|
RNase H-dependent PCR
RNase H-dependent PCR (rhPCR) is a modification of the standard PCR technique. In rhPCR, the primers are designed with a removable amplification block on the 3’ end. Amplification of the blocked primer is dependent on the cleavage activity of a hyperthermophilic archaeal Type II RNase H enzyme during hybridization to the complementary target sequence. This RNase H enzyme possesses several useful characteristics that enhance the PCR. First, it has very little enzymatic activity at low temperature, enabling a “ hot start PCR” without modifications to the DNA polymerase. Second, the cleavage efficiency of the enzyme is reduced in the presence of mismatches near the RNA residue. This allows for reduced primer dimer formation, detection of alternative splicing variants, ability to perform multiplex PCR with higher numbers of PCR primers, and the ability to detect single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Principle rhPCR primers consist of three sections. 1) The 5’ DNA se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RhPCR Mechanism
RNase H-dependent PCR (rhPCR) is a modification of the standard PCR technique. In rhPCR, the primers are designed with a removable amplification block on the 3’ end. Amplification of the blocked primer is dependent on the cleavage activity of a hyperthermophilic archaeal Type II RNase H enzyme during hybridization to the complementary target sequence. This RNase H enzyme possesses several useful characteristics that enhance the PCR. First, it has very little enzymatic activity at low temperature, enabling a “hot start PCR” without modifications to the DNA polymerase. Second, the cleavage efficiency of the enzyme is reduced in the presence of mismatches near the RNA residue. This allows for reduced primer dimer formation, detection of alternative splicing variants, ability to perform multiplex PCR with higher numbers of PCR primers, and the ability to detect single-nucleotide polymorphisms. Principle rhPCR primers consist of three sections. 1) The 5’ DNA sectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SYBR Green
SYBR Green I (SG) is an asymmetrical cyanine dye used as a nucleic acid stain in molecular biology. The SYBR family of dyes is produced by Molecular Probes Inc., now owned by Thermo Fisher Scientific. SYBR Green I binds to DNA. The resulting DNA-dye-complex best absorbs 497 nanometer blue light (λmax = 497 nm) and emits green light (λmax = 520 nm). The stain preferentially binds to double-stranded DNA, but will stain single-stranded (ss) DNA with lower performance. SYBR Green can also stain RNA with a lower performance than ssDNA. Uses SYBR Green finds usage in several areas of biochemistry and molecular biology. It is used as a dye for the quantification of double stranded DNA in some methods of quantitative PCR. It is also used to visualise DNA in gel electrophoresis. Higher concentrations of SYBR Green can be used to stain agarose gels in order to visualise the DNA present. In addition to labelling pure nucleic acids, SYBR Green can also be used for labelling o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Biology Techniques
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic bonds, are typically not considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by Károly Ereky in 1919, meaning the production of products from raw materials with the aid of living organisms. Definition The concept of biotechnology encompasses a wide range of procedures for modifying living organisms according to human purposes, going back to domestication of animals, cultivation of the plants, and "improvements" to these through breeding programs that employ artificial selection and hybridization. Modern usage also includes genetic engineering as well as cell and tissue culture technologies. The American Chemical Society defines biotechnology as the application of biological organisms, systems, or processes by various industries to learning about the science of life and the improvement of the value of materials ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Beacon
Molecular beacons, or molecular beacon probes, are oligonucleotide hybridization probes that can report the presence of specific nucleic acids in homogenous solutions. Molecular beacons are hairpin-shaped molecules with an internally quenched fluorophore whose fluorescence is restored when they bind to a target nucleic acid sequence. This is a novel non-radioactive method for detecting specific sequences of nucleic acids. They are useful in situations where it is either not possible or desirable to isolate the probe-target hybrids from an excess of the hybridization probes. Molecular beacon probes A typical molecular beacon probe is 25 nucleotides long. The middle 15 nucleotides are complementary to the target DNA or RNA and do not base pair with one another, while the five nucleotides at each terminus are complementary to each other rather than to the target DNA. A typical molecular beacon structure can be divided in 4 parts: 1) loop, an 18–30 base pair region of the molecular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is a laboratory technique combining reverse transcription of RNA into DNA (in this context called complementary DNA or cDNA) and amplification of specific DNA targets using polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It is primarily used to measure the amount of a specific RNA. This is achieved by monitoring the amplification reaction using fluorescence, a technique called real-time PCR or quantitative PCR (qPCR). Combined RT-PCR and qPCR are routinely used for analysis of gene expression and quantification of viral RNA in research and clinical settings. The close association between RT-PCR and qPCR has led to metonymic use of the term qPCR to mean RT-PCR. Such use may be confusing, as RT-PCR can be used without qPCR, for example to enable molecular cloning, sequencing or simple detection of RNA. Conversely, qPCR may be used without RT-PCR, for example to quantify the copy number of a specific piece of DNA. Nomenclature The combine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
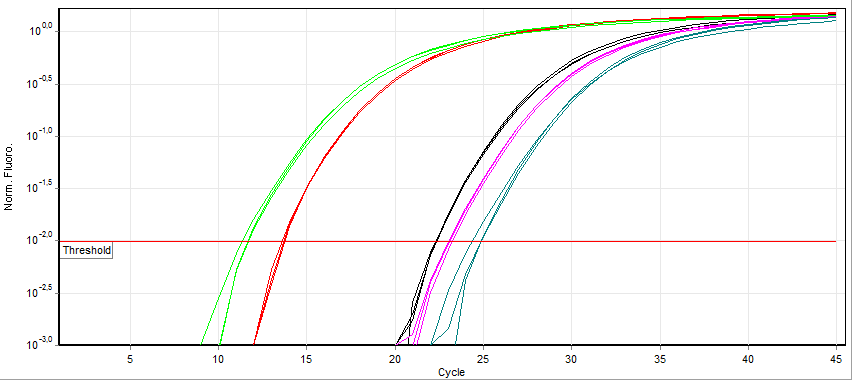
Quantitative PCR
A real-time polymerase chain reaction (real-time PCR, or qPCR) is a laboratory technique of molecular biology based on the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). It monitors the amplification of a targeted DNA molecule during the PCR (i.e., in real time), not at its end, as in conventional PCR. Real-time PCR can be used quantitatively (quantitative real-time PCR) and semi-quantitatively (i.e., above/below a certain amount of DNA molecules) (semi-quantitative real-time PCR). Two common methods for the detection of PCR products in real-time PCR are (1) non-specific fluorescent dyes that intercalate with any double-stranded DNA and (2) sequence-specific DNA probes consisting of oligonucleotides that are labelled with a fluorescent reporter, which permits detection only after hybridization of the probe with its complementary sequence. The Minimum Information for Publication of Quantitative Real-Time PCR Experiments ( MIQE) guidelines propose that the abbreviation ''qPCR'' be used for q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiplex PCR
Multiplex polymerase chain reaction (Multiplex PCR) refers to the use of polymerase chain reaction to amplify several different DNA sequences simultaneously (as if performing many separate PCR reactions all together in one reaction). This process amplifies DNA in samples using multiple primers and a temperature-mediated DNA polymerase in a thermal cycler. The primer design for all primers pairs has to be optimized so that all primer pairs can work at the same annealing temperature during PCR. Multiplex-PCR was first described in 1988 as a method to detect deletions in the dystrophin gene. It has also been used with the steroid sulfatase gene. In 2008, multiplex-PCR was used for analysis of microsatellites and SNPs. In 2020, RT-PCR multiplex assays were designed that combined multiple gene targets from the Center for Diseases and Control in a single reaction to increase molecular testing accessibility and throughput for SARS-CoV-2 diagnostics. Multiplex-PCR consists of multi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SNP Genotyping
SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is > 1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase of interest in SNPs has been reflected b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Splicing
Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be included within or excluded from the final, processed messenger RNA (mRNA) produced from that gene. This means the exons are joined in different combinations, leading to different (alternative) mRNA strands. Consequently, the proteins translated from alternatively spliced mRNAs will contain differences in their amino acid sequence and, often, in their biological functions (see Figure). Biologically relevant alternative splicing occurs as a normal phenomenon in eukaryotes, where it increases the number of proteins that can be encoded by the genome. In humans, it is widely believed that ~95% of multi-exonic genes are alternatively spliced to produce functional alternative products from the same gene but many scientists believe that most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |