|
Emotion Recognition
Emotion recognition is the process of identifying human emotion. People vary widely in their accuracy at recognizing the emotions of others. Use of technology to help people with emotion recognition is a relatively nascent research area. Generally, the technology works best if it uses multiple modalities in context. To date, the most work has been conducted on automating the recognition of facial expressions from video, spoken expressions from audio, written expressions from text, and physiology as measured by wearables. Human Humans show a great deal of variability in their abilities to recognize emotion. A key point to keep in mind when learning about automated emotion recognition is that there are several sources of "ground truth", or truth about what the real emotion is. Suppose we are trying to recognize the emotions of Alex. One source is "what would most people say that Alex is feeling?" In this case, the 'truth' may not correspond to what Alex feels, but may corr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emotion
Emotions are physical and mental states brought on by neurophysiology, neurophysiological changes, variously associated with thoughts, feelings, behavior, behavioral responses, and a degree of pleasure or suffering, displeasure. There is no scientific consensus on a definition. Emotions are often reciprocal determinism, intertwined with mood (psychology), mood, temperament, personality psychology, personality, disposition, or creativity. Research on emotion has increased over the past two decades, with many fields contributing, including psychology, medicine, history, sociology of emotions, computer science and philosophy. The numerous attempts to explain the origin, functional accounts of emotion, function, and other aspects of emotions have fostered intense research on this topic. Theorizing about the evolutionary origin and possible purpose of emotion dates back to Charles Darwin. Current areas of research include the neuroscience of emotion, using tools like positron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic
Semantics is the study of linguistic Meaning (philosophy), meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends on its parts. Part of this process involves the distinction between sense and reference. Sense is given by the ideas and concepts associated with an expression while reference is the object to which an expression points. Semantics contrasts with syntax, which studies the rules that dictate how to create grammatically correct sentences, and pragmatics, which investigates how people use language in communication. Lexical semantics is the branch of semantics that studies word meaning. It examines whether words have one or several meanings and in what lexical relations they stand to one another. Phrasal semantics studies the meaning of sentences by exploring the phenomenon of compositionality or how new meanings can be created by arranging words. Formal semantics (natural language), Formal semantics relies o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
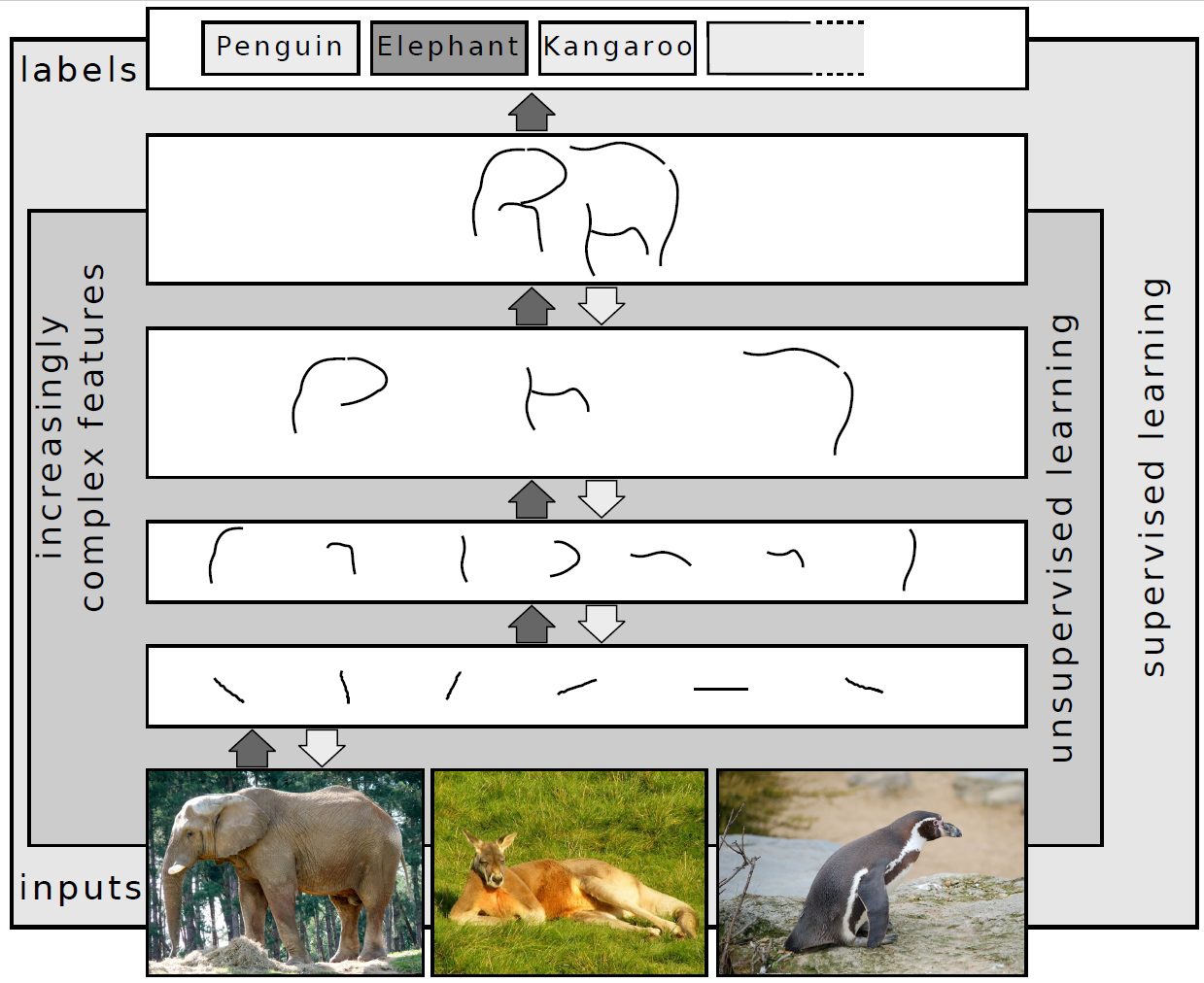
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that focuses on utilizing multilayered neural networks to perform tasks such as classification, regression, and representation learning. The field takes inspiration from biological neuroscience and is centered around stacking artificial neurons into layers and "training" them to process data. The adjective "deep" refers to the use of multiple layers (ranging from three to several hundred or thousands) in the network. Methods used can be either supervised, semi-supervised or unsupervised. Some common deep learning network architectures include fully connected networks, deep belief networks, recurrent neural networks, convolutional neural networks, generative adversarial networks, transformers, and neural radiance fields. These architectures have been applied to fields including computer vision, speech recognition, natural language processing, machine translation, bioinformatics, drug design, medical image analysis, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maximum Entropy Classifier
In statistics, multinomial logistic regression is a classification method that generalizes logistic regression to multiclass problems, i.e. with more than two possible discrete outcomes. That is, it is a model that is used to predict the probabilities of the different possible outcomes of a categorically distributed dependent variable, given a set of independent variables (which may be real-valued, binary-valued, categorical-valued, etc.). Multinomial logistic regression is known by a variety of other names, including polytomous LR, multiclass LR, softmax regression, multinomial logit (mlogit), the maximum entropy (MaxEnt) classifier, and the conditional maximum entropy model. Background Multinomial logistic regression is used when the dependent variable in question is nominal (equivalently ''categorical'', meaning that it falls into any one of a set of categories that cannot be ordered in any meaningful way) and for which there are more than two categories. Some examples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naive Bayes Classifier
In statistics, naive (sometimes simple or idiot's) Bayes classifiers are a family of " probabilistic classifiers" which assumes that the features are conditionally independent, given the target class. In other words, a naive Bayes model assumes the information about the class provided by each variable is unrelated to the information from the others, with no information shared between the predictors. The highly unrealistic nature of this assumption, called the naive independence assumption, is what gives the classifier its name. These classifiers are some of the simplest Bayesian network models. Naive Bayes classifiers generally perform worse than more advanced models like logistic regressions, especially at quantifying uncertainty (with naive Bayes models often producing wildly overconfident probabilities). However, they are highly scalable, requiring only one parameter for each feature or predictor in a learning problem. Maximum-likelihood training can be done by evaluating a c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Support Vector Machines
In machine learning, support vector machines (SVMs, also support vector networks) are supervised max-margin models with associated learning algorithms that analyze data for classification and regression analysis. Developed at AT&T Bell Laboratories, SVMs are one of the most studied models, being based on statistical learning frameworks of VC theory proposed by Vapnik (1982, 1995) and Chervonenkis (1974). In addition to performing linear classification, SVMs can efficiently perform non-linear classification using the ''kernel trick'', representing the data only through a set of pairwise similarity comparisons between the original data points using a kernel function, which transforms them into coordinates in a higher-dimensional feature space. Thus, SVMs use the kernel trick to implicitly map their inputs into high-dimensional feature spaces, where linear classification can be performed. Being max-margin models, SVMs are resilient to noisy data (e.g., misclassified examples). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task (computing), tasks without explicit Machine code, instructions. Within a subdiscipline in machine learning, advances in the field of deep learning have allowed Neural network (machine learning), neural networks, a class of statistical algorithms, to surpass many previous machine learning approaches in performance. ML finds application in many fields, including natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, email filtering, agriculture, and medicine. The application of ML to business problems is known as predictive analytics. Statistics and mathematical optimisation (mathematical programming) methods comprise the foundations of machine learning. Data mining is a related field of study, focusing on exploratory data analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corpus Linguistics
Corpus linguistics is an empirical method for the study of language by way of a text corpus (plural ''corpora''). Corpora are balanced, often stratified collections of authentic, "real world", text of speech or writing that aim to represent a given linguistic variety. Today, corpora are generally machine-readable data collections. Corpus linguistics proposes that a reliable analysis of a language is more feasible with corpora collected in the field—the natural context ("realia") of that language—with minimal experimental interference. Large collections of text, though corpora may also be small in terms of running words, allow linguists to run quantitative analyses on linguistic concepts that may be difficult to test in a qualitative manner. The text-corpus method uses the body of texts in any natural language to derive the set of abstract rules which govern that language. Those results can be used to explore the relationships between that subject language and other language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonym
In lexical semantics, opposites are words lying in an inherently incompatible binary relationship. For example, something that is ''even'' entails that it is not ''odd''. It is referred to as a 'binary' relationship because there are two members in a set of opposites. The relationship between opposites is known as opposition. A member of a pair of opposites can generally be determined by the question: "What is the opposite of ''X''" The term antonym (and the related antonymy) is commonly taken to be synonymous with opposite, but antonym also has other more restricted meanings. Graded (or gradable) antonyms are word pairs whose meanings are opposite and which lie on a continuous spectrum (''hot'', ''cold''). Complementary antonyms are word pairs whose meanings are opposite but whose meanings do not lie on a continuous spectrum (''push'', ''pull''). Relational antonyms are word pairs where opposite makes sense only in the context of the relationship between the two meanings (''teach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means precisely or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all synonyms of one another: they are ''synonymous''. The standard test for synonymy is substitution: one form can be replaced by another in a sentence without changing its meaning. Words may often be synonymous in only one particular sense: for example, ''long'' and ''extended'' in the context ''long time'' or ''extended time'' are synonymous, but ''long'' cannot be used in the phrase ''extended family''. Synonyms with exactly the same meaning share a seme or denotational sememe, whereas those with inexactly similar meanings share a broader denotational or connotational sememe and thus overlap within a semantic field. The former are sometimes called cognitive synonyms and the latter, near-synonyms, plesionyms or poecilonyms. Lexic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictionary
A dictionary is a listing of lexemes from the lexicon of one or more specific languages, often arranged Alphabetical order, alphabetically (or by Semitic root, consonantal root for Semitic languages or radical-and-stroke sorting, radical and stroke for Logogram, logographic languages), which may include information on definitions, usage, etymologies, pronunciations, Bilingual dictionary, translation, etc.Webster's New World College Dictionary, Fourth Edition, 2002 It is a Lexicography, lexicographical reference that shows inter-relationships among the data. A broad distinction is made between general and specialized dictionaries. Specialized dictionaries include words in specialist fields, rather than a comprehensive range of words in the language. Lexical items that describe concepts in specific fields are usually called terms instead of words, although there is no consensus whether lexicology and terminology are two different fields of study. In theory, general dictionarie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ConceptNet
Open Mind Common Sense (OMCS) is an artificial intelligence project based at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) Media Lab whose goal is to build and utilize a large commonsense knowledge base from the contributions of many thousands of people across the Web. It has been active from 1999 to 2016. Since its founding, it has accumulated more than a million English facts from over 15,000 contributors in addition to knowledge bases in other languages. Much of OMCS's software is built on three interconnected representations: the natural language corpus that people interact with directly, a semantic network built from this corpus called ConceptNet, and a matrix-based representation of ConceptNet called AnalogySpace that can infer new knowledge using dimensionality reduction. The knowledge collected by Open Mind Common Sense has enabled research projects at MIT and elsewhere. History The project was the brainchild of Marvin Minsky, Push Singh, Catherine Havasi, and othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |