Rajasthan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Rajasthan (; lit. 'Land of Kings') is a
 The Pratiharas ruled for many dynasties in this part of the country; the region was known as ''
The Pratiharas ruled for many dynasties in this part of the country; the region was known as ''
 During
During
File:Maharana Kumbhakarna of Mewar.jpg,
 The Aravalli Range runs across the state from the southwest peak
The Aravalli Range runs across the state from the southwest peak
File:Mt. Abu.jpg,
 The
The
 Rajasthan is also noted for its national parks and
Rajasthan is also noted for its national parks and

 Rajasthan is divided into 33 districts within seven divisions:
Rajasthan is divided into 33 districts within seven divisions:
File:Jaipur Airport.JPG,
 Rajasthani cuisine, Rajasthani cooking was influenced by both the war-like lifestyles of its inhabitants and the availability of ingredients in this arid region. Food that could last for several days and could be eaten without heating was preferred. Thus, pickles of Rajasthan are quite famous for their tangy and spicy flavour. The ''Panchkuta'' delicacy is also a famous one - meaning 5 vegetables - a dish that lasts for several days, and is made out of certain weed plants that only grow in the wild desert. The scarcity of water and fresh green vegetables have all had their effect on cooking. It is known for its snacks like Bikaneri Bhujia. Other famous dishes include ''bajre ki roti'' (millet bread) and ''lahsun ki chutney'' (hot garlic paste), ''mawa kachori'' Mirchi Bada, Pyaaj Kachori and ghevar from Jodhpur,
Rajasthani cuisine, Rajasthani cooking was influenced by both the war-like lifestyles of its inhabitants and the availability of ingredients in this arid region. Food that could last for several days and could be eaten without heating was preferred. Thus, pickles of Rajasthan are quite famous for their tangy and spicy flavour. The ''Panchkuta'' delicacy is also a famous one - meaning 5 vegetables - a dish that lasts for several days, and is made out of certain weed plants that only grow in the wild desert. The scarcity of water and fresh green vegetables have all had their effect on cooking. It is known for its snacks like Bikaneri Bhujia. Other famous dishes include ''bajre ki roti'' (millet bread) and ''lahsun ki chutney'' (hot garlic paste), ''mawa kachori'' Mirchi Bada, Pyaaj Kachori and ghevar from Jodhpur, 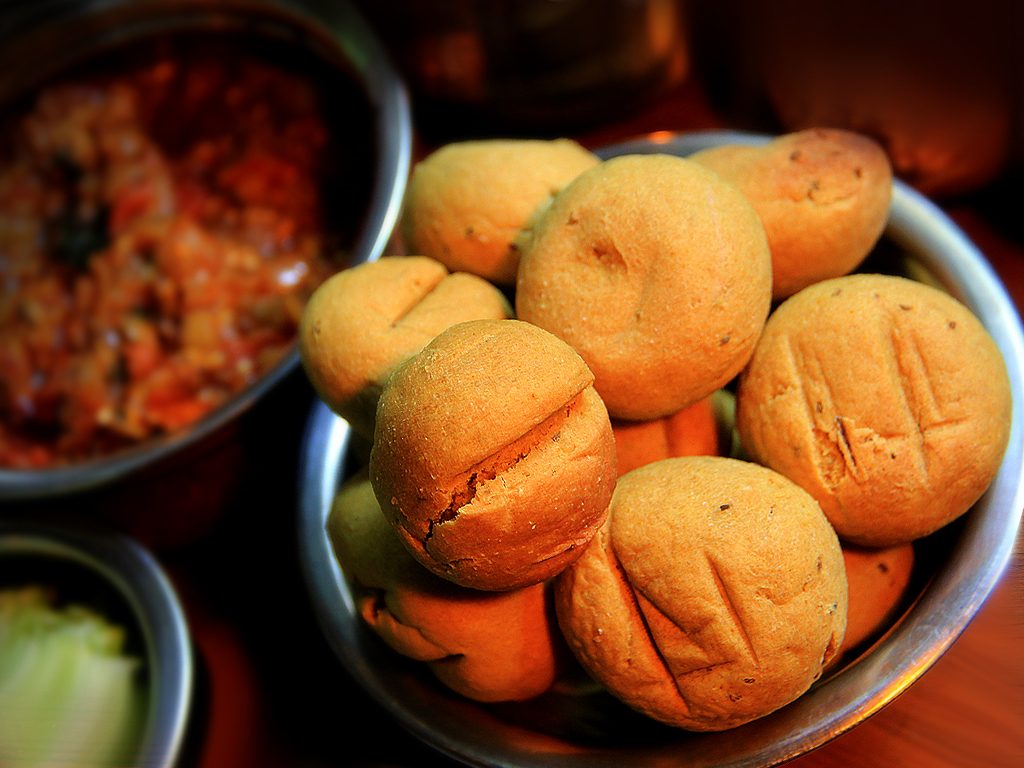 Dal baati, Dal-baati-churma is very popular in Rajasthan. The traditional way to serve it is to first coarsely mash the baati, and then pour pure ghee on top of it. It is served with daal (lentils) and spicy garlic chutney; it is also served with besan (gram flour) ki kadi. It is commonly served at all festivities, including religious occasions, wedding ceremonies, and birthday parties in Rajasthan.
Dal baati, Dal-baati-churma is very popular in Rajasthan. The traditional way to serve it is to first coarsely mash the baati, and then pour pure ghee on top of it. It is served with daal (lentils) and spicy garlic chutney; it is also served with besan (gram flour) ki kadi. It is commonly served at all festivities, including religious occasions, wedding ceremonies, and birthday parties in Rajasthan.
 In recent years, Rajasthan has worked on improving education. The state government has been making sustained efforts to raise the education standard.
In recent years, Rajasthan has worked on improving education. The state government has been making sustained efforts to raise the education standard.
 Rajasthan attracted a total of 45.9 million domestic and 1.6 million foreign tourists in 2017, which is the tenth highest in terms of domestic visitors and fifth highest in foreign tourists. The tourism industry in Rajasthan is growing effectively each year and is becoming one of the major income sources for the state government. Rajasthan is home to many attractions for domestic and foreign travellers, including the forts and palaces of
Rajasthan attracted a total of 45.9 million domestic and 1.6 million foreign tourists in 2017, which is the tenth highest in terms of domestic visitors and fifth highest in foreign tourists. The tourism industry in Rajasthan is growing effectively each year and is becoming one of the major income sources for the state government. Rajasthan is home to many attractions for domestic and foreign travellers, including the forts and palaces of
File:Camel rides in Thar desert.jpg, Camel rides in Thar desert
File:Temples at Pushkar Lake.jpg, Pushkar Lake and Ghat
File:Bhavai is a genre of folk dance popular in Rajasthan. The male or female performers balance a number of earthen pots while dancing.jpg, Kalbelia Folk dance popular in Rajasthan
File:Demoiselle cranes in Khichan near Bikaner (Rajasthan).jpg, Demoiselle cranes in Khichan near
Official Site of the Government of Rajasthan, India
Official Tourism Site of Rajasthan, India
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in northern India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central ...
. It covers or 10.4 per cent of India's total geographical area. It is the largest Indian state by area and the seventh largest by population. It is on India's northwestern side, where it comprises most of the wide and inhospitable Thar Desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent, Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's Li ...
(also known as the Great Indian Desert) and shares a border with the Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
i provinces of Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
to the northwest and Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
to the west, along the Sutlej
The Sutlej or Satluj River () is the longest of the five rivers that flow through the historic crossroads region of Punjab in northern India and Pakistan. The Sutlej River is also known as ''Satadru''. It is the easternmost tributary of the Ind ...
-Indus
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
River valley. It is bordered by five other Indian states: Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
to the north; Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ar ...
and Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
to the northeast; Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the seco ...
to the southeast; and Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
to the southwest. Its geographical location is 23.3 to 30.12 North latitude and 69.30 to 78.17 East longitude, with the Tropic of Cancer passing through its southernmost tip.
Its major features include the ruins of the Indus Valley civilisation
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
at Kalibangan
Kalibangān is a town located at on the left or southern banks of the Ghaggar (Ghaggar-Hakra River) in Tehsil Pilibangān, between Suratgarh and Hanumangarh in Hanumangarh District, Rajasthan, India 205 km. from Bikaner. It is also identifi ...
and Balathal
Balathal is an archaeological site located in Vallabhnagar tehsil of Udaipur district of Rajasthan state in western India. It is one of the ninety Ahar-Banas culture sites located in the Basins of the Banas river and its tributaries.
Excavatio ...
, the Dilwara Temples, a Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being ...
pilgrimage site at Rajasthan's only hill station
A hill station is a town located at a higher elevation than the nearby plain or valley. The term was used mostly in colonial Asia (particularly in India), but also in Africa (albeit rarely), for towns founded by European colonialists as refuges ...
, Mount Abu
Mount Abu () is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India.The mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. The highest peak on the mountain is Guru Shikhar at above s ...
, in the ancient Aravalli mountain range and eastern Rajasthan, the Keoladeo National Park
Keoladeo National Park or Keoladeo Ghana National Park (formerly known as the Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary) is a famous avifauna sanctuary in Bharatpur, Rajasthan, India, that hosts thousands of birds, especially during the winter season. Over 350 ...
of Bharatpur, a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
known for its bird life. Rajasthan is also home to three national tiger
The tiger (''Panthera tigris'') is the largest living cat species and a member of the genus '' Panthera''. It is most recognisable for its dark vertical stripes on orange fur with a white underside. An apex predator, it primarily preys on u ...
reserves, the Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park is a national park in Rajasthan, India, with an area of . It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River. It is named after the historic Ranthambore Fort, which lies within the park ...
in Sawai Madhopur
Sawai Madhopur is a city and Municipal Council (Nagar Parishad) in the Sawai Madhopur District in Rajasthan state, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Sawai Madhopur District of Rajasthan. Ranthambore National Park which is 7 ...
, Sariska Tiger Reserve
Sariska Tiger Reserve is a tiger reserve in Alwar district, Rajasthan, India. It stretches over an area of comprising scrub-thorn arid forests, dry deciduous forests, grasslands, and rocky hills. This area was a hunting preserve of the Alwa ...
in Alwar
Alwar (Pronunciation: Help:IPA/Hindi and Urdu, �lʋəɾ is a city located in India's National Capital Region (India), National Capital Region and the administrative headquarters of Alwar district, Alwar District in the state of Rajasthan. ...
and the Mukundra Hills Tiger Reserve in Kota.
The state was formed on 30 March 1949 when Rajputanathe name adopted by the British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent;
*
* it is also called Crown rule in India,
*
*
*
*
or Direct rule in India,
* Quote: "Mill, who was himsel ...
for its dependencies in the regionwas merged into the Dominion of India
The Dominion of India, officially the Union of India,* Quote: “The first collective use (of the word "dominion") occurred at the Colonial Conference (April to May 1907) when the title was conferred upon Canada and Australia. New Zealand and N ...
. Its capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and largest city is Jaipur
Jaipur (; Hindi Language, Hindi: ''Jayapura''), formerly Jeypore, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Rajasthan. , the city had a pop ...
. Other important cities are Jodhpur
Jodhpur (; ) is the second-largest city in the Indian state of Rajasthan and officially the second metropolitan city of the state. It was formerly the seat of the princely state of Jodhpur State. Jodhpur was historically the capital of the Ki ...
, Kota, Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. Bikaner city is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Formerly the capital of ...
, Ajmer
Ajmer is one of the major and oldest cities in the Indian state of Rajasthan and the centre of the eponymous Ajmer District. It is located at the centre of Rajasthan. It is also known as heart of Rajasthan. The city was established as "''Aj ...
, Bharatpur and Udaipur
Udaipur () (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura''), historically named as Udayapura, is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capit ...
. The economy of Rajasthan
Rajasthan is a mineral-rich state and has a diversified economy having agriculture, mining and tourism as its main engines of growth. The state mines produce gold, silver, sandstone, limestone, marble, rock phosphate, copper and lignite. It i ...
is the seventh-largest state economy in India with in gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a money, monetary Measurement in economics, measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjec ...
and a per capita GDP
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is ofte ...
of . Rajasthan ranks 29th among India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
n states in human development index
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a statistic composite index of life expectancy, education (mean years of schooling completed and expected years of schooling upon entering the education system), and per capita income indicators, whi ...
.
Etymology
Rajasthan literally means "The Land of Kings" and is a portmanteau ofSanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
"Rājā" (King) and Sanskrit "Sthāna"(Land) or Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
"St(h)ān" with the same meaning.'''' The oldest reference to ''Rajasthan'' is found in a stone inscription dated back to 625 CE. The first printed mention of the name ''Rajasthan'' appears in the 1829 publication ''Annals and Antiquities of Rajasthan or the Central and Western Rajpoot States of India'', while the earliest known record of ''Rajputana'' as a name for the region is in George Thomas's 1800 memoir ''Military Memories''. John Keay
John Stanley Melville Keay FRGS is a British historian, journalist, radio presenter and lecturer specialising in popular histories of India, the Far East and China, often with a particular focus on their colonisation and exploration by Europe ...
, in his book ''India: A History'', stated that ''Rajputana'' was coined by the British in 1829, John Briggs, translating Ferishta
Firishta or Ferešte ( fa, ), full name Muhammad Qasim Hindu Shah Astarabadi ( fa, مُحَمَّد قاسِم هِندو شاہ), was a Persian historian, who later settled in India and served the Deccan Sultans as their court historian. He wa ...
's history of early Islamic India, used the phrase " Rajpoot (Rajput) princes" rather than "Indian princes".
History
Ancient
Parts of what is now Rajasthan were partly part of theVedic Civilisation
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betwe ...
and the Indus Valley civilization
The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC), also known as the Indus Civilisation was a Bronze Age civilisation in the northwestern regions of South Asia, lasting from 3300 BCE to 1300 BCE, and in its mature form 2600 BCE to 1900&n ...
. Kalibangan
Kalibangān is a town located at on the left or southern banks of the Ghaggar (Ghaggar-Hakra River) in Tehsil Pilibangān, between Suratgarh and Hanumangarh in Hanumangarh District, Rajasthan, India 205 km. from Bikaner. It is also identifi ...
, in Hanumangarh district
Hanumangarh district is a district in the state of Rajasthan in India. The city of Hanumangarh is the district headquarters and its largest city.
District profile
The district is located in the extreme north of Rajasthan. It has an area of 12 ...
, was a major provincial capital of the Indus Valley Civilization. Another archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
excavation at the Balathal
Balathal is an archaeological site located in Vallabhnagar tehsil of Udaipur district of Rajasthan state in western India. It is one of the ninety Ahar-Banas culture sites located in the Basins of the Banas river and its tributaries.
Excavatio ...
site in Udaipur district shows a settlement contemporary with the Harrapan civilisation dating back to 3000–1500 BCE.
Stone Age tools dating from 5,000 to 200,000 years were found in Bundi
Bundi is a city in the Hadoti region of Rajasthan state in northwest India and capital of the former princely state of Rajputana agency. District of Bundi is named after the former princely state.
Demographics
According to the 2011 Indian cens ...
and Bhilwara
Bhilwara () is a city, administrative headquarters in Bhilwara district of the Mewar region of Rajasthan, India. It has been termed as 'Textile city'.
History
Stone Age tools dating from 5,012 to 200,000 years were found in Bundi and Bhilw ...
districts of the state.
The Matsya kingdom
Matsya ( sa, मत्स्य) was a Vedic kingdom and later became a part of sixteen Mahajanapadas, which also appears in Hindu Epic literature. The capital of Matsya was at Viratanagari (present-day Bairat, in Rajasthan) which is said to h ...
of the Vedic civilisation
The Vedic period, or the Vedic age (), is the period in the late Bronze Age and early Iron Age of the history of India when the Vedic literature, including the Vedas (ca. 1300–900 BCE), was composed in the northern Indian subcontinent, betwe ...
of India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
is said to roughly corresponded to the former state of Jaipur
Jaipur (; Hindi Language, Hindi: ''Jayapura''), formerly Jeypore, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Rajasthan. , the city had a pop ...
in Rajasthan and included the whole of Alwar with portions of Bharatpur. The capital of Matsya was at Viratanagar (modern Bairat), which is said to have been named after its founder King Virata
Virata ( sa, विराट, IAST ''virāṭa''), was the king of the Matsya Kingdom, in whose court the Pandavas spent a year in concealment during their exile. Virata was married to Queen Sudeshna and was the father of Prince Uttara and Pr ...
.
Bhargava identifies the two districts of Jhunjhunu
Jhunjhunu is a city and capital of Jhunjhunu district in the state of Rajasthan. This city is in the northern state of Rajasthan, India and the administrative headquarters of Jhunjhunu District.
History
Jhunjhunu is a very old and historical ...
and Sikar
Sikar is a city and municipal council in the Sikar district of the state of Rajasthan in India. It is the administrative headquarters of the Sikar district. It is part of the Shekhawati region, which consists of Sikar, Churu and Jhunjhunu.Sik ...
and parts of Jaipur
Jaipur (; Hindi Language, Hindi: ''Jayapura''), formerly Jeypore, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Rajasthan. , the city had a pop ...
district along with Haryana districts of Mahendragarh
Mahendragarh is a city and a municipal committee in Mahendragarh district in the Indian state of Haryana. It is from Gurgaon and comes under National Capital Region (India).
Etymology
Earlier named ''kanaud'', in early 1860s it was renam ...
and Rewari
Rewari is a city and a Municipal Council in Rewari district in the Indian state of Haryana. King of Rewari is Rao Onkar Singh.It is located in south-west Haryana around 82 km from Delhi
as part of Vedic
upright=1.2, The Vedas are ancient Sanskrit texts of Hinduism. Above: A page from the '' Atharvaveda''.
The Vedas (, , ) are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed in Vedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the ...
state of Brahmavarta The Hindu religious text ''Manusmriti'' describes Brahmavarta as the region between the rivers Saraswati and Drishadwati in India. The text defines the area as the place where the "good" people are born with "goodness" being dependent on location ra ...
. Bhargava also locates the present day Sahibi River
The Sahibi river, also called the Sabi River, is an ephemeral, rain-fed river flowing through Rajasthan, Haryana (where its canalised portion is called the "Outfall Drain No 8") and Delhi states in India. It drains into Yamuna in Delhi, where it ...
as the Vedic Drishadwati
The Drishadvati river (IAST:, "She with many stones") is a river hypothesized by Indologists to identify the route of the Vedic river Saraswati and the state of '' Brahmavarta''. According to ''Manusmriti'', the ''Brahmavarta'', where the Rishis ...
River, which along with Saraswati River
The Sarasvati River () is a deified Rigvedic rivers, river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Historical Vedic religion, Vedic religion, appearing in all but the fourth bo ...
formed the borders of the Vedic state of Brahmavarta. Manu and Bhrigu
Bhrigu ( sa, भृगु, ) was a rishi in Hinduism. He was one of the seven great sages, the Saptarshis, one of the many Prajapatis (the facilitators of Creation) created by Brahma. The first compiler of predictive astrology, and also th ...
narrated the Manusmriti
The ''Manusmṛiti'' ( sa, मनुस्मृति), also known as the ''Mānava-Dharmaśāstra'' or Laws of Manu, is one of the many legal texts and constitution among the many ' of Hinduism. In ancient India, the sages often wrote their ...
to a congregation of seers in this area. The ashrams of Vedic seers Bhrigu
Bhrigu ( sa, भृगु, ) was a rishi in Hinduism. He was one of the seven great sages, the Saptarshis, one of the many Prajapatis (the facilitators of Creation) created by Brahma. The first compiler of predictive astrology, and also th ...
and his son Chayvan Rishi, for whom Chyawanprash
Chyavanprash (), originally Chayavanaprasham, is a cooked mixture of sugar, honey, ghee, Indian gooseberry ( amla) jam, sesame oil, berries and various herbs and spices. It is prepared as per the instructions suggested in Ayurvedic texts. Chyavan ...
was formulated, were near Dhosi Hill
Dhosi Hill is an important Vedic period site, an extinct volcano, standing alone at the north-west end of the Aravalli mountain range. Its height varies from about 345 to 470 meters from the surrounding lands and 740 meters from the sea level. ...
, part of which lies in Dhosi village of Jhunjhunu
Jhunjhunu is a city and capital of Jhunjhunu district in the state of Rajasthan. This city is in the northern state of Rajasthan, India and the administrative headquarters of Jhunjhunu District.
History
Jhunjhunu is a very old and historical ...
district of Rajasthan and part of which lies in Mahendragarh
Mahendragarh is a city and a municipal committee in Mahendragarh district in the Indian state of Haryana. It is from Gurgaon and comes under National Capital Region (India).
Etymology
Earlier named ''kanaud'', in early 1860s it was renam ...
district of Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ar ...
.
The Western Kshatrapas
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi:, ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central part of India ( Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Prades ...
(405–35 BCE), the Saka
The Saka ( Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who hist ...
rulers of the western part of India, were successors to the Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centur ...
and were contemporaneous with the Kushans
The Kushan Empire ( grc, Βασιλεία Κοσσανῶν; xbc, Κυϸανο, ; sa, कुषाण वंश; Brahmi: , '; Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit, BHS: ; xpr, 𐭊𐭅𐭔𐭍 𐭇𐭔𐭕𐭓, ; zh, wikt:貴霜, 貴霜 ) was a Sync ...
, who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
. The Indo-Scythians invaded the area of Ujjain
Ujjain (, Hindustani language, Hindustani pronunciation: Help:IPA/Hindi and Urdu, �d͡ːʒɛːn is a city in Ujjain district of the States and territories of India, Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Prad ...
and established the Saka era
The Shaka era (IAST: Śaka, Śāka) is a historical Hindu calendar era (year numbering), the epoch (its year zero) of which corresponds to Julian year 78.
The era has been widely used in different regions of India as well as in SE Asia.
Hist ...
(with their calendar
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physi ...
), marking the beginning of the long-lived Saka Western Satraps
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi:, ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central part of India ( Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh ...
state.
Classical
Gurjara-Pratihara
 The Pratiharas ruled for many dynasties in this part of the country; the region was known as ''
The Pratiharas ruled for many dynasties in this part of the country; the region was known as ''Gurjaratra
Gurjaradesa ("Gurjara country") or Gurjaratra is a historical region in India comprising the eastern Rajasthan and northern Gujarat during the period of 6th -12th century CE. The predominant power of the region, the Gurjara-Pratiharas eventual ...
''. Up to the 10th century CE, almost all of North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central ...
acknowledged the supremacy of the Imperial Pratiharas, with their seat of power at Kannauj
Kannauj ( Hindustani pronunciation: ənːɔːd͡ʒ is a city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. The city's name is a corrupted form of the class ...
.
The Gurjara Pratihar Empire acted as a barrier for Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
invaders from the 8th to the 11th century. The chief accomplishment of the Gurjara-Pratihara Empire lies in its successful resistance to foreign invasions from the west, starting in the days of Junaid. Historian R. C. Majumdar says that this was openly acknowledged by the Arab writers. He further notes that historians of India have wondered at the slow progress of Muslim invaders in India, as compared with their rapid advance in other parts of the world. Now there seems little doubt that it was the power of the Pratihara army that effectively barred the progress of the Arabs beyond the confines of Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
, their only conquest for nearly 300 years.
Medieval and Early Modern
Prithviraj Chauhan
Prithviraja III (IAST: Pṛthvī-rāja; reign. – 1192 CE), popularly known as Prithviraj Chauhan or Rai Pithora, was a king from the Chauhan (Chahamana) dynasty who ruled the territory of Sapadalaksha, with his capital at Ajmer in present- ...
defeated the invading Muhammad Ghori
Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad ibn Sam ( fa, معز الدین محمد بن سام), also Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad Ghori, also Ghūri ( fa, معز الدین محمد غوری) (1144 – March 15, 1206), commonly known as Muhammad of Ghor, also Gh ...
in the First Battle of Tarain
The First Battle of Tarain, also spelt as the First Battle of Taroari, was fought in 1191 between the invading Ghurid army led by Muhammad of Ghor and the Rajput confederacy led by Prithviraj Chauhan, near Tarain (modern Taraori in Haryana, In ...
in 1191. In 1192 CE, Muhammad Ghori decisively defeated Prithviraj at the Second Battle of Tarain
The Second Battle of Tarain was fought in 1192 between the Ghurid forces of Muhammad Ghuri and the Rajput Confederacy of Prithviraj Chauhan. It took place near Tarain (modern Taraori), which is , north of Delhi. The battle ended in a decisi ...
. After the defeat of Chauhan in 1192 CE, a part of Rajasthan came under Muslim rulers. The principal centers of their powers were Nagaur
Nagaur is a city and municipal council in Nagaur district of the state of Rajasthan in India. It is the administrative headquarters of Nagaur District. The Nagaur city lies about midway between Jodhpur and Bikaner.
Nagaur is famous for spices ...
and Ajmer. Ranthambhore was also under their suzerainty. At the beginning of the 13th century, the most prominent and powerful state of Rajasthan was Mewar
Mewar or Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasthan, Neemuch and Man ...
. The Rajputs resisted the Muslim incursions into India, although a number of Rajput kingdoms eventually became subservient to the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
.
The Rajputs put up resistance to the Islamic invasions with their warfare and chivalry for centuries. The Rana's of Mewar led other kingdoms in its resistance to outside rule. Rana Hammir Singh
Maharana Hammir Singh (1314–1364), or Hammir (not to be confused with Hammir Singh of Ranthambore), was a 14th-century Hindu Rajput ruler of Mewar in present-day Rajasthan, India. Hammir Singh, was a scion of the cadet branch Rana of the Guhi ...
, defeated the Tughlaq dynasty
The Tughlaq dynasty ( fa, ), also referred to as Tughluq or Tughluk dynasty, was a Muslim dynasty of Indo- Turkic origin which ruled over the Delhi sultanate in medieval India. Its reign started in 1320 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the ...
and recovered a large portion of Rajasthan. The indomitable Rana Kumbha
Kumbhakarna Singh (r. 1433–1468 CE), popularly known as Maharana Kumbha, was the Maharana of Mewar kingdom in India. He belonged to the Sisodia clan of Rajputs. Rana Kumbha is known for his illustrious military career against various sultana ...
defeated the Sultans of Malwa
Malwa is a historical region of west-central India occupying a plateau of volcanic origin. Geologically, the Malwa Plateau generally refers to the volcanic upland north of the Vindhya Range. Politically and administratively, it is also syno ...
, Nagaur and Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
and made Mewar the most powerful Rajput Kingdom in India. The ambitious Rana Sanga
Sangram Singh I (IAST: Rāṇā Saṅgrāma Siṃha; c. 1482 – 1528 CE), popularly known as Rana Sanga or Maharana Sanga, was an Indian ruler from the Sisodia dynasty. He ruled Mewar, the traditional territory of Guhilas (Sisodias) in presen ...
united the various Rajput clans and fought against the foreign powers in India. Rana Sanga defeated the Afghan Lodi Empire
The Lodi dynasty ( ps, لودي سلسله; fa, سلسله لودی) was an Afghan dynasty that ruled the Delhi Sultanate from 1451 to 1526. It was the fifth and final dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate, and was founded by Bahlul Khan Lodi when h ...
of Delhi and crushed the Turkic Sultanates of Malwa and Gujarat. Rana Sanga then tried to create an Indian empire but was defeated by the first Mughal Emperor Babur
Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= Bābur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born Mīrzā Zahīr ud-Dīn Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his ...
at Khanua. The defeat was due to betrayal by the Tomar King Silhadi
Raja Shiladitya, also called Silhadi Tomar (died 1532), was a Ror chieftain of northeast Malwa in the early decades of 16th century India. He recruited Sanga of Mewar as an ally and Sanga helped him and Medini Rai in various battles and in conq ...
of Raisen. After Rana Sanga
Sangram Singh I (IAST: Rāṇā Saṅgrāma Siṃha; c. 1482 – 1528 CE), popularly known as Rana Sanga or Maharana Sanga, was an Indian ruler from the Sisodia dynasty. He ruled Mewar, the traditional territory of Guhilas (Sisodias) in presen ...
's death, Marwar
Marwar (also called Jodhpur region) is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. The word 'maru' is Sanskrit for desert. In Rajasthani languages, "wad" means a particular area. English tran ...
rose as a power center in Rajasthan under Rao Maldev Rathore. He conquered Jaisalmer, parts of Gujarat, Jalore, Nagaur, Ajmer, Sanchore, Bhinmal, Radhanpur, Bayana, Tonk, Toda and Nabhara. He expanded the territories of Marwar up to Sindh-Cholistan in west and his northern boundary was just fifty km from Delhi. After defeating Humayun, Sher Shah came towards Rajputana. He defeated Chiefs of Rathore army by trickery in Battle of Sammel
The Battle of Sammel, also known as the Battle of Giri-Sumel, was fought in 1544 near the villages, Giri and Sumel of the Jaitaran sub-division in the Pali district of Rajasthan between the Afghan Sur Dynasty under Sher Shah Suri and the Rathor ...
and captured some territory of Marwar but it was recovered by Rathores in 1545. After that Rajputana remained mostly free from Islamic occupation till the Akbar's conquest of Rajputana.
Hem Chandra Vikramaditya
Hemu (; also known as Hemu Vikramaditya and Hemchandra Vikramaditya; died 5 November 1556) was an Indian emperor who previously served as a general and Wazir of Adil Shah Suri of Sur Empire during a period in Indian history when Mughals and ...
, the Hindu Emperor, was born in the village of Machheri in Alwar District
Alwar is a district in the state of Rajasthan in northern India, whose district headquarters is Alwar city. The district covers 8,380 km2. It is bound on the north by Rewari district of Haryana, on the east by Bharatpur district of Rajas ...
in 1501. He won 22 battles against Afghans, from Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
to Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
including the states of Ajmer
Ajmer is one of the major and oldest cities in the Indian state of Rajasthan and the centre of the eponymous Ajmer District. It is located at the centre of Rajasthan. It is also known as heart of Rajasthan. The city was established as "''Aj ...
and Alwar
Alwar (Pronunciation: Help:IPA/Hindi and Urdu, �lʋəɾ is a city located in India's National Capital Region (India), National Capital Region and the administrative headquarters of Alwar district, Alwar District in the state of Rajasthan. ...
in Rajasthan, and defeated Akbar's forces twice, first at Agra
Agra (, ) is a city on the banks of the Yamuna river in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh, about south-east of the national capital New Delhi and 330 km west of the state capital Lucknow. With a population of roughly 1.6 million, Agra is ...
and then at Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
in 1556 at Battle of Delhi before acceding to the throne of Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
and establishing the "Hindu Raj" in North India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central ...
, albeit for a short duration, from Purana Quila
Purana Qila () is one of the oldest forts in Delhi, India. Built by the second Mughal Emperor Humayun and Surid Sultan Sher Shah Suri, it is thought by many to be located on the site of the ancient city of Indraprastha. The fort formed the in ...
in Delhi. Hem Chandra was killed in the battlefield at Second Battle of Panipat
The Second Battle of Panipat was fought on 5 November 1556, between Akbar and the king of Delhi, Hemu. Hemu had conquered Delhi and Agra a few weeks earlier by defeating Mughal forces under Tardi Beg Khan in the battle of Delhi and crowned him ...
fighting against Mughals on 5 November 1556.
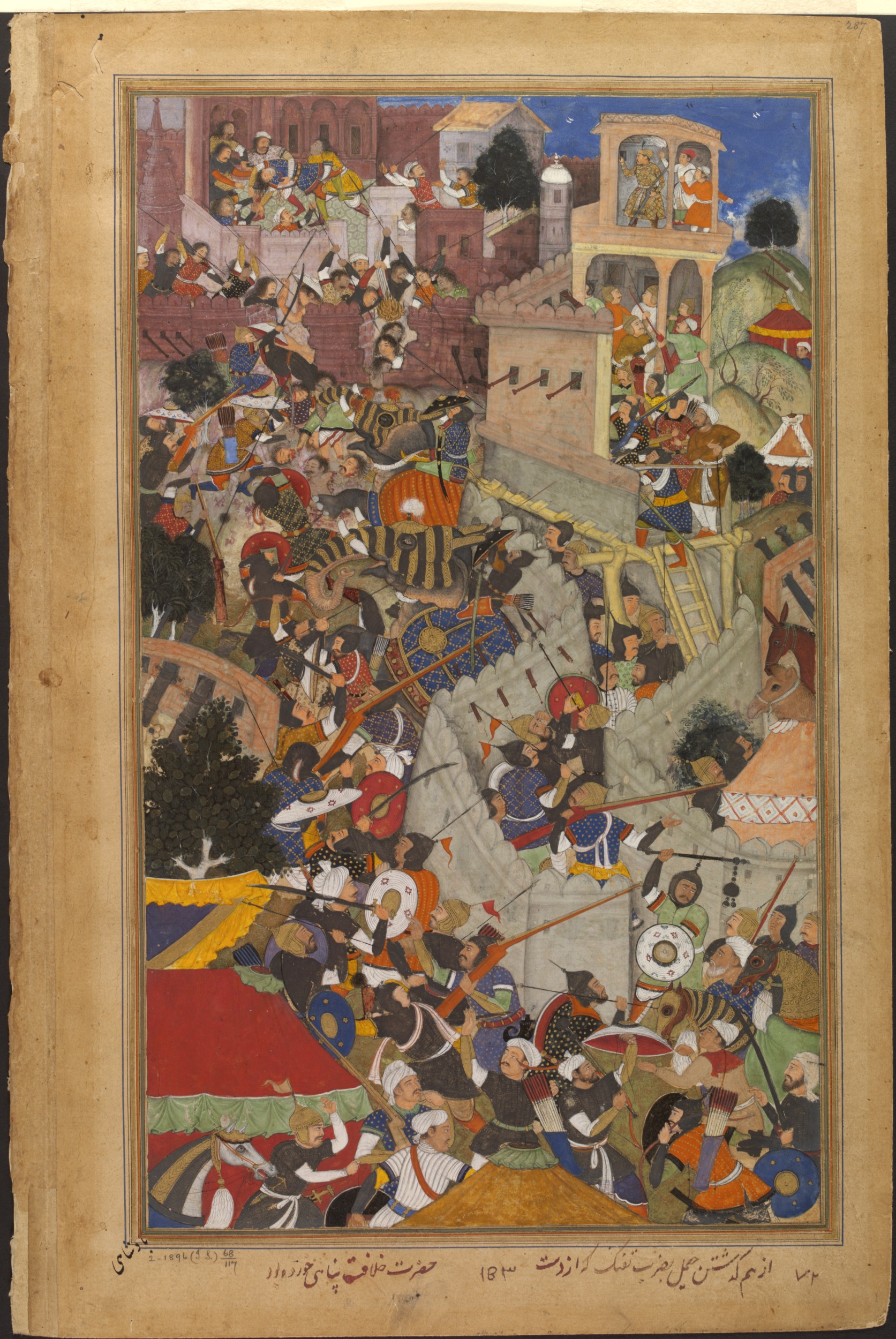
 During
During Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Hum ...
's reign most of the Rajput kings accepted Mughal suzerainty, but the rulers of Mewar (Rana Udai Singh II
Udai Singh II (4 August 1522 – 28 February 1572) was the Maharana of Mewar and the founder of the city of Udaipur in the present-day Rajasthan state of India. He was the 12th ruler of the Kingdom of Mewar. He was the fourth son of Rana Sanga ...
) and Marwar (Rao Chandrasen Rathore
Rao Chandrasen Rathore () was a Rathore ruler of Marwar (in the present day Rajasthan state of India). He was a younger son of Rao Maldev Rathore. Chandrasen followed his father's policy and stayed hostile to the ruling foreign powers in I ...
) refused to have any form of alliance with the Mughals. To teach the Rajputs a lesson Akbar attacked Udai Singh and killed Rajput commander Jaimal of Chitor and the citizens of Mewar in large numbers. Akbar killed 20,000 – 25,000 unarmed citizens in Chittor on the grounds that they had actively helped in the resistance.
Maharana Pratap
Pratap Singh I, popularly known as Maharana Pratap (c. 9 May 1540 – 19 January 1597), was a king of Mewar from the Sisodia dynasty. Pratap became a folk hero for his military resistance against the expansionism of the Mughal Empire under A ...
took an oath to avenge the citizens of Chittor, he fought the Mughal empire till his death and liberated most of Mewar apart from Chittor itself. Maharana Pratap
Pratap Singh I, popularly known as Maharana Pratap (c. 9 May 1540 – 19 January 1597), was a king of Mewar from the Sisodia dynasty. Pratap became a folk hero for his military resistance against the expansionism of the Mughal Empire under A ...
soon became the most celebrated warrior of Rajasthan and became famous all over India for his sporadic warfare and noble actions. According to Satish Chandra Satish Chandra is a given name of Hindu origin, and may refer to,
* Satish Chandra (politician), Indian National Congress leader
* Satish Chandra (historian), Indian academic
* Satish Chandra Agarwal, Indian politician
* Satish Chandra Basumatary, ...
, "Rana Pratap's defiance of the mighty Mughal empire, almost alone and unaided by the other Rajput states, constitutes a glorious saga of Rajput valor and the spirit of self-sacrifice for cherished principles. Rana Pratap's methods of sporadic warfare were later elaborated further by Malik Ambar, the Deccani general, and by Shivaji".
Rana Amar Singh I
Maharana Amar Singh I, the Maharana of Mewar (March 16, 1559 – January 26, 1620), was the eldest son and successor of Maharana Pratap of Mewar. He was the 16th Rana of Mewar dynasty of Sisodia Rajputs and ruler of Mewar from January 19, 1597 ...
continued his ancestor's war against the Mughals under Jehangir
Nur-ud-Din Muhammad Salim (30 August 1569 – 28 October 1627), known by his imperial name Jahangir (; ), was the fourth Mughal Emperor, who ruled from 1605 until he died in 1627. He was named after the Indian Sufi saint, Salim Chishti.
Ear ...
, he repelled the Mughal armies at Dewar. Later an expedition was again sent under the leadership of Prince Khurram, which caused much damage to life and property of Mewar. Many temples were destroyed, several villages were put on fire and women and children were captured and tortured to make Amar Singh accept surrender.
During Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling ...
's rule Rana Raj Singh I
Raj Singh I (24 September 1629 – 22 October 1680), was the Maharana of Mewar Kingdom (r. 1652–1680) and eldest son of Jagat Singh I by his wife, a princess of Marwar. He fought against Mughal Empire and annexed many Mughal territories He ...
and Veer Durgadas Rathore
Durgadas Rathore (13 August 1638 – 22 November 1718) was the Rathore Rajput General of Kingdom of Marwar. He is credited with having preserved the rule of the Rathore dynasty over Marwar, India, following the death of Maharaja Jaswant S ...
were chief among those who defied the intolerant emperor of Delhi. They took advantage of the Aravalli hills and caused heavy damage to the Mughal armies that were trying to occupy Rajasthan.
After Aurangzeb's death Bahadur Shah I
Bahadur Shah I (14 October 1643 – 27 February 1712), also known as Muhammad Mu'azzam and Shah Alam I. was the eighth Mughal Emperor who ruled from 1707 until his death in 1712. In his youth, he conspired to overthrow his father Aurangzeb, t ...
tried to subjugate Rajasthan like his ancestors but his plan backfired when the three Rajput
Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term Ra ...
Raja
''Raja'' (; from , IAST ') is a royal title used for South Asian monarchs. The title is equivalent to king or princely ruler in South Asia and Southeast Asia.
The title has a long history in South Asia and Southeast Asia, being attested f ...
s of Amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In Ma ...
, Udaipur
Udaipur () (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura''), historically named as Udayapura, is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capit ...
, and Jodhpur
Jodhpur (; ) is the second-largest city in the Indian state of Rajasthan and officially the second metropolitan city of the state. It was formerly the seat of the princely state of Jodhpur State. Jodhpur was historically the capital of the Ki ...
made a joint resistance to the Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
. The Rajputs first expelled the commandants of Jodhpur
Jodhpur (; ) is the second-largest city in the Indian state of Rajasthan and officially the second metropolitan city of the state. It was formerly the seat of the princely state of Jodhpur State. Jodhpur was historically the capital of the Ki ...
and Bayana
Bayana is a historical town and the headquarters of Bayana tehsil in Bharatpur district of Rajasthan in India. Hindaun City is nearest city of Bayana - 33 km. It was the site of famous Important Battle of Bayana in 1527 between the Rajput ...
and recovered Amer
Amer may refer to:
Places
* Amer (river), a river in the Dutch province of North Brabant
* Amer, Girona, a municipality in the province of Girona in Catalonia, Spain
* Amber, India (also known as Amer, India), former city of Rajasthan state
** Am ...
by a night attack. They next killed Sayyid Hussain Khan Barha, the commandant of Mewat
Mewat is a historical region of Haryana and Rajasthan states in northwestern India. The loose boundaries of Mewat generally include Hathin tehsil and Nuh district of Haryana, Alwar (Tijara, Kishangarh, Bas, Ramgarh, Laxmangarh, Kathumar tehsil ...
and many other Mughal officers. Bahadur Shah I
Bahadur Shah I (14 October 1643 – 27 February 1712), also known as Muhammad Mu'azzam and Shah Alam I. was the eighth Mughal Emperor who ruled from 1707 until his death in 1712. In his youth, he conspired to overthrow his father Aurangzeb, t ...
, then in the Deccan
The large Deccan Plateau in South India, southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bou ...
was forced to patch up a truce with the Rajput Rajas. The Jats
The Jat people ((), ()) are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in late medieval times, and subse ...
, under Suraj Mal
Suraj Mal (13 February 1707 – 25 December 1763) was a Jat ruler of Bharatpur in present-day state of Rajasthan. Under him, the Jat rule covered the present-day districts of Agra, Aligarh, Bharatpur, Dholpur, Etawa, Hathras, Mainpuri, M ...
, overran the Mughal garrison at Agra and plundered the city taking with them the two great silver doors of the entrance of the famous Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal (; ) is an Islamic ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in the Indian city of Agra. It was commissioned in 1631 by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan () to house the tomb of his favourite wife, Mu ...
which were then melted down by Suraj Mal in 1763.
Over the years, the Mughals began to have internal disputes which greatly distracted them at times. The Mughal Empire continued to weaken, and with the decline of the Mughal Empire in the late 18th century, Rajputana
Rājputana, meaning "Land of the Rajputs", was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the present-day Indian state of Rajasthan, as well as parts of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and some adjoining areas of Sindh in modern-day ...
came under the influence of the Marathas
The Marathi people (Marathi: मराठी लोक) or Marathis are an Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group who are indigenous to Maharashtra in western India. They natively speak Marathi, an Indo-Aryan language. Maharashtra was formed as a M ...
. The Maratha Empire, which had replaced the Mughal Empire as the overlord of the subcontinent, was finally replaced by the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
in 1818.
In the 19th century, the Rajput kingdoms were exhausted, they had been drained financially and in manpower after continuous wars and due to heavy tributes exacted by the Maratha Empire. To save their kingdoms from instability, rebellions and banditry the Rajput kings concluded treaties with the British in the early 19th century, accepting British suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...
and control over their external affairs in return for internal autonomy.
Rana Kumbha
Kumbhakarna Singh (r. 1433–1468 CE), popularly known as Maharana Kumbha, was the Maharana of Mewar kingdom in India. He belonged to the Sisodia clan of Rajputs. Rana Kumbha is known for his illustrious military career against various sultana ...
was the vanguard of the fifteenth century Rajput resurgence.
File:Maharaja Hemu Bhargava - Victor of Twenty Two Pitched Battles, 1910s.jpg, The emperor Hemu
Hemu (; also known as Hemu Vikramaditya and Hemchandra Vikramaditya; died 5 November 1556) was an Indian emperor who previously served as a general and Wazir of Adil Shah Suri of Sur Empire during a period in Indian history when Mughals and A ...
, who rose from obscurity and briefly established himself as ruler in northern India, from Punjab to Bengal, in defiance of the warring Sur and Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
s.
File:Rana-udai-singh-ii.jpg, Maharana Udai Singh II
Udai Singh II (4 August 1522 – 28 February 1572) was the Maharana of Mewar and the founder of the city of Udaipur in the present-day Rajasthan state of India. He was the 12th ruler of the Kingdom of Mewar. He was the fourth son of Rana Sanga ...
founded Udaipur
Udaipur () (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura''), historically named as Udayapura, is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capit ...
, which became the new capital of the Mewar kingdom
Kingdom of Mewar, sometimes known as Udaipur State, was ruled by the Sisodia dynasty. It was an independent kingdom in Rajputana region of India. It was established around the 7th century as minor rulers of the Nagada-Ahar region of Udaipur a ...
after Chittor Fort
The Chittorgarh (literally Chittor Fort), also known as Chittod Fort, is one of the largest forts in India. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The fort was the capital of Mewar and is located in the present-day city of Chittorgarh. It sprawls o ...
was conquered by the Mughal emperor Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Hum ...
.
File:RajaRaviVarma MaharanaPratap.jpg, Maharana Pratap Singh
Pratap Singh I, popularly known as Maharana Pratap (c. 9 May 1540 – 19 January 1597), was a king of Mewar from the Sisodia dynasty. Pratap became a folk hero for his military resistance against the expansionism of the Mughal Empire under A ...
, sixteenth-century Rajput ruler of Mewar
Mewar or Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasthan, Neemuch and Man ...
, known for his defence of his realm against Mughal invasion.
File:Maharaja Suraj Mal.jpg, Suraj Mal
Suraj Mal (13 February 1707 – 25 December 1763) was a Jat ruler of Bharatpur in present-day state of Rajasthan. Under him, the Jat rule covered the present-day districts of Agra, Aligarh, Bharatpur, Dholpur, Etawa, Hathras, Mainpuri, M ...
was ruler of Bharatpur, some contemporary historians described him as "the Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
of the Jat people
The Jat people ((), ()) are a traditionally agricultural community in Northern India and Pakistan. Originally pastoralists in the lower Indus river-valley of Sindh, Jats migrated north into the Punjab region in late medieval times, and subse ...
" and by a modern writer as the "Jat Odysseus
Odysseus ( ; grc-gre, Ὀδυσσεύς, Ὀδυσεύς, OdysseúsOdyseús, ), also known by the Latin variant Ulysses ( , ; lat, UlyssesUlixes), is a legendary Greek king of Ithaca and the hero of Homer's epic poem the ''Odyssey''. Odysse ...
", because of his political sagacity, steady intellect and clear vision.
Modern
Modern Rajasthan includes most ofRajputana
Rājputana, meaning "Land of the Rajputs", was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the present-day Indian state of Rajasthan, as well as parts of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and some adjoining areas of Sindh in modern-day ...
, which comprises the erstwhile nineteen princely state
A princely state (also called native state or Indian state) was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Raj, British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, ...
s, three chiefships, and the British district of Ajmer-Merwara
Ajmer-Merwara, also known as Ajmir Province and as Ajmer-Merwara-Kekri, was a former province of British India in the historical Ajmer region. The territory was ceded to the British by Daulat Rao Sindhia by a treaty on 25 June 1818.
It was und ...
. Jaisalmer
Jaisalmer , nicknamed "The Golden city", is a city in the Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur. The town stands on a ridge of yellowish sandstone and is crowned by the ancient Jaisalmer Fort. This fort contains a ...
, Marwar
Marwar (also called Jodhpur region) is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. The word 'maru' is Sanskrit for desert. In Rajasthani languages, "wad" means a particular area. English tran ...
(Jodhpur), Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. Bikaner city is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Formerly the capital of ...
, Mewar
Mewar or Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasthan, Neemuch and Man ...
(Chittorgarh), Alwar
Alwar (Pronunciation: Help:IPA/Hindi and Urdu, �lʋəɾ is a city located in India's National Capital Region (India), National Capital Region and the administrative headquarters of Alwar district, Alwar District in the state of Rajasthan. ...
and Dhundhar
Dhundhar, also known as ''Jaipur region'', is a historical region of Rajasthan state in western India. It includes the districts of Jaipur, parts of Sikar District lying to the east of the Aravalli Range, Dausa, Sawai Madhopur, and Tonk and t ...
(Jaipur) were some of the main Rajput princely states. Bharatpur and Dholpur
Dholpur is a city in the Dholpur district in Rajasthan state of India. It is situated on the left bank of the famous Chambal river. The city is the administrative headquarters of Dholpur District and was formerly seat of the Dholpur prin ...
were Jat princely states whereas Tonk was a princely state under Pathan
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically re ...
s. The three chiefships were Lawa, Neemrana and Kushalgarh.
Geography
The geographic features of Rajasthan are theThar Desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent, Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's Li ...
and the Aravalli Range
The Aravalli Range (also spelled ''Aravali'') is a mountain range in Northern-Western India, running approximately in a south-west direction, starting near Delhi, passing through southern Haryana, Rajasthan, and ending in Ahmedabad Gujarat. ...
, which runs through the state from southwest to northeast, almost from one end to the other, for more than . Mount Abu
Mount Abu () is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India.The mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. The highest peak on the mountain is Guru Shikhar at above s ...
lies at the southwestern end of the range, separated from the main ranges by the West Banas River
The West Banas is a river in western India. It originates from the southern Aravalli Range, in Sirohi District of the state of Rajasthan. It flows south, draining the valley between Mount Abu on the west and the easterly ridge of the Aravallis on ...
, although a series of broken ridges continues into Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ar ...
in the direction of Delhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
where it can be seen as outcrops in the form of the Raisina Hill
Raisina Hill ( IAST: ''Rāyasīnā Pahāṛī''), often used as a metonym for the seat of the Government of India, is an area of New Delhi, housing India's most important government buildings, including Rashtrapati Bhavan, the official residenc ...
and the ridges farther north. About three-fifths of Rajasthan lies northwest of the Aravallis, leaving two-fifths on the east and south direction.
 The Aravalli Range runs across the state from the southwest peak
The Aravalli Range runs across the state from the southwest peak Guru Shikhar
Guru Shikhar, a peak in the Arbuda Mountains of Sirohi district in Rajasthan, is the highest point of the Aravalli Range and Rajasthan. It rises to an elevation of . It is 75 km from Sirohi city, the district headquarter and 15 km from M ...
(Mount Abu), which is in height, to Khetri
Khetri Nagar is the town in Jhunjhunu district of Rajasthan in India. It is a part of the Shekhawati region. Khetri consists of two towns, "Khetri Town" founded by Raja Khet Singhji Nirwan and "Khetri Nagar" which is about 10 km away from ...
in the northeast. This range divides the state into 60% in the northwest of the range and 40% in the southeast. The northwest tract is sandy and unproductive with little water but improves gradually from desert land in the far west and northwest to comparatively fertile and habitable land towards the east. The area includes the Thar Desert. The south-eastern area, higher in elevation (100 to 350 m above sea level) and more fertile, has a very diversified topography. In the south lies the hilly tract of Mewar. In the southeast, a large area within the districts of Kota and Bundi
Bundi is a city in the Hadoti region of Rajasthan state in northwest India and capital of the former princely state of Rajputana agency. District of Bundi is named after the former princely state.
Demographics
According to the 2011 Indian cens ...
forms a tableland. To the northeast of these districts is a rugged region (badlands) following the line of the Chambal River
The Chambal River is a tributary of the Yamuna River in Central and Northern India, and thus forms part of the greater Gangetic drainage system. The river flows north-northeast through Madhya Pradesh, running for a time through Rajasthan then f ...
. Farther north the country levels out; the flat plains of the northeastern Bharatpur district
Bharatpur District is a district in Rajasthan States and territories of India, state in western India. The town of Bharatpur, India, Bharatpur is the District Headquarters, Division Headquarters and Headquarters of Bharatpur, India, Bharatpur ...
are part of an alluvial
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluv ...
basin. Merta City
Merta City is a city and a municipality located in Nagaur district in the Indian state of Rajasthan. Merta is also known for its link with Mira Bai, the devotee of Lord Krishna. Mira Mahal Museum houses memories related to Mira Bai's lifetime.
...
lies in the geographical center of Rajasthan.
The Aravalli Range and the lands to the east and southeast of the range are generally more fertile and better watered. This region is home to the Khathiar-Gir dry deciduous forests ecoregion, with tropical dry broadleaf forests that include teak
Teak (''Tectona grandis'') is a tropical hardwood tree species in the family Lamiaceae. It is a large, deciduous tree that occurs in mixed hardwood forests. ''Tectona grandis'' has small, fragrant white flowers arranged in dense clusters (panicl ...
, ''Acacia
''Acacia'', commonly known as the wattles or acacias, is a large genus of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa and Australasia. The genus na ...
'', and other trees. The hilly Vagad
Vagad (also known as Vagar, Hindi: वागड) is a region in southeastern Rajasthan state of western India. Its boundaries are roughly defined by those of the districts of Dungarpur and Banswara. Major cities of the region are Dungarpur and B ...
region, home to the cities of Dungarpur
Dungarpur is a city in the southernmost part of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Dungarpur District. It is the fastest developing town in the southern part of Rajasthan, alongside Aspur ''tehsil''.
History
Dungarpu ...
, Pratapgarh, and Banswara
Banswara is a city in the Banswara district in southern Rajasthan, India. The name, Banswara, came from "Bans wala" (bamboo) forests, as Bamboo grew in abundance around this place within the area.
Banswara is also known as "City of a Hundred ...
lies in southernmost Rajasthan, on the border with Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (, ; meaning 'central province') is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal, and the largest city is Indore, with Jabalpur, Ujjain, Gwalior, Sagar, and Rewa being the other major cities. Madhya Pradesh is the seco ...
. With the exception of Mount Abu, Vagad is the wettest region in Rajasthan, and the most heavily forested. North of Vagad lies the Mewar
Mewar or Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasthan, Neemuch and Man ...
region, home to the cities of Udaipur
Udaipur () (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura''), historically named as Udayapura, is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capit ...
and Chittaurgarh
Chittorgarh (also Chittor or Chittaurgarh) is a major city in Rajasthan state of western India. It lies on the Berach River, a tributary of the Banas, and is the administrative headquarters of Chittorgarh District. It was a major stronghol ...
. The Hadoti
Hadoti is a region of Rajasthan state in western India, which was once called the Bundi Kingdom. The biggest cities are Jhalawar and Kota. It includes the districts of Bundi, Baran, Jhalawar and Kota and is bounded on the west by the Mewar ...
region lies to the southeast, on the border with Madhya Pradesh. North of Hadoti and Mewar lies the Dhundhar
Dhundhar, also known as ''Jaipur region'', is a historical region of Rajasthan state in western India. It includes the districts of Jaipur, parts of Sikar District lying to the east of the Aravalli Range, Dausa, Sawai Madhopur, and Tonk and t ...
region, home to the state capital of Jaipur
Jaipur (; Hindi Language, Hindi: ''Jayapura''), formerly Jeypore, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Rajasthan. , the city had a pop ...
. Mewat
Mewat is a historical region of Haryana and Rajasthan states in northwestern India. The loose boundaries of Mewat generally include Hathin tehsil and Nuh district of Haryana, Alwar (Tijara, Kishangarh, Bas, Ramgarh, Laxmangarh, Kathumar tehsil ...
, the easternmost region of Rajasthan, borders Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ar ...
and Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh (; , 'Northern Province') is a state in northern India. With over 200 million inhabitants, it is the most populated state in India as well as the most populous country subdivision in the world. It was established in 1950 ...
. Eastern and southeastern Rajasthan is drained by the Banas and Chambal rivers, tributaries of the Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
.
The northwestern portion of Rajasthan is generally sandy and dry. Most of this region is covered by the Thar Desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent, Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's Li ...
which extends into adjoining portions of Pakistan. The Aravalli Range does not intercept the moisture-giving southwest monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
winds off the Arabian Sea
The Arabian Sea ( ar, اَلْبَحرْ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Bahr al-ˁArabī) is a region of the northern Indian Ocean bounded on the north by Pakistan, Iran and the Gulf of Oman, on the west by the Gulf of Aden, Guardafui Channel ...
, as it lies in a direction parallel to that of the coming monsoon winds, leaving the northwestern region in a rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
. The Thar Desert is thinly populated; the City of Jodhpur
Jodhpur (; ) is the second-largest city in the Indian state of Rajasthan and officially the second metropolitan city of the state. It was formerly the seat of the princely state of Jodhpur State. Jodhpur was historically the capital of the Ki ...
is the largest city in the desert and a major metropolitan area of India which is known as the gateway of the Thar desert. The desert has some major districts like Jodhpur
Jodhpur (; ) is the second-largest city in the Indian state of Rajasthan and officially the second metropolitan city of the state. It was formerly the seat of the princely state of Jodhpur State. Jodhpur was historically the capital of the Ki ...
, Jaisalmer, Barmer, Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. Bikaner city is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Formerly the capital of ...
, and Nagaur
Nagaur is a city and municipal council in Nagaur district of the state of Rajasthan in India. It is the administrative headquarters of Nagaur District. The Nagaur city lies about midway between Jodhpur and Bikaner.
Nagaur is famous for spices ...
. This area is also important from a defence point of view. Jodhpur airbase is one of the largest airbases in India, BSF and Military bases are also situated here. Currently four civil airports are located here: Jodhpur, Jaisalmer, Bikaner and Nagaur, of which Jodhpur is the major civil airport, being the 44th busiest airport in India and one of the oldest air strips of India, being built in the 1920s.
The Northwestern thorn scrub forests
The Northwestern thorn scrub forests, presently known as Aravalli west thorn scrub forests, is a xeric shrubland ecoregion of Pakistan and Northern India, stretching along the border lowlands and hills between the two countries. Once covered i ...
lie in a band around the Thar Desert, between the desert and the Aravallis. This region receives less than 400 mm of rain annually. Temperatures can sometimes exceed 45 °C in the summer months and drop below freezing point in the winter. The Godwar
Gorwar or Godwar, (in different periods also was called Chandravati Kingdom, Sirohi State) is a region of Rajasthan state in India, which lies in the southwest Rajasthan and borders with the state of Gujarat.
Geography
Gorwar stretches along t ...
, Marwar
Marwar (also called Jodhpur region) is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. The word 'maru' is Sanskrit for desert. In Rajasthani languages, "wad" means a particular area. English tran ...
, and Shekhawati
Shekhawati is a semi-arid historical region located in the northeast part of Rajasthan, India. The region was ruled by Shekhawat Rajputs.
Shekhawati is located in North Rajasthan, comprising the districts of Jhunjhunu district, Jhunjhunu,
part ...
regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
lie in the thorn scrub forest zone, along with the city of Jodhpur. The Luni River
The Luni is the largest river in the Thar Desert of northwest India. It originates in the Pushkar valley of the Aravalli Range, near Ajmer, passes through the southeastern portion of the Thar Desert, and ends in the marshy lands of Rann of Kutch ...
and its tributaries are the major river system of Godwar and Marwar regions, draining the western slopes of the Aravallis and emptying southwest into the great Rann of Kutch
The Rann of Kutch (alternately spelled as Kuchchh) is a large area of salt marshes that span the border between India and Pakistan. It is located in Gujarat (primarily the Kutch district), India, and in Sindh, Pakistan. It is divided into t ...
wetland in neighbouring Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the ninth ...
. This river is saline in the lower reaches and remains potable only up to Balotara in Barmer district
Barmer District is a district in Rajasthan state of India. It is located in the western part of Rajasthan state forming a part of the Thar Desert. Barmer is the third largest district by area in Rajasthan and fifth largest district in India. Oc ...
. The Ghaggar River
The Ghaggar-Hakra River is an intermittent river in India and Pakistan that flows only during the monsoon season. The river is known as Ghaggar in India, before the Ottu barrage, and as the Hakra in Pakistan, downstream of the barrage, ending ...
, which originates in Haryana
Haryana (; ) is an Indian state located in the northern part of the country. It was carved out of the former state of East Punjab on 1 Nov 1966 on a linguistic basis. It is ranked 21st in terms of area, with less than 1.4% () of India's land ar ...
, is an intermittent stream that disappears into the sands of the Thar Desert in the northern corner of the state and is seen as a remnant of the primitive Sarasvati river
The Sarasvati River () is a deified river first mentioned in the Rigveda and later in Vedic and post-Vedic texts. It played an important role in the Vedic religion, appearing in all but the fourth book of the Rigveda.
As a physical river, i ...
.
Mount Abu
Mount Abu () is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India.The mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. The highest peak on the mountain is Guru Shikhar at above s ...
is a popular hill station in Rajasthan.
File: A sunset on the dunes of the Great Indian Thar Desert Rajasthan India.jpg, The Thar Desert
The Thar Desert, also known as the Great Indian Desert, is an arid region in the north-western part of the Indian subcontinent, Subcontinent that covers an area of and forms a natural boundary between India and Pakistan. It is the world's Li ...
near Jaisalmer
Jaisalmer , nicknamed "The Golden city", is a city in the Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur. The town stands on a ridge of yellowish sandstone and is crowned by the ancient Jaisalmer Fort. This fort contains a ...
.
File: An aerial view of Udaipur and Aravali hills Rajasthan India 2012.jpg, Aerial view Udaipur and Aravali hills.
Flora and fauna
 The
The Desert National Park
Desert National Park is a national park situated in the Indian state of Rajasthan, near the towns of Jaisalmer and Barmer. This is one of the largest national parks, covering an area of 3162 km². The Desert National Park is an excellent ...
in Jaisalmer
Jaisalmer , nicknamed "The Golden city", is a city in the Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur. The town stands on a ridge of yellowish sandstone and is crowned by the ancient Jaisalmer Fort. This fort contains a ...
is spread over an area of , is an excellent example of the ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
of the Thar Desert and its diverse fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoo ...
. Seashells and massive fossilised
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved i ...
tree trunks in this park record the geological history of the desert. The region is a haven for migratory and resident birds of the desert. One can see many eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, just ...
s, harriers, falcon
Falcons () are birds of prey in the genus ''Falco'', which includes about 40 species. Falcons are widely distributed on all continents of the world except Antarctica, though closely related raptors did occur there in the Eocene.
Adult falcons ...
s, buzzard
Buzzard is the common name of several species of birds of prey.
''Buteo'' species
* Archer's buzzard (''Buteo archeri'')
* Augur buzzard (''Buteo augur'')
* Broad-winged hawk (''Buteo platypterus'')
* Common buzzard (''Buteo buteo'')
* Eastern ...
s, kestrel
The term kestrel (from french: crécerelle, derivative from , i.e. ratchet) is the common name given to several species of predatory birds from the falcon genus ''Falco''. Kestrels are most easily distinguished by their typical hunting behaviou ...
s and vulture
A vulture is a bird of prey that scavenges on carrion. There are 23 extant species of vulture (including Condors). Old World vultures include 16 living species native to Europe, Africa, and Asia; New World vultures are restricted to North and ...
s. Short-toed snake eagle
The short-toed snake eagle (''Circaetus gallicus''), also known as the short-toed eagle, is a medium-sized bird of prey in the family Accipitridae, which also includes many other diurnal raptors such as kites, buzzards and harriers. The genus n ...
s ''(Circaetus gallicus)'', tawny eagle
The tawny eagle (''Aquila rapax'') is a large bird of prey. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family ''Accipitridae''. Its heavily feathered legs mark it as a member of the subfamily Aquilinae, also known as booted eagles.Helbig, A. J., Kocum, ...
s ''(Aquila rapax)'', spotted eagle
''Clanga'' is a genus which contains the spotted eagles. The genus name is from Ancient Greek ''klangos'', "eagle".
Species
Notes
References
{{Taxonbar, from=Q9160388
Clanga (genus),
Bird genera
Birds of ...
s ''(Aquila clanga)'', laggar falcon
The laggar falcon (''Falco jugger''), also known as the lugger falcon or jugger (from Hindi जग्गर — jaggar, “falcon”) is a mid-sized bird of prey which occurs in the Indian subcontinent from extreme southeastern Iran, southeaste ...
s ''(Falco jugger)'' and kestrels are the commonest of these.
The Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park is a national park in Rajasthan, India, with an area of . It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River. It is named after the historic Ranthambore Fort, which lies within the park ...
located in Sawai Madhopur
Sawai Madhopur is a city and Municipal Council (Nagar Parishad) in the Sawai Madhopur District in Rajasthan state, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Sawai Madhopur District of Rajasthan. Ranthambore National Park which is 7 ...
, one of the well known tiger reserves in the country, became a part of Project Tiger
Project Tiger is a tiger conservation programme launched in April 1973 by the Government of India during Prime Minister Indira Gandhi's tenure. The project aims at ensuring a viable population of the Bengal tiger in its natural habitats, protecti ...
in 1973.
Tal Chhapar Sanctuary
Tal Chhapar Sanctuary is a sanctuary located in the Churu district of Northwestern Rajasthan, in the Shekhawati region of India. It is known for blackbucks and is also home to a variety of birds. The sanctuary is 210 km from Jaipur on the ...
is a very small sanctuary in Sujangarh, Churu District, from Jaipur
Jaipur (; Hindi Language, Hindi: ''Jayapura''), formerly Jeypore, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Rajasthan. , the city had a pop ...
in the Shekhawati
Shekhawati is a semi-arid historical region located in the northeast part of Rajasthan, India. The region was ruled by Shekhawat Rajputs.
Shekhawati is located in North Rajasthan, comprising the districts of Jhunjhunu district, Jhunjhunu,
part ...
region. This sanctuary is home to a large population of blackbuck
The blackbuck (''Antilope cervicapra''), also known as the Indian antelope, is an antelope native to India and Nepal. It inhabits grassy plains and lightly forested areas with perennial water sources.
It stands up to high at the shoulder. Mal ...
. Desert foxes and the caracal
The caracal (''Caracal caracal'') () is a medium-sized wild cat native to Africa, the Middle East, Central Asia, and arid areas of Pakistan and northwestern India. It is characterised by a robust build, long legs, a short face, long tufted e ...
, an apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the highest trophic lev ...
, also known as the ''desert lynx'', can also be spotted, along with birds such as the partridge
A partridge is a medium-sized Galliformes, galliform bird in any of several genera, with a wide Indigenous (ecology), native distribution throughout parts of Europe, Asia and Africa. Several species have been introduced to the Americas. They a ...
, harriers, eastern imperial eagle
The eastern imperial eagle (''Aquila heliaca'') is a large bird of prey that breeds in southeastern Europe and extensively through West and Central Asia. Most populations are migratory and winter in northeastern Africa, the Middle East and South ...
, pale harrier
The pale or pallid harrier (''Circus macrourus'') is a bird migration, migratory bird of prey of the harrier (bird), harrier subfamily. The scientific name is derived from the Ancient Greek. ''Circus'' is from ''kirkos'', referring to a bird of p ...
, marsh harrier
The marsh harriers are birds of prey of the harrier subfamily. They are medium-sized raptors and the largest and broadest-winged harriers. Most of them are associated with marshland and dense reedbeds. They are found almost worldwide, excluding ...
, short-toed eagle
The short-toed snake eagle (''Circaetus gallicus''), also known as the short-toed eagle, is a medium-sized bird of prey in the family Accipitridae, which also includes many other diurnal raptors such as kites, buzzards and harriers. The genus na ...
, tawny eagle
The tawny eagle (''Aquila rapax'') is a large bird of prey. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family ''Accipitridae''. Its heavily feathered legs mark it as a member of the subfamily Aquilinae, also known as booted eagles.Helbig, A. J., Kocum, ...
, sparrow hawk
Sparrowhawk (sometimes sparrow hawk) may refer to several species of small hawk in the genus ''Accipiter''. "Sparrow-hawk" or sparhawk originally referred to ''Accipiter nisus'', now called "Eurasian" or "northern" sparrowhawk to distinguish it f ...
, crested lark
The crested lark (''Galerida cristata'') is a species of lark widespread across Eurasia and northern Africa. It is a non-migratory bird, but can occasionally be found as a vagrant in Great Britain.
Taxonomy and systematics
The crested lark was ...
, demoiselle crane, skylarks
''Skylarks'' is a 1936 British comedy film directed by Thornton Freeland and starring Jimmy Nervo, Teddy Knox and Nancy Burne.Low p.386 Nervo and Knox were a comic team, who became associated with the larger Crazy Gang grouping with whom they s ...
, green bee-eater, brown dove, black ibis
The red-naped ibis (''Pseudibis papillosa'') also known as the Indian black ibis or black ibis is a species of ibis found in the plains of the Indian Subcontinent. Unlike other ibises in the region it is not very dependent on water and is often f ...
and sand grouse. The great Indian bustard
The great Indian bustard (''Ardeotis nigriceps'') or Indian bustard, is a bustard found on the Indian subcontinent. A large bird with a horizontal body and long bare legs, giving it an ostrich like appearance, this bird is among the heaviest of t ...
, known locally as the ''godavan'', and which is a state bird, has been classed as critically endangered since 2011.
Wildlife protection
wildlife
Wildlife refers to domestication, undomesticated animal species (biology), species, but has come to include all organisms that grow or live wilderness, wild in an area without being species, introduced by humans. Wildlife was also synonymous ...
sanctuaries. There are four national parks and wildlife sanctuaries: Keoladeo National Park
Keoladeo National Park or Keoladeo Ghana National Park (formerly known as the Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary) is a famous avifauna sanctuary in Bharatpur, Rajasthan, India, that hosts thousands of birds, especially during the winter season. Over 350 ...
of Bharatpur, Sariska Tiger Reserve
Sariska Tiger Reserve is a tiger reserve in Alwar district, Rajasthan, India. It stretches over an area of comprising scrub-thorn arid forests, dry deciduous forests, grasslands, and rocky hills. This area was a hunting preserve of the Alwa ...
of Alwar, Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park is a national park in Rajasthan, India, with an area of . It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River. It is named after the historic Ranthambore Fort, which lies within the park ...
of Sawai Madhopur
Sawai Madhopur is a city and Municipal Council (Nagar Parishad) in the Sawai Madhopur District in Rajasthan state, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Sawai Madhopur District of Rajasthan. Ranthambore National Park which is 7 ...
, and Desert National Park
Desert National Park is a national park situated in the Indian state of Rajasthan, near the towns of Jaisalmer and Barmer. This is one of the largest national parks, covering an area of 3162 km². The Desert National Park is an excellent ...
of Jaisalmer. A national-level institute, Arid Forest Research Institute
Arid Forest Research Institute (AFRI) is a research institute situated in Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India. The institute conducts scientific research in forestry in order to provide technologies to increase the vegetative cover and to conserve biodi ...
(AFRI) an autonomous institute of the ministry of forestry is situated in Jodhpur and continuously works on desert flora and their conservation.
Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park is a national park in Rajasthan, India, with an area of . It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River. It is named after the historic Ranthambore Fort, which lies within the park ...
is 7 km from Sawai Madhopur
Sawai Madhopur is a city and Municipal Council (Nagar Parishad) in the Sawai Madhopur District in Rajasthan state, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Sawai Madhopur District of Rajasthan. Ranthambore National Park which is 7 ...
Railway Station. It is known worldwide for its tiger population and is considered by both wilderness lovers and photographers as one of the best places in India to spot tigers. At one point, due to poaching and negligence, tigers became extinct at Sariska, but five tigers have been relocated there. Prominent among the wildlife sanctuaries are Mount Abu
Mount Abu () is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India.The mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. The highest peak on the mountain is Guru Shikhar at above s ...
Sanctuary, Bhensrod Garh Sanctuary, Darrah Sanctuary, Jaisamand Sanctuary, Kumbhalgarh Wildlife Sanctuary
Kumbhalgarh Wildlife Sanctuary is located in the Rajsamand District of Rajasthan State in western India. It surrounds the Kumbhalgarh fortress and covers an area of . The sanctuary extends across the Aravalli Range, covering parts of Rajsamand ...
, Jawahar Sagar Sanctuary, and Sita Mata Wildlife Sanctuary.
Communication
Major internet service provider (ISP) and telecom companies are present in Rajasthan includingAirtel
Bharti Airtel Limited, commonly known as (d/b/a) Airtel, is an Indian multinational telecommunications services company based in New Delhi. It operates in 18 countries across South Asia and Africa, as well as the Channel Islands. Current ...
, Data Infosys Limited
In the pursuit of knowledge, data (; ) is a collection of discrete values that convey information, describing quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted. ...
, Reliance Limited, Idea
In common usage and in philosophy, ideas are the results of thought. Also in philosophy, ideas can also be mental representational images of some object. Many philosophers have considered ideas to be a fundamental ontological category of being ...
, Jio
Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited, doing business as Jio, is an Indian telecommunications company and a subsidiary of Jio Platforms, headquartered in Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India. It operates a national LTE network with coverage across all 2 ...
, RailTel Corporation of India
RailTel Corporation of India Ltd. is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Indian Railways, Ministry of Railways, Government of India. It provides broadband and VPN services. RailTel was formed in September 2000 with the objective of creating a nati ...
, Software Technology Parks of India
Software Technology Parks of India (STPI) is an S&T organization under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) engaged in promoting IT/ ITES Industry, Innovation, R&D, Start-ups, Product/ IP creation in the field of emergin ...
(STPI), Tata Telecom and Vodafone
Vodafone Group Public limited company, plc () is a British Multinational corporation, multinational Telephone company, telecommunications company. Its registered office and Headquarters, global headquarters are in Newbury, Berkshire, England. It ...
. Data Infosys was the first ISP to bring the internet to Rajasthan in April 1999 and OASIS
In ecology, an oasis (; ) is a fertile area of a desert or semi-desert environment'ksar''with its surrounding feeding source, the palm grove, within a relational and circulatory nomadic system.”
The location of oases has been of critical imp ...
was the first private mobile telephone company. Today the largest coverage area and the clientele are with BSNL.
Government and politics
The politics of Rajasthan are dominated mainly by theBharatiya Janata Party
The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP; ; ) is a political party in India, and one of the two major Indian political parties alongside the Indian National Congress. Since 2014, it has been the ruling political party in India under Narendra Modi ...
and the Indian National Congress
The Indian National Congress (INC), colloquially the Congress Party but often simply the Congress, is a political party in India with widespread roots. Founded in 1885, it was the first modern nationalist movement to emerge in the British Em ...
.
Administrative divisions
 Rajasthan is divided into 33 districts within seven divisions:
Rajasthan is divided into 33 districts within seven divisions:
Economy
Rajasthan's economy is primarily agricultural andpastoral
A pastoral lifestyle is that of shepherds herding livestock around open areas of land according to seasons and the changing availability of water and pasture. It lends its name to a genre of literature, art, and music (pastorale) that depicts ...
. Wheat and barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley pr ...
are cultivated over large areas, as are pulses
In medicine, a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle (heartbeat) by trained fingertips. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body, such as at the nec ...
, sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with ...
, and oilseed
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of fruits. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed oils, or fat ...
s. Cotton and tobacco are the state's cash crops. Rajasthan is among the largest producers of edible oil
Cooking oil is plant, animal, or synthetic liquid fat used in frying, baking, and other types of cooking. It is also used in food preparation and flavoring not involving heat, such as salad dressings and bread dips, and may be called edible oil ...
s in India and the second-largest producer of oilseeds
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of fruits. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed oils, or fat ...
. Rajasthan is also the biggest wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
As ...
-producing state in India and the main opium
Opium (or poppy tears, scientific name: ''Lachryma papaveris'') is dried latex obtained from the seed capsules of the opium poppy ''Papaver somniferum''. Approximately 12 percent of opium is made up of the analgesic alkaloid morphine, which i ...
producer and consumer. There are mainly two crop seasons. The water for irrigation comes from wells and tanks. The Indira Gandhi Canal
The Indira Gandhi Canal (originally, Rajasthan Canal) is the longest canal in India. It starts at the Harike Barrage near Harike, a few kilometers downriver from the confluence of the Satluj and Beas rivers in Punjab state, and ends in irriga ...
irrigates northwestern Rajasthan.
The main industries are mineral based, agriculture-based, and textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
based. Rajasthan is the second-largest producer of polyester
Polyester is a category of polymers that contain the ester functional group in every repeat unit of their main chain. As a specific material, it most commonly refers to a type called polyethylene terephthalate (PET). Polyesters include natural ...
fibre in India. Several prominent chemical and engineering companies are located in the city of Kota, in southern Rajasthan. Rajasthan is pre-eminent in quarrying
A quarry is a type of open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some jurisdictions to reduce their environ ...
and mining in India. The Taj Mahal
The Taj Mahal (; ) is an Islamic ivory-white marble mausoleum on the right bank of the river Yamuna in the Indian city of Agra. It was commissioned in 1631 by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan () to house the tomb of his favourite wife, Mu ...
was built from white marble which was mined from a town called Makrana
Makrana is an urban city located at the centre of Rajasthan in Nagaur district. It also served as a tehsil headquarters, with 136 villages under its jurisdiction thus making it the largest tehsil in the district. The biggest village of Makra ...
. The state is the second-largest source of cement in India. It has rich salt deposits at Sambhar, copper mines at Khetri
Khetri Nagar is the town in Jhunjhunu district of Rajasthan in India. It is a part of the Shekhawati region. Khetri consists of two towns, "Khetri Town" founded by Raja Khet Singhji Nirwan and "Khetri Nagar" which is about 10 km away from ...
, Jhunjhunu
Jhunjhunu is a city and capital of Jhunjhunu district in the state of Rajasthan. This city is in the northern state of Rajasthan, India and the administrative headquarters of Jhunjhunu District.
History
Jhunjhunu is a very old and historical ...
, and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
mines at Dariba, Zawar mines and Rampura Agucha (opencast) near Bhilwara
Bhilwara () is a city, administrative headquarters in Bhilwara district of the Mewar region of Rajasthan, India. It has been termed as 'Textile city'.
History
Stone Age tools dating from 5,012 to 200,000 years were found in Bundi and Bhilw ...
. Dimensional stone mining is also undertaken in Rajasthan. Jodhpur sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) ...
is mostly used in monuments, important buildings, and residential buildings. This stone is termed as ''Chittar Patthar''. Jodhpur leads in the handicraft
A handicraft, sometimes more precisely expressed as artisanal handicraft or handmade, is any of a wide variety of types of work where useful and decorative objects are made completely by one’s hand or by using only simple, non-automated re ...
and guar gum
Guar gum, also called guaran, is a galactomannan polysaccharide extracted from guar beans that has thickening and stabilizing properties useful in food, feed, and industrial applications. The guar seeds are mechanically dehusked, hydrated, mil ...
industries.
Rajasthan is also a part of the Mumbai-Delhi Industrial corridor set to benefit economically. The state gets 39% of the DMIC, with major districts of Jaipur, Alwar, Kota and Bhilwara benefiting.
Rajasthan also has reserves of low-silica limestone.
Rajasthan connected 100% of its population to electricity power in 2019 (raising the rate of electricity access from 71% of the population in 2015). The renewable energy sector plays the most important role in the increase of generation capacities, with the main focus on solar energy. In 2020, Bhadla Solar Park
Bhadla Solar Park is the largest solar park in the world as of 2022 and is spread over a total area of in Bhadla, Phalodi tehsil, Jodhpur district, Rajasthan, India.
The park has a total capacity of 2245 MW. The park had witnessed the lo ...
was recognised as the largest cluster of photovoltaic power plants in a single region in the world, with the installed power exceeding the 2.2 gigawatt peak.
Transport
Rajasthan is connected by many national highways, the most renowned being NH 8, which is India's first 4–8 lane highway. Rajasthan also has an inter-city surface transport system both in terms of railways and bus network. All chief cities are connected by air, rail, and road.Air
There are six main airports at Rajasthan –Jaipur International Airport
Jaipur International Airport is an international airport serving Jaipur, the capital of Rajasthan. Jaipur International Airport has been declared as the 'World's Best Airport' in the category of 2 to 5 million passengers per annum for 2015 & ...
, Jodhpur Airport
Jodhpur Airport is a civil enclave airport in Jodhpur, Rajasthan, India. It is operated by the Airports Authority of India (AAI) and shares its airside with the Jodhpur Airforce Station of the Indian Air Force (IAF).
The Government of Rajas ...
, Udaipur Airport
Udaipur () ( ISO 15919: ''Udayapura''), historically named as Udayapura, is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capi ...
and the recently started Ajmer Airport, Bikaner Airport and Jaisalmer Airport
Jaisalmer Airport is a domestic airport serving Jaisalmer, Rajasthan, India. It is located from the city centre. The airport operates as a civil enclave on an Indian Air Force base.
The airport has a single runway of in length and in widt ...
. These airports connect Rajasthan with the major cities of India such as Delhi and Mumbai. There is another airport in Kota but it is not open for commercial/civilian flights yet.
Rail
Rajasthan is connected with the main cities of India by rail. Jaipur, Kota, Ajmer, Jodhpur, Bharatpur, Bikaner, Alwar, Abu Road, and Udaipur are the principal railway stations in Rajasthan. Kota City is the only electrified section served by three Rajdhani Expresses and trains to all major cities of India. There is also an international railway, theThar Express
The ''Thar Express'' ( hi, थार एक्सप्रेस, ur, , Sindhi: ٿر ايڪسپريس) was an international passenger train that ran between the a suburban area of Jodhpur in the Indian State of Rajasthan and of Karachi in t ...
from Jodhpur
Jodhpur (; ) is the second-largest city in the Indian state of Rajasthan and officially the second metropolitan city of the state. It was formerly the seat of the princely state of Jodhpur State. Jodhpur was historically the capital of the Ki ...
(India) to Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former cap ...
(Pakistan). However, this is not open to foreign nationals.
Road
Rajasthan is well-connected to the main cities of the country includingDelhi
Delhi, officially the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi, is a city and a union territory of India containing New Delhi, the capital of India. Straddling the Yamuna river, primarily its western or right bank, Delhi shares borders w ...
, Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ; Gujarati: Amdavad ) is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 (per t ...
and Indore by state and national highways and served by Rajasthan State Road Transport Corporation (RSRTC) and private operators. Now in March 2017, 75 per cent of all national highways are being built in Rajasthan according to the public works minister of Rajasthan.
Jaipur International Airport
Jaipur International Airport is an international airport serving Jaipur, the capital of Rajasthan. Jaipur International Airport has been declared as the 'World's Best Airport' in the category of 2 to 5 million passengers per annum for 2015 & ...
File:Maharajas' Express - Mayur Mahal, dining (4809207224).jpg, Maharajah's Express dining saloon
File:Jaipur 03-2016 34 Jaipur Metro.jpg, The Jaipur Metro is an important urban transportation link
File:National highway 841.jpg, NH 8 between Udaipur
Udaipur () (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura''), historically named as Udayapura, is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capit ...
and Ahmedabad
Ahmedabad ( ; Gujarati: Amdavad ) is the most populous city in the Indian state of Gujarat. It is the administrative headquarters of the Ahmedabad district and the seat of the Gujarat High Court. Ahmedabad's population of 5,570,585 (per t ...
Demographics
According to the 2011 Census of India, Rajasthan has a total population of 68,548,437. The native Rajasthani people make up the majority of the state's population. The state of Rajasthan is also populated by Sindhi people, Sindhis, who came to Rajasthan from Sindh province (now inPakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
) during the India-Pakistan separation in 1947. As for religion, Rajasthan's residents are mainly Hindus, who account for 88.49% of the population. Rajasthani Muslims, Muslims make up 9.07%, Sikhs 1.27% and Jainism, Jains 0.91% of the population.
Brahmins, according to ''Outlook (Indian magazine), Outlook'' constituted 8% to 10% of the population of Rajasthan as per a 2003 report, but only 7% in a 2007 report. According to a 2007 ''DNA India'' report, 12.5% of the state are Brahmins. According to a report by ''Moneycontrol.com'' at the time of 2018 Rajasthan Legislative Assembly election, the Scheduled Caste (SC) population was 18%, Scheduled Tribe (ST) was 13%, Jats 12%, Gurjars and Rajputs 9% each, Brahmins and Meenas 7% each. A ''Hindustan Times'' report from 2019 also agrees to the total ST population of 13%, of which Meenas constitute the biggest group at 7%. According to a Deutsche Welle report, the Jats constitute 12-15% of the population of Rajasthan, followed by Meenas with 10% and Gurjars with 6%. While as per a 2007 BBC Hindi report, Meenas were 14% and Gurjars were 4% of the state's population.
Language
Hindi is the official language of the state, while English language, English is the additional official language. The languages of Rajasthan primarily belong to the Rajasthani languages, Rajasthani group of Indo-Aryan languages, which most people regard as their own language. In the north are dialects of Punjabi language, Punjabi and Bagri language, Bagri, which is a transition between Rajasthani and Punjabi. In the northeast is spoken Shekhawati and Dhundari which gradually merge with Haryanvi language, Haryanvi. In the east is spoken Mewati language, Mewati in the Mewat, Mewat region, while in the far east is spoken Braj. To the southeast is spoken Haryanvi. To the west in the heart of the Thar Desert is spoken Marwari language, Marwari, which merges to Gujarati language, Gujarati in the southwest. In the south, in theMewar
Mewar or Mewad is a region in the south-central part of Rajasthan state of India. It includes the present-day districts of Bhilwara, Chittorgarh, Pratapgarh, Rajsamand, Udaipur, Pirawa Tehsil of Jhalawar District of Rajasthan, Neemuch and Man ...
region, is spoken Mewari language, Mewari, while in the hills of Vagad, Wagad is spoken Wagdi, a Bhil languages, Bhil language. Many speakers of Rajasthani languages refer to their language as Hindi, and Standard Hindi is the medium of education and is common in cities. Urdu is also common in cities although the vast majority of Muslims speak one of the Rajasthani languages as their first language. Sindhi is also common in the cities and along the border with Sindh in Pakistan where Dhatki language, Dhatki, a transition between Marwari and Sindhi, is the main dialect on both sides of the border.
The languages taught under the three-language formula are:
First language: Hindi
Second language: English
Third language: Gujarati, Punjabi, Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
, Sindhi or Urdu
Culture
Food
 Rajasthani cuisine, Rajasthani cooking was influenced by both the war-like lifestyles of its inhabitants and the availability of ingredients in this arid region. Food that could last for several days and could be eaten without heating was preferred. Thus, pickles of Rajasthan are quite famous for their tangy and spicy flavour. The ''Panchkuta'' delicacy is also a famous one - meaning 5 vegetables - a dish that lasts for several days, and is made out of certain weed plants that only grow in the wild desert. The scarcity of water and fresh green vegetables have all had their effect on cooking. It is known for its snacks like Bikaneri Bhujia. Other famous dishes include ''bajre ki roti'' (millet bread) and ''lahsun ki chutney'' (hot garlic paste), ''mawa kachori'' Mirchi Bada, Pyaaj Kachori and ghevar from Jodhpur,
Rajasthani cuisine, Rajasthani cooking was influenced by both the war-like lifestyles of its inhabitants and the availability of ingredients in this arid region. Food that could last for several days and could be eaten without heating was preferred. Thus, pickles of Rajasthan are quite famous for their tangy and spicy flavour. The ''Panchkuta'' delicacy is also a famous one - meaning 5 vegetables - a dish that lasts for several days, and is made out of certain weed plants that only grow in the wild desert. The scarcity of water and fresh green vegetables have all had their effect on cooking. It is known for its snacks like Bikaneri Bhujia. Other famous dishes include ''bajre ki roti'' (millet bread) and ''lahsun ki chutney'' (hot garlic paste), ''mawa kachori'' Mirchi Bada, Pyaaj Kachori and ghevar from Jodhpur, Alwar
Alwar (Pronunciation: Help:IPA/Hindi and Urdu, �lʋəɾ is a city located in India's National Capital Region (India), National Capital Region and the administrative headquarters of Alwar district, Alwar District in the state of Rajasthan. ...
ka Mawa (milk cake), ''Kadhi kachori'' from Ajmer, ''Malpua'' from Pushkar, Daal kachori (Kota kachori) from Kota and rassgullas from Bikaner. Originating from the Marwar
Marwar (also called Jodhpur region) is a region of western Rajasthan state in North Western India. It lies partly in the Thar Desert. The word 'maru' is Sanskrit for desert. In Rajasthani languages, "wad" means a particular area. English tran ...
region of the state is the concept of Marwari Bhojnalaya or vegetarian restaurants, today found in many parts of India, which offer vegetarian food popular among Marwari people. Ghee is an essential ingredient in most Rajasthani cuisines, and dollops of ghee are poured over food as a welcoming gesture for guests.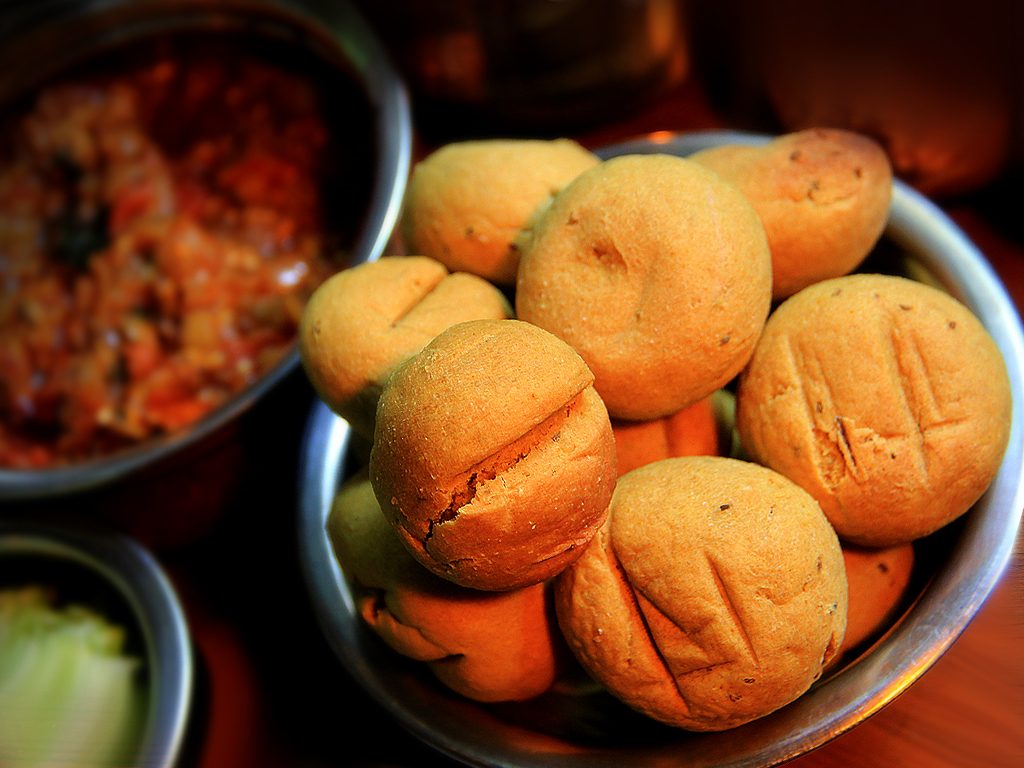 Dal baati, Dal-baati-churma is very popular in Rajasthan. The traditional way to serve it is to first coarsely mash the baati, and then pour pure ghee on top of it. It is served with daal (lentils) and spicy garlic chutney; it is also served with besan (gram flour) ki kadi. It is commonly served at all festivities, including religious occasions, wedding ceremonies, and birthday parties in Rajasthan.
Dal baati, Dal-baati-churma is very popular in Rajasthan. The traditional way to serve it is to first coarsely mash the baati, and then pour pure ghee on top of it. It is served with daal (lentils) and spicy garlic chutney; it is also served with besan (gram flour) ki kadi. It is commonly served at all festivities, including religious occasions, wedding ceremonies, and birthday parties in Rajasthan.
Music and Dance
The Ghoomar dance from Jaipur, Jodhpur, and Kalbelia of the Kalbelia tribe has gained international recognition. Folk music is a large part of the Rajasthani culture. The Manganiyar and Langha (tribe), Langa communities from Rajasthan are notable for their folk music. Kathputli (puppetry), Kathputli, Bhopa, Chang, Teratali, Ghindr, Gair dance, Kachchhi Ghori, and Tejaji are examples of traditional Rajasthani culture. Folk songs are commonly ballads that relate heroic deeds and love stories; and religious or devotional songs known as ''bhajans'' and ''banis'' which are often accompanied by musical instruments like dholak, sitar, and sarangi are also sung.Art
Rajasthan is known for its traditional, colourful art. The block prints, tie and dye prints, Gota (embroidery), gota patti (main), Bagaru prints, Sanganer prints, and Zari embroidery are major export products from Rajasthan. Handicraft items like wooden furniture and crafts, carpets, and blue pottery are commonly found here. Shopping reflects the colourful culture, Rajasthani clothes have a lot of mirror work and embroidery. A traditional Rajasthani dress for females comprises an ankle-length skirt and a short top, known as ''chaniya choli'' Mainly pure owned by traditional people. A piece of cloth is used to cover the head, both for protection from heat and maintenance of modesty. Rajasthani dresses are usually designed in bright colours like blue, yellow, and orange.Education
 In recent years, Rajasthan has worked on improving education. The state government has been making sustained efforts to raise the education standard.
In recent years, Rajasthan has worked on improving education. The state government has been making sustained efforts to raise the education standard.
Literacy
In recent decades the literacy rate of Rajasthan has increased significantly. In 1991, the state's literacy rate was only 38.55% (54.99% male and 20.44% female). In 2001, the literacy rate increased to 60.41% (75.70% male and 43.85% female). This was the highest leap in the percentage of literacy recorded in India (the rise in female literacy being 23%). At the Census 2011, Rajasthan had a literacy rate of 67.06% (80.51% male and 52.66% female). Although Rajasthan's literacy rate is below the national average of 74.04% and although its female literacy rate is the lowest in the country, the state has been praised for its efforts and achievements in raising literacy rates. In rural areas of Rajasthan, the literacy rate is 76.16% for males and 45.8% for females. This has been debated across all the party levels, when the governor of Rajasthan set a minimum educational qualification for the village panchayat elections.Tourism
 Rajasthan attracted a total of 45.9 million domestic and 1.6 million foreign tourists in 2017, which is the tenth highest in terms of domestic visitors and fifth highest in foreign tourists. The tourism industry in Rajasthan is growing effectively each year and is becoming one of the major income sources for the state government. Rajasthan is home to many attractions for domestic and foreign travellers, including the forts and palaces of
Rajasthan attracted a total of 45.9 million domestic and 1.6 million foreign tourists in 2017, which is the tenth highest in terms of domestic visitors and fifth highest in foreign tourists. The tourism industry in Rajasthan is growing effectively each year and is becoming one of the major income sources for the state government. Rajasthan is home to many attractions for domestic and foreign travellers, including the forts and palaces of Jaipur
Jaipur (; Hindi Language, Hindi: ''Jayapura''), formerly Jeypore, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Rajasthan. , the city had a pop ...
, the lakes of Udaipur
Udaipur () (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura''), historically named as Udayapura, is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capit ...
, the temples of Rajsamand and Pali, Rajasthan, Pali, sand dunes of Jaisalmer
Jaisalmer , nicknamed "The Golden city", is a city in the Indian state of Rajasthan, located west of the state capital Jaipur. The town stands on a ridge of yellowish sandstone and is crowned by the ancient Jaisalmer Fort. This fort contains a ...
and Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. Bikaner city is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Formerly the capital of ...
, Havelis of Mandawa and Fatehpur, Rajasthan, Fatehpur, the wildlife of Sawai Madhopur
Sawai Madhopur is a city and Municipal Council (Nagar Parishad) in the Sawai Madhopur District in Rajasthan state, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Sawai Madhopur District of Rajasthan. Ranthambore National Park which is 7 ...
, the scenic beauty of Mount Abu
Mount Abu () is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India.The mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. The highest peak on the mountain is Guru Shikhar at above s ...
, the tribes of Dungarpur
Dungarpur is a city in the southernmost part of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarters of Dungarpur District. It is the fastest developing town in the southern part of Rajasthan, alongside Aspur ''tehsil''.
History
Dungarpu ...
and Banswara
Banswara is a city in the Banswara district in southern Rajasthan, India. The name, Banswara, came from "Bans wala" (bamboo) forests, as Bamboo grew in abundance around this place within the area.
Banswara is also known as "City of a Hundred ...
, and the cattle fair of Pushkar.
Rajasthan is known for its customs, culture, colours, majestic forts, and palaces, folk dances and music, local festivals, local food, sand dunes, carved temples and beautiful Havelis. Rajasthan's Jaipur Jantar Mantar, Mehrangarh Fort and Stepwell of Jodhpur
Jodhpur (; ) is the second-largest city in the Indian state of Rajasthan and officially the second metropolitan city of the state. It was formerly the seat of the princely state of Jodhpur State. Jodhpur was historically the capital of the Ki ...
, Dilwara Temples, Chittor Fort
The Chittorgarh (literally Chittor Fort), also known as Chittod Fort, is one of the largest forts in India. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The fort was the capital of Mewar and is located in the present-day city of Chittorgarh. It sprawls o ...
, Lake Palace, miniature paintings in Bundi
Bundi is a city in the Hadoti region of Rajasthan state in northwest India and capital of the former princely state of Rajputana agency. District of Bundi is named after the former princely state.
Demographics
According to the 2011 Indian cens ...
, and numerous city palaces and Havelis are part of the architectural heritage of India. Jaipur, the ''Pink City'', is noted for the ancient houses made of a type of sandstone dominated by a pink hue. In Jodhpur, most houses are painted blue. At Ajmer
Ajmer is one of the major and oldest cities in the Indian state of Rajasthan and the centre of the eponymous Ajmer District. It is located at the centre of Rajasthan. It is also known as heart of Rajasthan. The city was established as "''Aj ...
, there is white marble Bara-dari on the Anasagar lake and Soniji Ki Nasiyan. Jain Temples dot Rajasthan from north to south and east to west. Dilwara Temples of Mount Abu, Shrinathji Temple of Nathdwara, Ranakpur Jain temple dedicated to Lord Rishabhanatha, Adinath in Pali District, Jain temples in the fort complexes of Chittor, Jaisalmer and Kumbhalgarh, Lodhruva, Lodurva Jain temples, Mirpur Jain Temple of Sirohi, Sarun Mata Temple at Kotputli, Bhandasar and Karni Mata Temple of Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. Bikaner city is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Formerly the capital of ...
and Mandore of Jodhpur
Jodhpur (; ) is the second-largest city in the Indian state of Rajasthan and officially the second metropolitan city of the state. It was formerly the seat of the princely state of Jodhpur State. Jodhpur was historically the capital of the Ki ...
are some of the best examples. Keoladeo National Park
Keoladeo National Park or Keoladeo Ghana National Park (formerly known as the Bharatpur Bird Sanctuary) is a famous avifauna sanctuary in Bharatpur, Rajasthan, India, that hosts thousands of birds, especially during the winter season. Over 350 ...
, Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park is a national park in Rajasthan, India, with an area of . It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River. It is named after the historic Ranthambore Fort, which lies within the park ...
, Sariska Tiger Reserve
Sariska Tiger Reserve is a tiger reserve in Alwar district, Rajasthan, India. It stretches over an area of comprising scrub-thorn arid forests, dry deciduous forests, grasslands, and rocky hills. This area was a hunting preserve of the Alwa ...
, Tal Chhapar Sanctuary
Tal Chhapar Sanctuary is a sanctuary located in the Churu district of Northwestern Rajasthan, in the Shekhawati region of India. It is known for blackbucks and is also home to a variety of birds. The sanctuary is 210 km from Jaipur on the ...
, are wildlife attractions of Rajasthan. Mewar festival of Udaipur, Teej festival and Gangaur festival in Jaipur, Rajasthan desert festival, Desert festival of Jodhpur, Brij Holi of Bharatpur, Matsya festival of Alwar, Kite festival of Jodhpur, Kolayat fair in Bikaner are some of the most popular fairs and festivals of Rajasthan.
Bikaner
Bikaner () is a city in the northwest of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is located northwest of the state capital, Jaipur. Bikaner city is the administrative headquarters of Bikaner District and Bikaner division.
Formerly the capital of ...
File:Hawa Mahal 2011.jpg, Hawa Mahal, Jaipur
Jaipur (; Hindi Language, Hindi: ''Jayapura''), formerly Jeypore, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Rajasthan. , the city had a pop ...
File:20191219 Fort Amber, Amer, Jaipur 0955 9481.jpg, Amber Fort has seen from the bank of Maotha Lake, Jaigarh Fort on the hills in the background
File:Nakki Lake during daytime.JPG, Nakki Lake, Mount Abu
Mount Abu () is a hill station in the Aravalli Range in Sirohi district of the state of Rajasthan in western India.The mountain forms a rocky plateau 22 km long by 9 km wide. The highest peak on the mountain is Guru Shikhar at above s ...
File:Mehrangarh Fort.jpg, Mehrangarh Fort
File:Kalpavruksha page.jpg, Delicate Marble carving at Dilwara Temples
File:Lake Pichola (1580558921).jpg, Lake Palace, Udaipur
Udaipur () (ISO 15919: ''Udayapura''), historically named as Udayapura, is a city and municipal corporation in Udaipur district of the state of Rajasthan, India. It is the administrative headquarter of Udaipur district. It is the historic capit ...
File:Kirti Stambha of Fort of Chittaur -Chittaurgarh -Rajasthan -IMG 8307.jpg, Kirti Stambha of Chittor Fort
The Chittorgarh (literally Chittor Fort), also known as Chittod Fort, is one of the largest forts in India. It is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The fort was the capital of Mewar and is located in the present-day city of Chittorgarh. It sprawls o ...
File:A Walk to remember.jpg, Tiger at Ranthambore National Park
Ranthambore National Park is a national park in Rajasthan, India, with an area of . It is bounded to the north by the Banas River and to the south by the Chambal River. It is named after the historic Ranthambore Fort, which lies within the park ...
File:Jaipur 03-2016 39 Jal Mahal - Water Palace.jpg, Jal Mahal, Jaipur
Jaipur (; Hindi Language, Hindi: ''Jayapura''), formerly Jeypore, is the List of state and union territory capitals in India, capital and largest city of the Indian States and union territories of India, state of Rajasthan. , the city had a pop ...
See also
* Jatan Sansthan (2001) * List of people from Rajasthan * Outline of RajasthanReferences
Further reading
* Bhattacharya, Manoshi. 2008. ''The Royal Rajputs: Strange Tales and Stranger Truths''. Rupa & Co, New Delhi. * Gahlot, Sukhvirsingh. 1992. ''RAJASTHAN: Historical & Cultural''. J. S. Gahlot Research Institute, Jodhpur. * Somani, Ram Vallabh. 1993. ''History of Rajasthan''. Jain Pustak Mandir, Jaipur. * Tod, James & Crooke, William. 1829. ''Annals and Antiquities of Rajasthan or the Central and Western Rajpoot States of India,''. Numerous reprints, including 3 Vols. Reprint: Low Price Publications, Delhi. 1990. (set of 3 vols.) * Mathur, P.C., 1995. ''Social and Economic Dynamics of Rajasthan Politics'' (Jaipur, Aaalekh)External links
Government
Official Site of the Government of Rajasthan, India
Official Tourism Site of Rajasthan, India
General information
* * {{Authority control Rajasthan, North India, * States and union territories of India States and territories established in 1950 1950 establishments in India