|
Mundigak
Mundigak ( ps, منډیګک) is an archaeological site in Kandahar province in Afghanistan Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere .... During the Bronze Age, it was a center of the Helmand culture. It is situated approximately northwest of Kandahar near Shāh Maqsūd, on the upper drainage of the Kushk-i Nakhud River. History Mundigak was a large prehistoric town with an important cultural sequence from the 5th–2nd millennia BCE. It was excavated by the French scholar Jean Marie Casal in the 1950s The mound was nine meters tall at the time of excavation. Pottery and other artifacts of the later 3rd millennium BCE, when this became a major urban center, indicate interaction with Turkmenistan, Baluchistan, and the Early Harappan Indus region. Mundigak flourished during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mundigak Iv English
Mundigak ( ps, منډیګک) is an archaeological site in Kandahar province in Afghanistan. During the Bronze Age, it was a center of the Helmand culture. It is situated approximately northwest of Kandahar near Shāh Maqsūd, on the upper drainage of the Kushk-i Nakhud River. History Mundigak was a large prehistoric town with an important cultural sequence from the 5th–2nd millennia BCE. It was excavated by the French scholar Jean Marie Casal in the 1950s The mound was nine meters tall at the time of excavation. Pottery and other artifacts of the later 3rd millennium BCE, when this became a major urban center, indicate interaction with Turkmenistan, Baluchistan, and the Early Harappan Indus region. Mundigak flourished during the culture of Helmand Basin (Seistan), also known as Helmand culture (Helmand Province). With an area of , this was the second largest centre of Helmand Culture, the first being Shahr-i-Sokhta which was as large as 150 acres (60 hectares), by 2400 BCE. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mundigak Temple Plan
Mundigak ( ps, منډیګک) is an archaeological site in Kandahar province in Afghanistan. During the Bronze Age, it was a center of the Helmand culture. It is situated approximately northwest of Kandahar near Shāh Maqsūd, on the upper drainage of the Kushk-i Nakhud River. History Mundigak was a large prehistoric town with an important cultural sequence from the 5th–2nd millennia BCE. It was excavated by the French scholar Jean Marie Casal in the 1950s The mound was nine meters tall at the time of excavation. Pottery and other artifacts of the later 3rd millennium BCE, when this became a major urban center, indicate interaction with Turkmenistan, Baluchistan, and the Early Harappan Indus region. Mundigak flourished during the culture of Helmand Basin (Seistan), also known as Helmand culture (Helmand Province). With an area of , this was the second largest centre of Helmand Culture, the first being Shahr-i-Sokhta which was as large as 150 acres (60 hectares), by 2400 BCE. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mundigak Level 1
Mundigak ( ps, منډیګک) is an archaeological site in Kandahar province in Afghanistan. During the Bronze Age, it was a center of the Helmand culture. It is situated approximately northwest of Kandahar near Shāh Maqsūd, on the upper drainage of the Kushk-i Nakhud River. History Mundigak was a large prehistoric town with an important cultural sequence from the 5th–2nd millennia BCE. It was excavated by the French scholar Jean Marie Casal in the 1950s The mound was nine meters tall at the time of excavation. Pottery and other artifacts of the later 3rd millennium BCE, when this became a major urban center, indicate interaction with Turkmenistan, Baluchistan, and the Early Harappan Indus region. Mundigak flourished during the culture of Helmand Basin (Seistan), also known as Helmand culture (Helmand Province). With an area of , this was the second largest centre of Helmand Culture, the first being Shahr-i-Sokhta which was as large as 150 acres (60 hectares), by 2400 BCE. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahr-e Sukhteh
Shahr-e Sukhteh ( fa, شهر سوخته, meaning " heBurnt City"), c. 3200–2350 BCE, also spelled as ''Shahr-e Sūkhté'' and ''Shahr-i Sōkhta'', is an archaeological site of a sizable Bronze Age urban settlement, associated with the Helmand culture. It is located in Sistan and Baluchistan Province, the southeastern part of Iran, on the bank of the Helmand River, near the Zahedan-Zabol road. It was placed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in June 2014. The reasons for the unexpected rise and fall of the city are still wrapped in mystery. Artifacts recovered from the city demonstrate a peculiar incongruity with nearby civilizations of the time and it has been speculated that Shahr-e-Sukhteh might ultimately provide concrete evidence of a civilization east of prehistoric Persia that was independent of ancient Mesopotamia. Archaeology Covering an area of 151 hectares, Shahr-e Sukhteh was one of the world's largest cities at the dawn of the urban era. It is located close to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahr-i-Sokhta
Shahr-e Sukhteh ( fa, شهر سوخته, meaning "[The] Burnt City"), c. 3200–2350 BCE, also spelled as ''Shahr-e Sūkhté'' and ''Shahr-i Sōkhta'', is an archaeological site of a sizable Bronze Age urban settlement, associated with the Helmand culture. It is located in Sistan and Baluchistan Province, the southeastern part of Iran, on the bank of the Helmand River, near the Zahedan-Zabol road. It was placed on the UNESCO World Heritage List in June 2014. The reasons for the unexpected rise and fall of the city are still wrapped in mystery. Artifacts recovered from the city demonstrate a peculiar incongruity with nearby civilizations of the time and it has been speculated that Shahr-e-Sukhteh might ultimately provide concrete evidence of a civilization east of prehistoric Persia that was independent of ancient Mesopotamia. Archaeology Covering an area of 151 hectares, Shahr-e Sukhteh was one of the world's largest cities at the dawn of the urban era. It is located close to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
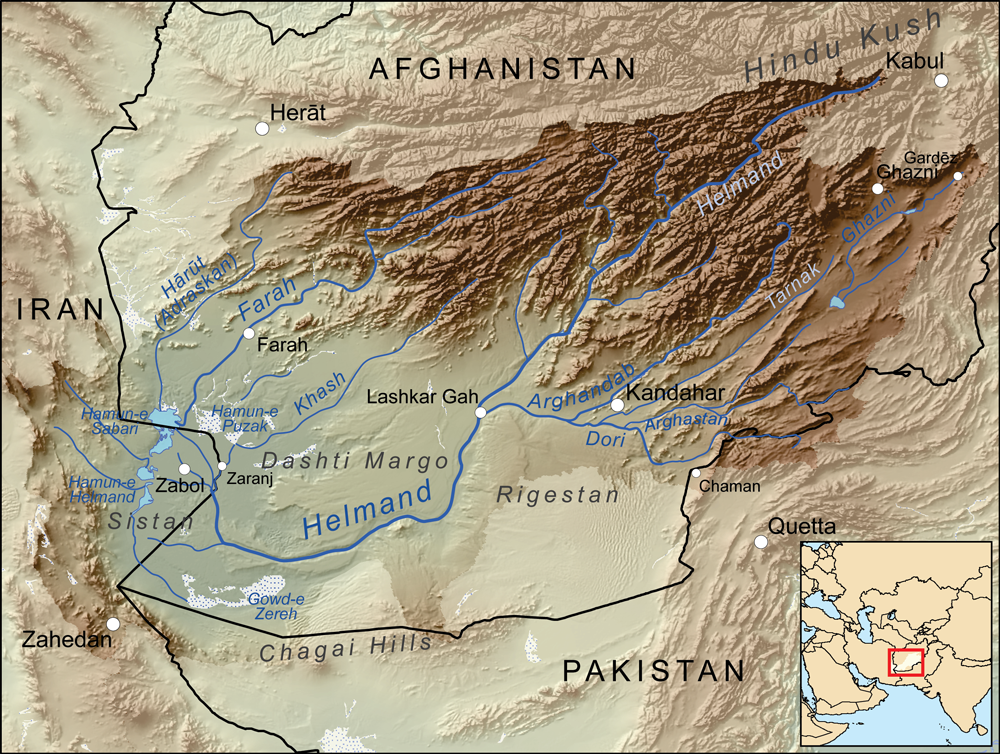
Helmand Culture
Pottery vessel from Shahr-e Sukhteh The Helmand culture (also Helmand civilization), c. 3300-2350 BCE,Vidale, Massimo, (15 March, 2021)"A Warehouse in 3rd Millennium B.C. Sistan and Its Accounting Technology" in Seminar "Early Urbanization in Iran". is a Bronze Age culture that flourished mainly in the middle and lower valley of the Helmand River, in southern Afghanistan (Kandahar, Helmand and Nimruz provinces) and eastern Iran ( Sistan and Baluchestan Province), predominantly in the third millennium BCE. The people of the Helmand culture lived partly in cities with temples and palaces, providing evidence for a complex and advanced social structure. The main cities so far known are Shahr-i Sokhta (in modern Iran) and Mundigak (Afghanistan). Research on the finds from both places showed that these cities shared the same culture. These are the earliest discovered cities in this part of the world, although the village Mehrgarh further to the south east is considerably older. It is pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmand Province
Helmand (Pashto/Dari: ; ), also known as Hillmand, in ancient times, as Hermand and Hethumand, is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan Afghanistan is divided into 34 provinces (, '' wilåyat''). The provinces of Afghanistan are the primary administrative divisions. Each province encompasses a number of districts or usually over 1,000 villages. Provincial governors played a cr ..., in the south of the country. It is the largest province by area, covering area. The province contains 13 Districts of Afghanistan, districts, encompassing over 1,000 villages, and roughly 1,446,230 settled people. Lashkargah serves as the provincial capital. Helmand was part of the ''Loy Kandahar, Greater Kandahar'' region until made into a separate province by the Politics of Afghanistan, Afghan government in the 20th century. The Helmand River flows through the mainly desert region of the province, providing water used for irrigation. The Kajaki Dam, which is one of List of dams and reservoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kandahar
Kandahar (; Kandahār, , Qandahār) is a List of cities in Afghanistan, city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118. It is the capital of Kandahar Province as well as the de facto capital of the Taliban, formally known as the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. It also happens to be the centre of the larger cultural region called Loy Kandahar. In 1709, Mirwais Hotak made the region an independent kingdom and turned Kandahar into the capital of the Hotak dynasty. In 1747, Ahmad Shah Durrani, founder of the Durrani dynasty, made Kandahar the capital of the Durrani Empire, Afghan Empire. Historically this province is considered as important political area for Afghanistan revelations. Kandahar is one of the most culturally significant cities of the Pashtun people, Pashtuns and has been their traditional seat of power for more than 300 years. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kot Diji
The ancient site at Kot Diji ( sd, ڪوٽ ڏیجي; ur, کوٹ ڈیجی) was the forerunner of the Indus Civilization. The occupation of this site is attested already at 3300 BCE. The remains consist of two parts; the citadel area on high ground (about )), and outer area. The Pakistan Department of Archaeology excavated at Kot Diji in 1955 and 1957. Located about ) south of Khairpur in the province of Sindh, Pakistan, it is on the east bank of the Indus opposite Mohenjo-daro. The site is situated at the foot of the Rohri Hills where a fort (Kot Diji Fort) was built around 1790 by the Talpur dynasty ruler of Upper Sindh, Mir Suhrab, who reigned from 1783 to 1830 AD. This fort built on the ridge of a steep narrow hill is well-preserved. Cultural context The earliest site of this culture is Kunal (4000 BCE) in Haryana which is older than Rehman Dheri (3300 BCE). The ''type site'', the first excavated site of this type of culture is Kot Diji. Rehman Dheri, which was consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran border, west, Turkmenistan to the Afghanistan–Turkmenistan border, northwest, Uzbekistan to the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan border, north, Tajikistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, northeast, and China to the Afghanistan–China border, northeast and east. Occupying of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains Afghan Turkestan, in the north and Sistan Basin, the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. , Demographics of Afghanistan, its population is 40.2 million (officially estimated to be 32.9 million), composed mostly of ethnic Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, and Uzbeks. Kabul is the country's largest city and ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bampur
Bampur ( bal, بُنپور, fa, بمپور, also Romanized as Bampūr and Bampoor) is a city in and capital of Bampur County, Sistan and Baluchestan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 9,073, in 1,664 families. Location It is located south-east of Kerman at an elevation of In 1911 its population was about 2,000 and it was the capital of the province. It is situated on the banks of the Bampur river which flows from east to west and empties itself about west into a ''hamun'', or depression, in length, and called Jaz Murian. History The old citadel of Bampur, on a hill about high north of the river, fell into ruins. A new fort called Kalah Nasseri, was built at Pahrah, which is known as Iranshahr, further east, in the 1880s. Fahraj, which in 1911 had a population of about 2,500, has become more important than Bampur. Fahraj, which is also known as Pahura (or Paharu or Puhra), is by some identified as the Poura where Alexander the Great halted on his ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deh Morasi Ghundai
Deh or DEH may refer to: *Deh (Pakistan), a type of administrative unit of Pakistan *Deh, India, a village in Nagaur, Rajasthan, India * Deh, Cambodia, a village in Bar Kham, Cambodia *''Dear Evan Hansen'', a 2015/2016 Broadway musical by Pasek and Paul ** ''Dear Evan Hansen'' (film), a 2021 film adaptation of the musical *Decorah Municipal Airport (IATA and FAA code: DEH), an airport near Decorah, in Winneshiek County, Iowa, U.S. *deh, the ISO 639-3 code of the Dehwari language Dehwari (, Dehwārī) is a southwestern Persian language spoken by c. 14,000 Dehwar people in Balochistan, Pakistan. Most of the Dehwari speakers are concentrated in Mastung, Khuzdar, Nushk, Kharan, Sarlath District, Dalbandin, and Kalat. I ... See also * {{Disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |