per unit area); SI units: W = J⋅s−1.
# Specific rate of energy transfe ...
(power per unit area) at its poles than along its equator.
Patches of the star's surface with a lower temperature and luminosity than average are known as starspots
Starspots are stellar phenomena, so-named by analogy with sunspots.
Spots as small as sunspots have not been detected on other stars, as they would cause undetectably small fluctuations in brightness. The commonly observed starspots are in gene ...
. Small, ''dwarf'' stars such as the Sun generally have essentially featureless disks with only small starspots. ''Giant'' stars have much larger, more obvious starspots, and
they exhibit strong stellar limb darkening
Limb darkening is an optical effect seen in stars (including the Sun), where the central part of the disk appears brighter than the edge, or ''limb''. Its understanding offered early solar astronomers an opportunity to construct models with such ...
. That is, the brightness decreases towards the edge of the stellar disk. Red dwarf flare star
A flare star is a variable star that can undergo unpredictable dramatic increases in brightness for a few minutes. It is believed that the flares on flare stars are analogous to solar flares in that they are due to the magnetic energy stored in th ...
s such as UV Ceti
Luyten 726-8, also known as Gliese 65, is a binary star system that is one of Earth's nearest neighbors, at about 8.7 light years from Earth in the constellation Cetus. The two component stars are both flare stars with the variable star ...
may possess prominent starspot features.
Magnitude
The apparentbrightness
Brightness is an attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to be radiating or reflecting light. In other words, brightness is the perception elicited by the luminance of a visual target. The perception is not linear to luminance, ...
of a star is expressed in terms of its apparent magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's li ...
. It is a function of the star's luminosity, its distance from Earth, the extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds ( taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed ...
effect of interstellar dust
Cosmic dust, also called extraterrestrial dust, star dust or space dust, is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 micrometers). Larger particles are c ...
and gas, and the altering of the star's light as it passes through Earth's atmosphere. Intrinsic or absolute magnitude is directly related to a star's luminosity, and is the apparent magnitude a star would be if the distance between the Earth and the star were 10 parsecs (32.6 light-years).
Both the apparent and absolute magnitude scales are logarithmic units: one whole number difference in magnitude is equal to a brightness variation of about 2.5 times (the 5th root of 100 or approximately 2.512). This means that a first magnitude star
First-magnitude stars are the brightest stars in the night sky, with apparent magnitudes lower (i.e. brighter) than +1.50. Hipparchus, in the 1st century B.C., introduced the magnitude scale. He allocated first magnitude to the 20 brightest stars ...
(+1.00) is about 2.5 times brighter than a second magnitude (+2.00) star, and about 100 times brighter than a sixth magnitude star
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the brightness of a star or other astronomical object observed from Earth. An object's apparent magnitude depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance from Earth, and any extinction of the object's lig ...
(+6.00). The faintest stars visible to the naked eye under good seeing conditions are about magnitude +6.
On both apparent and absolute magnitude scales, the smaller the magnitude number, the brighter the star; the larger the magnitude number, the fainter the star. The brightest stars, on either scale, have negative magnitude numbers. The variation in brightness (Δ''L'') between two stars is calculated by subtracting the magnitude number of the brighter star (''m''b) from the magnitude number of the fainter star (''m''f), then using the difference as an exponent for the base number 2.512; that is to say:
:
:
Relative to both luminosity and distance from Earth, a star's absolute magnitude (''M'') and apparent magnitude (''m'') are not equivalent; for example, the bright star Sirius has an apparent magnitude of −1.44, but it has an absolute magnitude of +1.41.
The Sun has an apparent magnitude of −26.7, but its absolute magnitude is only +4.83. Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky as seen from Earth, is approximately 23 times more luminous than the Sun, while Canopus
Canopus is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Carina and the second-brightest star in the night sky. It is also designated α Carinae, which is Latinised to Alpha Carinae. With a visual apparent magnitude of ...
, the second brightest star in the night sky with an absolute magnitude of −5.53, is approximately 14,000 times more luminous than the Sun. Despite Canopus being vastly more luminous than Sirius, the latter star appears the brighter of the two. This is because Sirius is merely 8.6 light-years from the Earth, while Canopus is much farther away at a distance of 310 light-years.
The most luminous known stars have absolute magnitudes of roughly −12, corresponding to 6 million times the luminosity of the Sun. Theoretically, the least luminous stars are at the lower limit of mass at which stars are capable of supporting nuclear fusion of hydrogen in the core; stars just above this limit have been located in the NGC 6397
NGC 6397 (also known as Caldwell 86) is a globular cluster in the constellation Ara. It is located about 7,800 light-years from Earth, making it one of the two nearest globular clusters to Earth (the other one being Messier 4). The cluster con ...
cluster. The faintest red dwarfs in the cluster are absolute magnitude 15, while a 17th absolute magnitude white dwarf has been discovered.
Classification
The current stellar classification system originated in the early 20th century, when stars were classified from ''A'' to ''Q'' based on the strength of thehydrogen line
The hydrogen line, 21 centimeter line, or H I line is the electromagnetic radiation spectral line that is created by a change in the energy state of neutral hydrogen atoms. This electromagnetic radiation has a precise frequency of , w ...
. It was thought that the hydrogen line strength was a simple linear function of temperature. Instead, it was more complicated: it strengthened with increasing temperature, peaked near 9000 K, and then declined at greater temperatures. The classifications were since reordered by temperature, on which the modern scheme is based.
Stars are given a single-letter classification according to their spectra, ranging from type ''O'', which are very hot, to ''M'', which are so cool that molecules may form in their atmospheres. The main classifications in order of decreasing surface temperature are: ''O, B, A, F, G, K'', and ''M''. A variety of rare spectral types are given special classifications. The most common of these are types ''L'' and ''T'', which classify the coldest low-mass stars and brown dwarfs. Each letter has 10 sub-divisions, numbered from 0 to 9, in order of decreasing temperature. However, this system breaks down at extreme high temperatures as classes ''O0'' and ''O1'' may not exist.
In addition, stars may be classified by the luminosity effects found in their spectral lines, which correspond to their spatial size and is determined by their surface gravity. These range from ''0'' (hypergiant
A hypergiant (luminosity class 0 or Ia+) is a very rare type of star that has an extremely high luminosity, mass, size and mass loss because of its extreme stellar winds. The term ''hypergiant'' is defined as luminosity class 0 (zero) in the MKK ...
s) through ''III'' (giants
A giant is a being of human appearance, sometimes of prodigious size and strength, common in folklore.
Giant(s) or The Giant(s) may also refer to:
Mythology and religion
*Giants (Greek mythology)
*Jötunn, a Germanic term often translated as 'gi ...
) to ''V'' (main sequence dwarfs); some authors add ''VII'' (white dwarfs). Main sequence stars fall along a narrow, diagonal band when graphed according to their absolute magnitude and spectral type. The Sun is a main sequence ''G2V'' yellow dwarf of intermediate temperature and ordinary size.
There is additional nomenclature in the form of lower-case letters added to the end of the spectral type to indicate peculiar features of the spectrum. For example, an "''e''" can indicate the presence of emission lines; "''m''" represents unusually strong levels of metals, and "''var''" can mean variations in the spectral type.
White dwarf stars have their own class that begins with the letter ''D''. This is further sub-divided into the classes ''DA'', ''DB'', ''DC'', ''DO'', ''DZ'', and ''DQ'', depending on the types of prominent lines found in the spectrum. This is followed by a numerical value that indicates the temperature.
Variable stars
 Variable stars have periodic or random changes in luminosity because of intrinsic or extrinsic properties. Of the intrinsically variable stars, the primary types can be subdivided into three principal groups.
During their stellar evolution, some stars pass through phases where they can become pulsating variables. Pulsating variable stars vary in radius and luminosity over time, expanding and contracting with periods ranging from minutes to years, depending on the size of the star. This category includes Cepheid and Cepheid-like stars, and long-period variables such as
Variable stars have periodic or random changes in luminosity because of intrinsic or extrinsic properties. Of the intrinsically variable stars, the primary types can be subdivided into three principal groups.
During their stellar evolution, some stars pass through phases where they can become pulsating variables. Pulsating variable stars vary in radius and luminosity over time, expanding and contracting with periods ranging from minutes to years, depending on the size of the star. This category includes Cepheid and Cepheid-like stars, and long-period variables such as Mira
Mira (), designation Omicron Ceti (ο Ceti, abbreviated Omicron Cet, ο Cet), is a red-giant star estimated to be 200–400 light-years from the Sun in the constellation Cetus.
ο Ceti is a binary stellar system, consisting of a va ...
.
Eruptive variables are stars that experience sudden increases in luminosity because of flares or mass ejection events. This group includes protostars, Wolf-Rayet stars, and flare stars, as well as giant and supergiant stars.
Cataclysmic or explosive variable stars are those that undergo a dramatic change in their properties. This group includes nova
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramati ...
e and supernovae. A binary star system that includes a nearby white dwarf can produce certain types of these spectacular stellar explosions, including the nova and a Type 1a supernova. The explosion is created when the white dwarf accretes hydrogen from the companion star, building up mass until the hydrogen undergoes fusion. Some novae are recurrent, having periodic outbursts of moderate amplitude.
Stars can vary in luminosity because of extrinsic factors, such as eclipsing binaries, as well as rotating stars that produce extreme starspots. A notable example of an eclipsing binary is Algol, which regularly varies in magnitude from 2.1 to 3.4 over a period of 2.87 days.
Structure
The interior of a stable star is in a state ofhydrostatic equilibrium
In fluid mechanics, hydrostatic equilibrium (hydrostatic balance, hydrostasy) is the condition of a fluid or plastic solid at rest, which occurs when external forces, such as gravity, are balanced by a pressure-gradient force. In the planetar ...
: the forces on any small volume almost exactly counterbalance each other. The balanced forces are inward gravitational force and an outward force due to the pressure gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function of several variables is the vector field (or vector-valued function) \nabla f whose value at a point p is the "direction and rate of fastest increase". If the gr ...
within the star. The pressure gradient
In atmospheric science, the pressure gradient (typically of air but more generally of any fluid) is a physical quantity that describes in which direction and at what rate the pressure increases the most rapidly around a particular location. The ...
is established by the temperature gradient of the plasma; the outer part of the star is cooler than the core. The temperature at the core of a main sequence or giant star is at least on the order of 107 K. The resulting temperature and pressure at the hydrogen-burning core of a main sequence star are sufficient for nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles (neutrons or protons). The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifest ...
to occur and for sufficient energy to be produced to prevent further collapse of the star.
As atomic nuclei are fused in the core, they emit energy in the form of gamma rays. These photons interact with the surrounding plasma, adding to the thermal energy at the core. Stars on the main sequence convert hydrogen into helium, creating a slowly but steadily increasing proportion of helium in the core. Eventually the helium content becomes predominant, and energy production ceases at the core. Instead, for stars of more than 0.4 , fusion occurs in a slowly expanding shell around the degenerate
Degeneracy, degenerate, or degeneration may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Degenerate'' (album), a 2010 album by the British band Trigger the Bloodshed
* Degenerate art, a term adopted in the 1920s by the Nazi Party in Germany to descr ...
helium core.
In addition to hydrostatic equilibrium, the interior of a stable star will maintain an energy balance of thermal equilibrium
Two physical systems are in thermal equilibrium if there is no net flow of thermal energy between them when they are connected by a path permeable to heat. Thermal equilibrium obeys the zeroth law of thermodynamics. A system is said to be in ...
. There is a radial temperature gradient throughout the interior that results in a flux of energy flowing toward the exterior. The outgoing flux of energy leaving any layer within the star will exactly match the incoming flux from below.
The radiation zone
A radiation zone, or radiative region is a layer of a star's interior where energy is primarily transported toward the exterior by means of radiative diffusion and thermal conduction, rather than by convection. Energy travels through the radiatio ...
is the region of the stellar interior where the flux of energy outward is dependent on radiative heat transfer, since convective heat transfer is inefficient in that zone. In this region the plasma will not be perturbed, and any mass motions will die out. Where this is not the case, then the plasma becomes unstable and convection will occur, forming a convection zone
A convection zone, convective zone or convective region of a star is a layer which is unstable due to convection. Energy is primarily or partially transported by convection in such a region. In a radiation zone, energy is transported by radiatio ...
. This can occur, for example, in regions where very high energy fluxes occur, such as near the core or in areas with high opacity
Opacity or opaque may refer to:
* Impediments to (especially, visible) light:
** Opacities, absorption coefficients
** Opacity (optics), property or degree of blocking the transmission of light
* Metaphors derived from literal optics:
** In lingu ...
(making radiatative heat transfer inefficient) as in the outer envelope.
The occurrence of convection in the outer envelope of a main sequence star depends on the star's mass. Stars with several times the mass of the Sun have a convection zone deep within the interior and a radiative zone in the outer layers. Smaller stars such as the Sun are just the opposite, with the convective zone located in the outer layers. Red dwarf stars with less than 0.4 are convective throughout, which prevents the accumulation of a helium core. For most stars the convective zones will vary over time as the star ages and the constitution of the interior is modified.
 The photosphere is that portion of a star that is visible to an observer. This is the layer at which the plasma of the star becomes transparent to photons of light. From here, the energy generated at the core becomes free to propagate into space. It is within the photosphere that
The photosphere is that portion of a star that is visible to an observer. This is the layer at which the plasma of the star becomes transparent to photons of light. From here, the energy generated at the core becomes free to propagate into space. It is within the photosphere that sun spots
Sunspots are phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as temporary spots that are darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. S ...
, regions of lower than average temperature, appear.
Above the level of the photosphere is the stellar atmosphere. In a main sequence star such as the Sun, the lowest level of the atmosphere, just above the photosphere, is the thin chromosphere
A chromosphere ("sphere of color") is the second layer of a star's atmosphere, located above the photosphere and below the solar transition region and corona. The term usually refers to the Sun's chromosphere, but not exclusively.
In the S ...
region, where spicules
Spicules are any of various small needle-like anatomical structures occurring in organisms
Spicule may also refer to:
* Spicule (sponge), small skeletal elements of sea sponges
* Spicule (nematode), reproductive structures found in male nematodes ...
appear and stellar flares begin. Above this is the transition region, where the temperature rapidly increases within a distance of only . Beyond this is the corona
Corona (from the Latin for 'crown') most commonly refers to:
* Stellar corona, the outer atmosphere of the Sun or another star
* Corona (beer), a Mexican beer
* Corona, informal term for the coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, which causes the COVID-19 di ...
, a volume of super-heated plasma that can extend outward to several million kilometres. The existence of a corona appears to be dependent on a convective zone in the outer layers of the star. Despite its high temperature, the corona emits very little light, due to its low gas density. The corona region of the Sun is normally only visible during a solar eclipse
A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby obscuring the view of the Sun from a small part of the Earth, totally or partially. Such an alignment occurs during an eclipse season, approximately every six mo ...
.
From the corona, a stellar wind of plasma particles expands outward from the star, until it interacts with the interstellar medium. For the Sun, the influence of its solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the ...
extends throughout a bubble-shaped region called the heliosphere
The heliosphere is the magnetosphere, astrosphere and outermost atmospheric layer of the Sun. It takes the shape of a vast, bubble-like region of space. In plasma physics terms, it is the cavity formed by the Sun in the surrounding interst ...
.
Nuclear fusion reaction pathways
When nuclei fuse, the mass of the fused product is less than the mass of the original parts. This lost mass is converted to electromagnetic energy, according to themass–energy equivalence
In physics, mass–energy equivalence is the relationship between mass and energy in a system's rest frame, where the two quantities differ only by a multiplicative constant and the units of measurement. The principle is described by the physicis ...
relationship . A variety of nuclear fusion reactions take place in the cores of stars, that depend upon their mass and composition.
The hydrogen fusion process is temperature-sensitive, so a moderate increase in the core temperature will result in a significant increase in the fusion rate. As a result, the core temperature of main sequence stars only varies from 4 million kelvin for a small M-class star to 40 million kelvin for a massive O-class star.
In the Sun, with a 16-million-kelvin core, hydrogen fuses to form helium in the proton–proton chain reaction:
:4 1H → 2 2H + 2 e+ + 2 νe(2 x 0.4 M eV)
:2 e+ + 2 e− → 2 γ (2 x 1.0 MeV)
:21H + 22H → 2 3He + 2 γ (2 x 5.5 MeV)
:23He → 4He + 21H (12.9 MeV)
There are a couple other paths, in which He and He combine to form Be, which eventually (with the addition of another proton) yields two He, a gain of one.
All these reactions result in the overall reaction:
:41H → 4He + 2γ + 2νe (26.7 MeV)
where γ is a gamma ray photon, νe is a neutrino, and H and He are isotopes of hydrogen and helium, respectively. The energy released by this reaction is in millions of electron volts. Each individual reaction produces only a tiny amount of energy, but because enormous numbers of these reactions occur constantly, they produce all the energy necessary to sustain the star's radiation output. In comparison, the combustion of two hydrogen gas molecules with one oxygen gas molecule releases only 5.7 eV.
In more massive stars, helium is produced in a cycle of reactions catalyzed
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycl ...
by carbon called the carbon-nitrogen-oxygen cycle
The CNO cycle (for carbon–nitrogen–oxygen; sometimes called Bethe–Weizsäcker cycle after Hans Albrecht Bethe and Carl Friedrich von Weizsäcker) is one of the two known sets of fusion reactions by which stars convert hydrogen to heliu ...
.
In evolved stars with cores at 100 million kelvin and masses between 0.5 and 10 , helium can be transformed into carbon in the triple-alpha process
The triple-alpha process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions by which three helium-4 nuclei (alpha particles) are transformed into carbon.
Triple-alpha process in stars
Helium accumulates in the cores of stars as a result of the proton–pr ...
that uses the intermediate element beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with other elements to form m ...
:
:4He + 4He + 92 keV → 8*Be
:4He + 8*Be + 67 keV → 12*C
:12*C → 12C + γ + 7.4 MeV
For an overall reaction of:
 :34He → 12C + γ + 7.2 MeV
In massive stars, heavier elements can be burned in a contracting core through the
:34He → 12C + γ + 7.2 MeV
In massive stars, heavier elements can be burned in a contracting core through the neon-burning process
The neon-burning process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions that take place in evolved massive stars with at least 8 Solar masses. Neon burning requires high temperatures and densities (around 1.2×109 K or 100 keV and 4×109 kg/m3).
At suc ...
and oxygen-burning process
The oxygen-burning process is a set of nuclear fusion reactions that take place in massive stars that have used up the lighter elements in their cores. Oxygen-burning is preceded by the neon-burning process and succeeded by the silicon-burning pr ...
. The final stage in the stellar nucleosynthesis process is the silicon-burning process
In astrophysics, silicon burning is a very brief sequence of nuclear fusion reactions that occur in massive stars with a minimum of about 8–11 solar masses. Silicon burning is the final stage of fusion for massive stars that have run out of the f ...
that results in the production of the stable isotope iron-56. Any further fusion would be an endothermic process that consumes energy, and so further energy can only be produced through gravitational collapse.
See also
*Fusor (astronomy)
Fusor is a proposed term for an astronomical object which is capable of core fusion. The term is a more inclusive term than "star".
Motivation
To help clarify the nomenclature of celestial bodies, Gibor BasriDr. Gibor Basri is a professor o ...
* Outline of astronomy
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to astronomy:
Astronomy – studies the universe beyond Earth, including its formation and development, and the evolution, physics, chemistry, meteorology, and motion of ce ...
* Sidereal time
Sidereal time (as a unit also sidereal day or sidereal rotation period) (sidereal ) is a timekeeping system that astronomers use to locate celestial objects. Using sidereal time, it is possible to easily point a telescope to the proper coor ...
* Star clock
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by its gravity. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night, but their immense distances from Earth ma ...
s
* Star count
Star counts are bookkeeping surveys of stars and the statistical and geometrical methods used to correct the survey data for bias. The surveys are most often made of nearby stars in the Milky Way galaxy.
One of the interests of astronomy is to de ...
* Stars and planetary systems in fiction
References
External links
* * * * * {{Authority control * Stellar astronomy Concepts in astronomy Light sources