Siberian Internees on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive
 Siberia in
Siberia in

 By the mid-17th century, Russia had established areas of control that extended to the Pacific Ocean. Some 230,000 Russians had settled in Siberia by 1709. Siberia became one of the destinations for sending internal
By the mid-17th century, Russia had established areas of control that extended to the Pacific Ocean. Some 230,000 Russians had settled in Siberia by 1709. Siberia became one of the destinations for sending internal
 In the early decades of the
In the early decades of the

 The Central Siberian Plateau is an ancient
The Central Siberian Plateau is an ancient
"Pleistocene Park: Return of the mammoths' ecosystem"
In: ''
www.pleistocenepark.ru/en/ – Materials.
Retrieved 5 May 2013. According to Vasily Kryuchkov, approximately 31,000 square kilometers of the Russian Arctic has been subjected to severe environmental disturbance.
 *
*
 *
*
 *
*
 * ''
* ''

 The term "Siberia" has both a long history and wide significance, and association. The understanding, and association of "Siberia" have gradually changed during the ages. Historically, Siberia was defined as the whole part of Russia and North Kazakhstan to the east of
The term "Siberia" has both a long history and wide significance, and association. The understanding, and association of "Siberia" have gradually changed during the ages. Historically, Siberia was defined as the whole part of Russia and North Kazakhstan to the east of 
 The Yenisey Krasnoyarsk basketball team has played in the
The Yenisey Krasnoyarsk basketball team has played in the
 The largest ethnic group in Siberia is Slavic-origin Russians, including their sub-ethnic group Siberians, and russified Ukrainians in Siberia, Ukrainians. Slavs, Slavic and other Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European ethnicities make up the vast majority (over 85%) of the Siberian population. There are also other groups of Indigenous Siberian and non-Indigenous ethnic origin. A minority of the current population are descendants of Mongol or Turkic people (mainly
The largest ethnic group in Siberia is Slavic-origin Russians, including their sub-ethnic group Siberians, and russified Ukrainians in Siberia, Ukrainians. Slavs, Slavic and other Proto-Indo-Europeans, Indo-European ethnicities make up the vast majority (over 85%) of the Siberian population. There are also other groups of Indigenous Siberian and non-Indigenous ethnic origin. A minority of the current population are descendants of Mongol or Turkic people (mainly
 There are a variety of beliefs throughout Siberia, including Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christianity, other denominations of Christianity, Tibetan Buddhism and Islam. The
There are a variety of beliefs throughout Siberia, including Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christianity, other denominations of Christianity, Tibetan Buddhism and Islam. The
''East of the Sun: the epic conquest and tragic history of Siberia''
(Henry Holt and Company, 1993); popular history * * Diment, Galya, and Yuri Slezkine, eds. ''Between Heaven and Hell: The Myth of Siberia in Russian Culture'' (3rd ed. 1993) * * Forsyth, James. ''A History of the Peoples of Siberia: Russia's North Asian Colony, 1581–1990'' (Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 1994). * * Kotkin, Stephen, and David Wolff, eds. (1995)
''Rediscovering Russia in Asia''
* * Lincoln, W. Bruce (1993
''The Conquest of a Continent''
Scholarly history. * * * * * Wood, Alan (ed.)(1991). ''The History of Siberia: From Russian Conquest to Revolution''. London: Routledge. * {{Authority control Siberia, Eurasian Steppe Geography of Russia Regions of Russia Geography of Kazakhstan
geographical region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
comprising all of North Asia
North Asia or Northern Asia () is the northern region of Asia, which is defined in geography, geographical terms and consists of three federal districts of Russia: Ural Federal District, Ural, Siberian Federal District, Siberian, and the Far E ...
, from the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ),; , ; , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north–south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.
in the west to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
and its predecessor states since the lengthy conquest of Siberia, which began with the fall
Autumn, also known as fall (especially in US & Canada), is one of the four temperate seasons on Earth. Outside the tropics, autumn marks the transition from summer to winter, in September (Northern Hemisphere) or March ( Southern Hemispher ...
of the Khanate of Sibir
The Khanate of Sibir (; ) was a Tatar state in western Siberia. It was founded at the end of the 15th century, following the break-up of the Golden Horde.Сибирское ханство // Большая советская энцикл ...
in 1582 and concluded with the annexation of Chukotka in 1778. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to roughly a quarter of Russia's population. Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siber ...
, Krasnoyarsk
Krasnoyarsk is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative center of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is situated along the Yenisey, Yenisey River, and is the second-largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk, with a p ...
, and Omsk
Omsk (; , ) is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Omsk Oblast, Russia. It is situated in southwestern Siberia and has a population of over one million. Omsk is the third List of cities and tow ...
are the largest cities in the area.
Because Siberia is a geographic and historic concept and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia spans the entire expanse of land from the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ),; , ; , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north–south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.
to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
, with the Ural River
The Ural, also known as the Yaik , is a river flowing through Russia and Kazakhstan in the continental border between Europe and Asia. It originates in the southern Ural Mountains and discharges into the Caspian Sea. At , it is the third-longes ...
usually forming the southernmost portion of its western boundary, and includes most of the drainage basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, ...
of the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
. It is further defined as stretching from the territories within the Arctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the northernmost of the five major circle of latitude, circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth at about 66° 34' N. Its southern counterpart is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circl ...
in the north to the northern borders of Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
, and China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
in the south, although the hills of north-central Kazakhstan are also commonly included. The Russian government divides the region into three federal districts
A federal district is a specific administrative division in one of various federations. These districts may be under the direct jurisdiction of a federation's national government, as in the case of federal territory (e.g., India, Malaysia), or th ...
(groupings of Russian federal subjects), of which only the central one is officially referred to as "Siberian
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states si ...
"; the other two are the Ural and Far Eastern
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In modern times, the term ''F ...
federal districts, named for the Ural and Russian Far East
The Russian Far East ( rus, Дальний Восток России, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asia, Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Easte ...
regions that correspond respectively to the western and eastern thirds of Siberia in the broader sense.
Siberia is known for its long, harsh winters, with a January average of −25 °C (−13 °F). Although it is geographically located in Asia, Russian sovereignty and colonization since the 16th century has led to perceptions of the region as culturally and ethnically European. Over 85% of its population are of European descent
White is a Race (human categorization), racial classification of people generally used for those of predominantly Ethnic groups in Europe, European ancestry. It is also a Human skin color, skin color specifier, although the definition can var ...
, chiefly Russian (comprising the Siberian
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states si ...
sub-ethnic group), and Eastern Slavic
East Slavic may refer to:
* East Slavic languages, one of three branches of the Slavic languages
* East Slavs, a subgroup of Slavic peoples who speak the East Slavic languages
See also
* Old East Slavic
Old East Slavic (traditionally also Ol ...
cultural influences predominate throughout the region. Nevertheless, there exist sizable ethnic minorities of Asian lineage, including various Turkic communities—many of which, such as the Yakuts
The Yakuts or Sakha (, ; , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to North Siberia, primarily the Republic of Sakha in the Russian Federation. They also inhabit some districts of the Krasnoyarsk Krai. They speak Yakut, which belongs to the Si ...
, Tuvans
The Tuvans (from Russian ) or Tyvans (from Tuvan ) are a Turkic ethnic group indigenous to Siberia that live in Tuva, Mongolia, and China. They speak the Tuvan language, a Siberian Turkic language. In Mongolia, they are regarded as one ...
, Altai, and Khakas
The Khakas are a Turkic indigenous people of Siberia, who live in the republic of Khakassia, Russia. They speak the Khakas language.
The Khakhassian people are direct descendants of various ancient cultures that have inhabited southern Siberia ...
, are Indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology)
In biogeography, a native species is indigenous to a given region or ecosystem if its presence in that region is the result of only local natural evolution (though often populari ...
—along with the Mongolic Buryats
The Buryats are a Mongolic ethnic group native to southeastern Siberia who speak the Buryat language. They are one of the two largest indigenous groups in Siberia, the other being the Yakuts. The majority of the Buryats today live in their ti ...
, ethnic Koreans
Koreans are an East Asian ethnic group native to the Korean Peninsula. The majority of Koreans live in the two Korean sovereign states of North and South Korea, which are collectively referred to as Korea. As of 2021, an estimated 7.3 m ...
, and smaller groups of Samoyedic and Tungusic peoples (several of whom are classified as Indigenous small-numbered peoples by the Russian government), among many others.
Etymology
The origin of the name is uncertain. In the Russian language, it was adopted as a toponym through contact with theKhanate of Sibir
The Khanate of Sibir (; ) was a Tatar state in western Siberia. It was founded at the end of the 15th century, following the break-up of the Golden Horde.Сибирское ханство // Большая советская энцикл ...
(Сибирское ханство) since the 15th century. The Russian name ''Yugra
Yugra or Yugor Land (; also spelled ''Iuhra'' in contemporary sources) was a collective name for lands and peoples in the region east of the northern Ural Mountains in modern Russia given by Russian chroniclers in the 12th to 17th centuries. Du ...
'' was applied to the northern lands east of the Urals
The Ural Mountains ( ),; , ; , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north–south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.
, which had been known of since the 11th century or earlier, while the name ''Siberia'' is first mentioned in Russian chronicles at the start of the 15th century in connection with the death of the khan Tokhtamysh
Tokhtamysh ( Turki/ Kypchak and Persian: توقتمش; ; ; – 1406) was Khan of the Golden Horde from 1380 to 1395. He briefly succeeded in consolidating the Blue and White Hordes into a single polity.
Tokhtamysh belonged to the House of Bo ...
, in "the Siberian land".
Some sources say that "Siberia" originates from the Siberian Tatar
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states sin ...
word for 'sleeping land' (''Sib-ir''), but this discourse does not correspond to the actual Siberian Tatar language. Mongolist György Kara
György Kara (born György Katulics, 23 June 1935 – 16 April 2022) was a Hungarian orientalist, philologist, and specialist in Mongol studies and Mongolian language, Mongolian philology.
Biography
György Kara came from a working class fami ...
posits that the toponym ''Siberia'' is derived from a Mongolic word ''sibir'', cognate with modern Buryat ''sheber'' 'dense forest'. A different hypothesis claims that the region was named after the Sibe people
The Sibe are a Tungusic languages, Tungusic-speaking East Asian people, East Asian ethnic group living mostly in Xinjiang, Jilin and Shenyang in Liaoning. The Sibe form one of the 56 List of ethnic groups in China, ethnic groups officially recogn ...
. Another account sees the name as the ancient tribal ethnonym of the Sihirtia or Sirtya (also ''Sypyr'' ʲɵpᵻr), a hypothetical Paleo-Asiatic ethnic group assimilated by the Nenets
The Nenets (; ), in the past also called 'Samoyeds' or 'Yuraks', are a Samoyedic ethnic group native to Arctic Russia, Russian Far North. According to the latest census in 2021, there were 49,646 Nenets in the Russian Federation, most of them l ...
.
The Polish historian Jan Chyliczkowski has proposed that the name derives from the Proto-Slavic
Proto-Slavic (abbreviated PSl., PS.; also called Common Slavic or Common Slavonic) is the unattested, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages. It represents Slavic speech approximately from the 2nd millennium BC through the 6th ...
word for 'north' (cf. Russian север ''sever''), as in Severia
Severia (, ; ) or Siveria ( / , ''Siveria'' / ''Sivershchyna'') is a historical region in present-day southwest Russia, northern Ukraine, and eastern Belarus. The largest part lies in modern Russia, while the central part of the region is the c ...
. Anatole Baikaloff has dismissed this explanation. He said that the neighboring Chinese, Turks, and Mongolians, who have similar names for the region, would not have known Russian. He suggested that the name might be a combination of two words with Turkic origin, ''su'' 'water' and ''bir'' 'wild land'.
History
Prehistory
 Siberia in
Siberia in Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma a ...
times formed the continent of Siberia/Angaraland, which fused to Euramerica
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pa ...
during the Late Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
, as part of the formation of Pangea
Pangaea or Pangea ( ) was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia (continent), Siberia during the Carboniferous period ...
.
The Siberian Traps
The Siberian Traps () are a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the trap rock, traps is one of the largest known Volcano, volcanic events in the last years ...
were formed by one of the largest-known volcanic events of the last 251 million years of Earth's geological history
The geological history of Earth follows the major geological events in Earth's past based on the geologic time scale, a system of chronological measurement based on the study of the planet's rock layers (stratigraphy). Earth formed approximat ...
. Their activity continued for a million years and some scientists consider it a possible cause of the " Great Dying" about 250 million years ago, – estimated to have killed 90% of species existing at the time.
The region has paleontological
Paleontology, also spelled as palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of the life of the past, mainly but not exclusively through the study of fossils. Paleontologists use fossils as a means to classify organisms, measure geolo ...
significance, as it contains bodies of prehistoric
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
animals from the Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
Epoch
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided b ...
, preserved in ice or permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
. Specimens of Goldfuss cave lion cubs, Yuka
Yuka may refer to:
*Yuka (music), an Afro-Cuban style of music
*Yuka (mammoth), mammoth specimen found in Yakutia, Russia
*Manshu Yuka Kogyo K.K. Ssuningkai, a Japanese-German pre-WWII industrial co-operation
People
*Yuka (name), a Japanese pers ...
the mammoth and another woolly mammoth
The woolly mammoth (''Mammuthus primigenius'') is an extinct species of mammoth that lived from the Middle Pleistocene until its extinction in the Holocene epoch. It was one of the last in a line of mammoth species, beginning with the African ...
from Oymyakon
Oymyakon is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, rural locality (a ''village#Russia, selo'') in Oymyakonsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located in the Yana-Oymyakon Highlands, along the Indigirka River, northwest of Tomtor, Oy ...
, a woolly rhinoceros
The woolly rhinoceros (''Coelodonta antiquitatis'') is an extinct species of rhinoceros that inhabited northern Eurasia during the Pleistocene epoch. The woolly rhinoceros was a member of the Pleistocene megafauna. The woolly rhinoceros was larg ...
from the Kolyma
Kolyma (, ) or Kolyma Krai () is a historical region in the Russian Far East that includes the basin of Kolyma River and the northern shores of the Sea of Okhotsk, as well as the Kolyma Mountains (the watershed of the two). It is bounded to ...
, and bison
A bison (: bison) is a large bovine in the genus ''Bison'' (from Greek, meaning 'wild ox') within the tribe Bovini. Two extant taxon, extant and numerous extinction, extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American ...
and horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
s from Yukagir
Yukagir (; ) is a rural locality (a '' selo''), the only inhabited locality and the administrative center of Yukagirsky National (Nomadic) Rural Okrug of Ust-Yansky District in the Sakha Republic, Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federatio ...
have been found. Remote Wrangel Island
Wrangel Island (, ; , , ) is an island of the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Russia. It is the List of islands by area, 92nd-largest island in the world and roughly the size of Crete. Located in the Arctic Ocean between the Chukchi Sea and East Si ...
and the Taymyr Peninsula
The Taymyr Peninsula ( ) is a peninsula in the Far North of Russia, in the Siberian Federal District, that forms the northernmost part of the mainland of Eurasia. Administratively it is part of the Krasnoyarsk Krai Federal subject of Russia.
Ge ...
are believed to have been the last places on Earth to support woolly mammoths as isolated populations until their extinction around 2000 BC.
At least three species of humans lived in southern Siberia around 40,000 years ago: '' H. sapiens'', ''H. neanderthalensis
Neanderthals ( ; ''Homo neanderthalensis'' or sometimes ''H. sapiens neanderthalensis'') are an extinct group of archaic humans who inhabited Europe and Western and Central Asia during the Middle to Late Pleistocene. Neanderthal extinctio ...
'', and the Denisovans
The Denisovans or Denisova hominins ( ) are an extinct species or subspecies of archaic human that ranged across Asia during the Lower Paleolithic, Lower and Middle Paleolithic, and lived, based on current evidence, from 285 thousand to 25 thou ...
.
In 2010, DNA evidence identified the last as a separate species.
Late Paleolithic southern Siberians appear to be related to Paleolithic Europeans and the Paleolithic Jōmon people
The Jōmon (縄文) were a prehistoric hunter-gatherer culture that inhabited the Japanese archipelago approximately between 14,000 BC and 300 BC. Both genetically and culturally, the Jōmon are among the earliest known ancestors of the modern ...
of Japan. Ancient DNA analysis has revealed that the oldest fossil known to carry the derived KITLG allele, which is responsible for blond
Blond () or blonde (), also referred to as fair hair, is a human hair color characterized by low levels of eumelanin, the dark pigment. The resultant visible hue depends on various factors, but always has some yellowish color. The color can be ...
hair in modern Europeans, is a 17,000 year old Ancient North Eurasian
In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) refers to an ancestral component that represents the lineage of the people of the Mal'ta–Buret' culture () and populations closely related to them, such as the Upper Paleolithic individ ...
specimen from Siberia., Ancient North Eurasian populations genetically similar to Mal'ta–Buret' culture
The Mal'ta–Buret' culture (also Maltinsko-buretskaya culture) is an archaeological culture of the Upper Paleolithic (generally dated to 24,000-23,000 BP but also sometimes to 15,000 BP). It is located roughly northwest of Lake Baikal, about ...
and Afontova Gora were an important genetic contributor to Native Americans, Europeans, Ancient Central Asians, South Asians, and some East Asian groups (such as the Ainu people
The Ainu are an Indigenous peoples, indigenous ethnic group who reside in northern Japan and southeastern Russia, including Hokkaido and the Tōhoku region of Honshu, as well as the land surrounding the Sea of Okhotsk, such as Sakhalin, the Ku ...
). Evidence from full genomic studies suggests that the first people in the Americas diverged from Ancient East Asians about 36,000 years ago and expanded northwards into Siberia, where they encountered and interacted with Ancient North Eurasians, giving rise to both Paleosiberian peoples
In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient Paleo-Siberian is the name given to an ancestral component that represents the lineage of the hunter-gatherer people of the 15th-10th millennia before present, in northern and northeastern Siberia. The Ancien ...
and Ancient Native Americans, which later migrated towards the Beringian region, became isolated from other populations, and subsequently populated the Americas.
Early history
During past millennia, different groups ofnomad
Nomads are communities without fixed habitation who regularly move to and from areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the population of nomadic pa ...
s – such as the Enets
The Enets (, ; singular: , ; also known as Yenetses, Entsy, Entsi, Yenisei or Yenisey Samoyeds) are a Samoyedic ethnic group who live on the east bank, near the mouth, of the Yenisei River. Historically they were nomadic people. As of 2002, most ...
, the Nenets
The Nenets (; ), in the past also called 'Samoyeds' or 'Yuraks', are a Samoyedic ethnic group native to Arctic Russia, Russian Far North. According to the latest census in 2021, there were 49,646 Nenets in the Russian Federation, most of them l ...
, the Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th centuries AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was par ...
, the Xiongnu
The Xiongnu (, ) were a tribal confederation of Nomad, nomadic peoples who, according to ancient Chinese historiography, Chinese sources, inhabited the eastern Eurasian Steppe from the 3rd century BC to the late 1st century AD. Modu Chanyu, t ...
, the Scythians
The Scythians ( or ) or Scyths (, but note Scytho- () in composition) and sometimes also referred to as the Pontic Scythians, were an Ancient Iranian peoples, ancient Eastern Iranian languages, Eastern Iranian peoples, Iranian Eurasian noma ...
, and the Yugur
The Yugurs, Yughurs, Yugu (; Western Yugur: ''Sarığ yoğır''; Eastern Yugur: ''Shera yogor''), traditionally known as Yellow Uyghurs, are a Turkic- Mongolic ethnic group and one of China's 56 officially recognized ethnic groups, consist ...
– inhabited various parts of Siberia. The Afanasievo
The Afanasievo culture, or Afanasevo culture (Afanasevan culture) ( ''Afanas'yevskaya kul'tura''), is an early archaeological culture of south Siberia, occupying the Minusinsk Hollow, Minusinsk Basin and the Altai Mountains during the eneolithic ...
and Tashtyk culture
The Tashtyk culture was a Late Iron Age archaeological culture that flourished in the Yenisei valley in Siberia from the 1st century CE to the 4th century CE. Located in the Minusinsk Depression, environs of modern Krasnoyarsk, eastern part of K ...
s of the Yenisey
The Yenisey or Yenisei ( ; , ) is the list of rivers by length, fifth-longest river system in the world, and the largest to drain into the Arctic Ocean.
Rising in Mungaragiyn-gol in Mongolia, it follows a northerly course through Lake Baikal a ...
valley and Altay Mountains are associated with the Indo-European migrations
The Indo-European migrations are hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-Europeans, peoples who spoke Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European (PIE) and the derived Indo-European languages, which took place from around 4000 to 1000 BCE, ...
across Eurasia. The proto-Mongol Khitan people
The Khitan people (Khitan small script: ; ) were a historical Eurasian nomads, nomadic people from Northeast Asia who, from the 4th century, inhabited an area corresponding to parts of modern Mongolia, Northeast China and the Russian Far East.
...
also occupied parts of the region.
In the 13th century, during the period of the Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
, the Mongols conquered a large part of this area. With the breakup of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as ''Ulug Ulus'' ( in Turkic) was originally a Mongols, Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the division of ...
, the autonomous Khanate of Sibir
The Khanate of Sibir (; ) was a Tatar state in western Siberia. It was founded at the end of the 15th century, following the break-up of the Golden Horde.Сибирское ханство // Большая советская энцикл ...
was formed in the late-15th century. Turkic-speaking Yakut
Yakut or Yakutian may refer to:
* Yakuts, the Turkic peoples indigenous to the Sakha Republic
* Yakut language, a Turkic language
* Yakut scripts, Scripts used to write the Yakut language
* Yakut (name)
* Yakut Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic ...
migrated north from the Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal is a rift lake and the deepest lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
region under pressure from the Mongol tribes from the 13th to 15th centuries. Siberia remained a sparsely populated area. Historian John F. Richards
John F. Richards (November 3, 1938 – August 23, 2007) was a historian of South Asia and in particular of the Mughal Empire. He was Professor of History at Duke University in North Carolina, and a recipient in 2007 of the Distinguished Contribut ...
wrote: "it is doubtful that the total early modern Siberian population exceeded 300,000 persons".
Early Russian exploration
The first mention of Siberia in chronicles is recorded in the year 1032. The city-state ofNovgorod
Veliky Novgorod ( ; , ; ), also known simply as Novgorod (), is the largest city and administrative centre of Novgorod Oblast, Russia. It is one of the oldest cities in Russia, being first mentioned in the 9th century. The city lies along the V ...
established two trade routes to the Ob River
The Ob (; ) is a major river in Russia. It is in western Siberia, and with its tributary the Irtysh forms the world's seventh-longest river system, at . The Ob forms at the confluence of the Biya and Katun which have their origins in the Alta ...
, and laid claim to the lands the Russians called ''Yugra
Yugra or Yugor Land (; also spelled ''Iuhra'' in contemporary sources) was a collective name for lands and peoples in the region east of the northern Ural Mountains in modern Russia given by Russian chroniclers in the 12th to 17th centuries. Du ...
''. The Russians were attracted by its furs in particular. Novgorod launched military campaigns to extract tribute from the local population, but often met resistance, such as two campaigns in 1187 and 1193 mentioned in chronicles that were defeated. After Novgorod was annexed by Moscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
, the newly emerging centralized Russian state also laid claim to the region, with Ivan III of Russia
Ivan III Vasilyevich (; 22 January 1440 – 27 October 1505), also known as Ivan the Great, was Grand Prince of Moscow and Sovereign of all Russia, all Russia from 1462 until his death in 1505. Ivan served as the co-ruler and regent for his bli ...
sending expeditionary forces to Siberia in 1483 and 1499–1500. The Russians received tribute, but contact with the tribes ceased after they left.
The growing power of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
began to undermine the Siberian Khanate in the 16th century. First, groups of traders and Cossack
The Cossacks are a predominantly East Slavic Eastern Christian people originating in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of eastern Ukraine and southern Russia. Cossacks played an important role in defending the southern borders of Ukraine and Rus ...
s began to enter the area. The Russian army was directed to establish forts farther and farther east to protect new Russian settlers who migrated from Europe. Towns such as Mangazeya
Mangazeya () was a Northwest Siberian trans- Ural trade colony and later city in the 17th century. Founded in 1600 by Cossacks from Tobolsk, it was situated on the Taz River, between the lower courses of the Ob and Yenisei Rivers flowing int ...
, Tara, Yeniseysk
Yeniseysk ( rus, Енисейск, p=jɪnʲɪˈsʲejsk) is a town in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located on the Yenisei River. Population: 20,000 (1970).
History
Yeniseysk was founded in 1619 as a stockaded town—the first town on the Yenisei ...
, and Tobolsk
Tobolsk (, ) is a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Tobol and Irtysh rivers. Founded in 1587, Tobolsk is the second-oldest Russian settlement east of the Ural Mountains in Asian Russia, and was the historic capita ...
developed, the last becoming the ''de facto'' capital of Siberia from 1590. At this time, ''Sibir'' was the name of a fortress at Qashliq
Qashliq, Isker or Sibir () was a medieval (14th–16th century) Siberian Tatar fortress, in the 16th century the capital of the Khanate of Sibir, located on the right bank of the Irtysh River at its confluence with the ''Sibirka'' rivulet, some ...
, near Tobolsk. Gerardus Mercator
Gerardus Mercator (; 5 March 1512 – 2 December 1594) was a Flemish people, Flemish geographer, cosmographer and Cartography, cartographer. He is most renowned for creating the Mercator 1569 world map, 1569 world map based on a new Mercator pr ...
, in a map published in 1595, marks ''Sibier'' both as the name of a settlement and of the surrounding territory along a left tributary of the Ob. Other sources contend that the Sibe
Sibe may refer to:
*Sibe people, an East Asian ethnic group living in China
*Xibe language, language of Sibe people
* Sibe Mardešić (1927–2016), Croatian mathematician
* Nagovisi language, a South Bougainville language spoken in Papua New Guin ...
, an Indigenous Tungusic people
Tungusic peoples are an ethnolinguistic group formed by the speakers of Tungusic languages (or Manchu–Tungus languages). They are native to Siberia, Mongolia and China.
The Tungusic language family is divided into two main branches, Northern ...
, offered fierce resistance to Russian expansion beyond the Urals. Some suggest that the term "Siberia" is a russification of their ethnonym.
Russian Empire
 By the mid-17th century, Russia had established areas of control that extended to the Pacific Ocean. Some 230,000 Russians had settled in Siberia by 1709. Siberia became one of the destinations for sending internal
By the mid-17th century, Russia had established areas of control that extended to the Pacific Ocean. Some 230,000 Russians had settled in Siberia by 1709. Siberia became one of the destinations for sending internal exile
Exile or banishment is primarily penal expulsion from one's native country, and secondarily expatriation or prolonged absence from one's homeland under either the compulsion of circumstance or the rigors of some high purpose. Usually persons ...
s. Exile was the main Russian punitive practice with more than 800,000 people exiled during the nineteenth century.
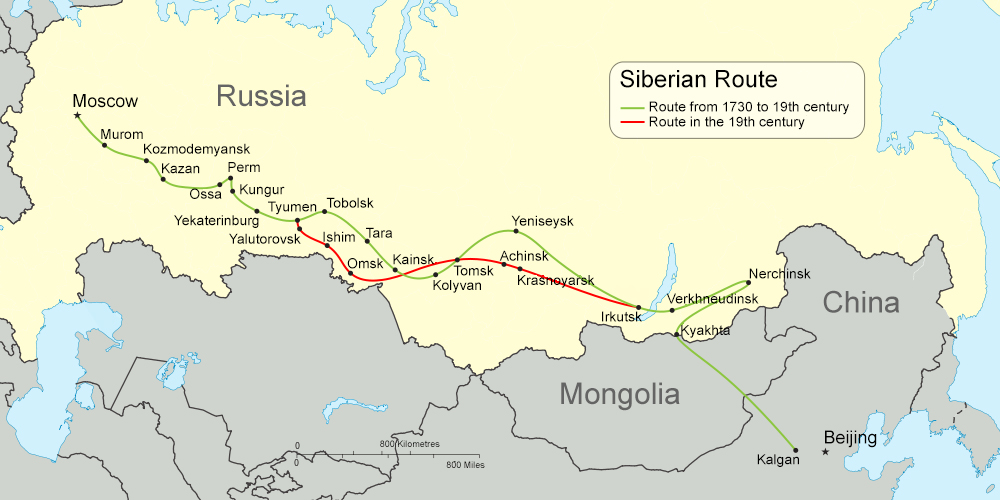
The first great modern change in Siberia was the Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway, historically known as the Great Siberian Route and often shortened to Transsib, is a large railway system that connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway ...
, constructed during 1891–1916. It linked Siberia more closely to the rapidly industrialising Russia of Nicholas II
Nicholas II (Nikolai Alexandrovich Romanov; 186817 July 1918) or Nikolai II was the last reigning Emperor of Russia, King of Congress Poland, and Grand Duke of Finland from 1 November 1894 until his abdication on 15 March 1917. He married ...
(). Around seven million Russians moved to Siberia from Europe between 1801 and 1914. Between 1859 and 1917, more than half a million people migrated to the Russian Far East. Siberia has extensive natural resources: during the 20th century, large-scale exploitation of these took place, and industrial towns cropped up throughout the region.
At 7:15 a.m. on 30 June 1908, the Tunguska Event
The Tunguska event was a large explosion of between 3 and 50 TNT equivalent, megatons that occurred near the Podkamennaya Tunguska River in Yeniseysk Governorate (now Krasnoyarsk Krai), Russia, on the morning of 30 June 1908. The explosion over ...
felled millions of trees near the Podkamennaya Tunguska River (Stony Tunguska River) in central Siberia. Most scientists believe this resulted from the air burst
An air burst or airburst is the detonation of an explosive device such as an anti-personnel artillery shell or a nuclear weapon in the air instead of on contact with the ground or target. The principal military advantage of an air burst over ...
of a meteor or a comet. Even though no crater
A crater is a landform consisting of a hole or depression (geology), depression on a planetary surface, usually caused either by an object hitting the surface, or by geological activity on the planet. A crater has classically been described ...
has ever been found, the landscape in the (sparsely inhabited) area still bears the scars of this event.
Soviet Union
 In the early decades of the
In the early decades of the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
(especially in the 1930s and 1940s), the government used the Gulag
The Gulag was a system of Labor camp, forced labor camps in the Soviet Union. The word ''Gulag'' originally referred only to the division of the Chronology of Soviet secret police agencies, Soviet secret police that was in charge of runnin ...
state agency to administer a system of penal labour camp
A labor camp (or labour camp, see British and American spelling differences, spelling differences) or work camp is a detention facility where inmates are unfree labour, forced to engage in penal labor as a form of punishment. Labor camps have ...
s, replacing the previous katorga
Katorga (, ; from medieval and modern ; and Ottoman Turkish: , ) was a system of penal labor in the Russian Empire and the Soviet Union (see Katorga labor in the Soviet Union).
Prisoners were sent to remote penal colonies in vast uninhabited a ...
system. According to semi-official Soviet estimates, which did not become public until after the fall of the Soviet government in 1991, from 1929 to 1953 more than 14 million people passed through these camps and prisons, many of them in Siberia. Another seven to eight million people were internally deported to remote areas of the Soviet Union (including entire nationalities or ethnicities in several cases).
Half a million (516,841) prisoners died in camps from 1941 to 1943 during World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. At other periods, mortality was comparatively lower. The size, scope, and scale of the Gulag slave-labour camps remain subjects of much research and debate. Many Gulag camps operated in extremely remote areas of northeastern Siberia. The best-known clusters included ''Sevvostlag
Sevvostlag (, North-Eastern Corrective Labor Camps) was a system of forced labor camps set up to satisfy the workforce requirements of the '' Dalstroy'' construction trust in the Kolyma region in April 1932. Organizationally being part of ''Dal ...
'' (''the North-East Camps'') along the Kolyma
Kolyma (, ) or Kolyma Krai () is a historical region in the Russian Far East that includes the basin of Kolyma River and the northern shores of the Sea of Okhotsk, as well as the Kolyma Mountains (the watershed of the two). It is bounded to ...
and ''Norillag
Norillag, Norilsk Corrective Labor Camp () was a gulag labor camp set by Norilsk, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia and headquartered there. It existed from June 25, 1935 to August 22, 1956.
*Karlo Štajner (1902-1992), Croatian writer
*Nikolay Urvantsev ( ...
'' near Norilsk
Norilsk ( rus, Нори́льск, p=nɐˈrʲilʲsk) is a closed city in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located south of the western Taymyr Peninsula, around 90 km east of the Yenisei, Yenisey River and 1,500 km north of Krasnoyarsk. Norilsk is 300 ...
, where 69,000 prisoners lived in 1952. Major industrial cities of Northern Siberia, such as Norilsk and Magadan
Magadan ( rus, Магадан, p=məɡɐˈdan) is a Port of Magadan, port types of inhabited localities in Russia, town and the administrative centre of Magadan Oblast, Russia. The city is located on the isthmus of the Staritsky Peninsula by the ...
, developed from camps built by prisoners and run by former prisoners.
Russian Federation
On 2 December 2019, the 'Power of Siberia
Power of Siberia (Sila Sibiri, formerly named the Yakutia–Khabarovsk–Vladivostok pipeline, also known as China–Russia East-Route Natural Gas pipeline; , ) is a Gazprom-operated pipeline in Eastern Siberia that transports natural gas from Ya ...
' gas pipeline started functioning. The project was started in 2014 to supply natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
from Siberia to China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
.
Geography
Siberia spans an area of , covering the vast majority of Russia's total territory, and almost 9% of Earth's land surface (). It geographically falls in Asia, but is culturally and politically considered European, since it is a part of Russia. Major geographical zones within Siberia include theWest Siberian Plain
The West Siberian Plain () is a large plain that occupies the western portion of Siberia, between the Ural Mountains in the west and the Yenisei, Yenisei River in the east, and the Altai Mountains on the southeast. Much of the plain is poorly d ...
and the Central Siberian Plateau
The Central Siberian Plateau (; ) is a vast mountainous area in Siberia, one of the Great Russian Regions.
Geography
The plateau occupies a great part of central Siberia between the Yenisei and Lena rivers. It is located in the Siberian Plat ...
.
Eastern and central Sakha comprises numerous north–south mountain ranges of various ages. These mountains extend up to almost , but above a few hundred metres they are almost completely devoid of vegetation. The Verkhoyansk Range
The Verkhoyansk Range (, ''Verhojanskiy Hrebet''; ) is a mountain range in the Sakha Republic, Russia near the settlement of Verkhoyansk, well-known for its frigid climate. It is part of the East Siberian Mountains.
The range lies just west o ...
was extensively glaciated in the Pleistocene, but the climate was too dry for glaciation to extend to low elevations. At these low elevations are numerous valleys, many of them deep and covered with larch
Larches are deciduous conifers in the genus ''Larix'', of the family Pinaceae (subfamily Laricoideae). Growing from tall, they are native to the cooler regions of the northern hemisphere, where they are found in lowland forests in the high la ...
forest, except in the extreme north where the tundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic ...
dominates. Soils are mainly turbels (a type of gelisol
Gelisols are an order in USDA soil taxonomy. They are soils of very cold climates which are defined as containing permafrost within of the soil surface. The word "Gelisol" comes from the Latin meaning "to freeze", a reference to the proce ...
). The active layer tends to be less than one metre deep, except near rivers.
The highest point in Siberia is the active volcano
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most oft ...
Klyuchevskaya Sopka
Klyuchevskaya Sopka (; also known as Klyuchevskoi, ) is a stratovolcano, the highest mountain of Siberia and the highest active volcano of Eurasia. Its steep, symmetrical cone towers about from the Bering Sea. The volcano is part of the natural ...
, on the Kamchatka Peninsula
The Kamchatka Peninsula (, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively.
Immediately offshore along the Pacific ...
. Its peak reaches .
Mountain ranges
*Altai Mountains
The Altai Mountains (), also spelled Altay Mountains, are a mountain range in Central Asia, Central and East Asia, where Russia, China, Mongolia, and Kazakhstan converge, and where the rivers Irtysh and Ob River, Ob have their headwaters. The ...
* Anadyr Highlands
The Anadyr Highlands () are a mountainous area in the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Far Eastern Federal District, Russia.
Geography
The Anadyr Highlands are one of the two main mountain regions of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. They rise southwest of ...
* Baikal Mountains
The Baikal Mountains or Baikal Range (, ''Baykalskiy khrebet''; , ''Baigalai dabaan'') are a mountain range that rises steeply over the northwestern shore of Lake Baikal in southern Siberia, Russia. The highest peak in the range is 2,572 m high ...
* Khamar-Daban
Khamar-Daban (; , from – "nut", and – "pass" or "ridge"), is a mountain range in Southern Siberia, Russia.
Geography
The range is located in Buryatia, with a small section in Irkutsk Oblast. It rises near the Baikal Mountains not far from ...
* Chersky Range
The Chersky Range (, ) is a chain of mountains in northeastern Siberia between the Yana River, Yana and Indigirka River, Indigirka Rivers. Administratively, the area of the range belongs to the Sakha Republic, although a small section in the eas ...
* Chukotka Mountains
The Chukotka Mountains () or Chukotka Upland (), is a mountainous area in the Chukotka Autonomous Okrug, Far Eastern Federal District, Russia.Dzhugdzhur Mountains
The Dzhugdzhur () or Jugjur, meaning "big bulge" in Evenki, are a mountain range along the western shores of the Sea of Okhotsk, located in Khabarovsk Krai in the far east of Siberia.
The mountains are quite deserted, the one exception bein ...
* Kolyma Mountains
The Kolyma Mountains or Kolyma Upland (), is a system of mountain ranges in northeastern Siberia, lying mostly within the Magadan Oblast, along the shores of the Sea of Okhotsk in the Kolyma region. It constitutes the watershed between the ba ...
* Koryak Mountains
The Koryak Mountains or Koryak Highlands () are an area of mountain ranges in Far-Eastern Siberia, Russia, located in Chukotka Autonomous Okrug and in Kamchatka Krai, with a small part in Magadan Oblast. The highest point in the system is the M ...
* Sayan Mountains
The Sayan Mountains (, ; ) are a mountain range in southern Siberia spanning southeastern Russia (Buryatia, Irkutsk Oblast, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Tuva and Khakassia) and northern Mongolia. Before the rapid expansion of the Tsardom of Russia, the mou ...
* Tannu-Ola Mountains
The Tannu-Ola mountains (, uniturk, Taᶇdь-Uula, – Tangdy-Uula mountains; , , , ) is a mountain range in southern Siberia, in the Tuva Republic of Russia. It extends in an east–west direction and curves along the Mongolian border. Its hig ...
* Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ),; , ; , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north–south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.
* Verkhoyansk Mountains
The Verkhoyansk Range (, ''Verhojanskiy Hrebet''; ) is a mountain range in the Sakha Republic, Russia near the settlement of Verkhoyansk, well-known for its frigid climate. It is part of the East Siberian Mountains.
The range lies just west of ...
* Yablonoi Mountains
The Yablonoi Mountains or Yablonovy Mountains (, , ; , ''Yablony nuruu'') are a mountain range, in Transbaikal (mainly in Zabaykalsky Krai), Siberia, Russia. The range is sparsely inhabited with most settlements engaged in mining. The area is e ...
Geomorphological regions
*Central Siberian Plateau
The Central Siberian Plateau (; ) is a vast mountainous area in Siberia, one of the Great Russian Regions.
Geography
The plateau occupies a great part of central Siberia between the Yenisei and Lena rivers. It is located in the Siberian Plat ...
* Central Yakutian Lowland
The Central Yakutian LowlandJohn Kimble (ed.), ''Cryosols: Permafrost-Affected Soils'' or the Central Yakutian Lowlands (; ), also known as the Central Yakut Plain or the Vilyuy Lowland, is a low alluvial plain in Siberia, Russia.
Administrati ...
* East Siberian Lowland
The East Siberian Lowland (), also known as Yana-Kolyma Lowland (),Oleg Leonidovič Kryžanovskij, ''A Checklist of the Ground-beetles of Russia and Adjacent Lands.'' p. 16 is a vast plain in North-eastern Siberia, Russia.East Siberian Mountains
The East Siberian Mountains or East Siberian Highlands () are one of the largest mountain systems of the Russia, Russian Federation. They are located between the Central Yakutian Lowland and the Bering Strait in Northeast Siberia. The area of th ...
* North Siberian Lowland
The North Siberian Lowland (; ), also known as Taymyr Lowland (), is a plain with a relatively flat relief separating the Byrranga Mountains of the Taymyr Peninsula in the north from the Central Siberian Plateau in the south. To the southeast ...
* South Siberian Mountains
The South Siberian Mountains () are one of the largest mountain systems in North Asia. The total area of the system of mountain ranges is more than 1.5 million km². The South Siberian Mountains are located in the Siberian and Far Eastern Federal ...
* West Siberian Lowland
Lakes and rivers
*Alazeya
The Alazeya (; ) is a river in the northeastern part of Yakutia, Russia which flows into the Arctic between the basins of the larger Indigirka to the west and the Kolyma to the east.
Mount Kisilyakh-Tas is a notable kigilyakh site on the right b ...
* Anabar Anabar may refer to:
* Anabar Bay, Laptev Sea
* Anabar Constituency, Nauru
* Anabar District, Nauru
* Anabar District, Russia, Sakha, Russia
* Anabar Highway, Russia
* Anabar Plateau, Russia
* Anabar (river)
The Anabar (, in its upper course ...
* Angara
The Angara (; ) or Angar ( мүрэн) is a major river in Siberia, which traces a course through Russia's Irkutsk Oblast and Krasnoyarsk Krai. It drains out of Lake Baikal and is the headwater tributary of the Yenisey. It is long, and has ...
* Indigirka
The Indigirka (; ) is a river in the Sakha Republic in Russia between the Yana to the west and the Kolyma to the east. It is long. The area of its basin is .
History
The isolated village of Russkoye Ustye, located on the delta of the Indigi ...
* Irtysh
The Irtysh is a river in Russia, China, and Kazakhstan. It is the chief tributary of the Ob (river), Ob and is also the longest tributary in the world.
The river's source lies in the Altai Mountains, Mongolian Altai in Dzungaria (the northern p ...
* Kolyma
Kolyma (, ) or Kolyma Krai () is a historical region in the Russian Far East that includes the basin of Kolyma River and the northern shores of the Sea of Okhotsk, as well as the Kolyma Mountains (the watershed of the two). It is bounded to ...
* Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal is a rift lake and the deepest lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
* Lena
Lena or LENA may refer to:
Places
* Léna Department, a department of Houet Province in Burkina Faso
* Lena, Manitoba, an unincorporated community located in Killarney-Turtle Mountain municipality in Manitoba, Canada
* Lena, Norway, a village in ...
* Nizhnyaya Tunguska
The Nizhnyaya Tunguska ( rus, Ни́жняя Тунгу́ска, p=ˈnʲiʐnʲɪjə tʊnˈɡuskə, meaning "Lower Tunguska") is a river in Siberia, Russia, that flows through the Irkutsk Oblast and the Krasnoyarsk Krai. The river is a right tributa ...
* Novosibirsk Reservoir
Novosibirsk Reservoir or Novosibirskoye Reservoir (), informally called the Ob Sea (), is the largest artificial lake in Novosibirsk Oblast and Altai Krai, Russian Federation. It was created by a 33 m high concrete dam on the Ob River built in Nov ...
* Ob
* Podkamennaya Tunguska
The Podkamennaya Tunguska (, literally ''Tunguska under the stones''; , Ket: Ӄо’ль) also known as ''Middle Tunguska'' or ''Stony Tunguska'', is a river in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia.
History
In 1908, an asteroid impacted near the river and l ...
* Popigay
* Upper Angara
* Uvs Nuur
Uvs Lake ( ) is a highly saline lake in an endorheic basin— Uvs Nuur Basin, primarily in Mongolia with a smaller part in Russia. It is the largest lake in Mongolia by surface area, covering 3,350 km2 at 759 m above sea level.
The no ...
* Yana
Yana may refer to:
Locations
*Yana, Burma, a village in Hkamti Township in Hkamti District in the Sagaing Region of northwestern Burma
* Yana, India, a village in the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka, India
* Yana, Nigeria, an administrative c ...
* Yenisey
The Yenisey or Yenisei ( ; , ) is the list of rivers by length, fifth-longest river system in the world, and the largest to drain into the Arctic Ocean.
Rising in Mungaragiyn-gol in Mongolia, it follows a northerly course through Lake Baikal a ...
Grasslands
*Ukok Plateau
Ukok Plateau () is a plateau covered by grasslands located in southwestern Siberia, in the Altai Mountains region of Russia near the borders with China, Kazakhstan and Mongolia. The plateau is recognized as part of the UNESCO World Heritage Sit ...
—part of a UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
World Heritage Site
World Heritage Sites are landmarks and areas with legal protection under an treaty, international treaty administered by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, or scientific significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural and natural ...
Geology
The West Siberian Plain, consisting mostly ofCenozoic
The Cenozoic Era ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterized by the dominance of mammals, insects, birds and angiosperms (flowering plants). It is the latest of three g ...
alluvial deposits, is somewhat flat. In the mid-Pleistocene, many deposits on this plain resulted from ice dams which produced a large glacial lake
A glacial lake is a body of water with origins from glacier activity. They are formed when a glacier erodes the land and then melts, filling the depression created by the glacier.
Formation
Near the end of the last glacial period, roughly 10,0 ...
. This mid- to late-Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( ; referred to colloquially as the ''ice age, Ice Age'') is the geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was fin ...
lake blocked the northward flow of the Ob and Yenisey
The Yenisey or Yenisei ( ; , ) is the list of rivers by length, fifth-longest river system in the world, and the largest to drain into the Arctic Ocean.
Rising in Mungaragiyn-gol in Mongolia, it follows a northerly course through Lake Baikal a ...
rivers, resulting in a redirection southwest into the Caspian Caspian can refer to:
*The Caspian Sea
*The Caspian Depression, surrounding the northern part of the Caspian Sea
*The Caspians, the ancient people living near the Caspian Sea
*The Caspian languages spoken in northern Iran and southeastern Azerbaij ...
and Aral Aral may refer to:
People
* Cahit Aral (1927–2011), Turkish engineer, politician and former government minister
* Coşkun Aral (born 1956), Turkish photo journalist and war correspondent
* Göran Aral (born 1953), Swedish footballer
* Meriç Ara ...
seas via the Turgai Valley. The area is very swampy, and soils are mostly peaty histosol
In both the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB) and the USDA soil taxonomy, a Histosol is a soil consisting primarily of organic materials. They are defined as having or more of organic soil material starting within 40 cm from the so ...
s and, in the treeless northern part, histels. In the south of the plain, where permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
is largely absent, rich grasslands that are an extension of the Kazakh Steppe
The Kazakh Steppe ( ), also known as the Great Steppe or Great Betpak-Dala, Dala ( ), is a vast region of open grassland in Central Asia, covering areas in northern Kazakhstan and adjacent areas of Russia. It lies east of the Pontic–Caspian step ...
formed the original vegetation, most of which is no longer visible.

 The Central Siberian Plateau is an ancient
The Central Siberian Plateau is an ancient craton
A craton ( , , or ; from "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and rifting of contine ...
(sometimes named ''Angaraland'') that formed an independent continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
before the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
(see the Siberian continent). It is exceptionally rich in minerals, containing large deposits of gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
s, and ores of manganese
Manganese is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese was first isolated in the 1770s. It is a transition m ...
, lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
, cobalt
Cobalt is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Co and atomic number 27. As with nickel, cobalt is found in the Earth's crust only in a chemically combined form, save for small deposits found in alloys of natural meteoric iron. ...
, and molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
. Much of the area includes the Siberian Traps
The Siberian Traps () are a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the trap rock, traps is one of the largest known Volcano, volcanic events in the last years ...
—a large igneous province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive ( sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The format ...
. A massive eruptive period approximately coincided with the Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic extinction event (also known as the P–T extinction event, the Late Permian extinction event, the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian extinction event, and colloquially as the Great Dying,) was an extinction ...
. The volcanic event is one of the largest known volcanic eruptions
A volcanic eruption occurs when material is expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure. Several types of volcanic eruptions have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior h ...
in Earth's history
The natural history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by consta ...
. Only the extreme northwest was glaciated
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires d ...
during the Quaternary
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), as well as the current and most recent of the twelve periods of the ...
, but almost all is under exceptionally deep permafrost, and the only tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only ...
that can thrive, despite the warm summers, is the deciduous Siberian Larch
''Larix sibirica'', the Siberian larch or Russian larch, is a frost-hardy tree native to western Russia, from close to the Finnish border east to the Yenisei valley in central Siberia, where it hybridises with the Dahurian larch ''L. gmelinii ...
(''Larix sibirica'') with its very shallow roots. Outside the extreme northwest, the taiga
Taiga or tayga ( ; , ), also known as boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches. The taiga, or boreal forest, is the world's largest land biome. In North A ...
is dominant, covering a significant fraction of the entirety of Siberia. Soils here are mainly turbels, giving way to spodosols
Podzols, also known as podosols, spodosols, or espodossolos, are the typical soils of coniferous or boreal forests and also the typical soils of eucalypt forests and heathlands in southern Australia. In Western Europe, podzols develop on heathland ...
where the active layer becomes thicker and the ice-content lower.
The ''Lena-Tunguska petroleum province'' includes the Central Siberian platform (some authors refer to it as the "Eastern Siberian platform"), bounded on the northeast and east by the Late Carboniferous
Late or LATE may refer to:
Everyday usage
* Tardy, or late, not being on time
* Late (or the late) may refer to a person who is dead
Music
* Late (The 77s album), ''Late'' (The 77s album), 2000
* Late (Alvin Batiste album), 1993
* Late!, a pseudo ...
through Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
Verkhoyansk foldbelt, on the northwest by the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma a ...
Taymr foldbelt, and on the southeast, south and southwest by the Middle Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
to Middle Devonian
In the geological timescale, the Middle Devonian epoch (from 393.3 ± 1.2 million years ago to 382.7 ± 1.6 million years ago) occurred during the Devonian period, after the end of the Emsian age.
The Middle Devonian epoch is subdivided into two ...
Baykalian foldbelt.Meyerhof, A. A., 1980, "Geology and Petroleum Fields in Proterozoic and Lower Cambrian Strata, Lena-Tunguska Petroleum Province, Eastern Siberia, USSR", in ''Giant Oil and Gas Fields of the Decade: 1968–1978'', AAPG Memoir 30, Halbouty, M. T., editor, Tulsa: American Association of Petroleum Geologists, A regional geologic reconnaissance study begun in 1932 and followed by surface and subsurface mapping revealed the Markova-Angara Arch (anticline
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of Fold (geology), fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest Bed (geology), beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex curve, c ...
). This led to the discovery of the Markovo Oil Field in 1962 with the Markovo—1 well, which produced from the Early Cambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordovic ...
Osa Horizon bar
Bar or BAR may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bar (establishment), selling alcoholic beverages
* Candy bar
** Chocolate bar
* Protein bar
Science and technology
* Bar (river morphology), a deposit of sediment
* Bar (tropical cyclone), a laye ...
-sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
at a depth of . The ''Sredne-Botuobin Gas Field'' was discovered in 1970, producing from the Osa and the Proterozoic
The Proterozoic ( ) is the third of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8 Mya, and is the longest eon of Earth's geologic time scale. It is preceded by the Archean and followed by the Phanerozo ...
Parfenovo Horizon. The Yaraktin Oil Field was discovered in 1971, producing from the Vendian
The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last ...
Yaraktin Horizon at depths of up to , which lies below Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
to Lower Jurassic
The Early Jurassic Epoch (in chronostratigraphy corresponding to the Lower Jurassic Series) is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, 201.3 Ma&nb ...
basalt traps.
Climate
The climate of Siberia varies dramatically, but it typically has warm but short summers and long, brutally cold winters. On the north coast, north of theArctic Circle
The Arctic Circle is one of the two polar circles, and the northernmost of the five major circle of latitude, circles of latitude as shown on maps of Earth at about 66° 34' N. Its southern counterpart is the Antarctic Circle.
The Arctic Circl ...
, there is a very short (about one month long) summer.
Almost all the population lives in the south, along the route of the Trans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway, historically known as the Great Siberian Route and often shortened to Transsib, is a large railway system that connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway ...
. The climate in this southernmost part is humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold ...
(Köppen ''Dfa/Dfb'' or ''Dwa/Dwb'') with cold winters but fairly warm summers lasting at least four months. The annual average temperature is about . January averages about and July about , while daytime temperatures in summer typically exceed . With a reliable growing season, an abundance of sunshine and exceedingly fertile chernozem
Chernozem ( ),; also called black soil, regur soil or black cotton soil, is a black-colored soil containing a high percentage of humus (4% to 16%) and high percentages of phosphorus and ammonia compounds. Chernozem is very fertile soil and can ...
soils, southern Siberia is good enough for profitable agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
, as was demonstrated in the early 20th century.
By far the most commonly occurring climate in Siberia is continental subarctic
The subarctic zone is a region in the Northern Hemisphere immediately south of the true Arctic, north of hemiboreal regions and covering much of Alaska, Canada, Iceland, the north of Fennoscandia, Northwestern Russia, Siberia, and the Cair ...
(Koppen ''Dfc'', ''Dwc'', or ''Dsc''), with the annual average temperature about and an average for January of and an average for July of , although this varies considerably, with a July average about in the taiga–tundra ecotone
An ecotone is a transitional area between two plant communities, where these meet and integrate. Examples include areas between grassland and forest, estuaries and lagoon, freshwater and sea water etc. An ecotone may be narrow or wide, and it ma ...
. The business
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for ...
-oriented website and blog ''Business Insider'' lists Verkhoyansk
Verkhoyansk ( rus, Верхоянск, p=vʲɪrxɐˈjansk; ) is a town in Verkhoyansky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located on the Yana River in the Arctic Circle, from Batagay, the administrative center of the district, and nor ...
and Oymyakon
Oymyakon is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, rural locality (a ''village#Russia, selo'') in Oymyakonsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located in the Yana-Oymyakon Highlands, along the Indigirka River, northwest of Tomtor, Oy ...
, in Siberia's Sakha Republic
Sakha, officially the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), is a republics of Russia, republic of Russia, and the largest federal subject of Russia by area. It is located in the Russian Far East, along the Arctic Ocean, with a population of one million ...
, as being in competition for the title of the Northern Hemisphere's ''Pole of Cold
Pole or poles may refer to:
People
*Poles (people), another term for Polish people, from the country of Poland
* Pole (surname), including a list of people with the name
* Pole (musician) (Stefan Betke, born 1967), German electronic music artist
...
''. Oymyakon
Oymyakon is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, rural locality (a ''village#Russia, selo'') in Oymyakonsky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located in the Yana-Oymyakon Highlands, along the Indigirka River, northwest of Tomtor, Oy ...
is a village which recorded a temperature of on 6 February 1933. Verkhoyansk
Verkhoyansk ( rus, Верхоянск, p=vʲɪrxɐˈjansk; ) is a town in Verkhoyansky District of the Sakha Republic, Russia, located on the Yana River in the Arctic Circle, from Batagay, the administrative center of the district, and nor ...
, a town further north and further inland, recorded a temperature of for three consecutive nights: 5, 6 and 7 February 1933. Each town is alternately considered the Northern Hemisphere's Pole of Cold – the coldest inhabited point in the Northern hemisphere. Each town also frequently reaches in the summer, giving them, and much of the rest of Russian Siberia, the world's greatest temperature variation between summer's highs and winter's lows, often well over between the seasons.
Southwesterly winds bring warm air from Central Asia and the Middle East. The climate in West Siberia (Omsk, or Novosibirsk) is several degrees warmer than in the East (Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and , ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 587,891 Irkutsk is the List of cities and towns in Russ ...
, or Chita) where in the north an extreme winter subarctic climate (Köppen ''Dfd'', ''Dwd'', or ''Dsd'') prevails. But summer temperatures in other regions can reach . In general, Sakha is the coldest Siberian region, and the basin of the Yana
Yana may refer to:
Locations
*Yana, Burma, a village in Hkamti Township in Hkamti District in the Sagaing Region of northwestern Burma
* Yana, India, a village in the Uttara Kannada district of Karnataka, India
* Yana, Nigeria, an administrative c ...
has the lowest temperatures of all, with permafrost reaching . Nevertheless, Imperial Russian plans of settlement never viewed cold as an impediment. In the winter, southern Siberia sits near the center of the semi-permanent Siberian High
The Siberian High (also Siberian Anticyclone; (''Aziatsky antitsiklon''); zh, 西伯利亞高壓; Pinyin ''Xībólìyǎ gāoyā''; Kazakh Азия антициклоны (''Aziya antitsiklonı'')) is a massive collection of cold dry air that a ...
, so winds are usually light in the winter.
Precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls from clouds due to gravitational pull. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, rain and snow mixed ("sleet" in Commonwe ...
in Siberia is generally low, exceeding only in Kamchatka
The Kamchatka Peninsula (, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively.
Immediately offshore along the Pacific ...
, where moist winds flow from the Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk; Historically also known as , or as ; ) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, Japan's island of Hokkaido on the sou ...
onto high mountains – producing the region's only major glacier
A glacier (; or ) is a persistent body of dense ice, a form of rock, that is constantly moving downhill under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires ...
s, though volcanic eruptions and low summer temperatures allow only limited forests to grow. Precipitation is high also in most of Primorye
Primorsky Krai, informally known as Primorye, is a federal subject (a krai) of Russia, part of the Far Eastern Federal District in the Russian Far East. The city of Vladivostok on the southern coast of the krai is its administrative center, an ...
in the extreme south, where monsoonal influences can produce quite heavy summer rainfall.
Global warming
Researchers, including Sergei Kirpotin atTomsk State University
The National Research Tomsk State University, TSU () is a public research university located in Tomsk, Russia. The university, which opened in 1888, was the first university in the Asian part of Russia and, in practice, the first Russian univ ...
and Judith Marquand at Oxford University
The University of Oxford is a collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the second-oldest continuously operating u ...
, warn that Western Siberia
Western Siberia or West Siberia ( rus, Западная Сибирь, p=ˈzapədnəjə sʲɪˈbʲirʲ; , ) is a region in North Asia. It is part of the wider region of Siberia that is mostly located in the Russia, Russian Federation, with a Sout ...
has begun to thaw as a result of global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
. The frozen peat bog
A bog or bogland is a wetland that accumulates peat as a deposit of dead plant materials often mosses, typically sphagnum moss. It is one of the four main types of wetlands. Other names for bogs include mire, mosses, quagmire, and muske ...
s in this region may hold billions of tons of methane gas
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
, which may be released into the atmosphere. Methane is a greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
22 times more powerful than carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
. In 2008 a research expedition for the American Geophysical Union
The American Geophysical Union (AGU) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization of Earth, Atmospheric science, atmospheric, Oceanography, ocean, Hydrology, hydrologic, Astronomy, space, and Planetary science, planetary scientists and enthusiasts that ...
detected levels of methane up to 100 times above normal in the atmosphere above the Siberian Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
, likely the result of methane clathrate
Methane clathrate (CH4·5.75H2O) or (4CH4·23H2O), also called methane hydrate, hydromethane, methane ice, fire ice, natural gas hydrate, or gas hydrate, is a solid clathrate compound (more specifically, a clathrate hydrate) in which a large a ...
s being released through holes in a frozen "lid" of seabed permafrost
Permafrost () is soil or underwater sediment which continuously remains below for two years or more; the oldest permafrost has been continuously frozen for around 700,000 years. Whilst the shallowest permafrost has a vertical extent of below ...
around the outfall of the Lena
Lena or LENA may refer to:
Places
* Léna Department, a department of Houet Province in Burkina Faso
* Lena, Manitoba, an unincorporated community located in Killarney-Turtle Mountain municipality in Manitoba, Canada
* Lena, Norway, a village in ...
and the area between the Laptev Sea
The Laptev Sea () is a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the northern coast of Siberia, the Taimyr Peninsula, Severnaya Zemlya, and the New Siberian Islands. Its northern boundary passes from the Arctic Cape to a point with ...
and East Siberian Sea
The East Siberian Sea (; ) is a marginal sea in the Arctic Ocean. It is located between the Arctic Cape to the north, the coast of Siberia to the south, the New Siberian Islands to the west and Cape Billings, close to Chukchi Peninsula, Chukotka, ...
.
Since 1988, experimentation at Pleistocene Park has proposed to restore the grasslands of prehistoric times by conducting research on the effects of large herbivores on permafrost, suggesting that animals, rather than climate, maintained the past ecosystem. The nature reserve park also conducts climatic research on the changes expected from the reintroduction of grazing animals or large herbivores, hypothesizing that a transition from tundra
In physical geography, a tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. There are three regions and associated types of tundra: #Arctic, Arctic, Alpine tundra, Alpine, and #Antarctic ...
to grassland would lead to a net change in energy emission to absorption ratios.Sergey A. Zimov (6 May 2005)"Pleistocene Park: Return of the mammoths' ecosystem"
In: ''
Science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
'', pages 796–798. Article also to be found iwww.pleistocenepark.ru/en/ – Materials.
Retrieved 5 May 2013. According to Vasily Kryuchkov, approximately 31,000 square kilometers of the Russian Arctic has been subjected to severe environmental disturbance.
Fauna
Birds
Order
Galliformes
Galliformes is an order (biology), order of heavy-bodied ground-feeding birds that includes turkey (bird), turkeys, chickens, Old World quail, quail, and other landfowl. Gallinaceous birds, as they are called, are important in their ecosystems ...
Family
Phasianidae
Phasianidae is a family (biology), family of heavy, ground-living birds, which includes pheasants, grouse, partridges, junglefowl, chickens, Turkey bird, turkeys, Old World quail, and peafowl. The family includes many of the most popular Game (hu ...
* Hazel grouse
The hazel grouse (''Tetrastes bonasia''), sometimes called the hazel hen, is one of the smaller members of the grouse family of birds. It is a sedentary species, breeding across the Palearctic as far east as Hokkaido, and as far west as eastern a ...
* Siberian grouse
The Siberian grouse (''Falcipennis falcipennis''), also known as Siberian spruce grouse, Amur grouse, or Asian spruce grouse, is a short, rotund forest-dwelling grouse. A sedentary, non-migratory bird, it is the only member of the genus ''Falcipe ...
* Black grouse
The black grouse (''Lyrurus tetrix''), also known as northern black grouse, Eurasian black grouse, blackgame or blackcock, is a large Aves, bird in the grouse family. It is a Bird migration, sedentary species, spanning across the Palearctic in m ...
* Black-billed capercaillie
The black-billed capercaillie (''Tetrao urogalloides''), also known as eastern capercaillie, Siberian capercaillie, spotted capercaillie or (in Russian) stone capercaillie, is a large grouse species closely related to the more widespread western ...
* Western capercaillie
* Willow ptarmigan
The willow ptarmigan ( ); ''Lagopus lagopus'') or willow grouse is a bird in the grouse subfamily Tetraoninae of the pheasant family Phasianidae. It is also known colloquially as awebo bird. The willow ptarmigan breeds in birch and other forests ...
* Rock ptarmigan
The rock ptarmigan (''Lagopus muta'') is a medium-sized game bird in the grouse family. It is known simply as the ptarmigan in Europe. It is the official bird for the Canadian territory of Nunavut, where it is known as the ''aqiggiq'' (ᐊᕿ� ...
* Daurian partridge
The Daurian partridge (''Perdix dauurica''), also known as steppe partridge, Asian grey partridge or bearded partridge, is a gamebird in the pheasant family Phasianidae of the order Galliformes (gallinaceous birds). Its name derives from the D ...
* Grey partridge
The grey partridge (''Perdix perdix'') is a bird in the pheasant family Phasianidae of the order Galliformes, gallinaceous birds. The scientific name is the Latin for "partridge".
Taxonomy
The grey partridge formally described in 1758 by the S ...
* Altai snowcock
* Japanese quail
The Japanese quail (''Coturnix japonica''), also known as the coturnix quail, is a species of Old World quail found in East Asia. First considered a subspecies of the common quail, it is now considered as a separate species. The Japanese quail h ...
* Common quail
The common quail (''Coturnix coturnix''), or European quail, is a small ground-nesting game bird in the pheasant family Phasianidae. It is mainly migratory, breeding in the western Palearctic and wintering in Africa and southern India.
With its ...
* Ring-necked pheasant
The common pheasant (''Phasianus colchicus''), ring-necked pheasant, or blue-headed pheasant, is a bird in the pheasant family (Phasianidae). The genus name comes from Latin ''phasianus'' 'pheasant'. The species name ''colchicus'' is Latin for ...
Mammals
Order
Artiodactyla
Artiodactyls are placental mammals belonging to the order (biology), order Artiodactyla ( , ). Typically, they are ungulates which bear weight equally on two (an even number) of their five toes (the third and fourth, often in the form of a hoof ...
 *
* Moose
The moose (: 'moose'; used in North America) or elk (: 'elk' or 'elks'; used in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is the world's tallest, largest and heaviest extant species of deer and the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is also the tal ...
* Bactrian camel
The Bactrian camel (''Camelus bactrianus''), also known as the Mongolian camel, domestic Bactrian camel or two-humped camel, is a camel native to the steppes of Central Asia. It has two humps on its back, in contrast to the single-humped drome ...
* Red deer
The red deer (''Cervus elaphus'') is one of the largest deer species. A male red deer is called a stag or Hart (deer), hart, and a female is called a doe or hind. The red deer inhabits most of Europe, the Caucasus Mountains region, Anatolia, Ir ...
* Wild boar
The wild boar (''Sus scrofa''), also known as the wild swine, common wild pig, Eurasian wild pig, or simply wild pig, is a Suidae, suid native to much of Eurasia and North Africa, and has been introduced to the Americas and Oceania. The speci ...
* Siberian roe deer
The Siberian roe deer, eastern roe deer, or Asian roe deer (''Capreolus pygargus''), is a species of roe deer found in northeastern Asia. In addition to Siberia and Mongolia, it is found in Kazakhstan, the Tian Shan Mountains of Kyrgyzstan, east ...
* Manchurian wapiti
The Manchurian wapiti (''Cervus canadensis xanthopygus'') is a putative subspecies of the wapiti native to East Asia. It may be identified as its own species, ''Cervus xanthopygus''.
Description
The Manchurian wapiti's coat is reddish brown dur ...
* Siberian musk deer
The Siberian musk deer (''Moschus moschiferus'') is a musk deer found in the mountain forests of Northeast Asia. It is most common in the taiga of southern Siberia, but is also found in parts of Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, Manchuria and the Korean ...
Database entry includes a brief justification of why this species is of vulnerable.
Order
Carnivora
Carnivora ( ) is an order of placental mammals specialized primarily in eating flesh, whose members are formally referred to as carnivorans. The order Carnivora is the sixth largest order of mammals, comprising at least 279 species. Carnivor ...
Family
Canidae
Canidae (; from Latin, ''canis'', "dog") is a family (biology), biological family of caniform carnivorans, constituting a clade. A member of this family is also called a canid (). The family includes three subfamily, subfamilies: the Caninae, a ...
* Grey wolf
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though gr ...
* Tundra wolf
The tundra wolf (''Canis lupus albus''), also known as the Turukhan wolf,Mech, L. David (1981), The Wolf: The Ecology and Behaviour of an Endangered Species', University of Minnesota Press, p. 353, is a subspecies of grey wolf native to Eurasia ...
* Arctic fox
The Arctic fox (''Vulpes lagopus''), also known as the white fox, polar fox, or snow fox, is a small species of fox native to the Arctic regions of the Northern Hemisphere and common throughout the Tundra#Arctic tundra, Arctic tundra biome. I ...
* Red fox
The red fox (''Vulpes vulpes'') is the largest of the true foxes and one of the most widely distributed members of the order Carnivora, being present across the entire Northern Hemisphere including most of North America, Europe and Asia, plus ...
Family
Felidae
Felidae ( ) is the Family (biology), family of mammals in the Order (biology), order Carnivora colloquially referred to as cats. A member of this family is also called a felid ( ).
The 41 extant taxon, extant Felidae species exhibit the gre ...
 *
* Snow leopard
The snow leopard (''Panthera uncia'') is a species of large cat in the genus ''Panthera'' of the family Felidae. The species is native to the mountain ranges of Central and South Asia. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List because ...
* Amur leopard
The Amur leopard (''Panthera pardus orientalis'') is a leopard subspecies native to the Primorye region of southeastern Russia and northern China. It is listed as Critically Endangered on the IUCN Red List, as in 2007, only 19–26 wild leopar ...
* Siberian tiger
The Siberian tiger or Amur tiger is a population of the tiger subspecies ''Panthera tigris tigris'' native to Northeast China, the Russian Far East, and possibly North Korea. It once ranged throughout the Korea, Korean Peninsula, but currently ...
* Eurasian lynx
The Eurasian lynx (''Lynx lynx'') is one of the four wikt:extant, extant species within the medium-sized wild Felidae, cat genus ''Lynx''. It is widely distributed from Northern Europe, Northern, Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe to Cent ...
* Pallas cat
The Pallas's cat (''Otocolobus manul''), also known as the manul, is a small wild cat with long and dense light grey fur, and rounded ears set low on the sides of the head. Its head-and-body length ranges from with a long bushy tail. It is w ...
Family
Mustelidae
The Mustelidae (; from Latin , weasel) are a diverse family of carnivora, carnivoran mammals, including weasels, badgers, otters, polecats, martens, grisons, and wolverines. Otherwise known as mustelids (), they form the largest family in the s ...
* Least weasel
The least weasel (''Mustela nivalis''), little weasel, common weasel, or simply weasel is the smallest member of the genus ''Mustela,'' Family (biology), family Mustelidae and Order (biology), order Carnivora. It is native to Eurasia, North Ame ...
* Stoat
The stoat (''Mustela erminea''), also known as the Eurasian ermine or ermine, is a species of mustelid native to Eurasia and the northern regions of North America. Because of its wide circumpolar distribution, it is listed as Least Concern on th ...
* Mountain weasel
The mountain weasel (''Mustela altaica''), also known as the pale weasel, Altai weasel or ''solongoi'', primarily lives in high-altitude environments, as well as rocky tundra and grassy woodlands. This weasel rests in rock crevices, tree trunks, ...
* Siberian weasel
The Siberian weasel or kolonok (''Mustela sibirica'') is a medium-sized weasel native to Asia, where it is widely distributed and inhabits various forest habitats and open areas. It is therefore listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.
Descr ...
* Steppe polecat
The steppe polecat (''Mustela eversmanii''), also known as the white or masked polecat, is a species of mustelid native to Central and Eastern Europe and Central and East Asia.It is listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List because of its wi ...
* Sable
The sable (''Martes zibellina'') is a species of marten, a small omnivorous mammal primarily inhabiting the forest environments of Russia, from the Ural Mountains throughout Siberia, and northern Mongolia. Its habitat also borders eastern Kaz ...
* Eurasian river otter
The Eurasian otter (''Lutra lutra''), also known as the European otter, Eurasian river otter, European river otter, common otter, and Old World otter, is a semiaquatic mammal native to Eurasia and the Maghreb. The most widely distributed member o ...
* Asian badger
The Asian badger (''Meles leucurus''), also known as the sand badger, is a species of badger native to Mongolia, China, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, the Korean Peninsula and Russia.
Characteristics
The Asian badger is mostly lighter in colour than th ...
* Wolverine
The wolverine ( , ; ''Gulo gulo''), also called the carcajou or quickhatch (from East Cree, ''kwiihkwahaacheew''), is the largest land-dwelling species, member of the family Mustelidae. It is a muscular carnivore and a solitary animal. The w ...
Family
Ursidae
Bears are carnivoran mammals of the family (biology), family Ursidae (). They are classified as caniforms, or doglike carnivorans. Although only eight species of bears are extant, they are widespread, appearing in a wide variety of habitats ...
 *
* Asian black bear
The Asian black bear (''Ursus thibetanus''), also known as the Asiatic black bear, moon bear and white-chested bear, is a medium-sized bear species native to Asia that is largely adapted to an arboreal lifestyle. It is distributed from southeast ...
* Brown bear
The brown bear (''Ursus arctos'') is a large bear native to Eurasia and North America. Of the land carnivorans, it is rivaled in size only by its closest relative, the polar bear, which is much less variable in size and slightly bigger on av ...
* Polar bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a large bear native to the Arctic and nearby areas. It is closely related to the brown bear, and the two species can Hybrid (biology), interbreed. The polar bear is the largest extant species of bear ...
Flora
 * ''
* ''Larix sibirica
''Larix sibirica'', the Siberian larch or Russian larch, is a frost-hardy tree native to western Russia, from close to the Finnish border east to the Yenisei valley in central Siberia, where it hybridises with the Dahurian larch ''L. gmelinii ...
''
* ''Larix gmelinii
''Larix gmelinii'', the Dahurian larch or East Siberian larch, is a species of larch native to eastern Siberia and adjacent northeastern Mongolia, northeastern China (Heilongjiang), South Korea and North Korea.
Description
''Larix gmelinii'' ...
''
* ''Picea obovata
''Picea obovata'', the Siberian spruce, is a spruce native to Siberia, from the Ural Mountains east to Magadan Oblast, and from the Arctic tree line south to the Altay Mountains in northwestern Mongolia.
It is a medium-sized evergreen tree grow ...
''
* ''Pinus pumila
''Pinus pumila'', commonly known as the Siberian dwarf pine, dwarf Siberian pine, dwarf stone pine, Japanese stone pine, or creeping pine, is a tree in the family Pinaceae native to northeastern Asia and the Japanese isles. It shares the commo ...
''
Politics
Notable
sovereign states
A sovereign state is a State (polity), state that has the highest authority over a territory. It is commonly understood that Sovereignty#Sovereignty and independence, a sovereign state is independent. When referring to a specific polity, the ter ...
in Siberia
* Xianbei state
The Xianbei (; ) were an ancient nomadic people that once resided in the eastern Eurasian steppes in what is today Mongolia, Inner Mongolia, and Northeastern China. The Xianbei were likely not of a single ethnicity, but rather a multiling ...
(1st–3rd century CE)
* First Turkic Khaganate
The First Turkic Khaganate, also referred to as the First Turkic Empire, the Turkic Khaganate or the Göktürk Khaganate, was a Turkic khaganate established by the Ashina clan of the Göktürks in medieval Inner Asia under the leadership of Bu ...
(6th–7th century)
* Eastern Turkic Khaganate
The Eastern Turkic Khaganate ( zh, t=東突厥, p=Dōng Tūjué or Dōng Tújué) was a Turkic khaganate formed as a result of the internecine wars in the beginning of the 7th century (AD 581–603) after the First Turkic Khaganate (found ...
(7th century)
* Second Turkic Khaganate
The Second Turkic Khaganate was a khaganate in Central and Eastern Asia founded by the Ashina clan of the Göktürks that lasted between 682–744. It was preceded by the Eastern Turkic Khaganate (552–630) and the early Tang dynasty period ( ...
(7th–8th century)
* Kyrgyz Khaganate
The Kyrgyz Khaganate () was a Turkic empire that existed between the early 6th and 13th centuries. It ruled over the Yenisei Kyrgyz people, who had been located in southern Siberia since the 6th century. By the 9th century, the Kyrgyz had asse ...
(8th–13th century)
* Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Euro ...
(13th–14th century)
* Khanate of Sibir
The Khanate of Sibir (; ) was a Tatar state in western Siberia. It was founded at the end of the 15th century, following the break-up of the Golden Horde.Сибирское ханство // Большая советская энцикл ...
(1468–1598)
* Tsardom of Russia
The Tsardom of Russia, also known as the Tsardom of Moscow, was the centralized Russian state from the assumption of the title of tsar by Ivan the Terrible, Ivan IV in 1547 until the foundation of the Russian Empire by Peter the Great in 1721.
...
(1598–1721)
* Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughl ...
(1721–1917)
* Russian Republic
The Russian Republic,. referred to as the Russian Democratic Federative Republic in the 1918 Constitution, was a short-lived state which controlled, ''de jure'', the territory of the former Russian Empire after its proclamation by the Rus ...
(1917–1918)
* Siberian Republic (1918)
* Russian State
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
(1918–1920)
* Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
(1918–1922)
* Far Eastern Republic
The Far Eastern Republic ( rus, Дальневосточная Республика, Dal'nevostochnaya Respublika, p=dəlʲnʲɪvɐˈstotɕnəjə rʲɪsˈpublʲɪkə, links=yes; ), sometimes called the Chita Republic (, ), was a nominally indep ...
(1920–1922)
* Tuvan People's Republic
The Tuvan People's Republic (TPR), known simply as Tannu Tuva, was a partially recognized socialist republic that existed between 1921 and 1944 in North Asia. It was located in the same territory as the former Imperial Russian protectorate of ...
(1921–1944)
* Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
(1922–1991)
** Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
(1922–1991)
* Russian Federation
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
(1991–present)
Borders and administrative division
Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ),; , ; , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north–south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.
, including the Russian Far East
The Russian Far East ( rus, Дальний Восток России, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asia, Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Easte ...
. According to this definition, Siberia extended eastward from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific coast, and southward from the Arctic Ocean to the border of Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
and the national borders of both Mongolia and China.
Soviet-era sources (''Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; , ''BSE'') is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Great Russian Enc ...
'' and others) and modern Russian ones usually define Siberia as a region extending eastward from the Ural Mountains to the watershed
Watershed may refer to:
Hydrology
* Drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
* Drainage basin, an area of land where surface water converges (North American usage)
Music
* Watershed Music Festival, an annual country ...
between Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
and Arctic
The Arctic (; . ) is the polar regions of Earth, polar region of Earth that surrounds the North Pole, lying within the Arctic Circle. The Arctic region, from the IERS Reference Meridian travelling east, consists of parts of northern Norway ( ...
drainage basins, and southward from the Arctic Ocean to the hills of north-central Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
and the national borders of both Mongolia and China. By this definition, Siberia includes the federal subjects
The federal subjects of Russia, also referred to as the subjects of the Russian Federation () or simply as the subjects of the federation (), are the constituent entities of Russia, its top-level political divisions. According to the Cons ...
of the Siberian Federal District
Siberian Federal District ( rus, Сибирский федеральный округ, p=sʲɪˈbʲirskʲɪj fʲɪdʲɪˈralʲnɨj ˈokrʊk) is one of the eight federal districts of Russia. Its population was 17,178,298 according to the 20 ...
, and some of the Ural Federal District
Ural Federal District ( rus, Уральский федеральный округ, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪj fʲɪdʲɪˈralʲnɨj ˈokrʊk) is one of the eight federal districts of Russia. Its population was 12,080,523 (79.9% urban) according to the ...
, as well as Sakha (Yakutia) Republic, which is a part of the Far Eastern Federal District
The Far Eastern Federal District ( rus, Дальневосточный федеральный округ, p=dəlʲnʲɪvɐˈstot͡ɕnɨj fʲɪdʲɪˈralʲnɨj ˈokrʊk) is the largest and the least populated federal districts of Russia, federa ...
. Geographically, this definition includes subdivisions of several other subjects of Urals and Far Eastern federal districts, but they are not included administratively. This definition excludes Sverdlovsk Oblast
Sverdlovsk Oblast ( rus, Свердловская область, Sverdlovskaya oblastʹ, p=svʲɪrdˈlofskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ) is a federal subject (an oblast) of Russia located in the Ural Federal District. Its administrative center is the c ...
and Chelyabinsk Oblast
Chelyabinsk Oblast; , is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (an oblast) of Russia in the Ural Mountains region, on the border of Europe and Asia. Its administrative center is the types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Chel ...
, both of which are included in some wider definitions of Siberia.
Other sources may use either a somewhat wider definition that states the Pacific coast, not the watershed, is the eastern boundary (thus including the whole Russian Far East), as well as all Northern Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
is its subregion in the south-west or a somewhat narrower one that limits Siberia to the Siberian Federal District (thus excluding all subjects of other districts). In Russian, 'Siberia' is commonly used as a substitute for the name of the federal district by those who live in the district itself, but less commonly used to denote the federal district by people residing outside of it. Due to the different interpretations of Siberia, starting from Tyumen
Tyumen ( ; rus, Тюмень, p=tʲʉˈmʲenʲ, a=Ru-Tyumen.ogg) is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Tyumen Oblast, Russia. It is situated just east of the Ural Mountains, along the Tura ( ...
, to Chita, the territory generally defined as 'Siberia', some people will define themselves as 'Siberian', while others not.
A number of factors in recent years, including the fomenting of Siberian separatism have made the definition of the territory of Siberia a potentially controversial subject. In the eastern extent of Siberia there are territories which are not clearly defined as either Siberia or the Far East
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North Asia, North, East Asia, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In mod ...
, making the question of "what is Siberia?" one with no clear answer, and what is a "Siberian", one of self-identification
In the psychology of self, one's self-concept (also called self-construction, self-identity, self-perspective or self-structure) is a collection of beliefs about oneself. Generally, self-concept embodies the answer to the question ''"Who am I ...
.

Major cities
The most populous city of Siberia, as well as the third most populous city of Russia, is the city ofNovosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siber ...
. Present-day Novosibirsk is an important business, science, manufacturing and cultural center of the Asian part of Russia.
Omsk
Omsk (; , ) is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Omsk Oblast, Russia. It is situated in southwestern Siberia and has a population of over one million. Omsk is the third List of cities and tow ...
played an important role in the Russian Civil War
The Russian Civil War () was a multi-party civil war in the former Russian Empire sparked by the 1917 overthrowing of the Russian Provisional Government in the October Revolution, as many factions vied to determine Russia's political future. I ...
serving as a provisional Russian capital, as well in the expansion into and governing of Central Asia
Central Asia is a region of Asia consisting of Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The countries as a group are also colloquially referred to as the "-stans" as all have names ending with the Persian language, Pers ...
. In addition to its cultural status, it has become a major oil-refining, education, transport and agriculture hub.
Other historic cities of Siberia include Tobolsk
Tobolsk (, ) is a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Tobol and Irtysh rivers. Founded in 1587, Tobolsk is the second-oldest Russian settlement east of the Ural Mountains in Asian Russia, and was the historic capita ...
(the first capital and the only kremlin
The Moscow Kremlin (also the Kremlin) is a fortified complex in Moscow, Russia. Located in the centre of the country's capital city, the Moscow Kremlin (fortification), Kremlin comprises five palaces, four cathedrals, and the enclosing Mosco ...
in Siberia), Tomsk
Tomsk (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Tomsk Oblast in Russia, on the Tom (river), Tom River. Population:
Founded in 1604, Tomsk is one of the oldest cities in Siberia. It has six univers ...
(formerly a wealthy merchant's town) and Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and , ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 587,891 Irkutsk is the List of cities and towns in Russ ...
(former seat of Eastern Siberia's governor general, near lake Baikal).
Other major cities include: Barnaul
Barnaul (, ) is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative centre of Altai Krai, Russia, located at the confluence of the Barnaulka and Ob (river), Ob rivers in the West Siberian Plain. As of the Russian Censu ...
, Kemerovo
Kemerovo ( rus, Ке́мерово, p=ˈkʲemʲɪrəvə) is an industrial types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Kemerovo Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Iskitimka River, Iskitimka and Tom ...
, Krasnoyarsk
Krasnoyarsk is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative center of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is situated along the Yenisey, Yenisey River, and is the second-largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk, with a p ...
, Novokuznetsk
Novokuznetsk (, , ; )Чиспияков Э. Ф. (1992) ''Учебник шорского языка''. Кемеровское книжное издательство. p. 27. is a city in Kemerovo Oblast (Kuzbass) in southwestern Siberia, Russia ...
, Tyumen
Tyumen ( ; rus, Тюмень, p=tʲʉˈmʲenʲ, a=Ru-Tyumen.ogg) is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Tyumen Oblast, Russia. It is situated just east of the Ural Mountains, along the Tura ( ...
.
Wider definitions of geographic Siberia also include the cities of: Chelyabinsk
Chelyabinsk; , is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Chelyabinsk Oblast, Russia. It is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, seventh-largest city in Russia, with a population ...
and Yekaterinburg
Yekaterinburg (, ; ), alternatively Romanization of Russian, romanized as Ekaterinburg and formerly known as Sverdlovsk ( ; 1924–1991), is a city and the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk Oblast and the Ural Federal District, Russia. The ci ...
in the Urals, Khabarovsk
Khabarovsk ( ) is the largest city and the administrative centre of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia,Law #109 located from the China–Russia border, at the confluence of the Amur and Ussuri Rivers, about north of Vladivostok. As of the 2021 Russian c ...
and Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( ; , ) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai and the capital of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia. It is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, covering an area o ...
in the Russian Far East, and even Petropavl
Petropavl ( ; ) is a city on the Ishim River in northern Kazakhstan close to the border with Russia. It is the capital of the North Kazakhstan Region. Population: 218,956.
Petropavl is about from Kökşetau, northwest of the national cap ...
ovsk in Kazakhstan and Harbin
Harbin, ; zh, , s=哈尔滨, t=哈爾濱, p=Hā'ěrbīn; IPA: . is the capital of Heilongjiang, China. It is the largest city of Heilongjiang, as well as being the city with the second-largest urban area, urban population (after Shenyang, Lia ...
in China.
Economy

Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siber ...
is the largest by population and the most important city for the Siberian economy; with an extra boost since 2000 when it was designated a regional center for the executive bureaucracy (Siberian Federal District
Siberian Federal District ( rus, Сибирский федеральный округ, p=sʲɪˈbʲirskʲɪj fʲɪdʲɪˈralʲnɨj ˈokrʊk) is one of the eight federal districts of Russia. Its population was 17,178,298 according to the 20 ...
). Omsk
Omsk (; , ) is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Omsk Oblast, Russia. It is situated in southwestern Siberia and has a population of over one million. Omsk is the third List of cities and tow ...
is a historic and currently the second largest city in the region, and since 1950s hosting Russia's largest oil refinery, the Omsk Refinery. Siberia is extraordinarily rich in mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid substance with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. (2011): Mi ...
s, containing ores of almost all economically valuable metal
A metal () is a material that, when polished or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electrical resistivity and conductivity, electricity and thermal conductivity, heat relatively well. These properties are all associated wit ...
s. It has some of the world's largest deposits of nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
, gold
Gold is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol Au (from Latin ) and atomic number 79. In its pure form, it is a brightness, bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile metal. Chemically, gold is a transition metal ...
, lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
, coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other Chemical element, elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal i ...
, molybdenum
Molybdenum is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Mo (from Neo-Latin ''molybdaenum'') and atomic number 42. The name derived from Ancient Greek ', meaning lead, since its ores were confused with lead ores. Molybdenum minerals hav ...
, gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate Hydrate, dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, drywall and blackboard or sidewalk ...
, diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of e ...
s, diopside
Diopside is a monoclinic pyroxene mineral with composition . It forms complete solid solution series with hedenbergite () and augite, and partial solid solutions with orthopyroxene and pigeonite. It forms variably colored, but typically dull ...
, silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
, as well as extensive unexploited resources of oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) and lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
and natural gas
Natural gas (also fossil gas, methane gas, and gas) is a naturally occurring compound of gaseous hydrocarbons, primarily methane (95%), small amounts of higher alkanes, and traces of carbon dioxide and nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide and helium ...
. Around 70% of Russia's developed oil fields
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations. Such reservoirs form when kerogen (ancient plant matter) is created in surrounding rock by the presen ...
are in the Khanty-Mansiysk
Khanty-Mansiysk (, lit. ''Khanty-Mansi Town''; Khanty: , ''Jomvoćś''; Mansi: , ''Abga'') is a city in west-central Russia. Technically, it is situated on the eastern bank of the Irtysh River, from its confluence with the Ob, in the oil-ri ...
region. Russia contains about 40% of the world's known resources of nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
at the Norilsk
Norilsk ( rus, Нори́льск, p=nɐˈrʲilʲsk) is a closed city in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia, located south of the western Taymyr Peninsula, around 90 km east of the Yenisei, Yenisey River and 1,500 km north of Krasnoyarsk. Norilsk is 300 ...
deposit in Siberia. Norilsk Nickel
Norilsk Nickel (), or Nornickel, is a Russian nickel and palladium mining and smelting company. Its largest operations are located in the Norilsk–Talnakh area near the Yenisei River in the north of Siberia. It also has holdings in Nikel, Zapo ...
is the world's biggest nickel and palladium
Palladium is a chemical element; it has symbol Pd and atomic number 46. It is a rare and lustrous silvery-white metal discovered in 1802 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. He named it after the asteroid Pallas (formally 2 Pallas), ...
producer. Siberian agriculture
Agriculture in Siberia was started many millennia ago by peoples indigenous to the region. While these native Siberians had little more than "digging sticks" called mattocks instead of ploughs at their disposal, Siberian agriculture would develop ...
is severely restricted by the short growing season of most of the region. However, in the southwest where soils consist of exceedingly fertile black earths and the climate is a little more moderate, there is extensive cropping of wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
, barley
Barley (), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains; it was domesticated in the Fertile Crescent around 9000 BC, giving it nonshattering spikele ...
, rye
Rye (''Secale cereale'') is a grass grown extensively as a grain, a cover crop and a forage crop. It is grown principally in an area from Eastern and Northern Europe into Russia. It is much more tolerant of cold weather and poor soil than o ...
and potato
The potato () is a starchy tuberous vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are underground stem tubers of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'', a perennial in the nightshade famil ...
es, along with the grazing
In agriculture, grazing is a method of animal husbandry whereby domestic livestock are allowed outdoors to free range (roam around) and consume wild vegetations in order to feed conversion ratio, convert the otherwise indigestible (by human diges ...
of large numbers of sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
and cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
. Elsewhere food production, owing to the poor fertility of the podzol
Podzols, also known as podosols, spodosols, or espodossolos, are the typical soils of coniferous or boreal forests and also the typical soils of eucalypt forests and heathlands in southern Australia. In Western Europe, podzols develop on heathlan ...
ic soils and the extremely short growing seasons, is restricted to the herding of reindeer in the tundra—which has been practiced by natives for over 10,000 years. Siberia has the world's largest forest
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, ...
s. Timber remains an important source of revenue, even though many forests in the east have been logged much more rapidly than they are able to recover. The Sea of Okhotsk
The Sea of Okhotsk; Historically also known as , or as ; ) is a marginal sea of the western Pacific Ocean. It is located between Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula on the east, the Kuril Islands on the southeast, Japan's island of Hokkaido on the sou ...
is one of the two or three richest fisheries in the world owing to its cold currents and very large tidal ranges, and thus Siberia produces over 10% of the world's annual fish catch, although fishing has declined somewhat since the collapse of the USSR in 1991. Reported in 2009, the development of renewable energy in Russia
Renewable energy in Russia mainly consists of hydroelectric energy. Russia is rich not only in oil, gas and coal, but also in wind, hydro, geothermal, biomass and solar energy – the resources of renewable energy. Practically all regions ha ...
is held back by the lack of a conducive government policy framework, , Siberia still offers special opportunities for off-grid renewable energy developments. Remote parts of Siberia are too costly to connect to central electricity and gas grids, and have therefore historically been supplied with costly diesel, sometimes flown in by helicopter. In such cases renewable energy is often cheaper.
Sport
 The Yenisey Krasnoyarsk basketball team has played in the
The Yenisey Krasnoyarsk basketball team has played in the VTB United League
The VTB United League () is an international professional men's club basketball league that was founded in 2009. It is made up of mostly Russian clubs, along with one each from Belarus and Kazakhstan. Since 2013, it is the first tier of Russian ...
since 2011–12.
Russia's third most popular sport, bandy
Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two team sport, teams wearing Ice skates#Bandy skates, ice skates on a large ice surface (either indoors or outdoors) while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal.
The playin ...
, is important in Siberia. In the 2015–16 Russian Bandy Super League season Yenisey
The Yenisey or Yenisei ( ; , ) is the list of rivers by length, fifth-longest river system in the world, and the largest to drain into the Arctic Ocean.
Rising in Mungaragiyn-gol in Mongolia, it follows a northerly course through Lake Baikal a ...
from Krasnoyarsk
Krasnoyarsk is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative center of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is situated along the Yenisey, Yenisey River, and is the second-largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk, with a p ...
became champions for the third year in a row by beating Baykal-Energiya
Baykal-Energiya () is a bandy club from Irkutsk, Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends ...
from Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and , ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 587,891 Irkutsk is the List of cities and towns in Russ ...
in the final. Two or three more teams (depending on the definition of Siberia) play in the Super League, the 2016–17 champions SKA-Neftyanik
SKA-Neftyanik () is a professional bandy club from Khabarovsk, Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the wor ...
from Khabarovsk
Khabarovsk ( ) is the largest city and the administrative centre of Khabarovsk Krai, Russia,Law #109 located from the China–Russia border, at the confluence of the Amur and Ussuri Rivers, about north of Vladivostok. As of the 2021 Russian c ...
as well as Kuzbass from Kemerovo
Kemerovo ( rus, Ке́мерово, p=ˈkʲemʲɪrəvə) is an industrial types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Kemerovo Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Iskitimka River, Iskitimka and Tom ...
and Sibselmash from Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siber ...
. In 2007 Kemerovo got Russia's first indoor arena specifically built for bandy. Now Khabarovsk has the world's largest indoor arena specifically built for bandy, Arena Yerofey
Arena Yerofey () is a bandy arena in Khabarovsk, Russia, which hosted the 2015 Bandy World Championship. The 2018 Bandy World Championship was also hosted there, but only Division A that time around. The arena was built in 2013, is 46,000 m2 an ...
. It was venue for Division A of the 2018 World Championship. In time for the 2020 World Championship, an indoor arena will be ready for use in Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and , ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 587,891 Irkutsk is the List of cities and towns in Russ ...
. That one will also have a speed skating oval. Krasnoyarsk
Krasnoyarsk is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative center of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is situated along the Yenisey, Yenisey River, and is the second-largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk, with a p ...
is also one of the centres of Rugby in Russia, with 2 of the largest clubs in the country, STM Enisei and Krasny Yar, are both based in the city.
The 2019 Winter Universiade
The 2019 Winter Universiade (), the XXIX Winter Universiade, was a multi-sport event for student and youth athletes which took place from 2 to 12 March 2019 in the Russian city of Krasnoyarsk. The 2019 Winter Universiade was the third Universia ...
was hosted by Krasnoyarsk.
Demographics
According to the Russian Census of 2010, theSiberian
Siberia ( ; , ) is an extensive geographical region comprising all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has formed a part of the sovereign territory of Russia and its predecessor states si ...
and Far Eastern
The Far East is the geographical region that encompasses the easternmost portion of the Asian continent, including North, East and Southeast Asia. South Asia is sometimes also included in the definition of the term. In modern times, the term ''F ...
Federal Districts, located entirely east of the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ),; , ; , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range in Eurasia that runs north–south mostly through Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the river Ural (river), Ural and northwestern Kazakhstan.
, together have a population of about 25.6 million. Tyumen
Tyumen ( ; rus, Тюмень, p=tʲʉˈmʲenʲ, a=Ru-Tyumen.ogg) is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Tyumen Oblast, Russia. It is situated just east of the Ural Mountains, along the Tura ( ...
and Kurgan Oblast, Kurgan Oblasts, which are geographically in Siberia but administratively part of the Urals Federal District, together have a population of about 4.3 million. Thus, the whole region of Siberia (in the broadest usage of the term) is home to approximately 30 million people. It has a population density of about three people per square kilometre.
Buryats
The Buryats are a Mongolic ethnic group native to southeastern Siberia who speak the Buryat language. They are one of the two largest indigenous groups in Siberia, the other being the Yakuts. The majority of the Buryats today live in their ti ...
, Yakuts
The Yakuts or Sakha (, ; , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to North Siberia, primarily the Republic of Sakha in the Russian Federation. They also inhabit some districts of the Krasnoyarsk Krai. They speak Yakut, which belongs to the Si ...
, Tuvans
The Tuvans (from Russian ) or Tyvans (from Tuvan ) are a Turkic ethnic group indigenous to Siberia that live in Tuva, Mongolia, and China. They speak the Tuvan language, a Siberian Turkic language. In Mongolia, they are regarded as one ...
, Altai and Khakas
The Khakas are a Turkic indigenous people of Siberia, who live in the republic of Khakassia, Russia. They speak the Khakas language.
The Khakhassian people are direct descendants of various ancient cultures that have inhabited southern Siberia ...
) or Indigenous small-numbered peoples of the North, Siberia and the Far East,
northern Indigenous people. Slavic-origin Russians outnumber all of the Indigenous peoples combined, except in the Republics of Tuva and Sakha.
According to the 2002 census there are 500,000 Tatars in Siberia, but of these, 300,000 are Volga Tatars who also settled in Siberia during periods of colonization and are thus also non-Indigenous Siberians, in contrast to the 200,000 Siberian Tatars which are Indigenous to Siberia. Of the Indigenous Siberians, the Mongol-speaking Buryats
The Buryats are a Mongolic ethnic group native to southeastern Siberia who speak the Buryat language. They are one of the two largest indigenous groups in Siberia, the other being the Yakuts. The majority of the Buryats today live in their ti ...
, numbering approximately 500,000, are the most numerous group in Siberia, and they are mainly concentrated in their homeland, the Buryatia, Buryat Republic. According to the Demographics of Russia#Ethnic groups, 2010 census there were 478,085 indigenous Turkic-speaking Yakuts
The Yakuts or Sakha (, ; , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to North Siberia, primarily the Republic of Sakha in the Russian Federation. They also inhabit some districts of the Krasnoyarsk Krai. They speak Yakut, which belongs to the Si ...
. Other ethnic groups Indigenous to Siberia include Ket people, Kets, Evenks, Chukchis, Koryaks, Yupik peoples, Yupiks, and Yukaghirs.
About seventy percent of Siberia's people live in cities, mainly in apartments. Many people also live in rural areas, in simple, spacious, log houses. Novosibirsk
Novosibirsk is the largest city and administrative centre of Novosibirsk Oblast and the Siberian Federal District in Russia. As of the 2021 Russian census, 2021 census, it had a population of 1,633,595, making it the most populous city in Siber ...
is the largest city in Siberia, with a population of about 1.6 million. Tobolsk
Tobolsk (, ) is a town in Tyumen Oblast, Russia, located at the confluence of the Tobol and Irtysh rivers. Founded in 1587, Tobolsk is the second-oldest Russian settlement east of the Ural Mountains in Asian Russia, and was the historic capita ...
, Tomsk
Tomsk (, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Tomsk Oblast in Russia, on the Tom (river), Tom River. Population:
Founded in 1604, Tomsk is one of the oldest cities in Siberia. It has six univers ...
, Tyumen
Tyumen ( ; rus, Тюмень, p=tʲʉˈmʲenʲ, a=Ru-Tyumen.ogg) is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Tyumen Oblast, Russia. It is situated just east of the Ural Mountains, along the Tura ( ...
, Krasnoyarsk
Krasnoyarsk is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative center of Krasnoyarsk Krai, Russia. It is situated along the Yenisey, Yenisey River, and is the second-largest city in Siberia after Novosibirsk, with a p ...
, Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, Иркутск, p=ɪrˈkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and , ''Erhüü'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 587,891 Irkutsk is the List of cities and towns in Russ ...
, and Omsk
Omsk (; , ) is the administrative center and largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Omsk Oblast, Russia. It is situated in southwestern Siberia and has a population of over one million. Omsk is the third List of cities and tow ...
are the older, historical centers.
Religion
 There are a variety of beliefs throughout Siberia, including Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christianity, other denominations of Christianity, Tibetan Buddhism and Islam. The
There are a variety of beliefs throughout Siberia, including Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christianity, other denominations of Christianity, Tibetan Buddhism and Islam. The Siberian Federal District
Siberian Federal District ( rus, Сибирский федеральный округ, p=sʲɪˈbʲirskʲɪj fʲɪdʲɪˈralʲnɨj ˈokrʊk) is one of the eight federal districts of Russia. Its population was 17,178,298 according to the 20 ...
alone has an estimation of 250,000 Muslims. An estimated 70,000 History of the Jews in Russia and the Soviet Union, Jews live in Siberia, some in the Jewish Autonomous Region. The predominant religious group is the Russian Orthodox Church.
Tradition regards Siberia the archetypal home of shamanism, and polytheism is popular.Hoppál 2005:13 These native sacred practices are considered by the tribes to be very ancient. There are records of Siberian tribal healing practices dating back to the 13th century. The vast territory of Siberia has many different local traditions of gods. These include: Ak Ana, Anapel, Bugady Musun, Kayra, Kara Khan, Khaltesh-Anki, Kini'je, Ku'urkil, Nga (god), Nga, Nu'tenut, Num-Torum, Yukaghir Pon, Pon, Pugu (deity), Pugu, Todote, Toko'yoto, Tomam, Xaya Iccita and Zonget. Places with sacred areas include Olkhon, an island in Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal is a rift lake and the deepest lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
.
Transport
Many cities in northern Siberia, such as Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky, cannot be reached by road, as there are virtually none connecting from other major cities in Russia or Asia. Siberia can be reached through theTrans-Siberian Railway
The Trans-Siberian Railway, historically known as the Great Siberian Route and often shortened to Transsib, is a large railway system that connects European Russia to the Russian Far East. Spanning a length of over , it is the longest railway ...
. The Trans-Siberian Railway operates from Moscow in the west to Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( ; , ) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai and the capital of the Far Eastern Federal District of Russia. It is located around the Zolotoy Rog, Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, covering an area o ...
in the east. Cities that are located far from the railway are reached by air or by the separate Baikal–Amur Mainline, Baikal–Amur Railway (BAM).
Culture
Cuisine
Stroganina is a raw fish dish of the Indigenous people of northern Arctic Siberia made from raw, thin, long-sliced frozen fish. It is a popular dish with native Siberians. Siberia is also known for its pelmeni dumpling; which in the winter are traditionally frozen and stored outdoors. In addition, there are various berry, nut and mushroom dishes making use of the riches of abundant nature.See also
* Siberian regionalism * Tunguska BasinReferences
Bibliography
* * * * Bobrick, Benson''East of the Sun: the epic conquest and tragic history of Siberia''
(Henry Holt and Company, 1993); popular history * * Diment, Galya, and Yuri Slezkine, eds. ''Between Heaven and Hell: The Myth of Siberia in Russian Culture'' (3rd ed. 1993) * * Forsyth, James. ''A History of the Peoples of Siberia: Russia's North Asian Colony, 1581–1990'' (Cambridge, Cambridge University Press, 1994). * * Kotkin, Stephen, and David Wolff, eds. (1995)
''Rediscovering Russia in Asia''
* * Lincoln, W. Bruce (1993
''The Conquest of a Continent''
Scholarly history. * * * * * Wood, Alan (ed.)(1991). ''The History of Siberia: From Russian Conquest to Revolution''. London: Routledge. * {{Authority control Siberia, Eurasian Steppe Geography of Russia Regions of Russia Geography of Kazakhstan