Soda (soft Drink) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A soft drink (see § Terminology for other names) is a
A soft drink (see § Terminology for other names) is a
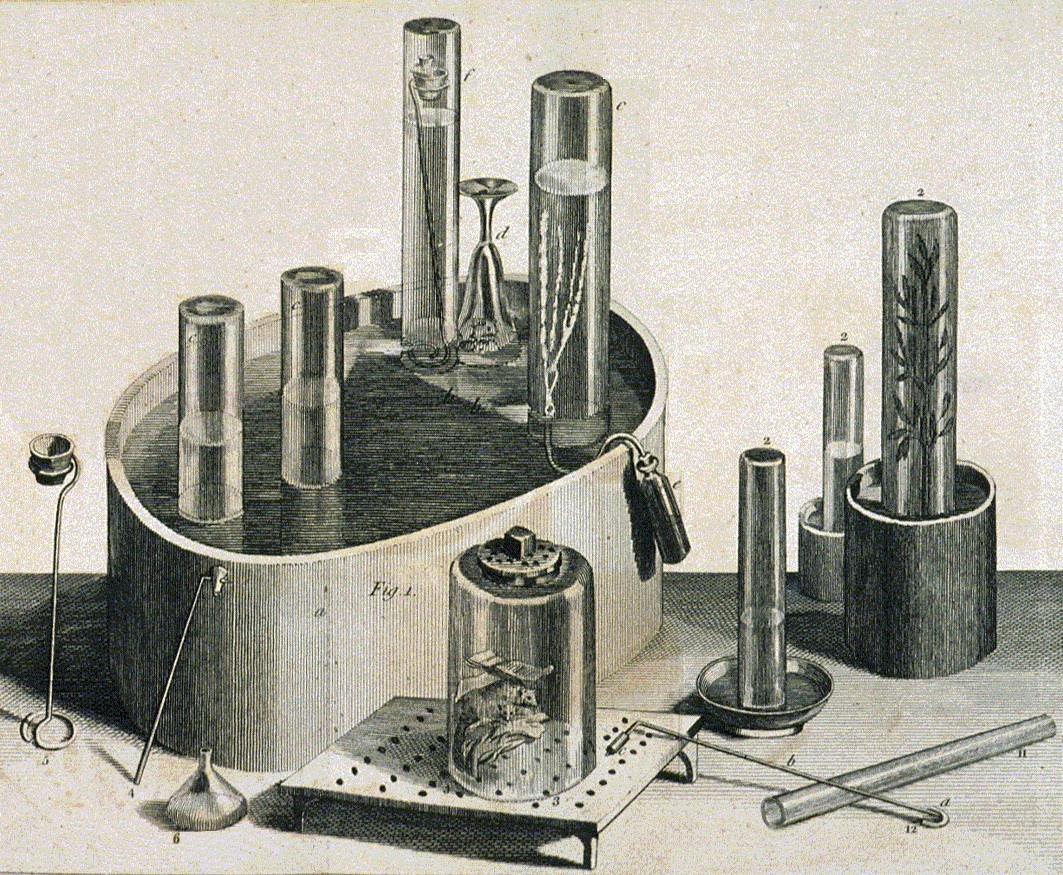 In the late 18th century, scientists made important progress in replicating naturally carbonated mineral waters. In 1767, Englishman Joseph Priestley first discovered a method of infusing water with carbon dioxide to make carbonated water when he suspended a bowl of distilled water above a beer vat at a local brewery in Leeds, England. His invention of carbonated water (later known as soda water, for the use of
In the late 18th century, scientists made important progress in replicating naturally carbonated mineral waters. In 1767, Englishman Joseph Priestley first discovered a method of infusing water with carbon dioxide to make carbonated water when he suspended a bowl of distilled water above a beer vat at a local brewery in Leeds, England. His invention of carbonated water (later known as soda water, for the use of
 Soft drinks soon outgrew their origins in the medical world and became a widely consumed product, available cheaply for the masses. By the 1840s, there were more than fifty soft drink manufacturers in London, an increase from just ten in the 1820s. Carbonated lemonade was widely available in British refreshment stalls in 1833, and in 1845,
Soft drinks soon outgrew their origins in the medical world and became a widely consumed product, available cheaply for the masses. By the 1840s, there were more than fifty soft drink manufacturers in London, an increase from just ten in the 1820s. Carbonated lemonade was widely available in British refreshment stalls in 1833, and in 1845,  A persistent problem in the soft drinks industry was the lack of an effective sealing of the bottles. Carbonated drink bottles are under great pressure from the gas, so inventors tried to find the best way to prevent the carbon dioxide or bubbles from escaping. The bottles could also explode if the pressure was too great. Hiram Codd devised a patented
A persistent problem in the soft drinks industry was the lack of an effective sealing of the bottles. Carbonated drink bottles are under great pressure from the gas, so inventors tried to find the best way to prevent the carbon dioxide or bubbles from escaping. The bottles could also explode if the pressure was too great. Hiram Codd devised a patented  In 1892, the " Crown Cork Bottle Seal" was patented by William Painter, a Baltimore, Maryland machine shop operator. It was the first bottle top to successfully keep the bubbles in the bottle. In 1899, the first patent was issued for a
In 1892, the " Crown Cork Bottle Seal" was patented by William Painter, a Baltimore, Maryland machine shop operator. It was the first bottle top to successfully keep the bubbles in the bottle. In 1899, the first patent was issued for a
 Soft drinks are made by mixing dry or fresh ingredients with water. Production of soft drinks can be done at factories or at home. Soft drinks can be made at home by mixing a syrup or dry ingredients with carbonated water, or by Lacto-fermentation. Syrups are commercially sold by companies such as Soda-Club; dry ingredients are often sold in pouches, in a style of the popular U.S. drink mix Kool-Aid. Carbonated water is made using a soda siphon or a home carbonation system or by dropping dry ice into water. Food-grade carbon dioxide, used for carbonating drinks, often comes from ammonia plants.
Drinks like ginger ale and root beer are often brewed using yeast to cause carbonation.
Of most importance is that the ingredient meets the agreed specification on all major parameters. This is not only the functional parameter (in other words, the level of the major constituent), but the level of impurities, the microbiological status, and physical parameters such as color, particle size, etc.
Some soft drinks contain measurable amounts of alcohol. In some older preparations, this resulted from natural fermentation used to build the carbonation. In the United States, soft drinks (as well as other products such as non-alcoholic beer) are allowed by law to contain up to 0.5%
Soft drinks are made by mixing dry or fresh ingredients with water. Production of soft drinks can be done at factories or at home. Soft drinks can be made at home by mixing a syrup or dry ingredients with carbonated water, or by Lacto-fermentation. Syrups are commercially sold by companies such as Soda-Club; dry ingredients are often sold in pouches, in a style of the popular U.S. drink mix Kool-Aid. Carbonated water is made using a soda siphon or a home carbonation system or by dropping dry ice into water. Food-grade carbon dioxide, used for carbonating drinks, often comes from ammonia plants.
Drinks like ginger ale and root beer are often brewed using yeast to cause carbonation.
Of most importance is that the ingredient meets the agreed specification on all major parameters. This is not only the functional parameter (in other words, the level of the major constituent), but the level of impurities, the microbiological status, and physical parameters such as color, particle size, etc.
Some soft drinks contain measurable amounts of alcohol. In some older preparations, this resulted from natural fermentation used to build the carbonation. In the United States, soft drinks (as well as other products such as non-alcoholic beer) are allowed by law to contain up to 0.5%
 Market control of the soft drink industry varies on a country-by-country basis. However,
Market control of the soft drink industry varies on a country-by-country basis. However,
 Most soft drinks contain high concentrations of simple carbohydrates: glucose,
Most soft drinks contain high concentrations of simple carbohydrates: glucose,
"Beverage group: Pull soda from primary schools"
'' USA Today'', August 17, 2005.
"After soda ban nutritionists say more can be done"
'' The Boston Globe'', May 4, 2006.
"Critics Say Soda Policy for Schools Lacks Teeth
'' The New York Times'', August 22, 2006.
 A soft drink (see § Terminology for other names) is a
A soft drink (see § Terminology for other names) is a drink
A drink or beverage is a liquid intended for human consumption. In addition to their basic function of satisfying thirst, drinks play important roles in human culture. Common types of drinks include plain drinking water, milk, juice, smoothies a ...
that usually contains water (often carbonated), a sweetener, and a natural and/or artificial flavoring
A flavoring (or flavouring), also known as flavor (or flavour) or flavorant, is a food additive used to improve the taste or Sense of smell, smell of food. It changes the perceptual impression of food as determined primarily by the chemoreceptor ...
. The sweetener may be a sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
, high-fructose corn syrup, fruit juice
Juice is a drink made from the extraction or pressing of the natural liquid contained in fruit and vegetables. It can also refer to liquids that are flavored with concentrate or other biological food sources, such as meat or seafood, such as ...
, a sugar substitute
A sugar substitute is a food additive that provides a sweetness like that of sugar while containing significantly less food energy than sugar-based sweeteners, making it a zero-calorie () or low-calorie sweetener. Artificial sweeteners may be d ...
(in the case of ''diet drinks''), or some combination of these. Soft drinks may also contain caffeine, colorings, preservatives, and/or other ingredients.
Soft drinks are called "soft" in contrast with "hard
Hard may refer to:
* Hardness, resistance of physical materials to deformation or fracture
* Hard water, water with high mineral content
Arts and entertainment
* ''Hard'' (TV series), a French TV series
* Hard (band), a Hungarian hard rock super ...
" alcoholic drinks. Small amounts of alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
may be present in a soft drink, but the alcohol content must be less than 0.5% of the total volume of the drink in many countries and localities See §7.71, paragraphs (e) and (f). if the drink is to be considered non-alcoholic
An alcohol-free or non-alcoholic drink, also known as a temperance drink, is a version of an alcoholic drink made without alcohol, or with the alcohol removed or reduced to almost zero. These may take the form of a non-alcoholic mixed drink (a "vi ...
. Types of soft drinks include lemon-lime drinks, orange soda, cola, grape soda, ginger ale, and root beer.
Soft drinks may be served cold, over ice cubes, or at room temperature. They are available in many container formats, including cans, glass bottles, and plastic bottles. Containers come in a variety of sizes, ranging from small bottles to large multi-liter containers. Soft drinks are widely available at fast food restaurants, movie theater
A movie theater (American English), cinema (British English), or cinema hall ( Indian English), also known as a movie house, picture house, the movies, the pictures, picture theater, the silver screen, the big screen, or simply theater is a ...
s, convenience store
A convenience store, convenience shop, corner store or corner shop is a small retail business that stocks a range of everyday items such as coffee, groceries, snack foods, confectionery, soft drinks, ice creams, tobacco products, lottery ticket ...
s, casual-dining restaurants, dedicated soda store
A soda shop, also often known as a malt shop (after malted milk) and as a “malted shop” in Canada, is a business akin to an ice cream parlor and a drugstore soda fountain. Interiors were often furnished with a large mirror behind a marble count ...
s, vending machines, and bar
Bar or BAR may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bar (establishment), selling alcoholic beverages
* Candy bar
* Chocolate bar
Science and technology
* Bar (river morphology), a deposit of sediment
* Bar (tropical cyclone), a layer of cloud
* Bar (u ...
s from soda fountain machines.
Within a decade of the invention of carbonated water by Joseph Priestley in 1767, inventors in Britain and in Europe had used his concept to produce the drink in greater quantities. One such inventor, J. J. Schweppe, formed Schweppes in 1783 and selling the world's first bottled soft drink. Soft drink brands founded in the 19th century include R. White's Lemonade
R. White's Lemonade is a British brand of a carbonated lemonade, which is produced and sold in the United Kingdom by Britvic. Robert and Mary White produced the first R. White's lemonade in Camberwell, south London, in 1845. The White Family took ...
in 1845, Dr Pepper in 1885 and Coca-Cola in 1886. Subsequent brands include Pepsi, Irn-Bru, Sprite, Fanta and 7 Up.
Terminology
The term "soft drink" is a category in the beverage industry, and is broadly used in product labeling and on restaurant menus. However, in many countries such drinks are more commonly referred to by regional names, including ''pop'', ''cool drink'', and ''fizzy drink''. Other lesser used terms include ''carbonated drink'', ''cold drink'', ''fizzy juice'', ''lolly water'', ''seltzer'', ''coke'', ''cola'', ''soda'', ''soda pop'', ''tonic'', and ''mineral''. Due to the high sugar content in typical soft drinks, they may also be called ''sugary drinks''. In the United States, the 2003Harvard
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
Dialect Survey tracked the usage of the nine most common names. Over half of the survey respondents preferred the term "soda", which was dominant in the Northeastern United States, California, and the areas surrounding Milwaukee and St. Louis. The term "pop", which was preferred by 25% of the respondents, was most popular in the Midwest and Pacific Northwest, while the genericized trademark "coke", used by 12% of the respondents, was most popular in the Southern United States. The term "tonic" is distinctive to eastern Massachusetts, although usage is declining.
In the English-speaking parts of Canada, the term "pop" is prevalent, but "soft drink" is the most common English term used in Montreal.
In the United Kingdom and Ireland, the term "fizzy drink" is common. "Pop" and "fizzy pop" are used in Northern England, South Wales, and the Midlands while "mineral" is used in Ireland. In Scotland, "fizzy juice" or even simply "juice" is colloquially encountered, as is "ginger". In Australia and New Zealand, "soft drink" or "fizzy drink" is typically used. In South African English
South African English (SAfrE, SAfrEng, SAE, en-ZA) is the set of English language dialects native to South Africans.
History
British settlers first arrived in the South African region in 1795, when they established a military holding op ...
, "cool drink" is any soft drink. U.S. soft drinks 7-Up or Sprite are called "lemonade" in the UK.
In other languages, various names are used: descriptive names as "non-alcoholic beverages", equivalents of "soda water", or generalized prototypical names. For example, the Bohemian variant of the Czech language (but not Moravian dialects) uses "limonáda" for all such beverages, not only for those from lemons. Similarly, the Slovak language uses "malinovka" (= "raspberry water") for all such beverages, not only for raspberry ones.
History
The origins of soft drinks lie in the development of fruit-flavored drinks. In themedieval Middle East
The Middle East, interchangeable with the Near East, is home to one of the Cradles of Civilization and has seen many of the world's oldest cultures and civilizations. The region's history started from the earliest human settlements and continues ...
, a variety of fruit-flavored soft drinks were widely drunk, such as sharbat, and were often sweetened with ingredients such as sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
, syrup and honey
Honey is a sweet and viscous substance made by several bees, the best-known of which are honey bees. Honey is made and stored to nourish bee colonies. Bees produce honey by gathering and then refining the sugary secretions of plants (primar ...
. Other common ingredients included lemon, apple, pomegranate, tamarind, jujube, sumac, musk, mint and ice. Middle Eastern drinks later became popular in medieval Europe, where the word "syrup" was derived from Arabic. In Tudor England, 'water imperial' was widely drunk; it was a sweetened drink with lemon flavor and containing cream of tartar. 'Manays Cryste' was a
sweetened cordial flavored with rosewater, violets or cinnamon.
Another early type of soft drink was lemonade, made of water and lemon juice sweetened with honey, but without carbonated water. The ''Compagnie des Limonadiers'' of Paris was granted a monopoly for the sale of lemonade soft drinks in 1676. Vendors carried tanks of lemonade on their backs and dispensed cups of the soft drink to Parisians.
Carbonated drinks
Carbonated drinks or fizzy drinks are beverages that contain dissolved carbon dioxide incarbonated water
Carbonated water (also known as soda water, sparkling water, fizzy water, club soda, water with gas, in many places as mineral water, or especially in the United States as seltzer or seltzer water) is water containing dissolved carbon dioxide gas, ...
. The dissolution of CO2 in a liquid
A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, a ...
, gives rise to '' effervescence'' or ''fizz''. Carbon dioxide is only weakly soluble in water, therefore it separates into a gas when the pressure is released. The process usually involves injecting carbon dioxide under high pressure. When the pressure is removed, the carbon dioxide is released from the solution as small bubbles, which causes the solution to become effervescent, or fizzy.
Carbonated beverages are prepared by mixing chilled flavored syrup with chilled carbonated water. Carbonation levels range up to 5 volumes of CO2 per liquid volume. Ginger ale, colas, and related drinks are carbonated with 3.5 volumes. Other drinks, often fruity ones, are carbonated less.
 In the late 18th century, scientists made important progress in replicating naturally carbonated mineral waters. In 1767, Englishman Joseph Priestley first discovered a method of infusing water with carbon dioxide to make carbonated water when he suspended a bowl of distilled water above a beer vat at a local brewery in Leeds, England. His invention of carbonated water (later known as soda water, for the use of
In the late 18th century, scientists made important progress in replicating naturally carbonated mineral waters. In 1767, Englishman Joseph Priestley first discovered a method of infusing water with carbon dioxide to make carbonated water when he suspended a bowl of distilled water above a beer vat at a local brewery in Leeds, England. His invention of carbonated water (later known as soda water, for the use of soda powder
Sherbet is a fizzy, sweet powder, usually eaten by dipping a lollipop or liquorice, using a small spoon, or licking it from a finger.
Etymology
The word "sherbet" is from Turkish ', which is from Persian , which in turn comes from "sharbat", ...
s in its commercial manufacture) is the major and defining component of most soft drinks.
Priestley found that water treated in this manner had a pleasant taste, and he offered it to his friends as a refreshing drink. In 1772, Priestley published a paper entitled ''Impregnating Water with Fixed Air'' in which he describes dripping ''oil of vitriol'' (or sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
as it is now called) onto chalk to produce carbon dioxide gas, and encouraging the gas to dissolve into an agitated bowl of water.
Another Englishman, John Mervin Nooth
John Mervin Nooth (5 September 1737 – 3 May 1828) was an English physician, scientist, and army officer. Nooth earned his medical degree from the University of Edinburgh in 1766 and was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1774. In the sa ...
, improved Priestley's design and sold his apparatus for commercial use in pharmacies. Swedish chemist Torbern Bergman invented a generating apparatus that made carbonated water from chalk by the use of sulfuric acid. Bergman's apparatus allowed imitation mineral water to be produced in large amounts. Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius
Baron Jöns Jacob Berzelius (; by himself and his contemporaries named only Jacob Berzelius, 20 August 1779 – 7 August 1848) was a Swedish chemist. Berzelius is considered, along with Robert Boyle, John Dalton, and Antoine Lavoisier, to be on ...
started to add flavors (spices, juices, and wine) to carbonated water in the late eighteenth century. Thomas Henry, an apothecary from Manchester, was the first to sell artificial mineral water to the general public for medicinal purposes, beginning in the 1770s. His recipe for 'Bewley's Mephitic Julep' consisted of 3 drachm
The dram (alternative British spelling drachm; apothecary symbol ʒ or ℨ; abbreviated dr) Earlier version first published in ''New English Dictionary'', 1897.National Institute of Standards and Technology (October 2011). Butcher, Tina; Cook, ...
s of fossil alkali to a quart of water, and the manufacture had to 'throw in streams of fixed air until all the alkaline taste is destroyed'.
Johann Jacob Schweppe
Johann Jacob Schweppe (, ) (16 March 1740 – 18 November 1821) was a German-Swiss watchmaker and amateur scientist who developed the first practical process to manufacture bottled carbonated mineral water, based on a process discovered by Joseph ...
developed a process to manufacture bottled carbonated mineral water. He founded the Schweppes Company in Geneva in 1783 to sell carbonated water, and relocated his business to London in 1792. His drink soon gained in popularity; among his newfound patrons was Erasmus Darwin
Erasmus Robert Darwin (12 December 173118 April 1802) was an English physician. One of the key thinkers of the Midlands Enlightenment, he was also a natural philosopher, physiologist, slave-trade abolitionist, inventor, and poet.
His poems ...
. In 1843, the Schweppes company commercialized Malvern Water at the Holywell Spring in the Malvern Hills, and received a royal warrant A royal warrant is a document issued by a monarch which confers rights or privileges on the recipient, or has the effect of law.
Royal warrant may refer to:
* Royal warrant of appointment, warrant to tradespeople who supply goods or services to a r ...
from King William IV.
It was not long before flavoring was combined with carbonated water. The earliest reference to carbonated ginger beer is in a ''Practical Treatise on Brewing''. published in 1809. The drinking of either natural or artificial mineral water was considered at the time to be a healthy practice, and was promoted by advocates of temperance. Pharmacists selling mineral waters began to add herbs and chemicals to unflavored mineral water. They used birch bark (see birch beer), dandelion, sarsaparilla, fruit extracts, and other substances.
Mass market and industrialization
 Soft drinks soon outgrew their origins in the medical world and became a widely consumed product, available cheaply for the masses. By the 1840s, there were more than fifty soft drink manufacturers in London, an increase from just ten in the 1820s. Carbonated lemonade was widely available in British refreshment stalls in 1833, and in 1845,
Soft drinks soon outgrew their origins in the medical world and became a widely consumed product, available cheaply for the masses. By the 1840s, there were more than fifty soft drink manufacturers in London, an increase from just ten in the 1820s. Carbonated lemonade was widely available in British refreshment stalls in 1833, and in 1845, R. White's Lemonade
R. White's Lemonade is a British brand of a carbonated lemonade, which is produced and sold in the United Kingdom by Britvic. Robert and Mary White produced the first R. White's lemonade in Camberwell, south London, in 1845. The White Family took ...
went on sale in the UK. For the Great Exhibition
The Great Exhibition of the Works of Industry of All Nations, also known as the Great Exhibition or the Crystal Palace Exhibition (in reference to the temporary The Crystal Palace, structure in which it was held), was an International Exhib ...
of 1851 held at Hyde Park
Hyde Park may refer to:
Places
England
* Hyde Park, London, a Royal Park in Central London
* Hyde Park, Leeds, an inner-city area of north-west Leeds
* Hyde Park, Sheffield, district of Sheffield
* Hyde Park, in Hyde, Greater Manchester
Austra ...
in London, Schweppes was designated the official drink supplier and sold over a million bottles of lemonade, ginger beer, Seltzer water and soda-water. There was a Schweppes soda water fountain, situated directly at the entrance to the exhibition.
Mixer drinks became popular in the second half of the century. Tonic water was originally quinine added to water as a prophylactic against malaria and was consumed by British officials stationed in the tropical areas of South Asia and Africa. As the quinine powder was so bitter people began mixing the powder with soda and sugar, and a basic tonic water was created. The first commercial tonic water was produced in 1858. The mixed drink gin and tonic also originated in British colonial India, when the British population would mix their medicinal quinine tonic with gin
Gin () is a distilled alcoholic drink that derives its flavour from juniper berries (''Juniperus communis'').
Gin originated as a medicinal liquor made by monks and alchemists across Europe, particularly in southern Italy, Flanders and the Ne ...
.
 A persistent problem in the soft drinks industry was the lack of an effective sealing of the bottles. Carbonated drink bottles are under great pressure from the gas, so inventors tried to find the best way to prevent the carbon dioxide or bubbles from escaping. The bottles could also explode if the pressure was too great. Hiram Codd devised a patented
A persistent problem in the soft drinks industry was the lack of an effective sealing of the bottles. Carbonated drink bottles are under great pressure from the gas, so inventors tried to find the best way to prevent the carbon dioxide or bubbles from escaping. The bottles could also explode if the pressure was too great. Hiram Codd devised a patented bottling
Bottling lines are production lines that fill a product, generally a beverage, into bottles on a large scale. Many prepared foods are also bottled, such as sauces, syrups, marinades, oils and vinegars.
Beer bottling process
Packaging of bottle ...
machine while working at a small mineral water works in the Caledonian Road, Islington
Islington () is a district in the north of Greater London, England, and part of the London Borough of Islington. It is a mainly residential district of Inner London, extending from Islington's High Street to Highbury Fields, encompassing the ar ...
, in London in 1870. His Codd-neck bottle was designed to enclose a marble and a rubber washer
Washer most commonly refers to:
*Washer (hardware), a thin usually disc-shaped plate with a hole in the middle typically used with a bolt or nut
*Washing machine, for cleaning clothes
Washer may also refer to:
*Dishwasher, a machine for cleani ...
in the neck. The bottles were filled upside down, and pressure of the gas in the bottle forced the marble against the washer, sealing in the carbonation. The bottle was pinched into a special shape to provide a chamber into which the marble was pushed to open the bottle. This prevented the marble from blocking the neck as the drink was poured. R. White's, by now the biggest soft drinks company in London and south-east England, featured a wide range of drinks on their price list in 1887, all of which were sold in Codd's glass bottles, with choices including strawberry soda, raspberry soda, cherryade and cream soda.
 In 1892, the " Crown Cork Bottle Seal" was patented by William Painter, a Baltimore, Maryland machine shop operator. It was the first bottle top to successfully keep the bubbles in the bottle. In 1899, the first patent was issued for a
In 1892, the " Crown Cork Bottle Seal" was patented by William Painter, a Baltimore, Maryland machine shop operator. It was the first bottle top to successfully keep the bubbles in the bottle. In 1899, the first patent was issued for a glass-blowing
Glassblowing is a glassforming technique that involves inflating molten glass into a bubble (or parison) with the aid of a blowpipe (or blow tube). A person who blows glass is called a ''glassblower'', ''glassmith'', or ''gaffer''. A '' lampworke ...
machine for the automatic production of glass bottles. Earlier glass bottles had all been hand-blown. Four years later, the new bottle-blowing machine was in operation. It was first operated by Michael Owens, an employee of Libby Glass Company. Within a few years, glass bottle production increased from 1,400 bottles a day to about 58,000 bottles a day.
In America, soda fountains were initially more popular, and many Americans would frequent the soda fountain daily. Beginning in 1806, Yale University chemistry professor Benjamin Silliman sold soda waters in New Haven, Connecticut. He used a Nooth apparatus to produce his waters. Businessmen in Philadelphia and New York City also began selling soda water in the early 19th century. In the 1830s, John Matthews of New York City and John Lippincott of Philadelphia began manufacturing soda fountains. Both men were successful and built large factories for fabricating fountains. Due to problems in the U.S. glass industry, bottled drinks remained a small portion of the market throughout much of the 19th century. (However, they were known in England. In ''The Tenant of Wildfell Hall
''The Tenant of Wildfell Hall'' is the second and final novel written by English author Anne Brontë. It was first published in 1848 under the pseudonym Acton Bell. Probably the most shocking of the Brontës' novels, it had an instant and ph ...
'', published in 1848, the caddish Huntingdon, recovering from months of debauchery, wakes at noon and gulps a bottle of soda-water.)
In the early 20th century, sales of bottled soda increased greatly around the world, and in the second half of the 20th century, canned soft drinks became an important share of the market. During the 1920s, "Home-Paks" was invented. "Home-Paks" is the familiar six-pack cartons made from cardboard. Vending machines also began to appear in the 1920s. Since then, soft drink vending machines have become increasingly popular. Both hot and cold drinks are sold in these self-service machines throughout the world.
Consumption
Per capita consumption of soda varies considerably around the world. As of 2014, the top consuming countries per capita were Argentina, the United States, Chile, and Mexico. Developed countries in Europe and elsewhere in the Americas had considerably lower consumption. Annual average consumption in the United States, at 153.5 liters, was about twice that in the United Kingdom (77.7) or Canada (85.3). In recent years, soda consumption has generally declined in the West. According to one estimate, per capita consumption in the United States reached its peak in 1998 and has continually fallen since. A study in the journal '' Obesity'' found that from 2003 to 2014 the proportion of Americans who drank a sugary beverage on a given day fell from approximately 62% to 50% for adults, and from 80% to 61% for children. The decrease has been attributed to, among other factors, an increased awareness of the dangers of obesity, and government efforts to improve diets. At the same time, soda consumption has increased in some low or middle income countries such as Cameroon, Georgia, India, and Vietnam as soda manufacturers increasingly target these markets and consumers have increasing discretionary income.Production
 Soft drinks are made by mixing dry or fresh ingredients with water. Production of soft drinks can be done at factories or at home. Soft drinks can be made at home by mixing a syrup or dry ingredients with carbonated water, or by Lacto-fermentation. Syrups are commercially sold by companies such as Soda-Club; dry ingredients are often sold in pouches, in a style of the popular U.S. drink mix Kool-Aid. Carbonated water is made using a soda siphon or a home carbonation system or by dropping dry ice into water. Food-grade carbon dioxide, used for carbonating drinks, often comes from ammonia plants.
Drinks like ginger ale and root beer are often brewed using yeast to cause carbonation.
Of most importance is that the ingredient meets the agreed specification on all major parameters. This is not only the functional parameter (in other words, the level of the major constituent), but the level of impurities, the microbiological status, and physical parameters such as color, particle size, etc.
Some soft drinks contain measurable amounts of alcohol. In some older preparations, this resulted from natural fermentation used to build the carbonation. In the United States, soft drinks (as well as other products such as non-alcoholic beer) are allowed by law to contain up to 0.5%
Soft drinks are made by mixing dry or fresh ingredients with water. Production of soft drinks can be done at factories or at home. Soft drinks can be made at home by mixing a syrup or dry ingredients with carbonated water, or by Lacto-fermentation. Syrups are commercially sold by companies such as Soda-Club; dry ingredients are often sold in pouches, in a style of the popular U.S. drink mix Kool-Aid. Carbonated water is made using a soda siphon or a home carbonation system or by dropping dry ice into water. Food-grade carbon dioxide, used for carbonating drinks, often comes from ammonia plants.
Drinks like ginger ale and root beer are often brewed using yeast to cause carbonation.
Of most importance is that the ingredient meets the agreed specification on all major parameters. This is not only the functional parameter (in other words, the level of the major constituent), but the level of impurities, the microbiological status, and physical parameters such as color, particle size, etc.
Some soft drinks contain measurable amounts of alcohol. In some older preparations, this resulted from natural fermentation used to build the carbonation. In the United States, soft drinks (as well as other products such as non-alcoholic beer) are allowed by law to contain up to 0.5% alcohol by volume
Alcohol by volume (abbreviated as ABV, abv, or alc/vol) is a standard measure of how much alcohol (ethanol) is contained in a given volume of an alcoholic beverage (expressed as a volume percent). It is defined as the number of millilitres (mL) o ...
. Modern drinks introduce carbon dioxide for carbonation, but there is some speculation that alcohol might result from fermentation of sugars in a non-sterile environment. A small amount of alcohol is introduced in some soft drinks where alcohol is used in the preparation of the flavoring extracts such as vanilla extract.
Producers
 Market control of the soft drink industry varies on a country-by-country basis. However,
Market control of the soft drink industry varies on a country-by-country basis. However, PepsiCo
PepsiCo, Inc. is an American multinational food, snack, and beverage corporation headquartered in Harrison, New York, in the hamlet of Purchase. PepsiCo's business encompasses all aspects of the food and beverage market. It oversees the manuf ...
and the Coca-Cola Company remain the two largest producers of soft drinks in most regions of the world. In North America, Keurig Dr Pepper and Jones Soda also hold a significant amount of market share.
Health concerns
The over-consumption of sugar-sweetened soft drinks is associated with obesity,hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high bl ...
, type 2 diabetes, dental caries, and low nutrient levels. Experimental studies tend to support a causal role for sugar-sweetened soft drinks in these ailments, though this is challenged by other researchers. According to a 2013 systematic review
A systematic review is a Literature review, scholarly synthesis of the evidence on a clearly presented topic using critical methods to identify, define and assess research on the topic. A systematic review extracts and interprets data from publ ...
of systematic reviews, 83.3% of the systematic reviews without reported conflict of interest
A conflict of interest (COI) is a situation in which a person or organization is involved in multiple interests, financial or otherwise, and serving one interest could involve working against another. Typically, this relates to situations i ...
concluded that sugar-sweetened soft drinks consumption could be a potential risk factor for weight gain.
Obesity and weight-related diseases
From 1977 to 2002, Americans doubled their consumption ofsweetened beverage
A sweetened beverage is any beverage with added sugar. It has been described as "liquid candy". Consumption of sweetened beverages has been linked to weight gain, obesity, and associated health risks. According to the CDC, consumption of sweetene ...
s—a trend that was paralleled by doubling the prevalence of obesity. The consumption of sugar-sweetened beverages is associated with weight and obesity, and changes in consumption can help predict changes in weight.
The consumption of sugar-sweetened soft drinks can also be associated with many weight-related diseases, including diabetes, metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a clustering of at least three of the following five medical conditions: abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, high serum triglycerides, and low serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL).
Metabolic syndrome ...
, and cardiovascular risk factors.
Dental decay
 Most soft drinks contain high concentrations of simple carbohydrates: glucose,
Most soft drinks contain high concentrations of simple carbohydrates: glucose, fructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galacto ...
, sucrose
Sucrose, a disaccharide, is a sugar composed of glucose and fructose subunits. It is produced naturally in plants and is the main constituent of white sugar. It has the molecular formula .
For human consumption, sucrose is extracted and refined ...
and other simple sugars. If oral bacteria ferment carbohydrates and produce acids that may dissolve tooth enamel and induce dental decay, then sweetened drinks may increase the risk of dental caries. The risk would be greater if the frequency of consumption is high.
A large number of soda pops are acid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
ic as are many fruits, sauces, and other foods. Drinking acidic drinks over a long period and continuous sipping may erode the tooth enamel. A 2007 study determined that some flavored sparkling waters are as erosive or more so than orange juice.
Using a drinking straw is often advised by dentists as the drink does not come into as much contact with the teeth. It has also been suggested that brushing teeth right after drinking soft drinks should be avoided as this can result in additional erosion to the teeth due to mechanical action of the toothbrush on weakened enamel.
Bone density and bone loss
A 2006 study of several thousand men and women, found that women who regularly drank cola-based sodas (three or more a day) had significantly lower bone mineral density (BMD) of about 4% in the hip compared to women who did not consume colas. The study found that the effect of regular consumption of cola sodas was not significant on men's BMD.Benzene
In 2006, the United Kingdom Food Standards Agency published the results of its survey of benzene levels in soft drinks, which tested 150 products and found that four contained benzene levels above the World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines for drinking water. The United States Food and Drug Administration released its own test results of several soft drinks containingbenzoates Benzoates (salts of benzoic acid) can refer to:
*Ammonium benzoate
*Calcium benzoate
*Magnesium benzoate
*Potassium benzoate
* Sodium benzoate
Sodium benzoate is the sodium salt of benzoic acid, widely used as a food preservative (with an E num ...
and ascorbic
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) an ...
or erythorbic acid
Erythorbic acid (isoascorbic acid, D-araboascorbic acid) is a stereoisomer of ascorbic acid (vitamin C). It is synthesized by a reaction between methyl 2-keto-D-gluconate and sodium methoxide. It can also be synthesized from sucrose or by strains ...
. Five tested drinks contained benzene levels above the Environmental Protection Agency's recommended standard of 5 ppb. As of 2006, the FDA stated its belief that "the levels of benzene found in soft drinks and other beverages to date do not pose a safety concern for consumers".
Kidney stones
A study published in the ''Clinical Journal of theAmerican Society of Nephrology
Founded in 1966, the American Society of Nephrology (ASN) is the world's largest professional society devoted to the study of kidney disease. Composed of over 20,000 physicians and scientists, ASN promotes expert patient care, advances medical r ...
'' in 2013 concluded that consumption of soft drinks was associated with a 23% higher risk of developing kidney stones.
Mortality, circulatory and digestive diseases
In a 2019 study, 451,743 people who had higher consumption of soft drinks (two or more a day) were associated with all-cause mortality, artificially sweetened drinks withcirculatory disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
s and sugar-sweetened drinks with digestive diseases
Gastrointestinal diseases (abbrev. GI diseases or GI illnesses) refer to diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, namely the oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum, and the accessory organs of digestion, the live ...
.
Government regulation
Schools
Since at least 2006, debate on whether high-calorie soft drink vending machines should be allowed in schools has been on the rise. Opponents of the soft drink vending machines believe that soft drinks are a significant contributor tochildhood obesity
Childhood obesity is a condition where excess body fat negatively affects a child's health or well-being. As methods to determine body fat directly are difficult, the diagnosis of obesity is often based on BMI. Due to the rising prevalence of ...
and tooth decay, and that allowing soft drink sales in schools encourages children to believe they are safe to consume in moderate to large quantities. Opponents also argue that schools have a responsibility to look after the health of the children in their care, and that allowing children easy access to soft drinks violates that responsibility. Vending machine proponents believe that obesity is a complex issue and soft drinks are not the only cause. A 2011 bill to tax soft drinks in California failed, with some opposing lawmakers arguing that parents—not the government—should be responsible for children's drink choices.
On May 3, 2006, the Alliance for a Healthier Generation, Cadbury Schweppes, the Coca-Cola Company, PepsiCo
PepsiCo, Inc. is an American multinational food, snack, and beverage corporation headquartered in Harrison, New York, in the hamlet of Purchase. PepsiCo's business encompasses all aspects of the food and beverage market. It oversees the manuf ...
, and the American Beverage Association
The American Beverage Association (ABA) is a government lobbying group that represents the beverage industry in the United States. Its members include producers and bottlers of soft drinks, such as Coca-Cola and PepsiCo, bottled water, and other ...
announced new guidelines that will voluntarily remove high-calorie soft drinks from all U.S. schools.
On May 19, 2006, the British education secretary, Alan Johnson, announced new minimum nutrition standards for school food. Among a wide range of measures, from September 2006, school lunches will be free from carbonated drinks. Schools will also end the sale of junk food (including carbonated drinks) in vending machines and tuck shops.
In 2008, Samantha K Graff published an article in the ''Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science'' regarding the "First Amendment Implications of Restricting Food and Beverages Marketing in Schools". The article examines a school district's policy regarding limiting the sale and marketing of soda in public schools, and how certain policies can invoke a violation of the First Amendment. Due to district budget cuts and loss in state funding, many school districts allow commercial businesses to market and advertise their product (including junk food and soda) to public school students for additional revenue. Junk food and soda companies have acquired exclusive rights to vending machines throughout many public school campuses. Opponents of corporate marketing and advertising on school grounds urge school officials to restrict or limit a corporation's power to promote, market, and sell their product to school students. In the 1970s, the Supreme Court ruled that advertising was not a form of free expression, but a form of business practices
Business ethics (also known as Corporate Ethics) is a form of applied ethics or professional ethics, that examines ethical principles and moral or ethical problems that can arise in a business environment. It applies to all aspects of business co ...
which should be regulated by the government. In the 1976 case of ''Virginia State Board of Pharmacy v. Virginia Citizens Consumer Council'', the Supreme Court ruled that advertising, or " commercial speech", to some degree is protected under the First Amendment. To avoid a First Amendment challenge by corporations, public schools could create contracts that restrict the sale of certain product and advertising. Public schools can also ban the selling of all food and drink products on campus, while not infringing on a corporation's right to free speech.
On December 13, 2010, President Obama signed the Healthy Hunger Free Kids Act of 2010 (effective in 2014) that mandates schools that receive federal funding must offer healthy snacks and drinks to students. The act bans the selling of soft drinks to students and requires schools to provide healthier options such as water, unflavored low-fat milk, 100% fruit and vegetable drinks or sugar-free carbonated drinks. The portion sizes available to students will be based on age: eight ounces for elementary schools, twelve ounces for middle and high schools. Proponents of the act predict the new mandate it will make it easier for students to make healthy drink choices while at school.
In 2015, Terry-McElarth and colleagues published a study in the ''American Journal of Preventive Medicine'' on regular soda policies and their effect on school drink availability and student consumption. The purpose of the study was to determine the effectiveness of a program beginning in the 2014–2015 school year that requires schools participating in federally reimbursable meal programs to remove all competitive venues (a la carte cafeteria sales, vending machines, and stores/snack bars/carts), on the availability of unhealthy drinks at schools and student consumption. The study analyzed state- and school district-level policies mandating soda bans and found that state bans were associated with significantly lower school soda availability but district bans showed no significant associations. In addition, no significant correlation was observed between state policies and student consumption. Among student populations, state policy was directly associated with significantly lower school soda availability and indirectly associated with lower student consumption. The same was not observed for other student populations.
Taxation
In the United States, legislators, health experts and consumer advocates are considering levying higher taxes on the sale of soft drinks and other sweetened products to help curb the epidemic of obesity among Americans, and its harmful impact on overall health. Some speculate that higher taxes could help reduce soda consumption. Others say that taxes should help fund education to increase consumer awareness of the unhealthy effects of excessive soft drink consumption, and also help cover costs of caring for conditions resulting from overconsumption. Thefood
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is inge ...
and drink industry holds considerable clout in Washington, DC, as it has contributed more than $50 million to legislators since 2000.
In January 2013, a British lobby group
In politics, lobbying, persuasion or interest representation is the act of lawfully attempting to influence the actions, policies, or decisions of government officials, most often legislators or members of regulatory agencies. Lobbying, which ...
called for the price of sugary fizzy drinks to be increased, with the money raised (an estimated £1 billion at 20p per litre) to be put towards a "Children's Future Fund", overseen by an independent body, which would encourage children to eat healthily in school.
In 2017, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and the Kingdom of Bahrain imposed a 50% tax on soft drinks and a 100% tax on energy drinks to curb excess consumption of the commodity and for additional revenue.
Attempted ban
In March 2013, New York City's mayorMichael Bloomberg
Michael Rubens Bloomberg (born February 14, 1942) is an American businessman, politician, philanthropist, and author. He is the majority owner, co-founder and CEO of Bloomberg L.P. He was Mayor of New York City from 2002 to 2013, and was a ca ...
proposed to ban the sale of non-diet soft drinks larger than 16 ounces, except in convenience stores and supermarkets. A lawsuit against the ban was upheld by a state judge, who voiced concerns that the ban was "fraught with arbitrary and capricious consequences". Bloomberg announced that he would be appealing the verdict. The state appellate courts upheld the trial court decision, and the ban remains unenforceable as of 2021.
See also
* Ade *Craft soda
Craft soda is a soft drink that is produced in small quantities from natural ingredients. Craft soda is in most cases made with sweeteners other than sucrose (sugar) or high-fructose corn syrup and contains sparing amounts of preservatives. Craf ...
* Diet Coke and Mentos eruption
A Diet Coke and Mentos eruption (also known as a soda geyser) is a reaction between the carbonated beverage Diet Coke and Mentos mints that causes the beverage to be expelled from its container. The candies catalyze the release of gas from the ...
* Diet soda
* Phosphate soda
Phosphate soda is a type of beverage that has a tangy or sour taste. These beverages became popular among children in the 1870s in the United States. Phosphate beverages were made with fruit flavorings, egg, malt, or wine. In the 1900s, the bever ...
* Fizz-Keeper
A Fizz-Keeper is a type of closure that is marketed as a way to keep carbonation in soft drinks. It consists of a small round hand pump that is screwed onto the top of a plastic soft drink bottle, which is then used to pump air into the bottle, p ...
* Hard soda
* Industrial gas
Industrial gases are the gaseous materials that are manufactured for use in industry. The principal gases provided are nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, argon, hydrogen, helium and acetylene, although many other gases and mixtures are also avail ...
* Kombucha
* List of brand name soft drink products
This article is a list of brand name soft drink products. In some cases, the relevant article is the parent brand or brand family.
By company
Coca-Cola Company
* Ambasa
*Ameyal
*Appletiser
*Aquarius
*Barq's
*Beat
* Beverly (discontinued i ...
* List of soft drink flavors
A soft drink is a beverage that typically contains carbonated water, one or more flavourings and sweeteners such as sugar, HFCS, fruit juices, and/or sugar substitutes such as sucralose, acesulfame-K, aspartame and cyclamate. Soft drinks may als ...
* List of soft drinks by country
* List of drinks
* Low-alcohol beer
* Nitrogenation
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at seven ...
* Nucleation
In thermodynamics, nucleation is the first step in the formation of either a new thermodynamic phase or structure via self-assembly or self-organization within a substance or mixture. Nucleation is typically defined to be the process that deter ...
* Premix and postmix
Premix and postmix are two methods of serving – usually carbonated – soft drinks that are alternatives to bottles and cans.
Premix
Premix refers to a ready-mixed, ready-to-drink soft drink that has usually been packaged in 5-gallon stain ...
* Soda fountain
* Squash (drink)
References
Further reading
"Beverage group: Pull soda from primary schools"
'' USA Today'', August 17, 2005.
"After soda ban nutritionists say more can be done"
'' The Boston Globe'', May 4, 2006.
"Critics Say Soda Policy for Schools Lacks Teeth
'' The New York Times'', August 22, 2006.
External links
* * * * {{Authority control Convenience foods