Sharp Stewart and Company on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Sharp, Stewart and Company was a

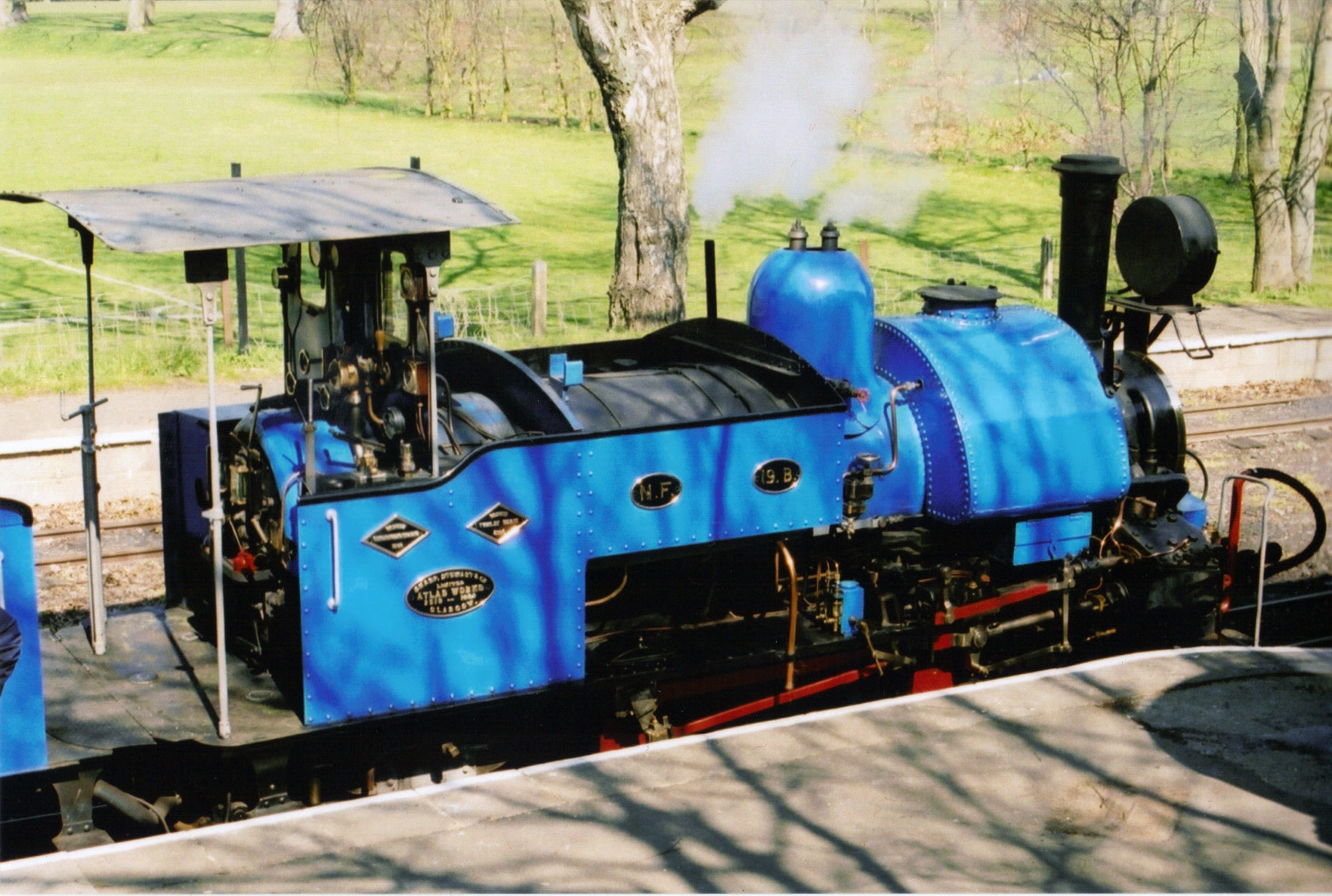 In 1852, the senior partner, John Sharp, retired and was replaced by Charles Patrick Stewart, the name of the company changing to Sharp Stewart and Company. Thomas Sharp also retired and was succeeded by Stephen Robinson. In 1860 sole rights were obtained for Giffard's patent injector. The company acquired limited liability in 1864.
The company provided a number of
In 1852, the senior partner, John Sharp, retired and was replaced by Charles Patrick Stewart, the name of the company changing to Sharp Stewart and Company. Thomas Sharp also retired and was succeeded by Stephen Robinson. In 1860 sole rights were obtained for Giffard's patent injector. The company acquired limited liability in 1864.
The company provided a number of
steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the locomot ...
manufacturer, initially located in Manchester, England. The company was formed in 1843 upon the demise of Sharp, Roberts & Co.. It moved to Glasgow, Scotland, in 1888, eventually amalgamating with two other Glaswegian locomotive manufacturers to form the North British Locomotive Company
The North British Locomotive Company (NBL, NB Loco or North British) was created in 1903 through the merger of three Glasgow locomotive manufacturing companies; Sharp, Stewart and Company (Atlas Works), Neilson, Reid and Company (Hyde Park Wor ...
.
Early days
Iron merchant Thomas Sharp and mechanical engineer Richard Roberts first formed a partnership, Sharp, Roberts & Co. (about which, see also company section in article on Roberts), to manufacture textile machinery and machine tools. They opened the Atlas Works in Manchester in 1828. They had built a few stationary steam engines, and in 1833 built a locomotive, ''Experiment'' for the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. It was a four-wheeled2-2-0
Under Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-2-0 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, two powered driving wheels on one axle, and no trailing wheels. This configuration, which became very p ...
with vertical cylinders over the leading wheels. After a number of modifications, three similar locomotives (Britannia, Manchester, and '' Hibernia'') were built in 1834 for the Dublin and Kingstown Railway. Although they were relatively fast, the vertical cylinders meant they were too hard on the track at speed.
However, in 1834 Charles Beyer also joined the firm and contributed to its success in locomotive building as Roberts soon delegated most of the locomotive design work to him. A new 2-2-2
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, 2-2-2 represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, two powered driving wheels on one axle, and two trailing wheels on one axle. The wheel arrangement both ...
design was soon produced with horizontal inside cylinders under the smokebox and additional bearings to support the crank axle. Around 600 of these Sharp Single locomotives were built between 1837 and 1857. Ten of the first were sold to the Grand Junction Railway, with the "Sharpies" becoming a standard to compare with the "Bury" engines.
Sharp Brothers and Company
In 1843, Roberts left and the firm became Sharp Brothers and Company. Between 1846 and 1848 the company provided eight 2-2-2 passenger and two 0-4-2 goods locomotives to the Lynn and Dereham Railway. From 1851 to 1853 twenty engines were built for theLondon and North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the L&NWR was the largest joint stock company in the United Kingdom.
In 1923, it became a constituent of the Lo ...
to the design of James Edward McConnell
James Edward McConnell (1815–1883) was one of the first locomotive engineers of the London and North Western Railway (LNWR). He was Locomotive Superintendent of the LNWR's Southern Division at Wolverton railway works from 1847 to 1862 and o ...
, the so-called " Bloomers", subcontracted from Wolverton.
Sharp, Stewart and Company

 In 1852, the senior partner, John Sharp, retired and was replaced by Charles Patrick Stewart, the name of the company changing to Sharp Stewart and Company. Thomas Sharp also retired and was succeeded by Stephen Robinson. In 1860 sole rights were obtained for Giffard's patent injector. The company acquired limited liability in 1864.
The company provided a number of
In 1852, the senior partner, John Sharp, retired and was replaced by Charles Patrick Stewart, the name of the company changing to Sharp Stewart and Company. Thomas Sharp also retired and was succeeded by Stephen Robinson. In 1860 sole rights were obtained for Giffard's patent injector. The company acquired limited liability in 1864.
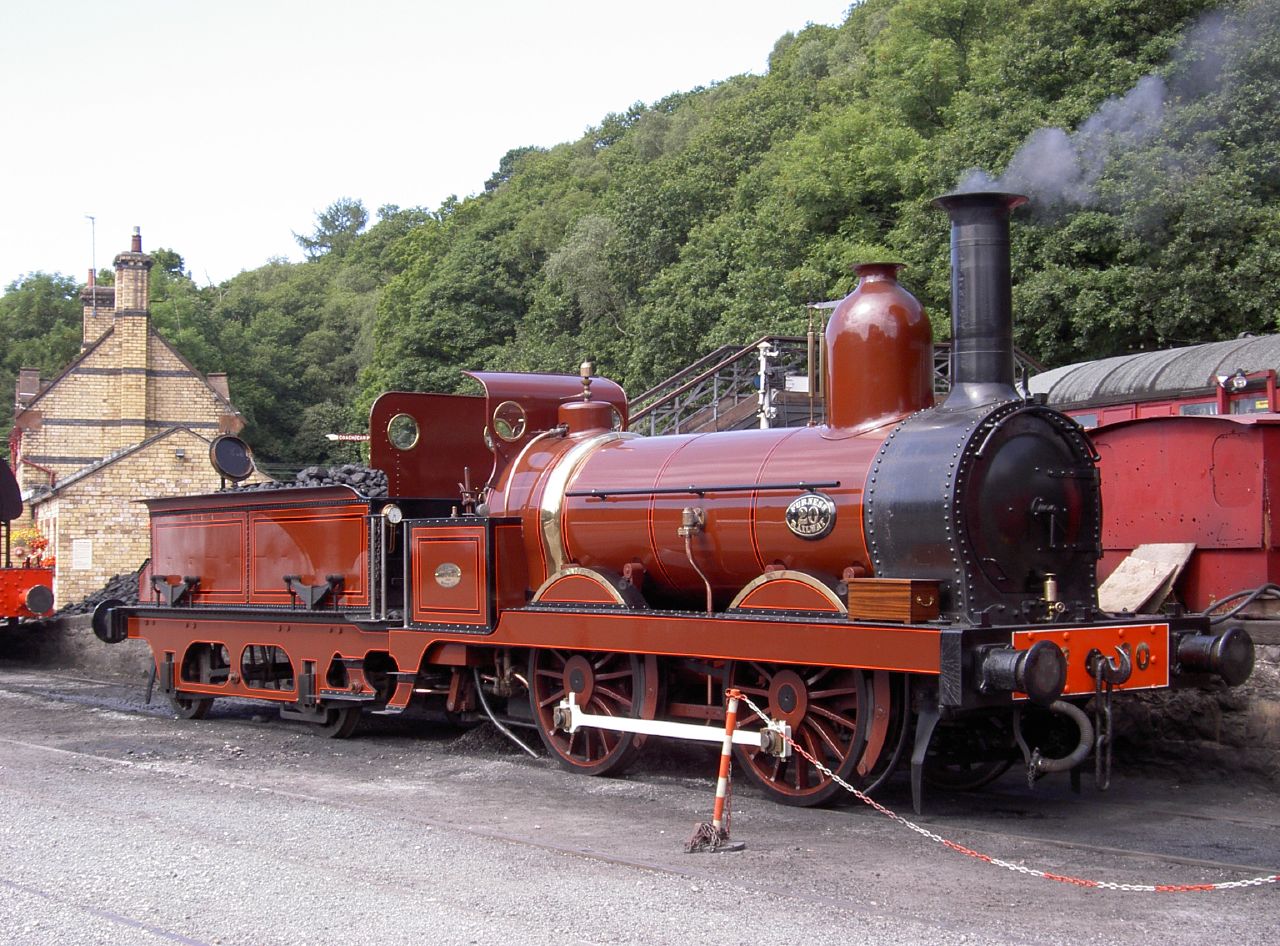
The company provided a number of 0-4-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents one of the simplest possible types, that with two axles and four coupled wheels, all of which are driven. The wheels on the earliest four-coupled locomotives were ...
tender engines for the Furness Railway of which Number 20, built in 1863 has been restored to working order by the Lakeside & Haverthwaite Railway in Cumbria. In 1862, the company began making larger engines, first some 4-6-0
A 4-6-0 steam locomotive, under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, has four leading wheels on two axles in a leading bogie and six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles with the abse ...
saddle tank engines for the Great Indian Peninsula Railway. By 1865 they were building 0-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and no trailing wheels. Locomotives of this type are also referre ...
s, again for India.
Move to Glasgow
Since they were also dealing in general brass and ironmongery, and machine tools, it became necessary to move, which they did in 1888. They took over and moved to the works of theClyde Locomotive Company
The Clyde Locomotive Company was a firm of locomotive manufacturers in Springburn, Glasgow, Scotland.
The company was founded in 1884 by Walter Montgomerie Neilson, after he left the partnership of Neilson, Reid and Company in 1876 following a ...
in Springburn, Glasgow, renaming it Atlas Works.
A number of compounds were built for the Argentine Central Railway
The Argentine Central Railway was a narrow gauge railroad in the United States built from the Colorado and Southern Railway at Silver Plume, Colorado, to Waldorf, Colorado, (now a ghost town) and onward to the summit of Mount McClellan. Co ...
in 1889, some 4-4-0
4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four po ...
and some 2-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of two leading wheels on one axle, usually in a leading truck, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles, and no trailing wheels. ...
. In 1892 they received an order for seventy five 4-4-0
4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four po ...
s and 0-6-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of no leading wheels, six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles and no trailing wheels. This was the most common wheel arrangemen ...
s from the Midland Railway. By now they had built a number of 4-6-0
A 4-6-0 steam locomotive, under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, has four leading wheels on two axles in a leading bogie and six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles with the abse ...
engines for overseas railways, but in 1894 came their first Glasgow order for a British line, the "Jones Goods" of the Highland Railway. By the end of the century they were supplying railways at home and all over the world.
Between 1898 and 1901, Sharp Stewart and Company supplied no less than 16 4-6-0
A 4-6-0 steam locomotive, under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, has four leading wheels on two axles in a leading bogie and six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles with the abse ...
and 4 4-8-0
Under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives, represents the wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles, usually in a leading truck or bogie, eight powered and coupled driving wheels on four axles and no traili ...
locomotives to New Zealand Railways. The 4-8-0 B class locomotives survived till the end of steam either as-built, or as 4-6-4T engines of the We class. The 4-6-0 locomotives were dumped in rivers and on the coast as erosion protection when their time was up. 3 have since been salvaged for preservation.
North British
In 1903, having built over 5000 engines, the company amalgamated withNeilson, Reid and Company
Neilson and Company was a locomotive manufacturer in Glasgow, Scotland.
The company was started in 1836 at McAlpine Street by Walter Neilson and James Mitchell to manufacture marine and stationary engines. In 1837 the firm moved to Hyde Par ...
and Dübs and Company to form the North British Locomotive Company
The North British Locomotive Company (NBL, NB Loco or North British) was created in 1903 through the merger of three Glasgow locomotive manufacturing companies; Sharp, Stewart and Company (Atlas Works), Neilson, Reid and Company (Hyde Park Wor ...
.
See also
* :Sharp Stewart locomotivesReferences and sources
References
{{ReflistSources
* Lowe, J.W., (1989) ''British Steam Locomotive Builders,'' Guild Publishing Locomotive manufacturers of the United Kingdom Defunct companies based in Manchester Manufacturing companies based in Glasgow Manufacturing companies based in Manchester Vehicle manufacturing companies established in 1852 Vehicle manufacturing companies disestablished in 1903 British companies established in 1852 British companies disestablished in 1903 Springburn 1852 establishments in England 1903 disestablishments in Scotland