Somerset cricketers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
( en, All The People of Somerset) , locator_map = , coordinates =
, region =
, coordinates =
, region =  , districts_list =
County council area:
, districts_list =
County council area:
, MPs = * Rebecca Pow
 After the Romans left, Britain was invaded by Anglo-Saxon peoples. By 600 CE they had established control over much of what is now England, but Somerset was still in native British hands. The British held back Saxon advance into the south-west for some time longer, but by the early eighth century King Ine of Wessex had pushed the boundaries of the West Saxon kingdom far enough west to include Somerset. The Saxon royal palace in Cheddar was used several times in the 10th century to host the
After the Romans left, Britain was invaded by Anglo-Saxon peoples. By 600 CE they had established control over much of what is now England, but Somerset was still in native British hands. The British held back Saxon advance into the south-west for some time longer, but by the early eighth century King Ine of Wessex had pushed the boundaries of the West Saxon kingdom far enough west to include Somerset. The Saxon royal palace in Cheddar was used several times in the 10th century to host the
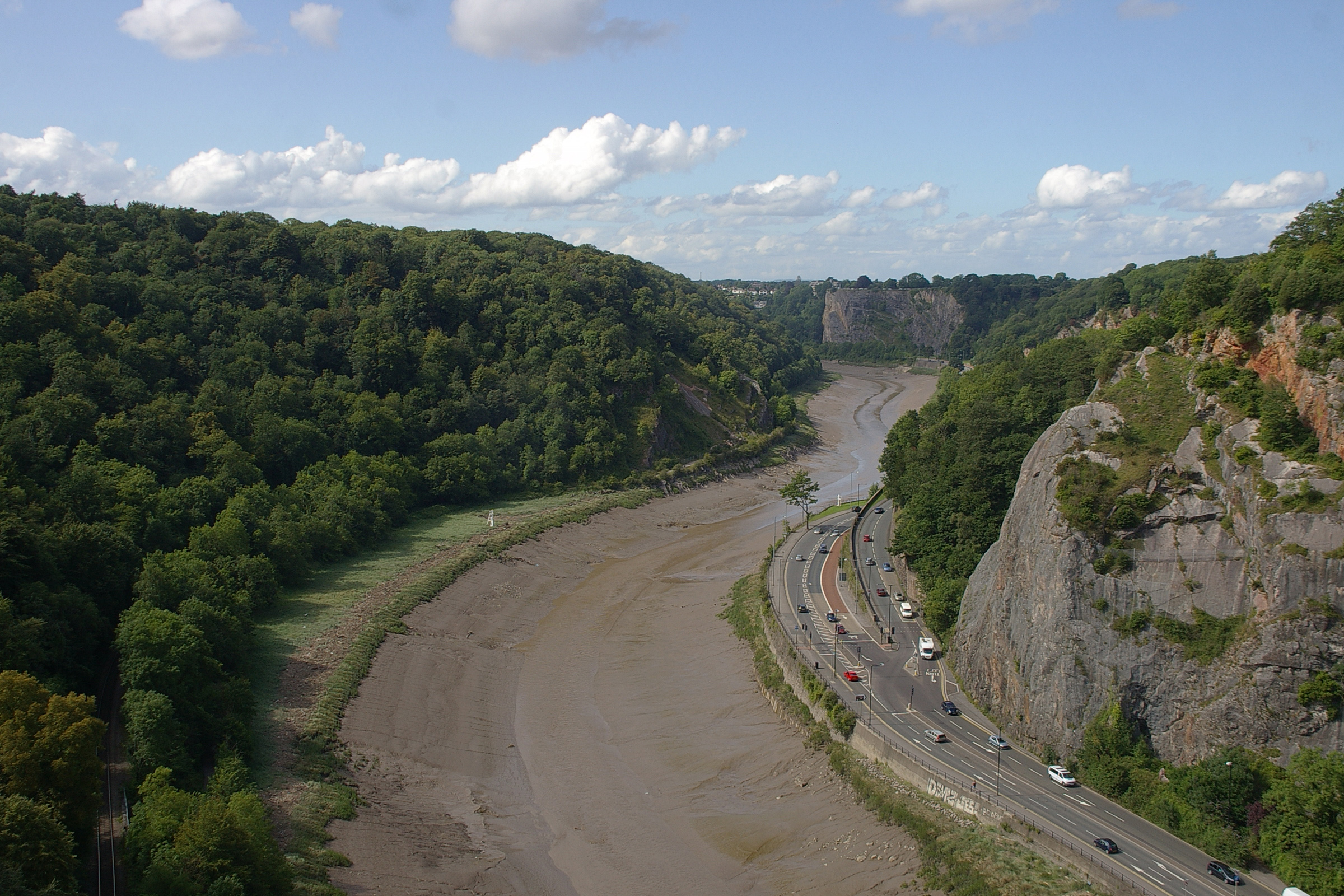 The boundaries of Somerset are very similar to how they were in medieval times. They have been largely unaltered. The River Avon formed much of the border with Gloucestershire, except that the hundred of Bath Forum, which straddles the Avon, formed part of Somerset. Bristol began as a town on the Gloucestershire side of the Avon, however as it grew it extended across the river into Somerset. In 1373
The boundaries of Somerset are very similar to how they were in medieval times. They have been largely unaltered. The River Avon formed much of the border with Gloucestershire, except that the hundred of Bath Forum, which straddles the Avon, formed part of Somerset. Bristol began as a town on the Gloucestershire side of the Avon, however as it grew it extended across the river into Somerset. In 1373
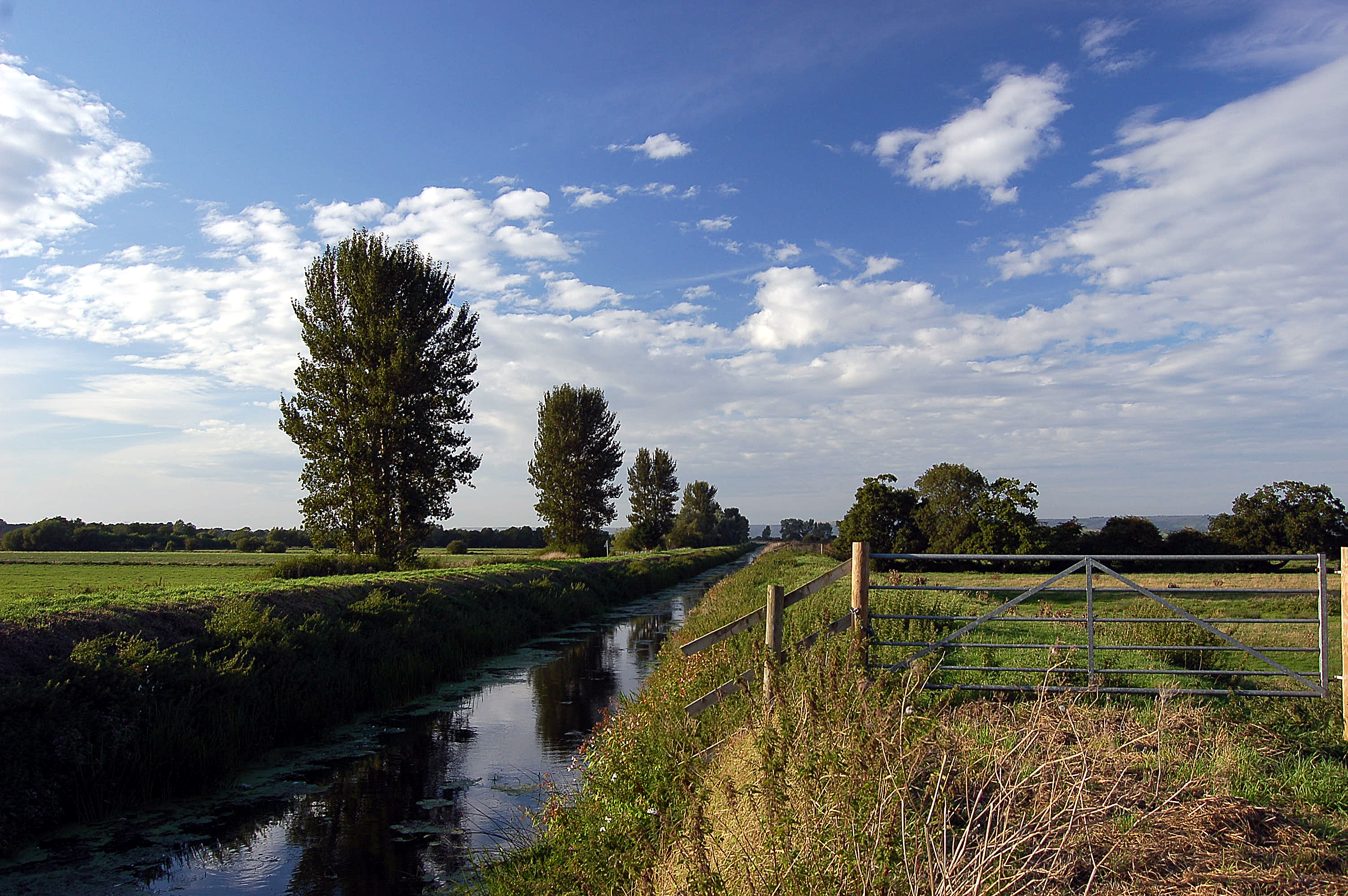 To the north-east of the Somerset Levels, the Mendip Hills are moderately high limestone hills. The central and western Mendip Hills was designated an
To the north-east of the Somerset Levels, the Mendip Hills are moderately high limestone hills. The central and western Mendip Hills was designated an
 The Somerset Levels (or Somerset Levels and Moors as they are less commonly but more correctly known) are a sparsely populated
The Somerset Levels (or Somerset Levels and Moors as they are less commonly but more correctly known) are a sparsely populated  The North Somerset Levels basin, north of the Mendips, covers a smaller geographical area than the Somerset Levels; and forms a coastal area around Avonmouth. It too was reclaimed by draining.Rippon, Stephen (1997). ''The Severn Estuary: Landscape Evolution and Wetland Reclamation''. London: Leicester University. It is mirrored, across the Severn Estuary, in Wales, by a similar low-lying area: the Caldicot and Wentloog Levels.
In the far west of the county, running into Devon, is Exmoor, a high Devonian sandstone moor, which was designated as a
The North Somerset Levels basin, north of the Mendips, covers a smaller geographical area than the Somerset Levels; and forms a coastal area around Avonmouth. It too was reclaimed by draining.Rippon, Stephen (1997). ''The Severn Estuary: Landscape Evolution and Wetland Reclamation''. London: Leicester University. It is mirrored, across the Severn Estuary, in Wales, by a similar low-lying area: the Caldicot and Wentloog Levels.
In the far west of the county, running into Devon, is Exmoor, a high Devonian sandstone moor, which was designated as a

 The coastline of the
The coastline of the
 The
The
 Somerset has few industrial centres, but it does have a variety of light industry and high technology businesses, along with traditional agriculture and an increasingly important tourism sector, resulting in an unemployment rate of 2.5%. Tourism was estimated in 2013 to support around 26,000 people.
Bridgwater was developed during the Industrial Revolution as the area's leading port. The River Parrett was navigable by large ships as far as Bridgwater. Cargoes were then loaded onto smaller boats at Langport Quay, next to the Bridgwater Bridge, to be carried further up river to Langport;Lawrence, J.F. (2005). ''A History of Bridgwater''. (revised and compiled by J. C. Lawrence) Chichester: Phillimore & Co. . or they could turn off at Burrowbridge and then travel via the River Tone to Taunton. The Parrett is now only navigable as far as Dunball Wharf. Bridgwater, in the 19th and 20th centuries, was a centre for the manufacture of bricks and clay roof tiles, and later cellophane, but those industries have now stopped.
With its good links to the motorway system, Bridgwater has developed as a distribution hub for companies such as Argos, Toolstation,
Somerset has few industrial centres, but it does have a variety of light industry and high technology businesses, along with traditional agriculture and an increasingly important tourism sector, resulting in an unemployment rate of 2.5%. Tourism was estimated in 2013 to support around 26,000 people.
Bridgwater was developed during the Industrial Revolution as the area's leading port. The River Parrett was navigable by large ships as far as Bridgwater. Cargoes were then loaded onto smaller boats at Langport Quay, next to the Bridgwater Bridge, to be carried further up river to Langport;Lawrence, J.F. (2005). ''A History of Bridgwater''. (revised and compiled by J. C. Lawrence) Chichester: Phillimore & Co. . or they could turn off at Burrowbridge and then travel via the River Tone to Taunton. The Parrett is now only navigable as far as Dunball Wharf. Bridgwater, in the 19th and 20th centuries, was a centre for the manufacture of bricks and clay roof tiles, and later cellophane, but those industries have now stopped.
With its good links to the motorway system, Bridgwater has developed as a distribution hub for companies such as Argos, Toolstation,  Agriculture and food and drink production continue to be major industries in the county, employing over 15,000 people. Apple orchards were once plentiful, and Somerset is still a major producer of cider. The towns of Taunton and
Agriculture and food and drink production continue to be major industries in the county, employing over 15,000 people. Apple orchards were once plentiful, and Somerset is still a major producer of cider. The towns of Taunton and  The county has a long tradition of supplying freestone and
The county has a long tradition of supplying freestone and
 In
In 
 The county has several museums; those at Bath include the
The county has several museums; those at Bath include the
 Somerset has of roads. The main arterial routes, which include the M5 motorway, A303, A37, A38, A39, A358 and A361 give good access across the county, but many areas can only be accessed via narrow country lanes.
Rail services are provided by the West of England Main Line through Yeovil Junction, the Bristol to Exeter line,
Somerset has of roads. The main arterial routes, which include the M5 motorway, A303, A37, A38, A39, A358 and A361 give good access across the county, but many areas can only be accessed via narrow country lanes.
Rail services are provided by the West of England Main Line through Yeovil Junction, the Bristol to Exeter line,
( en, All The People of Somerset) , locator_map =
South West England
South West England, or the South West of England, is one of nine official regions of England. It consists of the counties of Bristol, Cornwall (including the Isles of Scilly), Dorset, Devon, Gloucestershire, Somerset and Wiltshire. Cities and ...
, established_date = Ancient
, established_by =
, preceded_by =
, origin =
, lord_lieutenant_office =Lord Lieutenant of Somerset
, lord_lieutenant_name = Mohammed Saddiq
Mohammed Habedat Saddiq is Lord-lieutenant of Somerset. A utilities-sector engineer and manager he was born in Leeds, Yorkshire in June 1970 after his parents came to England in the late 1960s from Pakistan.
Career
He has held management and en ...
, high_sheriff_office =High Sheriff of Somerset
, high_sheriff_name = Mrs Mary-Clare Rodwell (2020–21)
, area_total_km2 = 4171
, area_total_rank = 7th
, ethnicity = 98.5% White
, county_council =
, unitary_council =
, government =
, joint_committees =
, admin_hq = Taunton
Taunton () is the county town of Somerset, England, with a 2011 population of 69,570. Its thousand-year history includes a 10th-century monastic foundation, Taunton Castle, which later became a priory. The Normans built a castle owned by t ...
, area_council_km2 = 3451
, area_council_rank = 10th
, iso_code = GB-SOM
, ons_code = 40
, gss_code =
, nuts_code = UKK23
, districts_map = , MPs = * Rebecca Pow
(C)
An uppercase (C) (parenthetical C) may refer to:
* Copyright symbol (©)
*
* , indicating NSA-controlled cryptographic/classified items
See also
* Circle-c (disambiguation)
* Copyright symbol (disambiguation)
* C (disambiguation)
C is the ...
* Wera Hobhouse ( LD)
* Liam Fox (C)
* David Warburton
David John Warburton (born 28 October 1965) is a British politician serving as Member of Parliament (MP) for Somerton and Frome. On his election in the 2015 general election he represented the Conservative Party, but was suspended from the p ...
(C)
* Marcus Fysh (C)
* Ian Liddell-Grainger
Ian or Iain is a name of Scottish Gaelic origin, derived from the Hebrew given name (Yohanan, ') and corresponding to the English name John. The spelling Ian is an Anglicization of the Scottish Gaelic forename ''Iain''. It is a popular name in ...
(C)
* James Heappey (C)
* Jacob Rees-Mogg (C)
* John Penrose
John David Penrose (born 22 June 1964) is a British politician serving as Member of Parliament (MP) for Weston-super-Mare since 2005. A member of the Conservative Party, he was the United Kingdom Anti-Corruption Champion at the Home Office f ...
(C)
, police = Avon and Somerset Police
Avon and Somerset Police is the territorial police force responsible for law enforcement in the county of Somerset and in four districts that used to be in the defunct county of Avon: Bristol, Bath and North East Somerset, North Somerset and ...
, website =http://www.somerset.gov.uk/
Somerset ( , ; archaically Somersetshire , , ) is a county
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes Chambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
in South West England
South West England, or the South West of England, is one of nine official regions of England. It consists of the counties of Bristol, Cornwall (including the Isles of Scilly), Dorset, Devon, Gloucestershire, Somerset and Wiltshire. Cities and ...
which borders Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire ( abbreviated Glos) is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean.
The county town is the city of Gl ...
and Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city i ...
to the north, Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershir ...
to the east, Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset. Covering an area of ...
to the south-east and Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devon is ...
to the south-west. It is bounded to the north and west by the Severn Estuary and the Bristol Channel
The Bristol Channel ( cy, Môr Hafren, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales from Devon and Somerset in South West England. It extends from the lower estuary of the River S ...
, its coastline facing southeastern Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
. Its traditional border with Gloucestershire is the River Avon. Somerset is currently formed of six council areas, of which two are unitary authorities, until the four second-tier district councils are merged on 1 April 2023, after which the county will comprise three unitary authorities. Its county town is Taunton
Taunton () is the county town of Somerset, England, with a 2011 population of 69,570. Its thousand-year history includes a 10th-century monastic foundation, Taunton Castle, which later became a priory. The Normans built a castle owned by t ...
.
Somerset is a rural county of rolling hills, the Blackdown Hills
The Blackdown Hills are a range of hills along the Somerset-Devon border in south-western England, which were designated an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) in 1991.
The plateau is dominated by hard chert bands of Upper Greensand wit ...
, Mendip Hills, Quantock Hills and Exmoor National Park, and large flat expanses of land including the Somerset Levels
The Somerset Levels are a coastal plain and wetland area of Somerset, England, running south from the Mendips to the Blackdown Hills.
The Somerset Levels have an area of about and are bisected by the Polden Hills; the areas to the south are ...
. There is evidence of human occupation from Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός '' palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone to ...
times, and of subsequent settlement by the Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
, Romans and Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
s. The county played a significant part in Alfred the Great's rise to power, and later the English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians ("Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of Kingdom of England, England's governanc ...
and the Monmouth Rebellion
The Monmouth Rebellion, also known as the Pitchfork Rebellion, the Revolt of the West or the West Country rebellion, was an attempt to depose James II, who in February 1685 succeeded his brother Charles II as king of England, Scotland and Ire ...
. The city of Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
is famous for its Georgian architecture and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
.
Toponymy
Somerset's name derives from Old English '' Sumorsǣte'', short for ''Sumortūnsǣte'', meaning "the people living at or dependent on Sumortūn ( Somerton)". The first known use of ''Somersæte'' is in the law code ofKing Ine
Ine, also rendered Ini or Ina, ( la, Inus; c. AD 670 – after 726) was King of Wessex from 689 to 726. At Ine's accession, his kingdom dominated much of southern England. However, he was unable to retain the territorial gains of his predecessor ...
who was the Saxon King of Wessex from 688 to 726 CE, making Somerset along with Hampshire
Hampshire (, ; abbreviated to Hants) is a ceremonial county, ceremonial and non-metropolitan county, non-metropolitan counties of England, county in western South East England on the coast of the English Channel. Home to two major English citi ...
, Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershir ...
and Dorset
Dorset ( ; archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a county in South West England on the English Channel coast. The ceremonial county comprises the unitary authority areas of Bournemouth, Christchurch and Poole and Dorset. Covering an area of ...
one of the oldest extant units of local government in the world. An alternative suggestion is the name derives from ''Seo-mere-saetan'' meaning "settlers by the sea lakes".
The Old English name is used in the motto
A motto (derived from the Latin , 'mutter', by way of Italian , 'word' or 'sentence') is a sentence or phrase expressing a belief or purpose, or the general motivation or intention of an individual, family, social group, or organisation. Mo ...
of the county, , meaning "all the people of Somerset". Adopted as the motto in 1911, the phrase is taken from the ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle''. Somerset was a shire of the Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
kingdom of Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
, and the phrase refers to the wholehearted support the people of Somerset gave to King Alfred
Alfred the Great (alt. Ælfred 848/849 – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who ...
in his struggle to save Wessex from Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and s ...
invaders.
Somerset settlement names are mostly Anglo-Saxon in origin (for example, Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
, Somerton, Wells
Wells most commonly refers to:
* Wells, Somerset, a cathedral city in Somerset, England
* Well, an excavation or structure created in the ground
* Wells (name)
Wells may also refer to:
Places Canada
* Wells, British Columbia
England
* Wel ...
and Keynsham), but numerous place names include British Celtic elements, such as the rivers Frome and Avon, and names of hills. For example, an Anglo-Saxon charter of 682 refers to Creechborough Hill as "the hill the British call ''Cructan'' and the Anglo-Saxons call ''Crychbeorh''". Some modern names are wholly Brittonic in origin, like Tarnock, Priddy, and Chard, while others have both Saxon and Brittonic elements, such as Pen Hill
Pen Hill forms part of the Mendip Hills plateau in Somerset, England. The hill is located in St Cuthbert Out civil parish in Mendip district.
The name Pen is believed to be Celtic for hill or tor. It gives its name to one of the four periclin ...
.
History

Prehistory
The caves of the Mendip Hills were settled during the Palaeolithic period, and contain extensive archaeological sites such as those atCheddar Gorge
Cheddar Gorge is a limestone gorge in the Mendip Hills, near the village of Cheddar, Somerset, England. The gorge is the site of the Cheddar show caves, where Britain's oldest complete human skeleton, Cheddar Man, estimated to be 9,000 yea ...
. Bones from Gough's Cave have been dated to 12,000 BCE, and a complete skeleton, known as Cheddar Man, dates from 7150 BCE. Examples of cave art have been found in Aveline's Hole
Aveline's Hole is a cave at Burrington Combe in the limestone of the Mendip Hills, in Somerset, England.
The earliest scientifically dated cemetery in Britain, 10,200 and 10,400 years old, was found at Aveline's Hole, constituting the larges ...
. Some caves continued to be occupied until modern times, including Wookey Hole.
The Somerset Levels
The Somerset Levels are a coastal plain and wetland area of Somerset, England, running south from the Mendips to the Blackdown Hills.
The Somerset Levels have an area of about and are bisected by the Polden Hills; the areas to the south are ...
—specifically dry point
In geography, a dry point is an area of firm or flood-free ground in an area of wetland, marsh or flood plains. The term typically applies to settlements, and dry point settlements were common in history.
In the United Kingdom extreme examples ...
s at Glastonbury
Glastonbury (, ) is a town and civil parish in Somerset, England, situated at a dry point on the low-lying Somerset Levels, south of Bristol. The town, which is in the Mendip district, had a population of 8,932 in the 2011 census. Glastonb ...
and Brent Knoll— also have a long history of settlement, and are known to have been settled by Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymo ...
hunters. Travel in the area was facilitated by the construction of one of the world's oldest known engineered roadways, the Sweet Track, which dates from 3807 BCE or 3806 BCE.
The exact age of the henge monument at Stanton Drew stone circles
The Stanton Drew stone circles are just outside the village of Stanton Drew in the English county of Somerset. The largest stone circle is the Great Circle, in diameter and the second largest stone circle in Britain (after Avebury); it is con ...
is unknown, but it is believed to be Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
. There are numerous Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
hill fort
A hillfort is a type of earthwork used as a fortified refuge or defended settlement, located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typically European and of the Bronze Age or Iron Age. Some were used in the post- ...
s, some of which, like Cadbury Castle and Ham Hill, were later reoccupied in the Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the M ...
.
Roman invasion
On the authority of the future emperorVespasian
Vespasian (; la, Vespasianus ; 17 November AD 9 – 23/24 June 79) was a Roman emperor who reigned from AD 69 to 79. The fourth and last emperor who reigned in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty that ruled the Em ...
, as part of the ongoing expansion of the Roman presence in Britain, the Second Legion Augusta invaded Somerset from the south-east in 47 CE. The county remained part of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
until around 409 CE, when the Roman occupation of Britain came to an end.
A variety of Roman remains have been found, including Pagans Hill Roman temple in Chew Stoke, Low Ham Roman Villa
The Low Ham Roman Villa was a Roman courtyard villa located near Low Ham in the civil parish of High Ham in the English county of Somerset. It is best known for the extraordinary figured mosaic depicting the story of Aeneas and Dido.
Th ...
and the Roman Baths that gave their name to the city of Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
.
Saxon and Norman invasions
 After the Romans left, Britain was invaded by Anglo-Saxon peoples. By 600 CE they had established control over much of what is now England, but Somerset was still in native British hands. The British held back Saxon advance into the south-west for some time longer, but by the early eighth century King Ine of Wessex had pushed the boundaries of the West Saxon kingdom far enough west to include Somerset. The Saxon royal palace in Cheddar was used several times in the 10th century to host the
After the Romans left, Britain was invaded by Anglo-Saxon peoples. By 600 CE they had established control over much of what is now England, but Somerset was still in native British hands. The British held back Saxon advance into the south-west for some time longer, but by the early eighth century King Ine of Wessex had pushed the boundaries of the West Saxon kingdom far enough west to include Somerset. The Saxon royal palace in Cheddar was used several times in the 10th century to host the Witenagemot
The Witan () was the king's council in Anglo-Saxon England from before the seventh century until the 11th century. It was composed of the leading magnates, both ecclesiastic and secular, and meetings of the council were sometimes called the Wi ...
.
The nature of the relations between the Britons and the Saxons in Somerset is not entirely clear. Ine's laws demonstrate that the Britons were considered to be a significant enough population in Wessex to merit provisions; however, the laws also suggest that Britons could not attain the same social standing as the Saxons, and that many were slaves. In light of such policies, many Britons might have chosen to emigrate to places such as Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period o ...
while those who remained would have had incentives to adopt Anglo-Saxon culture.
After the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conq ...
, the county was divided into 700 fiefs, and large areas were owned by the crown, with fortifications such as Dunster Castle used for control and defence. Somerset came under the political influence of several different nobles during the Middle Ages. During the Wars of the Roses, an important magnate was Humphrey Stafford, earl of Devon whose wider influence stretched from Cornwall to Wiltshire. After 1485, one of the county's most influential figures was Henry VII's chamberlain Giles Daubeney.
The 17th–19th centuries
Somerset contains HM Prison Shepton Mallet, which was England's oldest prison still in use prior to its closure in 2013, having opened in 1610. During theEnglish Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians ("Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I ("Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of Kingdom of England, England's governanc ...
, Somerset was largely Parliamentarian, with key engagements being the Sieges of Taunton and the Battle of Langport.
In 1685, the Monmouth Rebellion
The Monmouth Rebellion, also known as the Pitchfork Rebellion, the Revolt of the West or the West Country rebellion, was an attempt to depose James II, who in February 1685 succeeded his brother Charles II as king of England, Scotland and Ire ...
was played out in Somerset and neighbouring Dorset. The rebels landed at Lyme Regis
Lyme Regis is a town in west Dorset, England, west of Dorchester and east of Exeter. Sometimes dubbed the "Pearl of Dorset", it lies by the English Channel at the Dorset–Devon border. It has noted fossils in cliffs and beaches on the Heri ...
and travelled north, hoping to capture Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city i ...
and Bath, but they were defeated in the Battle of Sedgemoor at Westonzoyland, the last pitched battle fought in England. Arthur Wellesley took his title, Duke of Wellington
Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington, (1 May 1769 – 14 September 1852) was an Anglo-Irish soldier and Tory statesman who was one of the leading military and political figures of 19th-century Britain, serving twice as prime minister o ...
from the town of Wellington
Wellington ( mi, Te Whanganui-a-Tara or ) is the capital city of New Zealand. It is located at the south-western tip of the North Island, between Cook Strait and the Remutaka Range. Wellington is the second-largest city in New Zealand by m ...
; he is commemorated on a nearby hill by a large, spotlit obelisk
An obelisk (; from grc, ὀβελίσκος ; diminutive of ''obelos'', " spit, nail, pointed pillar") is a tall, four-sided, narrow tapering monument which ends in a pyramid-like shape or pyramidion at the top. Originally constructed by An ...
, known as the Wellington Monument.
The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
in the Midlands and Northern England spelled the end for most of Somerset's cottage industries. Farming continued to flourish, and the Bath and West of England Society for the Encouragement of Agriculture, Arts, Manufactures and Commerce was founded in 1777 to improve farming methods. Despite this, two decades later agriculturist John Billingsley conducted a survey of the county's agriculture in 1795 and found that agricultural methods could still be improved.
Coal mining was an important industry in north Somerset during the 18th and 19th centuries, and by 1800 it was prominent in Radstock
Radstock is a town and civil parish on the northern slope of the Mendip Hills in Somerset, England, about south-west of Bath and north-west of Frome. It is within the area of the unitary authority of Bath and North East Somerset. The Rads ...
.
The Somerset Coalfield reached its peak production by the 1920s. All the pits have now been closed, the last in 1973. Most of the surface buildings have been removed, and apart from a winding wheel outside Radstock Museum
Radstock Museum in Radstock, Somerset, England has a range of exhibits which offer an insight into North Somerset life since the nineteenth century.
History
The museum was originally opened in 1989 in barns in Haydon. The museum moved to its c ...
, little evidence of their former existence remains. Further west, the Brendon Hills were mined for iron ore in the late 19th century; this was taken by the West Somerset Mineral Railway to Watchet
Watchet is a harbour town, civil parish and electoral ward in the county of Somerset, England, with a population in 2011 of 3,785. It is situated west of Bridgwater, north-west of Taunton, and east of Minehead. The town lies at the mouth ...
Harbour for shipment to the furnaces at Ebbw Vale.
20th century
Many Somerset soldiers died during theFirst World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fig ...
, with the Somerset Light Infantry
The Somerset Light Infantry (Prince Albert's) was a light infantry regiment of the British Army, which served under various titles from 1685 to 1959. In 1959, the regiment was amalgamated with the Duke of Cornwall's Light Infantry to form the So ...
suffering nearly 5,000 casualties. War memorials were put up in most of the county's towns and villages; only nine, described as the Thankful Villages
Thankful Villages (also known as Blessed Villages; ) are settlements in England and Wales from which all their members of the armed forces survived World War I. The term Thankful Village was popularised by the writer Arthur Mee in the 1930s; in ' ...
, had none of their residents killed. During the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
the county was a base for troops preparing for the D-Day landings. Some of the hospitals which were built for the casualties of the war remain in use. The Taunton Stop Line was set up to repel a potential German invasion. The remains of its pill boxes can still be seen along the coast, and south through Ilminster and Chard.
A number of decoy towns were constructed in Somerset in World War II to protect Bristol and other towns. They were designed to mimic the nighttime geometry of "blacked out" streets, railway lines, and Bristol Temple Meads railway station, to encourage German bombers away from these targets. One, on the German radio navigation beam flight path to Bristol, was constructed on Beacon Batch. It was laid out by Shepperton Studios, based on aerial photographs of the city's railway marshalling yards. The decoys were fitted with dim red lights, simulating activities such as the stoking of steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the loco ...
s. Burning bales of straw soaked in creosote were used to simulate the effects of incendiary bombs dropped by the first wave of Pathfinder night bombers; meanwhile, incendiary bombs dropped on the correct location were quickly smothered, wherever possible. Drums of oil were also ignited to simulate the effect of a blazing city or town, with the aim of fooling subsequent waves of bombers into dropping their bombs on the wrong location.
The Chew Magna decoy town was hit by half a dozen bombs on 2 December 1940, and over a thousand incendiaries on 3 January 1941. The following night the Uphill decoy town, protecting the airfield at Weston-super-Mare
Weston-super-Mare, also known simply as Weston, is a seaside town in North Somerset, England. It lies by the Bristol Channel south-west of Bristol between Worlebury Hill and Bleadon Hill. It includes the suburbs of Mead Vale, Milton, Oldmi ...
, was bombed; a herd of dairy cows
Dairy cattle (also called dairy cows) are cattle bred for the ability to produce large quantities of milk, from which dairy products are made. Dairy cattle generally are of the species '' Bos taurus''.
Historically, little distinction was m ...
was hit, killing some and severely injuring others.
Geography
Boundaries
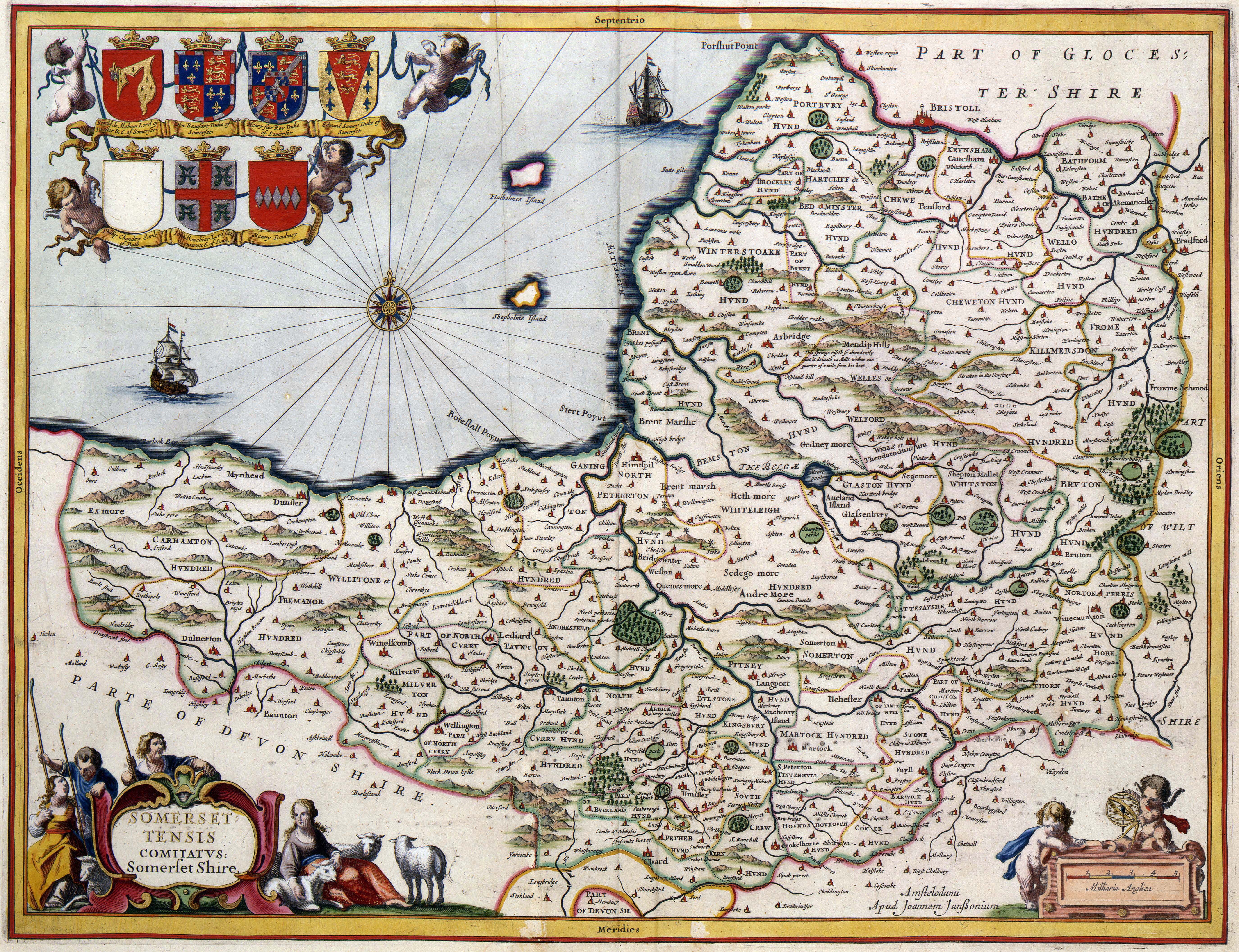
 The boundaries of Somerset are very similar to how they were in medieval times. They have been largely unaltered. The River Avon formed much of the border with Gloucestershire, except that the hundred of Bath Forum, which straddles the Avon, formed part of Somerset. Bristol began as a town on the Gloucestershire side of the Avon, however as it grew it extended across the river into Somerset. In 1373
The boundaries of Somerset are very similar to how they were in medieval times. They have been largely unaltered. The River Avon formed much of the border with Gloucestershire, except that the hundred of Bath Forum, which straddles the Avon, formed part of Somerset. Bristol began as a town on the Gloucestershire side of the Avon, however as it grew it extended across the river into Somerset. In 1373 Edward III
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring r ...
proclaimed "that the town of Bristol with its suburbs and precincts shall henceforth be separate from the counties of Gloucester and Somerset ... and that it should be a county by itself".
The present-day northern border of Somerset (adjoining the counties of Bristol and Gloucestershire) runs along the southern bank of the Avon from the Bristol Channel, then follows around the southern edge of the Bristol built-up area, before continuing upstream along the Avon and then diverges from the river to include Bath and its historic hinterland to the north of the Avon, before meeting Wiltshire at the ''Three Shire Stones'' on the ''Fosse Way
The Fosse Way was a Roman road built in Britain during the first and second centuries AD that linked Isca Dumnoniorum (Exeter) in the southwest and Lindum Colonia ( Lincoln) to the northeast, via Lindinis (Ilchester), Aquae Sulis (Bath), C ...
'' at Batheaston
Batheaston is a village and civil parish east of the English city of Bath, on the north bank of the River Avon. The parish had a population of 2,735 in 2011. The northern area of the parish, on the road to St Catherine, is an area known as N ...
.Ordnance Survey
Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose (see ordnance and surveying), which was to map Scotland in the wake of the Jacobite rising of 1745. There was ...
mapping
Cities and towns
Somerton took over fromIlchester
Ilchester is a village and civil parishes in England, civil parish, situated on the River Yeo (South Somerset), River Yeo or Ivel, five miles north of Yeovil, in the England, English county of Somerset. Originally a Roman Britain, Roman town, and ...
as the county town in the late thirteenth century, but it declined in importance and the status of county town transferred to Taunton
Taunton () is the county town of Somerset, England, with a 2011 population of 69,570. Its thousand-year history includes a 10th-century monastic foundation, Taunton Castle, which later became a priory. The Normans built a castle owned by t ...
about 1366. The county has two cities
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
, Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
and Wells
Wells most commonly refers to:
* Wells, Somerset, a cathedral city in Somerset, England
* Well, an excavation or structure created in the ground
* Wells (name)
Wells may also refer to:
Places Canada
* Wells, British Columbia
England
* Wel ...
, and 30 towns (including the county town of Taunton, which has no town council but instead is the chief settlement of the county's only extant borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle ...
). The largest urban areas in terms of population are Bath, Weston-super-Mare
Weston-super-Mare, also known simply as Weston, is a seaside town in North Somerset, England. It lies by the Bristol Channel south-west of Bristol between Worlebury Hill and Bleadon Hill. It includes the suburbs of Mead Vale, Milton, Oldmi ...
, Taunton, Yeovil
Yeovil ( ) is a town and civil parish in the district of South Somerset, England. The population of Yeovil at the last census (2011) was 45,784. More recent estimates show a population of 48,564. It is close to Somerset's southern border with ...
and Bridgwater
Bridgwater is a large historic market town and civil parish in Somerset, England. Its population currently stands at around 41,276 as of 2022. Bridgwater is at the edge of the Somerset Levels, in level and well-wooded country. The town lies alon ...
.
Many settlements developed because of their strategic importance in relation to geographical features, such as river crossings or valleys in ranges of hills. Examples include Axbridge on the River Axe, Castle Cary on the River Cary
The River Cary is a river in Somerset, England. It is sourced from the Park Pond in Castle Cary and flows towards the southwest.
Etymology
The origin of the name ''Cary'' is uncertain. It may be derived from pre-Celtic ''kar-'', meaning "stony, ...
, North Petherton on the River Parrett
The River Parrett flows through the counties of Dorset and Somerset in South West England, from its source in the Thorney Mills springs in the hills around Chedington in Dorset. Flowing northwest through Somerset and the Somerset Levels to i ...
, and Ilminster, where there was a crossing point on the River Isle
The River Isle (also known as the River Ile) flows from its source near Combe St Nicholas, through Somerset, England and discharges into the River Parrett south of Langport near Midelney.
Several small springs merge into the river near Wade ...
. Midsomer Norton
Midsomer Norton is a town near the Mendip Hills in Bath and North East Somerset, England, south-west of Bath, north-east of Wells, north-west of Frome, west of Trowbridge and south-east of Bristol. It has a population of around 13,00 ...
lies on the River Somer; while the Wellow Brook and the ''Fosse Way'' Roman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman R ...
run through Radstock. Chard is the most southerly town in Somerset and one of the highest, though at an altitude of Wiveliscombe is the highest town in the county.
Green belt
The county contains several-miles-wide sections of the Avongreen belt
A green belt is a policy and land-use zone designation used in land-use planning to retain areas of largely undeveloped, wilderness, wild, or agricultural landscape, land surrounding or neighboring urban areas. Similar concepts are greenway (lan ...
area, which is primarily in place to prevent urban sprawl from the Bristol
Bristol () is a city, ceremonial county and unitary authority in England. Situated on the River Avon, it is bordered by the ceremonial counties of Gloucestershire to the north and Somerset to the south. Bristol is the most populous city i ...
and Bath built up areas encroaching into the rural areas of North Somerset, Bath and North East Somerset, and Mendip districts in the county, as well as maintaining surrounding countryside. It stretches from the coastline between the towns of Portishead and Clevedon, extending eastwards past Nailsea, around the Bristol conurbation, and through to the city of Bath. The green belt border intersects with the Mendip Hills Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB) along its south boundary, and meets the Cotswolds AONB by its eastern extent along the Wiltshire county border, creating an extended area protected from inappropriate development.
Geology
Much of the landscape of Somerset falls into types determined by the underlying geology. These landscapes are thelimestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
karst and lias of the north, the clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay part ...
vales and wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
s of the centre, the oolite
Oolite or oölite (''egg stone'') is a sedimentary rock formed from ooids, spherical grains composed of concentric layers. The name derives from the Ancient Greek word for egg (ᾠόν). Strictly, oolites consist of ooids of diameter 0.25� ...
s of the east and south, and the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, w ...
sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
of the west.
 To the north-east of the Somerset Levels, the Mendip Hills are moderately high limestone hills. The central and western Mendip Hills was designated an
To the north-east of the Somerset Levels, the Mendip Hills are moderately high limestone hills. The central and western Mendip Hills was designated an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty
An Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONB; , AHNE) is an area of countryside in England, Wales, and Northern Ireland, that has been designated for conservation due to its significant landscape value. Areas are designated in recognition of th ...
in 1972 and covers . The main habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
on these hills is calcareous grassland, with some arable
Arable relates to the growing of crops:
* Arable farming or agronomy, the cultivation of field crops
* Arable land, land upon which crops are cultivated
* Arable crops program The arable crops program is a consolidated support system operated und ...
agriculture. To the south-west of the Somerset Levels are the Quantock Hills which was England's first Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty designated in 1956 which is covered in heathland, oak woodlands, ancient parklands with plantations of conifer and covers 99 square kilometres. The Somerset Coalfield is part of a larger coalfield which stretches into Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire ( abbreviated Glos) is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean.
The county town is the city of Gl ...
. To the north of the Mendip hills is the Chew Valley and to the south, on the clay substrate, are broad valleys which support dairy farming and drain into the Somerset Levels.
Caves and rivers
There is an extensive network ofcaves
A cave or cavern is a natural void in the ground, specifically a space large enough for a human to enter. Caves often form by the weathering of rock and often extend deep underground. The word ''cave'' can refer to smaller openings such as sea ...
, including Wookey Hole, underground rivers, and gorges, including the Cheddar Gorge and Ebbor Gorge. The county has many rivers, including the Axe, Brue, Cary, Parrett, Sheppey, Tone and Yeo. These both feed and drain the flat levels and moors of mid and west Somerset. In the north of the county the River Chew flows into the Bristol Avon. The Parrett is tidal almost to Langport
Langport is a small town and civil parish in Somerset, England, west of Somerton in the South Somerset district. The parish, which covers only part of the town, has a population of 1,081. Langport is contiguous with Huish Episcopi, a separate ...
, where there is evidence of two Roman wharfs. Hadfield, Charles (1999). ''Canals of Southern England''. London: Phoenix House Ltd. At the same site during the reign of King Charles I, river tolls were levied on boats to pay for the maintenance of the bridge.
Levels and moors
 The Somerset Levels (or Somerset Levels and Moors as they are less commonly but more correctly known) are a sparsely populated
The Somerset Levels (or Somerset Levels and Moors as they are less commonly but more correctly known) are a sparsely populated wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
area of central Somerset, between the Quantock and Mendip hills. They consist of marine clay levels along the coast, and the inland (often peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficien ...
based) moors. The Levels are divided into two by the Polden Hills. Land to the south is drained by the River Parrett
The River Parrett flows through the counties of Dorset and Somerset in South West England, from its source in the Thorney Mills springs in the hills around Chedington in Dorset. Flowing northwest through Somerset and the Somerset Levels to i ...
while land to the north is drained by the River Axe and the River Brue. The total area of the Levels amounts to about
and broadly corresponds to the administrative district of Sedgemoor
Sedgemoor is a low-lying area of land in Somerset, England. It lies close to sea level south of the Polden Hills, historically largely marsh (or "moor" in its older sense). The eastern part is known as King's Sedgemoor, and the western part Wes ...
but also includes the south west of Mendip district
Mendip is a local government district of Somerset in England. The district covers a largely rural area of with a population of approximately 112,500, ranging from the Wiltshire border in the east to part of the Somerset Levels in the west ...
. Approximately 70% of the area is grassland and 30% is arable.
Stretching about inland, this expanse of flat land barely rises above sea level. Before it was drained, much of the land was under a shallow brackish sea in winter and was marsh land in summer. Drainage began with the Romans, and was restarted at various times: by the Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened wit ...
; in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
by the Glastonbury Abbey
Glastonbury Abbey was a monastery in Glastonbury, Somerset, England. Its ruins, a grade I listed building and scheduled ancient monument, are open as a visitor attraction.
The abbey was founded in the 8th century and enlarged in the 10th. It ...
, during 1400–1770; and during the Second World War, with the construction of the Huntspill River. Pumping and management of water levels still continues.Williams, Michael (1970). ''The Draining of the Somerset Levels''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. .
 The North Somerset Levels basin, north of the Mendips, covers a smaller geographical area than the Somerset Levels; and forms a coastal area around Avonmouth. It too was reclaimed by draining.Rippon, Stephen (1997). ''The Severn Estuary: Landscape Evolution and Wetland Reclamation''. London: Leicester University. It is mirrored, across the Severn Estuary, in Wales, by a similar low-lying area: the Caldicot and Wentloog Levels.
In the far west of the county, running into Devon, is Exmoor, a high Devonian sandstone moor, which was designated as a
The North Somerset Levels basin, north of the Mendips, covers a smaller geographical area than the Somerset Levels; and forms a coastal area around Avonmouth. It too was reclaimed by draining.Rippon, Stephen (1997). ''The Severn Estuary: Landscape Evolution and Wetland Reclamation''. London: Leicester University. It is mirrored, across the Severn Estuary, in Wales, by a similar low-lying area: the Caldicot and Wentloog Levels.
In the far west of the county, running into Devon, is Exmoor, a high Devonian sandstone moor, which was designated as a national park
A national park is a natural park in use for conservation purposes, created and protected by national governments. Often it is a reserve of natural, semi-natural, or developed land that a sovereign state declares or owns. Although individua ...
in 1954, under the 1949 National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act
The National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949 is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which created the National Parks Commission which later became the Countryside Commission and then the Countryside Agency, which becam ...
.
The highest point in Somerset is Dunkery Beacon on Exmoor, with a maximum elevation of . Over 100 sites in Somerset have been designated as Sites of Special Scientific Interest.
Coastline

 The coastline of the
The coastline of the Bristol Channel
The Bristol Channel ( cy, Môr Hafren, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales from Devon and Somerset in South West England. It extends from the lower estuary of the River S ...
and Severn Estuary forms part of the northern border of Somerset.
The Bristol Channel has the second largest tidal range
Tidal range is the difference in height between high tide and low tide. Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by gravitational forces exerted by the Moon and Sun and the rotation of Earth. Tidal range depends on time and location.
...
in the world. At Burnham-on-Sea, for example, the tidal range of a spring tide is more than .
Proposals for the construction of a Severn Barrage aim to harness this energy. The island of Steep Holm in the Bristol Channel is within the ceremonial county and is now administered by North Somerset Council.
The main coastal towns are, from the west to the north-east, Minehead
Minehead is a coastal town and civil parish in Somerset, England. It lies on the south bank of the Bristol Channel, north-west of the county town of Taunton, from the boundary with the county of Devon and in proximity of the Exmoor National P ...
, Watchet, Burnham-on-Sea, Weston-super-Mare, Clevedon and Portishead. The coastal area between Minehead and the eastern extreme of the administrative county's coastline at Brean Down is known as Bridgwater Bay, and is a National Nature Reserve.
North of that, the coast forms Weston Bay and Sand Bay whose northern tip, Sand Point, marks the lower limit of the Severn Estuary. In the mid and north of the county the coastline is low as the level wetlands of the levels meet the sea. In the west, the coastline is high and dramatic where the plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
of Exmoor meets the sea, with high cliffs and waterfalls.
Climate
Along with the rest ofSouth West England
South West England, or the South West of England, is one of nine official regions of England. It consists of the counties of Bristol, Cornwall (including the Isles of Scilly), Dorset, Devon, Gloucestershire, Somerset and Wiltshire. Cities and ...
, Somerset has a temperate climate which is generally wetter and milder than the rest of the country. The annual mean temperature is approximately . Seasonal temperature variation is less extreme than most of the United Kingdom because of the adjacent sea temperatures. The summer months of July and August are the warmest with mean daily maxima of approximately . In winter mean minimum temperatures of or are common. In the summer the Azores
)
, motto=
( en, "Rather die free than subjected in peace")
, anthem=( en, "Anthem of the Azores")
, image_map=Locator_map_of_Azores_in_EU.svg
, map_alt=Location of the Azores within the European Union
, map_caption=Location of the Azores wi ...
high pressure affects the south-west of England, but convective cloud sometimes forms inland, reducing the number of hours of sunshine. Annual sunshine rates are slightly less than the regional average of 1,600 hours.
In December 1998 there were 20 days without sun recorded at Yeovilton. Most of the rainfall in the south-west is caused by Atlantic depressions or by convection. Most of the rainfall in autumn and winter is caused by the Atlantic depressions, which is when they are most active. In summer, a large proportion of the rainfall is caused by sun heating the ground leading to convection and to showers and thunderstorms. Average rainfall is around . About 8–15 days of snowfall is typical. November to March have the highest mean wind speeds, and June to August the lightest winds. The predominant wind direction is from the south-west.
Governance
 The
The ceremonial county
The counties and areas for the purposes of the lieutenancies, also referred to as the lieutenancy areas of England and informally known as ceremonial counties, are areas of England to which lords-lieutenant are appointed. Legally, the areas i ...
of Somerset currently consists of a two-tier non-metropolitan county
A non-metropolitan county, or colloquially, shire county, is a county-level entity in England that is not a metropolitan county. The counties typically have populations of 300,000 to 1.8 million. The term ''shire county'' is, however, an unoffi ...
, which is administered by Somerset County Council
Somerset County Council is the county council of Somerset in the South West of England, an elected local government authority responsible for the most significant local government services in most of the county.
On 1 April 2023 the county coun ...
and four district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municipa ...
councils, and two unitary authority
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governme ...
areas (whose councils combine the functions of a county and a district). The four districts of Somerset are Somerset West and Taunton
Somerset West and Taunton is a local government district in Somerset, England. It was established on 1 April 2019 by the Somerset West and Taunton (Local Government Changes) Order 2018. The council replaced the Taunton Deane and West Somerset ...
, South Somerset
South Somerset is a Non-metropolitan district, local government district in Somerset, England.
The South Somerset district covers an area of ranging from the borders with Devon, Wiltshire and Dorset to the edge of the Somerset Levels. It has ...
, Mendip, and Sedgemoor
Sedgemoor is a low-lying area of land in Somerset, England. It lies close to sea level south of the Polden Hills, historically largely marsh (or "moor" in its older sense). The eastern part is known as King's Sedgemoor, and the western part Wes ...
, and will be replaced by a new single unitary authority in April 2023. The two existing unitary authorities – which were established on 1 April 1996 following the break-up of the short-lived county of Avon — are North Somerset, and Bath & North East Somerset
Bath and North East Somerset (B&NES) is a unitary authority district in England. Bath and North East Somerset Council was created on 1 April 1996 following the abolition of the county of Avon. It is part of the ceremonial county of Somerset.
...
. In 2019 West Somerset and Taunton Deane merged to form Somerset West and Taunton
Somerset West and Taunton is a local government district in Somerset, England. It was established on 1 April 2019 by the Somerset West and Taunton (Local Government Changes) Order 2018. The council replaced the Taunton Deane and West Somerset ...
.
These unitary authorities formed part of the administrative county of Somerset before the creation of Avon (a county created to cover Bristol and its environs in north Somerset and south Gloucestershire) in 1974. Bath however was a largely independent county borough
County borough is a term introduced in 1889 in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, to refer to a borough or a city independent of county council control, similar to the unitary authorities created since the 1990s. An equivalent t ...
during the existence of the administrative county of Somerset (from 1889 to 1974).
In 2007, proposals to abolish the five district councils in favour of a unitary authority (covering the existing two-tier county) were rejected following local opposition. In September 2016, West Somerset and Taunton Deane councils agreed in principle to merge the districts. This was achieved on 1 April 2019 with the first elections to the new council being held in May 2019. The new district is not a unitary authority, with Somerset County Council still performing its functions.
In July 2021 the Ministry of Housing, Communities and Local Government
The Department for Levelling Up, Housing and Communities (DLUHC), formerly the Ministry for Housing, Communities and Local Government (MHCLG), is a department of His Majesty's Government responsible for housing, communities, local government ...
announced that in April 2023, the non-metropolitan county will be reorganised into a unitary authority. The four district
A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or county, counties, several municipality, municipa ...
councils (Somerset West and Taunton, South Somerset, Mendip, and Sedgemoor) are to be abolished and their functions transferred to a single authority. The existing unitary authorities will not be altered.
UK Parliament
The county is divided into nineconstituencies
An electoral district, also known as an election district, legislative district, voting district, constituency, riding, ward, division, or (election) precinct is a subdivision of a larger state (a country, administrative region, or other polit ...
, each returning one Member of Parliament (MP) to the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
. In the June 2017 general election, eight constituencies of the county elected Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
MPs, while Bath elected a Liberal Democrat. The ceremonial county of Somerset contains the constituencies of Bridgwater and West Somerset, North East Somerset, North Somerset, Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
, Somerton and Frome
Somerton and Frome is a constituency in Somerset represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 2015 by David Warburton, who was elected as a Conservative, but currently sits as an Independent after losing the Conservative whip in ...
, Taunton Deane, Wells
Wells most commonly refers to:
* Wells, Somerset, a cathedral city in Somerset, England
* Well, an excavation or structure created in the ground
* Wells (name)
Wells may also refer to:
Places Canada
* Wells, British Columbia
England
* Wel ...
, Yeovil
Yeovil ( ) is a town and civil parish in the district of South Somerset, England. The population of Yeovil at the last census (2011) was 45,784. More recent estimates show a population of 48,564. It is close to Somerset's southern border with ...
and Weston-super-Mare
Weston-super-Mare, also known simply as Weston, is a seaside town in North Somerset, England. It lies by the Bristol Channel south-west of Bristol between Worlebury Hill and Bleadon Hill. It includes the suburbs of Mead Vale, Milton, Oldmi ...
. Traditionally several of these have been relatively strong constituencies for the Liberal Democrats, with Labour often getting few votes, even in larger towns such as Yeovil. In the 2019 general election, all nine seats were held, with Jacob Rees-Mogg increasing his majority in North East Somerset, as well as Wera Hobhouse doubling her majority in the Liberal Democrat Bath seat.
European Parliament
From 1984 to 1994, Somerset was represented byConservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy that seeks to promote and to preserve traditional institutions, practices, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civilization in ...
Margaret Daly
Margaret Daly (born 26 January 1938 the older of twins, Robert) was a British Conservative Party politician who represented Somerset and West Dorset in the European Parliament from 1984 to 1994.
She attended Methodist College Belfast.
Daly was ...
as part of the Somerset and Dorset West constituency for elections to the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it adop ...
.
From 1994 to 1999, Somerset was represented by Liberal Democrat Graham Watson as part of the Somerset and North Devon constituency for elections to the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it adop ...
.
From 1999 to 2020, Somerset was part of the South West England
South West England, or the South West of England, is one of nine official regions of England. It consists of the counties of Bristol, Cornwall (including the Isles of Scilly), Dorset, Devon, Gloucestershire, Somerset and Wiltshire. Cities and ...
constituency for elections to the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it adop ...
.
Civil parishes
Almost all of the county is covered by the lowest/most local form of English local government, thecivil parish
In England, a civil parish is a type of Parish (administrative division), administrative parish used for Local government in England, local government. It is a territorial designation which is the lowest tier of local government below district ...
, with either a town or parish council (a city council in the instance of Wells) or a parish meeting; some parishes group together, with a single council or meeting for the group. The city of Bath (the area of the former county borough) and much of the town of Taunton are unparished area
In England, an unparished area is an area that is not covered by a civil parish (the lowest level of local government, not to be confused with an ecclesiastical parish). Most urbanised districts of England are either entirely or partly unparis ...
s.
Demography
In the 2011 census the population of theSomerset County Council
Somerset County Council is the county council of Somerset in the South West of England, an elected local government authority responsible for the most significant local government services in most of the county.
On 1 April 2023 the county coun ...
area was 571,600
with 193,400 in Bath and North East Somerset
Bath and North East Somerset (B&NES) is a unitary authority district in England. Bath and North East Somerset Council was created on 1 April 1996 following the abolition of the county of Avon. It is part of the ceremonial county of Somerset.
T ...
, and 216,700 in North Somerset giving a total for the ceremonial county of 981,700.
Population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to ...
is higher than the national average, with a 6.4% increase, in the Somerset County Council area, since 1991, and a 17% increase since 1981. The population density is 1.4 persons per hectare, which can be compared to 2.07 persons per hectare for the South West region. Within the county, population density ranges 0.5 in West Somerset to 2.2 persons per hectare in Taunton Deane. The percentage of the population who are economically active is higher than the regional and national average, and the unemployment rate is lower than the regional and national average.
Somerset has a high indigenous British population, with 94.6% registering as white British
White British is an ethnicity classification used for the native white population identifying as English, Scottish, Welsh, Cornish, Northern Irish, or British in the United Kingdom Census. In the 2011 census, the White British population w ...
, and 2.0% as belonging to black and ethnic minority (BME) groups, according to the 2011 Census. Over 25% of Somerset's population is concentrated in Taunton, Bridgwater and Yeovil. The rest of the county is rural and sparsely populated. Over 9 million tourist nights are spent in Somerset each year, which significantly increases the population at peak times.
Economy
 Somerset has few industrial centres, but it does have a variety of light industry and high technology businesses, along with traditional agriculture and an increasingly important tourism sector, resulting in an unemployment rate of 2.5%. Tourism was estimated in 2013 to support around 26,000 people.
Bridgwater was developed during the Industrial Revolution as the area's leading port. The River Parrett was navigable by large ships as far as Bridgwater. Cargoes were then loaded onto smaller boats at Langport Quay, next to the Bridgwater Bridge, to be carried further up river to Langport;Lawrence, J.F. (2005). ''A History of Bridgwater''. (revised and compiled by J. C. Lawrence) Chichester: Phillimore & Co. . or they could turn off at Burrowbridge and then travel via the River Tone to Taunton. The Parrett is now only navigable as far as Dunball Wharf. Bridgwater, in the 19th and 20th centuries, was a centre for the manufacture of bricks and clay roof tiles, and later cellophane, but those industries have now stopped.
With its good links to the motorway system, Bridgwater has developed as a distribution hub for companies such as Argos, Toolstation,
Somerset has few industrial centres, but it does have a variety of light industry and high technology businesses, along with traditional agriculture and an increasingly important tourism sector, resulting in an unemployment rate of 2.5%. Tourism was estimated in 2013 to support around 26,000 people.
Bridgwater was developed during the Industrial Revolution as the area's leading port. The River Parrett was navigable by large ships as far as Bridgwater. Cargoes were then loaded onto smaller boats at Langport Quay, next to the Bridgwater Bridge, to be carried further up river to Langport;Lawrence, J.F. (2005). ''A History of Bridgwater''. (revised and compiled by J. C. Lawrence) Chichester: Phillimore & Co. . or they could turn off at Burrowbridge and then travel via the River Tone to Taunton. The Parrett is now only navigable as far as Dunball Wharf. Bridgwater, in the 19th and 20th centuries, was a centre for the manufacture of bricks and clay roof tiles, and later cellophane, but those industries have now stopped.
With its good links to the motorway system, Bridgwater has developed as a distribution hub for companies such as Argos, Toolstation, Morrisons
Wm Morrison Supermarkets, trading as Morrisons, is the fifth largest supermarket chain in the United Kingdom. As of 2021, the company had 497 supermarkets across England, Wales and Scotland, as well as one in Gibraltar. The company is headqu ...
and Gerber Juice. AgustaWestland manufactures helicopters in Yeovil
Yeovil ( ) is a town and civil parish in the district of South Somerset, England. The population of Yeovil at the last census (2011) was 45,784. More recent estimates show a population of 48,564. It is close to Somerset's southern border with ...
, and Normalair Garratt, builder of aircraft oxygen systems, is also based in the town.
Somerset is an important supplier of defence equipment and technology. A Royal Ordnance Factory, ROF Bridgwater was built at the start of the Second World War, between the villages of Puriton and Woolavington, to manufacture explosives. The site was decommissioned and closed in July 2008. Templecombe
Templecombe is a village in Somerset, England, situated on the A357 road five miles south of Wincanton, east of Yeovil, and west of Salisbury. The village has a population of 1,560. Along with the hamlet of Combe Throop, it forms the paris ...
has Thales Underwater Systems
Thales Underwater Systems or TUS (formerly Thomson Sintra ASM, Thomson CSF DASM and then Thomson Marconi Sonar) is a subsidiary of the French defense electronics specialist Thales Group. It was created in 2001 and belongs to its naval division. It ...
, and Taunton presently has the United Kingdom Hydrographic Office and Avimo, which became part of Thales Optics. It was announced twice, in 2006 and 2007, that manufacturing is to end at Thales Optics' Taunton site, but the trade unions and Taunton Deane District Council are working to reverse or mitigate these decisions. Other high-technology companies include the optics company Gooch and Housego, at Ilminster. There are Ministry of Defence
{{unsourced, date=February 2021
A ministry of defence or defense (see spelling differences), also known as a department of defence or defense, is an often-used name for the part of a government responsible for matters of defence, found in state ...
offices in Bath, and Norton Fitzwarren is the home of 40 Commando Royal Marines. The Royal Naval Air Station in Yeovilton, is one of Britain's two active Fleet Air Arm
The Fleet Air Arm (FAA) is one of the five fighting arms of the Royal Navy and is responsible for the delivery of naval air power both from land and at sea. The Fleet Air Arm operates the F-35 Lightning II for maritime strike, the AW159 Wil ...
bases and is home to the Royal Navy's AgustaWestland AW159 Wildcat helicopters and the Royal Marines Commando AgustaWestland AW101 Merlins.
 Agriculture and food and drink production continue to be major industries in the county, employing over 15,000 people. Apple orchards were once plentiful, and Somerset is still a major producer of cider. The towns of Taunton and
Agriculture and food and drink production continue to be major industries in the county, employing over 15,000 people. Apple orchards were once plentiful, and Somerset is still a major producer of cider. The towns of Taunton and Shepton Mallet
Shepton Mallet is a market town and civil parish in the Mendip District of Somerset, England, some south-west of Bath, south of Bristol and east of Wells. It had an estimated population of 10,810 in 2019. Mendip District Council is based the ...
are involved with the production of cider, especially Blackthorn Cider, which is sold nationwide, and there are specialist producers such as Burrow Hill Cider Farm and Thatchers Cider
Thatchers Cider is a family-owned cider maker in Sandford, North Somerset, England.
History
The Thatchers company was founded by William Thatcher in 1904. His son Stanley Thatcher, born in 1910, began selling draught cider to pubs in Somer ...
. Gerber Products Company in Bridgwater is the largest producer of fruit juices in Europe, producing brands such as Sunny Delight and Ocean Spray. Development of the milk-based industries, such as Ilchester Cheese Company
The Ilchester Cheese Company is a cheese company based in Ilchester, Somerset. The Ilchester brands are part of Norseland, a subsidiary of Norwegian dairy company Tine SA.
History
In 1962, Ken Seaton, a hotelier in Ilchester, Somerset, England ...
and Yeo Valley Organic, have resulted in the production of ranges of desserts, yoghurts and cheeses.
Traditional willow
Willows, also called sallows and osiers, from the genus ''Salix'', comprise around 400 speciesMabberley, D.J. 1997. The Plant Book, Cambridge University Press #2: Cambridge. of typically deciduous trees and shrubs, found primarily on moist ...
growing and weaving (such as basket weaving
Basket weaving (also basketry or basket making) is the process of weaving or sewing pliable materials into three-dimensional artifacts, such as baskets, mats, mesh bags or even furniture. Craftspeople and artists specialized in making basket ...
) is not as extensive as it used to be but is still carried out on the Somerset Levels and is commemorated at the Willows and Wetlands Visitor Centre
The Willows and Wetlands Visitor Centre is situated at Stoke St Gregory, on the Somerset Levels, north east of Taunton, England. Based on a working farm, growing and processing willow, the centre offers tours of over of withies, willow yards and ...
. Fragments of willow basket were found near the Glastonbury Lake Village, and it was also used in the construction of several Iron Age causeways. The willow was harvested using a traditional method of pollarding
Pollarding is a pruning system involving the removal of the upper branches of a tree, which promotes the growth of a dense head of foliage and branches. In ancient Rome, Propertius mentioned pollarding during the 1st century BCE. The practice ...
, where a tree would be cut back to the main stem. During the 1930s more than of willow were being grown commercially on the Levels. Largely due to the displacement of baskets with plastic bags and cardboard boxes, the industry has severely declined since the 1950s. By the end of the 20th century only about were grown commercially, near the villages of Burrowbridge, Westonzoyland and North Curry.
Towns such as Castle Cary and Frome
Frome ( ) is a town and civil parish in eastern Somerset, England. The town is built on uneven high ground at the eastern end of the Mendip Hills, and centres on the River Frome. The town, about south of Bath, is the largest in the Mendip ...
grew around the medieval weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudin ...
industry. Street
A street is a public thoroughfare in a built environment. It is a public parcel of land adjoining buildings in an urban context, on which people may freely assemble, interact, and move about. A street can be as simple as a level patch of d ...
developed as a centre for the production of woollen slippers and, later, boots and shoes, with C&J Clark
C. & J. Clark International Ltd, doing business as Clarks, is a British international shoe manufacturer and retailer. It was founded in 1825 by Cyrus Clark in the village of Street, Somerset, England, where the company's headquarters rema ...
establishing its headquarters in the village. C&J Clark's shoes are no longer manufactured there as the work was transferred to lower-wage areas, such as China and Asia.
 The county has a long tradition of supplying freestone and
The county has a long tradition of supplying freestone and building stone
Building material is material used for construction. Many naturally occurring substances, such as clay, rocks, sand, wood, and even twigs and leaves, have been used to construct buildings. Apart from naturally occurring materials, many man-mad ...
. Quarries at Doulting supplied freestone used in the construction of Wells Cathedral. Bath stone is also widely used. Ralph Allen promoted its use in the early 18th century, as did Hans Price in the 19th century, but it was used long before then. It was mined underground at Combe Down and Bathampton Down Mines
Combe Down and Bathampton Down Quarries () make up a 6.22 hectare (15.37 acre) Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Bath and North East Somerset, England, important for its bat population. The disused quarries date from the 17th and 1 ...
, and as a result of cutting the Box Tunnel, at locations in Wiltshire such as Box.Hudson (1971). ''The Fashionable Stone''. Bath: Adams & Dart. Bezzant, Norman (1980). ''Out of the Rock..''. London: William Heinemann Ltd. Perkins, J.W., Brooks, A.T. and McR. Pearce, A.E. (1979). ''Bath Stone: a quarry history''. Cardiff: Department of Extra-mural Studies, University College Cardiff. Bath stone is still used on a reduced scale today, but more often as a cladding rather than a structural material. Further south, Hamstone is the colloquial name given to stone from Ham Hill, which is also widely used in the construction industry. Blue Lias has been used locally as a building stone and as a raw material for lime mortar and Portland cement
Portland cement is the most common type of cement in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete, mortar, stucco, and non-specialty grout. It was developed from other types of hydraulic lime in England in the early 19th cen ...
. Until the 1960s, Puriton had Blue Lias stone quarries, as did several other Polden villages. Its quarries also supplied a cement factory at Dunball, adjacent to the King's Sedgemoor Drain. Its derelict, early 20th century remains, was removed when the M5 motorway
The M5 is a motorway in England linking the Midlands with the South West England, South West. It runs from junction 8 of the M6 motorway, M6 at West Bromwich near Birmingham to Exeter in Devon. Heading south-west, the M5 runs east of West Brom ...
was constructed in the mid-1970s.(n/a)(1998).''Images of England: Bridgwater (Compiled from the collections at Admiral Blake Museum)''. Stroud: Tempus Publishing. Since the 1920s, the county has supplied aggregates. Foster Yeoman is Europe's large supplier of limestone aggregates, with quarries at Merehead Quarry
Torr Works quarry, is a limestone quarry at East Cranmore, near Shepton Mallet on the Mendip Hills, Somerset, England. The quarry was formerly known as Merehead, a name which has been retained for its rail depot on the opposite side of the A3 ...
. It has a dedicated railway operation, Mendip Rail, which is used to transport aggregates by rail from a group of Mendip quarries.Shannon, Paul (2007). "Mendip Stone," In: ''The Railway Magazine
''The Railway Magazine'' is a monthly British railway magazine, aimed at the railway enthusiast market, that has been published in London since July 1897. it was, for three years running, the railway magazine with the largest circulation in ...
'', Vol. 153, No. 1,277, pp 22–26. (September 2007). .
In November 2008, a public sector inward investment organisation was launched, called Into Somerset
Into Somerset was an inward investment agency for the county of Somerset, England. It worked with local authorities, other economic agencies and private sector partners, to encourage business relocation to Somerset.
Into Somerset was created in ...
, with the intention of growing the county's economy by promoting it to businesses that may wish to relocate from other parts of the UK (especially London) and the world. This now part of the Heart of the South West Growth Hub.
Nuclear electricity
Hinkley Point C nuclear power station
Hinkley Point C nuclear power station (HPC) is a two-unit, 3,200 MWe EPR nuclear power station under construction in Somerset, England.
The site was one of eight announced by the British government in 2010, and in November 2012 a nuclear site ...
is a project to construct a 3,200 MW two reactor nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced ...
station. On 18 October 2010, the British government announced that Hinkley Point – already the site of the disused Hinkley Point A and the still operational Hinkley Point B power stations – was one of the eight sites it considered suitable for future nuclear power stations. NNB Generation Company, a subsidiary of EDF, submitted an application for development consent to the Infrastructure Planning Commission on 31 October 2011. A protest group, Stop Hinkley, was formed to campaign for the closure of Hinkley Point B and oppose any expansion at the Hinkley Point site. In December 2013, the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
opened an investigation to assess whether the project breaks state-aid rules. On 8 October 2014 it was announced that the European Commission has approved the project, with an overwhelming majority and only four commissioners voting against the decision. Construction is underway and is projected to be completed in 2025.
Emergency services
All of the ceremonial county of Somerset is covered by theAvon and Somerset Police
Avon and Somerset Police is the territorial police force responsible for law enforcement in the county of Somerset and in four districts that used to be in the defunct county of Avon: Bristol, Bath and North East Somerset, North Somerset and ...
, a police force which also covers Bristol and South Gloucestershire. The police force is governed by the elected Avon and Somerset Police and Crime Commissioner
The Avon and Somerset Police and Crime Commissioner is the police and crime commissioner, an elected official tasked with setting out the way crime is tackled by Avon and Somerset Police in the English counties and unitary authorities of Bristol, ...
. The Devon and Somerset Fire and Rescue Service was formed in 2007 upon the merger of the Somerset Fire and Rescue Service with its neighbouring Devon service; it covers the area of Somerset County Council as well as the entire ceremonial county of Devon. The unitary districts of North Somerset and Bath & North East Somerset are instead covered by the Avon Fire and Rescue Service, a service which also covers Bristol and South Gloucestershire. The South Western Ambulance Service covers the entire South West of England, including all of Somerset; prior to February 2013 the unitary districts of Somerset came under the Great Western Ambulance Service, which merged into South Western. The Dorset and Somerset Air Ambulance
The Dorset and Somerset Air Ambulance is a registered charity, which uses a helicopter to provide an air ambulance service to the English counties of Dorset and Somerset. The air ambulance came into service in March 2000, following the succ ...
is a charitable organisation based in the county.
Culture
Arthurian legend
The Matter of Britain is the body of medieval literature and legendary material associated with Great Britain and Brittany and the legendary kings and heroes associated with it, particularly King Arthur. It was one of the three great Weste ...
, Avalon became associated with Glastonbury Tor
Glastonbury Tor is a hill near Glastonbury in the English county of Somerset, topped by the roofless St Michael's Tower, a Grade I listed building. The entire site is managed by the National Trust and has been designated a scheduled monument ...
when monks at Glastonbury Abbey claimed to have discovered the bones of King Arthur and his queen. What is more certain is that Glastonbury was an important religious centre by 700 and claims to be "the oldest above-ground Christian church in the World" situated "in the mystical land of Avalon". The claim is based on dating the founding of the community of monks at AD 63, the year of the legendary visit of Joseph of Arimathea, who was supposed to have brought the Holy Grail.
During the Middle Ages there were also important religious sites at Woodspring Priory and Muchelney Abbey
Muchelney Abbey is an English Heritage property in the village of Muchelney in the Somerset Levels, England. The site consists of ruined walls showing the layout of the abbey buildings constructed from the 7th to 16th centuries, and the rema ...
. The present Diocese of Bath and Wells covers Somerset – with the exception of the Parish of Abbots Leigh with Leigh Woods in North Somerset – and a small area of Dorset. The Episcopal seat of the Bishop of Bath and Wells is now in the Cathedral Church of Saint Andrew in the city of Wells, having previously been at Bath Abbey
The Abbey Church of Saint Peter and Saint Paul, commonly known as Bath Abbey, is a parish church of the Church of England and former Benedictine monastery in Bath, Somerset, England. Founded in the 7th century, it was reorganised in the 10th ...
. Before the English Reformation, it was a Roman Catholic diocese; the county now falls within the Roman Catholic Diocese of Clifton. The Benedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG
, caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal
, abbreviation = OSB
, formation =
, motto = (English: 'Pray and Work')
, found ...
monastery Saint Gregory's Abbey, commonly known as Downside Abbey, is at Stratton-on-the-Fosse, and the ruins of the former Cistercian
The Cistercians, () officially the Order of Cistercians ( la, (Sacer) Ordo Cisterciensis, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Sain ...
Cleeve Abbey are near the village of Washford.
Somerset has traditions of art, music and literature. Wordsworth and Coleridge wrote while staying in Coleridge Cottage, Nether Stowey
Nether Stowey is a large village in the Sedgemoor district of Somerset, South West England. It sits in the foothills of the Quantock Hills (England's first Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty), just below Over Stowey. The parish of Nether Stowey c ...
. The novelist John Cowper Powys (1872–1963) lived in the Somerset village of Montacute
Montacute is a village and civil parish in Somerset, England, west of Yeovil. The village has a population of 831 (2011 census). The name Montacute is thought by some to derive from the Latin "Mons Acutus", referring to the conically acute St ...
from 1885 until 1894 and his novels ''Wood and Stone'' (1915) and '' A Glastonbury Romance'' (1932) are set in Somerset. The writer Evelyn Waugh
Arthur Evelyn St. John Waugh (; 28 October 1903 – 10 April 1966) was an English writer of novels, biographies, and travel books; he was also a prolific journalist and book reviewer. His most famous works include the early satires '' Decl ...
spent his last years in the village of Combe Florey.
Traditional folk music, both song and dance, was important in the agricultural communities. Somerset songs were collected by Cecil Sharp
Cecil James Sharp (22 November 1859 – 23 June 1924) was an English-born collector of folk songs, folk dances and instrumental music, as well as a lecturer, teacher, composer and musician. He was the pre-eminent activist in the development of t ...
and incorporated into works such as Holst's ''A Somerset Rhapsody
A, or a, is the first letter and the first vowel of the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''a'' (pronounced ), plural ''aes'' ...
''. Halsway Manor near Williton is an international centre for folk music. The tradition continues today with groups such as The Wurzels
The Wurzels are an English Scrumpy and Western band from Somerset, England, best known for their number one hit "The Combine Harvester" and number three hit " I Am a Cider Drinker" in 1976. They are known for using British West Country phra ...
specialising in Scrumpy and Western music.
The Glastonbury Festival of Contemporary Performing Arts
Glastonbury Festival (formally Glastonbury Festival of Contemporary Performing Arts and known colloquially as Glasto) is a five-day festival of contemporary performing arts that takes place in Pilton, Somerset, England. In addition to contempo ...
takes place most years in Pilton, near Shepton Mallet, attracting over 170,000 music and culture lovers from around the world to see world-famous entertainers.
The Big Green Gathering which grew out of the Green fields at the Glastonbury Festival is held in the Mendip Hills between Charterhouse and Compton Martin each summer.
The annual Bath Literature Festival is one of several local festivals in the county; others include the Frome Festival and the Trowbridge Village Pump Festival, which, despite its name, is held at Farleigh Hungerford in Somerset. The annual circuit of West Country Carnivals is held in a variety of Somerset towns during the autumn, forming a major regional festival, and the largest Festival of Lights in Europe.

 The county has several museums; those at Bath include the
The county has several museums; those at Bath include the American Museum in Britain
The American Museum and Gardens (formerly American Museum in Britain) is a museum of American art and culture based at Claverton, near Bath, England. Its world-renowned collections of American furniture, quilts and folk art are displayed in a ...
, the Museum of Bath Architecture, the Herschel Museum of Astronomy, the Jane Austen Centre, and the Roman Baths. Other visitor attractions which reflect the cultural heritage of the county include: Claverton Pumping Station, Dunster Working Watermill, the Fleet Air Arm Museum at Yeovilton, Nunney Castle, The Helicopter Museum in Weston-super-Mare, King John's Hunting Lodge in Axbridge, Blake Museum Bridgwater, Radstock Museum, Museum of Somerset in Taunton, the Somerset Rural Life Museum in Glastonbury, and Westonzoyland Pumping Station Museum.
Somerset has 11,500 listed building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern I ...
s, 523 scheduled monuments, 192 conservation areas, 41 parks and gardens including those at Barrington Court
Barrington Court is a Tudor manor house begun around 1538 and completed in the late 1550s, with a vernacular stable court (1675), situated in Barrington, near Ilminster, Somerset, England.
The house was owned by several families by 1745 afte ...
, Holnicote Estate, Prior Park Landscape Garden and Tintinhull Garden, 36 English Heritage
English Heritage (officially the English Heritage Trust) is a charity that manages over 400 historic monuments, buildings and places. These include prehistoric sites, medieval castles, Roman forts and country houses.
The charity states that i ...
sites and 19 National Trust
The National Trust, formally the National Trust for Places of Historic Interest or Natural Beauty, is a charity and membership organisation for heritage conservation in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. In Scotland, there is a separate and ...
sites, including Clevedon Court, Fyne Court, Montacute House and Tyntesfield as well as Stembridge Tower Mill
Stembridge Tower Mill in High Ham, Somerset, England, is the last remaining thatched windmill in England. The mill is a grade II* listed building.
The stone tower mill was built in 1822 with four floors and a thatched "cap". A steam engine ...
, the last remaining thatched windmill in England. Other historic houses in the county which have remained in private ownership or used for other purposes include Halswell House and Marston Bigot. A key contribution of Somerset architecture is its medieval church towers. Jenkins writes, "These structures, with their buttresses, bell-opening tracery and crowns, rank with Nottinghamshire alabaster as England's finest contribution to medieval art."
Bath Rugby play at the Recreation Ground in Bath, and the Somerset County Cricket Club
Somerset County Cricket Club is one of eighteen first-class county clubs within the domestic cricket structure of England and Wales. It represents the historic county of Somerset. Founded in 1875, Somerset was initially regarded as a minor ...
are based at the County Ground in Taunton. The county's highest ranked football club is Yeovil Town, currently playing in the National League
The National League of Professional Baseball Clubs, known simply as the National League (NL), is the older of two leagues constituting Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, and the world's oldest extant professional team ...
. Horse racing courses are at Taunton
Taunton () is the county town of Somerset, England, with a 2011 population of 69,570. Its thousand-year history includes a 10th-century monastic foundation, Taunton Castle, which later became a priory. The Normans built a castle owned by t ...
, Bath
Bath may refer to:
* Bathing, immersion in a fluid
** Bathtub, a large open container for water, in which a person may wash their body
** Public bathing, a public place where people bathe
* Thermae, ancient Roman public bathing facilities
Plac ...
and Wincanton.
The county is served by the regional ''Western Daily Press
The ''Western Daily Press'' is a regional newspaper covering parts of South West England, mainly Gloucestershire, Wiltshire and Somerset as well as the metropolitan areas of Bath and North East Somerset and the Bristol area. It is published M ...
'' and local newspapers including the ''Weston & Somerset Mercury
''The Weston, Worle & Somerset Mercury'' is a weekly paid for newspaper that covers Weston-super-Mare and the surrounding areas of Somerset and North Somerset in England. The ''Weston Mercury'' was established 1 April 1843 and was family-owned ...
'', the '' Bath Chronicle'', '' Chew Valley Gazette'', ''Somerset County Gazette
The Somerset County Gazette is a weekly tabloid newspaper in Somerset, England.
It is published in a tabloid format on a weekly basis and has a circulation of about 10,195 based on its last published ABC figures to December 2018.Since then it has ...
,'' '' Clevedon Mercury'' '' Mendip Times'', and the ''West Somerset Free Press''. Television is provided by BBC West and ITV West Country, while southwestern parts of the county can receive BBC South West
BBC South West is the BBC English Region serving Cornwall, Devon, Isles of Scilly, West Somerset, West Dorset and Channel Islands.
Services Television
''BBC South Wests television service (broadcast on BBC One South West) consists of the flagshi ...
. Local radio stations are BBC Radio Somerset
BBC Radio Somerset is the BBC's local radio station serving the county of Somerset.
It broadcasts on FM, AM, DAB, digital TV and via BBC Sounds from studios in the Blackbrook area of Taunton.
According to RAJAR, the station has a weekly au ...
, BBC Radio Bristol (in northern parts of the county), Heart West, and Greatest Hits Radio South West in Yeovil.
The Flag of Somerset, representing the ceremonial county, has been registered with the Flag Institute following a competition in July 2013.
Transport
 Somerset has of roads. The main arterial routes, which include the M5 motorway, A303, A37, A38, A39, A358 and A361 give good access across the county, but many areas can only be accessed via narrow country lanes.
Rail services are provided by the West of England Main Line through Yeovil Junction, the Bristol to Exeter line,
Somerset has of roads. The main arterial routes, which include the M5 motorway, A303, A37, A38, A39, A358 and A361 give good access across the county, but many areas can only be accessed via narrow country lanes.
Rail services are provided by the West of England Main Line through Yeovil Junction, the Bristol to Exeter line,