Siege Of Aleppo (994–995) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A siege () . is a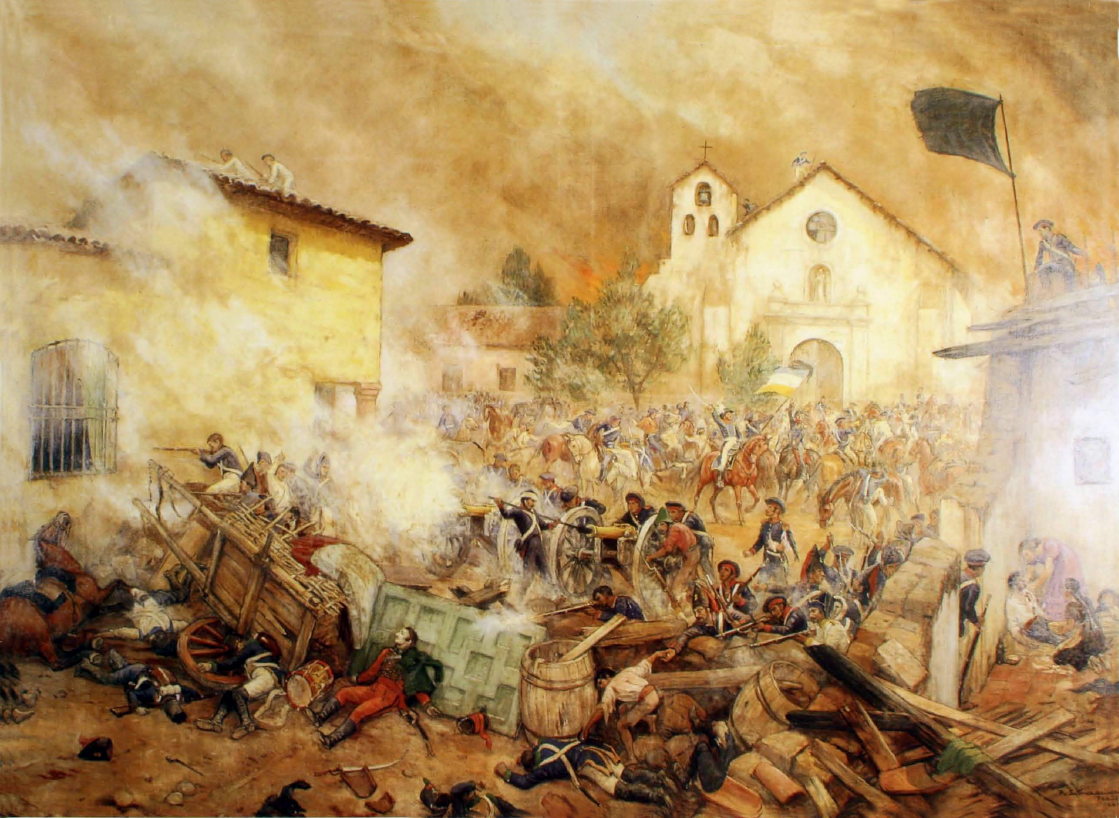  Ancient cities in the Middle East show
Ancient cities in the Middle East show
 Although there are depictions of sieges from the ancient Near East in historical sources and in art, there are very few examples of siege systems that have been found archaeologically. Of the few examples, several are noteworthy:
* The late 9th-century BC siege system surrounding
Although there are depictions of sieges from the ancient Near East in historical sources and in art, there are very few examples of siege systems that have been found archaeologically. Of the few examples, several are noteworthy:
* The late 9th-century BC siege system surrounding
 To end a siege more rapidly, various methods were developed in ancient and medieval times to counter fortifications, and a large variety of
To end a siege more rapidly, various methods were developed in ancient and medieval times to counter fortifications, and a large variety of
 When enemies attempted to dig tunnels under walls for mining or entry into the city, the defenders used large
When enemies attempted to dig tunnels under walls for mining or entry into the city, the defenders used large
 The importance of siege warfare in the ancient period should not be underestimated. One of the contributing causes of
The importance of siege warfare in the ancient period should not be underestimated. One of the contributing causes of
 However, the Chinese were not completely defenseless, and from AD 1234 until 1279, the Southern Song Chinese held out against the enormous barrage of Mongol attacks. Much of this success in defense lay in the world's first use of gunpowder (i.e. with early
However, the Chinese were not completely defenseless, and from AD 1234 until 1279, the Southern Song Chinese held out against the enormous barrage of Mongol attacks. Much of this success in defense lay in the world's first use of gunpowder (i.e. with early
 However, new fortifications, designed to withstand gunpowder weapons, were soon constructed throughout Europe. During the
However, new fortifications, designed to withstand gunpowder weapons, were soon constructed throughout Europe. During the
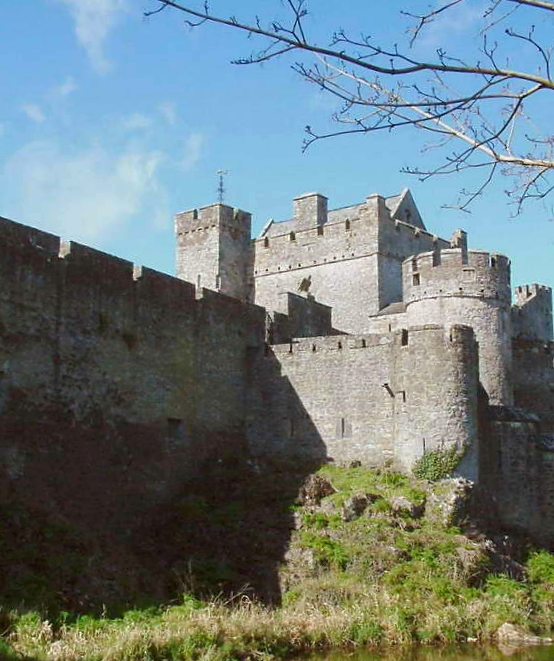
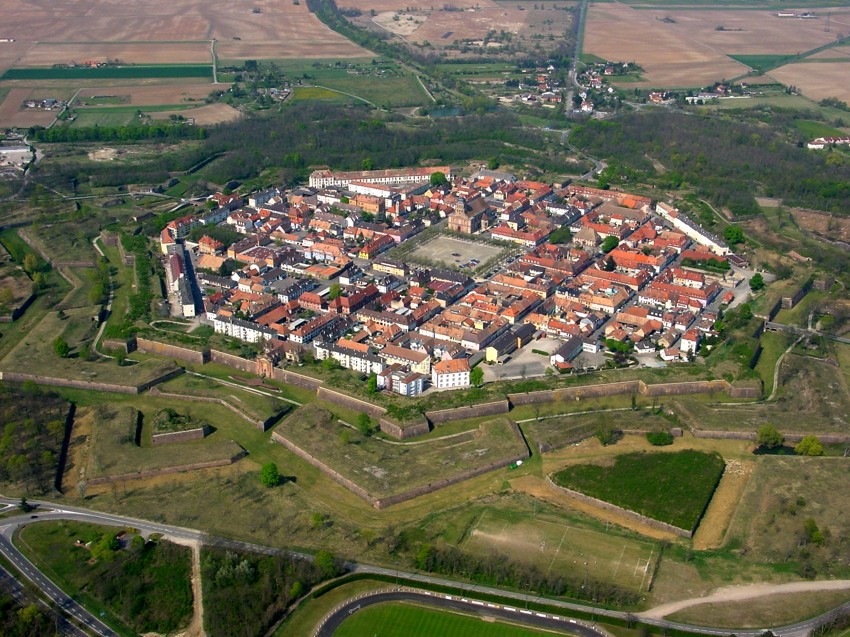
 The most effective way to protect walls against cannon fire proved to be depth (increasing the width of the defenses) and angles (ensuring that attackers could only fire on walls at an oblique angle, not square on). Initially, walls were lowered and backed, in front and behind, with earth. Towers were reformed into triangular bastions. This design matured into the ''trace italienne''. Star fort, Star-shaped fortresses surrounding towns and even cities with outlying defenses proved very difficult to capture, even for a well-equipped army. Fortresses built in this style throughout the 16th century did not become fully obsolete until the 19th century, and were still in use throughout World War I (though modified for 20th-century warfare). During World War II, ''trace italienne'' fortresses could still present a formidable challenge, for example, in the last days of World War II, during the Battle in Berlin, that saw some of the heaviest urban fighting of the war, the Soviets did not attempt to storm the Spandau Citadel (built between 1559 and 1594), but chose to investment (military), invest it and negotiate its surrender.
However, the cost of building such vast modern fortifications was incredibly high, and was often too much for individual cities to undertake. Many were bankrupted in the process of building them; others, such as Siena, spent so much money on fortifications that they were unable to maintain their armies properly, and so lost their wars anyway. Nonetheless, innumerable large and impressive fortresses were built throughout northern Italy in the first decades of the 16th century to resist repeated French invasions that became known as the Italian Wars. Many stand to this day.
The most effective way to protect walls against cannon fire proved to be depth (increasing the width of the defenses) and angles (ensuring that attackers could only fire on walls at an oblique angle, not square on). Initially, walls were lowered and backed, in front and behind, with earth. Towers were reformed into triangular bastions. This design matured into the ''trace italienne''. Star fort, Star-shaped fortresses surrounding towns and even cities with outlying defenses proved very difficult to capture, even for a well-equipped army. Fortresses built in this style throughout the 16th century did not become fully obsolete until the 19th century, and were still in use throughout World War I (though modified for 20th-century warfare). During World War II, ''trace italienne'' fortresses could still present a formidable challenge, for example, in the last days of World War II, during the Battle in Berlin, that saw some of the heaviest urban fighting of the war, the Soviets did not attempt to storm the Spandau Citadel (built between 1559 and 1594), but chose to investment (military), invest it and negotiate its surrender.
However, the cost of building such vast modern fortifications was incredibly high, and was often too much for individual cities to undertake. Many were bankrupted in the process of building them; others, such as Siena, spent so much money on fortifications that they were unable to maintain their armies properly, and so lost their wars anyway. Nonetheless, innumerable large and impressive fortresses were built throughout northern Italy in the first decades of the 16th century to resist repeated French invasions that became known as the Italian Wars. Many stand to this day.
 In the 1530s and 1540s, the new style of fortification began to spread out of Italy into the rest of Europe, particularly to France, the Netherlands, and Spain. Italian engineers were in enormous demand throughout Europe, especially in war-torn areas such as the Netherlands, which became dotted by towns encircled in modern fortifications. The densely populated areas of Northern Italy and the Dutch Republic, United Provinces (the Netherlands) were infamous for their high degree of fortification of cities. It made campaigns in these areas very hard to successfully conduct, considering even minor cities had to be captured by siege within the span of the campaigning season. In the Dutch case, the possibility of flooding large parts of the land provided an additional obstacle to besiegers, for example at the siege of Leiden. For many years, defensive and offensive tactics were well balanced, leading to protracted and costly wars such as Europe had never known, involving more and more planning and government involvement. The new fortresses ensured that war rarely extended beyond a series of sieges. Because the new fortresses could easily hold 10,000 men, an attacking army could not ignore a powerfully fortified position without serious risk of counterattack. As a result, virtually all towns had to be taken, and that was usually a long, drawn-out affair, potentially lasting from several months to years, while the members of the town were starved to death. Most battles in this period were between besieging armies and relief columns sent to rescue the besieged.
In the 1530s and 1540s, the new style of fortification began to spread out of Italy into the rest of Europe, particularly to France, the Netherlands, and Spain. Italian engineers were in enormous demand throughout Europe, especially in war-torn areas such as the Netherlands, which became dotted by towns encircled in modern fortifications. The densely populated areas of Northern Italy and the Dutch Republic, United Provinces (the Netherlands) were infamous for their high degree of fortification of cities. It made campaigns in these areas very hard to successfully conduct, considering even minor cities had to be captured by siege within the span of the campaigning season. In the Dutch case, the possibility of flooding large parts of the land provided an additional obstacle to besiegers, for example at the siege of Leiden. For many years, defensive and offensive tactics were well balanced, leading to protracted and costly wars such as Europe had never known, involving more and more planning and government involvement. The new fortresses ensured that war rarely extended beyond a series of sieges. Because the new fortresses could easily hold 10,000 men, an attacking army could not ignore a powerfully fortified position without serious risk of counterattack. As a result, virtually all towns had to be taken, and that was usually a long, drawn-out affair, potentially lasting from several months to years, while the members of the town were starved to death. Most battles in this period were between besieging armies and relief columns sent to rescue the besieged.
 At the end of the 17th century, two influential military engineers, the French Marshal Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, Vauban and the Dutch military engineer Menno van Coehoorn, developed modern fortification to its pinnacle, refining siege warfare without fundamentally altering it: ditches would be dug; walls would be protected by glacis; and bastions would enfilade an attacker. Both engineers developed their ideas independently, but came to similar general rules regarding defensive construction and offensive action against fortifications. Both were skilled in conducting sieges and defenses themselves. Before Vauban and Van Coehoorn, sieges had been somewhat slapdash operations. Vauban and Van Coehoorn refined besieging to a science with a methodical process that, if uninterrupted, would break even the strongest fortifications. Examples of their styles of fortifications are Arras (Vauban) and the no-longer-existent fortress of Bergen op Zoom (Van Coehoorn). The main differences between the two lay in the difference in terrain on which Vauban and Van Coehoorn constructed their defenses: Vauban in the sometimes more hilly and mountainous terrain of France, Van Coehoorn in the flat and floodable lowlands of the Netherlands.
Planning and maintaining a siege is just as difficult as fending one off. A besieging army must be prepared to repel both sortie (siege warfare), sorties from the besieged area and also any attack that may try to relieve the defenders. It was thus usual to construct lines of trenches and defenses facing in both directions. The outermost lines, known as the lines of
At the end of the 17th century, two influential military engineers, the French Marshal Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, Vauban and the Dutch military engineer Menno van Coehoorn, developed modern fortification to its pinnacle, refining siege warfare without fundamentally altering it: ditches would be dug; walls would be protected by glacis; and bastions would enfilade an attacker. Both engineers developed their ideas independently, but came to similar general rules regarding defensive construction and offensive action against fortifications. Both were skilled in conducting sieges and defenses themselves. Before Vauban and Van Coehoorn, sieges had been somewhat slapdash operations. Vauban and Van Coehoorn refined besieging to a science with a methodical process that, if uninterrupted, would break even the strongest fortifications. Examples of their styles of fortifications are Arras (Vauban) and the no-longer-existent fortress of Bergen op Zoom (Van Coehoorn). The main differences between the two lay in the difference in terrain on which Vauban and Van Coehoorn constructed their defenses: Vauban in the sometimes more hilly and mountainous terrain of France, Van Coehoorn in the flat and floodable lowlands of the Netherlands.
Planning and maintaining a siege is just as difficult as fending one off. A besieging army must be prepared to repel both sortie (siege warfare), sorties from the besieged area and also any attack that may try to relieve the defenders. It was thus usual to construct lines of trenches and defenses facing in both directions. The outermost lines, known as the lines of  Another element of a fortress was the
Another element of a fortress was the
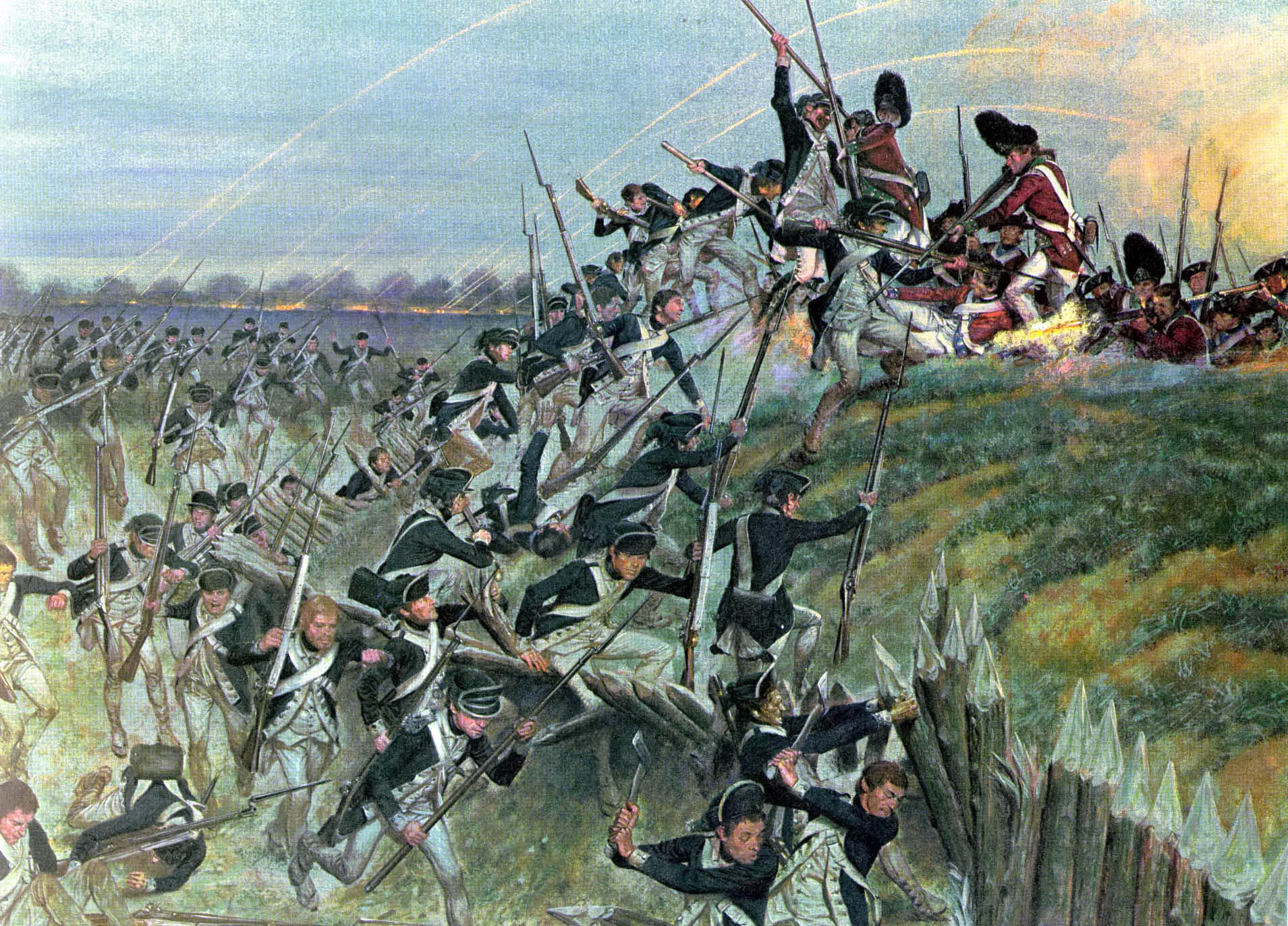 The exception to this rule were the English. During the English Civil War, anything which tended to prolong the struggle, or seemed like want of energy and avoidance of a decision, was bitterly resented by the men of both sides. In France and Germany, the prolongation of a war meant continued employment for the soldiers, but in England, both sides were looking to end the war quickly. Even when in the end the New Model Army—a regular professional army—developed the original decision-compelling spirit permeated the whole organisation, as was seen when pitched against regular professional continental troops the Battle of the Dunes (1658), Battle of the Dunes during the Interregnum (England), Interregnum.
The exception to this rule were the English. During the English Civil War, anything which tended to prolong the struggle, or seemed like want of energy and avoidance of a decision, was bitterly resented by the men of both sides. In France and Germany, the prolongation of a war meant continued employment for the soldiers, but in England, both sides were looking to end the war quickly. Even when in the end the New Model Army—a regular professional army—developed the original decision-compelling spirit permeated the whole organisation, as was seen when pitched against regular professional continental troops the Battle of the Dunes (1658), Battle of the Dunes during the Interregnum (England), Interregnum.
 Experienced commanders on both sides in the English Civil War recommended the abandonment of garrisoned fortifications for two primary reasons. The first, as for example proposed by the Royalist Sir Richard Willis, 1st Baronet, Sir Richard Willis to King Charles, was that by abandoning the garrisoning of all but the most strategic locations in one's own territory, far more troops would be available for the field armies, and it was the field armies which would decide the conflict. The other argument was that by slighting potential strong points in one's own territory, an enemy expeditionary force, or local enemy rising, would find it more difficult to consolidate territorial gains against an inevitable counterattack. Sir John Meldrum put forward just such an argument to the Parliamentary Committee of Both Kingdoms, to justify his slighting of Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, Gainsborough in Lincolnshire.
Sixty years later, during the War of the Spanish Succession, the John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, Duke of Marlborough preferred to engage the enemy in pitched battles, rather than engage in siege warfare, although he was very proficient in both types of warfare.
On 15 April 1746, the day before the Battle of Culloden, at Dunrobin Castle, a party of William Sutherland, 17th Earl of Sutherland, William Sutherland's militia conducted the last siege fought on the mainland of Great Britain against Jacobite members of Clan MacLeod.
Experienced commanders on both sides in the English Civil War recommended the abandonment of garrisoned fortifications for two primary reasons. The first, as for example proposed by the Royalist Sir Richard Willis, 1st Baronet, Sir Richard Willis to King Charles, was that by abandoning the garrisoning of all but the most strategic locations in one's own territory, far more troops would be available for the field armies, and it was the field armies which would decide the conflict. The other argument was that by slighting potential strong points in one's own territory, an enemy expeditionary force, or local enemy rising, would find it more difficult to consolidate territorial gains against an inevitable counterattack. Sir John Meldrum put forward just such an argument to the Parliamentary Committee of Both Kingdoms, to justify his slighting of Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, Gainsborough in Lincolnshire.
Sixty years later, during the War of the Spanish Succession, the John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, Duke of Marlborough preferred to engage the enemy in pitched battles, rather than engage in siege warfare, although he was very proficient in both types of warfare.
On 15 April 1746, the day before the Battle of Culloden, at Dunrobin Castle, a party of William Sutherland, 17th Earl of Sutherland, William Sutherland's militia conducted the last siege fought on the mainland of Great Britain against Jacobite members of Clan MacLeod.
 Mainly as a result of the increasing firepower (such as machine guns) available to defensive forces, World War I, First World War trench warfare briefly revived a form of siege warfare. Although siege warfare had moved out from an urban setting because city walls had become ineffective against modern weapons, trench warfare was nonetheless able to use many of the techniques of siege warfare in its prosecution (sapping, mining, Artillery, barrage and, of course, Attrition warfare, attrition), but on a much larger scale and on a greatly extended front.
More traditional sieges of fortifications took place in addition to trench sieges. The siege of Tsingtao was one of the first major sieges of the war, but the inability for significant resupply of the German garrison made it a relatively one-sided battle. The Germans and the crew of an Austro-Hungarian protected cruiser put up a hopeless defense and, after holding out for more than a week, surrendered to the Japanese, forcing the German East Asia Squadron to steam towards South America for a new coal source.
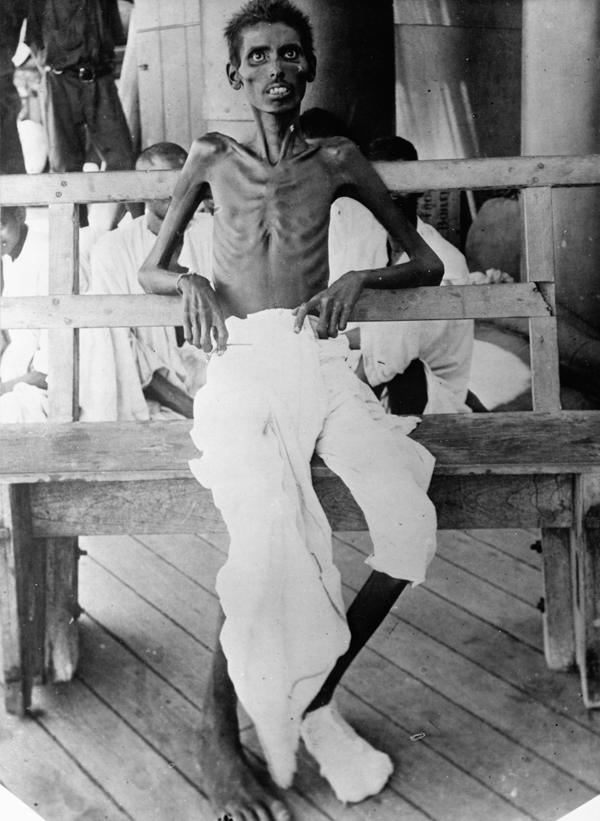
The other major siege outside Europe during the First World War was in Mesopotamia, at the siege of Kut. After a failed attempt to move on Baghdad, stopped by the Ottomans at the bloody Battle of Ctesiphon (1915), Battle of Ctesiphon, the British and their large contingent of Indian sepoy soldiers were forced to retreat to Kut, where the Ottomans under German General Colmar Freiherr von der Goltz, Baron Colmar von der Goltz laid siege. The British attempts to resupply the force via the Tigris river failed, and rationing was complicated by the refusal of many Indian troops to eat cattle products. By the time the garrison fell on 29 April 1916, starvation was rampant. Conditions did not improve greatly under Turkish imprisonment. Along with the battles of Battle of Tanga, Tanga, Battle of Sandfontein, Sandfontein, Gallipoli campaign, Gallipoli, and Battle of Namacurra, Namacurra, it would be one of Britain's numerous embarrassing colonial defeats of the war.
Mainly as a result of the increasing firepower (such as machine guns) available to defensive forces, World War I, First World War trench warfare briefly revived a form of siege warfare. Although siege warfare had moved out from an urban setting because city walls had become ineffective against modern weapons, trench warfare was nonetheless able to use many of the techniques of siege warfare in its prosecution (sapping, mining, Artillery, barrage and, of course, Attrition warfare, attrition), but on a much larger scale and on a greatly extended front.
More traditional sieges of fortifications took place in addition to trench sieges. The siege of Tsingtao was one of the first major sieges of the war, but the inability for significant resupply of the German garrison made it a relatively one-sided battle. The Germans and the crew of an Austro-Hungarian protected cruiser put up a hopeless defense and, after holding out for more than a week, surrendered to the Japanese, forcing the German East Asia Squadron to steam towards South America for a new coal source.
The other major siege outside Europe during the First World War was in Mesopotamia, at the siege of Kut. After a failed attempt to move on Baghdad, stopped by the Ottomans at the bloody Battle of Ctesiphon (1915), Battle of Ctesiphon, the British and their large contingent of Indian sepoy soldiers were forced to retreat to Kut, where the Ottomans under German General Colmar Freiherr von der Goltz, Baron Colmar von der Goltz laid siege. The British attempts to resupply the force via the Tigris river failed, and rationing was complicated by the refusal of many Indian troops to eat cattle products. By the time the garrison fell on 29 April 1916, starvation was rampant. Conditions did not improve greatly under Turkish imprisonment. Along with the battles of Battle of Tanga, Tanga, Battle of Sandfontein, Sandfontein, Gallipoli campaign, Gallipoli, and Battle of Namacurra, Namacurra, it would be one of Britain's numerous embarrassing colonial defeats of the war.
 The largest sieges of the war, however, took place in Europe. The initial German advance into Belgium produced four major sieges: the Battle of Liège, the Siege of Namur (1914), siege of Namur, the siege of Maubeuge, and the Siege of Antwerp (1914), siege of Antwerp. All four would prove crushing German victories, at Liège and Namur against the Belgians, at Maubeuge against the French and at Antwerp against a combined Anglo-Belgian force. The weapon that made these victories possible were the German Big Bertha (howitzer), Big Berthas and the Skoda 305 mm Model 1911 siege mortars, one of the best siege mortars of the war, on loan from Austria-Hungary. These huge guns were the decisive weapon of siege warfare in the 20th century, taking part at Przemyśl, the Belgian sieges, on the Italian Front and Serbian Front, and even being reused in World War II.
The largest sieges of the war, however, took place in Europe. The initial German advance into Belgium produced four major sieges: the Battle of Liège, the Siege of Namur (1914), siege of Namur, the siege of Maubeuge, and the Siege of Antwerp (1914), siege of Antwerp. All four would prove crushing German victories, at Liège and Namur against the Belgians, at Maubeuge against the French and at Antwerp against a combined Anglo-Belgian force. The weapon that made these victories possible were the German Big Bertha (howitzer), Big Berthas and the Skoda 305 mm Model 1911 siege mortars, one of the best siege mortars of the war, on loan from Austria-Hungary. These huge guns were the decisive weapon of siege warfare in the 20th century, taking part at Przemyśl, the Belgian sieges, on the Italian Front and Serbian Front, and even being reused in World War II.
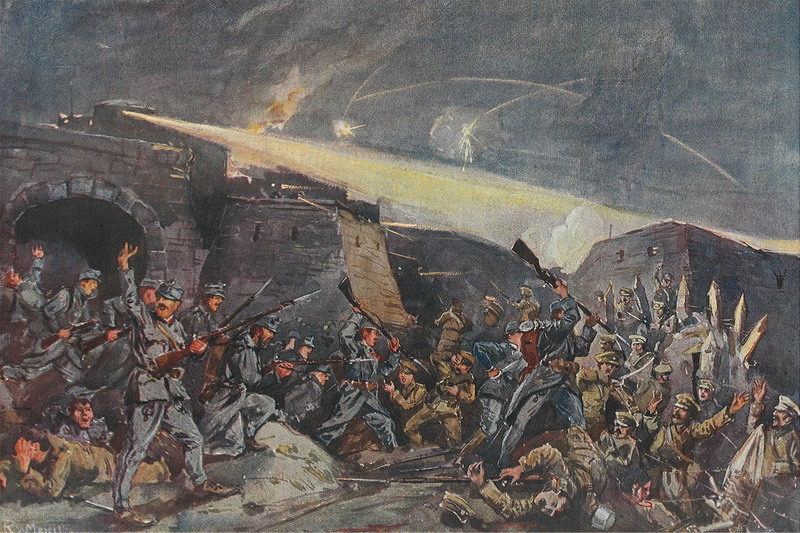 At the siege of Przemyśl, during World War I, the Austro-Hungarian Army, Austro-Hungarian garrison showed excellent knowledge of siege warfare, not only waiting for relief, but sending sorties into Russian lines and employing an active defense that resulted in the capture of the Russian General Lavr Kornilov. Despite its excellent performance, the garrison's food supply had been requisitioned for earlier offensives, a relief expedition was stalled by the weather, ethnic rivalries flared up between the defending soldiers, and a breakout attempt failed. When the commander of the garrison Hermann Kusmanek finally surrendered, his troops were eating their horses and the first attempt of large-scale air supply had failed. It was one of the few great victories obtained by either side during the war; 110,000 Austro-Hungarian prisoners were marched back to Russia. Use of aircraft for siege running, bringing supplies to areas under siege, would nevertheless prove useful in many sieges to come.
The largest siege of the war, and arguably the roughest, most gruesome battle in history, was the Battle of Verdun. Whether the battle can be considered true siege warfare is debatable. Under the theories of Erich von Falkenhayn, it is more distinguishable as purely attrition with a coincidental presence of fortifications on the battlefield. When considering the plans of Wilhelm, German Crown Prince, Crown Prince Wilhelm, purely concerned with taking the citadel and not with French casualty figures, it can be considered a true siege. The main fortifications were Fort Douaumont, Fort Vaux, and the fortified city of Verdun itself. The Germans, through the use of huge artillery bombardments, flamethrowers, and infiltration tactics, were able to capture both Vaux and Douaumont, but were never able to take the city, and eventually lost most of their gains. It was a battle that, despite the French ability to fend off the Germans, neither side won. The German losses were not worth the potential capture of the city, and the French casualties were not worth holding the symbol of her defense.
The development of the armored tank and improved infantry military tactics, tactics at the end of World War I swung the pendulum back in favor of maneuver, and with the advent of Blitzkrieg in 1939, the end of traditional siege warfare was at hand. The Maginot Line would be the prime example of the failure of immobile, post–World War I fortifications. Although sieges would continue, it would be in a totally different style and on a reduced scale.
At the siege of Przemyśl, during World War I, the Austro-Hungarian Army, Austro-Hungarian garrison showed excellent knowledge of siege warfare, not only waiting for relief, but sending sorties into Russian lines and employing an active defense that resulted in the capture of the Russian General Lavr Kornilov. Despite its excellent performance, the garrison's food supply had been requisitioned for earlier offensives, a relief expedition was stalled by the weather, ethnic rivalries flared up between the defending soldiers, and a breakout attempt failed. When the commander of the garrison Hermann Kusmanek finally surrendered, his troops were eating their horses and the first attempt of large-scale air supply had failed. It was one of the few great victories obtained by either side during the war; 110,000 Austro-Hungarian prisoners were marched back to Russia. Use of aircraft for siege running, bringing supplies to areas under siege, would nevertheless prove useful in many sieges to come.
The largest siege of the war, and arguably the roughest, most gruesome battle in history, was the Battle of Verdun. Whether the battle can be considered true siege warfare is debatable. Under the theories of Erich von Falkenhayn, it is more distinguishable as purely attrition with a coincidental presence of fortifications on the battlefield. When considering the plans of Wilhelm, German Crown Prince, Crown Prince Wilhelm, purely concerned with taking the citadel and not with French casualty figures, it can be considered a true siege. The main fortifications were Fort Douaumont, Fort Vaux, and the fortified city of Verdun itself. The Germans, through the use of huge artillery bombardments, flamethrowers, and infiltration tactics, were able to capture both Vaux and Douaumont, but were never able to take the city, and eventually lost most of their gains. It was a battle that, despite the French ability to fend off the Germans, neither side won. The German losses were not worth the potential capture of the city, and the French casualties were not worth holding the symbol of her defense.
The development of the armored tank and improved infantry military tactics, tactics at the end of World War I swung the pendulum back in favor of maneuver, and with the advent of Blitzkrieg in 1939, the end of traditional siege warfare was at hand. The Maginot Line would be the prime example of the failure of immobile, post–World War I fortifications. Although sieges would continue, it would be in a totally different style and on a reduced scale.
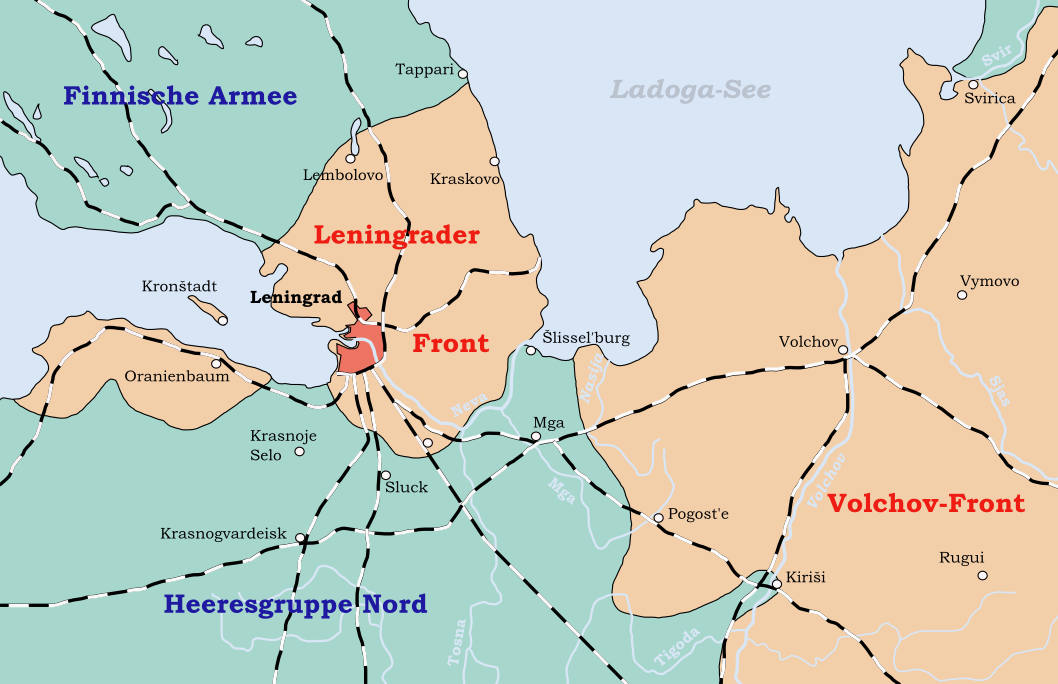 The most important siege was the siege of Leningrad, which lasted over 29 months, about half of the duration of the entire Second World War. The siege of Leningrad resulted in the deaths of some List of battles by casualties, one million of the city's inhabitants. Along with the Battle of Stalingrad, the siege of Leningrad on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front was the deadliest siege of a city in history. In the west, apart from the Battle of the Atlantic, the sieges were not on the same scale as those on the European Eastern front; however, there were several notable or critical sieges: the island of Malta, for which the population won the George Cross and Siege of Tobruk, Tobruk. In the South-East Asian theatre of World War II, South-East Asian theatre, there was the siege of Singapore, and in the Burma campaign, sieges of Myitkyina, the Battle of the Admin Box, Admin Box, Battle of Imphal, Imphal, and Battle of Kohima, Kohima, which was the high-water mark for the Japanese advance into British India, India.
The Siege of Sevastopol (1941–1942), siege of Sevastopol saw the use of the heaviest and most powerful individual siege engines ever to be used: the German Schwerer Gustav, 800 mm railway gun and the Karl-Gerät, 600 mm siege mortar. Though a single shell could have disastrous local effect, the guns were susceptible to air attack in addition to being slow to move.
The most important siege was the siege of Leningrad, which lasted over 29 months, about half of the duration of the entire Second World War. The siege of Leningrad resulted in the deaths of some List of battles by casualties, one million of the city's inhabitants. Along with the Battle of Stalingrad, the siege of Leningrad on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front was the deadliest siege of a city in history. In the west, apart from the Battle of the Atlantic, the sieges were not on the same scale as those on the European Eastern front; however, there were several notable or critical sieges: the island of Malta, for which the population won the George Cross and Siege of Tobruk, Tobruk. In the South-East Asian theatre of World War II, South-East Asian theatre, there was the siege of Singapore, and in the Burma campaign, sieges of Myitkyina, the Battle of the Admin Box, Admin Box, Battle of Imphal, Imphal, and Battle of Kohima, Kohima, which was the high-water mark for the Japanese advance into British India, India.
The Siege of Sevastopol (1941–1942), siege of Sevastopol saw the use of the heaviest and most powerful individual siege engines ever to be used: the German Schwerer Gustav, 800 mm railway gun and the Karl-Gerät, 600 mm siege mortar. Though a single shell could have disastrous local effect, the guns were susceptible to air attack in addition to being slow to move.


 Several times during the Cold War the western powers had to use their airbridge expertise.
* The Berlin Blockade from June 1948 to September 1949, the Western Powers flew over 200,000 flights, providing to West Berlin up to 8,893 tons of necessities each day.
* Airbridge was used extensively during the Battle of Dien Bien Phu during the First Indochina War, but failed to prevent its fall to the Việt Minh in 1954.
* In Vietnam War, the next Vietnam War, airbridge proved crucial during the siege of the American base at Battle of Khe Sanh, Khe Sanh in 1968. The resupply it provided kept the People's Army of Vietnam, North Vietnamese Army from capturing the base.
In both Vietnamese cases, the Viet Minh and National Front for the Liberation of South Vietnam, NLF were able to cut off the opposing army by capturing the surrounding rugged terrain. At Dien Bien Phu, the French were unable to use air power to overcome the siege and were defeated. However, at Khe Sanh, a mere 14 years later, advances in air power—and a reduction in Vietnamese anti-aircraft capability—allowed the United States to withstand the siege. The resistance of US forces was assisted by the People's Army of Vietnam, PAVN and Viet Cong, PLAF forces' decision to use the Khe Sanh siege as a strategic distraction to allow their mobile warfare offensive, the first Tet Offensive, to unfold securely.
The Battle of Khe Sanh displays typical features of modern sieges, as the defender has greater capacity to withstand the siege, the attacker's main aim is to bottle operational forces or create a strategic distraction, rather than take the siege to a conclusion.
In neighboring Cambodia, at that time known as the Cambodian coup of 1970, Khmer Republic, the Khmer Rouge used siege tactics to cut off supplies from Phnom Penh to other government-held enclaves in an attempt to break the will of the government to continue fighting.
In 1972, during the Easter offensive, the siege of An Lộc, Bình Phước, An Lộc Vietnam occurred. ARVN troops and U.S. advisers and air power successfully defeated communist forces. The Battle of An Lộc pitted some 6,350 ARVN men against a force three times that size. During the peak of the battle, ARVN had access to only one 105 mm howitzer to provide close support, while the enemy attack was backed by an entire artillery division. ARVN had no tanks, the NVA communist forces had two armoured regiments. ARVN prevailed after over two months of continuous fighting. As General Paul Vanuxem, a French veteran of the Indochina War, wrote in 1972 after visiting the liberated city of An Lộc: "An Lộc was the Verdun of Vietnam, where Vietnam received as in baptism the supreme consecration of her will."
During the 1982 Lebanon War, the Israel Defence Forces Siege of Beirut, besieged Beirut, the capital of Lebanon, to quickly realize their goals including the eviction of the Palestine Liberation Organization from the country.
During the Yugoslav Wars in the 1990s, Republika Srpska forces Siege of Sarajevo, besieged Sarajevo, the capital of Bosnia-Herzegovina. The siege lasted from April 1992 until February 1996.
Numerous sieges haven taken place during the Syrian civil war, such as the siege of Homs, siege of Kobanî, siege of Deir ez-Zor (2014–2017), siege of Nubl and al-Zahraa, and siege of al-Fu'ah and Kafriya.
During various points in the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict, Azerbaijan Siege of Stepanakert, besieged the capital of Stepanakert (1991-1992), as well as the entire Republic of Artsakh, de facto Armenian-controlled republic during the Blockade of Nagorno-Karabakh, Blockade of Nagorno-Karabakh (2022-2023)..
Multiple sieges took place in the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, notably the siege of Mariupol. Other sieges in the war include the Siege of Chernihiv and Siege of Sloviansk.
The Gaza war contained multiple sieges, including the siege of Gaza City and the siege of Khan Yunis.
Several times during the Cold War the western powers had to use their airbridge expertise.
* The Berlin Blockade from June 1948 to September 1949, the Western Powers flew over 200,000 flights, providing to West Berlin up to 8,893 tons of necessities each day.
* Airbridge was used extensively during the Battle of Dien Bien Phu during the First Indochina War, but failed to prevent its fall to the Việt Minh in 1954.
* In Vietnam War, the next Vietnam War, airbridge proved crucial during the siege of the American base at Battle of Khe Sanh, Khe Sanh in 1968. The resupply it provided kept the People's Army of Vietnam, North Vietnamese Army from capturing the base.
In both Vietnamese cases, the Viet Minh and National Front for the Liberation of South Vietnam, NLF were able to cut off the opposing army by capturing the surrounding rugged terrain. At Dien Bien Phu, the French were unable to use air power to overcome the siege and were defeated. However, at Khe Sanh, a mere 14 years later, advances in air power—and a reduction in Vietnamese anti-aircraft capability—allowed the United States to withstand the siege. The resistance of US forces was assisted by the People's Army of Vietnam, PAVN and Viet Cong, PLAF forces' decision to use the Khe Sanh siege as a strategic distraction to allow their mobile warfare offensive, the first Tet Offensive, to unfold securely.
The Battle of Khe Sanh displays typical features of modern sieges, as the defender has greater capacity to withstand the siege, the attacker's main aim is to bottle operational forces or create a strategic distraction, rather than take the siege to a conclusion.
In neighboring Cambodia, at that time known as the Cambodian coup of 1970, Khmer Republic, the Khmer Rouge used siege tactics to cut off supplies from Phnom Penh to other government-held enclaves in an attempt to break the will of the government to continue fighting.
In 1972, during the Easter offensive, the siege of An Lộc, Bình Phước, An Lộc Vietnam occurred. ARVN troops and U.S. advisers and air power successfully defeated communist forces. The Battle of An Lộc pitted some 6,350 ARVN men against a force three times that size. During the peak of the battle, ARVN had access to only one 105 mm howitzer to provide close support, while the enemy attack was backed by an entire artillery division. ARVN had no tanks, the NVA communist forces had two armoured regiments. ARVN prevailed after over two months of continuous fighting. As General Paul Vanuxem, a French veteran of the Indochina War, wrote in 1972 after visiting the liberated city of An Lộc: "An Lộc was the Verdun of Vietnam, where Vietnam received as in baptism the supreme consecration of her will."
During the 1982 Lebanon War, the Israel Defence Forces Siege of Beirut, besieged Beirut, the capital of Lebanon, to quickly realize their goals including the eviction of the Palestine Liberation Organization from the country.
During the Yugoslav Wars in the 1990s, Republika Srpska forces Siege of Sarajevo, besieged Sarajevo, the capital of Bosnia-Herzegovina. The siege lasted from April 1992 until February 1996.
Numerous sieges haven taken place during the Syrian civil war, such as the siege of Homs, siege of Kobanî, siege of Deir ez-Zor (2014–2017), siege of Nubl and al-Zahraa, and siege of al-Fu'ah and Kafriya.
During various points in the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict, Azerbaijan Siege of Stepanakert, besieged the capital of Stepanakert (1991-1992), as well as the entire Republic of Artsakh, de facto Armenian-controlled republic during the Blockade of Nagorno-Karabakh, Blockade of Nagorno-Karabakh (2022-2023)..
Multiple sieges took place in the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, notably the siege of Mariupol. Other sieges in the war include the Siege of Chernihiv and Siege of Sloviansk.
The Gaza war contained multiple sieges, including the siege of Gaza City and the siege of Khan Yunis.
 Siege tactics continue to be employed in police contexts; such a siege is typically called a standoff or, in law enforcement jargon, a barricade situation. Standoffs may result from crimes and incidents such as Robbery, robberies, Police raid, raids, Search warrant, search and arrest warrants, prison riots, or Terrorism, terrorist attacks. Standoffs occur due to a variety of factors, most prominently the safety of police (against whom the besieged may have the upper hand), the besieged suspects (who police generally intend to arrest), bystanders (who may be in the crossfire), and hostages (who may be injured or killed by the suspects).
The optimal result of most standoffs is a peaceful resolution: the safe extraction of hostages and bystanders, and the peaceful surrender and arrest of the hostage-takers. To ensure this, police make use of trained Crisis negotiation, negotiators and Criminal psychology, psychologists to learn the hostage-takers' demands (and meet said demands if feasible or permissible), gain the hostage-takers' trust, clarify that police do not intend to kill them or will even Crime scene getaway, let them go (regardless of whether such claims are true), and coax the hostage-takers into surrendering or at least releasing hostages. In the event a peaceful resolution is impossible—negotiations fail or do not proceed, hostages are released but the hostage-takers refuse to surrender, the hostage-takers resist violently, or hostages are killed—police may respond in force, generally being able to rely on police tactical units or even
Siege tactics continue to be employed in police contexts; such a siege is typically called a standoff or, in law enforcement jargon, a barricade situation. Standoffs may result from crimes and incidents such as Robbery, robberies, Police raid, raids, Search warrant, search and arrest warrants, prison riots, or Terrorism, terrorist attacks. Standoffs occur due to a variety of factors, most prominently the safety of police (against whom the besieged may have the upper hand), the besieged suspects (who police generally intend to arrest), bystanders (who may be in the crossfire), and hostages (who may be injured or killed by the suspects).
The optimal result of most standoffs is a peaceful resolution: the safe extraction of hostages and bystanders, and the peaceful surrender and arrest of the hostage-takers. To ensure this, police make use of trained Crisis negotiation, negotiators and Criminal psychology, psychologists to learn the hostage-takers' demands (and meet said demands if feasible or permissible), gain the hostage-takers' trust, clarify that police do not intend to kill them or will even Crime scene getaway, let them go (regardless of whether such claims are true), and coax the hostage-takers into surrendering or at least releasing hostages. In the event a peaceful resolution is impossible—negotiations fail or do not proceed, hostages are released but the hostage-takers refuse to surrender, the hostage-takers resist violently, or hostages are killed—police may respond in force, generally being able to rely on police tactical units or even  Most standoffs are much shorter than military sieges, often lasting hours or days at most. Lengthy sieges may still occur, albeit rarely, such as the 51-day-long 1993 Waco siege. Most standoffs end in a peaceful resolution (i.e. 1973 Brooklyn hostage crisis, 1997 Roby standoff), though some may end in a police or military assault (i.e. 1994 Air France Flight 8969, Air France Flight 8969 hijacking, 1980 Iranian Embassy siege) or, in the worst-case scenarios, the deaths of authorities, hostage-takers, or hostages (i.e. 1985 1985 MOVE bombing, MOVE bombing, 1985 EgyptAir Flight 648, EgyptAir Flight 648 hijacking, 2004 Beslan school siege, 2022 Robb Elementary School shooting). The aforementioned worst-case scenarios often result from poor planning, tactics, or negotiations on the part of the authorities (e.g. accidental killings of hostages by Unit 777 during the EgyptAir Flight 648 hijacking), or from violent acts committed by the hostage-takers (e.g. Suicide attack, suicide bombings and executions during the Beslan school siege).
In some jurisdictions, depending on certain circumstances, standoffs that would usually be handled by police may be transferred to the military. For example, in the United Kingdom, standoffs with terrorists may be transferred to military responsibility for a military assault on the besieged. The threat of such an action ended the 1975 Balcombe Street siege, but the 1980 Iranian Embassy siege ended in a military assault and the deaths of all but one of the hostage-takers.
Most standoffs are much shorter than military sieges, often lasting hours or days at most. Lengthy sieges may still occur, albeit rarely, such as the 51-day-long 1993 Waco siege. Most standoffs end in a peaceful resolution (i.e. 1973 Brooklyn hostage crisis, 1997 Roby standoff), though some may end in a police or military assault (i.e. 1994 Air France Flight 8969, Air France Flight 8969 hijacking, 1980 Iranian Embassy siege) or, in the worst-case scenarios, the deaths of authorities, hostage-takers, or hostages (i.e. 1985 1985 MOVE bombing, MOVE bombing, 1985 EgyptAir Flight 648, EgyptAir Flight 648 hijacking, 2004 Beslan school siege, 2022 Robb Elementary School shooting). The aforementioned worst-case scenarios often result from poor planning, tactics, or negotiations on the part of the authorities (e.g. accidental killings of hostages by Unit 777 during the EgyptAir Flight 648 hijacking), or from violent acts committed by the hostage-takers (e.g. Suicide attack, suicide bombings and executions during the Beslan school siege).
In some jurisdictions, depending on certain circumstances, standoffs that would usually be handled by police may be transferred to the military. For example, in the United Kingdom, standoffs with terrorists may be transferred to military responsibility for a military assault on the besieged. The threat of such an action ended the 1975 Balcombe Street siege, but the 1980 Iranian Embassy siege ended in a military assault and the deaths of all but one of the hostage-takers.
Secrets of Lost Empires: Medieval Siege
(PBS) Informative and interactive webpages about medieval siege tactics. {{Authority control Sieges, Military strategy Siege warfare, *
military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force.
A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are ...
of a city, or fortress
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from L ...
, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or by well-prepared assault. Siege warfare (also called siegecrafts or poliorcetics) is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characterized by one party holding a strong, static, defensive position. Consequently, an opportunity for negotiation
Negotiation is a dialogue between two or more parties to resolve points of difference, gain an advantage for an individual or Collective bargaining, collective, or craft outcomes to satisfy various interests. The parties aspire to agree on m ...
between combatants is common, as proximity and fluctuating advantage can encourage diplomacy
Diplomacy is the communication by representatives of State (polity), state, International organization, intergovernmental, or Non-governmental organization, non-governmental institutions intended to influence events in the international syste ...
.
A siege occurs when an attacker encounters a city or fortress that cannot be easily taken by a quick assault, and which refuses to surrender. Sieges involve surrounding the target to block provision of supplies and reinforcement or escape of troops (a tactic known as "investment
Investment is traditionally defined as the "commitment of resources into something expected to gain value over time". If an investment involves money, then it can be defined as a "commitment of money to receive more money later". From a broade ...
"). This is typically coupled with attempts to reduce the fortifications by means of siege engine
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while othe ...
s, artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
bombardment, mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
(also known as sapping), or the use of deception or treachery to bypass defenses.
Failing a military outcome, sieges can often be decided by starvation, thirst, or disease, which can afflict either the attacker or defender. This form of siege, though, can take many months or even years, depending upon the size of the stores of food the fortified position holds. The attacking force can circumvallate the besieged place, which is to build a line of earth-works, consisting of a rampart
Rampart may refer to:
* Rampart (fortification), a defensive wall or bank around a castle, fort or settlement
Rampart may also refer to:
* LAPD Rampart Division, a division of the Los Angeles Police Department
** Rampart scandal, a blanket ter ...
and trench, surrounding it. During the process of circumvallation, the attacking force can be set upon by another force, an ally of the besieged place, due to the lengthy amount of time required to force it to capitulate. A defensive ring of forts outside the ring of circumvallated forts, called contravallation, is also sometimes used to defend the attackers from outside.
 Ancient cities in the Middle East show
Ancient cities in the Middle East show archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, ...
evidence of fortified city wall
A defensive wall is a fortification usually used to protect a city, town or other settlement from potential aggressors. The walls can range from simple palisades or Earthworks (military), earthworks to extensive military fortifications such as ...
s. During the Warring States period
The Warring States period in history of China, Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and ...
of ancient China
The history of China spans several millennia across a wide geographical area. Each region now considered part of the Chinese world has experienced periods of unity, fracture, prosperity, and strife. Chinese civilization first emerged in the Y ...
, there is both textual and archaeological evidence of prolonged sieges and siege machinery used against the defenders of city walls. Siege machinery was also a tradition of the ancient Greco-Roman world
The Greco-Roman world , also Greco-Roman civilization, Greco-Roman culture or Greco-Latin culture (spelled Græco-Roman or Graeco-Roman in British English), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and co ...
. During the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
and the early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
, siege warfare dominated the conduct of war in Europe. Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 1452 - 2 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested o ...
gained some of his renown from design of fortifications. Medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the West ...
campaigns were generally designed around a succession of sieges. In the Napoleonic era
The Napoleonic era is a period in the history of France and history of Europe, Europe. It is generally classified as including the fourth and final stage of the French Revolution, the first being the National Assembly (French Revoluti ...
, increasing use of ever more powerful cannon
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder during th ...
s reduced the value of fortifications. In the 20th century, the significance of the classical siege declined. With the advent of mobile warfare
Mobile warfare () is a military strategy of the People's Republic of China employing conventional forces on fluid fronts with units maneuvering to exploit opportunities for tactical surprise, or where a local superiority of forces can be realiz ...
, a single fortified stronghold is no longer as decisive as it once was. While traditional sieges do still occur, they are not as common as they once were due to changes in modes of battle, principally the ease by which huge volumes of destructive power can be directed onto a static target. Modern sieges are more commonly the result of smaller hostage, militant, or extreme resisting arrest
An arrest is the act of apprehending and taking a person into custody (legal protection or control), usually because the person has been suspected of or observed committing a crime. After being taken into custody, the person can be Interroga ...
situations.
Ancient period
The necessity of city walls
TheAssyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
ns deployed large labour forces to build new palaces, temples, and defensive walls. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation, was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form from 2600 BCE ...
were also fortified. By about 3500 BC, hundreds of small farming villages dotted the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayas, Himalayan river of South Asia, South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in the Western Tibet region of China, flows northw ...
floodplain. Many of these settlements had fortifications and planned streets.
The stone and mud brick houses of Kot Diji
Kot Diji (; ) is an ancient site which was part of the Indus Valley Civilization, estimated to have been occupied around 3300 BCE. Located about south of Khairpur in the modern-day province of Sindh, India, it is on the east bank of the Indus R ...
were clustered behind massive stone flood dikes and defensive walls, for neighbouring communities quarrelled constantly about the control of prime agricultural land. Mundigak
Mundigak () is an archaeological site in Kandahar province in Afghanistan. During the Bronze Age, it was a center of the Helmand culture. It is situated approximately northwest of Kandahar near Shāh Maqsūd, on the upper drainage of the Kushk- ...
(c. 2500 BC) in present-day south-east Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
has defensive walls and square bastions of sun-dried bricks.
City walls and fortifications were essential for the defence of the first cities in the ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was home to many cradles of civilization, spanning Mesopotamia, Egypt, Iran (or Persia), Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, and the Arabian Peninsula. As such, the fields of ancient Near East studies and Nea ...
. The walls were built of mudbricks, stone, wood, or a combination of these materials, depending on local availability. They may also have served the dual purpose of showing potential enemies the might of the kingdom. The great walls surrounding the Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization, located in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (now south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and Early Bronze Age, early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. ...
ian city of Uruk
Uruk, the archeological site known today as Warka, was an ancient city in the Near East, located east of the current bed of the Euphrates River, on an ancient, now-dried channel of the river in Muthanna Governorate, Iraq. The site lies 93 kilo ...
gained a widespread reputation. The walls were in length, and up to in height.
Later, the walls of Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
, reinforced by towers, moats, and ditches, gained a similar reputation. In Anatolia
Anatolia (), also known as Asia Minor, is a peninsula in West Asia that makes up the majority of the land area of Turkey. It is the westernmost protrusion of Asia and is geographically bounded by the Mediterranean Sea to the south, the Aegean ...
, the Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian peoples, Anatolian Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European people who formed one of the first major civilizations of the Bronze Age in West Asia. Possibly originating from beyond the Black Sea, they settled in mo ...
built massive stone walls around their cities atop hillsides, taking advantage of the terrain. In Shang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty that ruled in the Yellow River valley during the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and followed by the Western Zhou d ...
China, at the site of Ao, large walls were erected in the 15th century BC that had dimensions of in width at the base and enclosed an area of some squared.Needham, Volume 4, Part 2, 43. The ancient Chinese capital for the State of Zhao
Zhao () was one of the seven major states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It emerged from the tripartite division of Jin, along with Han and Wei, in the 5th century BC. Zhao gained considerable strength from the military ...
, Handan
Handan is a prefecture-level city located in the southwest of Hebei province, China. The southernmost prefecture-level city of the province, it borders Xingtai on the north, and the provinces of Shanxi on the west, Henan on the south and Shando ...
, founded in 386 BC, also had walls that were wide at the base; they were tall, with two separate sides of its rectangular enclosure at a length of .
The cities of the Indus Valley Civilization showed less effort in constructing defences, as did the Minoan civilization
The Minoan civilization was a Bronze Age culture which was centered on the island of Crete. Known for its monumental architecture and energetic art, it is often regarded as the first civilization in Europe. The ruins of the Minoan palaces at K ...
on Crete
Crete ( ; , Modern Greek, Modern: , Ancient Greek, Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the List of islands by area, 88th largest island in the world and the List of islands in the Mediterranean#By area, fifth la ...
. These civilizations probably relied more on the defence of their outer borders or sea shores. Unlike the ancient Minoan civilization, the Mycenaean Greeks
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age in ancient Greece, spanning the period from approximately 1750 to 1050 BC.. It represents the first advanced and distinctively Greek civilization in mainla ...
emphasized the need for fortifications alongside natural defences of mountainous terrain, such as the massive Cyclopean walls
Cyclopean masonry is a type of stonework found in Mycenaean architecture, built with massive limestone boulders, roughly fitted together with minimal clearance between adjacent stones and with clay mortar or no use of mortar. The boulders typi ...
built at Mycenae
Mycenae ( ; ; or , ''Mykē̂nai'' or ''Mykḗnē'') is an archaeological site near Mykines, Greece, Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos, Peloponnese, Argos; and sou ...
and other adjacent Late Bronze Age (c. 1600–1100 BC) centers of central and southern Greece.
Archaeological evidence
 Although there are depictions of sieges from the ancient Near East in historical sources and in art, there are very few examples of siege systems that have been found archaeologically. Of the few examples, several are noteworthy:
* The late 9th-century BC siege system surrounding
Although there are depictions of sieges from the ancient Near East in historical sources and in art, there are very few examples of siege systems that have been found archaeologically. Of the few examples, several are noteworthy:
* The late 9th-century BC siege system surrounding Tell es-Safi
Tell es-Safi (, "White hill"; , ''Tel Tzafit'') was an Arab Palestinian village, located in the Shephelah region on the southern banks of Wadi 'Ajjur, northwest of Hebron, which had its Arab population expelled during the 1948 Arab–Israeli w ...
/ Gath, Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
, consists of a long siege trench, towers, and other elements, and is the earliest evidence of a circumvallation
Investment is the military process of surrounding an enemy fort (or town) with armed forces to prevent entry or escape. It serves both to cut communications with the outside world and to prevent supplies and reinforcements from being introduced ...
system known in the world. It was apparently built by Hazael
Hazael (; ; Old Aramaic 𐤇𐤆𐤀𐤋 ''Ḥzʔl'') was a king of Aram-Damascus mentioned in the Bible. Under his reign, Aram-Damascus became an empire that ruled over large parts of contemporary Syria and Israel-Samaria. While he was likely ...
of Aram Damascus
Aram-Damascus ( ) was an Aramean polity that existed from the late-12th century BCE until 732 BCE, and was centred around the city of Damascus in the Southern Levant. Alongside various tribal lands, it was bounded in its later years by the po ...
, as part of his siege and conquest of Philistine
Philistines (; Septuagint, LXX: ; ) were ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan during the Iron Age in a confederation of city-states generally referred to as Philistia.
There is compelling evidence to suggest that the Philist ...
Gath in the late 9th century BC (mentioned in II Kings
The Book of Kings (, '' Sēfer Məlāḵīm'') is a book in the Hebrew Bible, found as two books (1–2 Kings) in the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. It concludes the Deuteronomistic history, a history of ancient Israel also including t ...
12:18).
* The late 8th-century BC siege system surrounding the site of Lachish
Lachish (; ; ) was an ancient Canaanite and later Israelite city in the Shephelah ("lowlands of Judea") region of Canaan on the south bank of the Lakhish River mentioned several times in the Hebrew Bible. The current '' tell'' by that name, kn ...
(Tell el-Duweir) in Israel, built by Sennacherib
Sennacherib ( or , meaning "Sin (mythology), Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 705BC until his assassination in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynasty, Sennacherib is one of the most famous A ...
of Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
in 701 BC, is not only evident in the archaeological remains, but is described in Assyrian and biblical
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) biblical languages ...
sources and in the reliefs of Sennacherib's palace in Nineveh
Nineveh ( ; , ''URUNI.NU.A, Ninua''; , ''Nīnəwē''; , ''Nīnawā''; , ''Nīnwē''), was an ancient Assyrian city of Upper Mesopotamia, located in the modern-day city of Mosul (itself built out of the Assyrian town of Mepsila) in northern ...
.
* The siege of Alt-Paphos
Paphos, also spelled as Pafos, is a coastal city in southwest Cyprus and the capital of Paphos District. In classical antiquity, two locations were called Paphos: #Old Paphos, Old Paphos, today known as Kouklia, and #New Paphos, New Paphos. It i ...
, Cyprus
Cyprus (), officially the Republic of Cyprus, is an island country in the eastern Mediterranean Sea. Situated in West Asia, its cultural identity and geopolitical orientation are overwhelmingly Southeast European. Cyprus is the List of isl ...
by the Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
army in the 4th century BC.
Depictions
The earliest representations of siege warfare have been dated to theProtodynastic Period of Egypt
Naqada III is the last phase of the Naqada culture of ancient Egyptian prehistory, dating from approximately 3200 to 3000 BC. It is the period during which the process of state formation, which began in Naqada II, became highly visible, ...
, . These show the symbolic destruction of city walls by divine animals using hoes.
The first siege equipment is known from Egyptian tomb reliefs of the 24th century BC, showing Egyptian soldiers storming Canaan
CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
ite town walls on wheeled siege ladders. Later Egyptian temple reliefs of the 13th century BC portray the violent siege of Dapur, a Syrian city, with soldiers climbing scale ladders supported by archers.
Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
n palace reliefs of the 9th to 7th centuries BC display sieges of several Near Eastern cities. Though a simple battering ram had come into use in the previous millennium, the Assyrians improved siege warfare and used huge wooden tower-shaped battering rams with archers positioned on top.
In ancient China, sieges of city walls (along with naval battles) were portrayed on bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals (such as phosphorus) or metalloid ...
'hu' vessels, like those found in Chengdu
Chengdu; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Chinese pronunciation: ; Chinese postal romanization, previously Romanization of Chinese, romanized as Chengtu. is the capital city of the Chinese province of Sichuan. With a ...
, Sichuan
Sichuan is a province in Southwestern China, occupying the Sichuan Basin and Tibetan Plateau—between the Jinsha River to the west, the Daba Mountains to the north, and the Yunnan–Guizhou Plateau to the south. Its capital city is Cheng ...
in 1965, which have been dated to the Warring States period
The Warring States period in history of China, Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and ...
(5th to 3rd centuries BC).Needham, Volume 5, Part 6, 446.
Tactics
Offensive
An attacker's first act in a siege might be a surprise attack, attempting to overwhelm the defenders before they were ready or were even aware there was a threat. This was how William de Forz capturedFotheringhay Castle
Fotheringhay Castle, also known as Fotheringay Castle, was a High Middle Age Norman Motte-and-bailey castle in the village of Fotheringhay to the north of the market town of Oundle, Northamptonshire, England (). It was probably founded ar ...
in 1221.
The most common practice of siege warfare was to lay siege and just wait for the surrender of the enemies inside or, quite commonly, to coerce someone inside to betray the fortification. During the medieval period, negotiations would frequently take place during the early part of the siege. An attacker – aware of a prolonged siege's great cost in time, money, and lives – might offer generous terms to a defender who surrendered quickly. The defending troops would be allowed to march away unharmed, often retaining their weapons. However, a garrison commander who was thought to have surrendered too quickly might face execution by his own side for treason.
As a siege progressed, the surrounding army would build earthworks (a line of circumvallation
Investment is the military process of surrounding an enemy fort (or town) with armed forces to prevent entry or escape. It serves both to cut communications with the outside world and to prevent supplies and reinforcements from being introduced ...
) to completely encircle their target, preventing food, water, and other supplies from reaching the besieged city. If sufficiently desperate as the siege progressed, defenders and civilians might have been reduced to eating anything vaguely edible – horses, family pets, the leather from shoes, and even each other.
The Hittite siege of a rebellious Anatolian vassal in the 14th century BC ended when the queen mother came out of the city and begged for mercy on behalf of her people. The Hittite campaign against the kingdom of Mitanni
Mitanni (–1260 BC), earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, ; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat in Assyrian records, or in Ancient Egypt, Egyptian texts, was a Hurrian language, Hurrian-speaking state in northern Syria (region), Syria an ...
in the 14th century BC bypassed the fortified city of Carchemish
Carchemish ( or ), also spelled Karkemish (), was an important ancient capital in the northern part of the region of Syria. At times during its history the city was independent, but it was also part of the Mitanni, Hittite and Neo-Assyrian ...
. If the main objective of a campaign was not the conquest of a particular city, it could simply be passed by. When the main objective of the campaign had been fulfilled, the Hittite army returned to Carchemish and the city fell after an eight-day siege.
Disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function (biology), function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical condi ...
was another effective siege weapon, although the attackers were often as vulnerable as the defenders. In some instances, catapults or similar weapons were used to fling diseased animals over city walls in an early example of biological warfare
Biological warfare, also known as germ warfare, is the use of biological toxins or Pathogen, infectious agents such as bacteria, viruses, insects, and Fungus, fungi with the intent to kill, harm or incapacitate humans, animals or plants as an ...
. If all else failed, a besieger could claim the booty of his conquest undamaged, and retain his men and equipment intact, for the price of a well-placed bribe
Bribery is the corrupt solicitation, payment, or acceptance of a private favor (a bribe) in exchange for official action. The purpose of a bribe is to influence the actions of the recipient, a person in charge of an official duty, to act contrar ...
to a disgruntled gatekeeper. The Assyrian siege of Jerusalem
The Assyrian siege of Jerusalem () was an aborted siege of Jerusalem, then capital of the Kingdom of Judah, carried out by Sennacherib, king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire. The siege concluded Sennacharib's campaign in the Levant, in which he att ...
in the 8th century BC came to an end when the Israelites
Israelites were a Hebrew language, Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group, consisting of tribes that lived in Canaan during the Iron Age.
Modern scholarship describes the Israelites as emerging from indigenous Canaanites, Canaanite populations ...
bought them off with gifts and tribute, according to the Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
n account, or when the Assyrian camp was struck by mass death, according to the Biblical
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) biblical languages ...
account. Due to logistics, long-lasting sieges involving a minor force could seldom be maintained. A besieging army, encamped in possibly squalid field conditions and dependent on the countryside and its own supply lines for food, could very well be threatened with the disease and starvation intended for the besieged.
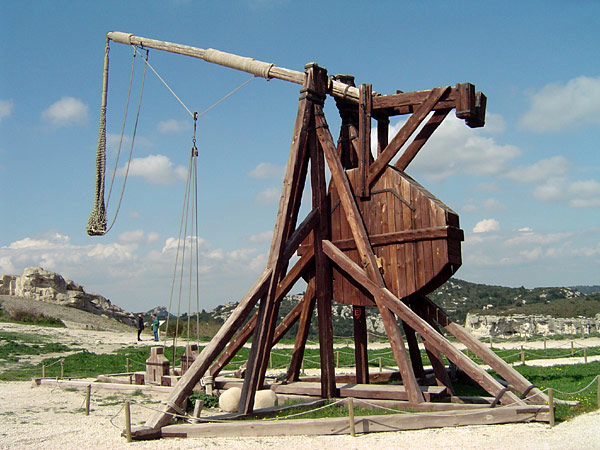
 To end a siege more rapidly, various methods were developed in ancient and medieval times to counter fortifications, and a large variety of
To end a siege more rapidly, various methods were developed in ancient and medieval times to counter fortifications, and a large variety of siege engine
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while othe ...
s was developed for use by besieging armies. Ladders could be used to escalade
Escalade is the act of scaling defensive walls or ramparts with the aid of ladders. Escalade was a prominent feature of sieges in ancient and medieval warfare. Although no longer common in modern warfare, escalade technologies are still deve ...
over the defenses. Battering ram
A battering ram is a siege engine that originated in ancient times and was designed to break open the masonry walls of fortifications or splinter their wooden gates. In its simplest form, a battering ram is just a large, heavy log carried ...
s and siege hook
A siege hook is a weapon used to pull stones from a wall during a siege. The method used was to penetrate the protective wall with the hook and then retract it, pulling away some of the wall with it.
The Greek historian Polybius
Polybius ...
s could also be used to force through gates or walls, while catapult
A catapult is a ballistics, ballistic device used to launch a projectile at a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden rel ...
s, ballista
The ballista (Latin, from Ancient Greek, Greek βαλλίστρα ''ballistra'' and that from βάλλω ''ballō'', "throw"), plural ballistae or ballistas, sometimes called bolt thrower, was an Classical antiquity, ancient missile weapon tha ...
e, trebuchet
A trebuchet () is a type of catapult that uses a hinged arm with a sling attached to the tip to launch a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles ...
s, mangonel
The mangonel, also called the traction trebuchet, was a type of trebuchet used in Ancient China starting from the Warring States period, and later across Eurasia by the 6th century AD. Unlike the later counterweight trebuchet, the mangonel was ...
s, and onagers
The onager (, ) (''Equus hemionus''), also known as hemione or Asiatic wild ass, is a species of the family Equidae native to Asia. A member of the subgenus ''Asinus'', the onager was described and given its binomial name by German zoologist Pe ...
could be used to launch projectiles to break down a city's fortifications and kill its defenders. A siege tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege ...
, a substantial structure built to equal or greater height than the fortification's walls, could allow the attackers to fire down upon the defenders and also advance troops to the wall with less danger than using ladders.
In addition to launching projectiles at the fortifications or defenders, it was also quite common to attempt to undermine the fortifications, causing them to collapse. This could be accomplished by digging a tunnel beneath the foundations
Foundation(s) or The Foundation(s) may refer to: Common uses
* Foundation (cosmetics), a skin-coloured makeup cream applied to the face
* Foundation (engineering), the element of a structure which connects it to the ground, and transfers loads f ...
of the walls, and then deliberately collapsing or exploding the tunnel. This process is known as mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
. The defenders could dig counter-tunnels to cut into the attackers' works and collapse them prematurely.
Fire was often used as a weapon when dealing with wooden fortifications. The Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
used Greek fire
Greek fire was an incendiary weapon system used by the Byzantine Empire from the seventh to the fourteenth centuries. The recipe for Greek fire was a closely-guarded state secret; historians have variously speculated that it was based on saltp ...
, which contained additives that made it hard to extinguish. Combined with a primitive flamethrower
A flamethrower is a ranged incendiary device designed to project a controllable jet of fire. First deployed by the Byzantine Empire in the 7th century AD, flamethrowers saw use in modern times during World War I, and more widely in World W ...
, it proved an effective offensive and defensive weapon. A sallying out might also occur with such weapons, or if the siege was of a location on a coastline, from ships launched from the harbor of the location.
Defensive
The universal method for defending against siege is the use of fortifications, principally walls andditches
A ditch is a small to moderate trench created to channel water. A ditch can be used for drainage, to drain water from low-lying areas, alongside roadways or fields, or to channel water from a more distant source for plant irrigation. Ditches a ...
, to supplement natural features. A sufficient supply of food and water was also important to defeat the simplest method of siege warfare: starvation
Starvation is a severe deficiency in caloric energy intake, below the level needed to maintain an organism's life. It is the most extreme form of malnutrition. In humans, prolonged starvation can cause permanent organ damage and eventually, de ...
. On occasion, the defenders would drive 'surplus' civilians out to reduce the demands on stored food and water.
During the Warring States period
The Warring States period in history of China, Chinese history (221 BC) comprises the final two and a half centuries of the Zhou dynasty (256 BC), which were characterized by frequent warfare, bureaucratic and military reforms, and ...
in China (481–221 BC), warfare lost its honorable, gentlemen's duty that was found in the previous era of the Spring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period () was a period in History of China, Chinese history corresponding roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou (256 BCE), characterized by the gradual erosion of royal power as local lords nominally subject t ...
, and became more practical, competitive, cut-throat, and efficient for gaining victory. The Chinese invention of the hand-held, trigger-mechanism crossbow
A crossbow is a ranged weapon using an Elasticity (physics), elastic launching device consisting of a Bow and arrow, bow-like assembly called a ''prod'', mounted horizontally on a main frame called a ''tiller'', which is hand-held in a similar f ...
during this period revolutionized warfare, giving greater emphasis to infantry and cavalry and less to traditional chariot
A chariot is a type of vehicle similar to a cart, driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid Propulsion, motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk O ...
warfare.
The philosophically pacifist
Pacifism is the opposition to war or violence. The word ''pacifism'' was coined by the French peace campaigner Émile Arnaud and adopted by other peace activists at the tenth Universal Peace Congress in Glasgow in 1901. A related term is ''a ...
Mohist
Mohism or Moism (, ) was an ancient Chinese philosophy of ethics and logic, rational thought, and scientific technology developed by the scholars who studied under the ancient Chinese philosopher Mozi (), embodied in an eponymous book: the '' ...
s (followers of the philosopher Mozi
Mozi, personal name Mo Di,
was a Chinese philosopher, logician, and founder of the Mohist school of thought, making him one of the most important figures of the Warring States period (221 BCE). Alongside Confucianism, Mohism became the ...
) of the 5th century BC believed in aiding the defensive warfare of smaller Chinese states against the hostile offensive warfare of larger domineering states. The Mohists were renowned in the smaller states (and the enemies of the larger states) for the inventions of siege machinery to scale or destroy walls. These included traction trebuchet catapult
A catapult is a ballistics, ballistic device used to launch a projectile at a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden rel ...
s, high ballista
The ballista (Latin, from Ancient Greek, Greek βαλλίστρα ''ballistra'' and that from βάλλω ''ballō'', "throw"), plural ballistae or ballistas, sometimes called bolt thrower, was an Classical antiquity, ancient missile weapon tha ...
s, a wheeled siege ramp with grappling hook
A grappling hook or grapnel is a device that typically has multiple hooks (known as ''claws'' or ''flukes'') attached to a rope or cable; it is thrown, dropped, sunk, projected, or fastened directly by hand to where at least one hook may cat ...
s known as the Cloud Bridge (the protractible, folded ramp slinging forward by means of a counterweight with rope and pulley), and wheeled 'hook-carts' used to latch large iron hooks onto the tops of walls to pull them down.
 When enemies attempted to dig tunnels under walls for mining or entry into the city, the defenders used large
When enemies attempted to dig tunnels under walls for mining or entry into the city, the defenders used large bellows
A bellows or pair of bellows is a device constructed to furnish a strong blast of air. The simplest type consists of a flexible bag comprising a pair of rigid boards with handles joined by flexible leather sides enclosing an approximately airtig ...
(the type the Chinese commonly used in heating up a blast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being supplied above atmospheric pressure.
In a ...
for smelting cast iron
Cast iron is a class of iron–carbon alloys with a carbon content of more than 2% and silicon content around 1–3%. Its usefulness derives from its relatively low melting temperature. The alloying elements determine the form in which its car ...
) to pump smoke into the tunnels in order to suffocate the intruders.
Advances in the prosecution of sieges in ancient and medieval times naturally encouraged the development of a variety of defensive countermeasures. In particular, medieval fortification
Medieval fortification refers to medieval military methods that cover the development of fortification construction and use in Europe, roughly from the fall of the Western Roman Empire to the Renaissance. During this millennium, fortifications ...
s became progressively stronger—for example, the advent of the concentric castle
A concentric castle is a castle with two or more concentric Curtain wall (fortification), curtain walls, such that the outer wall is lower than the inner and can be defended from it. The layout was square (at Belvoir Fortress, Belvoir and ...
from the period of the Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding t ...
—and more dangerous to attackers—witness the increasing use of machicolation
In architecture, a machicolation () is an opening between the supporting corbels of a battlement through which defenders could target attackers who had reached the base of the defensive wall. A smaller related structure that only protects key ...
s and murder-hole
A murder hole or meurtrière is a hole in the ceiling of a gateway or passageway in a fortification through which the defenders could shoot, throw or pour harmful substances or objects such as rocks, arrows, scalding water, hot sand, quicklime ...
s, as well the preparation of hot or incendiary substances. Arrowslit
An arrowslit (often also referred to as an arrow loop, loophole or loop hole, and sometimes a balistraria) is a narrow vertical aperture in a fortification through which an archer can launch arrows or a crossbowman can launch Crossbow bolt, bolts ...
s (also called arrow loops or loopholes), sally port
A sallyport is a secure, controlled entry way to an enclosure, e.g., a fortification or prison. The entrance is usually protected by some means, such as a fixed wall on the outside, parallel to the door, which must be circumvented to enter and ...
s (airlock-like doors) for sallies and deep water wells were also integral means of resisting siege at this time. Particular attention would be paid to defending entrances, with gates protected by drawbridge
A drawbridge or draw-bridge is a type of moveable bridge typically at the entrance to a castle or tower surrounded by a moat. In some forms of English, including American English, the word ''drawbridge'' commonly refers to all types of moveable b ...
s, portcullis
A portcullis () is a heavy, vertically closing gate typically found in medieval fortifications. It consists of a latticed Grille (architecture), grille made of wood and/or metal, which slides down grooves inset within each jamb of the gateway.
...
es, and barbican
A barbican (from ) is a fortified outpost or fortified gateway, such as at an outer defense perimeter of a city or castle, or any tower situated over a gate or bridge which was used for defensive purposes.
Europe
Medieval Europeans typically b ...
s. Moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch dug around a castle, fortification, building, or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. Moats can be dry or filled with water. In some places, moats evolved into more extensive water d ...
s and other water defenses, whether natural or augmented, were also vital to defenders.
In the European Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, virtually all large cities had city walls—Dubrovnik
Dubrovnik, historically known as Ragusa, is a city in southern Dalmatia, Croatia, by the Adriatic Sea. It is one of the most prominent tourist destinations in the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean, a Port, seaport and the centre of the Dubrovni ...
in Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; ; ) is a historical region located in modern-day Croatia and Montenegro, on the eastern shore of the Adriatic Sea. Through time it formed part of several historical states, most notably the Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Croatia (925 ...
is a well-preserved example—and more important cities had citadel
A citadel is the most fortified area of a town or city. It may be a castle, fortress, or fortified center. The term is a diminutive of ''city'', meaning "little city", because it is a smaller part of the city of which it is the defensive core.
...
s, fort
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from La ...
s, or castle
A castle is a type of fortification, fortified structure built during the Middle Ages predominantly by the nobility or royalty and by Military order (monastic society), military orders. Scholars usually consider a ''castle'' to be the private ...
s. Great effort was expended to ensure a good water supply inside the city in case of siege. In some cases, long tunnels were constructed to carry water into the city. Complex systems of tunnels were used for storage and communications in medieval cities like Tábor
Tábor (; ) is a town in the South Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 34,000 inhabitants, making it the second most populated town in the region. The town was founded by the Hussites in 1420. The historic town centre is well pres ...
in Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
, similar to those used much later in Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
during the Vietnam War
The Vietnam War (1 November 1955 – 30 April 1975) was an armed conflict in Vietnam, Laos, and Cambodia fought between North Vietnam (Democratic Republic of Vietnam) and South Vietnam (Republic of Vietnam) and their allies. North Vietnam w ...
.
Until the invention of gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
-based weapons (and the resulting higher-velocity projectiles), the balance of power and logistics definitely favored the defender. With the invention of gunpowder, cannon and mortars and howitzer
The howitzer () is an artillery weapon that falls between a cannon (or field gun) and a mortar. It is capable of both low angle fire like a field gun and high angle fire like a mortar, given the distinction between low and high angle fire break ...
s (in modern times), the traditional methods of defense became less effective against a determined siege.
Siege accounts
Although there are numerous ancient accounts of cities being sacked, few contain any clues to how this was achieved. Some popular tales existed on how the cunning heroes succeeded in their sieges. The best-known is theTrojan Horse
In Greek mythology, the Trojan Horse () was a wooden horse said to have been used by the Greeks during the Trojan War to enter the city of Troy and win the war. The Trojan Horse is not mentioned in Homer, Homer's ''Iliad'', with the poem ending ...
of the Trojan War
The Trojan War was a legendary conflict in Greek mythology that took place around the twelfth or thirteenth century BC. The war was waged by the Achaeans (Homer), Achaeans (Ancient Greece, Greeks) against the city of Troy after Paris (mytho ...
, and a similar story tells how the Canaan
CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
ite city of Joppa was conquered by the Egyptians in the 15th century BC. The Biblical Book of Joshua
The Book of Joshua is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Israel from the conquest of Canaan to the Babylonian captivity, Babylonian exile. It tells of the ...
contains the story of the miraculous Battle of Jericho
The Fall of Jericho, as described in the biblical Book of Joshua, was the first military engagement fought by the Israelites in the course of the conquest of Canaan. According to , the walls of Jericho fell after the Israelites marched around ...
.
A more detailed historical account from the 8th century BC, called the Piankhi stela, records how the Nubians
Nubians () ( Nobiin: ''Nobī,'' ) are a Nilo-Saharan speaking ethnic group indigenous to the region which is now northern Sudan and southern Egypt. They originate from the early inhabitants of the central Nile valley, believed to be one of th ...
laid siege to and conquered several Egyptian cities by using battering rams, archers, and slingers and building causeway
A causeway is a track, road or railway on the upper point of an embankment across "a low, or wet place, or piece of water". It can be constructed of earth, masonry, wood, or concrete. One of the earliest known wooden causeways is the Sweet T ...
s across moats.
Classical antiquity
During thePeloponnesian War
The Second Peloponnesian War (431–404 BC), often called simply the Peloponnesian War (), was an Ancient Greece, ancient Greek war fought between Classical Athens, Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Ancien ...
, one hundred sieges were attempted and fifty-eight ended with the surrender of the besieged area.
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon (; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), most commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia (ancient kingdom), Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip ...
's army successfully besieged many powerful cities during his conquests. Two of his most impressive achievements in siegecraft took place in the siege of Tyre and the siege of the Sogdian Rock
The Sogdian Rock or Rock of Ariamazes, a fortress located north of Bactria in Sogdiana (near Samarkand), ruled by Arimazes, was captured by the forces of Alexander the Great in the early spring of 327 BC as part of his conquest of the Achaeme ...
. His engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who Invention, invent, design, build, maintain and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials. They aim to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while ...
s built a causeway
A causeway is a track, road or railway on the upper point of an embankment across "a low, or wet place, or piece of water". It can be constructed of earth, masonry, wood, or concrete. One of the earliest known wooden causeways is the Sweet T ...
that was originally wide and reached the range of his torsion-powered artillery, while his soldiers pushed siege tower
A Roman siege tower or breaching tower (or in the Middle Ages, a belfry''Castle: Stephen Biesty's Cross-Sections''. Dorling Kindersley Pub (T); 1st American edition (September 1994). Siege towers were invented in 300 BC. ) is a specialized siege ...
s housing stone throwers and light catapults to bombard the city walls.
Most conquerors before him had found Tyre, a Phoenicia
Phoenicians were an Ancient Semitic-speaking peoples, ancient Semitic group of people who lived in the Phoenician city-states along a coastal strip in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily modern Lebanon and the Syria, Syrian ...
n island-city about from the mainland, impregnable. The Macedonians built a mole
Mole (or Molé) may refer to:
Animals
* Mole (animal) or "true mole"
* Golden mole, southern African mammals
* Marsupial mole
Marsupial moles, the Notoryctidae family, are two species of highly specialized marsupial mammals that are found i ...
, a raised spit of earth across the water, by piling stones up on a natural land bridge
In biogeography, a land bridge is an isthmus or wider land connection between otherwise separate areas, over which animals and plants are able to cross and colonize new lands. A land bridge can be created by marine regression, in which sea le ...
that extended underwater to the island, and although the Tyrians rallied by sending a fire ship
A fire ship or fireship is a large wooden vessel set on fire to be used against enemy ships during a ramming attack or similar maneuver. Fireships were used to great effect against wooden ships throughout naval military history up until the ad ...
to destroy the towers, and captured the mole in a swarming frenzy, the city eventually fell to the Macedonians after a seven-month siege. In complete contrast to Tyre, Sogdian Rock was captured by stealthy attack. Alexander used commando-like tactics to scale the cliffs and capture the high ground, and the demoralized defenders surrendered.
 The importance of siege warfare in the ancient period should not be underestimated. One of the contributing causes of
The importance of siege warfare in the ancient period should not be underestimated. One of the contributing causes of Hannibal
Hannibal (; ; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Punic people, Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Ancient Carthage, Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
Hannibal's fat ...
's inability to defeat Rome was his lack of siege engines
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while othe ...
, thus, while he was able to defeat Roman armies in the field, he was unable to capture Rome itself. The legionary armies of the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
and Empire
An empire is a political unit made up of several territories, military outpost (military), outposts, and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a hegemony, dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the ...
are noted as being particularly skilled and determined in siege warfare. An astonishing number and variety of sieges, for example, formed the core of Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil wa ...
's mid-1st-century BC conquest of Gaul
Gaul () was a region of Western Europe first clearly described by the Roman people, Romans, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, and parts of Switzerland, the Netherlands, Germany, and Northern Italy. It covered an area of . Ac ...
(modern France).
In his ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico
''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (; ), also ''Bellum Gallicum'' (), is Julius Caesar's first-hand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it, Caesar describes the battles and intrigues that took place in the nine yea ...
'' (''Commentaries on the Gallic War''), Caesar describes how, at the Battle of Alesia
The Battle of Alesia or siege of Alesia (September 52 BC) was the climactic military engagement of the Gallic Wars, fought around the Gauls, Gallic ''oppidum'' (fortified settlement) of Alesia (city), Alesia in modern France, a major centre ...
, the Roman legion
The Roman legion (, ) was the largest military List of military legions, unit of the Roman army, composed of Roman citizenship, Roman citizens serving as legionary, legionaries. During the Roman Republic the manipular legion comprised 4,200 i ...
s created two huge fortified walls around the city. The inner circumvallation, , held in Vercingetorix
Vercingetorix (; ; – 46 BC) was a Gauls, Gallic king and chieftain of the Arverni tribe who united the Gauls in a failed revolt against Roman Republic, Roman forces during the last phase of Julius Caesar's Gallic Wars. After surrendering to C ...
's forces, while the outer contravallation
Investment is the military process of surrounding an enemy fort (or town) with armed forces to prevent entry or escape. It serves both to cut communications with the outside world and to prevent supplies and reinforcements from being introduced ...
kept relief from reaching them. The Romans held the ground in between the two walls. The besieged Gauls, facing starvation, eventually surrendered after their relief force met defeat against Caesar's auxiliary cavalry.
The Sicarii
The Sicarii were a group of Jewish assassins who were active throughout Judaea in the years leading up to and during the First Jewish–Roman War, which took place at the end of the Second Temple period. Often associated with the Zealots (altho ...
Zealots
The Zealots were members of a Jewish political movements, Jewish political movement during the Second Temple period who sought to incite the people of Judaea (Roman province), Judaea to rebel against the Roman Empire and expel it from the Land ...
who defended Masada
Masada ( ', 'fortress'; ) is a mountain-top fortress complex in the Judaean Desert, overlooking the western shore of the Dead Sea in southeastern Israel. The fort, built in the first century BCE, was constructed atop a natural plateau rising ov ...
in AD 73 were defeated by the Roman legions, who built a ramp high up to the fortress's west wall.
During the Roman–Persian Wars, siege warfare was extensively used by both sides.
Medieval period
Mongols and Chinese
In the Middle Ages, theMongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
's campaign against China (then comprising the Western Xia dynasty, Jin dynasty
Jin may refer to:
States Jìn 晉
* Jin (Chinese state) (晉國), major state of the Zhou dynasty, existing from the 11th century BC to 376 BC
* Jin dynasty (266–420) (晉朝), also known as Liang Jin and Sima Jin
* Jin (Later Tang precursor) ...
, and Southern Song dynasty
The Song dynasty ( ) was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 960 to 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song, who usurped the throne of the Later Zhou dynasty and went on to conquer the rest of the Ten Kingdoms, endin ...
) by Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; August 1227), also known as Chinggis Khan, was the founder and first khan (title), khan of the Mongol Empire. After spending most of his life uniting the Mongols, Mongol tribes, he launched Mongol invasions and ...
until Kublai Khan
Kublai Khan (23 September 1215 – 18 February 1294), also known by his temple name as the Emperor Shizu of Yuan and his regnal name Setsen Khan, was the founder and first emperor of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty of China. He proclaimed the ...
, who eventually established the Yuan dynasty
The Yuan dynasty ( ; zh, c=元朝, p=Yuáncháo), officially the Great Yuan (; Mongolian language, Mongolian: , , literally 'Great Yuan State'), was a Mongol-led imperial dynasty of China and a successor state to the Mongol Empire after Div ...
in 1271, was very effective, allowing the Mongols to sweep through large areas. Even if they could not enter some of the more well-fortified cities, they used innovative battle tactics to grab hold of the land and the people:
Another Mongol tactic was to use catapults to launch corpses of plague victims into besieged cities. The disease-carrying flea
Flea, the common name for the order (biology), order Siphonaptera, includes 2,500 species of small flightless insects that live as external parasites of mammals and birds. Fleas live by hematophagy, ingesting the blood of their hosts. Adult f ...
s from the bodies would then infest the city, and the plague would spread, allowing the city to be easily captured, although this transmission mechanism was not known at the time. In 1346, the bodies of Mongol warriors of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as ''Ulug Ulus'' ( in Turkic) was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of ...
who had died of plague were thrown over the walls of the Crimea
Crimea ( ) is a peninsula in Eastern Europe, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, almost entirely surrounded by the Black Sea and the smaller Sea of Azov. The Isthmus of Perekop connects the peninsula to Kherson Oblast in mainland Ukrain ...
n city of Kaffa (now Feodosiya
Feodosia (, ''Feodosiia, Teodosiia''; , ''Feodosiya''), also called in English Theodosia (from ), is a city on the Crimean coast of the Black Sea. Feodosia serves as the administrative center of Feodosia Municipality, one of the regions into w ...
) during the siege of Caffa
The siege of Caffa was a 14th-century military encounter when Jani Beg of the Golden Horde besieged the city of Caffa (modern-day Feodosia), between two periods in the 1340s. The city of Caffa, a Genoese colony, was a vital trading hub located ...
. It has been speculated that this operation may have been responsible for the advent of the Black Death in Europe. The Black Death is estimated to have killed 30%–60% of Europe's population.
On the first night while laying siege to a city, the leader of the Mongol forces would lead from a white tent: if the city surrendered, all would be spared. On the second day, he would use a red tent: if the city surrendered, the men would all be killed, but the rest would be spared. On the third day, he would use a black tent: no quarter would be given.
 However, the Chinese were not completely defenseless, and from AD 1234 until 1279, the Southern Song Chinese held out against the enormous barrage of Mongol attacks. Much of this success in defense lay in the world's first use of gunpowder (i.e. with early
However, the Chinese were not completely defenseless, and from AD 1234 until 1279, the Southern Song Chinese held out against the enormous barrage of Mongol attacks. Much of this success in defense lay in the world's first use of gunpowder (i.e. with early flamethrower
A flamethrower is a ranged incendiary device designed to project a controllable jet of fire. First deployed by the Byzantine Empire in the 7th century AD, flamethrowers saw use in modern times during World War I, and more widely in World W ...
s, grenades, firearms, cannons, and land mines) to fight back against the Khitan people, Khitans, the Tanguts, the Jurchens, and then the Mongols.
The Chinese of the Song period also discovered the explosive potential of packing hollowed cannonball shells with gunpowder. Written later in the ''Jiao Yu, Huo Long Jing'', this manuscript of Jiao Yu recorded an earlier Song-era cast-iron cannon known as the 'flying-cloud thunderclap eruptor' (fei yun pi-li pao). The manuscript stated that (Wade–Giles spelling):
The shells (''phao'') are made of cast iron, as large as a bowl and shaped like a ball. Inside they contain half a pound of 'magic' gunpowder (''shen huo''). They are sent flying towards the enemy camp from an eruptor (''mu phao''); and when they get there a sound like a thunder-clap is heard, and flashes of light appear. If ten of these shells are fired successfully into the enemy camp, the whole place will be set ablaze...Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, 264.During the Ming dynasty (AD 1368–1644), the Chinese were very concerned with city planning in regards to gunpowder warfare. The site for constructing the walls and the thickness of the walls in Beijing's Forbidden City were favoured by the Chinese Yongle Emperor (r. 1402–1424) because they were in pristine position to resist cannon volley and were built thick enough to withstand attacks from cannon fire. ''For more, see Technology of the Song dynasty.''
Age of gunpowder
The introduction of gunpowder and the use ofcannon
A cannon is a large-caliber gun classified as a type of artillery, which usually launches a projectile using explosive chemical propellant. Gunpowder ("black powder") was the primary propellant before the invention of smokeless powder during th ...
s brought about a new age in siege warfare. Cannons were first used in Song dynasty China during the early 13th century, but did not become significant weapons for another 150 years or so. In early decades, cannons could do little against strong castles and fortresses, providing little more than smoke and fire. By the 16th century, however, they were an essential and regularized part of any campaigning army, or castle's defences.
The greatest advantage of cannons over other siege weapons was the ability to fire a heavier projectile, farther, faster, and more often than previous weapons. They could also fire projectiles in a straight line, so that they could destroy the bases of high walls. Thus, 'old fashioned' walls – that is, high and, relatively, thin – were excellent targets, and, over time, easily demolished. In 1453, the Walls of Constantinople, Theodosian Walls of Constantinople, the capital of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, were broken through in Fall of Constantinople, just six weeks by the 62 cannons of Mehmed the Conqueror, Mehmed II's army, although in the end the conquest was a long and extremely difficult siege with heavy Ottoman casualties due to the repeated attempts at taking the city by assault.
 However, new fortifications, designed to withstand gunpowder weapons, were soon constructed throughout Europe. During the
However, new fortifications, designed to withstand gunpowder weapons, were soon constructed throughout Europe. During the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
and the early modern period
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There i ...
, siege warfare continued to dominate the conduct of the European wars.
Once siege guns were developed, the techniques for assaulting a town or fortress became well known and ritualized. The attacking army would surround a town. Then the town would be asked to surrender. If they did not comply, the besieging army would surround the town with temporary fortifications to stop Sally (military), sallies from the stronghold or relief getting in. The attackers would next build a length of trenches parallel to the defenses (these are known as the "first parallel") and just out of range of the defending artillery. They would dig a trench (known as a forward) towards the town in a zigzag pattern so that it could not be enfiladed by defending fire. Once they were within artillery range, they would dig another parallel (the "second parallel") trench and fortify it with gun emplacements. This technique is commonly called entrenchment.
If necessary, using the first artillery fire for cover, the forces conducting the siege would repeat the process until they placed their guns close enough to be laid (aimed) accurately to make a breach in the fortifications. In order to allow the forlorn hope and support troops to get close enough to exploit the breach, more zigzag trenches could be dug even closer to the walls, with more parallel trenches to protect and conceal the attacking troops. After each step in the process, the besiegers would ask the besieged to surrender. If the forlorn hope stormed the breach successfully, the defenders could expect no mercy.
Emerging theories
The castles that in earlier years had been formidable obstacles were easily breached by the new weapons. For example, in Spain, the newly equipped army of Ferdinand and Isabella was able to conquer Moors, Moorish strongholds in Granada in 1482–1492 that had held out for centuries before the invention of cannons. In the early 15th century, Italian architect Leon Battista Alberti wrote a treatise entitled ''De Re aedificatoria'', which theorized methods of building fortifications capable of withstanding the new guns. He proposed that walls be "built in uneven lines, like the teeth of a saw". He proposed star-shaped fortresses with low, thick walls. However, few rulers paid any attention to his theories. A few towns in Italy began building in the new style late in the 1480s, but it was only with the French invasion of the Italian peninsula in 1494–1495 that the new fortifications were built on a large scale. Charles VIII of France, Charles VIII invaded Italy with an army of 18,000 men and a horse-drawn siege-train. As a result, he could defeat virtually any city or state, no matter how well defended. In a panic, military strategy was completely rethought throughout the Italian states of the time, with a strong emphasis on the new fortifications that could withstand a modern siege.New fortresses
 The most effective way to protect walls against cannon fire proved to be depth (increasing the width of the defenses) and angles (ensuring that attackers could only fire on walls at an oblique angle, not square on). Initially, walls were lowered and backed, in front and behind, with earth. Towers were reformed into triangular bastions. This design matured into the ''trace italienne''. Star fort, Star-shaped fortresses surrounding towns and even cities with outlying defenses proved very difficult to capture, even for a well-equipped army. Fortresses built in this style throughout the 16th century did not become fully obsolete until the 19th century, and were still in use throughout World War I (though modified for 20th-century warfare). During World War II, ''trace italienne'' fortresses could still present a formidable challenge, for example, in the last days of World War II, during the Battle in Berlin, that saw some of the heaviest urban fighting of the war, the Soviets did not attempt to storm the Spandau Citadel (built between 1559 and 1594), but chose to investment (military), invest it and negotiate its surrender.
However, the cost of building such vast modern fortifications was incredibly high, and was often too much for individual cities to undertake. Many were bankrupted in the process of building them; others, such as Siena, spent so much money on fortifications that they were unable to maintain their armies properly, and so lost their wars anyway. Nonetheless, innumerable large and impressive fortresses were built throughout northern Italy in the first decades of the 16th century to resist repeated French invasions that became known as the Italian Wars. Many stand to this day.
The most effective way to protect walls against cannon fire proved to be depth (increasing the width of the defenses) and angles (ensuring that attackers could only fire on walls at an oblique angle, not square on). Initially, walls were lowered and backed, in front and behind, with earth. Towers were reformed into triangular bastions. This design matured into the ''trace italienne''. Star fort, Star-shaped fortresses surrounding towns and even cities with outlying defenses proved very difficult to capture, even for a well-equipped army. Fortresses built in this style throughout the 16th century did not become fully obsolete until the 19th century, and were still in use throughout World War I (though modified for 20th-century warfare). During World War II, ''trace italienne'' fortresses could still present a formidable challenge, for example, in the last days of World War II, during the Battle in Berlin, that saw some of the heaviest urban fighting of the war, the Soviets did not attempt to storm the Spandau Citadel (built between 1559 and 1594), but chose to investment (military), invest it and negotiate its surrender.
However, the cost of building such vast modern fortifications was incredibly high, and was often too much for individual cities to undertake. Many were bankrupted in the process of building them; others, such as Siena, spent so much money on fortifications that they were unable to maintain their armies properly, and so lost their wars anyway. Nonetheless, innumerable large and impressive fortresses were built throughout northern Italy in the first decades of the 16th century to resist repeated French invasions that became known as the Italian Wars. Many stand to this day.
 In the 1530s and 1540s, the new style of fortification began to spread out of Italy into the rest of Europe, particularly to France, the Netherlands, and Spain. Italian engineers were in enormous demand throughout Europe, especially in war-torn areas such as the Netherlands, which became dotted by towns encircled in modern fortifications. The densely populated areas of Northern Italy and the Dutch Republic, United Provinces (the Netherlands) were infamous for their high degree of fortification of cities. It made campaigns in these areas very hard to successfully conduct, considering even minor cities had to be captured by siege within the span of the campaigning season. In the Dutch case, the possibility of flooding large parts of the land provided an additional obstacle to besiegers, for example at the siege of Leiden. For many years, defensive and offensive tactics were well balanced, leading to protracted and costly wars such as Europe had never known, involving more and more planning and government involvement. The new fortresses ensured that war rarely extended beyond a series of sieges. Because the new fortresses could easily hold 10,000 men, an attacking army could not ignore a powerfully fortified position without serious risk of counterattack. As a result, virtually all towns had to be taken, and that was usually a long, drawn-out affair, potentially lasting from several months to years, while the members of the town were starved to death. Most battles in this period were between besieging armies and relief columns sent to rescue the besieged.
In the 1530s and 1540s, the new style of fortification began to spread out of Italy into the rest of Europe, particularly to France, the Netherlands, and Spain. Italian engineers were in enormous demand throughout Europe, especially in war-torn areas such as the Netherlands, which became dotted by towns encircled in modern fortifications. The densely populated areas of Northern Italy and the Dutch Republic, United Provinces (the Netherlands) were infamous for their high degree of fortification of cities. It made campaigns in these areas very hard to successfully conduct, considering even minor cities had to be captured by siege within the span of the campaigning season. In the Dutch case, the possibility of flooding large parts of the land provided an additional obstacle to besiegers, for example at the siege of Leiden. For many years, defensive and offensive tactics were well balanced, leading to protracted and costly wars such as Europe had never known, involving more and more planning and government involvement. The new fortresses ensured that war rarely extended beyond a series of sieges. Because the new fortresses could easily hold 10,000 men, an attacking army could not ignore a powerfully fortified position without serious risk of counterattack. As a result, virtually all towns had to be taken, and that was usually a long, drawn-out affair, potentially lasting from several months to years, while the members of the town were starved to death. Most battles in this period were between besieging armies and relief columns sent to rescue the besieged.
Marshal Vauban and Van Coehoorn
 At the end of the 17th century, two influential military engineers, the French Marshal Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, Vauban and the Dutch military engineer Menno van Coehoorn, developed modern fortification to its pinnacle, refining siege warfare without fundamentally altering it: ditches would be dug; walls would be protected by glacis; and bastions would enfilade an attacker. Both engineers developed their ideas independently, but came to similar general rules regarding defensive construction and offensive action against fortifications. Both were skilled in conducting sieges and defenses themselves. Before Vauban and Van Coehoorn, sieges had been somewhat slapdash operations. Vauban and Van Coehoorn refined besieging to a science with a methodical process that, if uninterrupted, would break even the strongest fortifications. Examples of their styles of fortifications are Arras (Vauban) and the no-longer-existent fortress of Bergen op Zoom (Van Coehoorn). The main differences between the two lay in the difference in terrain on which Vauban and Van Coehoorn constructed their defenses: Vauban in the sometimes more hilly and mountainous terrain of France, Van Coehoorn in the flat and floodable lowlands of the Netherlands.
Planning and maintaining a siege is just as difficult as fending one off. A besieging army must be prepared to repel both sortie (siege warfare), sorties from the besieged area and also any attack that may try to relieve the defenders. It was thus usual to construct lines of trenches and defenses facing in both directions. The outermost lines, known as the lines of
At the end of the 17th century, two influential military engineers, the French Marshal Sébastien Le Prestre de Vauban, Vauban and the Dutch military engineer Menno van Coehoorn, developed modern fortification to its pinnacle, refining siege warfare without fundamentally altering it: ditches would be dug; walls would be protected by glacis; and bastions would enfilade an attacker. Both engineers developed their ideas independently, but came to similar general rules regarding defensive construction and offensive action against fortifications. Both were skilled in conducting sieges and defenses themselves. Before Vauban and Van Coehoorn, sieges had been somewhat slapdash operations. Vauban and Van Coehoorn refined besieging to a science with a methodical process that, if uninterrupted, would break even the strongest fortifications. Examples of their styles of fortifications are Arras (Vauban) and the no-longer-existent fortress of Bergen op Zoom (Van Coehoorn). The main differences between the two lay in the difference in terrain on which Vauban and Van Coehoorn constructed their defenses: Vauban in the sometimes more hilly and mountainous terrain of France, Van Coehoorn in the flat and floodable lowlands of the Netherlands.
Planning and maintaining a siege is just as difficult as fending one off. A besieging army must be prepared to repel both sortie (siege warfare), sorties from the besieged area and also any attack that may try to relieve the defenders. It was thus usual to construct lines of trenches and defenses facing in both directions. The outermost lines, known as the lines of contravallation
Investment is the military process of surrounding an enemy fort (or town) with armed forces to prevent entry or escape. It serves both to cut communications with the outside world and to prevent supplies and reinforcements from being introduced ...
, would surround the entire besieging army and protect it from attackers.
This would be the first construction effort of a besieging army, built soon after a fortress or city had been invested. A line of circumvallation would also be constructed, facing in towards the besieged area, to protect against sorties by the defenders and to prevent the besieged from escaping. The next line, which Vauban usually placed at about from the target, would contain the main batteries of heavy cannons so that they could hit the target without being vulnerable themselves. Once this line was established, work crews would move forward, creating another line at . This line contained smaller guns. The final line would be constructed only from the fortress. This line would contain the Mortar (weapon), mortars and would act as a staging area for attack parties once the walls were breached. Van Coehoorn developed a small and easily movable mortar named the coehorn, variations of which were used in sieges until the 19th century. It would also be from this line that miners working to undermine the fortress would operate.
The trenches connecting the various lines of the besiegers could not be built perpendicular to the walls of the fortress, as the defenders would have a clear line of fire along the whole trench. Thus, these lines (known as Sapping, saps) needed to be sharply jagged.
 Another element of a fortress was the
Another element of a fortress was the citadel
A citadel is the most fortified area of a town or city. It may be a castle, fortress, or fortified center. The term is a diminutive of ''city'', meaning "little city", because it is a smaller part of the city of which it is the defensive core.
...
. Usually, a citadel was a "mini fortress" within the larger fortress, sometimes designed as a reduit, but more often as a means of protecting the garrison from potential revolt in the city. The citadel was used in wartime and peacetime to keep the residents of the city in line.
As in ages past, most sieges were decided with very little fighting between the opposing armies. An attacker's army was poorly served, incurring the high casualties that a direct assault on a fortress would entail. Usually, they would wait until supplies inside the fortifications were exhausted or disease had weakened the defenders to the point that they were willing to surrender. At the same time, diseases, especially typhus, were a constant danger to the encamped armies outside the fortress, and often forced a premature retreat. Sieges were often won by the army that lasted the longest.
An important element of strategy for the besieging army was whether or not to allow the encamped city to surrender. Usually, it was preferable to graciously allow a Surrender (military), surrender, both to save on casualties, and to set an example for future defending cities. A city that was allowed to surrender with minimal loss of life was much better off than a city that held out for a long time and was brutally butchered at the end. Moreover, if an attacking army had a reputation of killing and pillaging regardless of a surrender, then other cities' defensive efforts would be redoubled. Usually, a city would surrender (with no honour lost) when its inner lines of defense were reached by the attacker. In case of refusal, however, the inner lines would have to be stormed by the attacker and the attacking troops would be seen to be justified in sacking the city.
Siege warfare
Siege warfare dominated in Western Europe for most of the 17th and 18th centuries. An entire campaign, or longer, could be used in a single siege (for example, Siege of Ostend, Ostend in 1601–1604; Siege of La Rochelle, La Rochelle in 1627–1628). This resulted in extremely prolonged conflicts. The balance was that, while siege warfare was extremely expensive and very slow, it was very successful—or, at least, more so than encounters in the field. Battles arose through clashes between besiegers and relieving armies, but the principle was a slow, grinding victory by the greater economic power. The relatively rare attempts at forcing pitched battles (Gustavus Adolphus in 1630; the French against the Dutch in 1672 or 1688) were almost always expensive failures. The exception to this rule were the English. During the English Civil War, anything which tended to prolong the struggle, or seemed like want of energy and avoidance of a decision, was bitterly resented by the men of both sides. In France and Germany, the prolongation of a war meant continued employment for the soldiers, but in England, both sides were looking to end the war quickly. Even when in the end the New Model Army—a regular professional army—developed the original decision-compelling spirit permeated the whole organisation, as was seen when pitched against regular professional continental troops the Battle of the Dunes (1658), Battle of the Dunes during the Interregnum (England), Interregnum.
The exception to this rule were the English. During the English Civil War, anything which tended to prolong the struggle, or seemed like want of energy and avoidance of a decision, was bitterly resented by the men of both sides. In France and Germany, the prolongation of a war meant continued employment for the soldiers, but in England, both sides were looking to end the war quickly. Even when in the end the New Model Army—a regular professional army—developed the original decision-compelling spirit permeated the whole organisation, as was seen when pitched against regular professional continental troops the Battle of the Dunes (1658), Battle of the Dunes during the Interregnum (England), Interregnum.
 Experienced commanders on both sides in the English Civil War recommended the abandonment of garrisoned fortifications for two primary reasons. The first, as for example proposed by the Royalist Sir Richard Willis, 1st Baronet, Sir Richard Willis to King Charles, was that by abandoning the garrisoning of all but the most strategic locations in one's own territory, far more troops would be available for the field armies, and it was the field armies which would decide the conflict. The other argument was that by slighting potential strong points in one's own territory, an enemy expeditionary force, or local enemy rising, would find it more difficult to consolidate territorial gains against an inevitable counterattack. Sir John Meldrum put forward just such an argument to the Parliamentary Committee of Both Kingdoms, to justify his slighting of Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, Gainsborough in Lincolnshire.
Sixty years later, during the War of the Spanish Succession, the John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, Duke of Marlborough preferred to engage the enemy in pitched battles, rather than engage in siege warfare, although he was very proficient in both types of warfare.
On 15 April 1746, the day before the Battle of Culloden, at Dunrobin Castle, a party of William Sutherland, 17th Earl of Sutherland, William Sutherland's militia conducted the last siege fought on the mainland of Great Britain against Jacobite members of Clan MacLeod.
Experienced commanders on both sides in the English Civil War recommended the abandonment of garrisoned fortifications for two primary reasons. The first, as for example proposed by the Royalist Sir Richard Willis, 1st Baronet, Sir Richard Willis to King Charles, was that by abandoning the garrisoning of all but the most strategic locations in one's own territory, far more troops would be available for the field armies, and it was the field armies which would decide the conflict. The other argument was that by slighting potential strong points in one's own territory, an enemy expeditionary force, or local enemy rising, would find it more difficult to consolidate territorial gains against an inevitable counterattack. Sir John Meldrum put forward just such an argument to the Parliamentary Committee of Both Kingdoms, to justify his slighting of Gainsborough, Lincolnshire, Gainsborough in Lincolnshire.
Sixty years later, during the War of the Spanish Succession, the John Churchill, 1st Duke of Marlborough, Duke of Marlborough preferred to engage the enemy in pitched battles, rather than engage in siege warfare, although he was very proficient in both types of warfare.
On 15 April 1746, the day before the Battle of Culloden, at Dunrobin Castle, a party of William Sutherland, 17th Earl of Sutherland, William Sutherland's militia conducted the last siege fought on the mainland of Great Britain against Jacobite members of Clan MacLeod.
Strategic concepts
In the French Revolutionary Wars, French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, new techniques stressed the division of armies into all-arms corps that would march separately and only come together on the battlefield. The less-concentrated army could now live off the country and move more rapidly over a larger number of roads. Fortresses commanding lines of communication could be bypassed and would no longer stop an invasion. Since armies could not live off the land indefinitely, Napoleon Bonaparte always sought a quick end to any conflict by pitched battle. This military revolution was described and codified by Carl von Clausewitz, Clausewitz.Industrial advances
Advances in artillery made previously impregnable defenses useless. For example, the walls of Battle of Vienna, Vienna that had held off the Ottoman Empire, Turks in the mid-17th century were no obstacle to Napoleon in the early 19th. Where sieges occurred (such as the siege of Delhi and the siege of Cawnpore during the Indian Rebellion of 1857), the attackers were usually able to defeat the defenses within a matter of days or weeks, rather than weeks or months as previously. The great Swedish white-elephant fortress of Karlsborg Fortress, Karlsborg was built in the tradition of Vauban and intended as a reserve capital for Sweden, but it was obsolete before it was completed in 1869. Railways, when they were introduced, made possible the movement and supply of larger armies than those that fought in the Napoleonic Wars. It also reintroduced siege warfare, as armies seeking to use railway lines in enemy territory were forced to capture fortresses which blocked these lines. During the Franco-Prussian War, the battlefield front lines moved rapidly through France. However, the Prussian and other German armies were delayed for months at the Siege of Metz (1870), siege of Metz and the Siege of Paris (1870–1871), siege of Paris, due to the greatly increased firepower of the defending infantry, and the principle of detached or semi-detached forts with heavy-caliberartillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
. This resulted in the later construction of fortress works across Europe, such as the massive fortifications at Verdun-sur-Meuse, Verdun. It also led to the introduction of tactics which sought to induce surrender by bombarding the civilian population within a fortress, rather than the defending works themselves.
The Siege of Sevastopol (1854–1855), siege of Sevastopol during the Crimean War and the siege of Petersburg (1864–1865) during the American Civil War showed that modern citadels, when improved by improvised defences, could still resist an enemy for many months. The siege of Plevna during the Russo-Turkish War (1877–1878) proved that hastily constructed field defenses could resist attacks prepared without proper resources, and were a portent of the trench warfare of World War I.
Advances in firearms technology without the necessary advances in battlefield communications gradually led to the defense again gaining the ascendancy. An example of siege during this time, prolonged during 337 days due to the isolation of the surrounded troops, was the siege of Baler, in which a reduced group of Spanish soldiers was besieged in a small church by the Philippines, Philippine rebels in the course of the Philippine Revolution and the Spanish–American War, until months after the Treaty of Paris (1898), Treaty of Paris, the end of the conflict.
Furthermore, the development of steamships availed greater speed to blockade runners, ships with the purpose of bringing cargo, e.g. food, to cities under blockade, as with Charleston, South Carolina, during the American Civil War.
Modern warfare
World War I
 Mainly as a result of the increasing firepower (such as machine guns) available to defensive forces, World War I, First World War trench warfare briefly revived a form of siege warfare. Although siege warfare had moved out from an urban setting because city walls had become ineffective against modern weapons, trench warfare was nonetheless able to use many of the techniques of siege warfare in its prosecution (sapping, mining, Artillery, barrage and, of course, Attrition warfare, attrition), but on a much larger scale and on a greatly extended front.
More traditional sieges of fortifications took place in addition to trench sieges. The siege of Tsingtao was one of the first major sieges of the war, but the inability for significant resupply of the German garrison made it a relatively one-sided battle. The Germans and the crew of an Austro-Hungarian protected cruiser put up a hopeless defense and, after holding out for more than a week, surrendered to the Japanese, forcing the German East Asia Squadron to steam towards South America for a new coal source.
The other major siege outside Europe during the First World War was in Mesopotamia, at the siege of Kut. After a failed attempt to move on Baghdad, stopped by the Ottomans at the bloody Battle of Ctesiphon (1915), Battle of Ctesiphon, the British and their large contingent of Indian sepoy soldiers were forced to retreat to Kut, where the Ottomans under German General Colmar Freiherr von der Goltz, Baron Colmar von der Goltz laid siege. The British attempts to resupply the force via the Tigris river failed, and rationing was complicated by the refusal of many Indian troops to eat cattle products. By the time the garrison fell on 29 April 1916, starvation was rampant. Conditions did not improve greatly under Turkish imprisonment. Along with the battles of Battle of Tanga, Tanga, Battle of Sandfontein, Sandfontein, Gallipoli campaign, Gallipoli, and Battle of Namacurra, Namacurra, it would be one of Britain's numerous embarrassing colonial defeats of the war.
Mainly as a result of the increasing firepower (such as machine guns) available to defensive forces, World War I, First World War trench warfare briefly revived a form of siege warfare. Although siege warfare had moved out from an urban setting because city walls had become ineffective against modern weapons, trench warfare was nonetheless able to use many of the techniques of siege warfare in its prosecution (sapping, mining, Artillery, barrage and, of course, Attrition warfare, attrition), but on a much larger scale and on a greatly extended front.
More traditional sieges of fortifications took place in addition to trench sieges. The siege of Tsingtao was one of the first major sieges of the war, but the inability for significant resupply of the German garrison made it a relatively one-sided battle. The Germans and the crew of an Austro-Hungarian protected cruiser put up a hopeless defense and, after holding out for more than a week, surrendered to the Japanese, forcing the German East Asia Squadron to steam towards South America for a new coal source.
The other major siege outside Europe during the First World War was in Mesopotamia, at the siege of Kut. After a failed attempt to move on Baghdad, stopped by the Ottomans at the bloody Battle of Ctesiphon (1915), Battle of Ctesiphon, the British and their large contingent of Indian sepoy soldiers were forced to retreat to Kut, where the Ottomans under German General Colmar Freiherr von der Goltz, Baron Colmar von der Goltz laid siege. The British attempts to resupply the force via the Tigris river failed, and rationing was complicated by the refusal of many Indian troops to eat cattle products. By the time the garrison fell on 29 April 1916, starvation was rampant. Conditions did not improve greatly under Turkish imprisonment. Along with the battles of Battle of Tanga, Tanga, Battle of Sandfontein, Sandfontein, Gallipoli campaign, Gallipoli, and Battle of Namacurra, Namacurra, it would be one of Britain's numerous embarrassing colonial defeats of the war.
 The largest sieges of the war, however, took place in Europe. The initial German advance into Belgium produced four major sieges: the Battle of Liège, the Siege of Namur (1914), siege of Namur, the siege of Maubeuge, and the Siege of Antwerp (1914), siege of Antwerp. All four would prove crushing German victories, at Liège and Namur against the Belgians, at Maubeuge against the French and at Antwerp against a combined Anglo-Belgian force. The weapon that made these victories possible were the German Big Bertha (howitzer), Big Berthas and the Skoda 305 mm Model 1911 siege mortars, one of the best siege mortars of the war, on loan from Austria-Hungary. These huge guns were the decisive weapon of siege warfare in the 20th century, taking part at Przemyśl, the Belgian sieges, on the Italian Front and Serbian Front, and even being reused in World War II.
The largest sieges of the war, however, took place in Europe. The initial German advance into Belgium produced four major sieges: the Battle of Liège, the Siege of Namur (1914), siege of Namur, the siege of Maubeuge, and the Siege of Antwerp (1914), siege of Antwerp. All four would prove crushing German victories, at Liège and Namur against the Belgians, at Maubeuge against the French and at Antwerp against a combined Anglo-Belgian force. The weapon that made these victories possible were the German Big Bertha (howitzer), Big Berthas and the Skoda 305 mm Model 1911 siege mortars, one of the best siege mortars of the war, on loan from Austria-Hungary. These huge guns were the decisive weapon of siege warfare in the 20th century, taking part at Przemyśl, the Belgian sieges, on the Italian Front and Serbian Front, and even being reused in World War II.
 At the siege of Przemyśl, during World War I, the Austro-Hungarian Army, Austro-Hungarian garrison showed excellent knowledge of siege warfare, not only waiting for relief, but sending sorties into Russian lines and employing an active defense that resulted in the capture of the Russian General Lavr Kornilov. Despite its excellent performance, the garrison's food supply had been requisitioned for earlier offensives, a relief expedition was stalled by the weather, ethnic rivalries flared up between the defending soldiers, and a breakout attempt failed. When the commander of the garrison Hermann Kusmanek finally surrendered, his troops were eating their horses and the first attempt of large-scale air supply had failed. It was one of the few great victories obtained by either side during the war; 110,000 Austro-Hungarian prisoners were marched back to Russia. Use of aircraft for siege running, bringing supplies to areas under siege, would nevertheless prove useful in many sieges to come.
The largest siege of the war, and arguably the roughest, most gruesome battle in history, was the Battle of Verdun. Whether the battle can be considered true siege warfare is debatable. Under the theories of Erich von Falkenhayn, it is more distinguishable as purely attrition with a coincidental presence of fortifications on the battlefield. When considering the plans of Wilhelm, German Crown Prince, Crown Prince Wilhelm, purely concerned with taking the citadel and not with French casualty figures, it can be considered a true siege. The main fortifications were Fort Douaumont, Fort Vaux, and the fortified city of Verdun itself. The Germans, through the use of huge artillery bombardments, flamethrowers, and infiltration tactics, were able to capture both Vaux and Douaumont, but were never able to take the city, and eventually lost most of their gains. It was a battle that, despite the French ability to fend off the Germans, neither side won. The German losses were not worth the potential capture of the city, and the French casualties were not worth holding the symbol of her defense.
The development of the armored tank and improved infantry military tactics, tactics at the end of World War I swung the pendulum back in favor of maneuver, and with the advent of Blitzkrieg in 1939, the end of traditional siege warfare was at hand. The Maginot Line would be the prime example of the failure of immobile, post–World War I fortifications. Although sieges would continue, it would be in a totally different style and on a reduced scale.
At the siege of Przemyśl, during World War I, the Austro-Hungarian Army, Austro-Hungarian garrison showed excellent knowledge of siege warfare, not only waiting for relief, but sending sorties into Russian lines and employing an active defense that resulted in the capture of the Russian General Lavr Kornilov. Despite its excellent performance, the garrison's food supply had been requisitioned for earlier offensives, a relief expedition was stalled by the weather, ethnic rivalries flared up between the defending soldiers, and a breakout attempt failed. When the commander of the garrison Hermann Kusmanek finally surrendered, his troops were eating their horses and the first attempt of large-scale air supply had failed. It was one of the few great victories obtained by either side during the war; 110,000 Austro-Hungarian prisoners were marched back to Russia. Use of aircraft for siege running, bringing supplies to areas under siege, would nevertheless prove useful in many sieges to come.
The largest siege of the war, and arguably the roughest, most gruesome battle in history, was the Battle of Verdun. Whether the battle can be considered true siege warfare is debatable. Under the theories of Erich von Falkenhayn, it is more distinguishable as purely attrition with a coincidental presence of fortifications on the battlefield. When considering the plans of Wilhelm, German Crown Prince, Crown Prince Wilhelm, purely concerned with taking the citadel and not with French casualty figures, it can be considered a true siege. The main fortifications were Fort Douaumont, Fort Vaux, and the fortified city of Verdun itself. The Germans, through the use of huge artillery bombardments, flamethrowers, and infiltration tactics, were able to capture both Vaux and Douaumont, but were never able to take the city, and eventually lost most of their gains. It was a battle that, despite the French ability to fend off the Germans, neither side won. The German losses were not worth the potential capture of the city, and the French casualties were not worth holding the symbol of her defense.
The development of the armored tank and improved infantry military tactics, tactics at the end of World War I swung the pendulum back in favor of maneuver, and with the advent of Blitzkrieg in 1939, the end of traditional siege warfare was at hand. The Maginot Line would be the prime example of the failure of immobile, post–World War I fortifications. Although sieges would continue, it would be in a totally different style and on a reduced scale.
World War II
The Blitzkrieg of the Second World War truly showed that fixed fortifications are easily defeated by manoeuvre instead of frontal assault or long sieges. The great Maginot Line was bypassed, and battles that would have taken weeks of siege could now be avoided with the careful application of air power (such as the German paratrooper capture of Fort Eben-Emael, Belgium, early in World War II). The most important siege was the siege of Leningrad, which lasted over 29 months, about half of the duration of the entire Second World War. The siege of Leningrad resulted in the deaths of some List of battles by casualties, one million of the city's inhabitants. Along with the Battle of Stalingrad, the siege of Leningrad on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front was the deadliest siege of a city in history. In the west, apart from the Battle of the Atlantic, the sieges were not on the same scale as those on the European Eastern front; however, there were several notable or critical sieges: the island of Malta, for which the population won the George Cross and Siege of Tobruk, Tobruk. In the South-East Asian theatre of World War II, South-East Asian theatre, there was the siege of Singapore, and in the Burma campaign, sieges of Myitkyina, the Battle of the Admin Box, Admin Box, Battle of Imphal, Imphal, and Battle of Kohima, Kohima, which was the high-water mark for the Japanese advance into British India, India.
The Siege of Sevastopol (1941–1942), siege of Sevastopol saw the use of the heaviest and most powerful individual siege engines ever to be used: the German Schwerer Gustav, 800 mm railway gun and the Karl-Gerät, 600 mm siege mortar. Though a single shell could have disastrous local effect, the guns were susceptible to air attack in addition to being slow to move.
The most important siege was the siege of Leningrad, which lasted over 29 months, about half of the duration of the entire Second World War. The siege of Leningrad resulted in the deaths of some List of battles by casualties, one million of the city's inhabitants. Along with the Battle of Stalingrad, the siege of Leningrad on the Eastern Front (World War II), Eastern Front was the deadliest siege of a city in history. In the west, apart from the Battle of the Atlantic, the sieges were not on the same scale as those on the European Eastern front; however, there were several notable or critical sieges: the island of Malta, for which the population won the George Cross and Siege of Tobruk, Tobruk. In the South-East Asian theatre of World War II, South-East Asian theatre, there was the siege of Singapore, and in the Burma campaign, sieges of Myitkyina, the Battle of the Admin Box, Admin Box, Battle of Imphal, Imphal, and Battle of Kohima, Kohima, which was the high-water mark for the Japanese advance into British India, India.
The Siege of Sevastopol (1941–1942), siege of Sevastopol saw the use of the heaviest and most powerful individual siege engines ever to be used: the German Schwerer Gustav, 800 mm railway gun and the Karl-Gerät, 600 mm siege mortar. Though a single shell could have disastrous local effect, the guns were susceptible to air attack in addition to being slow to move.
Airbridge
Throughout the war both the Western Allies and the Germans tried to supply forces besieged behind enemy lines with ad-hoc Airbridge (logistics), airbridges. Sometimes these attempts failed, as happened to the besieged 6th Army (Wehrmacht), German Sixth Army the Battle of Stalingrad#Sixth Army surrounded, Battle of Stalingrad, and sometimes they succeeded as happened during the Battle of the Admin Box (5 – 23 February 1944) and the short Siege of Bastogne (December 1944). The logistics of strategic airbridge operations were developed by the Americans flying military transport aircraft from India to Republic of China (1912-1949), China over the Hump (1942–1945), to resupply the Second Sino-Japanese War, Chinese war effort of Chiang Kai-shek, and to the USAAF XX Bomber Command (during Operation Matterhorn). Tactical airbridge methods were developed and, as planned, used extensively for supplying the Chindits during Operation Thursday (February – May 1944). The Chindits, a specially trained division of the British Army, British and British Indian Army, Indian armies, were flown deep behind Japanese front lines in the South-East Asian theatre to jungle clearings in Burma where they set up fortified airheads from which they sailed out to attack Japanese lines of communications, while defending the bases from Japanese counterattacks. The bases were re-supplied by air with casualties flown out by returning aircraft. When the Japanese attacked in strength the Chindits abandoned the bases and either moved to new bases, or back to Allied lines.Post-World War II


 Several times during the Cold War the western powers had to use their airbridge expertise.
* The Berlin Blockade from June 1948 to September 1949, the Western Powers flew over 200,000 flights, providing to West Berlin up to 8,893 tons of necessities each day.
* Airbridge was used extensively during the Battle of Dien Bien Phu during the First Indochina War, but failed to prevent its fall to the Việt Minh in 1954.
* In Vietnam War, the next Vietnam War, airbridge proved crucial during the siege of the American base at Battle of Khe Sanh, Khe Sanh in 1968. The resupply it provided kept the People's Army of Vietnam, North Vietnamese Army from capturing the base.
In both Vietnamese cases, the Viet Minh and National Front for the Liberation of South Vietnam, NLF were able to cut off the opposing army by capturing the surrounding rugged terrain. At Dien Bien Phu, the French were unable to use air power to overcome the siege and were defeated. However, at Khe Sanh, a mere 14 years later, advances in air power—and a reduction in Vietnamese anti-aircraft capability—allowed the United States to withstand the siege. The resistance of US forces was assisted by the People's Army of Vietnam, PAVN and Viet Cong, PLAF forces' decision to use the Khe Sanh siege as a strategic distraction to allow their mobile warfare offensive, the first Tet Offensive, to unfold securely.
The Battle of Khe Sanh displays typical features of modern sieges, as the defender has greater capacity to withstand the siege, the attacker's main aim is to bottle operational forces or create a strategic distraction, rather than take the siege to a conclusion.
In neighboring Cambodia, at that time known as the Cambodian coup of 1970, Khmer Republic, the Khmer Rouge used siege tactics to cut off supplies from Phnom Penh to other government-held enclaves in an attempt to break the will of the government to continue fighting.
In 1972, during the Easter offensive, the siege of An Lộc, Bình Phước, An Lộc Vietnam occurred. ARVN troops and U.S. advisers and air power successfully defeated communist forces. The Battle of An Lộc pitted some 6,350 ARVN men against a force three times that size. During the peak of the battle, ARVN had access to only one 105 mm howitzer to provide close support, while the enemy attack was backed by an entire artillery division. ARVN had no tanks, the NVA communist forces had two armoured regiments. ARVN prevailed after over two months of continuous fighting. As General Paul Vanuxem, a French veteran of the Indochina War, wrote in 1972 after visiting the liberated city of An Lộc: "An Lộc was the Verdun of Vietnam, where Vietnam received as in baptism the supreme consecration of her will."
During the 1982 Lebanon War, the Israel Defence Forces Siege of Beirut, besieged Beirut, the capital of Lebanon, to quickly realize their goals including the eviction of the Palestine Liberation Organization from the country.
During the Yugoslav Wars in the 1990s, Republika Srpska forces Siege of Sarajevo, besieged Sarajevo, the capital of Bosnia-Herzegovina. The siege lasted from April 1992 until February 1996.
Numerous sieges haven taken place during the Syrian civil war, such as the siege of Homs, siege of Kobanî, siege of Deir ez-Zor (2014–2017), siege of Nubl and al-Zahraa, and siege of al-Fu'ah and Kafriya.
During various points in the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict, Azerbaijan Siege of Stepanakert, besieged the capital of Stepanakert (1991-1992), as well as the entire Republic of Artsakh, de facto Armenian-controlled republic during the Blockade of Nagorno-Karabakh, Blockade of Nagorno-Karabakh (2022-2023)..
Multiple sieges took place in the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, notably the siege of Mariupol. Other sieges in the war include the Siege of Chernihiv and Siege of Sloviansk.
The Gaza war contained multiple sieges, including the siege of Gaza City and the siege of Khan Yunis.
Several times during the Cold War the western powers had to use their airbridge expertise.
* The Berlin Blockade from June 1948 to September 1949, the Western Powers flew over 200,000 flights, providing to West Berlin up to 8,893 tons of necessities each day.
* Airbridge was used extensively during the Battle of Dien Bien Phu during the First Indochina War, but failed to prevent its fall to the Việt Minh in 1954.
* In Vietnam War, the next Vietnam War, airbridge proved crucial during the siege of the American base at Battle of Khe Sanh, Khe Sanh in 1968. The resupply it provided kept the People's Army of Vietnam, North Vietnamese Army from capturing the base.
In both Vietnamese cases, the Viet Minh and National Front for the Liberation of South Vietnam, NLF were able to cut off the opposing army by capturing the surrounding rugged terrain. At Dien Bien Phu, the French were unable to use air power to overcome the siege and were defeated. However, at Khe Sanh, a mere 14 years later, advances in air power—and a reduction in Vietnamese anti-aircraft capability—allowed the United States to withstand the siege. The resistance of US forces was assisted by the People's Army of Vietnam, PAVN and Viet Cong, PLAF forces' decision to use the Khe Sanh siege as a strategic distraction to allow their mobile warfare offensive, the first Tet Offensive, to unfold securely.
The Battle of Khe Sanh displays typical features of modern sieges, as the defender has greater capacity to withstand the siege, the attacker's main aim is to bottle operational forces or create a strategic distraction, rather than take the siege to a conclusion.
In neighboring Cambodia, at that time known as the Cambodian coup of 1970, Khmer Republic, the Khmer Rouge used siege tactics to cut off supplies from Phnom Penh to other government-held enclaves in an attempt to break the will of the government to continue fighting.
In 1972, during the Easter offensive, the siege of An Lộc, Bình Phước, An Lộc Vietnam occurred. ARVN troops and U.S. advisers and air power successfully defeated communist forces. The Battle of An Lộc pitted some 6,350 ARVN men against a force three times that size. During the peak of the battle, ARVN had access to only one 105 mm howitzer to provide close support, while the enemy attack was backed by an entire artillery division. ARVN had no tanks, the NVA communist forces had two armoured regiments. ARVN prevailed after over two months of continuous fighting. As General Paul Vanuxem, a French veteran of the Indochina War, wrote in 1972 after visiting the liberated city of An Lộc: "An Lộc was the Verdun of Vietnam, where Vietnam received as in baptism the supreme consecration of her will."
During the 1982 Lebanon War, the Israel Defence Forces Siege of Beirut, besieged Beirut, the capital of Lebanon, to quickly realize their goals including the eviction of the Palestine Liberation Organization from the country.
During the Yugoslav Wars in the 1990s, Republika Srpska forces Siege of Sarajevo, besieged Sarajevo, the capital of Bosnia-Herzegovina. The siege lasted from April 1992 until February 1996.
Numerous sieges haven taken place during the Syrian civil war, such as the siege of Homs, siege of Kobanî, siege of Deir ez-Zor (2014–2017), siege of Nubl and al-Zahraa, and siege of al-Fu'ah and Kafriya.
During various points in the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict, Nagorno-Karabakh Conflict, Azerbaijan Siege of Stepanakert, besieged the capital of Stepanakert (1991-1992), as well as the entire Republic of Artsakh, de facto Armenian-controlled republic during the Blockade of Nagorno-Karabakh, Blockade of Nagorno-Karabakh (2022-2023)..
Multiple sieges took place in the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine, notably the siege of Mariupol. Other sieges in the war include the Siege of Chernihiv and Siege of Sloviansk.
The Gaza war contained multiple sieges, including the siege of Gaza City and the siege of Khan Yunis.
Police sieges
 Siege tactics continue to be employed in police contexts; such a siege is typically called a standoff or, in law enforcement jargon, a barricade situation. Standoffs may result from crimes and incidents such as Robbery, robberies, Police raid, raids, Search warrant, search and arrest warrants, prison riots, or Terrorism, terrorist attacks. Standoffs occur due to a variety of factors, most prominently the safety of police (against whom the besieged may have the upper hand), the besieged suspects (who police generally intend to arrest), bystanders (who may be in the crossfire), and hostages (who may be injured or killed by the suspects).
The optimal result of most standoffs is a peaceful resolution: the safe extraction of hostages and bystanders, and the peaceful surrender and arrest of the hostage-takers. To ensure this, police make use of trained Crisis negotiation, negotiators and Criminal psychology, psychologists to learn the hostage-takers' demands (and meet said demands if feasible or permissible), gain the hostage-takers' trust, clarify that police do not intend to kill them or will even Crime scene getaway, let them go (regardless of whether such claims are true), and coax the hostage-takers into surrendering or at least releasing hostages. In the event a peaceful resolution is impossible—negotiations fail or do not proceed, hostages are released but the hostage-takers refuse to surrender, the hostage-takers resist violently, or hostages are killed—police may respond in force, generally being able to rely on police tactical units or even
Siege tactics continue to be employed in police contexts; such a siege is typically called a standoff or, in law enforcement jargon, a barricade situation. Standoffs may result from crimes and incidents such as Robbery, robberies, Police raid, raids, Search warrant, search and arrest warrants, prison riots, or Terrorism, terrorist attacks. Standoffs occur due to a variety of factors, most prominently the safety of police (against whom the besieged may have the upper hand), the besieged suspects (who police generally intend to arrest), bystanders (who may be in the crossfire), and hostages (who may be injured or killed by the suspects).
The optimal result of most standoffs is a peaceful resolution: the safe extraction of hostages and bystanders, and the peaceful surrender and arrest of the hostage-takers. To ensure this, police make use of trained Crisis negotiation, negotiators and Criminal psychology, psychologists to learn the hostage-takers' demands (and meet said demands if feasible or permissible), gain the hostage-takers' trust, clarify that police do not intend to kill them or will even Crime scene getaway, let them go (regardless of whether such claims are true), and coax the hostage-takers into surrendering or at least releasing hostages. In the event a peaceful resolution is impossible—negotiations fail or do not proceed, hostages are released but the hostage-takers refuse to surrender, the hostage-takers resist violently, or hostages are killed—police may respond in force, generally being able to rely on police tactical units or even military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
support if possible and required.
 Most standoffs are much shorter than military sieges, often lasting hours or days at most. Lengthy sieges may still occur, albeit rarely, such as the 51-day-long 1993 Waco siege. Most standoffs end in a peaceful resolution (i.e. 1973 Brooklyn hostage crisis, 1997 Roby standoff), though some may end in a police or military assault (i.e. 1994 Air France Flight 8969, Air France Flight 8969 hijacking, 1980 Iranian Embassy siege) or, in the worst-case scenarios, the deaths of authorities, hostage-takers, or hostages (i.e. 1985 1985 MOVE bombing, MOVE bombing, 1985 EgyptAir Flight 648, EgyptAir Flight 648 hijacking, 2004 Beslan school siege, 2022 Robb Elementary School shooting). The aforementioned worst-case scenarios often result from poor planning, tactics, or negotiations on the part of the authorities (e.g. accidental killings of hostages by Unit 777 during the EgyptAir Flight 648 hijacking), or from violent acts committed by the hostage-takers (e.g. Suicide attack, suicide bombings and executions during the Beslan school siege).
In some jurisdictions, depending on certain circumstances, standoffs that would usually be handled by police may be transferred to the military. For example, in the United Kingdom, standoffs with terrorists may be transferred to military responsibility for a military assault on the besieged. The threat of such an action ended the 1975 Balcombe Street siege, but the 1980 Iranian Embassy siege ended in a military assault and the deaths of all but one of the hostage-takers.
Most standoffs are much shorter than military sieges, often lasting hours or days at most. Lengthy sieges may still occur, albeit rarely, such as the 51-day-long 1993 Waco siege. Most standoffs end in a peaceful resolution (i.e. 1973 Brooklyn hostage crisis, 1997 Roby standoff), though some may end in a police or military assault (i.e. 1994 Air France Flight 8969, Air France Flight 8969 hijacking, 1980 Iranian Embassy siege) or, in the worst-case scenarios, the deaths of authorities, hostage-takers, or hostages (i.e. 1985 1985 MOVE bombing, MOVE bombing, 1985 EgyptAir Flight 648, EgyptAir Flight 648 hijacking, 2004 Beslan school siege, 2022 Robb Elementary School shooting). The aforementioned worst-case scenarios often result from poor planning, tactics, or negotiations on the part of the authorities (e.g. accidental killings of hostages by Unit 777 during the EgyptAir Flight 648 hijacking), or from violent acts committed by the hostage-takers (e.g. Suicide attack, suicide bombings and executions during the Beslan school siege).
In some jurisdictions, depending on certain circumstances, standoffs that would usually be handled by police may be transferred to the military. For example, in the United Kingdom, standoffs with terrorists may be transferred to military responsibility for a military assault on the besieged. The threat of such an action ended the 1975 Balcombe Street siege, but the 1980 Iranian Embassy siege ended in a military assault and the deaths of all but one of the hostage-takers.
See also
* ''Battleplan'' (documentary TV series) * Blitzkrieg * Breastwork (fortification) * Infiltration tactics, Infiltration * Last stand * Maneuver warfare * Medieval warfare * Sangar (fortification) * :Siege engines, Siege engines * :Siege equipment, Siege equipment * Tunnel warfare ; Lists: * List of established military terms * List of siegesNotes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * * Historiography *External links
Secrets of Lost Empires: Medieval Siege
(PBS) Informative and interactive webpages about medieval siege tactics. {{Authority control Sieges, Military strategy Siege warfare, *