Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Soviet occupation of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina took place from June 28 to July 3, 1940, as a result of an ultimatum by the
East Central Europe between the two World Wars
' On August 2, 1940, the
On August 2, 1940, the
 The
The
 On August 23, 1939, the
On August 23, 1939, the

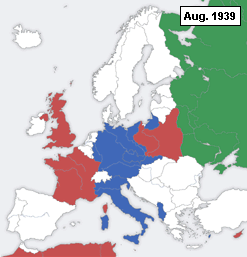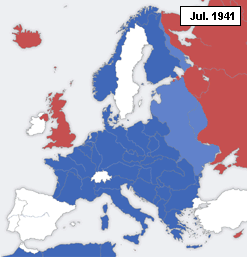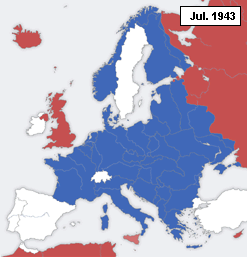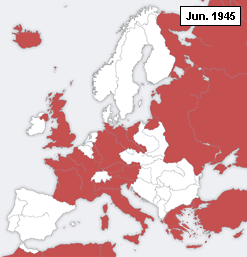 Assured by the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact of Soviet non-interference, Germany started World War II one week later by invading Poland from the west on September 1, 1939. The Soviet Union attacked Poland from the east on September 17, and by October 6,
Assured by the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact of Soviet non-interference, Germany started World War II one week later by invading Poland from the west on September 1, 1939. The Soviet Union attacked Poland from the east on September 17, and by October 6,
, in Ioan Scurtu, Theodora Stănescu-Stanciu, Georgiana Margareta Scurtu, ''Istoria Românilor între anii 1918-1940'',
Report Axis to Aid Romania if Reds Overstep
. ''Associated Press''. Daily News (New York, New York). p. 3C. Soviet forces also occupied the
 On June 28, at 9:00, Communique no. 25 of the General Staff of the Romanian Army officially announced the terms of the ultimatum to the population, its acceptance by the Romanian government, and the intent to evacuate the army and administration to the
On June 28, at 9:00, Communique no. 25 of the General Staff of the Romanian Army officially announced the terms of the ultimatum to the population, its acceptance by the Romanian government, and the intent to evacuate the army and administration to the

 As Romania agreed to satisfy Soviet territorial demands, the second plan was immediately put into action, with the Red Army immediately moving into Bessarabia and north Bukovina on the morning of June 28. By June 30, the Red Army reached the border along the Prut River. On July 3, the border was closed completely from the Soviet side.
One month after the military occupation, on August 2, 1940, the
As Romania agreed to satisfy Soviet territorial demands, the second plan was immediately put into action, with the Red Army immediately moving into Bessarabia and north Bukovina on the morning of June 28. By June 30, the Red Army reached the border along the Prut River. On July 3, the border was closed completely from the Soviet side.
One month after the military occupation, on August 2, 1940, the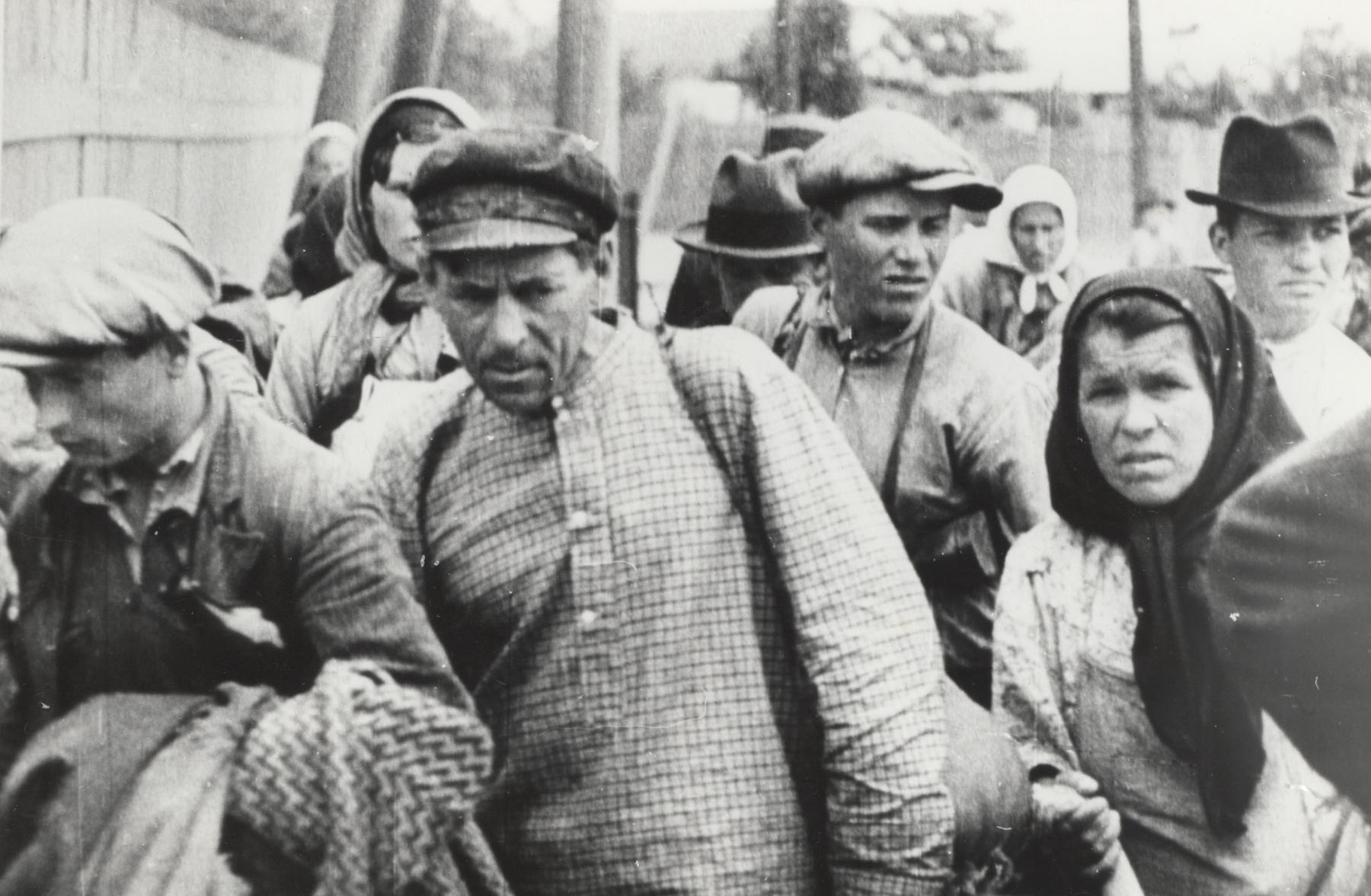  Serious incidents occurred in Northern Bukovina, where attempts by the locals to force the border towards Romania resulted in the Soviet border guards opening fire against unarmed civilians. In one case, at Fântâna Albă, that resulted in a massacre in which between 50 and 3,000 Romanians were killed. The situation was the same on the other side of the border: roughly 300 (or between 80 and 400, according to other sources) civilians, most of them Jews, waiting to leave for Soviet-controlled Bessarabia were shot by the Romanian army in
Serious incidents occurred in Northern Bukovina, where attempts by the locals to force the border towards Romania resulted in the Soviet border guards opening fire against unarmed civilians. In one case, at Fântâna Albă, that resulted in a massacre in which between 50 and 3,000 Romanians were killed. The situation was the same on the other side of the border: roughly 300 (or between 80 and 400, according to other sources) civilians, most of them Jews, waiting to leave for Soviet-controlled Bessarabia were shot by the Romanian army in
 The territorial concessions of 1940 produced deep sorrow and resentment among Romanians and hastened the decline in popularity of the regime led by King
The territorial concessions of 1940 produced deep sorrow and resentment among Romanians and hastened the decline in popularity of the regime led by King  That led to a near-uprising in the country. On September 5, King Carol II proposed to General (later Marshal)
That led to a near-uprising in the country. On September 5, King Carol II proposed to General (later Marshal)
 On the backdrop of increased anti-Semitism in Romania in the late 1930s, the government of Ion Antonescu officially adopted the myth of
On the backdrop of increased anti-Semitism in Romania in the late 1930s, the government of Ion Antonescu officially adopted the myth of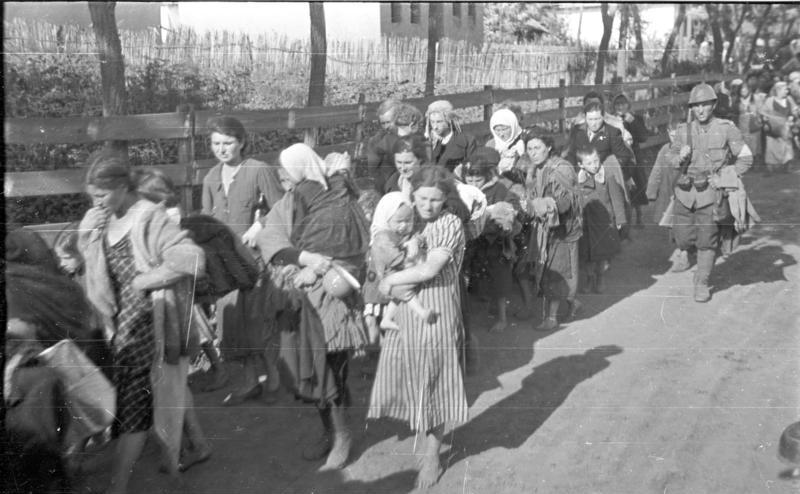  In 1941 to 1944, many young male inhabitants of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina were recruited into the
In 1941 to 1944, many young male inhabitants of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina were recruited into the
 In early 1944, the Soviet Union gradually took over the territory through the Uman–Botoșani and Second Jassy–Kishinev offensives. On August 23, 1944, with Soviet troops advancing and the Eastern Front falling within Romania's territory, a coup led by
In early 1944, the Soviet Union gradually took over the territory through the Uman–Botoșani and Second Jassy–Kishinev offensives. On August 23, 1944, with Soviet troops advancing and the Eastern Front falling within Romania's territory, a coup led by
 At the moment of the Soviet occupation, the regions had a total population of 3,776,309 inhabitants. According to Romanian official statistics, this was distributed among the ethnic groups as follows:
At the moment of the Soviet occupation, the regions had a total population of 3,776,309 inhabitants. According to Romanian official statistics, this was distributed among the ethnic groups as follows:
 During the Soviet takeover in 1940, Bessarabian Germans (82,000) and Bukovinian Germans (40,000–45,000) were repatriated to Germany at the request of Hitler's government. Some of them were forcibly settled by the Nazis in the German-occupied Poland and had to move again in 1944–1945. The people affected by the resettlement were not persecuted, but they were given no choice to stay or live and had to change their entire livelihood within weeks or even days.
During the Soviet takeover in 1940, Bessarabian Germans (82,000) and Bukovinian Germans (40,000–45,000) were repatriated to Germany at the request of Hitler's government. Some of them were forcibly settled by the Nazis in the German-occupied Poland and had to move again in 1944–1945. The people affected by the resettlement were not persecuted, but they were given no choice to stay or live and had to change their entire livelihood within weeks or even days.
"Romanian Army in the Second World War"
International Commission on the Holocaust in Romania: Final Report
(2004)
The June/July 1940 Romanian Withdrawal from Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina and its Consequences on Interethnic Relations in Romania
*
*
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20100527162751/http://ebooks.unibuc.ro/istorie/istorie1918-1940/13-4.htm "The Ultimatum notes and Romanian responses"* {{Nazi-Soviet relations Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic Romania in World War II History of Chernivtsi Oblast History of Budjak Moldova in World War II June 1940 events in Romania July 1940 events in Romania 1940 in the Soviet Union 1940 in international relations Battles and operations of the Eastern Front of World War II Bessarabian and Northern Bukovina Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
to Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, a ...
on June 26, 1940, that threatened the use of force. Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of ...
had been part of the Kingdom of Romania
The Kingdom of Romania ( ro, Regatul României) was a constitutional monarchy that existed in Romania from 13 March ( O.S.) / 25 March 1881 with the crowning of prince Karl of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen as King Carol I (thus beginning the Romanian ...
since the time of the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
and Bukovina
Bukovinagerman: Bukowina or ; hu, Bukovina; pl, Bukowina; ro, Bucovina; uk, Буковина, ; see also other languages. is a historical region, variously described as part of either Central or Eastern Europe (or both).Klaus Peter Berge ...
since the dissolution of Austria-Hungary
The dissolution of Austria-Hungary was a major geopolitical event that occurred as a result of the growth of internal social contradictions and the separation of different parts of Austria-Hungary. The reason for the collapse of the state was Worl ...
, and Hertsa
Hertsa or Hertza ( ; ro, Herța ) is a city located in Chernivtsi Raion, Chernivtsi Oblast in western Ukraine. It hosts the administration of Hertsa urban hromada, one of the hromadas of Ukraine, and has a population of
The town is locate ...
was a district of the Romanian Old Kingdom
The Romanian Old Kingdom ( ro, Vechiul Regat or just ''Regat''; german: Regat or ) is a colloquial term referring to the territory covered by the first independent Romanian nation state, which was composed of the Romanian Principalities: Wallachia ...
. Those regions, with a total area of and a population of 3,776,309 inhabitants, were incorporated into the Soviet Union. On October 26, 1940, six Romanian islands on the Chilia branch
The Chilia branch (; ) is one of three main distributary channels of the river Danube that contributes to forming the Danube Delta. Lying at the northernmost area of the delta, the distributary creates a natural border between Romania and Ukrai ...
of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , ...
, with an area of , were also occupied by the Soviet Army
uk, Радянська армія
, image = File:Communist star with golden border and red rims.svg
, alt =
, caption = Emblem of the Soviet Army
, start_date ...
.
The Soviet Union had planned to accomplish the annexation with a full-scale invasion, but the Romanian government, responding to the Soviet ultimatum delivered on June 26, agreed to withdraw from the territories to avoid a military conflict. The use of force had been made illegal by the Conventions for the Definition of Aggression in July 1933, but from an international legal standpoint, the new status of the annexed territories was eventually based on a formal agreement through which Romania consented to the retrocession of Bessarabia and cession of Northern Bukovina. As it was not mentioned in the ultimatum, the annexation of the Hertsa region was not consented to by Romania, and the same is true of the subsequent Soviet occupation of the Danube islands. On June 24, Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, which had acknowledged the Soviet interest in Bessarabia in a secret protocol to the 1939 Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that enabled those powers to partition Poland between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ri ...
, had been made aware prior to the planned ultimatum but did not inform the Romanian authorities and was willing to provide support.Bossy, G.H., Bossy, M-A. ''Recollections of a Romanian Diplomat, 1918–1969'', Volume 2, Hoover Press
The Hoover Institution (officially The Hoover Institution on War, Revolution, and Peace; abbreviated as Hoover) is an American public policy think tank and research institution that promotes personal and economic liberty, free enterprise, and ...
, 2003. On June 22, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, a guarantor of Romanian borders, fell to Nazi advances. This is considered to be an important factor in the Soviets' decision to issue the ultimatum.Joseph Rothschild, East Central Europe between the two World Wars
'
University of Washington Press
The University of Washington Press is an American academic publishing house. The organization is a division of the University of Washington, based in Seattle. Although the division functions autonomously, they have worked to assist the universi ...
, Seattle, 1977; , p.314 The Soviet invasion of Bukovina in 1940 violated the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, since it went beyond the Soviet sphere of influence that had been agreed with the Axis.
 On August 2, 1940, the
On August 2, 1940, the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic ( ro, Republica Sovietică Socialistă Moldovenească, Moldovan Cyrillic: ) was one of the 15 republics of the Soviet Union which existed from 1940 to 1991. The republic was formed on 2 August 1940 ...
was proclaimed as a constituent republic of the Soviet Union, encompassing most of Bessarabia and part of the Moldavian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
* ro, Proletari din toate țările, uniți-vă! ( Moldovan Cyrillic: )
* uk, Пролетарі всіх країн, єднайтеся!
* russian: Пролетарии всех стран, соединяйтесь!
, title_leader = First Secr ...
, an autonomous republic of the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
on the left bank of the Dniester
The Dniester, ; rus, Дне́стр, links=1, Dnéstr, ˈdⁿʲestr; ro, Nistru; grc, Τύρᾱς, Tyrās, ; la, Tyrās, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and ...
(now the breakaway Transnistria
Transnistria, officially the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (PMR), is an unrecognised breakaway state that is internationally recognised as a part of Moldova. Transnistria controls most of the narrow strip of land between the Dniester riv ...
). The Hertsa region
The Hertsa region, also known as the Hertza region ( uk, Край Герца, Kraj Herca; ro, Ținutul Herța), is a region around the town of Hertsa within Chernivtsi Raion in the southern part of Chernivtsi Oblast in southwestern Ukraine, n ...
and the regions inhabited by Slavic majorities ( Northern Bukovina, Northern and Southern Bessarabia
Southern Bessarabia or South Bessarabia is a territory of Bessarabia which, as a result of the Crimean War, was returned to the Moldavian Principality in 1856. As a result of the unification of the latter with Wallachia, these lands became part ...
) were included in the Ukrainian SSR. A period of political persecution, including executions, deportations to labour camps and arrests, occurred during the Soviet administration.
In July 1941, Romanian and German troops occupied Bessarabia, Northern Bukovina and Hertsa during the Axis invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
. A military administration was established, and the region's Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
population was executed on the spot or deported to Transnistria
Transnistria, officially the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (PMR), is an unrecognised breakaway state that is internationally recognised as a part of Moldova. Transnistria controls most of the narrow strip of land between the Dniester riv ...
, where large numbers were killed. In August 1944, during the Soviet Second Jassy–Kishinev Offensive
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds eac ...
, the Axis war effort on the Eastern Front collapsed. The coup of 23 August 1944 caused the Romanian army to cease resisting the Soviet advance and to join the fight against Germany. Soviet forces advanced from Bessarabia into Romania, captured much of its standing army as prisoners-of-war and occupied the country. On September 12, 1944, Romania signed the Moscow Armistice with the Allies. The Armistice and the subsequent peace treaty of 1947 confirmed the Soviet-Romanian border as it was on January 1, 1941.
Bessarabia, Northern Bukovina and Hertsa remained part of the Soviet Union until it collapsed in 1991, when they became part of the newly independent states of Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnist ...
and Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invas ...
. The Declaration of Independence of Moldova of August 27, 1991, declared the Soviet occupation illegal.
Background
As a historical region, Bessarabia was the eastern part of thePrincipality of Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Centr ...
. In 1812, under the terms of the Treaty of Bucharest, the region was ceded by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, to which Moldavia was a vassal state
A vassal state is any state that has a mutual obligation to a superior state or empire, in a status similar to that of a vassal in the feudal system in medieval Europe. Vassal states were common among the empires of the Near East, dating back ...
, to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the List of Russian monarchs, Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended th ...
.
Interwar Soviet-Romanian relations
Bessarabian question
The Bessarabian question, Bessarabian issue or Bessarabian problem ( ro, Problema basarabeană or ; russian: Бессарабский вопрос or ) is the name given to the controversy over the ownership of the geographic region of Bessarabia ...
was both political and national in nature. According to the 1897 census, Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of ...
, then a guberniya of the Russian Empire, had a population that was 47.6% Moldovans
Moldovans, sometimes referred to as Moldavians ( ro, moldoveni , Moldovan Cyrillic: молдовень), are a Romance-speaking ethnic group and the largest ethnic group of the Republic of Moldova (75.1% of the population as of 2014) and a si ...
, 19.6% Ukrainians, 8% Russians, 11.8% Jews, 5.3% Bulgarians, 3.1% Germans and 2.9% Gagauz. The figures showed a strong decrease in the proportion of Moldovans and Romanians compared to the census of 1817, which had been conducted shortly after the Russian Empire annexed Bessarabia in 1812. In that survey, Moldovans and Romanians represented 86% of the population. The decrease seen in the census of 1897 was caused by the Russian policies of settling of other nationalities and of Russification
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cultur ...
in Bessarabia.
During the 1917 Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and adopt a socialist form of government ...
, a National Council was formed in Bessarabia to manage the province. The council, known locally as Sfatul Țării, initiated several national and social reforms, and on December 2/15 1917, it declared the Moldavian Democratic Republic
The Moldavian Democratic Republic (MDR; ro, Republica Democratică Moldovenească, ), also known as the Moldavian Republic, was a state proclaimed on by the '' Sfatul Țării'' (National Council) of Bessarabia, elected in October–Novem ...
an autonomous republic within the Russian Federative Democratic Republic.
The Rumcherod, a rival council that was loyal to the Petrograd Soviet, was also formed and by late December, it had gained control over the capital, Chișinău and proclaimed itself the sole authority over Bessarabia. With the consent of the Allies and, according to Romanian historiography, on the request of ''Sfatul Țării'', Romanian troops entered Bessarabia in early January 1918 and, by February, had pushed the Soviets over the Dniester
The Dniester, ; rus, Дне́стр, links=1, Dnéstr, ˈdⁿʲestr; ro, Nistru; grc, Τύρᾱς, Tyrās, ; la, Tyrās, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and ...
. Despite later declarations by the Romanian prime minister that the military occupation had been consented to by the Bessarabian government, the intervention was met with protest by the locals, notably by Ion Inculeț
Ion Constantin Inculeț (; 5 April 1884, Răzeni, Bessarabia Governorate, Russian Empire, now the Republic of Moldova – 18 November 1940, Bucharest, Romania) was a Bessarabian and Romanian politician, the President of the Country Council of the ...
, the president of ''Sfatul Țării'', and Pantelimon Erhan, the head of the provisional Moldavian executive. The executive even authorised the badly organised Moldavian militia to resist the Romanian advance although with little success. In the wake of the intervention, Soviet Russia broke off diplomatic relations with Romania and confiscated the Romanian Treasure
The Romanian Treasure ( ro, Tezaurul României) is a collection of valuable objects and the gold reserves (~120 tonnes) of the Romanian government sent to Russia for safekeeping during World War I. After the Romanian Army entered Bessarabia, at ...
, which was stored in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
for safekeeping. To calm the situation, Entente representatives in Iași issued a guarantee that the presence of the Romanian Army was only a temporary military measure for the stabilisation of the front, without further affecting the political life of the region. In January 1918, the Ukrainian People's Republic
The Ukrainian People's Republic (UPR), or Ukrainian National Republic (UNR), was a country in Eastern Europe that existed between 1917 and 1920. It was declared following the February Revolution in Russia by the First Universal. In March 1 ...
declared its independence from Russia, which left Bessarabia physically isolated from the Petrograd government and led to the declaration of independence of the Moldavian Republic on January 24/February 5. Some historians consider that the declaration was made under Romanian pressure. Following several Soviet protests, on February 20/March 5, the Romanian prime minister, General Alexandru Averescu
Alexandru Averescu (; 9 March 1859 – 2 October 1938) was a Romanian marshal, diplomat and populist politician. A Romanian Armed Forces Commander during World War I, he served as Prime Minister of three separate cabinets (as well as being ''int ...
, signed a treaty with the Soviet representative in Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrat ...
, Christian Rakovsky
Christian Georgievich Rakovsky (russian: Христиа́н Гео́ргиевич Рако́вский; bg, Кръстьо Георги́ев Рако́вски; – September 11, 1941) was a Bulgarian-born socialist revolutionary, a Bolshevi ...
, which provided that Romanian troops be evacuated from Bessarabia within two months in exchange for the repatriation of Romanian prisoners-of-war held by the Rumcherod. After the White Army
The White Army (russian: Белая армия, Belaya armiya) or White Guard (russian: Бѣлая гвардія/Белая гвардия, Belaya gvardiya, label=none), also referred to as the Whites or White Guardsmen (russian: Бѣлогв� ...
forced the Soviets to withdraw from Odessa, and the German Empire agreed to the Romanian annexation of Bessarabia in a secret agreement (part of the Buftea Peace Treaty) on March 5/18, Romanian diplomacy repudiated the treaty by claiming that the Soviets were unable to fulfill their obligations.
On March 27/April 9, 1918, the ''Sfatul Țării'' voted for the Union of Bessarabia with Romania
The union of Bessarabia with Romania was proclaimed on by Sfatul Țării, the legislative body of the Moldavian Democratic Republic. This state had the same borders of the region of Bessarabia, which was annexed by the Russian Empire following t ...
, conditional upon the fulfilment of an agrarian reform (despite having no quorum). There were 86 votes for union, 3 votes against, 36 deputies abstaining, and 13 deputies absent. The vote is regarded as controversial by several historians, including Romanian ones such as Cristina Petrescu and Sorin Alexandrescu. According to historian Charles King, with Romanian troops already in Chișinău, Romanian planes circling above the meeting hall and the Romanian prime minister waiting in the foyer, many minority deputies chose simply not to vote. On April 18 Georgy Chicherin
Georgy Vasilyevich Chicherin (24 November 1872 – 7 July 1936), also spelled Tchitcherin, was a Russian Marxist revolutionary and a Soviet politician who served as the first People's Commissar for Foreign Affairs in the Soviet government from ...
, the Soviet Commissar for Foreign Affairs, sent a note of protest against the incorporation of Bessarabia into Romania.
In August 1916, the Entente and the neutral Romania signed a secret convention that stipulated Romania would join the war against the Central Powers in exchange for several territories of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
, such as Bukovina
Bukovinagerman: Bukowina or ; hu, Bukovina; pl, Bukowina; ro, Bucovina; uk, Буковина, ; see also other languages. is a historical region, variously described as part of either Central or Eastern Europe (or both).Klaus Peter Berge ...
. During the end of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, national movements of the Romanians and the Ukrainians began to emerge in the province, but both movements had conflicting aims, each seeking to unite the province with their national state. Thus, on October 25, 1918, a Ukrainian National Committee, gaining the upper hand in Czernowitz, declared Northern Bukovina, populated by a Ukrainian majority, part of the West Ukrainian People's Republic
The West Ukrainian People's Republic (WUPR) or West Ukrainian National Republic (WUNR), known for part of its existence as the Western Oblast of the Ukrainian People's Republic, was a short-lived polity that controlled most of Eastern Galic ...
. On October 27, the Romanians followed suit, proclaiming the whole region united with Romania, and calling in Romanian troops. The Romanian intervention quickly established the Romanian Assembly as the dominant force, and on November 28, a Congress of the Romanians, Germans, and Poles voted to unite with Romania. The representatives of the Ukrainian and Jewish populations boycotted the Congress, and the struggle between ethnic factions continued for several months.
During the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
, the Soviet governments of Ukraine and Russia, prompted by the unrest in Bessarabia from the Romanian occupation, issued a joint ultimatum to Romania on May 1, 1919, for its withdrawal from Bessarabia, and the next day, Christian Rakovsky, the chairman of the Ukrainian Soviet government, issued another ultimatum for the withdrawal of Romanian troops from Bukovina as well. The Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
pushed the Romanians over the Dniester, and a Bessarabian Soviet Socialist Republic was proclaimed. The ultimatum also came in the context of the Hungarian Soviet Republic
The Socialist Federative Republic of Councils in Hungary ( hu, Magyarországi Szocialista Szövetséges Tanácsköztársaság) (due to an early mistranslation, it became widely known as the Hungarian Soviet Republic in English-language sources ( ...
, with the Soviets hoping to prevent a Romanian intervention in Hungary. A massive rebellion in Ukraine prevented further Soviet advances. Soviet Russia would continue its policy of non-recognition of Romanian sovereignty over Bessarabia, which it considered Romanian-occupied territory, until 1940.
During the negotiations before the Treaty of Paris, the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
' representative asked for a plebiscite
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
to be held in Bessarabia to decide its future, but the proposal was rejected by the head of the Romanian delegation, Ion I. C. Brătianu
Ion Ionel Constantin Brătianu (, also known as Ionel Brătianu; 20 August 1864 – 24 November 1927) was a Romanian politician, leader of the National Liberal Party (PNL), Prime Minister of Romania for five terms, and Foreign Minister on seve ...
, who claimed such an undertaking would allow the distribution of Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
propaganda in Bessarabia and Romania. A plebiscite was also requested at the Peace Conference by the White Russians, only to be rejected again. The Soviets would continue to press for a plebiscite during the following decade, only to be dismissed every time by the Romanian government.
Romanian sovereignty over Bessarabia was ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legall ...
'' recognized by the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, and Japan in the Bessarabian Treaty, signed on October 28, 1920. Soviet Russia and Ukraine promptly notified Romania that they did not recognize the treaty's validity and did not consider themselves bound by it. Ultimately, Japan failed to ratify the treaty and so it never came into force, leaving Romania without a valid international act to justify its possession of Bessarabia. The United States refused to discuss territorial changes in the former Russian Empire without the participation of a Russian government. Thus, it declined to recognize the incorporation of Bessarabia into Romania, and, unlike its position of recognizing the independence of the Baltic States
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, ...
, it insisted that Bessarabia was a territory under Romanian military occupation and incorporated the Bessarabian emigration quota into the Russian one in 1923. In 1933, the US government tacitly included the Bessarabian emigration quota into that of Romania, an act that was considered a ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by l ...
'' recognition by Romanian diplomacy. However, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, the US argued it had never recognized Bessarabia's union with Romania.
In 1924, after the failure of the Tatarbunary Uprising, the Soviet government created a Moldavian Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
* ro, Proletari din toate țările, uniți-vă! ( Moldovan Cyrillic: )
* uk, Пролетарі всіх країн, єднайтеся!
* russian: Пролетарии всех стран, соединяйтесь!
, title_leader = First Secr ...
on the left bank of the Dniester river within the Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
. The Romanian government saw that as a threat and a possible staging ground for a communist invasion of Romania. Throughout the 1920s, Romania considered itself a pillar in the '' cordon sanitaire'', the policy of containment of the Bolshevik threat, and avoided direct relations with the Soviet Union.
On August 27, 1928, both Romania and the Soviet Union signed and ratified the Kellogg-Briand Pact, renouncing war as an instrument of national policy. On February 9, 1929, the Soviet Union signed a protocol with its western neighbors, Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and t ...
, Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
, and Romania, confirming adherence to the terms of the Pact. In signing the Pact, the contracting parties agreed to condemn war as a recourse to solving conflict, to renounce it as an instrument of policy and to agree that all conflicts and disputes would only by peaceful means. At the time, the Soviet ambassador, Maxim Litvinov
Maxim Maximovich Litvinov (; born Meir Henoch Wallach; 17 July 1876 – 31 December 1951) was a Russian revolutionary and prominent Soviet statesman and diplomat.
A strong advocate of diplomatic agreements leading towards disarmament, Litvinov ...
, made it clear that neither the pact nor the protocol meant renunciation of Soviet rights over the "territories occupied by Romanians". On July 3, 1933, Romania and the Soviet Union were signatories the London Convention for the Definition of Aggression, Article II of which defined several forms of aggression: "There shall be recognized as an aggressor that State which shall be the first to have committed one of the following actions: First—a declaration of war on another State. Second—invasion by armed forces of the territory of another State even without a declaration of war. (...)" and "No political, military, economic or other considerations may serve as an excuse or justification for the aggression referred to in Article II."
In January 1932 in Riga
Riga (; lv, Rīga , liv, Rīgõ) is the capital and largest city of Latvia and is home to 605,802 inhabitants which is a third of Latvia's population. The city lies on the Gulf of Riga at the mouth of the Daugava river where it meets the B ...
and in September 1932 in Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situ ...
, Soviet-Romanian negotiations were held as a prelude to a non-aggression treaty, and on June 9, 1934, diplomatic relations were established between both countries. On July 21, 1936, Litvinov and Nicolae Titulescu
Nicolae Titulescu (; 4 March 1882 – 17 March 1941) was a Romanian diplomat, at various times government minister, finance and foreign minister, and for two terms president of the General Assembly of the League of Nations (1930–32).
Early y ...
, the Soviet and Romanian Ministers of Foreign Affairs, agreed upon a draft of a Mutual Assistance Pact. It was sometimes interpreted as a non-aggression treaty, which would ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by l ...
'' recognize the existing Soviet-Romanian border. The protocol stipulated that any common Romanian-Soviet action should be approved by France ahead of time. In negotiating with the Soviets for the agreement, Titulescu was highly criticized by the Romanian far right. The protocol was to be signed in September 1936, but Titulescu was dismissed in August 1936, leading the Soviet side to declare the agreement null and void. Subsequently, no further attempts were made to reach a political rapprochement between Romania and the Soviet Union. Moreover, by 1937, Litvinov and the Soviet press revived the dormant claim over Bessarabia.
Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact and aftermath
 On August 23, 1939, the
On August 23, 1939, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
and Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
signed the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that enabled those powers to partition Poland between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ri ...
, a non-aggression treaty that contained an additional secret protocol with maps in which a demarcation line through Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, wh ...
was drawn and divided it into the German and Soviet interest zones. Bessarabia was among the regions assigned to the Soviet sphere of interest by the Pact. Article III of its Secret Additional Protocol stated:
With regard to Southeastern Europe attention is called by the Soviet side to its interest in Bessarabia. The German side declares its complete political disinterestedness in these areas.On 29 March 1940, Molotov declared on the Sixth session of the Supreme Soviet: "We do not have a pact of non-aggression with Romania. This is due to the presence of an unsolved issue, the issue of Bessarabia, the seizure of which the Soviet Union never recognized although it never raised the issue of returning it by military means". That was seen as a threat to Romania.
International context
 Assured by the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact of Soviet non-interference, Germany started World War II one week later by invading Poland from the west on September 1, 1939. The Soviet Union attacked Poland from the east on September 17, and by October 6,
Assured by the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact of Soviet non-interference, Germany started World War II one week later by invading Poland from the west on September 1, 1939. The Soviet Union attacked Poland from the east on September 17, and by October 6, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
had fallen. Romanian Prime Minister Armand Călinescu, a strong supporter of Poland in its conflict with Germany, was assassinated on September 21 by elements of the far-right Iron Guard
The Iron Guard ( ro, Garda de Fier) was a Romanian militant revolutionary fascist movement and political party founded in 1927 by Corneliu Zelea Codreanu as the Legion of the Archangel Michael () or the Legionnaire Movement (). It was strong ...
with Nazi support. Romania remained formally neutral in the conflict but aided Poland by providing access to Allied military supplies from the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, ...
to the Polish border and also a route for the Polish government and army to withdraw after their defeat. The Polish government also preferred a formally neutral Romania to ensure the safety from German bombardments of supplies transported through Romanian territory. (See also Romanian Bridgehead.)
On June 2, 1940, Germany informed the Romanian government that to receive territorial guarantees, Romania should consider negotiations with the Soviet Union.
From June 14 to 17, 1940, the Soviet Union gave ultimatum notes to Lithuania, Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, and t ...
and Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
, and when the ultimata were satisfied, it used the bases that it had gained to occupy those territories.
The Fall of France
The Battle of France (french: bataille de France) (10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign ('), the French Campaign (german: Frankreichfeldzug, ) and the Fall of France, was the German invasion of France during the Second Wo ...
on June 22 and the subsequent British retreat from the Continent rendered the assurances of assistance to Romania meaningless.
Political and military developments
Soviet preparations
By directives OV/583 and OV/584 of the Soviet People Commissariat of Defense, military units of theOdessa Military District
The Odesa Military District (russian: Одесский военный округ, ОВО; , abbreviated ) was a military administrative division of the Armed Forces of Ukraine. In 1998 most of its territory was transformed into the Southern Opera ...
were ordered into battle-ready state in the spring of 1940. Soviet troops were concentrated along the Romanian border between April 15 and June 10, 1940. To co-ordinate the efforts of the Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper, Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the List of European cities by populat ...
and Odessa military districts in the preparation of action against Romania, the Soviet Army created the Southern Front under General Georgy Zhukov
Georgy Konstantinovich Zhukov ( rus, Георгий Константинович Жуков, p=ɡʲɪˈorɡʲɪj kənstɐnʲˈtʲinəvʲɪtɕ ˈʐukəf, a=Ru-Георгий_Константинович_Жуков.ogg; 1 December 1896 – ...
, which was composed of the 5th
Fifth is the ordinal form of the number five.
Fifth or The Fifth may refer to:
* Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution, as in the expression "pleading the Fifth"
* Fifth column, a political term
* Fifth disease, a contagious rash tha ...
, 9th
9 (nine) is the natural number following and preceding .
Evolution of the Arabic digit
In the beginning, various Indians wrote a digit 9 similar in shape to the modern closing question mark without the bottom dot. The Kshatrapa, Andhra and ...
and 12th Armies. The Southern Front had 32 infantry divisions, 2 motorized infantry divisions, 6 cavalry divisions, 11 tank brigades, 3 paratrooper brigades, 30 artillery regiments and smaller auxiliary units.Ioan Scurtu,Istoria Basarabiei de la inceputuri pana in 2003, Editura Institutului Cultural Roman, pg. 327
On 25 June, the Soviet Southern Front received a directive:
1. The soldiery and the bourgeois-capitalist clique of Romania, preparing provocationary acts against the USSR, concentrated on the borders of the USSR large armed forces, increased the border posts to 100 persons, enlarged the number of commandos sent to guard the border and is with enforced tempo constructing defense facilities on its border and the close rear.Two action plans were devised. The first plan was prepared for if Romania did not agree to evacuate Bessarabia and Bukovina. The Soviet 12th Army was to strike southward along the
2. The commander of the Southern Front set the troops of the Southern district the task to: a) clear of mines, seize and hold bridges over the borderline rivers; b) firmly defend state borders in the front of the 12th army where the troops of the Workers' and Peasants' Red Army are going to act; c) to provide the Workers' and Peasants' Red Army with guides; d) to cleanse the rear of the 12th army from possible pockets of enemy in the near-border belt of Romania.
Prut River
The Prut (also spelled in English as Pruth; , uk, Прут) is a long river in Eastern Europe. It is a left tributary of the Danube. In part of its course it forms Romania's border with Moldova and Ukraine.
Characteristics
The Prut originates ...
towards Iași while the Soviet 9th Army was to strike westwards, south of Chișinău towards Huși
Huși (, Yiddish/ he, חוש ''Khush'', hu, Huszváros, German: ''Hussburg'') is a city in Vaslui County, Romania, former capital of the disbanded Fălciu County in the historical region of Western Moldavia, Romanian Orthodox episcopal see, ...
. The objective of the plan was to surround the Romanian troops in the Bălți
Bălți (; russian: Бельцы, , uk, Бєльці, , yi, בעלץ ) is a city in Moldova. It is the second largest city in terms of population, area and economic importance, after Chișinău. The city is one of the five Moldovan municipali ...
–Iași area.
The second plan took into consideration the possibility that Romania would agree to Soviet demands and evacuate its military forces. In such a situation, Soviet troops were given the mission to quickly reach the Prut River and oversee the evacuation of Romanian troops. The first plan was taken as the default course of action. Along the portions of the border in which the offensive was planned to take place, the Soviets prepared at least a triple superiority of men and materiel.
Soviet ultimatum
On June 26, 1940, at 22:00, Soviet People's CommissarVyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Mikhaylovich Molotov. ; (;. 9 March O. S. 25 February">Old_Style_and_New_Style_dates.html" ;"title="nowiki/>Old Style and New Style dates">O. S. 25 February1890 – 8 November 1986) was a Russian politician and diplomat, an Old Bol ...
presented an ultimatum
An ultimatum (; ) is a demand whose fulfillment is requested in a specified period of time and which is backed up by a threat to be followed through in case of noncompliance (open loop). An ultimatum is generally the final demand in a series o ...
note to Gheorghe Davidescu
Gheorghe Davidescu ( – January 3, 1973) was a Romanian lawyer and career diplomat.
Early life
Davidescu was born in Brașov, when the city belonged to Austria-Hungary. His parents, George and Paraschiva (''née'' Vlaicu), lived in the Șc ...
, the Romanian plenipotentiary minister to Moscow, in which the Soviet Union demanded the evacuation of the Romanian military and civil administration from Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of ...
and the northern part of Bukovina
Bukovinagerman: Bukowina or ; hu, Bukovina; pl, Bukowina; ro, Bucovina; uk, Буковина, ; see also other languages. is a historical region, variously described as part of either Central or Eastern Europe (or both).Klaus Peter Berge ...
. The Soviets stressed their sense of urgency: "Now that the military weakness of the USSR is a thing of the past, and the international situation that was created requires the rapid solution of the items inherited from the past, in order to fix the basis of a solid peace between countries..."."Soviet Ultimata and Replies of the Romanian Government", in Ioan Scurtu, Theodora Stănescu-Stanciu, Georgiana Margareta Scurtu, ''Istoria Românilor între anii 1918-1940'',
University of Bucharest
The University of Bucharest ( ro, Universitatea din București), commonly known after its abbreviation UB in Romania, is a public university founded in its current form on by a decree of Prince Alexandru Ioan Cuza to convert the former Princ ...
, 2002 The German Minister of Foreign Affairs, Joachim von Ribbentrop
Ulrich Friedrich Wilhelm Joachim von Ribbentrop (; 30 April 1893 – 16 October 1946) was a German politician and diplomat who served as Minister of Foreign Affairs of Nazi Germany from 1938 to 1945.
Ribbentrop first came to Adolf Hitler's not ...
, was informed by the Soviets of their intentions to send an ultimatum to Romania regarding Bessarabia and Bukovina on June 24, 1940. In the ensuing diplomatic co-ordination, Ribbentrop expressed mainly concern for the fate of the ethnic Germans in both provinces, claimed the number of Germans in Bessarabia to be 100,000, and affirmed that Soviet demands regarding Bukovina
Bukovinagerman: Bukowina or ; hu, Bukovina; pl, Bukowina; ro, Bucovina; uk, Буковина, ; see also other languages. is a historical region, variously described as part of either Central or Eastern Europe (or both).Klaus Peter Berge ...
were new. He also pointed out that Germany had strong economic interests in the rest of Romania.
The text of the ultimatum note sent to Romania on June 26, 1940, incorrectly stated that Bessarabia was populated mainly by Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Or ...
: " ..centuries-old union of Bessarabia, populated mainly by Ukrainians, with the Ukrainian Soviet Republic". The Soviet government demanded the northern part of Bukovina as a "minor reparation for the enormous loss inflicted on the Soviet Union and Bessarabia's population by 22 years of Romanian reign over Bessarabia" and because its "fate is linked mainly with Soviet Ukraine by the community of its historical fate, and by the community of language and ethnic composition". Northern Bukovina had some historical connections with Galicia
Galicia may refer to:
Geographic regions
* Galicia (Spain), a region and autonomous community of northwestern Spain
** Gallaecia, a Roman province
** The post-Roman Kingdom of the Suebi, also called the Kingdom of Gallaecia
** The medieval King ...
, annexed by the Soviet Union in 1939 as part of its invasion of Poland
The invasion of Poland (1 September – 6 October 1939) was a joint attack on the Republic of Poland by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union which marked the beginning of World War II. The German invasion began on 1 September 1939, one week af ...
, in the sense that both had been part of Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
from the second half of the 18th century to 1918. Northern Bukovina was inhabited by a compact Ukrainian population, which outnumbered Romanians, but Bessarabia was regarded as having a Romanian majority even though most of the population adopted a "Moldavian" identity.
On the morning of June 27, a mobilization
Mobilization is the act of assembling and readying military troops and supplies for war. The word ''mobilization'' was first used in a military context in the 1850s to describe the preparation of the Prussian Army. Mobilization theories an ...
of Romanian troops started. In the early hours of June 27, King
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen, which title is also given to the consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contemporary indigenous peoples, the ...
Carol II had a meeting with his prime minister, Gheorghe Tătărescu
: ''For the artist, see Gheorghe Tattarescu.''
Gheorghe I. Tătărescu (also known as ''Guță Tătărescu'', with a slightly antiquated pet form of his given name; 2 November 1886 – 28 March 1957) was a Romanian politician who served twice as P ...
, and his minister for external affairs, Ion Gigurtu
Ion Gigurtu (; 24 June 1886 – 24 November 1959) was a far-right Romanian politician, Land Forces officer, engineer and industrialist who served a brief term as Prime Minister from 4 July to 4 September 1940, under the personal regime of King ...
, and he summoned the ambassadors of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
and Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
. Carol communicated his wish to stand against the Soviet Union and asked for their countries to influence Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
and Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Mac ...
in the hopes of not declaring war against Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, a ...
and to reclaim Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the ...
and Southern Dobruja
Southern Dobruja, South Dobruja or Quadrilateral ( Bulgarian: Южна Добруджа, ''Yuzhna Dobrudzha'' or simply Добруджа, ''Dobrudzha''; ro, Dobrogea de Sud, or ) is an area of northeastern Bulgaria comprising Dobrich and Silist ...
. Stating that it would be "in the name of peace" to accede to Soviet demands, the ambassadors urged the King to stand down.
On June 27, Molotov declared that if the Romanians rejected Soviet demands, the Soviet troops would cross the border. Molotov gave the Romanian government 24 hours to respond to the ultimatum.
On the same day, the Romanian government replied by suggesting it would agree to "immediate negotiations on a wide range of questions". The Soviets considered the Romanian government's response to be "imprecise" because it did not directly accept the immediate transfer of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina. On June 27, a second Soviet ultimatum note put forward a specific time frame that requested the evacuation of the Romanian government from Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina within four days. It stated the Soviet military's intention to enter the Bessarabian cities of Chișinău and Cetatea Albă and the Bukovinian city of Cernăuți.
On the morning of June 28, 1940, following advice by both Germany and Italy, the Romanian government, led by Gheorghe Tătărescu, under the semi-authoritarian rule of Carol II, agreed to submit to the Soviet demands.St. John, Robert (June 30, 1940).Report Axis to Aid Romania if Reds Overstep
. ''Associated Press''. Daily News (New York, New York). p. 3C. Soviet forces also occupied the
Hertsa region
The Hertsa region, also known as the Hertza region ( uk, Край Герца, Kraj Herca; ro, Ținutul Herța), is a region around the town of Hertsa within Chernivtsi Raion in the southern part of Chernivtsi Oblast in southwestern Ukraine, n ...
, part of the Romanian Old Kingdom
The Romanian Old Kingdom ( ro, Vechiul Regat or just ''Regat''; german: Regat or ) is a colloquial term referring to the territory covered by the first independent Romanian nation state, which was composed of the Romanian Principalities: Wallachia ...
, which was in neither Bessarabia nor Bukovina. The Soviets said that was "probably a military error". As well, the final border line cut off about 1.7 km2 from Maramures, as the extending westerly border line ran south of the old historical border between Maramureș, Bukovina and Galitzia, which extended to the north to the Muncel river and border marker N542 (as seen on cold war Soviet military cartography maps), a tributary of Pârcālab river, which flows into Ceremuș river.
The decision to accept the Soviet ultimatum and to start a "withdrawal" (avoiding the use of ''ceding'') from Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina was deliberated upon by the Romanian Crown Council during the night of June 27–28. The second (decisive) vote outcome, according to the journal of King Carol II, was:
* ''Reject the ultimatum'': Ștefan Ciobanu, Silviu Dragomir Silviu may refer to:
*Silviu Bălace (born 1978), Romanian football player
*Silviu Berejan (1927–2007), Bessarabian writer from Moldova and member of the Academy of Sciences of Moldova
*Silviu Bindea (1912–1992), Romanian football player
*Silvi ...
, Victor Iamandi
Victor Iamandi (February 15, 1891 – 26 November 1940) was a Romanian politician who served as the Romanian Minister of Justice in 1938–1939, in several successive cabinets.
He was born in Hodora, Iași County, the son of Ion and Lucreția ...
, Nicolae Iorga, Traian Pop
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presid ...
, Ernest Urdăreanu
* ''Accept the ultimatum'': Petre Andrei, Constantin Angelescu
Constantin Angelescu (10 June 1869 – 14 September 1948) was a Romanian politician who served as ad interim/acting Prime Minister of Romania for five days, between 30 December 1933 and 3 January 1934.
He was: Doctor of Medicine in Paris, Ple ...
, Constantin Argetoianu, Ernest Ballif
Ernest is a given name derived from Germanic word ''ernst'', meaning "serious". Notable people and fictional characters with the name include:
People
*Archduke Ernest of Austria (1553–1595), son of Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor
*Ernest, M ...
, Aurelian Bentoiu
Aurelian ( la, Lucius Domitius Aurelianus; 9 September 214 October 275) was a Roman emperor, who reigned during the Crisis of the Third Century, from 270 to 275. As emperor, he won an unprecedented series of military victories which reunited t ...
, Mircea Cancicov
Mircea is a Romanian language, Romanian masculine given name, a form of the South Slavic name Mirče (Мирче) that derives from the Slavic word ''mir'', meaning 'peace'. It may refer to:
People Princes of Wallachia
* Mircea I of Wallachi ...
, Ioan Christu
Ioan is a variation on the name John found in Romanian, Bulgarian, Russian, Welsh (), and Sardinian. It is usually masculine. The female equivalent in Romanian and Bulgarian is Ioana. In Russia, the name Ioann is usually reserved for the cler ...
, Mitiță Constantinescu
Mitiţă Constantinescu (October 20, 1890—1946) was a Romanian economist and liberal politician. He was an advocate of industrialization and a degree of ''dirigisme''.
Biography
Born in Bucharest, he graduated from the Gheorghe Lazăr High ...
, Mihail Ghelmegeanu
Mihail Ghelmegeanu (25 June 1896 – 1984) was a Romanian politician.
Born in Craiova, he attended high school in Pitești. Subsequently, he entered the Faculties of Law and Literature at the University of Bucharest, and received a doctorate in ...
, Ion Gigurtu
Ion Gigurtu (; 24 June 1886 – 24 November 1959) was a far-right Romanian politician, Land Forces officer, engineer and industrialist who served a brief term as Prime Minister from 4 July to 4 September 1940, under the personal regime of King ...
, Constantin C. Giurescu, Nicolae Hortolomei, Ioan Ilcuș
Ioan is a variation on the name John found in Romanian, Bulgarian, Russian, Welsh (), and Sardinian. It is usually masculine. The female equivalent in Romanian and Bulgarian is Ioana. In Russia, the name Ioann is usually reserved for the clergy ...
(minister of defence), Ion Macovei Ion Macovei (August 25, 1885–October 12, 1950) was a Romanian engineer who briefly served in government in 1940.
Born in Nereju, Vrancea County, he attended a polytechnic institute in Germany and became an engineer. Cicerone Ionițoiu"Victim ...
, Gheorghe Mironescu, Radu Portocală
Radu may refer to:
People
* Radu (given name), Romanian masculine given name
* Radu (surname), Romanian surname
* Rulers of Wallachia, see
* Prince Radu of Romania (born 1960), disputed pretender to the former Romanian throne
Other uses
* Radu ( ...
, Mihai Ralea, Victor Slăvescu, Gheorghe Tătărescu (prime-minister), Florea Țenescu Florea is both a Romanian surname and a masculine Romanian given name. Notable people with the name include:
Surname:
*Daniel Florea, Romanian footballer
*Daniel Florea, Romanian politician
*Daniel Constantin Florea, Romanian footballer
*Dick Flore ...
(chief of the General Staff of the Army)
* ''Abstained'': Victor Antonescu.
The same night, Carol II also convinced Alexandru Vaida-Voevod
Alexandru Vaida-Voevod or Vaida-Voievod (27 February 1872 – 19 March 1950) was an Austro-Hungarian-born Romanian politician who was a supporter and promoter of the union of Transylvania (before 1920 part of Hungary) with the Romanian Old King ...
to be sworn in as minister. Vaida, along with all of the above, signed the final Crown Council recommendation in which Carol II ordered the army to stand down.
Romanian withdrawal
 On June 28, at 9:00, Communique no. 25 of the General Staff of the Romanian Army officially announced the terms of the ultimatum to the population, its acceptance by the Romanian government, and the intent to evacuate the army and administration to the
On June 28, at 9:00, Communique no. 25 of the General Staff of the Romanian Army officially announced the terms of the ultimatum to the population, its acceptance by the Romanian government, and the intent to evacuate the army and administration to the Prut River
The Prut (also spelled in English as Pruth; , uk, Прут) is a long river in Eastern Europe. It is a left tributary of the Danube. In part of its course it forms Romania's border with Moldova and Ukraine.
Characteristics
The Prut originates ...
. By 14:00, three key cities ( Chișinău, Cernăuți, and Cetatea Albă) had to be turned over to the Soviets. The military installations and casemate
A casemate is a fortified gun emplacement or armored structure from which guns are fired, in a fortification, warship, or armoured fighting vehicle.Webster's New Collegiate Dictionary
When referring to antiquity, the term "casemate wall" mean ...
s, built during a 20-year period for the event of a Soviet attack, were relinquished without a fight, the Romanian Army being placed by its command under strict orders not to respond to provocations. In a declaration to the local population, the Soviet command stated: "The great hour of your liberation from the yoke of Romanian boyars, landowners, capitalists and Siguranța
Siguranța was the generic name for the successive secret police services in the Kingdom of Romania. The official title of the organization changed throughout its history, with names including Directorate of the Police and General Safety ( ro, Di ...
has arrived".
Part of the population left the regions with the Romanian administration. According to the April 1941 Romanian census, the total number of refugees from the evacuated territories amounted to 68,953, but as the ultimatum came unexpectedly, many people did not have time to evacuate, and over 70,000 request for repatriation to Romania were later recorded. On the other hand, by early August 1940, between 112,000 and 149,974 people had left the other territories of Romania for the Soviet-ruled Bessarabia. That figure comprised Romanians of the region but also included Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
, both from Bessarabia and from the Old Kingdom
In ancient Egyptian history, the Old Kingdom is the period spanning c. 2700–2200 BC. It is also known as the "Age of the Pyramids" or the "Age of the Pyramid Builders", as it encompasses the reigns of the great pyramid-builders of the Fourt ...
, who wanted to escape the officially endorsed anti-semitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Ant ...
in Romania.
Incorporation of annexed territories into the Soviet Union
 As Romania agreed to satisfy Soviet territorial demands, the second plan was immediately put into action, with the Red Army immediately moving into Bessarabia and north Bukovina on the morning of June 28. By June 30, the Red Army reached the border along the Prut River. On July 3, the border was closed completely from the Soviet side.
One month after the military occupation, on August 2, 1940, the
As Romania agreed to satisfy Soviet territorial demands, the second plan was immediately put into action, with the Red Army immediately moving into Bessarabia and north Bukovina on the morning of June 28. By June 30, the Red Army reached the border along the Prut River. On July 3, the border was closed completely from the Soviet side.
One month after the military occupation, on August 2, 1940, the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic ( ro, Republica Sovietică Socialistă Moldovenească, Moldovan Cyrillic: ) was one of the 15 republics of the Soviet Union which existed from 1940 to 1991. The republic was formed on 2 August 1940 ...
was established on the main part of the annexed
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
territory, and smaller portions were given to the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
. Six Bessarabian counties and small portions of the other three counties, along with parts of the Moldavian ASSR (formerly part of the Ukrainian SSR), which was disbanded on that occasion, formed the Moldavian SSR, which became one of 15 union republics of the Soviet Union. The Soviet governmental commission headed by Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and chairman of the country's Council of Ministers from 1958 to 1964. During his rule, Khrushchev ...
, the Communist Party chief of Ukrainian SSR, allotted Northern Bukovina
Bukovinagerman: Bukowina or ; hu, Bukovina; pl, Bukowina; ro, Bucovina; uk, Буковина, ; see also other languages. is a historical region, variously described as part of either Central or Eastern Europe (or both).Klaus Peter Berger ...
, Hertsa region
The Hertsa region, also known as the Hertza region ( uk, Край Герца, Kraj Herca; ro, Ținutul Herța), is a region around the town of Hertsa within Chernivtsi Raion in the southern part of Chernivtsi Oblast in southwestern Ukraine, n ...
and larger parts of Hotin (Northern Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of Be ...
), Ismail, and Cetatea Albă (Budjak
Budjak or Budzhak ( Bulgarian and Ukrainian: Буджак; ro, Bugeac; Gagauz and Turkish: ''Bucak''), historically part of Bessarabia until 1812, is a historical region in Ukraine and Moldova. Lying along the Black Sea between the Danube ...
) counties to the Ukrainian SSR.
In 1940 to 1941, political persecution of certain categories of locals took the form of arrests, executions and deportations to the eastern parts of the Soviet Union. According to Alexandru Usatiuc-Bulgăr
Alexandru Usatiuc-Bulgăr (1915–2003) was a Moldovan activist and a political prisoner in the former Soviet Union.
Biography
Between 1969 and 1971, he was a founder of a clandestine National Patriotic Front of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina ...
,Alexandru Usatiuc-Bulgăr ''"Cu gîndul la "O lume între două lumi": eroi, martiri, oameni-legendă"'' ("Thinking of 'A World between Two Worlds': Heroes, Martyrs, Legendary People"), Publisher: Lyceum, Orhei (1999) 32,433 people received a politically motivated sentence, of which 8,360 were sentenced to death or died during interrogations.
 Serious incidents occurred in Northern Bukovina, where attempts by the locals to force the border towards Romania resulted in the Soviet border guards opening fire against unarmed civilians. In one case, at Fântâna Albă, that resulted in a massacre in which between 50 and 3,000 Romanians were killed. The situation was the same on the other side of the border: roughly 300 (or between 80 and 400, according to other sources) civilians, most of them Jews, waiting to leave for Soviet-controlled Bessarabia were shot by the Romanian army in
Serious incidents occurred in Northern Bukovina, where attempts by the locals to force the border towards Romania resulted in the Soviet border guards opening fire against unarmed civilians. In one case, at Fântâna Albă, that resulted in a massacre in which between 50 and 3,000 Romanians were killed. The situation was the same on the other side of the border: roughly 300 (or between 80 and 400, according to other sources) civilians, most of them Jews, waiting to leave for Soviet-controlled Bessarabia were shot by the Romanian army in Galați
Galați (, , ; also known by other alternative names) is the capital city of Galați County in the historical region of Western Moldavia, in eastern Romania. Galați is a port town on the Danube River. It has been the only port for the most pa ...
railway station on June 30, 1940.
The installation of the Soviet administration was also accompanied by major changes in the economic domain, as medium and large commercial and industrial enterprises were nationalized
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to priv ...
. The Soviet government also instituted a land reform
Land reform is a form of agrarian reform involving the changing of laws, regulations, or customs regarding land ownership. Land reform may consist of a government-initiated or government-backed property redistribution, generally of agricultur ...
that redistributed 229,752 hectares to 184,715 poor peasant households and limited estates to 20 hectares in the south and 10 hectares elsewhere. A collectivisation drive was also started in 1941, but the lack of agricultural machinery made the progress extremely slow, with 3.7% of the peasant households being included in a kolkhoz
A kolkhoz ( rus, колхо́з, a=ru-kolkhoz.ogg, p=kɐlˈxos) was a form of collective farm in the Soviet Union. Kolkhozes existed along with state farms or sovkhoz., a contraction of советское хозяйство, soviet ownership o ...
or a sovkhoz
A sovkhoz ( rus, совхо́з, p=sɐfˈxos, a=ru-sovkhoz.ogg, abbreviated from ''советское хозяйство'', "sovetskoye khozyaystvo (sovkhoz)"; ) was a form of state-owned farm in the Soviet Union.
It is usually contrasted wit ...
by the middle of year. To bolster the government's image, much of the 1941 budget was directed towards social and cultural needs, with 20% allocated to health services and 24% to education and literacy campaigns. The theological institute in Chișinău was closed, but six new higher education institutions were created, including a conservatory and a polytechnic
Polytechnic is most commonly used to refer to schools, colleges, or universities that qualify as an institute of technology or vocational university also sometimes called universities of applied sciences.
Polytechnic may also refer to:
Educat ...
. Furthermore, the salaries of industrial workers and administrative personnel were increased two to three times the pre-Soviet levels.
In September 1941, Romanian authorities uncovered evidence of torture perpetrated at the NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union.
...
headquarters and in the basement of the Metropolitan Palace in Chișinău. Some 80 bodies were discovered, of which 15 in a common grave, with their hands and feet tied. The bodies had been mutilated and burned, then doused with quicklime and acids; from the remains of the clothing it was inferred that the victims were priests and students.
Aftermath
International reactions
Of all of the regional allies with which Romania had treaties with military clauses, onlyTurkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
replied that it would live up to its treaty obligations by providing support against Soviet military aggression.
According to ''Time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, t ...
'' from Monday, July 1, 1940,
Political developments in Romania
 The territorial concessions of 1940 produced deep sorrow and resentment among Romanians and hastened the decline in popularity of the regime led by King
The territorial concessions of 1940 produced deep sorrow and resentment among Romanians and hastened the decline in popularity of the regime led by King Carol II of Romania
Carol II (4 April 1953) was King of Romania from 8 June 1930 until his forced abdication on 6 September 1940. The eldest son of Ferdinand I, he became crown prince upon the death of his grand-uncle, King Carol I in 1914. He was the first of th ...
. Three days after the annexation, Romania renounced the 1939 Anglo-French guarantee. A new government of Ion Gigurtu
Ion Gigurtu (; 24 June 1886 – 24 November 1959) was a far-right Romanian politician, Land Forces officer, engineer and industrialist who served a brief term as Prime Minister from 4 July to 4 September 1940, under the personal regime of King ...
was sworn in on July 5, 1940, which withdrew the country from the League of Nations on July 11 and announced its desire to join the Axis camp on July 13. A series of measures taken by Gigurtu, including official persecution of Jews inspired by the German Nuremberg Laws
The Nuremberg Laws (german: link=no, Nürnberger Gesetze, ) were antisemitic and Racism, racist laws that were enacted in Nazi Germany on 15 September 1935, at a special meeting of the Reichstag (Nazi Germany), Reichstag convened during ...
in July and August 1940, failed to sway Germany from awarding Northern Transylvania
Northern Transylvania ( ro, Transilvania de Nord, hu, Észak-Erdély) was the region of the Kingdom of Romania that during World War II, as a consequence of the August 1940 territorial agreement known as the Second Vienna Award, became part of ...
to Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
in the Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award, also known as the Vienna Diktat, was the second of two territorial disputes that were arbitrated by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. On 30 August 1940, they assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania, including all o ...
on August 30, 1940.
 That led to a near-uprising in the country. On September 5, King Carol II proposed to General (later Marshal)
That led to a near-uprising in the country. On September 5, King Carol II proposed to General (later Marshal) Ion Antonescu
Ion Antonescu (; ; – 1 June 1946) was a Romanian military officer and marshal who presided over two successive wartime dictatorships as Prime Minister and '' Conducător'' during most of World War II.
A Romanian Army career officer who ma ...
to form a new government. Antonescu's first act was to force the King to abdicate, for the fourth and final time, and to flee Romania. An alliance was formed by Ion Antonescu with remnants of the Iron Guard
The Iron Guard ( ro, Garda de Fier) was a Romanian militant revolutionary fascist movement and political party founded in 1927 by Corneliu Zelea Codreanu as the Legion of the Archangel Michael () or the Legionnaire Movement (). It was strong ...
(partly destroyed in 1938), an anti-Semitic
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
fascist
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy and the ...
party, and took power on September 6, 1940. Mihai, the son of Carol II, succeeded him as King of Romania. The country was declared a National Legionary State
The National Legionary State was a totalitarian fascist regime which governed Romania for five months, from 14 September 1940 until its official dissolution on 14 February 1941. The regime was led by General Ion Antonescu in partnership with th ...
. Between October 1940 and June 1941, around 550,000 German troops entered Romania. In November, Antonescu signed the Tripartite Pact
The Tripartite Pact, also known as the Berlin Pact, was an agreement between Germany, Italy, and Japan signed in Berlin on 27 September 1940 by, respectively, Joachim von Ribbentrop, Galeazzo Ciano and Saburō Kurusu. It was a defensive militar ...
, which tied Romania militarily to Germany, Italy and Japan. In January 1941, the Iron Guard attempted a coup, which failed and placed Antonescu firmly in power, with the approval of Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Germany from 1933 until his death in 1945. He rose to power as the leader of the Nazi Party, becoming the chancellor in 1933 and the ...
. The authoritarian regime of Antonescu (1940–1944) did not restore political parties and democracy but only co-opted several individual civilians in the government.
Overall, the desire to regain the lost territories was invoked as a justification by Romania for its entry into World War II on the side of the Axis against the Soviet Union.
Romanian recovery of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina and wartime administration
On June 22, 1941, Romania participated alongsideHungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
on the side of the Axis Powers in the German invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
to recover Bessarabia and Bukovina. The Axis armies accomplished this objective by July 26, 1941.
King Michael of Romania, his mother Helen, and Mihai Antonescu
Mihai Antonescu (18 November 1904 – 1 June 1946) was a Romanian politician who served as Deputy Prime Minister and Foreign Minister during World War II, executed in 1946 as a war criminal.
Early career
Born in Nucet, Dâmbovița County, w ...
joined the opening ceremony of the monumental Liberation Tower in Ghidighici
Ghidighici is a village in Chișinău municipality, Moldova.
It is the location of the Ghidighici Reservoir.
History
On November 1, 1942, King Michael I of Romania, his mother Helen, and Foreign Minister Mihai Antonescu
Mihai Antonescu ...
, on November 1, 1942.
On July 27, 1941, despite opposition from all political parties, Romania's military dictator, Ion Antonescu
Ion Antonescu (; ; – 1 June 1946) was a Romanian military officer and marshal who presided over two successive wartime dictatorships as Prime Minister and '' Conducător'' during most of World War II.
A Romanian Army career officer who ma ...
, ordered the Romanian Army
The Romanian Land Forces ( ro, Forțele Terestre Române) is the army of Romania, and the main component of the Romanian Armed Forces. In recent years, full professionalisation and a major equipment overhaul have transformed the nature of the La ...
to continue the war eastward into Soviet territory proper to fight at Odessa
Odesa (also spelled Odessa) is the third most populous city and municipality in Ukraine and a major seaport and transport hub located in the south-west of the country, on the northwestern shore of the Black Sea. The city is also the administrat ...
, Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
, Kharkov
Kharkiv ( uk, Ха́рків, ), also known as Kharkov (russian: Харькoв, ), is the second-largest city and municipality in Ukraine.
, Stalingrad
Volgograd ( rus, Волгогра́д, a=ru-Volgograd.ogg, p=vəɫɡɐˈɡrat), formerly Tsaritsyn (russian: Цари́цын, Tsarítsyn, label=none; ) (1589–1925), and Stalingrad (russian: Сталингра́д, Stalingrád, label=none; ) ...
and the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia (country), Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range ...
. Between late 1941 and early 1944, Romania occupied and administered the region between the Dniester
The Dniester, ; rus, Дне́стр, links=1, Dnéstr, ˈdⁿʲestr; ro, Nistru; grc, Τύρᾱς, Tyrās, ; la, Tyrās, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and ...
and Southern Bug
, ''Pivdennyi Buh''
, name_etymology =
, image = Sunset S Bug Vinnitsa 2007 G1.jpg
, image_size = 270
, image_caption = Southern Bug River in the vicinity of Vinnytsia, Ukraine
, map = PietinisBug ...
rivers, known as Transnistria
Transnistria, officially the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (PMR), is an unrecognised breakaway state that is internationally recognised as a part of Moldova. Transnistria controls most of the narrow strip of land between the Dniester riv ...
, and sent expeditionary troops to several different areas to support the German advance further into the Soviet Union.
 On the backdrop of increased anti-Semitism in Romania in the late 1930s, the government of Ion Antonescu officially adopted the myth of
On the backdrop of increased anti-Semitism in Romania in the late 1930s, the government of Ion Antonescu officially adopted the myth of Jewish Bolshevism
Jewish Bolshevism, also Judeo–Bolshevism, is an anti-communist and antisemitic canard, which alleges that the Jews were the originators of the Russian Revolution in 1917, and that they held primary power among the Bolsheviks who led the revo ...
, which made Jews responsible for the territorial losses Romania suffered during the summer of 1940. That made the government, in an agreement with Germany, embark on a campaign to "cleanse" the recaptured territories by deporting and/or killing the Jews of Bukovina and Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of ...
who did not flee to the interior of the Soviet Union before Romania regained the territory in July 1941. Only in 1941, between 45,000 and 60,000 Jews were killed in Bessarabia and Bukovina by the Romanian and German armies. Surviving Jews were quickly gathered in temporary ghettos and 154,449 to 170,737 were then deported to Transnistria; only 49,927 of them were still alive by September 16, 1943. Only 19,475 Jews of Bukovina and of Dorohoi County survived in those territories from 1941 to 1944 without being deported, most of them in Cernăuți. Romanian gendarmerie units also participated, along German troops and local militias, in the destruction of the Jewish community in Transnistria, by murdering between 115,000 and 180,000 local Jews. (See History of the Jews in Moldova#The Holocaust).
 In 1941 to 1944, many young male inhabitants of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina were recruited into the
In 1941 to 1944, many young male inhabitants of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina were recruited into the Romanian Army
The Romanian Land Forces ( ro, Forțele Terestre Române) is the army of Romania, and the main component of the Romanian Armed Forces. In recent years, full professionalisation and a major equipment overhaul have transformed the nature of the La ...
. From February to August 1944, hostilities took place in the region, as Romania attempted to keep the territory from being overrun by the Soviet Union. Overall during World War II, the Romanian Army lost 475,070 people on the Eastern Front, of which 245,388 were killed in action, disappeared, or died in hospitals or non-battle circumstances, and 229,682 (according to Soviet archival documents) were taken as prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
by the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
, of whom 187,367 were counted as Romanian prisoners of war in NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union.
...
camps (on April 22, 1956, 54,612 were counted as having died in captivity, and 132,755 as freshly released), 27,800 were counted as Romanians released by the front levels of the Soviet Army and 14,515 as Moldovans released by the front levels of the Soviet Army.
Restoration of Soviet administration
 In early 1944, the Soviet Union gradually took over the territory through the Uman–Botoșani and Second Jassy–Kishinev offensives. On August 23, 1944, with Soviet troops advancing and the Eastern Front falling within Romania's territory, a coup led by
In early 1944, the Soviet Union gradually took over the territory through the Uman–Botoșani and Second Jassy–Kishinev offensives. On August 23, 1944, with Soviet troops advancing and the Eastern Front falling within Romania's territory, a coup led by King Michael
Michael may refer to:
People
* Michael (given name), a given name
* Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael
Given name "Michael"
* Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian and ...
, with support from opposition politicians and the army, deposed the Antonescu dictatorship, ceased military actions against the Allies and later put Romania's battered armies on their side. In the days immediately after the coup, as Romania's action was unilateral and no armistice had been agreed with the Allied Powers, the Red Army continued to treat the Romanian troops as enemy combatants, and in the confusion, the Romanian troops did not oppose them. As a consequence, the Soviets took a large number of Romanian troops as prisoners of war
A prisoner of war (POW) is a person who is held Captivity, captive by a belligerent power during or immediately after an armed conflict. The earliest recorded usage of the phrase "prisoner of war" dates back to 1610.
Belligerents hold priso ...
with little or no fighting. Some of the prisoners were Bessarabian-born. Michael acquiesced to Soviet terms, and Romania was occupied by the Soviet Army.
From August 1944 to May 1945, about 300,000 people were conscripted into the Soviet Army from Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina and were sent to fight against Germany in Lithuania, East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostpreißen, label= Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Rytų Prūsija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 1 ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 mill ...
and Czechoslovakia.
In 1947, as part of the Paris Peace Treaties, Romania and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
signed a border treaty confirming the border fixed in 1940. Several additional uninhabited islands in the Danube Delta
The Danube Delta ( ro, Delta Dunării, ; uk, Дельта Дунаю, Deľta Dunaju, ) is the second largest river delta in Europe, after the Volga Delta, and is the best preserved on the continent. The greater part of the Danube Delta lies i ...
as well as the Snake Island, not mentioned in the treaty, were transferred from communist Romania to the Soviet Union in 1948.
Social and cultural consequences
Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym '' Vlachs'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2011 Roman ...
(53.49%), Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Or ...
and Ruthenians
Ruthenian and Ruthene are exonyms of Latin origin, formerly used in Eastern and Central Europe as common ethnonyms for East Slavs, particularly during the late medieval and early modern periods. The Latin term Rutheni was used in medieval sourc ...
(15.3%), Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
(10.34%), Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""T ...
(7.27%), Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not complete ...
(4.91%), Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
(3.31%), others (5.12%).
Population movements
 During the Soviet takeover in 1940, Bessarabian Germans (82,000) and Bukovinian Germans (40,000–45,000) were repatriated to Germany at the request of Hitler's government. Some of them were forcibly settled by the Nazis in the German-occupied Poland and had to move again in 1944–1945. The people affected by the resettlement were not persecuted, but they were given no choice to stay or live and had to change their entire livelihood within weeks or even days.
During the Soviet takeover in 1940, Bessarabian Germans (82,000) and Bukovinian Germans (40,000–45,000) were repatriated to Germany at the request of Hitler's government. Some of them were forcibly settled by the Nazis in the German-occupied Poland and had to move again in 1944–1945. The people affected by the resettlement were not persecuted, but they were given no choice to stay or live and had to change their entire livelihood within weeks or even days.
Deportations and political repression
Deportation
Deportation is the expulsion of a person or group of people from a place or country. The term ''expulsion'' is often used as a synonym for deportation, though expulsion is more often used in the context of international law, while deportation ...
s of locals on grounds of belonging to the intelligentsia
The intelligentsia is a status class composed of the university-educated people of a society who engage in the complex mental labours by which they critique, shape, and lead in the politics, policies, and culture of their society; as such, the i ...
or kulak
Kulak (; russian: кула́к, r=kulák, p=kʊˈlak, a=Ru-кулак.ogg; plural: кулаки́, ''kulakí'', 'fist' or 'tight-fisted'), also kurkul () or golchomag (, plural: ), was the term which was used to describe peasants who owned ove ...
classes, or of having anti-Soviet
Anti-Sovietism, anti-Soviet sentiment, called by Soviet authorities ''antisovetchina'' (russian: антисоветчина), refers to persons and activities actually or allegedly aimed against the Soviet Union or government power within the S ...
nationalist ideas occurred in 1940 to 1941 and 1944 to 1951. The deportations touched all local ethnic groups: Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym '' Vlachs'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2011 Roman ...
, Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Or ...
, Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
, Jews, Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not complete ...
, Gagauz. Significant deportations happened on three separate occasions: according to Alexandru Usatiuc-Bulgăr, 29,839 people were deported to Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part o ...
on 13 June 1941. In total, in the first year of Soviet occupation, no fewer than 86,604 people from Bessarabia, Northern Bukovina, and Hertsa Region suffered political repression. That number is close to the one calculated by Russian historians following documents in the Moscow archives, of ca. 90,000 people repressed (arrested, executed, deported or conscripted for work) in the first year of Soviet occupation. The greater part of the figure (53,356) was represented by forced conscription for labour across the Soviet Union. The classification of such labourers as victims of political repression is, however, disputed since the poverty of the locals and Soviet propaganda are also considered important factors leading to the emigration of the local workforce. The arrests continued even after 22 June 1941.
Based on postwar statistics, the historian Igor Cașu has shown that Moldovans and Romanians comprised roughly 50 percent of the deportees, with the rest being Jews, Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 ''Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
, Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Or ...
, Gagauzes, Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not complete ...
and Roma people
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have diaspora populations located worldwide, with si ...
. Considering the ethnic make-up of the region, he concludes that the prewar and postwar repressions were not directed at any specific ethnic or national group but could be characterised as "genocide" or "crime against humanity". The 1941 deportation targeted "anti-Soviet elements" and comprised former representatives of the Romanian interwar administration (policemen, gendarmes, prison guards, clerks), large landowners, tradesmen, former officers of the Romanian, Polish and Tsarist armies and people who had defected the Soviet Union before 1940. Kulaks did not become main targets of repression until the postwar period. Before Soviet archives were made accessible, R. J. Rummel had estimated between 1940 and 1941, 200,000 to 300,000 Romanian Bessarabians were deported, of whom 18,000 to 68,000 were killed according to him.
Religious persecution
After the installation of the Soviet administration, religious life inBessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of ...
and Northern Bukovina
Bukovinagerman: Bukowina or ; hu, Bukovina; pl, Bukowina; ro, Bucovina; uk, Буковина, ; see also other languages. is a historical region, variously described as part of either Central or Eastern Europe (or both).Klaus Peter Berge ...
underwent a persecution similar to the one in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eigh ...
between the World Wars
A world war is an international conflict which involves all or most of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World WarI (1914 ...
. In the first days of occupation, certain population groups welcomed the Soviet power, and some of them joined the newly established Soviet ''nomenklatura'', including the NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union.
...
, the Soviet political police. The latter had used those locals to find and arrest numerous priests. ''Martiri pentru Hristos, din România, în perioada regimului comunist'', Editura Institutului Biblic și de Misiune al Bisericii Ortodoxe Române, București, 2007, pp.34–35 Other priests were arrested and interrogated by the Soviet NKVD itself, deported to the interior of the Soviet Union and killed. Research on the subject is still at an early stage. As of 2007, the Orthodox Church has recognized the martyrdom
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an external ...
to about 50 clergymen, who died in the first year of Soviet rule (1940–1941).
Legacy
In the Soviet Union
In earlySoviet historiography
Soviet historiography is the methodology of history studies by historians in the Soviet Union (USSR). In the USSR, the study of history was marked by restrictions imposed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU). Soviet historiography ...
, the chain of events that led to the creation of the Moldavian SSR was described as a "liberation of the Moldovan people from a 22-year-old occupation by boyar Romania." The Soviet authors went into great length to describe scenes how the liberated Bessarabian people eagerly welcomed Soviet troops ending the "22 years of yoke under the Romanian capitalists and landowners", organized demonstrations under red flags and liberated imprisoned communists from the Siguranța
Siguranța was the generic name for the successive secret police services in the Kingdom of Romania. The official title of the organization changed throughout its history, with names including Directorate of the Police and General Safety ( ro, Di ...
torture chamber
A torture chamber is a room where torture is inflicted.
s. In 1940 to 1989, the Soviet authorities promoted the events of June 28, 1940 as a "liberation", and the day itself was a holiday in the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic ( ro, Republica Sovietică Socialistă Moldovenească, Moldovan Cyrillic: ) was one of the 15 republics of the Soviet Union which existed from 1940 to 1991. The republic was formed on 2 August 1940 ...
.
However, in 2010, the Russian political analyst Leonid Mlechin stated that the term occupation is not adequate but that "it is more an annexation of a part of the territory of Romania".
Pre-independence Moldova
From June 26 to 28, 1991, an International Conference "Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact and its consequences for Bessarabia" took place in Chișinău, gathering scholars such asNicholas Dima
Nicholas is a male given name and a surname.
The Eastern Orthodox Church, the Roman Catholic Church, and the Anglican Churches celebrate Saint Nicholas every year on December 6, which is the name day for "Nicholas". In Greece, the name and it ...
, Kurt Treptow
Kurt is a male given name of Germanic or Turkish origin. ''Kurt'' or ''Curt'' originated as short forms of the Germanic Conrad, depending on geographical usage, with meanings including counselor or advisor.
In Turkish, Kurt means "Wolf" and is ...
, Dennis Deletant, Michael Mikelson
Michael may refer to:
People
* Michael (given name), a given name
* Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael
Given name "Michael"
* Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian and ...
, Stephen Bowers, Lowry Wymann Lowry may refer to:
People
* Calvin Lowry (born 1983), American football player
* Dave Lowry (born 1965), Canadian ice hockey player
* Desiree Lowry (born 1972), Puerto Rican beauty pageant titleholder
* Hiram Harrison Lowry (1843–1924), Amer ...
, Michael Bruchis
Michael may refer to:
People
* Michael (given name), a given name
* Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael
Given name "Michael"
* Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian and ...
, in addition to other Moldovan, Soviet and Romanian authors. An informal ''Declaration of Chișinău'' was adopted, according to which the Pact and its Secret Protocol "constituted the apogee of collaboration between the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany, and following these agreements, Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina were occupied by the Soviet Army on June 28, 1940 as a result of ultimative notes addressed to the Romanian government". It further stated that the events were a "pregnant manifestation of imperialist policy of annexation and diktat, a shameless aggression against the sovereignty (...) of neighboring states, members of the League of Nations. The Stalinist aggression constituted a serious breach of the legal norms of behavior of states in international relations, of the obligations assumed under the Briand-Kellog Pact of 1928, and under the London Convention on the Definition of the Aggressor of 1933". The declaration stated that "the Pact and the Secret Additional Protocol are legally null ''ab initio'', and their consequences must be eliminated". For the latter, it called for "political solutions that would lead to the elimination of the acts of injustice and abuse committed through the use of force, diktat and annexations,... olutionsin full consensus with the principles of the Final Act of Helsinki, and the Paris Charter for a new Europe".
United States
On June 28, 1991, theUS Senate
The United States Senate is the upper chamber of the United States Congress, with the House of Representatives being the lower chamber. Together they compose the national bicameral legislature of the United States.
The composition and p ...
voted a resolution sponsored by Senators Jesse Helms
Jesse Alexander Helms Jr. (October 18, 1921 – July 4, 2008) was an American politician. A leader in the conservative movement, he served as a senator from North Carolina from 1973 to 2003. As chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee ...
(R-NC) and Larry Pressler
Larry Lee Pressler (born March 29, 1942) is an American lawyer and politician from South Dakota who served in the United States House of Representatives (1975–1979) and United States Senate (1979–1997) as a Republican. He remained active in ...
(R-SD), members of the US Senate Committee on Foreign Relations, which recommended the US government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 states, a city within a feder ...
to
# support the right to self-determination of the people of Moldova and Northern Bukovina, occupied by the Soviets, and to draft a decision to this end;
# support the future efforts of the Government of Moldova to negotiate, if it desires so, a peaceful reunification of Moldova and Northern Bukovina with Romania, as established in the Treaty of Paris (1920), respecting the existing norms of international law and principle 1 of the Helsinki Act.
In the clauses of this Senate resolution it has been stated, among other things, that "(...) The armed forces of the Soviet Union invaded the Kingdom of Romania and occupied Eastern Moldova, Northern Bukovina and Hertsa Region. (...) The annexation was prepared beforehand in a Secret Agreement to a Non-Aggression Treaty signed by the Governments of the Soviet Union and the German Reich on August 23, 1939. (...) Between 1940 and 1953 hundreds of thousand of Romanian from Moldova and Northern Bukovina were deported by the USSR to Central Asia and Siberia (...)."
Modern Moldova
* Mihai Ghimpu, interim president of Moldova in 2010, has decreed June 28, 1940, as the Soviet Occupation Day. The move was met with disapproval and calls for the decree's revocation inside the ruling coalition and for Ghimpu's resignation by the opposition parties. Dorin Chirtoacă, mayor of Chișinău and member of the same party as Ghimpu, ordered the erection of amemorial stone
A headstone, tombstone, or gravestone is a stele or marker, usually stone, that is placed over a grave. It is traditional for burials in the Christian, Jewish, and Muslim religions, among others. In most cases, it has the deceased's name, ...
in the National Assembly Square, in front of the cabinet building, where a Lenin monument used to stand. The members of the coalitions argued that the time has not come for such a decree and that it would only help the communists win more votes. The Academy of Sciences of Moldova declared that "in the view of recent disagreements regarding June 28, 1940 ..we must take action and inform the public opinion about the academic community views". The Academy declared: "Archival documents and historical research of international experts shows that the annexation of Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina was designed and built by Soviet Command as a military occupation of these territories. Ordinance of Interim President Michael Ghimpu reflects, in principle, the historical truth." The Constitutional Court
A constitutional court is a high court that deals primarily with constitutional law. Its main authority is to rule on whether laws that are challenged are in fact unconstitutional, i.e. whether they conflict with constitutionally established ...
cancelled Ghimpu's decree on July 12, 2010.
* On June 30, 2010, First Vlad Filat Cabinet decided to create the Museum of Victims of Communism and Vlad Filat opened the museum on July 6, 2010.
* The Party of Communists of the Republic of Moldova
The Party of Communists of the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Партидул Комуништилор дин Република Молдова, italic=no, Partidul Comuniștilor din Republica Moldova; russian: Партия коммунистов Р ...
, as well ad the Party of Socialists of the Republic of Moldova still regard the date of 28 June 1940 as the day of the Moldovan liberation from the Romanian occupationhttp://www.e-democracy.md/parties/docs/pcrm/201706281/
See also
*European Day of Remembrance for Victims of Stalinism and Nazism
The Black Ribbon Day, officially known in the European Union as the European Day of Remembrance for Victims of Stalinism and Nazism and also referred to as the Europe-wide Day of Remembrance for the victims of all totalitarian and authoritarian ...
* Declaration on Crimes of Communism
* Prague Declaration on European Conscience and Communism
* Vilnius Declaration The Vilnius Declaration was a declaration adopted by the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) during the 18th annual session of its parliamentary assembly, that took place in Vilnius from 29 June to 3 July 2009.
The declarat ...
* Comparison of Nazism and Stalinism
Comparison or comparing is the act of evaluating two or more things by determining the relevant, comparable characteristics of each thing, and then determining which characteristics of each are similar to the other, which are different, and t ...
* Soviet occupation of Romania
Notes
References
* * *Mikhail Meltyukhov
Mikhail Ivanovich Meltyukhov (russian: Russian: Михаил Иванович Мельтюхов, ), (born 14 March 1966), is a Russian military historian.
Works
Meltyukhov was born in Moscow.
In 1995, he defended the dissertation “Contemporary ...
, ''Stalin's Missed Chance
''Stalin's Missed Chance'' is a study by Russian military historian Mikhail Ivanovich Meltyukhov, author of several books and articles on Soviet military history.
''Stalin's Missed Chance'' covers a theory of planned Soviet invasion raised by ...
''
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
* Read, A., & Fisher, D. (1988). ''Deadly Embrace: Hitler, Stalin and the Nazi-Soviet Pact, 1939-1941''. W W Norton & Co. * Rieber, A. J. (2022). ''Stalin as Warlord''. Yale University Press. * Sontag, R. J., & Beddie, J. S. (Eds.). (2003). ''Nazi Soviet Relations, 1939-1941: Documents From The Archives Of The German Foreign Office''. University Press of the Pacific. * Treptow, K. W. (2022). ''Romania and World War II''. Center for Romanian Studies.External links
* "Molotov–Ribbentrop pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union that enabled those powers to partition Poland between them. The pact was signed in Moscow on 23 August 1939 by German Foreign Minister Joachim von Ri ...
", from Wikisource
"Romanian Army in the Second World War"
International Commission on the Holocaust in Romania: Final Report
(2004)
The June/July 1940 Romanian Withdrawal from Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina and its Consequences on Interethnic Relations in Romania
*
*
* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20100527162751/http://ebooks.unibuc.ro/istorie/istorie1918-1940/13-4.htm "The Ultimatum notes and Romanian responses"* {{Nazi-Soviet relations Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic Romania in World War II History of Chernivtsi Oblast History of Budjak Moldova in World War II June 1940 events in Romania July 1940 events in Romania 1940 in the Soviet Union 1940 in international relations Battles and operations of the Eastern Front of World War II Bessarabian and Northern Bukovina Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina
Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of ...
Ultimata
Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds of ...
Romania–Soviet Union relations
Wars involving the Soviet Union
June 1940 events
July 1940 events
Attacks in Moldova