Romford Bombers Riders on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Romford is a large town in
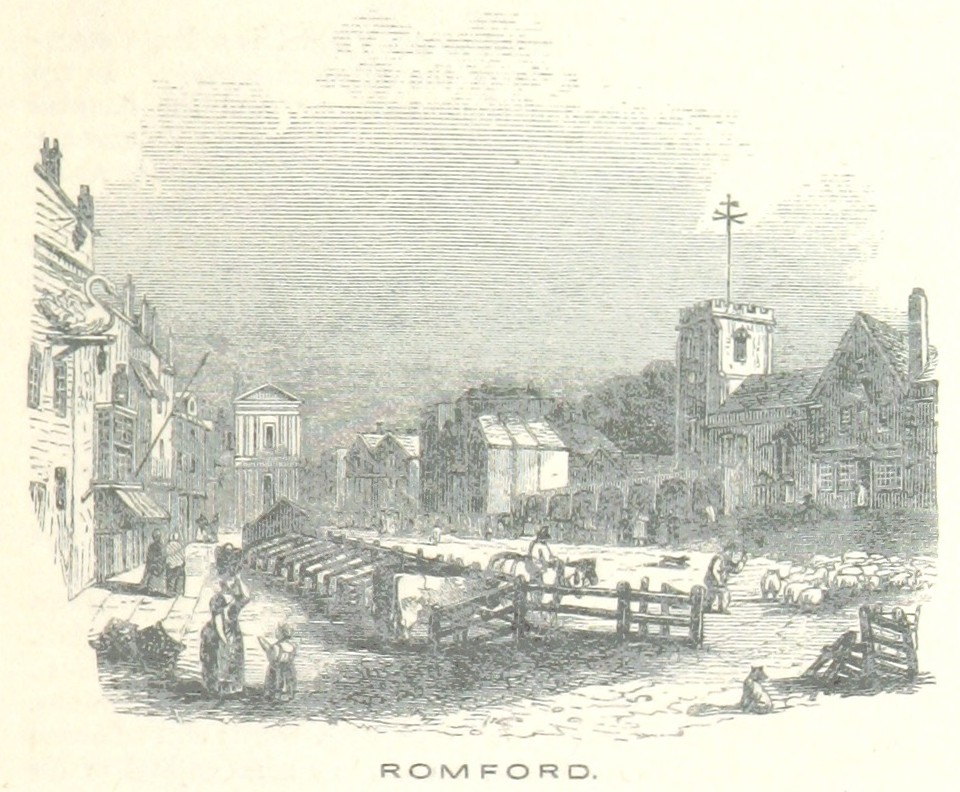 The town developed in the Middle Ages on the main road to London and the regionally significant Romford Market was established in 1247. The original site of the town was to the south, in an area still known as Oldchurch. It was moved northwards to the present site in the later medieval period to avoid the frequent flooding of the River Rom. The first building on the new site was the 1410 Chapel of St Edward (since replaced by the 1850 Parish Church of St Edward the Confessor. The early history of Romford and the immediate area is agricultural and it is recorded as being the location of a number of mills used to grind corn. The area was a focus of the leather industry from the 15th to the early 19th centuries and there is record of a wide range of industries such as cloth making, weaving, charcoal burning, metal working and brewing. Communications played an important part in its development; the main road to London was maintained by the Middlesex and Essex Turnpike Trust from 1721 and Romford became a coaching town in the 18th century.
Several failed attempts were made in the early 19th century to connect the town to the Thames via a Romford Canal. It was initially intended to terminate at a basin near to the
The town developed in the Middle Ages on the main road to London and the regionally significant Romford Market was established in 1247. The original site of the town was to the south, in an area still known as Oldchurch. It was moved northwards to the present site in the later medieval period to avoid the frequent flooding of the River Rom. The first building on the new site was the 1410 Chapel of St Edward (since replaced by the 1850 Parish Church of St Edward the Confessor. The early history of Romford and the immediate area is agricultural and it is recorded as being the location of a number of mills used to grind corn. The area was a focus of the leather industry from the 15th to the early 19th centuries and there is record of a wide range of industries such as cloth making, weaving, charcoal burning, metal working and brewing. Communications played an important part in its development; the main road to London was maintained by the Middlesex and Essex Turnpike Trust from 1721 and Romford became a coaching town in the 18th century.
Several failed attempts were made in the early 19th century to connect the town to the Thames via a Romford Canal. It was initially intended to terminate at a basin near to the
east London
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the f ...
and the administrative centre of the London Borough of Havering. It is located northeast of Charing Cross
Charing Cross ( ) is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Clockwise from north these are: the east side of Trafalgar Square leading to St Martin's Place and then Charing Cross Road; the Strand leading to the City; ...
and is one of the major metropolitan centres identified in the London Plan. Historically, Romford was a market town in the county of Essex, and formed the administrative centre of the liberty of Havering before that liberty was dissolved in 1892. Good road links to London and the opening of the railway station in 1839 were key to the development of the town. The economic history of Romford is characterised by a shift from agriculture to light industry and then to retail and commerce. As part of the suburban growth of London throughout the 20th century, Romford significantly expanded and increased in population, becoming a municipal borough in 1937 and was incorporated into Greater London in 1965. Today, it is one of the largest commercial, retail, entertainment and leisure districts in London and has a well-developed night-time economy as well. Its population, as of 2011, was 122,854.
History
Toponymy
Romford is first recorded in 1177 as ''Romfort'', which is formed fromOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
'rūm' and ' ford' and means "the wide or spacious ford". The naming of the River Rom is a local ' back-formation' from the name of the town; and the river is elsewhere known as the Beam. The ford most likely existed on the main London to Colchester road where it crossed that river.
Economic development
 The town developed in the Middle Ages on the main road to London and the regionally significant Romford Market was established in 1247. The original site of the town was to the south, in an area still known as Oldchurch. It was moved northwards to the present site in the later medieval period to avoid the frequent flooding of the River Rom. The first building on the new site was the 1410 Chapel of St Edward (since replaced by the 1850 Parish Church of St Edward the Confessor. The early history of Romford and the immediate area is agricultural and it is recorded as being the location of a number of mills used to grind corn. The area was a focus of the leather industry from the 15th to the early 19th centuries and there is record of a wide range of industries such as cloth making, weaving, charcoal burning, metal working and brewing. Communications played an important part in its development; the main road to London was maintained by the Middlesex and Essex Turnpike Trust from 1721 and Romford became a coaching town in the 18th century.
Several failed attempts were made in the early 19th century to connect the town to the Thames via a Romford Canal. It was initially intended to terminate at a basin near to the
The town developed in the Middle Ages on the main road to London and the regionally significant Romford Market was established in 1247. The original site of the town was to the south, in an area still known as Oldchurch. It was moved northwards to the present site in the later medieval period to avoid the frequent flooding of the River Rom. The first building on the new site was the 1410 Chapel of St Edward (since replaced by the 1850 Parish Church of St Edward the Confessor. The early history of Romford and the immediate area is agricultural and it is recorded as being the location of a number of mills used to grind corn. The area was a focus of the leather industry from the 15th to the early 19th centuries and there is record of a wide range of industries such as cloth making, weaving, charcoal burning, metal working and brewing. Communications played an important part in its development; the main road to London was maintained by the Middlesex and Essex Turnpike Trust from 1721 and Romford became a coaching town in the 18th century.
Several failed attempts were made in the early 19th century to connect the town to the Thames via a Romford Canal. It was initially intended to terminate at a basin near to the Star Brewery
The Star Brewery was a brewery in Romford, England. For much of its history, it was a main industryCollier Row, whereby timber from
 There was early expansion in the 1840s when 200 cottages were built in the area formerly occupied by an army barracks; it was known as ''New Romford''. To acknowledge the military connection, when in 1961 these were in turn replaced with new housing the name ''Waterloo Road Estate'' was applied. To the east of the market place from 1850 middle class suburban housing was constructed with a much larger area of built-over to the south of the railway from 1851. Through a gradual process of selling off former manors, houses were built radiating from the town in all directions for about a mile. More significant growth occurred between 1910 and 1911 with the construction of
There was early expansion in the 1840s when 200 cottages were built in the area formerly occupied by an army barracks; it was known as ''New Romford''. To acknowledge the military connection, when in 1961 these were in turn replaced with new housing the name ''Waterloo Road Estate'' was applied. To the east of the market place from 1850 middle class suburban housing was constructed with a much larger area of built-over to the south of the railway from 1851. Through a gradual process of selling off former manors, houses were built radiating from the town in all directions for about a mile. More significant growth occurred between 1910 and 1911 with the construction of
 The Romford UK Parliament constituency consists of the Havering wards of Brooklands, Havering Park, Hylands, Mawneys, Pettits, Romford Town, and Squirrel's Heath.
The current MP is Andrew Rosindell, a native of the town. Romford forms part of the Havering and Redbridge London Assembly constituency.
Each ward elects three councillors to Havering London Borough Council. As of the 2018 council elections, all the elected councillors for the wards in Romford constituency were Conservative.
The Romford UK Parliament constituency consists of the Havering wards of Brooklands, Havering Park, Hylands, Mawneys, Pettits, Romford Town, and Squirrel's Heath.
The current MP is Andrew Rosindell, a native of the town. Romford forms part of the Havering and Redbridge London Assembly constituency.
Each ward elects three councillors to Havering London Borough Council. As of the 2018 council elections, all the elected councillors for the wards in Romford constituency were Conservative.


 The town centre is about above sea level on a gravel terrace rising from the River Thames. The north of the town has developed on London Clay and is situated as much as above sea level. A continuous gentle rise in the eastern suburbs towards Gidea Park and Harold Wood peaks around around the Harold Court. On the northern side, Harold Hill peaks at . The semi-rural area north of Collier Row and Harold Hill consists of many rolls of hills, with elevation peaking at the village of Havering-atte-Bower, .
The town centre is for the most part contained within a ring road formed of St Edwards Way, Mercury Gardens, Thurloe Gardens, Oldchurch Road and Waterloo Road. The market place and much of South Street and the High Street are pedestrianised. The railway cuts through the town from east to west on a viaduct, with the bulk of the central Romford area to its north. The River Rom flows through the town in underground channels and joins the Thames after flowing through Hornchurch; elsewhere along its course it is known as the River Beam and forms part of the strategic waterways
The town centre is about above sea level on a gravel terrace rising from the River Thames. The north of the town has developed on London Clay and is situated as much as above sea level. A continuous gentle rise in the eastern suburbs towards Gidea Park and Harold Wood peaks around around the Harold Court. On the northern side, Harold Hill peaks at . The semi-rural area north of Collier Row and Harold Hill consists of many rolls of hills, with elevation peaking at the village of Havering-atte-Bower, .
The town centre is for the most part contained within a ring road formed of St Edwards Way, Mercury Gardens, Thurloe Gardens, Oldchurch Road and Waterloo Road. The market place and much of South Street and the High Street are pedestrianised. The railway cuts through the town from east to west on a viaduct, with the bulk of the central Romford area to its north. The River Rom flows through the town in underground channels and joins the Thames after flowing through Hornchurch; elsewhere along its course it is known as the River Beam and forms part of the strategic waterways

 Romford is recognised in the London Plan as one of 13 regionally significant metropolitan centres in Greater London, with a considerable catchment area. The total commercial floorspace in the town was in 2002, of which was retail space and was offices. The retail space is growing and in 2005 consisted of . The retail economy is complemented by a
Romford is recognised in the London Plan as one of 13 regionally significant metropolitan centres in Greater London, with a considerable catchment area. The total commercial floorspace in the town was in 2002, of which was retail space and was offices. The retail space is growing and in 2005 consisted of . The retail economy is complemented by a
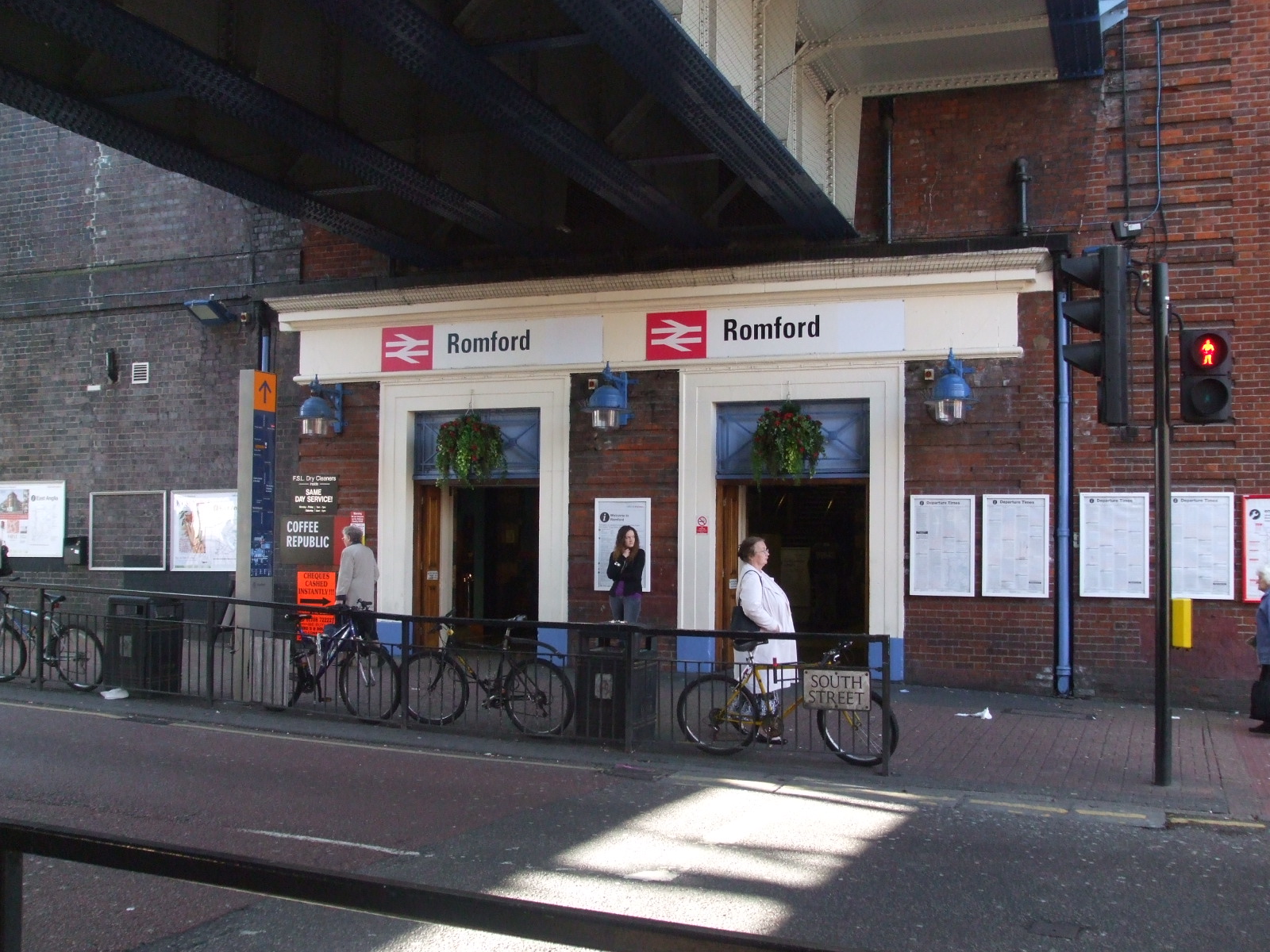 The town is served by Romford railway station; it is situated on the
The town is served by Romford railway station; it is situated on the
Transport for London Services will extend through central London to Reading when the line is opened fully. Some

 Havering Council's urban strategy aims to make Romford a cultural destination, whilst recognising that Hornchurch forms the main cultural hub of the borough with a large theatre and arts spaces. As a former market and coaching town, Romford is well served by public houses and two that are located in the market place are listed buildings. The market and adjacent streets also form a conservation area.
Mass entertainment facilities in the town include the Brookside Theatre, Romford Greyhound Stadium, one of the few remaining dog racing tracks in London; 2 multi-screen cinemas; and until April 2013
Havering Council's urban strategy aims to make Romford a cultural destination, whilst recognising that Hornchurch forms the main cultural hub of the borough with a large theatre and arts spaces. As a former market and coaching town, Romford is well served by public houses and two that are located in the market place are listed buildings. The market and adjacent streets also form a conservation area.
Mass entertainment facilities in the town include the Brookside Theatre, Romford Greyhound Stadium, one of the few remaining dog racing tracks in London; 2 multi-screen cinemas; and until April 2013
Bedrock Radio
(a community health and hospital radio station).
Hainault Forest
Hainault Forest Country Park is a Country Park located in Greater London, with portions in: Hainault in the London Borough of Redbridge; the London Borough of Havering; and in the Lambourne parish of the Epping Forest District in Essex.
Geograp ...
could be transported to the Thames for use in the Royal Dockyards. Only two miles of canal were constructed and the canal company were unable to reach the town.
The development of the town was accelerated by the opening of the railway station in 1839 which stimulated the local economy and was key to the development of the Star Brewery. Initially Eastern Counties Railway services operated between Mile End and Romford, with extensions to Brentwood and to Shoreditch in 1840. A second station was opened on South Street in 1892 by the London, Tilbury and Southend Railway on the line to Upminster and Grays, giving Romford a rail connection to Tilbury Docks. The two stations were combined into one in 1934. Light industry slowly developed, reaching a peak in the 1970s with a number of factories on the edge of town, such as the Roneo Vickers office machinery company, Colvern manufacturers of wireless components, May's Sheet Metal Works and brush manufacturers Betterware. Suburban expansion increased the population and reinforced Romford's position as a significant regional town centre. The Liberty Shopping Centre
The Liberty Shopping Centre is a covered shopping centre in Romford, the largest such centre in the town. It was originally built in 1968 and underwent a four-year redevelopment completed in 2003. The centre takes its name from the former Libert ...
was constructed in the 1960s, and has been modernised and supplemented with further shopping centres throughout the town, including The Mall, opened in 1990 (as 'Liberty 2'); and The Brewery, opened in 2000 on the site of the old Star Brewery.
Local government
Romford formed a chapelry in the large ancient parish of Hornchurch in the Becontree hundred of Essex; as well as the town it included the wards of Collier Row, Harold Wood, and Noak Hill. Through ancient custom the area enjoyed special status and a charter in 1465 removed the parish from the Becontree hundred and the county of Essex and it instead formed the independent liberty of Havering governed from a court house in the market place. Over time the vestry of Romford chapelry absorbed the local powers that would usually be held by the parish authorities in Hornchurch and in 1849 Romford became a separate parish within the liberty. Improvement commissioners were set up in 1819 for paving, lighting, watching, and cleansing of the marketplace and main streets. As the town grew this arrangement became ineffective at controlling sanitation and in 1851 a local board of health was set up for the parish; although its area was reduced in 1855 to cover only the town ward. The remainder of the parish became part of the Romford rural sanitary district in 1875. These changes and the introduction of the Romford Poor Law Union in 1836 eroded the powers of the liberty and it was finally abolished in 1892 and reincorporated into Essex. The Local Government Act 1894 reformed local government and created the Romford Urban District and Romford Rural District to replace the local board and sanitary district; following which the Romford parish was split into ''Romford Urban'' and ''Romford Rural'' along the lines of the urban district. In 1900 the parish was recombined and the urban district expanded to cover all of the former area of the historic chapelry, except for Noak Hill which remained in the rural district and had become a parish in its own right in 1895. The enlarged urban district formed part of the London Traffic Area from 1924 and the London Passenger Transport Area from 1933. The suburban expansion of London caused an increase in population during the 1930s and the urban district was expanded further in 1934, taking in the parishes of Havering-atte-Bower and Noak Hill. It was incorporated as the Municipal Borough of Romford in 1937. In 1965 the municipal borough was abolished and its former area was combined with that of Hornchurch Urban District; it was again removed from Essex and since then has formed the northern part of the London Borough of Havering inGreater London
Greater may refer to:
*Greatness, the state of being great
*Greater than, in inequality (mathematics), inequality
*Greater (film), ''Greater'' (film), a 2016 American film
*Greater (flamingo), the oldest flamingo on record
*Greater (song), "Greate ...
.
Suburban expansion
 There was early expansion in the 1840s when 200 cottages were built in the area formerly occupied by an army barracks; it was known as ''New Romford''. To acknowledge the military connection, when in 1961 these were in turn replaced with new housing the name ''Waterloo Road Estate'' was applied. To the east of the market place from 1850 middle class suburban housing was constructed with a much larger area of built-over to the south of the railway from 1851. Through a gradual process of selling off former manors, houses were built radiating from the town in all directions for about a mile. More significant growth occurred between 1910 and 1911 with the construction of
There was early expansion in the 1840s when 200 cottages were built in the area formerly occupied by an army barracks; it was known as ''New Romford''. To acknowledge the military connection, when in 1961 these were in turn replaced with new housing the name ''Waterloo Road Estate'' was applied. To the east of the market place from 1850 middle class suburban housing was constructed with a much larger area of built-over to the south of the railway from 1851. Through a gradual process of selling off former manors, houses were built radiating from the town in all directions for about a mile. More significant growth occurred between 1910 and 1911 with the construction of Romford Garden Suburb
Romford Garden Suburb (otherwise known as the Gidea Park Exhibition Estate), is a late-Edwardian housing development in Gidea Park, in the London Borough of Havering. The object of the new suburb, which was built on land belonging to Gidea Hall, ...
, which included Raphael Park and Gidea Park railway station. Large sections of land to the north of the town at Collier Row were developed in the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the World War I, First World War to the beginning of the World War II, Second World War. The in ...
and after World War II, the London County Council built the Harold Hill estate to the north east from 1948 to 1958.
The right to supply electricity to the town was secured by the County of London Electricity Supply Company in 1913. Initially power was generated within the Star Brewery site, with the supply switching to Barking Power Station in 1925. Gas supply began in 1825 with gas works of constructed by 1938. Following the Telegraph Act 1899
The Telegraph Act 1899 is an Act of Parliament in the United Kingdom that allowed urban district, borough and burgh councils to construct and operate telephone exchanges, on a similar basis to the then-usual municipal provision of other utiliti ...
Romford became part of the Post Office London telephone area
020 is the national dialling code for London in the United Kingdom. All subscriber numbers within the area code consist of eight digits and it has capacity for approaching 100 million telephone numbers. The code is used at 170 telephone exch ...
and the Romford exchange was recorded as having 240 subscribers in 1916. The town water supply initially came from the Havering Well, and 1859 a new public well and pump was built at the east end of the market. The South Essex Waterworks Company
Essex and Suffolk Water is a water supply company in the United Kingdom. It operates in two geographically distinct areas, one serving parts of Norfolk and Suffolk, and the other serving parts of Essex and Greater London. The total population se ...
started installing mains water supply in 1863 and had offices in South Street. By 1905 its supply was serving Ilford, Collier Row, Ardleigh Green, Brentwood, and Hornchurch. Sewage works were installed by the local board at Oldchurch in 1862, with further works built in Hornchurch in 1869.
Governance
Sport
Romford F.C., who currently play in the Essex Senior League, is the local football team. The London Raiders ice hockey team is based in Romford. Romford is home to the Romford and Gidea Park Rugby Football Club, which was established in 1927. In 2003, the club became one of the first in the country to have a ladies Rugby team.Geography


 The town centre is about above sea level on a gravel terrace rising from the River Thames. The north of the town has developed on London Clay and is situated as much as above sea level. A continuous gentle rise in the eastern suburbs towards Gidea Park and Harold Wood peaks around around the Harold Court. On the northern side, Harold Hill peaks at . The semi-rural area north of Collier Row and Harold Hill consists of many rolls of hills, with elevation peaking at the village of Havering-atte-Bower, .
The town centre is for the most part contained within a ring road formed of St Edwards Way, Mercury Gardens, Thurloe Gardens, Oldchurch Road and Waterloo Road. The market place and much of South Street and the High Street are pedestrianised. The railway cuts through the town from east to west on a viaduct, with the bulk of the central Romford area to its north. The River Rom flows through the town in underground channels and joins the Thames after flowing through Hornchurch; elsewhere along its course it is known as the River Beam and forms part of the strategic waterways
The town centre is about above sea level on a gravel terrace rising from the River Thames. The north of the town has developed on London Clay and is situated as much as above sea level. A continuous gentle rise in the eastern suburbs towards Gidea Park and Harold Wood peaks around around the Harold Court. On the northern side, Harold Hill peaks at . The semi-rural area north of Collier Row and Harold Hill consists of many rolls of hills, with elevation peaking at the village of Havering-atte-Bower, .
The town centre is for the most part contained within a ring road formed of St Edwards Way, Mercury Gardens, Thurloe Gardens, Oldchurch Road and Waterloo Road. The market place and much of South Street and the High Street are pedestrianised. The railway cuts through the town from east to west on a viaduct, with the bulk of the central Romford area to its north. The River Rom flows through the town in underground channels and joins the Thames after flowing through Hornchurch; elsewhere along its course it is known as the River Beam and forms part of the strategic waterways Blue Ribbon Network
The Blue Ribbon Network is a policy element of the London Plan relating to the waterways of London, England.
Aside from the River Thames, the major components of the network are:
#Grand Union Canal
#Regent's Canal
#River Lee Navigation
#River Br ...
. Romford has formed part of the continuously built-up area of London since the 1930s and is contiguous with Rush Green Rush Green may refer to:
* Rush Green, London
* Rush Green, Essex
*Rush Green, East Hertfordshire
Rush Green is a hamlet on the outskirts of Hertford , Hertfordshire. The Roman road Ermine Street passed through Rush Green.http://www.hertfordhe ...
to the west, Collier Row to the north, Gidea Park to the east and Hornchurch to the south east.
The Romford post town covers all of the former municipal borough and extends over a much wider area, including parts of Barking and Dagenham and Epping Forest.
Neighbourhoods of Romford include: Collier Row, Gidea Park, Harold Hill, Harold Park, Harold Wood, Havering-atte-Bower, Rise Park and Rush Green Rush Green may refer to:
* Rush Green, London
* Rush Green, Essex
*Rush Green, East Hertfordshire
Rush Green is a hamlet on the outskirts of Hertford , Hertfordshire. The Roman road Ermine Street passed through Rush Green.http://www.hertfordhe ...
.
Romford is located northeast of Charing Cross
Charing Cross ( ) is a junction in Westminster, London, England, where six routes meet. Clockwise from north these are: the east side of Trafalgar Square leading to St Martin's Place and then Charing Cross Road; the Strand leading to the City; ...
in central London; northeast of Ilford; north of Dagenham
Dagenham () is a town in East London, England, within the London Borough of Barking and Dagenham. Dagenham is centred east of Charing Cross.
It was historically a rural parish in the Becontree Hundred of Essex, stretching from Hainault Forest ...
; northwest of Grays
Grays or Greys may refer to:
Places
* Grays Bay, Nunavut, Canada
* Grays, Essex, a town in Essex, England
** Grays railway station
** Grays School
* Grays, Kent, a hamlet in Kent, England
* Rotherfield Greys or Greys, a village in Oxfordshire, En ...
; south-west of Brentwood; west of Basildon; and southeast of Epping.
Climate
Climate data for Romford is taken from the nearest weather station at Greenwich, around southwest of the marketplace.Demography
The Havering committee area for Romford is defined as the wards of Romford Town and Brooklands. Demographic data is produced by the Office for National Statistics for these wards. In 2001 the population of Romford Town was 13,200 and Brooklands was 13,024, giving a total population of 26,224. In contrast, the approximate population of the area within the 2005 Romford Urban Strategy was estimated to be 36,500. 71.52% in Romford Town and 70.48% in Brooklands report their religion as Christian, compared to 76.13% for Havering, 58.23% in London and 71.74% in England. 15.71% in Romford Town and 16.62% in Brooklands report having no religion, compared to 13.18% in Havering, 15.76% in London and 14.59% in England. In 2011, the Romford Parliament constituency was 82% White British, 5.8% Asian, 5% Other White and 4.7% Black out of a total population of 95,894. The constituency is predominantly Christian with 64% of the residents reporting that religion. Out of the wards that make up Romford overall, the highest male life expectancy was in Squirrel's Heath (80.7 years) while the highest female expectancy was in Romford Town (85.7 years). The lowest were Heaton (76.2 years) and Heaton and Gooshays (both 81.3 years) respectively. The average house price as of 2014 was £225,000 in Romford Town ward. In the Pettits ward, 87.5% of houses were owned by households; the lowest figure, and the only minority one, was Gooshays ward with 48.6%.Economy

 Romford is recognised in the London Plan as one of 13 regionally significant metropolitan centres in Greater London, with a considerable catchment area. The total commercial floorspace in the town was in 2002, of which was retail space and was offices. The retail space is growing and in 2005 consisted of . The retail economy is complemented by a
Romford is recognised in the London Plan as one of 13 regionally significant metropolitan centres in Greater London, with a considerable catchment area. The total commercial floorspace in the town was in 2002, of which was retail space and was offices. The retail space is growing and in 2005 consisted of . The retail economy is complemented by a central business district
A central business district (CBD) is the commercial and business centre of a city. It contains commercial space and offices, and in larger cities will often be described as a financial district. Geographically, it often coincides with the "city ...
close to the railway station, where the offices of employers such as Aon
Aon or AON may refer to:
* Aon (mythology), son of Poseidon in Greek mythology
* ''Aon'' (moth), a genus of moths in the family Erebidae
* Aon (trigraph), a Latin trigraph
* "Aon", a composition by jazz pianist Harold Mabern, 1968
Business an ...
are located. Employment in the town centre was categorised in 2002 as approximately 40% commercial office, 40% comparison retail, 10% hospitality, 5% public sector, 2.5% service retail and 2.5% arts and entertainment. Compared to the similar east London areas of Ilford, Stratford and Barking, there is more comparison retail and commercial office employment in Romford and less public sector work. The total turnover of £413,395,000 in 2002 for Romford was larger than any other comparable town centre in east London and approximately 70% came from the commercial office businesses.
There is a developed night time economy, greater than in any other metropolitan centre in Greater London, with of cinemas, theatres and concert hall space; of bars and pubs; of cafés and restaurants; and of fast food and take away venues. The night time economy is almost as significant as the day economy with around 12,000 visits to Romford during the day and 11,000 visits to pubs, clubs and bars at night.
As of 2012, Romford has of total town centre floorspace (retail, leisure and vacant), placing it fifth in Greater London only behind the West End, Croydon, Kingston upon Thames and Stratford for "town centre vitality and viability".
Transport
Railway
Great Eastern Main Line
The Great Eastern Main Line (GEML, sometimes referred to as the East Anglia Main Line) is a major railway line on the British railway system which connects Liverpool Street station in central London with destinations in east London and t ...
and the Elizabeth line, in London fare zone 6. Elizabeth line trains call at the station, formed of high-frequency services between London Liverpool Street and Shenfield.Romford Rail StationTransport for London Services will extend through central London to Reading when the line is opened fully. Some
Greater Anglia
Greater Anglia (legal name Transport UK East Anglia Limited) is a British train operating company owned as a joint venture by Transport UK Group and Mitsui & Co. It operates the East Anglia franchise, providing the commuter and inter-city ser ...
services to/from and also call at the station. A branch line shuttle on the Romford to Upminster Line is operated by London Overground.
Buses
Romford is a hub of theLondon Buses
London Buses is the subsidiary of Transport for London (TfL) that manages most bus services in London, England. It was formed following the Greater London Authority Act 1999 that transferred control of London Regional Transport (LRT) bus se ...
network, with services to Canning Town
Canning Town is a district in the London Borough of Newham, East London. The district is located to the north of the Royal Victoria Dock, and has been described as the "Child of the Victoria Docks" as the timing and nature of its urbanisation ...
, Stratford, Leytonstone and Dagenham
Dagenham () is a town in East London, England, within the London Borough of Barking and Dagenham. Dagenham is centred east of Charing Cross.
It was historically a rural parish in the Becontree Hundred of Essex, stretching from Hainault Forest ...
; there are also feeder services from the large housing developments at Collier Row and Harold Hill. There are night bus services to Stratford, Harold Hill and Paddington. Romford town centre has a very high Public Transport Accessibility Level
The public transport accessibility level (PTAL) is a method sometimes used in United Kingdom transport planning to assess the access level of geographical areas to public transport.
PTAL is a simple, easily calculated approach that hinges on th ...
score of 6.
There is a proposal that Romford will be served by a future extension of the East London Transit.
Roads
The A12 trunk road passes to the north of Romford, while theA118 road
The A118 is a road in east London, England which links Bow Interchange with Gallows Corner in Romford via Stratford and Ilford. The section from Bow Interchange to Gallows Corner formed the original route of the A12 until the designatio ...
from Stratford connects with it at Gallows Corner at the start of the A127 road to Southend.
Culture

 Havering Council's urban strategy aims to make Romford a cultural destination, whilst recognising that Hornchurch forms the main cultural hub of the borough with a large theatre and arts spaces. As a former market and coaching town, Romford is well served by public houses and two that are located in the market place are listed buildings. The market and adjacent streets also form a conservation area.
Mass entertainment facilities in the town include the Brookside Theatre, Romford Greyhound Stadium, one of the few remaining dog racing tracks in London; 2 multi-screen cinemas; and until April 2013
Havering Council's urban strategy aims to make Romford a cultural destination, whilst recognising that Hornchurch forms the main cultural hub of the borough with a large theatre and arts spaces. As a former market and coaching town, Romford is well served by public houses and two that are located in the market place are listed buildings. The market and adjacent streets also form a conservation area.
Mass entertainment facilities in the town include the Brookside Theatre, Romford Greyhound Stadium, one of the few remaining dog racing tracks in London; 2 multi-screen cinemas; and until April 2013 Romford Ice Arena
Romford Ice Arena was an ice rink located in Romford in the London Borough of Havering, England. The venue was built in the 1980s and at the time of opening in 1987 was equipped with a full range of facilities, including a cafe and arcade games. ...
, which was home to the local Romford Raiders ice hockey team. The Dolphin Centre
The Dolphin Centre was a swimming and leisure facility in Romford, in the London Borough of Havering, England.
History
Havering London Borough Council approved the design and £7.5 million construction of the Dolphin Centre in April 1980; it wa ...
was a popular swimming and leisure facility located in the town from 1982 to 1995, but the site was redeveloped into the current Axis residential tower block and Asda superstore in the mid-2000s. There is also a Romford F.C. associated with the town. Romford Bowls Club is based in Lodge Farm Park. 1980s Post Punk bands Department S and Purple Hearts both have origins in Romford. The town is strongly associated with the electronic music group Underworld, who cite Romford in their hit "Born Slippy
"Born Slippy .NUXX" is a song by British electronic music group Underworld. It was first released as the B-side to "Born Slippy", in May 1995. The fragmented lyrics, by vocalist Karl Hyde, describe the perspective of an alcoholic.
After it w ...
", affiliated to the movie ''Trainspotting
Trainspotting may refer to:
* Trainspotting (hobby), an amateur interest in railways/railroads
* ''Trainspotting'' (novel), a 1993 novel by Irvine Welsh
** ''Trainspotting'' (film), a 1996 film based on the novel
*** ''Trainspotting'' (soundtr ...
''.
Romford's position as a focus for electronic music production was reinforced by the presence of the Strictly Underground and Suburban Base
Suburban Base Records is a British breakbeat hardcore, rave and jungle/drum and bass record label. It is based in Romford, Havering, England. It was established by Danny Donnelly and operated in the UK from 1990 to 1997 and in the United States ...
record labels, with Suburban Base developing from the Boogie Times record store. According to a Billboard
A billboard (also called a hoarding in the UK and many other parts of the world) is a large outdoor advertising structure (a billing board), typically found in high-traffic areas such as alongside busy roads. Billboards present large advertise ...
article in 1992, Romford-produced dance music formed part of a trend favouring suburban and provincial "bedroom" record labels over those in central London. In 2013, the film '' Death Walks'' was filmed in Romford over a four-month period. The cult TV series '' Garth Marenghi's Darkplace'' was set in the fictional Darkplace Hospital, in Romford. The local newspapers for the town and the borough of Havering are the '' Romford Recorder'', ''Romford and Havering Post
Archant Limited is a newspaper and magazine publishing company headquartered in Norwich, England. The group publishes four daily newspapers, around 50 weekly newspapers, and 80 consumer and contract magazines.
Archant employs around 1,250 empl ...
'' and ''Romford Yellow Advertiser
The Tindle Group is a British multimedia company operating regional newspapers and radio stations across the British Isles.
It publishes over 200 local newspapers in the UK, a number of which are over 100 years old.
The company is based in Fa ...
''. Two radio stations are located in the area: Time 107.5
Time 107.5 is an independent local radio station, based in Romford and broadcasting to East London and parts of Essex.
The station strapline is "All Time Favourites" and the station is available on FM on 107.5 MHz in the broadcast area and ...
anBedrock Radio
(a community health and hospital radio station).
See also
* List of people from Havering * List of schools in HaveringReferences
Further reading
*External links
* {{Authority control Areas of London Districts of the London Borough of Havering Metropolitan centres of London Market towns in London District centres of London