
Robotics is the
interdisciplinary
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, economi ...
study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of
robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
s.
Within
mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines and mechanism (engineering), mechanisms that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and engineering mathematics, mathematics principl ...
, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in
computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
, robotics focuses on robotic automation algorithms. Other disciplines contributing to robotics include
electrical
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
,
control,
software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
,
information
Information is an Abstraction, abstract concept that refers to something which has the power Communication, to inform. At the most fundamental level, it pertains to the Interpretation (philosophy), interpretation (perhaps Interpretation (log ...
,
electronic,
telecommunication
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
,
computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
,
mechatronic, and
materials
A material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their ge ...
engineering.
The goal of most robotics is to design machines that can help and assist
humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
. Many robots are built to do jobs that are hazardous to people, such as finding survivors in unstable ruins, and exploring space, mines and shipwrecks. Others replace people in jobs that are boring, repetitive, or unpleasant, such as cleaning, monitoring, transporting, and assembling. Today, robotics is a rapidly growing field, as technological advances continue; researching, designing, and building new robots serve various practical purposes.
Robotics aspects
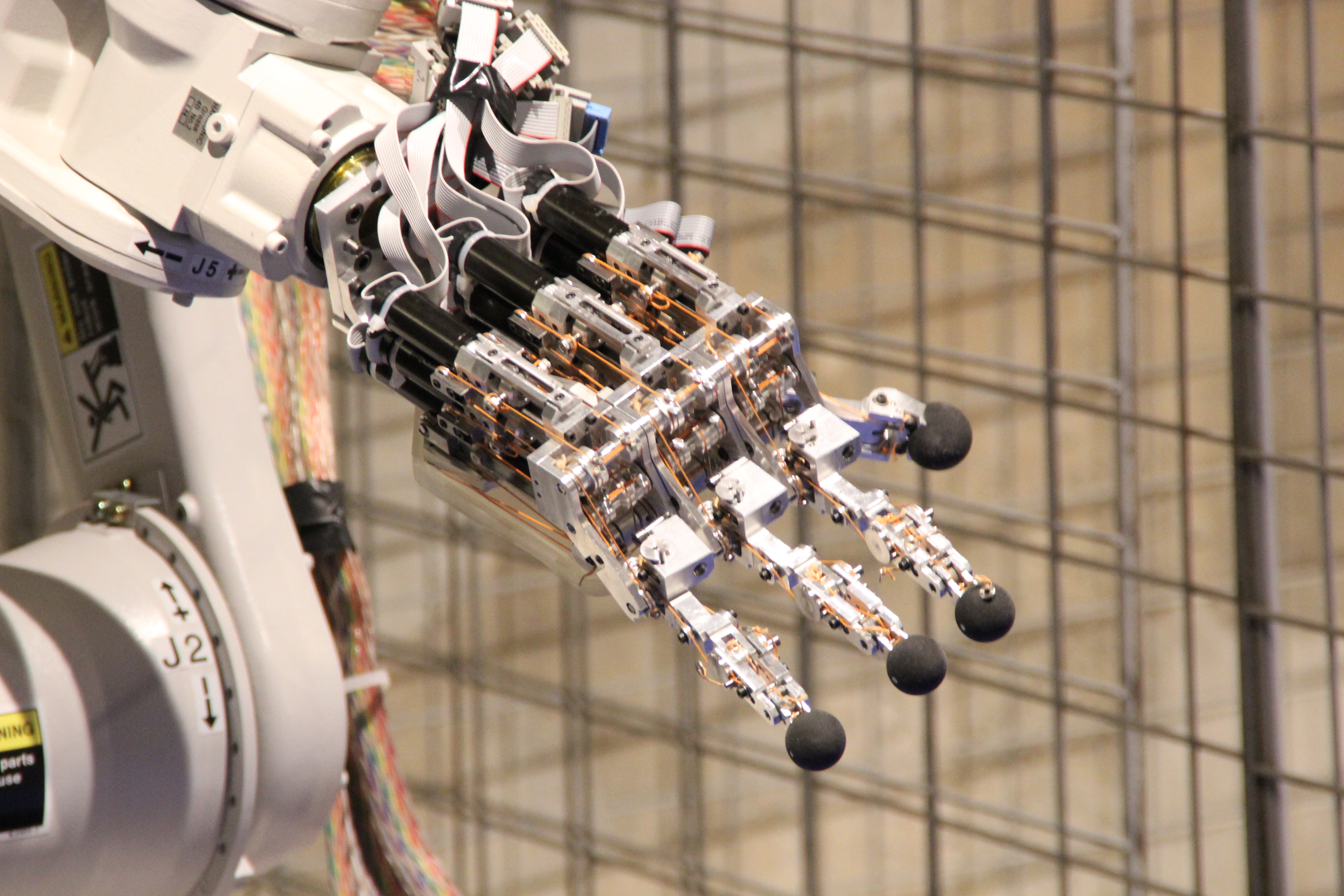
Robotics usually combines three aspects of design work to create
robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
systems:
# Mechanical construction: a frame, form or shape designed to achieve a particular task. For example, a robot designed to travel across heavy dirt or mud might use caterpillar tracks. Origami inspired robots can sense and analyze in extreme environments. The mechanical aspect of the robot is mostly the creator's solution to completing the assigned task and dealing with the physics of the environment around it. Form follows function.
# Electrical components that power and control the machinery. For example, the robot with
caterpillar tracks would need some kind of power to move the tracker treads. That power comes in the form of electricity, which will have to travel through a wire and originate from a battery, a basic
electrical circuit
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., battery (electricity), batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e. ...
. Even petrol-powered
machines
A machine is a physical system that uses power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolec ...
that get their power mainly from petrol still require an electric current to start the combustion process which is why most petrol-powered machines like cars, have batteries. The electrical aspect of robots is used for movement (through motors), sensing (where electrical signals are used to measure things like heat, sound, position, and energy status), and operation (robots need some level of
electrical energy
Electrical energy is the energy transferred as electric charges move between points with different electric potential, that is, as they move across a voltage, potential difference. As electric potential is lost or gained, work is done changing the ...
supplied to their motors and sensors in order to activate and perform basic operations)
#
Software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
. A program is how a robot decides when or how to do something. In the caterpillar track example, a robot that needs to move across a muddy road may have the correct mechanical construction and receive the correct amount of power from its battery, but would not be able to go anywhere without a program telling it to move. Programs are the core essence of a robot, it could have excellent mechanical and electrical construction, but if its program is poorly structured, its performance will be very poor (or it may not perform at all). There are three different types of robotic programs: remote control, artificial intelligence, and hybrid. A robot with
remote control
A remote control, also known colloquially as a remote or clicker, is an consumer electronics, electronic device used to operate another device from a distance, usually wirelessly. In consumer electronics, a remote control can be used to operat ...
programming has a preexisting set of commands that it will only perform if and when it receives a signal from a control source, typically a human being with remote control. It is perhaps more appropriate to view devices controlled primarily by human commands as falling in the discipline of automation rather than robotics. Robots that use
artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
interact with their environment on their own without a control source, and can determine reactions to objects and problems they encounter using their preexisting programming. A hybrid is a form of programming that incorporates both AI and RC functions in them.
Applied robotics
As many robots are designed for specific tasks, this method of classification becomes more relevant. For example, many robots are designed for assembly work, which may not be readily adaptable for other applications. They are termed "assembly robots". For seam welding, some suppliers provide complete welding systems with the robot i.e. the welding equipment along with other material handling facilities like turntables, etc. as an integrated unit. Such an integrated robotic system is called a "welding robot" even though its discrete manipulator unit could be adapted to a variety of tasks. Some robots are specifically designed for heavy load manipulation, and are labeled as "heavy-duty robots".
Current and potential applications include:
*
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
. Robots have been increasingly used in manufacturing since the 1960s. According to the
Robotic Industries Association
The Association for Advancing Automation (A3) is an international trade group that serves the robotics industry. It was founded in 1974 and is headquartered in Ann Arbor, Michigan
Ann Arbor is a city in Washtenaw County, Michigan, United Stat ...
US data, in 2016 the automotive industry was the main customer of industrial robots with 52% of total sales. In the auto industry, they can amount for more than half of the "labor". There are even "
lights off" factories such as an IBM keyboard manufacturing factory in Texas that was fully automated as early as 2003.
*
Autonomous transport
Vehicular automation is using technology to assist or replace the operator of a vehicle such as a car, truck, aircraft, rocket, military vehicle, or boat. Assisted vehicles are ''semi-autonomous'', whereas vehicles that can travel without a ...
including airplane
autopilot
An autopilot is a system used to control the path of a vehicle without requiring constant manual control by a human operator. Autopilots do not replace human operators. Instead, the autopilot assists the operator's control of the vehicle, allow ...
and
self-driving cars
*
Domestic robots including
robotic vacuum cleaners,
robotic lawn mowers, dishwasher loading and
flatbread baking.
*
Construction robots. Construction robots can be separated into three types: traditional robots,
robotic arm
A robotic arm is a type of mechanical arm, usually programmable, with similar functions to a human arm; the arm may be the sum total of the mechanism or may be part of a more complex robot. The links of such a manipulator are connected by join ...
, and
robotic exoskeleton.
*
Automated mining.
* Space exploration, including
Mars rovers.
* Energy applications including cleanup of nuclear contaminated areas; and cleaning solar panel arrays.
*
Medical robots and
Robot-assisted surgery designed and used in clinics.
*
Agricultural robots. The use of robots in agriculture is closely linked to the concept of
AI-assisted
precision agriculture and
drone usage.
* Food processing. Commercial examples of kitchen automation are Flippy (burgers), Zume Pizza (pizza), Cafe X (coffee), Makr Shakr (cocktails), Frobot (frozen yogurts), Sally (salads), salad or food bowl robots manufactured by Dexai (a
Draper Laboratory spinoff, operating on military bases), and integrated food bowl assembly systems manufactured by
Spyce Kitchen (acquired by
Sweetgreen) and
Silicon Valley
Silicon Valley is a region in Northern California that is a global center for high technology and innovation. Located in the southern part of the San Francisco Bay Area, it corresponds roughly to the geographical area of the Santa Clara Valley ...
startup Hyphen. Other examples may include manufacturing technologies based on
3D Food Printing.
*
Military robot
Military robots are autonomous robots or remote-controlled mobile robots designed for military applications, from transport to search & rescue and attack.
Some such systems are currently in use, and many are under development. The difference b ...
s.
* Robot sports for entertainment and education, including
Robot combat,
Autonomous racing,
drone racing
Drone racing is a motorsport where participants operate radio-controlled aircraft (typically small quadcopter unmanned aerial vehicle, drones) equipped with onboard digital camera, digital video cameras, with the operator looking at a compa ...
, and
FIRST Robotics.
Mechanical robotics areas
Power source

At present, mostly (lead–acid)
batteries are used as a power source. Many different types of batteries can be used as a power source for robots. They range from lead–acid batteries, which are safe and have relatively long shelf lives but are rather heavy compared to silver–cadmium batteries which are much smaller in volume and are currently much more expensive. Designing a battery-powered robot needs to take into account factors such as safety, cycle lifetime, and
weight
In science and engineering, the weight of an object is a quantity associated with the gravitational force exerted on the object by other objects in its environment, although there is some variation and debate as to the exact definition.
Some sta ...
. Generators, often some type of
internal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal comb ...
, can also be used. However, such designs are often mechanically complex and need fuel, require heat dissipation, and are relatively heavy. A tether connecting the robot to a power supply would remove the power supply from the robot entirely. This has the advantage of saving weight and space by moving all power generation and storage components elsewhere. However, this design does come with the drawback of constantly having a cable connected to the robot, which can be difficult to manage.
Potential power sources could be:
*
pneumatic
Pneumatics (from Greek 'wind, breath') is the use of gas or pressurized air in mechanical systems.
Pneumatic systems used in Industrial sector, industry are commonly powered by compressed air or compressed inert gases. A centrally located a ...
(compressed gases)
*
Solar power
Solar power, also known as solar electricity, is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Solar panels use the photovoltaic effect to c ...
(using the sun's energy and converting it into electrical power)
*
hydraulic
Hydraulics () is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counterpart of pneumatics, which concer ...
s (liquids)
*
flywheel energy storage
* organic garbage (through
anaerobic digestion
Anaerobic digestion is a sequence of processes by which microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. The process is used for industrial or domestic purposes to Waste management, manage waste or to produce fuels. Mu ...
)
*
nuclear
Actuation

Actuators are the "
muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
s" of a robot, the parts which convert
stored energy into movement. By far the most popular actuators are electric motors that rotate a wheel or gear, and linear actuators that control industrial robots in factories. There are some recent advances in alternative types of actuators, powered by electricity, chemicals, or compressed air.
Electric motors
The vast majority of robots use
electric motor
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a electromagnetic coil, wire winding to gene ...
s, often
brushed and
brushless DC motors in portable robots or AC motors in industrial robots and
CNC machines. These motors are often preferred in systems with lighter loads, and where the predominant form of motion is rotational.
Linear actuators
Various types of linear actuators move in and out instead of by spinning, and often have quicker direction changes, particularly when very large forces are needed such as with industrial robotics. They are typically powered by compressed and oxidized air (
pneumatic actuator) or an oil (
hydraulic actuator
A hydraulic cylinder (also called a linear hydraulic motor) is a mechanical actuator that is used to give a unidirectional force through a unidirectional stroke. It has many applications, notably in construction equipment ( engineering vehicles ...
) Linear actuators can also be powered by electricity which usually consists of a motor and a leadscrew. Another common type is a mechanical linear actuator such as a rack and pinion on a car.
Series elastic actuators
Series elastic actuation (SEA) relies on the idea of introducing intentional elasticity between the motor actuator and the load for robust force control. Due to the resultant lower reflected inertia, series elastic actuation improves safety when a robot interacts with the environment (e.g., humans or workpieces) or during collisions. Furthermore, it also provides
energy efficiency and shock absorption (mechanical filtering) while reducing excessive wear on the transmission and other mechanical components. This approach has successfully been employed in various robots, particularly advanced manufacturing robots and walking
humanoid
A humanoid (; from English ''human'' and '' -oid'' "resembling") is a non-human entity with human form or characteristics. By the 20th century, the term came to describe fossils which were morphologically similar, but not identical, to those of ...
robots.
The controller design of a series elastic actuator is most often performed within the
passivity framework as it ensures the safety of interaction with unstructured environments. Despite its remarkable stability and robustness, this framework suffers from the stringent limitations imposed on the controller which may trade-off performance. The reader is referred to the following survey which summarizes the common controller architectures for SEA along with the corresponding ''sufficient'' passivity conditions. One recent study has derived the ''necessary and sufficient'' passivity conditions for one of the most common
impedance control architectures, namely velocity-sourced SEA. This work is of particular importance as it drives the non-conservative passivity bounds in an SEA scheme for the first time which allows a larger selection of control gains.
Air muscles
Pneumatic artificial muscles also known as air muscles, are special tubes that expand (typically up to 42%) when air is forced inside them. They are used in some robot applications.
Wire muscles
Muscle wire, also known as shape memory alloy, is a material that contracts (under 5%) when electricity is applied. They have been used for some small robot applications.
Electroactive polymers
EAPs or EPAMs are a plastic material that can contract substantially (up to 380% activation strain) from electricity, and have been used in facial muscles and arms of humanoid robots, and to enable new robots to float, fly, swim or walk.
Piezo motors
Recent alternatives to DC motors are
piezo motors or
ultrasonic motors. These work on a fundamentally different principle, whereby tiny
piezoceramic elements, vibrating many thousands of times per second, cause linear or rotary motion. There are different mechanisms of operation; one type uses the vibration of the piezo elements to step the motor in a circle or a straight line. Another type uses the piezo elements to cause a nut to vibrate or to drive a screw. The advantages of these motors are
nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the Molecule">molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm), or nanometer (American spelling
Despite the va ...
resolution, speed, and available force for their size. These motors are already available commercially and being used on some robots.
Elastic nanotubes
Elastic nanotubes are a promising artificial muscle technology in early-stage experimental development. The absence of defects in
carbon nanotube
A carbon nanotube (CNT) is a tube made of carbon with a diameter in the nanometre range ( nanoscale). They are one of the allotropes of carbon. Two broad classes of carbon nanotubes are recognized:
* ''Single-walled carbon nanotubes'' (''S ...
s enables these filaments to deform elastically by several percent, with energy storage levels of perhaps 10
J/cm
3 for metal nanotubes. Human biceps could be replaced with an 8 mm diameter wire of this material. Such compact "muscle" might allow future robots to outrun and outjump humans.
Sensing
Sensors allow robots to receive information about a certain measurement of the environment, or internal components. This is essential for robots to perform their tasks, and act upon any changes in the environment to calculate the appropriate response. They are used for various forms of measurements, to give the robots warnings about safety or malfunctions, and to provide real-time information about the task it is performing.
Touch
Current
robotic and
prosthetic hands receive far less
tactile information than the human hand. Recent research has developed a tactile
sensor array
A sensor array is a group of sensors, usually deployed in a certain geometry pattern, used for collecting and processing electromagnetic or acoustic signals. The advantage of using a sensor array over using a single sensor lies in the fact that an ...
that mimics the mechanical properties and touch receptors of human fingertips. The sensor array is constructed as a rigid core surrounded by conductive fluid contained by an elastomeric skin. Electrodes are mounted on the surface of the rigid core and are connected to an impedance-measuring device within the core. When the artificial skin touches an object the fluid path around the electrodes is deformed, producing impedance changes that map the forces received from the object. The researchers expect that an important function of such artificial fingertips will be adjusting the robotic grip on held objects.
Scientists from several
European countries and
Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
developed a
prosthetic
In medicine, a prosthesis (: prostheses; from ), or a prosthetic implant, is an artificial device that replaces a missing body part, which may be lost through physical trauma, disease, or a condition present at birth (Congenital, congenital disord ...
hand in 2009, called SmartHand, which functions like a real one —allowing patients to write with it, type on a
keyboard, play piano, and perform other fine movements. The prosthesis has sensors which enable the patient to sense real feelings in its fingertips.
Other
Other common forms of sensing in robotics use lidar, radar, and sonar.
Lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected li ...
measures the distance to a target by illuminating the target with laser light and measuring the reflected light with a sensor.
Radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
uses radio waves to determine the range, angle, or velocity of objects.
Sonar
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances ( ranging), communicate with or detect objects o ...
uses sound propagation to navigate, communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water.
Mechanical grippers
One of the most common types of end-effectors are "grippers". In its simplest manifestation, it consists of just two fingers that can open and close to pick up and let go of a range of small objects. Fingers can, for example, be made of a chain with a metal wire running through it. Hands that resemble and work more like a human hand include the
Shadow Hand and the
Robonaut hand. Hands that are of a mid-level complexity include the
Delft
Delft () is a List of cities in the Netherlands by province, city and Municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality in the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of South Holland, Netherlands. It is located between Rotterdam, to the southeast, ...
hand. Mechanical grippers can come in various types, including friction and encompassing jaws. Friction jaws use all the force of the gripper to hold the object in place using friction. Encompassing jaws cradle the object in place, using less friction.
Suction end-effectors
Suction end-effectors, powered by vacuum generators, are very simple astrictive devices that can hold very large loads provided the
prehension surface is smooth enough to ensure suction.
Pick and place robots for electronic components and for large objects like car windscreens, often use very simple vacuum end-effectors.
Suction is a highly used type of end-effector in industry, in part because the natural
compliance of soft suction end-effectors can enable a robot to be more robust in the presence of imperfect robotic perception. As an example: consider the case of a robot vision system that estimates the position of a water bottle but has 1 centimeter of error. While this may cause a rigid mechanical gripper to puncture the water bottle, the soft suction end-effector may just bend slightly and conform to the shape of the water bottle surface.
General purpose effectors
Some advanced robots are beginning to use fully humanoid hands, like the Shadow Hand, MANUS, and the Schunk hand. They have powerful
robot dexterity intelligence (RDI), with as many as 20
degrees of freedom
In many scientific fields, the degrees of freedom of a system is the number of parameters of the system that may vary independently. For example, a point in the plane has two degrees of freedom for translation: its two coordinates; a non-infinite ...
and hundreds of tactile sensors.
Control robotics areas



The mechanical structure of a robot must be controlled to perform tasks.
The control of a robot involves three distinct phases –
perception
Perception () is the organization, identification, and interpretation of sensory information in order to represent and understand the presented information or environment. All perception involves signals that go through the nervous syste ...
, processing, and action (
robotic paradigms).
Sensor
A sensor is often defined as a device that receives and responds to a signal or stimulus. The stimulus is the quantity, property, or condition that is sensed and converted into electrical signal.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a devi ...
s give information about the environment or the robot itself (e.g. the position of its joints or its end effector). This information is then processed to be stored or transmitted and to calculate the appropriate signals to the actuators (
motors), which move the mechanical structure to achieve the required co-ordinated motion or force actions.
The processing phase can range in complexity. At a reactive level, it may translate raw sensor information directly into actuator commands (e.g. firing motor power electronic gates based directly upon encoder feedback signals to achieve the required torque/velocity of the shaft).
Sensor fusion and internal models may first be used to estimate parameters of interest (e.g. the position of the robot's gripper) from noisy sensor data. An immediate task (such as moving the gripper in a certain direction until an object is detected with a proximity sensor) is sometimes inferred from these estimates. Techniques from
control theory
Control theory is a field of control engineering and applied mathematics that deals with the control system, control of dynamical systems in engineered processes and machines. The objective is to develop a model or algorithm governing the applic ...
are generally used to convert the higher-level tasks into individual commands that drive the actuators, most often using kinematic and dynamic models of the mechanical structure.
At longer time scales or with more sophisticated tasks, the robot may need to build and reason with a "cognitive" model.
Cognitive model
A cognitive model is a representation of one or more cognitive processes in humans or other animals for the purposes of comprehension and prediction. There are many types of cognitive models, and they can range from box-and-arrow diagrams to a se ...
s try to represent the robot, the world, and how the two interact. Pattern recognition and computer vision can be used to track objects.
techniques can be used to build maps of the world. Finally,
motion planning
Motion planning, also path planning (also known as the navigation problem or the piano mover's problem) is a computational problem to find a sequence of valid configurations that moves the object from the source to destination. The term is used ...
and other
artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
techniques may be used to figure out how to act. For example, a planner may figure out how to achieve a task without hitting obstacles, falling over, etc.
Modern commercial robotic control systems are highly complex, integrate multiple sensors and effectors, have many interacting degrees-of-freedom (DOF) and require operator interfaces, programming tools and real-time capabilities.
They are oftentimes interconnected to wider communication networks and in many cases are now both
IoT-enabled and mobile. Progress towards open architecture, layered, user-friendly and 'intelligent' sensor-based interconnected robots has emerged from earlier concepts related to
Flexible Manufacturing Systems (FMS), and several 'open or 'hybrid'
reference architectures exist which assist developers of robot control software and hardware to move beyond traditional, earlier notions of 'closed' robot control systems have been proposed.
Open architecture controllers are said to be better able to meet the growing requirements of a wide range of robot users, including system developers, end users and research scientists, and are better positioned to deliver the advanced robotic concepts related to
Industry 4.0.
In addition to utilizing many established features of robot controllers, such as position, velocity and force control of end effectors, they also enable IoT interconnection and the implementation of more advanced sensor fusion and control techniques, including adaptive control,
Fuzzy control
A fuzzy control system is a control system based on fuzzy logic – a mathematical system that analyzes analog input values in terms of logical variables that take on continuous values between 0 and 1, in contrast to classical or digital logi ...
and
Artificial Neural Network
In machine learning, a neural network (also artificial neural network or neural net, abbreviated ANN or NN) is a computational model inspired by the structure and functions of biological neural networks.
A neural network consists of connected ...
(ANN)-based control.
When implemented in real-time, such techniques can potentially improve the stability and performance of robots operating in unknown or uncertain environments by enabling the control systems to learn and adapt to environmental changes.
There are several examples of reference architectures for robot controllers, and also examples of successful implementations of actual robot controllers developed from them. One example of a generic reference architecture and associated interconnected, open-architecture robot and controller implementation was used in a number of research and development studies, including prototype implementation of novel advanced and intelligent control and environment mapping methods in real-time.
Manipulation
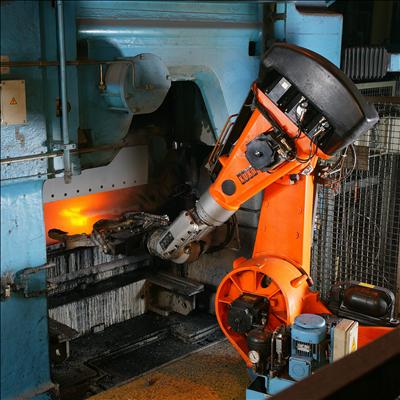


A definition of robotic manipulation has been provided by Matt Mason as: "manipulation refers to an agent's control of its environment through selective contact".
Robots need to manipulate objects; pick up, modify, destroy, move or otherwise have an effect. Thus the functional end of a robot arm intended to make the effect (whether a hand, or tool) are often referred to as ''
end effectors'', while the "arm" is referred to as a ''manipulator''. Most robot arms have replaceable end-effectors, each allowing them to perform some small range of tasks. Some have a fixed manipulator that cannot be replaced, while a few have one very general-purpose manipulator, for example, a humanoid hand.
Locomotion
Rolling robots

For simplicity, most mobile robots have four
wheel
A wheel is a rotating component (typically circular in shape) that is intended to turn on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machin ...
s or a number of
continuous track
Continuous track or tracked treads are a system of vehicle propulsion used in tracked vehicles, running on a continuous band of treads or track plates driven by two or more wheels. The large surface area of the tracks distributes the w ...
s. Some researchers have tried to create more complex wheeled robots with only one or two wheels. These can have certain advantages such as greater efficiency and reduced parts, as well as allowing a robot to navigate in confined places that a four-wheeled robot would not be able to.
= Two-wheeled balancing robots
=
Balancing robots generally use a
gyroscope
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining Orientation (geometry), orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in ...
to detect how much a robot is falling and then drive the wheels proportionally in the same direction, to counterbalance the fall at hundreds of times per second, based on the dynamics of an
inverted pendulum
An inverted pendulum is a pendulum that has its center of mass above its Lever, pivot point. It is unstable equilibrium, unstable and falls over without additional help. It can be suspended stably in this inverted position by using a control s ...
. Many different balancing robots have been designed. While the
Segway is not commonly thought of as a robot, it can be thought of as a component of a robot, when used as such Segway refer to them as RMP (Robotic Mobility Platform). An example of this use has been as
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
's
Robonaut that has been mounted on a Segway.
= One-wheeled balancing robots
=
A one-wheeled balancing robot is an extension of a two-wheeled balancing robot so that it can move in any 2D direction using a round ball as its only wheel. Several one-wheeled balancing robots have been designed recently, such as
Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. The institution was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools. In 1912, it became the Carnegie Institu ...
's "
Ballbot" which is the approximate height and width of a person, and
Tohoku Gakuin University
is a private university in Sendai, Miyagi, Sendai, Miyagi Prefecture, Japan. It was founded in 1886 under the influence of the Reformed Church in the United States, German Reformed Church missionaries. Miyagi Gakuin Women's University is its sist ...
's "BallIP". Because of the long, thin shape and ability to maneuver in tight spaces, they have the potential to function better than other robots in environments with people.
= Spherical orb robots
=
Several attempts have been made in robots that are completely inside a spherical ball, either by spinning a weight inside the ball, or by rotating the outer shells of the sphere. These have also been referred to as an
orb bot or a ball bot.
= Six-wheeled robots
=
Using six wheels instead of four wheels can give better traction or grip in outdoor terrain such as on rocky dirt or grass.
= Tracked robots
=
Tracks provide even more traction than a six-wheeled robot. Tracked wheels behave as if they were made of hundreds of wheels, therefore are very common for outdoor off-road robots, where the robot must drive on very rough terrain. However, they are difficult to use indoors such as on carpets and smooth floors. Examples include NASA's Urban Robot "Urbie".
Walking robots
Walking is a difficult and dynamic problem to solve. Several robots have been made which can walk reliably on two legs, however, none have yet been made which are as robust as a human. There has been much study on human-inspired walking, such as AMBER lab which was established in 2008 by the Mechanical Engineering Department at Texas A&M University. Many other robots have been built that walk on more than two legs, due to these robots being significantly easier to construct. Walking robots can be used for uneven terrains, which would provide better mobility and energy efficiency than other locomotion methods. Typically, robots on two legs can walk well on flat floors and can occasionally walk up
stairs
Stairs are a structure designed to bridge a large vertical direction, vertical distance between lower and higher levels by dividing it into smaller vertical distances. This is achieved as a diagonal series of horizontal platforms called steps wh ...
. None can walk over rocky, uneven terrain. Some of the methods which have been tried are:
= ZMP technique
=
The zero moment point (ZMP) is the algorithm used by robots such as
Honda
commonly known as just Honda, is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Conglomerate (company), conglomerate automotive manufacturer headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Founded in October 1946 by Soichiro Honda, Honda has bee ...
's
ASIMO
ASIMO (Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility) is a humanoid robot created by Honda in 2000.
In 2002, there were 20 units of the first ASIMO model produced; three different ASIMO models subsequently followed. As of February 2009, there were over ...
. The robot's onboard computer tries to keep the total
inertial forces (the combination of
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
's
gravity
In physics, gravity (), also known as gravitation or a gravitational interaction, is a fundamental interaction, a mutual attraction between all massive particles. On Earth, gravity takes a slightly different meaning: the observed force b ...
and the
acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the Rate (mathematics), rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Acceleration is one of several components of kinematics, the study of motion. Accelerations are Euclidean vector, vector ...
and deceleration of walking), exactly opposed by the floor
reaction force (the force of the floor pushing back on the robot's foot). In this way, the two forces cancel out, leaving no
moment (force causing the robot to rotate and fall over). However, this is not exactly how a human walks, and the difference is obvious to human observers, some of whom have pointed out that ASIMO walks as if it needs the
lavatory. ASIMO's walking algorithm is not static, and some dynamic balancing is used (see below). However, it still requires a smooth surface to walk on.
= Hopping
=
Several robots, built in the 1980s by
Marc Raibert at the
MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Established in 1861, MIT has played a significant role in the development of many areas of modern technology and sc ...
Leg Laboratory, successfully demonstrated very dynamic walking. Initially, a robot with only one leg, and a very small foot could stay upright simply by
hopping. The movement is the same as that of a person on a
pogo stick. As the robot falls to one side, it would jump slightly in that direction, in order to catch itself. Soon, the algorithm was generalised to two and four legs. A bipedal robot was demonstrated running and even performing
somersault
A somersault (also ''flip'', ''heli'', and in gymnastics ''salto'') is an acrobatics, acrobatic exercise in which a person's body Rotation#Sports, rotates 360° around a horizontal axis with the feet passing over the Human head, head. A somersau ...
s. A
quadruped
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion in which animals have four legs that are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four legs is said to be a quadruped (fr ...
was also demonstrated which could
trot, run,
pace, and bound. For a full list of these robots, see the MIT Leg Lab Robots page.
= Dynamic balancing (controlled falling)
=
A more advanced way for a robot to walk is by using a dynamic balancing algorithm, which is potentially more robust than the Zero Moment Point technique, as it constantly monitors the robot's motion, and places the feet in order to maintain stability. This technique was recently demonstrated by
Anybots' Dexter Robot, which is so stable, it can even jump. Another example is the
TU Delft Flame.
= Passive dynamics
=
Perhaps the most promising approach uses
passive dynamics where the
momentum
In Newtonian mechanics, momentum (: momenta or momentums; more specifically linear momentum or translational momentum) is the product of the mass and velocity of an object. It is a vector quantity, possessing a magnitude and a direction. ...
of swinging limbs is used for greater
efficiency
Efficiency is the often measurable ability to avoid making mistakes or wasting materials, energy, efforts, money, and time while performing a task. In a more general sense, it is the ability to do things well, successfully, and without waste.
...
. It has been shown that totally unpowered humanoid mechanisms can walk down a gentle slope, using only
gravity
In physics, gravity (), also known as gravitation or a gravitational interaction, is a fundamental interaction, a mutual attraction between all massive particles. On Earth, gravity takes a slightly different meaning: the observed force b ...
to propel themselves. Using this technique, a robot need only supply a small amount of motor power to walk along a flat surface or a little more to walk up a
hill
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct summit, and is usually applied to peaks which are above elevation compared to the relative landmass, though not as prominent as Mountain, mountains. Hills ...
. This technique promises to make walking robots at least ten times more efficient than ZMP walkers, like ASIMO.
Flying
A modern
passenger airliner is essentially a
flying robot, with two humans to manage it. The
autopilot
An autopilot is a system used to control the path of a vehicle without requiring constant manual control by a human operator. Autopilots do not replace human operators. Instead, the autopilot assists the operator's control of the vehicle, allow ...
can control the plane for each stage of the journey, including takeoff, normal flight, and even landing. Other flying robots are uninhabited and are known as
unmanned aerial vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) or unmanned aircraft system (UAS), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft with no human pilot, crew, or passengers onboard, but rather is controlled remotely or is autonomous.De Gruyter Handbook of Dron ...
s (UAVs). They can be smaller and lighter without a human pilot on board, and fly into dangerous territory for military surveillance missions. Some can even fire on targets under command. UAVs are also being developed which can fire on targets automatically, without the need for a command from a human. Other flying robots include
cruise missile
A cruise missile is an unmanned self-propelled guided missile that sustains flight through aerodynamic lift for most of its flight path. Cruise missiles are designed to deliver a large payload over long distances with high precision. Modern cru ...
s, the
Entomopter, and the
Epson micro helicopter robot. Robots such as the Air Penguin, Air Ray, and Air Jelly have lighter-than-air bodies, are propelled by paddles, and are guided by sonar.
= Biomimetic flying robots (BFRs)
=

BFRs take inspiration from flying mammals, birds, or insects. BFRs can have flapping wings, which generate the lift and thrust, or they can be propeller actuated. BFRs with flapping wings have increased stroke efficiencies, increased maneuverability, and reduced energy consumption in comparison to propeller actuated BFRs. Mammal and bird inspired BFRs share similar flight characteristics and design considerations. For instance, both mammal and bird inspired BFRs minimize
edge fluttering and
pressure-induced wingtip curl by increasing the rigidity of the wing edge and wingtips. Mammal and insect inspired BFRs can be impact resistant, making them useful in cluttered environments.
Mammal inspired BFRs typically take inspiration from bats, but the flying squirrel has also inspired a prototype.
Examples of bat inspired BFRs include Bat Bot and the DALER.
Mammal inspired BFRs can be designed to be multi-modal; therefore, they're capable of both flight and terrestrial movement. To reduce the impact of landing, shock absorbers can be implemented along the wings.
Alternatively, the BFR can pitch up and increase the amount of drag it experiences.
By increasing the drag force, the BFR will decelerate and minimize the impact upon grounding. Different land gait patterns can also be implemented.

Bird inspired BFRs can take inspiration from raptors, gulls, and everything in-between. Bird inspired BFRs can be feathered to increase the angle of attack range over which the prototype can operate before stalling.
The wings of bird inspired BFRs allow for in-plane deformation, and the in-plane wing deformation can be adjusted to maximize flight efficiency depending on the flight gait.
An example of a raptor inspired BFR is the prototype by Savastano et al. The prototype has fully deformable flapping wings and is capable of carrying a payload of up to 0.8 kg while performing a parabolic climb, steep descent, and rapid recovery. The gull inspired prototype by Grant et al. accurately mimics the elbow and wrist rotation of gulls, and they find that lift generation is maximized when the elbow and wrist deformations are opposite but equal.
Insect inspired BFRs typically take inspiration from beetles or dragonflies. An example of a beetle inspired BFR is the prototype by Phan and Park, and a dragonfly inspired BFR is the prototype by Hu et al. The flapping frequency of insect inspired BFRs are much higher than those of other BFRs; this is because of the
aerodynamics of insect flight. Insect inspired BFRs are much smaller than those inspired by mammals or birds, so they are more suitable for dense environments.
= Biologically-inspired flying robots
=

A class of robots that are biologically inspired, but which do not attempt to mimic biology, are creations such as the
Entomopter. Funded by
DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Adva ...
,
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
, the
United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the Air force, air service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is one of the six United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Tracing its ori ...
, and the
Georgia Tech Research Institute and patented by Prof.
Robert C. Michelson for covert terrestrial missions as well as flight in the lower
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun. It is also known as the "Red Planet", because of its orange-red appearance. Mars is a desert-like rocky planet with a tenuous carbon dioxide () atmosphere. At the average surface level the atmosph ...
atmosphere, the Entomopter flight propulsion system uses low
Reynolds number
In fluid dynamics, the Reynolds number () is a dimensionless quantity that helps predict fluid flow patterns in different situations by measuring the ratio between Inertia, inertial and viscous forces. At low Reynolds numbers, flows tend to ...
wings similar to those of the
hawk moth (Manduca sexta), but flaps them in a non-traditional "opposed x-wing fashion" while "blowing" the surface to enhance lift based on the
Coandă effect as well as to control vehicle attitude and direction. Waste gas from the propulsion system not only facilitates the blown wing aerodynamics, but also serves to create ultrasonic emissions like that of a
Bat for obstacle avoidance. The Entomopter and other biologically-inspired robots leverage features of biological systems, but do not attempt to create mechanical analogs.
= Snaking
=

Several
snake
Snakes are elongated limbless reptiles of the suborder Serpentes (). Cladistically squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales much like other members of the group. Many species of snakes have s ...
robots have been successfully developed. Mimicking the way real snakes move, these robots can navigate very confined spaces, meaning they may one day be used to search for people trapped in collapsed buildings. The Japanese ACM-R5 snake robot can even navigate both on land and in water.
=Skating
=
A small number of
skating robots have been developed, one of which is a multi-mode walking and skating device. It has four legs, with unpowered wheels, which can either step or roll. Another robot, Plen, can use a miniature skateboard or roller-skates, and skate across a desktop.
= Climbing
=
Several different approaches have been used to develop robots that have the ability to climb vertical surfaces. One approach mimics the movements of a human
climber on a wall with protrusions; adjusting the
center of mass
In physics, the center of mass of a distribution of mass in space (sometimes referred to as the barycenter or balance point) is the unique point at any given time where the weight function, weighted relative position (vector), position of the d ...
and moving each limb in turn to gain leverage. An example of this is Capuchin, built by Ruixiang Zhang at Stanford University, California. Another approach uses the specialized toe pad method of wall-climbing
gecko
Geckos are small, mostly carnivorous lizards that have a wide distribution, found on every continent except Antarctica. Belonging to the infraorder Gekkota, geckos are found in warm climates. They range from .
Geckos are unique among lizards ...
es, which can run on smooth surfaces such as vertical glass. Examples of this approach include Wallbot and Stickybot.
China's ''Technology Daily'' reported on 15 November 2008, that Li Hiu Yeung and his research group of New Concept Aircraft (
Zhuhai
Zhuhai; Yale romanization of Cantonese, Yale: ''Jyūhói''; Chinese postal romanization, also known as Chuhai is a prefecture-level city located on the west bank of the Pearl River (China), Pearl River estuary on the central coast of southern ...
) Co., Ltd. had successfully developed a bionic gecko robot named "
Speedy Freelander". According to Yeung, the gecko robot could rapidly climb up and down a variety of building walls, navigate through ground and wall fissures, and walk upside-down on the ceiling. It was also able to adapt to the surfaces of smooth glass, rough, sticky or dusty walls as well as various types of metallic materials. It could also identify and circumvent obstacles automatically. Its flexibility and speed were comparable to a natural gecko. A third approach is to mimic the motion of a snake climbing a pole.
= Swimming (Piscine)
=
It is calculated that when
swimming
Swimming is the self-propulsion of a person through water, such as saltwater or freshwater environments, usually for recreation, sport, exercise, or survival. Swimmers achieve locomotion by coordinating limb and body movements to achieve hydrody ...
some fish can achieve a
propulsive efficiency greater than 90%. Furthermore, they can accelerate and maneuver far better than any man-made
boat
A boat is a watercraft of a large range of types and sizes, but generally smaller than a ship, which is distinguished by its larger size or capacity, its shape, or its ability to carry boats.
Small boats are typically used on inland waterways s ...
or
submarine
A submarine (often shortened to sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. (It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability.) The term "submarine" is also sometimes used historically or infor ...
, and produce less noise and water disturbance. Therefore, many researchers studying underwater robots would like to copy this type of locomotion. Notable examples are the Robotic Fish G9, and Robot Tuna built to analyze and mathematically model
thunniform motion. The Aqua Penguin, copies the streamlined shape and propulsion by front "flippers" of
penguin
Penguins are a group of aquatic flightless birds from the family Spheniscidae () of the order Sphenisciformes (). They live almost exclusively in the Southern Hemisphere. Only one species, the Galápagos penguin, is equatorial, with a sm ...
s. The Aqua Ray and Aqua Jelly emulate the locomotion of manta ray, and jellyfish, respectively.

In 2014, ''iSplash''-II was developed as the first
robotic fish capable of outperforming real carangiform fish in terms of average maximum velocity (measured in body lengths/ second) and endurance, the duration that top speed is maintained. This build attained swimming speeds of 11.6BL/s (i.e. 3.7 m/s). The first build, ''iSplash''-I (2014) was the first robotic platform to apply a full-body length
carangiform swimming motion which was found to increase swimming speed by 27% over the traditional approach of a posterior confined waveform.
= Sailing
=

Sailboat robots have also been developed in order to make measurements at the surface of the ocean. A typical sailboat robot is ''
Vaimos''. Since the propulsion of sailboat robots uses the wind, the energy of the batteries is only used for the computer, for the communication and for the actuators (to tune the rudder and the sail). If the robot is equipped with solar panels, the robot could theoretically navigate forever. The two main competitions of sailboat robots are
WRSC, which takes place every year in Europe, an
Sailbot
Computational robotics areas

Control systems may also have varying levels of autonomy.
# Direct interaction is used for
haptic or teleoperated devices, and the human has nearly complete control over the robot's motion.
# Operator-assist modes have the operator commanding medium-to-high-level tasks, with the robot automatically figuring out how to achieve them.
# An autonomous robot may go without human interaction for extended periods of time . Higher levels of autonomy do not necessarily require more complex cognitive capabilities. For example, robots in assembly plants are completely autonomous but operate in a fixed pattern.
Another classification takes into account the interaction between human control and the machine motions.
#
Teleoperation. A human controls each movement, each machine actuator change is specified by the operator.
# Supervisory. A human specifies general moves or position changes and the machine decides specific movements of its actuators.
# Task-level autonomy. The operator specifies only the task and the robot manages itself to complete it.
# Full autonomy. The machine will create and complete all its tasks without human interaction.
Vision
Computer vision
Computer vision tasks include methods for image sensor, acquiring, Image processing, processing, Image analysis, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical ...
is the science and technology of machines that see. As a scientific discipline, computer vision is concerned with the theory behind artificial systems that extract information from images. The image data can take many forms, such as video sequences and views from cameras.
In most practical computer vision applications, the computers are pre-programmed to solve a particular task, but methods based on learning are now becoming increasingly common.
Computer vision systems rely on image sensors that detect electromagnetic radiation which is typically in the form of either
visible light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400–700 nanometres (nm ...
or
infra-red light. The sensors are designed using
solid-state physics
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as solid-state chemistry, quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state phy ...
. The process by which light propagates and reflects off surfaces is explained using
optics
Optics is the branch of physics that studies the behaviour and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of optical instruments, instruments that use or Photodetector, detect it. Optics usually describes t ...
. Sophisticated image sensors even require
quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
to provide a complete understanding of the image formation process. Robots can also be equipped with multiple vision sensors to be better able to compute the sense of depth in the environment. Like human eyes, robots' "eyes" must also be able to focus on a particular area of interest, and also adjust to variations in light intensities.
There is a subfield within computer vision where artificial systems are designed to mimic the processing and behavior of
biological system
A biological system is a complex Biological network inference, network which connects several biologically relevant entities. Biological organization spans several scales and are determined based different structures depending on what the system is ...
, at different levels of complexity. Also, some of the learning-based methods developed within computer vision have a background in biology.
Environmental interaction and navigation

Though a significant percentage of robots in commission today are either human controlled or operate in a static environment, there is an increasing interest in robots that can operate autonomously in a dynamic environment. These robots require some combination of
navigation hardware and software in order to traverse their environment. In particular, unforeseen events (e.g. people and other obstacles that are not stationary) can cause problems or collisions. Some highly advanced robots such as
ASIMO
ASIMO (Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility) is a humanoid robot created by Honda in 2000.
In 2002, there were 20 units of the first ASIMO model produced; three different ASIMO models subsequently followed. As of February 2009, there were over ...
and
Meinü robot have particularly good robot navigation hardware and software. Also,
self-controlled cars,
Ernst Dickmanns'
driverless car, and the entries in the
DARPA Grand Challenge
The DARPA Grand Challenge is a prize competition for American vehicle automation, autonomous vehicles, funded by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency, the most prominent research organization of the United States Department of Defense. Uni ...
, are capable of sensing the environment well and subsequently making navigational decisions based on this information, including by a swarm of autonomous robots.
Most of these robots employ a
GPS navigation device with waypoints, along with
radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track ...
, sometimes combined with other sensory data such as
lidar
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected li ...
,
video cameras, and
inertial guidance system
An inertial navigation system (INS; also inertial guidance system, inertial instrument) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors (accelerometers), rotation sensors ( gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning ...
s for better navigation between waypoints.
Human-robot interaction
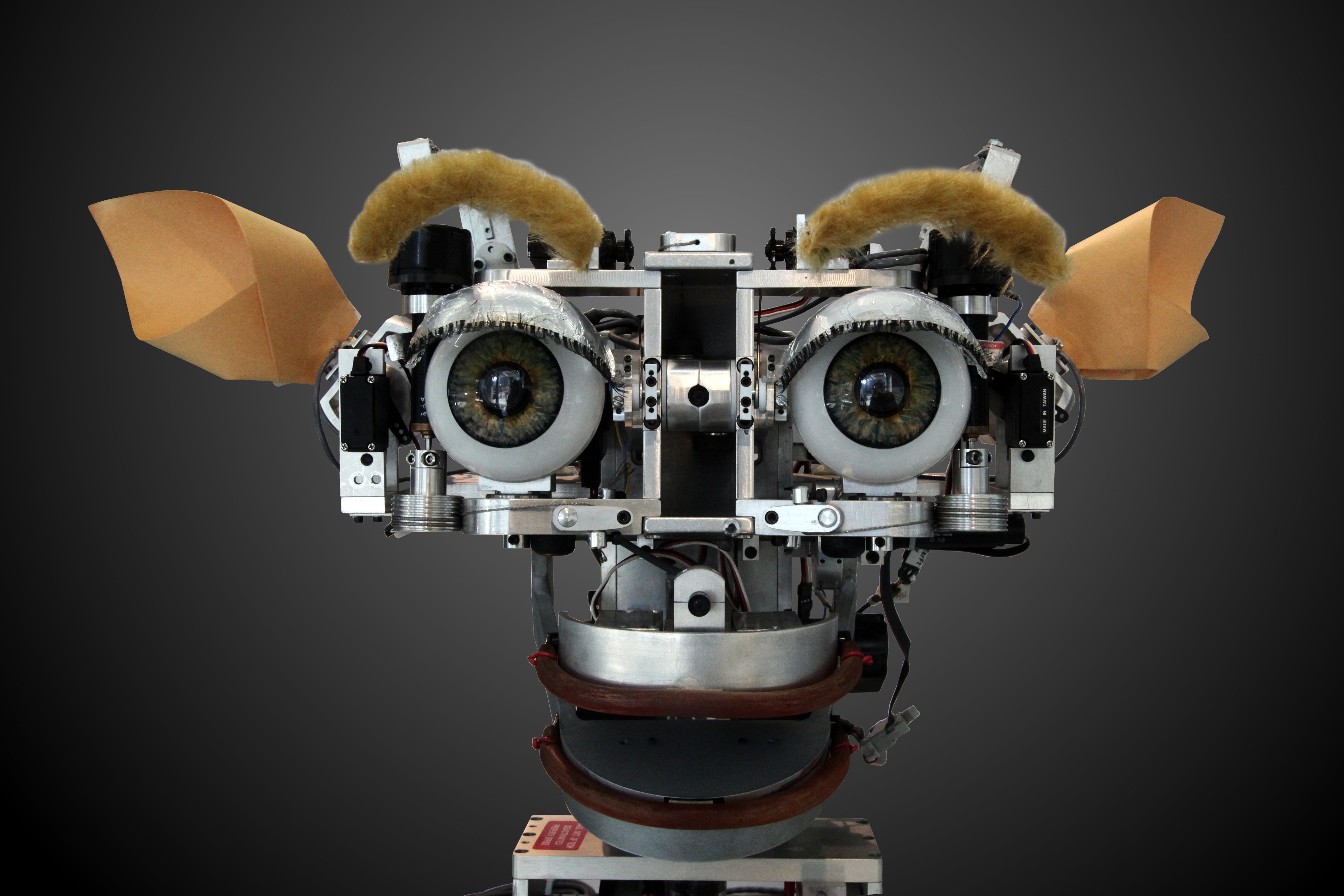
The state of the art in sensory intelligence for robots will have to progress through several orders of magnitude if we want the robots working in our homes to go beyond vacuum-cleaning the floors. If robots are to work effectively in homes and other non-industrial environments, the way they are instructed to perform their jobs, and especially how they will be told to stop will be of critical importance. The people who interact with them may have little or no training in robotics, and so any interface will need to be extremely intuitive. Science fiction authors also typically assume that robots will eventually be capable of communicating with humans through
speech
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, suc ...
,
gesture
A gesture is a form of nonverbal communication or non-vocal communication in which visible bodily actions communicate particular messages, either in place of, or in conjunction with, speech. Gestures include movement of the hands, face, or othe ...
s, and
facial expression
Facial expression is the motion and positioning of the muscles beneath the skin of the face. These movements convey the emotional state of an individual to observers and are a form of nonverbal communication. They are a primary means of conveying ...
s, rather than a
command-line interface
A command-line interface (CLI) is a means of interacting with software via command (computing), commands each formatted as a line of text. Command-line interfaces emerged in the mid-1960s, on computer terminals, as an interactive and more user ...
. Although speech would be the most natural way for the human to communicate, it is unnatural for the robot. It will probably be a long time before robots interact as naturally as the fictional
C-3PO
C-3PO () or See-Threepio is a humanoid robot character in the ''Star Wars'' franchise. He is a protocol droid (Star Wars), droid designed to assist in etiquette and translation, and is fluent in over six million forms of communication. The chara ...
, or
Data of Star Trek, Next Generation. Even though the current state of robotics cannot meet the standards of these robots from science-fiction, robotic media characters (e.g., Wall-E, R2-D2) can elicit audience sympathies that increase people's willingness to accept actual robots in the future. Acceptance of social robots is also likely to increase if people can meet a social robot under appropriate conditions. Studies have shown that interacting with a robot by looking at, touching, or even imagining interacting with the robot can reduce negative feelings that some people have about robots before interacting with them.
However, if pre-existing negative sentiments are especially strong, interacting with a robot can increase those negative feelings towards robots.
Speech recognition
Interpreting the continuous flow of
sound
In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as an acoustic wave through a transmission medium such as a gas, liquid or solid.
In human physiology and psychology, sound is the ''reception'' of such waves and their ''perception'' by the br ...
s coming from a human, in
real time, is a difficult task for a computer, mostly because of the great variability of
speech
Speech is the use of the human voice as a medium for language. Spoken language combines vowel and consonant sounds to form units of meaning like words, which belong to a language's lexicon. There are many different intentional speech acts, suc ...
. The same word, spoken by the same person may sound different depending on local
acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician ...
,
volume
Volume is a measure of regions in three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch) ...
, the previous word, whether or not the speaker has a
cold
Cold is the presence of low temperature, especially in the atmosphere. In common usage, cold is often a subjectivity, subjective perception. A lower bound to temperature is absolute zero, defined as 0.00K on the Kelvin scale, an absolute t ...
, etc.. It becomes even harder when the speaker has a different
accent. Nevertheless, great strides have been made in the field since Davis, Biddulph, and Balashek designed the first "voice input system" which recognized "ten digits spoken by a single user with 100% accuracy" in 1952. Currently, the best systems can recognize continuous, natural speech, up to 160 words per minute, with an accuracy of 95%. With the help of artificial intelligence, machines nowadays can use people's voice to
identify their emotions such as satisfied or angry.
Robotic voice
Other hurdles exist when allowing the robot to use voice for interacting with humans. For social reasons,
synthetic voice proves suboptimal as a communication medium, making it necessary to develop the emotional component of robotic voice through various techniques. An advantage of diphonic branching is the emotion that the robot is programmed to project, can be carried on the voice tape, or phoneme, already pre-programmed onto the voice media. One of the earliest examples is a teaching robot named Leachim developed in 1974 by
Michael J. Freeman. Leachim was able to convert digital memory to rudimentary verbal speech on pre-recorded computer discs.
It was programmed to teach students in
The Bronx, New York
The Bronx ( ) is the northernmost of the five boroughs of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the U.S. state of New York. It shares a land border with Westchester County to its north; to its south and west, the New York City bo ...
.
Facial expression
Facial expressions can provide rapid feedback on the progress of a dialog between two humans, and soon may be able to do the same for humans and robots. Robotic faces have been constructed by
Hanson Robotics using their elastic polymer called
Frubber, allowing a large number of facial expressions due to the elasticity of the rubber facial coating and embedded subsurface motors (
servos). The coating and servos are built on a metal
skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
. A robot should know how to approach a human, judging by their facial expression and
body language
Body language is a type of nonverbal communication in which physical behaviors, as opposed to words, are used to express or convey information. Such behavior includes facial expressions, body posture, gestures, eye movement, touch and the use o ...
. Whether the person is happy, frightened, or crazy-looking affects the type of interaction expected of the robot. Likewise, robots like
Kismet and the more recent addition, Nexi can produce a range of facial expressions, allowing it to have meaningful social exchanges with humans.
Gestures
One can imagine, in the future, explaining to a robot chef how to make a pastry, or asking directions from a robot police officer. In both of these cases, making hand
gesture
A gesture is a form of nonverbal communication or non-vocal communication in which visible bodily actions communicate particular messages, either in place of, or in conjunction with, speech. Gestures include movement of the hands, face, or othe ...
s would aid the verbal descriptions. In the first case, the robot would be recognizing gestures made by the human, and perhaps repeating them for confirmation. In the second case, the robot police officer would gesture to indicate "down the road, then turn right". It is likely that gestures will make up a part of the interaction between humans and robots. A great many systems have been developed to recognize human hand gestures.
Proxemics
Proxemics
Proxemics is the study of human use of space and the effects that population density has on behavior, communication, and social interaction. Proxemics is one among several subcategories in the study of nonverbal communication, including Haptic co ...
is the study of personal space, and HRI systems may try to model and work with its concepts for human interactions.
Artificial emotions
Artificial emotions can also be generated, composed of a sequence of facial expressions or gestures. As can be seen from the movie ''
Final Fantasy: The Spirits Within'', the programming of these artificial emotions is complex and requires a large amount of human observation. To simplify this programming in the movie, presets were created together with a special software program. This decreased the amount of time needed to make the film. These presets could possibly be transferred for use in real-life robots. An example of a robot with artificial emotions is Robin the Robot developed by an
Armenia
Armenia, officially the Republic of Armenia, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of West Asia. It is a part of the Caucasus region and is bordered by Turkey to the west, Georgia (country), Georgia to the north and Azerbaijan to ...
n IT company Expper Technologies, which uses AI-based peer-to-peer interaction. Its main task is achieving emotional well-being, i.e. overcome stress and anxiety. Robin was trained to analyze facial expressions and use his face to display his emotions given the context. The robot has been tested by kids in US clinics, and observations show that Robin increased the appetite and cheerfulness of children after meeting and talking.
Personality
Many of the robots of science fiction have a
personality
Personality is any person's collection of interrelated behavioral, cognitive, and emotional patterns that comprise a person’s unique adjustment to life. These interrelated patterns are relatively stable, but can change over long time per ...
, something which may or may not be desirable in the commercial robots of the future. Nevertheless, researchers are trying to create robots which appear to have a personality: i.e. they use sounds, facial expressions, and body language to try to convey an internal state, which may be joy, sadness, or fear. One commercial example is
Pleo, a toy robot dinosaur, which can exhibit several apparent emotions.
Research robotics
Much of the research in robotics focuses not on specific industrial tasks, but on investigations into new
types of robots, alternative ways to think about or design robots, and new ways to manufacture them. Other investigations, such as MIT's
cyberflora project, are almost wholly academic.
To describe the level of advancement of a robot, the term "Generation Robots" can be used. This term is coined by Professor
Hans Moravec, Principal Research Scientist at the
Carnegie Mellon University
Carnegie Mellon University (CMU) is a private research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, United States. The institution was established in 1900 by Andrew Carnegie as the Carnegie Technical Schools. In 1912, it became the Carnegie Institu ...
Robotics Institute in describing the near future evolution of robot technology. ''First-generation'' robots, Moravec predicted in 1997, should have an intellectual capacity comparable to perhaps a
lizard
Lizard is the common name used for all Squamata, squamate reptiles other than snakes (and to a lesser extent amphisbaenians), encompassing over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most Island#Oceanic isla ...
and should become available by 2010. Because the ''first generation'' robot would be incapable of
learning
Learning is the process of acquiring new understanding, knowledge, behaviors, skills, value (personal and cultural), values, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, and preferences. The ability to learn is possessed by humans, non-human animals, and ...
, however, Moravec predicts that the ''second generation'' robot would be an improvement over the ''first'' and become available by 2020, with the intelligence maybe comparable to that of a
mouse
A mouse (: mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
. The ''third generation'' robot should have intelligence comparable to that of a
monkey
Monkey is a common name that may refer to most mammals of the infraorder Simiiformes, also known as simians. Traditionally, all animals in the group now known as simians are counted as monkeys except the apes. Thus monkeys, in that sense, co ...
. Though ''fourth generation'' robots, robots with
human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
intelligence, professor Moravec predicts, would become possible, he does not predict this happening before around 2040 or 2050.
Dynamics and kinematics
The study of motion can be divided into
kinematics
In physics, kinematics studies the geometrical aspects of motion of physical objects independent of forces that set them in motion. Constrained motion such as linked machine parts are also described as kinematics.
Kinematics is concerned with s ...
and
dynamics. Direct kinematics or forward kinematics refers to the calculation of end effector position, orientation,
velocity
Velocity is a measurement of speed in a certain direction of motion. It is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of physical objects. Velocity is a vector (geometry), vector Physical q ...
, and
acceleration
In mechanics, acceleration is the Rate (mathematics), rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Acceleration is one of several components of kinematics, the study of motion. Accelerations are Euclidean vector, vector ...
when the corresponding joint values are known.
Inverse kinematics refers to the opposite case in which required joint values are calculated for given end effector values, as done in path planning. Some special aspects of kinematics include handling of redundancy (different possibilities of performing the same movement),
collision
In physics, a collision is any event in which two or more bodies exert forces on each other in a relatively short time. Although the most common use of the word ''collision'' refers to incidents in which two or more objects collide with great for ...
avoidance, and
singularity avoidance. Once all relevant positions, velocities, and accelerations have been calculated using
kinematics
In physics, kinematics studies the geometrical aspects of motion of physical objects independent of forces that set them in motion. Constrained motion such as linked machine parts are also described as kinematics.
Kinematics is concerned with s ...
, methods from the field of
dynamics are used to study the effect of
force
In physics, a force is an influence that can cause an Physical object, object to change its velocity unless counterbalanced by other forces. In mechanics, force makes ideas like 'pushing' or 'pulling' mathematically precise. Because the Magnitu ...
s upon these movements. Direct dynamics refers to the calculation of accelerations in the robot once the applied forces are known. Direct dynamics is used in
computer simulation
Computer simulation is the running of a mathematical model on a computer, the model being designed to represent the behaviour of, or the outcome of, a real-world or physical system. The reliability of some mathematical models can be determin ...
s of the robot.
Inverse dynamics refers to the calculation of the actuator forces necessary to create a prescribed end-effector acceleration. This information can be used to improve the control algorithms of a robot.
In each area mentioned above, researchers strive to develop new concepts and strategies, improve existing ones, and improve the interaction between these areas. To do this, criteria for "optimal" performance and ways to optimize design, structure, and control of robots must be developed and implemented.
Open source robotics
Open source robotics research seeks standards for defining, and methods for designing and building, robots so that they can easily be reproduced by anyone. Research includes legal and technical definitions; seeking out alternative tools and materials to reduce costs and simplify builds; and creating interfaces and standards for designs to work together. Human usability research also investigates how to best document builds through visual, text or video instructions.
Evolutionary robotics
Evolutionary robots is a
methodology
In its most common sense, methodology is the study of research methods. However, the term can also refer to the methods themselves or to the philosophical discussion of associated background assumptions. A method is a structured procedure for bri ...
that uses
evolutionary computation
Evolutionary computation from computer science is a family of algorithms for global optimization inspired by biological evolution, and the subfield of artificial intelligence and soft computing studying these algorithms. In technical terms ...
to help design robots, especially the body form, or motion and behavior
controllers. In a similar way to
natural evolution, a large population of robots is allowed to compete in some way, or their ability to perform a task is measured using a
fitness function
A fitness function is a particular type of objective or cost function that is used to summarize, as a single figure of merit, how close a given candidate solution is to achieving the set aims. It is an important component of evolutionary algorit ...
. Those that perform worst are removed from the population and replaced by a new set, which have new behaviors based on those of the winners. Over time the population improves, and eventually a satisfactory robot may appear. This happens without any direct programming of the robots by the researchers. Researchers use this method both to create better robots, and to explore the nature of evolution. Because the process often requires many generations of robots to be simulated, this technique may be run entirely or mostly in
simulation
A simulation is an imitative representation of a process or system that could exist in the real world. In this broad sense, simulation can often be used interchangeably with model. Sometimes a clear distinction between the two terms is made, in ...
, using a
robot simulator
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
software package, then tested on real robots once the evolved algorithms are good enough. Currently, there are about 10 million industrial robots toiling around the world, and Japan is the top country having high density of utilizing robots in its manufacturing industry.
Bionics and biomimetics
Bionics
Bionics or biologically inspired engineering is the application of biological methods and systems found in nature to the study and design of engineering systems and modern technology.
The word ''bionic'', coined by Jack E. Steele in August 195 ...
and
biomimetics
Biomimetics or biomimicry is the emulation of the models, systems, and elements of nature for the purpose of solving complex human problems. The terms "biomimetics" and "biomimicry" are derived from (''bios''), life, and μίμησις (''mimes ...
apply the physiology and methods of locomotion of animals to the design of robots. For example, the design of
BionicKangaroo was based on the way kangaroos jump.
Swarm robotics
Swarm robotics is an approach to the coordination of multiple robots as a system which consist of large numbers of mostly simple physical robots. ″In a robot swarm, the collective behavior of the robots results from local interactions between the robots and between the robots and the environment in which they act.″*
Quantum computing
There has been some research into whether robotics algorithms can be run more quickly on
quantum computers than they can be run on
digital computers. This area has been referred to as quantum robotics.
Other research areas
*
Nanorobots.
*
Cobots (collaborative robots).
*
Autonomous drones.
* High temperature crucibles allow robotic systems to automate sample analysis.
The main venues for robotics research are the international conferences ICRA and IROS.
Human factors
Education and training

Robotics engineers design robots, maintain them, develop new applications for them, and conduct research to expand the potential of robotics. Robots have become a popular educational tool in some middle and high schools, particularly in parts of the USA,
as well as in numerous youth summer camps, raising interest in programming, artificial intelligence, and robotics among students.
Employment
Robotics is an essential component in many modern manufacturing environments. As factories increase their use of robots, the number of robotics–related jobs grow and have been observed to be steadily rising. The employment of robots in industries has increased productivity and efficiency savings and is typically seen as a long-term investment for benefactors. A study found that 47 percent of US jobs are at risk to automation "over some unspecified number of years". These claims have been criticized on the ground that social policy, not AI, causes unemployment. In a 2016 article in The Guardian, Stephen Hawking stated "The automation of factories has already decimated jobs in traditional manufacturing, and the rise of artificial intelligence is likely to extend this job destruction deep into the middle classes, with only the most caring, creative or supervisory roles remaining". The rise of robotics is thus often used as an argument for
universal basic income
Universal basic income (UBI) is a social welfare proposal in which all citizens of a given population regularly receive a minimum income in the form of an unconditional transfer payment, i.e., without a means test or need to perform Work (hu ...
.
According to a GlobalData September 2021 report, the robotics industry was worth $45bn in 2020, and by 2030, it will have grown at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 29% to $568bn, driving jobs in robotics and related industries.
Occupational safety and health implications
A discussion paper drawn up by
EU-OSHA highlights how the spread of robotics presents both opportunities and challenges for occupational safety and health (OSH).
The greatest OSH benefits stemming from the wider use of robotics should be substitution for people working in unhealthy or dangerous environments. In space, defense, security, or the nuclear industry, but also in logistics, maintenance, and inspection, autonomous robots are particularly useful in replacing human workers performing dirty, dull or unsafe tasks, thus avoiding workers' exposures to hazardous agents and conditions and reducing physical, ergonomic and psychosocial risks. For example, robots are already used to perform repetitive and monotonous tasks, to handle radioactive material or to work in explosive atmospheres. In the future, many other highly repetitive, risky or unpleasant tasks will be performed by robots in a variety of sectors like agriculture, construction, transport, healthcare, firefighting or cleaning services.
Moreover, there are certain skills to which humans will be better suited than machines for some time to come and the question is how to achieve the best combination of human and robot skills. The advantages of robotics include heavy-duty jobs with precision and repeatability, whereas the advantages of humans include creativity, decision-making, flexibility, and adaptability. This need to combine optimal skills has resulted in
collaborative robots and humans sharing a common workspace more closely and led to the development of new approaches and standards to guarantee the safety of the "man-robot merger". Some European countries are including robotics in their national programs and trying to promote a safe and flexible cooperation between robots and operators to achieve better productivity. For example, the German Federal Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (
BAuA) organises annual workshops on the topic "human-robot collaboration".
In the future, cooperation between robots and humans will be diversified, with robots increasing their autonomy and human-robot collaboration reaching completely new forms. Current approaches and technical standards aiming to protect employees from the risk of working with collaborative robots will have to be revised.
User experience
Great user experience predicts the needs, experiences, behaviors, language and cognitive abilities, and other factors of each user group. It then uses these insights to produce a product or solution that is ultimately useful and usable. For robots, user experience begins with an understanding of the robot's intended task and environment, while considering any possible social impact the robot may have on human operations and interactions with it.
It defines that communication as the transmission of information through signals, which are elements perceived through touch, sound, smell and sight.
The author states that the signal connects the sender to the receiver and consists of three parts: the signal itself, what it refers to, and the interpreter. Body postures and gestures, facial expressions, hand and head movements are all part of nonverbal behavior and communication. Robots are no exception when it comes to human-robot interaction. Therefore, humans use their verbal and nonverbal behaviors to communicate their defining characteristics. Similarly, social robots need this coordination to perform human-like behaviors.
Careers
Robotics is an interdisciplinary field, combining primarily
mechanical engineering
Mechanical engineering is the study of physical machines and mechanism (engineering), mechanisms that may involve force and movement. It is an engineering branch that combines engineering physics and engineering mathematics, mathematics principl ...
and
computer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
but also drawing on
electronic engineering
Electronic engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering that emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current flo ...
and other subjects. The usual way to build a career in robotics is to complete an undergraduate degree in one of these established subjects, followed by a graduate (masters') degree in Robotics. Graduate degrees are typically joined by students coming from all of the contributing disciplines, and include familiarization of relevant undergraduate level subject matter from each of them, followed by specialist study in pure robotics topics which build upon them. As an interdisciplinary subject, robotics graduate programmes tend to be especially reliant on students working and learning together and sharing their knowledge and skills from their home discipline first degrees.
Robotics industry careers then follow the same pattern, with most roboticists working as part of interdisciplinary teams of specialists from these home disciplines followed by the robotics graduate degrees which enable them to work together. Workers typically continue to identify as members of their home disciplines who work in robotics, rather than as 'roboticists'. This structure is reinforced by the nature of some engineering professions, which grant chartered engineer status to members of home disciplines rather than to robotics as a whole.
Robotics careers are widely predicted to grow in the 21st century, as robots replace more manual and intellectual human work. Some workers who lose their jobs to robotics may be well-placed to retrain to build and maintain these robots, using their domain-specific knowledge and skills.
History
See also
*
Artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
*
Autonomous robot
An autonomous robot is a robot that acts without recourse to human control. Historic examples include space probes. Modern examples include self-driving Robotic vacuum cleaner, vacuums and Self-driving car, cars.
Industrial robot, Industrial robot ...
*
Cloud robotics
*
Cognitive robotics
*
Evolutionary robotics
*
Fog robotics
*
Glossary of robotics
Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots. Robotics is related to the sciences of electronics, engineering, mechanics, and computer soft ...
*
Index of robotics articles
*
Mechatronics
Mechatronics engineering, also called mechatronics, is the synergistic integration of mechanical, electrical, and computer systems employing mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, electronic engineering and computer engineering, and also ...
*
Multi-agent system
*
Outline of robotics
*
Quantum robotics
*
Roboethics
*
Robot rights
*
Robotic art
*
Robotic governance
*
Self-reconfiguring modular robot
Modular self-reconfiguring robotic systems or self-reconfigurable modular robots are autonomous kinematic machines with variable morphology. Beyond conventional actuation, sensing and control typically found in fixed-morphology robots, self-reco ...
*
Soft robotics
Soft robotics is a subfield of robotics that concerns the design, control, and fabrication of robots composed of Stiffness#Compliance, compliant materials, instead of kinematic chain, rigid links.
In contrast to rigid-bodied robots built from met ...
*
Telerobotics
Telerobotics is the area of robotics concerned with the control of semi-autonomous robots from a distance, chiefly using television, wireless networks (like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and the Deep Space Network) or tethered connections. It is a combinatio ...
Notes
References
Further reading
*
*
*
*
External links
IEEE Robotics and Automation Society* Investigation o
– Robots that mimic human behaviors and gestures.
to the '50 best robots ever', a mix of robots in fiction (Hal, R2D2, K9) to real robots (Roomba, Mobot, Aibo).
{{Authority control
 Robotics is the
Robotics is the  Robotics usually combines three aspects of design work to create
Robotics usually combines three aspects of design work to create  At present, mostly (lead–acid) batteries are used as a power source. Many different types of batteries can be used as a power source for robots. They range from lead–acid batteries, which are safe and have relatively long shelf lives but are rather heavy compared to silver–cadmium batteries which are much smaller in volume and are currently much more expensive. Designing a battery-powered robot needs to take into account factors such as safety, cycle lifetime, and
At present, mostly (lead–acid) batteries are used as a power source. Many different types of batteries can be used as a power source for robots. They range from lead–acid batteries, which are safe and have relatively long shelf lives but are rather heavy compared to silver–cadmium batteries which are much smaller in volume and are currently much more expensive. Designing a battery-powered robot needs to take into account factors such as safety, cycle lifetime, and  Actuators are the "
Actuators are the "

 The mechanical structure of a robot must be controlled to perform tasks. The control of a robot involves three distinct phases –
The mechanical structure of a robot must be controlled to perform tasks. The control of a robot involves three distinct phases – 
 A definition of robotic manipulation has been provided by Matt Mason as: "manipulation refers to an agent's control of its environment through selective contact".
Robots need to manipulate objects; pick up, modify, destroy, move or otherwise have an effect. Thus the functional end of a robot arm intended to make the effect (whether a hand, or tool) are often referred to as '' end effectors'', while the "arm" is referred to as a ''manipulator''. Most robot arms have replaceable end-effectors, each allowing them to perform some small range of tasks. Some have a fixed manipulator that cannot be replaced, while a few have one very general-purpose manipulator, for example, a humanoid hand.
A definition of robotic manipulation has been provided by Matt Mason as: "manipulation refers to an agent's control of its environment through selective contact".
Robots need to manipulate objects; pick up, modify, destroy, move or otherwise have an effect. Thus the functional end of a robot arm intended to make the effect (whether a hand, or tool) are often referred to as '' end effectors'', while the "arm" is referred to as a ''manipulator''. Most robot arms have replaceable end-effectors, each allowing them to perform some small range of tasks. Some have a fixed manipulator that cannot be replaced, while a few have one very general-purpose manipulator, for example, a humanoid hand.
 BFRs take inspiration from flying mammals, birds, or insects. BFRs can have flapping wings, which generate the lift and thrust, or they can be propeller actuated. BFRs with flapping wings have increased stroke efficiencies, increased maneuverability, and reduced energy consumption in comparison to propeller actuated BFRs. Mammal and bird inspired BFRs share similar flight characteristics and design considerations. For instance, both mammal and bird inspired BFRs minimize edge fluttering and pressure-induced wingtip curl by increasing the rigidity of the wing edge and wingtips. Mammal and insect inspired BFRs can be impact resistant, making them useful in cluttered environments.
Mammal inspired BFRs typically take inspiration from bats, but the flying squirrel has also inspired a prototype. Examples of bat inspired BFRs include Bat Bot and the DALER. Mammal inspired BFRs can be designed to be multi-modal; therefore, they're capable of both flight and terrestrial movement. To reduce the impact of landing, shock absorbers can be implemented along the wings. Alternatively, the BFR can pitch up and increase the amount of drag it experiences. By increasing the drag force, the BFR will decelerate and minimize the impact upon grounding. Different land gait patterns can also be implemented.
BFRs take inspiration from flying mammals, birds, or insects. BFRs can have flapping wings, which generate the lift and thrust, or they can be propeller actuated. BFRs with flapping wings have increased stroke efficiencies, increased maneuverability, and reduced energy consumption in comparison to propeller actuated BFRs. Mammal and bird inspired BFRs share similar flight characteristics and design considerations. For instance, both mammal and bird inspired BFRs minimize edge fluttering and pressure-induced wingtip curl by increasing the rigidity of the wing edge and wingtips. Mammal and insect inspired BFRs can be impact resistant, making them useful in cluttered environments.
Mammal inspired BFRs typically take inspiration from bats, but the flying squirrel has also inspired a prototype. Examples of bat inspired BFRs include Bat Bot and the DALER. Mammal inspired BFRs can be designed to be multi-modal; therefore, they're capable of both flight and terrestrial movement. To reduce the impact of landing, shock absorbers can be implemented along the wings. Alternatively, the BFR can pitch up and increase the amount of drag it experiences. By increasing the drag force, the BFR will decelerate and minimize the impact upon grounding. Different land gait patterns can also be implemented.
 Bird inspired BFRs can take inspiration from raptors, gulls, and everything in-between. Bird inspired BFRs can be feathered to increase the angle of attack range over which the prototype can operate before stalling. The wings of bird inspired BFRs allow for in-plane deformation, and the in-plane wing deformation can be adjusted to maximize flight efficiency depending on the flight gait. An example of a raptor inspired BFR is the prototype by Savastano et al. The prototype has fully deformable flapping wings and is capable of carrying a payload of up to 0.8 kg while performing a parabolic climb, steep descent, and rapid recovery. The gull inspired prototype by Grant et al. accurately mimics the elbow and wrist rotation of gulls, and they find that lift generation is maximized when the elbow and wrist deformations are opposite but equal.
Insect inspired BFRs typically take inspiration from beetles or dragonflies. An example of a beetle inspired BFR is the prototype by Phan and Park, and a dragonfly inspired BFR is the prototype by Hu et al. The flapping frequency of insect inspired BFRs are much higher than those of other BFRs; this is because of the aerodynamics of insect flight. Insect inspired BFRs are much smaller than those inspired by mammals or birds, so they are more suitable for dense environments.
Bird inspired BFRs can take inspiration from raptors, gulls, and everything in-between. Bird inspired BFRs can be feathered to increase the angle of attack range over which the prototype can operate before stalling. The wings of bird inspired BFRs allow for in-plane deformation, and the in-plane wing deformation can be adjusted to maximize flight efficiency depending on the flight gait. An example of a raptor inspired BFR is the prototype by Savastano et al. The prototype has fully deformable flapping wings and is capable of carrying a payload of up to 0.8 kg while performing a parabolic climb, steep descent, and rapid recovery. The gull inspired prototype by Grant et al. accurately mimics the elbow and wrist rotation of gulls, and they find that lift generation is maximized when the elbow and wrist deformations are opposite but equal.
Insect inspired BFRs typically take inspiration from beetles or dragonflies. An example of a beetle inspired BFR is the prototype by Phan and Park, and a dragonfly inspired BFR is the prototype by Hu et al. The flapping frequency of insect inspired BFRs are much higher than those of other BFRs; this is because of the aerodynamics of insect flight. Insect inspired BFRs are much smaller than those inspired by mammals or birds, so they are more suitable for dense environments.
 A class of robots that are biologically inspired, but which do not attempt to mimic biology, are creations such as the Entomopter. Funded by
A class of robots that are biologically inspired, but which do not attempt to mimic biology, are creations such as the Entomopter. Funded by  Several
Several 
 In 2014, ''iSplash''-II was developed as the first robotic fish capable of outperforming real carangiform fish in terms of average maximum velocity (measured in body lengths/ second) and endurance, the duration that top speed is maintained. This build attained swimming speeds of 11.6BL/s (i.e. 3.7 m/s). The first build, ''iSplash''-I (2014) was the first robotic platform to apply a full-body length carangiform swimming motion which was found to increase swimming speed by 27% over the traditional approach of a posterior confined waveform.
In 2014, ''iSplash''-II was developed as the first robotic fish capable of outperforming real carangiform fish in terms of average maximum velocity (measured in body lengths/ second) and endurance, the duration that top speed is maintained. This build attained swimming speeds of 11.6BL/s (i.e. 3.7 m/s). The first build, ''iSplash''-I (2014) was the first robotic platform to apply a full-body length carangiform swimming motion which was found to increase swimming speed by 27% over the traditional approach of a posterior confined waveform.
 Sailboat robots have also been developed in order to make measurements at the surface of the ocean. A typical sailboat robot is '' Vaimos''. Since the propulsion of sailboat robots uses the wind, the energy of the batteries is only used for the computer, for the communication and for the actuators (to tune the rudder and the sail). If the robot is equipped with solar panels, the robot could theoretically navigate forever. The two main competitions of sailboat robots are WRSC, which takes place every year in Europe, an
Sailboat robots have also been developed in order to make measurements at the surface of the ocean. A typical sailboat robot is '' Vaimos''. Since the propulsion of sailboat robots uses the wind, the energy of the batteries is only used for the computer, for the communication and for the actuators (to tune the rudder and the sail). If the robot is equipped with solar panels, the robot could theoretically navigate forever. The two main competitions of sailboat robots are WRSC, which takes place every year in Europe, an Control systems may also have varying levels of autonomy.
# Direct interaction is used for haptic or teleoperated devices, and the human has nearly complete control over the robot's motion.
# Operator-assist modes have the operator commanding medium-to-high-level tasks, with the robot automatically figuring out how to achieve them.
# An autonomous robot may go without human interaction for extended periods of time . Higher levels of autonomy do not necessarily require more complex cognitive capabilities. For example, robots in assembly plants are completely autonomous but operate in a fixed pattern.
Another classification takes into account the interaction between human control and the machine motions.
# Teleoperation. A human controls each movement, each machine actuator change is specified by the operator.
# Supervisory. A human specifies general moves or position changes and the machine decides specific movements of its actuators.
# Task-level autonomy. The operator specifies only the task and the robot manages itself to complete it.
# Full autonomy. The machine will create and complete all its tasks without human interaction.
Control systems may also have varying levels of autonomy.
# Direct interaction is used for haptic or teleoperated devices, and the human has nearly complete control over the robot's motion.
# Operator-assist modes have the operator commanding medium-to-high-level tasks, with the robot automatically figuring out how to achieve them.
# An autonomous robot may go without human interaction for extended periods of time . Higher levels of autonomy do not necessarily require more complex cognitive capabilities. For example, robots in assembly plants are completely autonomous but operate in a fixed pattern.
Another classification takes into account the interaction between human control and the machine motions.
# Teleoperation. A human controls each movement, each machine actuator change is specified by the operator.
# Supervisory. A human specifies general moves or position changes and the machine decides specific movements of its actuators.
# Task-level autonomy. The operator specifies only the task and the robot manages itself to complete it.
# Full autonomy. The machine will create and complete all its tasks without human interaction.
 Though a significant percentage of robots in commission today are either human controlled or operate in a static environment, there is an increasing interest in robots that can operate autonomously in a dynamic environment. These robots require some combination of navigation hardware and software in order to traverse their environment. In particular, unforeseen events (e.g. people and other obstacles that are not stationary) can cause problems or collisions. Some highly advanced robots such as
Though a significant percentage of robots in commission today are either human controlled or operate in a static environment, there is an increasing interest in robots that can operate autonomously in a dynamic environment. These robots require some combination of navigation hardware and software in order to traverse their environment. In particular, unforeseen events (e.g. people and other obstacles that are not stationary) can cause problems or collisions. Some highly advanced robots such as  The state of the art in sensory intelligence for robots will have to progress through several orders of magnitude if we want the robots working in our homes to go beyond vacuum-cleaning the floors. If robots are to work effectively in homes and other non-industrial environments, the way they are instructed to perform their jobs, and especially how they will be told to stop will be of critical importance. The people who interact with them may have little or no training in robotics, and so any interface will need to be extremely intuitive. Science fiction authors also typically assume that robots will eventually be capable of communicating with humans through
The state of the art in sensory intelligence for robots will have to progress through several orders of magnitude if we want the robots working in our homes to go beyond vacuum-cleaning the floors. If robots are to work effectively in homes and other non-industrial environments, the way they are instructed to perform their jobs, and especially how they will be told to stop will be of critical importance. The people who interact with them may have little or no training in robotics, and so any interface will need to be extremely intuitive. Science fiction authors also typically assume that robots will eventually be capable of communicating with humans through  Robotics engineers design robots, maintain them, develop new applications for them, and conduct research to expand the potential of robotics. Robots have become a popular educational tool in some middle and high schools, particularly in parts of the USA, as well as in numerous youth summer camps, raising interest in programming, artificial intelligence, and robotics among students.
Robotics engineers design robots, maintain them, develop new applications for them, and conduct research to expand the potential of robotics. Robots have become a popular educational tool in some middle and high schools, particularly in parts of the USA, as well as in numerous youth summer camps, raising interest in programming, artificial intelligence, and robotics among students.