RNase H on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ribonuclease H (abbreviated RNase H or RNH) is a family of non-
 The
The
 The
The
 In small studies, mutations in human RNase H1 have been associated with
In small studies, mutations in human RNase H1 have been associated with
 Two groups of
Two groups of
GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Aicardi-Goutières Syndrome
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Rnase H Ribonucleases EC 3.1.26 Molecular biology
sequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is calle ...
-specific endonuclease
Endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain. Some, such as deoxyribonuclease I, cut DNA relatively nonspecifically (without regard to sequence), while many, typically called restriction endonucleases ...
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s that catalyze
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recyc ...
the cleavage of RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
in an RNA/ DNA substrate via a hydrolytic
Hydrolysis (; ) is any chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Biological hydrolysi ...
mechanism
Mechanism may refer to:
* Mechanism (engineering), rigid bodies connected by joints in order to accomplish a desired force and/or motion transmission
*Mechanism (biology), explaining how a feature is created
*Mechanism (philosophy), a theory that ...
. Members of the RNase H family can be found in nearly all organisms, from bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
to archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
to eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
s.
The family is divided into evolutionarily related groups with slightly different substrate preferences, broadly designated ribonuclease H1 and H2. The human genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the n ...
encodes both H1 and H2. Human ribonuclease H2 is a heterotrimeric complex composed of three subunits, mutations in any of which are among the genetic causes of a rare disease
A rare disease is any disease that affects a small percentage of the population. In some parts of the world, an orphan disease is a rare disease whose rarity means there is a lack of a market large enough to gain support and resources for discove ...
known as Aicardi–Goutières syndrome
Aicardi–Goutières syndrome (AGS), which is completely distinct from the similarly named Aicardi syndrome, is a rare, usually early onset childhood, inflammatory disorder most typically affecting the brain and the skin (neurodevelopmental disor ...
. A third type, closely related to H2, is found only in a few prokaryote
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connec ...
s, whereas H1 and H2 occur in all domains of life. Additionally, RNase H1-like retroviral ribonuclease H domains occur in multidomain reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, ...
proteins, which are encoded by retrovirus
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase ...
es such as HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the immune ...
and are required for viral replication.
In eukaryotes, ribonuclease H1 is involved in DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritanc ...
of the mitochondrial genome
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial D ...
. Both H1 and H2 are involved in genome maintenance tasks such as processing of R-loop
An R-loop is a three-stranded nucleic acid structure, composed of a DNA: RNA hybrid and the associated non-template single-stranded DNA. R-loops may be formed in a variety of circumstances, and may be tolerated or cleared by cellular components. ...
structures.
Classification and nomenclature
Ribonuclease H is a family ofendonuclease
Endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain. Some, such as deoxyribonuclease I, cut DNA relatively nonspecifically (without regard to sequence), while many, typically called restriction endonucleases ...
enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
s with a shared substrate specificity for the RNA strand of RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
- DNA duplexes
A duplex house plan has two living units attached to each other, either next to each other as townhouses, condominiums or above each other like apartments. By contrast, a building comprising two attached units on two distinct properties is ...
. By definition, RNases H cleave RNA backbone phosphodiester
In chemistry, a phosphodiester bond occurs when exactly two of the hydroxyl groups () in phosphoric acid react with hydroxyl groups on other molecules to form two ester bonds. The "bond" involves this linkage . Discussion of phosphodiesters is d ...
bonds to leave a 3' hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
and a 5' phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
group. RNases H have been proposed as members of an evolutionarily related superfamily encompassing other nucleases and nucleic acid processing enzymes such as retroviral integrase
Retroviral integrase (IN) is an enzyme produced by a retrovirus (such as HIV) that integrates—forms covalent links between—its genetic information into that of the host cell it infects. Retroviral INs are not to be confused with phage int ...
s, DNA transposase
A transposase is any of a class of enzymes capable of binding to the end of a transposon and catalysing its movement to another part of a genome, typically by a cut-and-paste mechanism or a replicative mechanism, in a process known as transpositio ...
s, Holliday junction resolvase
Crossover junction endodeoxyribonuclease, also known as Holliday junction resolvase, Holliday junction endonuclease, Holliday junction-cleaving endonuclease, Holliday junction-resolving endoribonuclease, crossover junction endoribonuclease, and cru ...
s, Piwi
Piwi (or PIWI) genes were identified as regulatory proteins responsible for stem cell and germ cell differentiation. Piwi is an abbreviation of P-element Induced WImpy testis in ''Drosophila''. Piwi proteins are highly conserved RNA-bindi ...
and Argonaute
The Argonaute protein family, first discovered for its evolutionarily conserved stem cell function, plays a central role in RNA silencing processes as essential components of the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). RISC is responsible for the g ...
proteins, various exonuclease
Exonucleases are enzymes that work by cleaving nucleotides one at a time from the end (exo) of a polynucleotide chain. A hydrolyzing reaction that breaks phosphodiester bonds at either the 3′ or the 5′ end occurs. Its close relative is the ...
s, and the spliceosomal protein Prp8.
RNases H can be broadly divided into two subtypes, H1 and H2, which for historical reasons are given Arabic numeral designations in eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacte ...
s and Roman numeral designations in prokaryote
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connec ...
s. Thus the ''Escherichia coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escher ...
'' RNase HI is a homolog of the ''Homo sapiens
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
'' RNase H1. In ''E. coli'' and many other prokaryotes, the ''rnhA'' gene encodes HI and the ''rnhB'' gene encodes HII. A third related class, called HIII, occurs in a few bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
and archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
; it is closely related to prokaryotic HII enzymes.
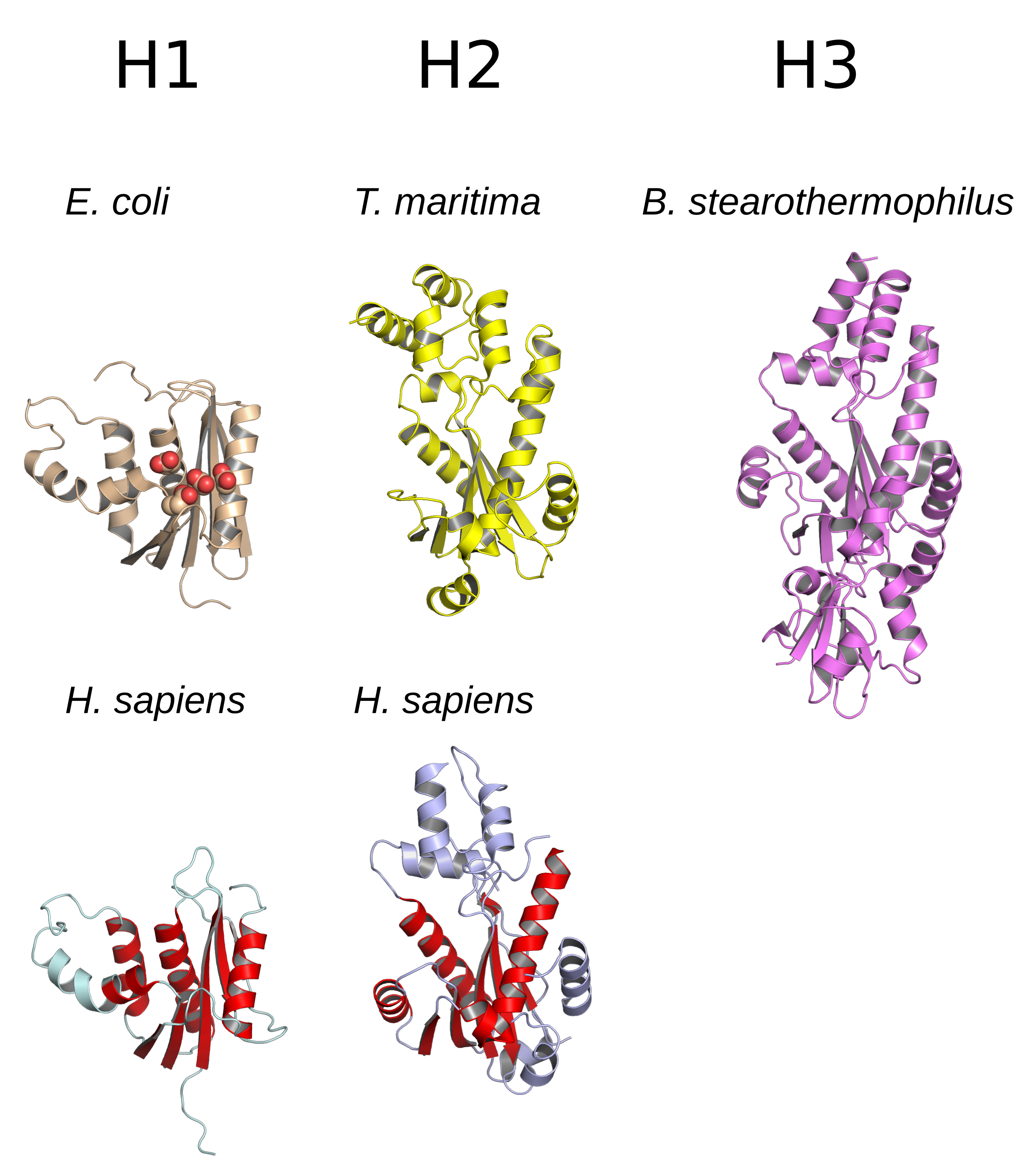
Structure
 The
The structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as ...
of RNase H commonly consists of a 5-stranded β-sheet
The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydrogen bonds, forming a g ...
surrounded by a distribution of α-helices
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues ear ...
. All RNases H have an active site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate (binding site) a ...
centered on a conserved sequence motif
In biology, a sequence motif is a nucleotide or amino-acid sequence pattern that is widespread and usually assumed to be related to biological function of the macromolecule. For example, an ''N''-glycosylation site motif can be defined as ''As ...
composed of aspartate and glutamate
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can syn ...
residues, often referred to as the DEDD motif. These residues interact with catalytically required magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
ions.
RNases H2 are larger than H1 and usually have additional helices. The domain
Domain may refer to:
Mathematics
*Domain of a function, the set of input values for which the (total) function is defined
**Domain of definition of a partial function
**Natural domain of a partial function
**Domain of holomorphy of a function
* Do ...
organization of the enzymes varies; some prokaryotic and most eukaryotic members of the H1 group have an additional small domain at the N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the ami ...
known as the "hybrid binding domain", which facilitates binding to RNA:DNA hybrid duplexes and sometimes confers increased processivity
In molecular biology and biochemistry, processivity is an enzyme's ability to catalyze "consecutive reactions without releasing its substrate".
For example, processivity is the average number of nucleotides added by a polymerase enzyme, such as ...
. While all members of the H1 group and the prokaryotic members of the H2 group function as monomers, eukaryotic H2 enzymes are obligate heterotrimers. Prokaryotic HIII enzymes are members of the broader H2 group and share most structural features with H2, with the addition of an N-terminal TATA box binding domain. Retroviral RNase H domains occurring in multidomain reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, ...
proteins have structures closely resembling the H1 group.
RNases H1 have been extensively studied to explore the relationships between structure and enzymatic activity. They are also used, especially the '' E. coli'' homolog, as model systems to study protein folding
Protein folding is the physical process by which a protein chain is translated to its native three-dimensional structure, typically a "folded" conformation by which the protein becomes biologically functional. Via an expeditious and reproduci ...
. Within the H1 group, a relationship has been identified between higher substrate-binding affinity and the presence of structural elements consisting of a helix and flexible loop providing a larger and more basic
BASIC (Beginners' All-purpose Symbolic Instruction Code) is a family of general-purpose, high-level programming languages designed for ease of use. The original version was created by John G. Kemeny and Thomas E. Kurtz at Dartmouth College ...
substrate-binding surface. The C-helix has a scattered taxonomic distribution; it is present in the ''E. coli'' and human RNase H1 homologs and absent in the HIV RNase H domain, but examples of retroviral domains with C-helices do exist.
Function
Ribonuclease H enzymes cleave thephosphodiester
In chemistry, a phosphodiester bond occurs when exactly two of the hydroxyl groups () in phosphoric acid react with hydroxyl groups on other molecules to form two ester bonds. The "bond" involves this linkage . Discussion of phosphodiesters is d ...
bonds of RNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydra ...
in a double-stranded RNA:DNA hybrid, leaving a 3' hydroxyl
In chemistry, a hydroxy or hydroxyl group is a functional group with the chemical formula and composed of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. In organic chemistry, alcohols and carboxylic acids contain one or more hydroxy ...
and a 5' phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
group on either end of the cut site with a two-metal-ion catalysis mechanism, in which two divalent cations, such as Mg2+ and Mn2+, directly participate in the catalytic function. Depending on the differences in their amino acid sequences, these RNases H are classified into type 1 and type 2 RNases H. Type 1 RNases H have prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNases H1 and retroviral RNase H. Type 2 RNases H have prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNases H2 and bacterial RNase H3. These RNases H exist in a monomeric form, except for eukaryotic RNases H2, which exist in a heterotrimeric form. RNase H1 and H2 have distinct substrate preferences and distinct but overlapping functions in the cell. In prokaryotes and lower eukaryotes, neither enzyme is essential, whereas both are believed to be essential in higher eukaryotes. The combined activity of both H1 and H2 enzymes is associated with maintenance of genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
stability due to the enzymes' degradation of the RNA component of R-loop
An R-loop is a three-stranded nucleic acid structure, composed of a DNA: RNA hybrid and the associated non-template single-stranded DNA. R-loops may be formed in a variety of circumstances, and may be tolerated or cleared by cellular components. ...
s.
Ribonuclease H1
Ribonuclease H1 enzymes require at least fourribonucleotide
In biochemistry, a ribonucleotide is a nucleotide containing ribose as its pentose component. It is considered a molecular precursor of nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the basic building blocks of DNA and RNA. Ribonucleotides themselves are basic ...
-containing base pair
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
s in a substrate and cannot remove a single ribonucleotide from a strand that is otherwise composed of deoxyribonucleotides. For this reason, it is considered unlikely that RNase H1 enzymes are involved in the processing of RNA primers from Okazaki fragment
Okazaki fragments are short sequences of DNA nucleotides (approximately 150 to 200 base pairs long in eukaryotes) which are synthesized discontinuously and later linked together by the enzyme DNA ligase to create the lagging strand during DNA ...
s during DNA replication
In molecular biology, DNA replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule. DNA replication occurs in all living organisms acting as the most essential part for biological inheritanc ...
. RNase H1 is not essential in unicellular organisms where it has been investigated; in '' E. coli'', RNase H1 knockout
A knockout (abbreviated to KO or K.O.) is a fight-ending, winning criterion in several full-contact combat sports, such as boxing, kickboxing, muay thai, mixed martial arts, karate, some forms of taekwondo and other sports involving striking, a ...
s confer a temperature-sensitive phenotype, and in ''S. cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have bee ...
'', they produce defects in stress response.
In many eukaryotes, including mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s, RNase H1 genes include a mitochondrial targeting sequence
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and fungi. Mitochondria have a double membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is use ...
, leading to expression of isoforms
A protein isoform, or "protein variant", is a member of a set of highly similar proteins that originate from a single gene or gene family and are the result of genetic differences. While many perform the same or similar biological roles, some isof ...
with and without the MTS present. As a result, RNase H1 is localized to both mitochondria
A mitochondrion (; ) is an organelle found in the Cell (biology), cells of most Eukaryotes, such as animals, plants and Fungus, fungi. Mitochondria have a double lipid bilayer, membrane structure and use aerobic respiration to generate adenosi ...
and the nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
. In knockout mouse
A knockout mouse, or knock-out mouse, is a genetically modified mouse (''Mus musculus'') in which researchers have inactivated, or "knocked out", an existing gene by replacing it or disrupting it with an artificial piece of DNA. They are importan ...
models, RNase H1-null mutants are lethal
Lethality (also called deadliness or perniciousness) is how capable something is of causing death. Most often it is used when referring to diseases, chemical weapons, biological weapons, or their toxic chemical components. The use of this ter ...
during embryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
due to defects in replicating mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA or mDNA) is the DNA located in mitochondria, cellular organelles within eukaryotic cells that convert chemical energy from food into a form that cells can use, such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Mitochondrial D ...
. The defects in mitochondrial DNA replication induced by loss of RNase H1 are likely due to defects in R-loop
An R-loop is a three-stranded nucleic acid structure, composed of a DNA: RNA hybrid and the associated non-template single-stranded DNA. R-loops may be formed in a variety of circumstances, and may be tolerated or cleared by cellular components. ...
processing.
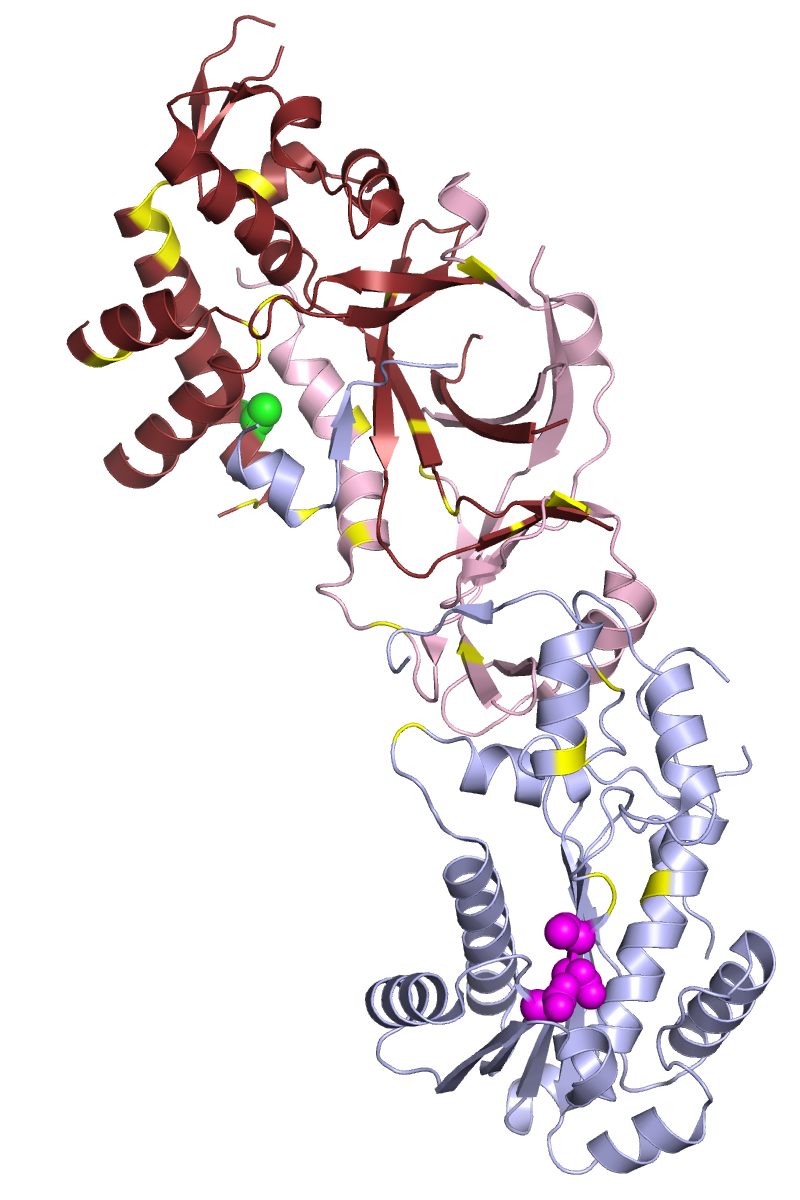
Ribonuclease H2
In prokaryotes, RNase H2 is enzymatically active as a monomeric protein. In eukaryotes, it is an obligate heterotrimer composed of a catalytic subunit A and structural subunits B and C. While the A subunit is closely homologous to the prokaryotic RNase H2, the B and C subunits have no apparent homologs in prokaryotes and are poorly conserved at thesequence
In mathematics, a sequence is an enumerated collection of objects in which repetitions are allowed and order matters. Like a set, it contains members (also called ''elements'', or ''terms''). The number of elements (possibly infinite) is calle ...
level even among eukaryotes. The B subunit mediates protein-protein interactions between the H2 complex and PCNA
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) is a DNA clamp that acts as a processivity factor for DNA polymerase δ in eukaryotic cells and is essential for replication. PCNA is a homotrimer and achieves its processivity by encircling the DNA, wh ...
, which localizes H2 to replication foci.
Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic H2 enzymes can cleave single ribonucleotides in a strand. however, they have slightly different cleavage patterns and substrate preferences: prokaryotic enzymes have lower processivity
In molecular biology and biochemistry, processivity is an enzyme's ability to catalyze "consecutive reactions without releasing its substrate".
For example, processivity is the average number of nucleotides added by a polymerase enzyme, such as ...
and hydrolyze successive ribonucleotides more efficiently than ribonucleotides with a 5' deoxyribonucleotide, while eukaryotic enzymes are more processive and hydrolyze both types of substrate with similar efficiency. The substrate specificity of RNase H2 gives it a role in ribonucleotide excision repair, removing misincorporated ribonucleotides from DNA, in addition to R-loop
An R-loop is a three-stranded nucleic acid structure, composed of a DNA: RNA hybrid and the associated non-template single-stranded DNA. R-loops may be formed in a variety of circumstances, and may be tolerated or cleared by cellular components. ...
processing. Although both H1 and H2 are present in the mammalian cell nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, h ...
, H2 is the dominant source of RNase H activity there and is important for maintaining genome stability.
Some prokaryotes possess an additional H2-type gene designated RNase HIII in the Roman-numeral nomenclature used for the prokaryotic genes. HIII proteins are more closely related to the H2 group by sequence identity
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Ali ...
and structural similarity, but have substrate preferences that more closely resemble H1. Unlike HI and HII, which are both widely distributed among prokaryotes, HIII is found in only a few organisms with a scattered taxonomic distribution; it is somewhat more common in archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
and is rarely or never found in the same prokaryotic genome as HI.
Mechanism
active site
In biology and biochemistry, the active site is the region of an enzyme where substrate molecules bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The active site consists of amino acid residues that form temporary bonds with the substrate (binding site) a ...
of nearly all RNases H contains four negatively charged amino acid residues, known as the DEDD motif; often a histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the de ...
e.g. in HIV-1, human or E. coli is also present.
The charged residues bind two metal ions that are required for catalysis; under physiological conditions these are magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
ions, but manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
also usually supports enzymatic activity, while calcium
Calcium is a chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. As an alkaline earth metal, calcium is a reactive metal that forms a dark oxide-nitride layer when exposed to air. Its physical and chemical properties are most similar to ...
or high concentration of Mg2+ inhibits activity.
Based on experimental evidence and computer simulations the enzyme activates a water molecule bound to one of the metal ions with the conserved histidine. The transition state is associative in nature and forms an intermediate with protonated phosphate and deprotonated alkoxide leaving group. The leaving group is protonated via the glutamate which has an elevated pKa and is likely to be protonated.
The mechanism is similar to RNase T
Ribonuclease (commonly abbreviated RNase) is a type of nuclease that catalyzes the degradation of RNA into smaller components. Ribonucleases can be divided into endoribonucleases and exoribonucleases, and comprise several sub-classes within t ...
and the RuvC subunit in the Cas9
Cas9 (CRISPR associated protein 9, formerly called Cas5, Csn1, or Csx12) is a 160 kilodalton protein which plays a vital role in the immunological defense of certain bacteria against DNA viruses and plasmids, and is heavily utilized in genetic e ...
enzyme which both also use a histidine and a two-metal ion mechanism.
The mechanism of the release of the cleaved product is still unresolved. Experimental evidence from time-resolved crystallography and similar nucleases points to a role of a third ion in the reaction recruited to the active site.
In human biology
Thehuman genome
The human genome is a complete set of nucleic acid sequences for humans, encoded as DNA within the 23 chromosome pairs in cell nuclei and in a small DNA molecule found within individual mitochondria. These are usually treated separately as the n ...
contains four genes encoding RNase H:
* RNASEH1
Ribonuclease H1 also known as RNase H1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RNASEH1'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning '' ...
, an example of the H1 (monomeric) subtype
* RNASEH2A
Ribonuclease H2 subunit A, also known as RNase H2 subunit A, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''RNASEH2A'' gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene is a component of the heterotrimeric type II ribonuclease H enzyme (RNaseH2 ...
, the catalytic subunit of the trimeric H2 complex
* RNASEH2B
Ribonuclease H2, subunit B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''RNASEH2B'' gene. RNase H2 is composed of a single catalytic subunit ( A) and two non-catalytic subunits (B and C), and degrades the RNA of RNA:DNA hybrids. The non-cataly ...
, a structural subunit of the trimeric H2 complex
* RNASEH2C
Ribonuclease H2 subunit C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RNASEH2C gene.
Ribonuclease H, RNase H2 is composed of a single catalytic subunit (RNASEH2A, A) and two non-catalytic subunits (RNASEH2B, B and C), and degrades the RNA of R ...
, a structural subunit of the trimeric H2 complex
In addition, genetic material of retroviral
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptas ...
origin appears frequently in the genome, reflecting integration of the genomes of human endogenous retrovirus
Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) are endogenous viral elements in the genome that closely resemble and can be derived from retroviruses. They are abundant in the genomes of jawed vertebrates, and they comprise up to 5–8% of the human genome ( ...
es. Such integration events result in the presence of genes encoding retroviral reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, ...
, which includes an RNase H domain. An example is ERVK6
HERV-K_19q12 provirus ancestral Pol protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ERVK6'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meani ...
. Long terminal repeat
A long terminal repeat (LTR) is a pair of identical sequences of DNA, several hundred base pairs long, which occur in eukaryotic genomes on either end of a series of genes or pseudogenes that form a retrotransposon or an endogenous retrovirus or ...
(LTR) and non-long terminal repeat (non-LTR) retrotransposon
Retrotransposons (also called Class I transposable elements or transposons via RNA intermediates) are a type of genetic component that copy and paste themselves into different genomic locations (transposon) by converting RNA back into DNA through ...
s are also common in the genome and often include their own RNase H domains, with a complex evolutionary history.
Role in disease
 In small studies, mutations in human RNase H1 have been associated with
In small studies, mutations in human RNase H1 have been associated with chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia
Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia (CPEO) is a type of eye disorder characterized by slowly progressive inability to move the eyes and eyebrows. It is often the only feature of mitochondrial disease, in which case the term CPEO may be g ...
, a common feature of mitochondrial disease
Mitochondrial disease is a group of disorders caused by mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondria are the organelles that generate energy for the cell and are found in every cell of the human body except red blood cells. They convert the energy of ...
.
Mutations in any of the three RNase H2 subunits are well-established as causes of a rare genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders ...
known as Aicardi–Goutières syndrome
Aicardi–Goutières syndrome (AGS), which is completely distinct from the similarly named Aicardi syndrome, is a rare, usually early onset childhood, inflammatory disorder most typically affecting the brain and the skin (neurodevelopmental disor ...
(AGS), which manifests as neurological
Neurology (from el, νεῦρον (neûron), "string, nerve" and the suffix -logia, "study of") is the branch of medicine dealing with the diagnosis and treatment of all categories of conditions and disease involving the brain, the spinal ...
and dermatological
Dermatology is the branch of medicine dealing with the skin.''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary.'' Random House, Inc. 2001. Page 537. . It is a speciality with both medical and surgical aspects. A dermatologist is a specialist medical ...
symptoms at an early age. The symptoms of AGS closely resemble those of congenital viral infection and are associated with inappropriate upregulation of type I interferon
The type-I interferons (IFN) are cytokines which play essential roles in inflammation, immunoregulation, tumor cells recognition, and T cell, T-cell responses. In the human genome, a cluster of thirteen functional IFN genes is located at the 9p2 ...
. AGS can also be caused by mutations in other genes: TREX1
Three prime repair exonuclease 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''TREX1'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes the major 3'->5' DNA exonuclease in human cells. The protein is a non-processive exonuclease that may serve a proofrea ...
, SAMHD1
SAM domain and HD domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SAMHD1'' gene. SAMHD1 is a cellular enzyme, responsible for blocking replication of HIV in dendritic cells, macrophages, monocytes and resting CD4+ T ly ...
, ADAR
Adar ( he, אֲדָר ; from Akkadian ''adaru'') is the sixth month of the civil year and the twelfth month of the religious year on the Hebrew calendar, roughly corresponding to the month of March in the Gregorian calendar. It is a month of 29 d ...
, and MDA5
MDA5 (melanoma differentiation-associated protein 5) is a RIG-I-like receptor dsRNA helicase enzyme that is encoded by the ''IFIH1'' gene in humans. MDA5 is part of the RIG-I-like receptor (RLR) family, which also includes RIG-I and LGP2, and ...
/IFIH1, all of which are involved in nucleic acid processing. Characterization of mutational distribution in an AGS patient population found 5% of all AGS mutations in RNASEH2A, 36% in 2B, and 12% in 2C. Mutations in 2B have been associated with somewhat milder neurological impairment and with an absence of interferon-induced gene upregulation that can be detected in patients with other AGS-associated genotypes.
In viruses
 Two groups of
Two groups of virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
es use reverse transcription as part of their life cycles: retrovirus
A retrovirus is a type of virus that inserts a DNA copy of its RNA genome into the DNA of a host cell that it invades, thus changing the genome of that cell. Once inside the host cell's cytoplasm, the virus uses its own reverse transcriptase ...
es, which encode their genomes in single-stranded RNA and replicate through a double-stranded DNA intermediate; and dsDNA-RT virus
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a dis ...
es, which replicate their double-stranded DNA genomes through an RNA "pregenome" intermediate. Pathogen
In biology, a pathogen ( el, πάθος, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of") in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a germ ...
ic examples include human immunodeficiency virus
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of ''Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause AIDS, acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the ...
and hepatitis B virus
''Hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, a species of the genus ''Orthohepadnavirus'' and a member of the ''Hepadnaviridae'' family of viruses. This virus causes the disease hepatitis B.
Disease
Despite there bein ...
, respectively. Both encode large multifunctional reverse transcriptase
A reverse transcriptase (RT) is an enzyme used to generate complementary DNA (cDNA) from an RNA template, a process termed reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptases are used by viruses such as HIV and hepatitis B to replicate their genomes, ...
(RT) proteins containing RNase H domains.
Retroviral RT proteins from HIV-1
The subtypes of HIV include two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to viruses found in chimpanzees and gorillas living in western Africa, while HIV-2 viruses are related to viruses found in the sooty mangabey ...
and murine leukemia virus are the best-studied members of the family. Retroviral RT is responsible for converting the virus' single-stranded RNA genome into double-stranded DNA. This process requires three steps: first, RNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity produces minus-strand DNA from the plus-strand RNA template, generating an RNA:DNA hybrid intermediate; second, the RNA strand is destroyed; and third, DNA-dependent DNA polymerase activity synthesizes plus-strand DNA, generating double-stranded DNA as the final product. The second step of this process is carried out by an RNase H domain located at the C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is ...
of the RT protein.
RNase H performs three types of cleaving actions: non-specific degradation of the plus-strand RNA genome, specific removal of the minus-strand tRNA
Transfer RNA (abbreviated tRNA and formerly referred to as sRNA, for soluble RNA) is an adaptor molecule composed of RNA, typically 76 to 90 nucleotides in length (in eukaryotes), that serves as the physical link between the mRNA and the amino ac ...
primer, and removal of the plus-strand purine-rich polypurine tract (PPT) primer. RNase H plays a role in the priming of the plus-strand, but not in the conventional method of synthesizing a new primer sequence. Rather RNase H creates a "primer" from the PPT that is resistant to RNase H cleavage. By removing all bases but the PPT, the PPT is used as a marker for the end of the U3 region of its long terminal repeat
A long terminal repeat (LTR) is a pair of identical sequences of DNA, several hundred base pairs long, which occur in eukaryotic genomes on either end of a series of genes or pseudogenes that form a retrotransposon or an endogenous retrovirus or ...
.
Because RNase H activity is required for viral proliferation, this domain has been considered a drug target
A biological target is anything within a living organism to which some other entity (like an endogenous ligand or a drug) is directed and/or binds, resulting in a change in its behavior or function. Examples of common classes of biological targets ...
for the development of antiretroviral
The management of HIV/AIDS normally includes the use of multiple antiretroviral drugs as a strategy to control HIV infection. There are several classes of antiretroviral agents that act on different stages of the HIV life-cycle. The use of multipl ...
drugs used in the treatment of HIV/AIDS
Human immunodeficiency virus infection and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS) is a spectrum of conditions caused by infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), a retrovirus. Following initial infection an individual ...
and other conditions caused by retroviruses. Inhibitors of retroviral RNase H of several different chemotypes have been identified, many of which have a mechanism of action
In pharmacology, the term mechanism of action (MOA) refers to the specific biochemical interaction through which a drug substance produces its pharmacological effect. A mechanism of action usually includes mention of the specific molecular targe ...
based on chelation
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a Denticity, polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These l ...
of the active-site cations. Reverse-transcriptase inhibitors
Reverse-transcriptase inhibitors (RTIs) are a class of antiretroviral drugs used to treat HIV infection or AIDS, and in some cases hepatitis B. RTIs inhibit activity of reverse transcriptase, a viral DNA polymerase that is required for replicatio ...
that specifically inhibit the polymerase function of RT are in widespread clinical use, but not inhibitors of the RNase H function; it is the only enzymatic function encoded by HIV that is not yet targeted by drugs in clinical use.
Evolution
RNases H are widely distributed and occur in all domains of life. The family belongs to a larger superfamily of nuclease enzymes and is considered to be evolutionarily ancient. In prokaryotic genomes, multiple RNase H genes are often present, but there is little correlation between occurrence of HI, HII, and HIII genes and overallphylogenetic relationship
In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ...
s, suggesting that horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between Unicellular organism, unicellular and/or multicellular organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offsprin ...
may have played a role in establishing the distribution of these enzymes. RNase HI and HIII rarely or never appear in the same prokaryotic genome. When an organism's genome contains more than one RNase H gene, they sometimes have significant differences in activity level. These observations have been suggested to reflect an evolutionary pattern that minimizes functional redundancy among RNase H genes. RNase HIII, which is unique to prokaryotes, has a scattered taxonomic distribution and is found in both bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
and archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebac ...
; it is believed to have diverged from HII fairly early.
The evolutionary trajectory of RNase H2 in eukaryotes, especially the mechanism by which eukaryotic homologs became obligate heterotrimers, is unclear; the B and C subunits have no apparent homologs in prokaryotes.
Applications
Because RNase H specifically degrades only the RNA in double-stranded RNA:DNA hybrids, it is commonly used as a laboratory reagent inmolecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and physi ...
. Purified preparations of ''E. coli'' RNase HI and HII are commercially available. RNase HI is often used to destroy the RNA template after first-strand complementary DNA
In genetics, complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA synthesized from a single-stranded RNA (e.g., messenger RNA (mRNA) or microRNA (miRNA)) template in a reaction catalyzed by the enzyme reverse transcriptase. cDNA is often used to express a spe ...
(cDNA) synthesis by reverse transcription. It can also be used to cleave specific RNA sequences in the presence of short complementary segments of DNA. Highly sensitive techniques such as surface plasmon resonance
Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) is the resonant oscillation of conduction electrons at the interface between negative and positive permittivity material in a particle stimulated by incident light. SPR is the basis of many standard tools for measu ...
can be used for detection. RNase HII can be used to degrade the RNA primer component of an Okazaki fragment
Okazaki fragments are short sequences of DNA nucleotides (approximately 150 to 200 base pairs long in eukaryotes) which are synthesized discontinuously and later linked together by the enzyme DNA ligase to create the lagging strand during DNA ...
or to introduce single-stranded nicks at positions containing a ribonucleotide. A variant of hot start PCR, known as RNase H-dependent PCR or rhPCR, has been described using a thermostable RNase HII from the hyperthermophilic
A hyperthermophile is an organism that thrives in extremely hot environments—from 60 °C (140 °F) upwards. An optimal temperature for the existence of hyperthermophiles is often above 80 °C (176 °F). Hyperthermophiles are often within the doma ...
archaeon
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebact ...
''Pyrococcus abyssi
''Pyrococcus abyssi'' is a hyperthermophilic archaeon isolated from a deep-sea hydrothermal vent in the North Fiji Basin at . It is anaerobic, sulfur-metabolizing, gram-negative, coccus-shaped and highly motile. Its optimum growth temperature is ...
''. Of note, the ribonuclease inhibitor
Ribonuclease inhibitor (RI) is a large (~450 residues, ~49 kDa), acidic (pI ~4.7), leucine-rich repeat protein that forms extremely tight complexes with certain ribonucleases. It is a major cellular protein, comprising ~0.1% of all cellular prot ...
protein commonly used as a reagent is not effective at inhibiting the activity of either HI or HII.
History
Ribonucleases H were first discovered in the laboratory of Peter Hausen when researchers found RNA:DNA hybridendonuclease
Endonucleases are enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain. Some, such as deoxyribonuclease I, cut DNA relatively nonspecifically (without regard to sequence), while many, typically called restriction endonucleases ...
activity in calf
Calf most often refers to:
* Calf (animal), the young of domestic cattle.
* Calf (leg), in humans (and other primates), the back portion of the lower leg
Calf or calves may also refer to:
Biology and animal byproducts
* Veal, meat from calves
* ...
thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. ...
in 1969 and gave it the name "ribonuclease ''H''" to designate its ''hybrid'' specificity. RNase H activity was subsequently discovered in '' E. coli'' and in a sample of oncovirus
An oncovirus or oncogenic virus is a virus that can cause cancer. This term originated from studies of acutely transforming retroviruses in the 1950–60s, when the term "oncornaviruses" was used to denote their RNA virus origin. With the lette ...
es with RNA genome
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydr ...
s during early studies of viral reverse transcription. It later became clear that calf thymus extract contained more than one protein with RNase H activity and that ''E. coli'' contained two RNase H genes. Originally, the enzyme now known as RNase H2 in eukaryotes was designated H1 and vice versa, but the names of the eukaryotic enzymes were switched to match those in ''E. coli'' to facilitate comparative analysis, yielding the modern nomenclature in which the prokaryotic enzymes are designated with Roman numerals and the eukaryotic enzymes with Arabic numerals. The prokaryotic RNase HIII, reported in 1999, was the last RNase H subtype to be identified.
Characterizing eukaryotic RNase H2 was historically a challenge, in part due to its low abundance. Careful efforts at purification of the enzyme suggested that, unlike the ''E. coli'' RNase H2, the eukaryotic enzyme had multiple subunits. The ''S. cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have bee ...
'' homolog of the ''E. coli'' protein (that is, the H2A subunit) was easily identifiable by bioinformatics
Bioinformatics () is an interdisciplinary field that develops methods and software tools for understanding biological data, in particular when the data sets are large and complex. As an interdisciplinary field of science, bioinformatics combi ...
when the yeast genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding ge ...
was sequenced, but the corresponding protein was found not to have enzymatic activity in isolation. Eventually, the yeast B and C subunits were isolated by co-purification and found to be required for enzymatic activity. However, the yeast B and C subunits have very low sequence identity
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Ali ...
to their homologs in other organisms, and the corresponding human proteins were conclusively identified only after mutations in all three were found to cause Aicardi–Goutières syndrome
Aicardi–Goutières syndrome (AGS), which is completely distinct from the similarly named Aicardi syndrome, is a rare, usually early onset childhood, inflammatory disorder most typically affecting the brain and the skin (neurodevelopmental disor ...
.
References
External links
GeneReviews/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Aicardi-Goutières Syndrome
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Rnase H Ribonucleases EC 3.1.26 Molecular biology