|
Saka Era
The Shaka era (IAST: Śaka, Śāka) is a historical Hindu calendar era (year numbering), the epoch (its year zero) of which corresponds to Julian year 78. The era has been widely used in different regions of India as well as in SE Asia. History There are two Shaka era systems in scholarly use, one is called ''Old Shaka Era'', whose epoch is uncertain, probably sometime in the 1st millennium BCE because ancient Buddhist and Jaina inscriptions and texts use it, but this is a subject of dispute among scholars. The other is called ''Saka Era of 78 CE'', or simply ''Saka Era'', a system that is common in epigraphic evidence from southern India. A parallel northern India system is the ''Vikrama Era'', which is used by the Vikrami calendar linked to Vikramaditya. The beginning of the Shaka era is now widely equated to the ascension of king Chashtana in 78 CE. His inscriptions, dated to the years 11 and 52, have been found at Andhau in Kutch region. These years are interpreted as S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Satrap Damasena Year 153
Western may refer to: Places *Western, Nebraska, a village in the US * Western, New York, a town in the US * Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia * Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia *Western world, countries that identify with shared "Western" culture Arts and entertainment Films * ''Western'' (1997 film), a French road movie directed by Manuel Poirier * ''Western'' (2017 film), a German-Austrian film Genres *Western (genre), a category of fiction and visual art centered on the American Old West **Western fiction, the Western genre as featured in literature **Western music (North America), a type of American folk music Music * ''Westerns'' (EP), an EP by Pete Yorn *WSTRN, a British hip hop group from west London Business * The Western, a closed hotel/casino in Las Vegas, United States *Western Cartridge Company, a manufacturer of ammunition *Western Publishing, a defunct publishing company Educational institutions *Western Washington Universi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gautamiputra Satakarni
Gautamiputra Satakarni (Brahmi: 𑀕𑁄𑀢𑀫𑀺𑀧𑀼𑀢 𑀲𑀸𑀢𑀓𑀡𑀺, ''Gotamiputa Sātakaṇi'', IAST: ) was a ruler of the Satavahana Empire in present-day Deccan region of India. He was mentioned as the important and greatest ruler of Satavahana Dynasty. He ruled in the 1st or 2nd century CE, although his exact period is uncertain. His reign is dated variously: 86-110 CE, c. 103-127 CE, 106-130 CE, or more recently and specifically ca. 60-85 CE. The information available about Gautamiputra Satakarni comes from his coins, the Satavahana inscriptions, and the royal genealogies in the various Puranas. The best known of these is the Nashik '' prashasti'' ( eulogy) inscription of his mother Gautami Balashri, which credits him with extensive military conquests. Historical evidence suggests that Gautamiputra revived the Satavahana power after a decline caused by Saka invasions. Ancestry Except the '' Brahmanda Purana'', all the Puranas that contain th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
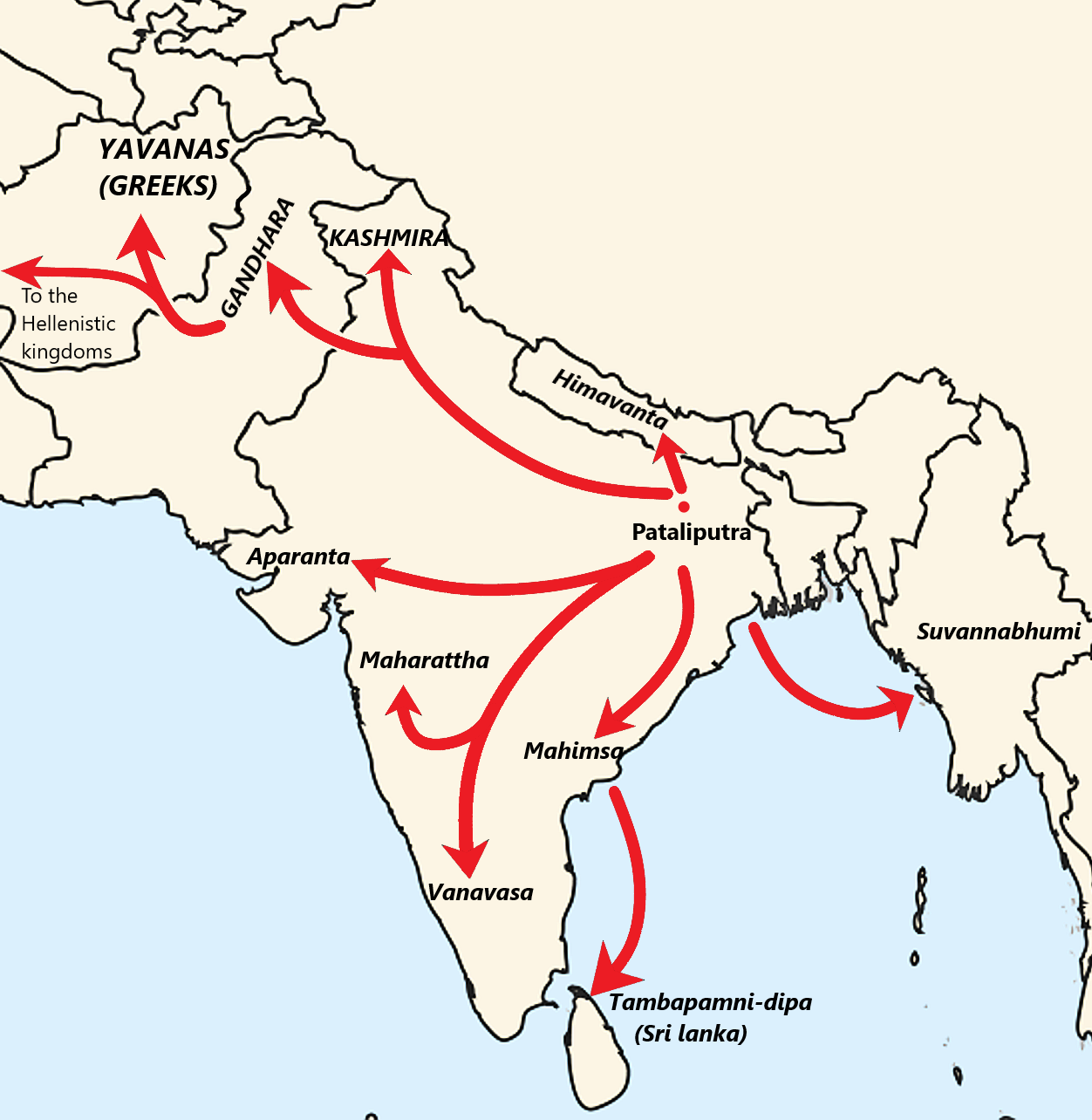
Decline Of Buddhism In India
Buddhism, which originated in India, gradually dwindled and was replaced by approximately the 12th century. According to Lars Fogelin, this was "not a singular event, with a singular cause; it was a centuries-long process." The decline of Buddhism has been attributed to various factors, especially the regionalisation of India after the end of the Gupta Empire (320–650 CE). Another factor was invasions of north India by various groups such as Indo-Iranian Huns, Hephthalites, Turkic-Mongolians, Arabs and Persians and subsequent destruction of Buddhist institutions such as Taxila and Nalanda and religious persecutions. Religious competition with other Indic religions and later Islam were also important factors. The invasions of Huns in 5th century and subsequent destruction of Buddhist centres caused the decline of Buddhism in the northwest Indian subcontinent. A similar process occurred in northeast, where Islamization of Bengal and demolitions of Nalanda, Vikramasil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global population, known as Hindus. The word ''Hindu'' is an exonym, and while Hinduism has been called the oldest religion in the world, many practitioners refer to their religion as '' Sanātana Dharma'' ( sa, सनातन धर्म, lit='the Eternal Dharma'), a modern usage, which refers to the idea that its origins lie beyond human history, as revealed in the Hindu texts. Another endonym is ''Vaidika dharma'', the dharma related to the Vedas. Hinduism is a diverse system of thought marked by a range of philosophies and shared concepts, rituals, cosmological systems, pilgrimage sites, and shared textual sources that discuss theology, metaphysics, mythology, Vedic yajna, yoga, agamic rituals, and temple building, among other to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gupta Period
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Golden Age of India by historians. The ruling dynasty of the empire was founded by the king Sri Gupta; the most notable rulers of the dynasty were Chandragupta I, Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and Skandagupta. The 5th-century CE Sanskrit poet Kalidasa credits the Guptas with having conquered about twenty-one kingdoms, both in and outside India, including the kingdoms of Parasikas, the Hunas, the Kambojas, tribes located in the west and east Oxus valleys, the Kinnaras, Kiratas, and others.Raghu Vamsa v 4.60–75 The high points of this period are the great cultural developments which took place primarily during the reigns of Samudragupta, Chandragupta II and Kumaragupta I. Many Hindu epics and literary sources, such as Mahabharata an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmi Numerals
The Brahmi numerals are a numeral system attested from the 3rd century BCE (somewhat later in the case of most of the tens). They are a non positional decimal system. They are the direct graphic ancestors of the modern Hindu–Arabic numeral system. However, they were conceptually distinct from these later systems, as they were not used as a positional system with a zero. Rather, there were separate numerals for each of the tens (10, 20, 30, etc.). There were also symbols for 100 and 1000 which were combined in ligatures with the units to signify 200, 300, 2000, 3000, etc. In computers, these ligatures are written with the Brahmi Number Joiner at U+1107F. Origins The source of the first three numerals seems clear: they are collections of 1, 2, and 3 strokes, in Ashoka's era vertical I, II, III like Roman numerals, but soon becoming horizontal like the ancient Han Chinese numerals. In the oldest inscriptions, 4 looks like a +, reminiscent of the X of neighboring , and perh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rudrasimha I
300px, Gunda inscription of Rudrasimha, Saka year 103. Rudrasimha I was a Western Kshatrapa ruler, who reigned from 178 to 197 CE. He was son of Rudradaman I, grandson of Jayadaman, and grand-grandson of Chashtana. During his reign, the Abhiras became increasingly important. Some of them were even serving as generals. Ashvini Agrawal thinks that the Abhira king '' Isvardatta'' was a general in the service of Rudrasimha I who deposed his master in 188 A.D and ascended the throne. Ashvini Agrawal further says that Rudrasimha I soon deposed him and regained the throne in 190 A.D. Reign Numismatics and Epigraphics From the reigns of Jivadaman and Rudrasimha I, the date of minting of each coin, reckoned in the Saka era, is usually written on the obverse behind the king's head in Brahmi numerals, allowing for a quite precise datation of the rule of each king. This is a rather uncommon case in Indian numismatics. Some, such as the numismat R.C Senior considered that these dates mig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ujjain
Ujjain (, Hindustani pronunciation: �d͡ːʒɛːn is a city in Ujjain district of the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It is the fifth-largest city in Madhya Pradesh by population and is the administrative centre of Ujjain district and Ujjain division. It is one of the Hindu pilgrimage centres of Sapta Puri famous for the '' Kumbh Mela'' held there every 12 years. The famous temple of Mahakaleshwar Jyotirlinga is located in the center of the city. An ancient city situated on the eastern bank of the Shipra River, Ujjain was the most prominent city on the Malwa plateau of central India for much of its history. It emerged as the political centre of central India around 600 BCE. It was the capital of the ancient Avanti kingdom, one of the sixteen Mahajanapadas. During the 18th century, the city briefly became the capital of Scindia state of the Maratha Empire, when Ranoji Scindia established his capital at Ujjain in 1731. It remained an important political, commercial and cult ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th century CE. The first Saka king of India was Maues/Moga (1st century BCE) who established Saka power in Gandhara, Pakistan and the Indus Valley. The Indo-Scythians extended their supremacy over north-western India, conquering the Indo-Greeks and other local kingdoms. The Indo-Scythians were apparently subjugated by the Kushan Empire, by either Kujula Kadphises or Kanishka. Yet the Saka continued to govern as satrapies, forming the Northern Satraps and Western Satraps. The power of the Saka rulers started to decline in the 2nd century CE after the Indo-Scythians were defeated by the Satavahana emperor Gautamiputra Satakarni. Indo-Scythian rule in the northwestern Indian subcontinent ceased when the last Western Satrap Rudrasimha III wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saka
The Saka ( Old Persian: ; Kharoṣṭhī: ; Ancient Egyptian: , ; , old , mod. , ), Shaka (Sanskrit ( Brāhmī): , , ; Sanskrit (Devanāgarī): , ), or Sacae (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples who historically inhabited the northern and eastern Eurasian Steppe and the Tarim Basin. "Modern scholars have mostly used the name Saka to refer specifically to Iranians of the Eastern Steppe and Tarim Basin" "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Central Asia and Eastern Turkestan to distinguish them from the related Massagetae of the Aral region and the Scythians of the Pontic steppes. These tribes spoke Iranian languages, and their chief occupation was nomadic pastoralism." The Sakas were closely related to the European Scythians, and both groups formed part of the wider Scythian cultures and ultimately derived from the earlier Andronovo culture, and the Saka language formed part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Satraps
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi:, ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central part of India ( Saurashtra and Malwa: modern Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh states), between 35 to 415 CE. The Western Satraps were contemporaneous with the Kushans who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, and were possibly vassals of the Kushans. They were also contemporaneous with the Satavahana ( Andhra) who ruled in Central India. They are called "Western Satraps" in modern historiography in order to differentiate them from the "Northern Satraps", who ruled in Punjab and Mathura until the 2nd century CE. The power of the Western Satraps started to decline in the 2nd century CE after the Saka rulers were defeated by the Emperor Gautamiputra Satakarni of the Satavahana dynasty. After this, the Saka kingdom revived, but was ultimately destroyed by Chandragupta II of the Gupta Empire in the 4th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian Educational Services
Asian Educational Services (AES) is a New Delhi, India-based publishing house that specialises in antiquarian reprints of books that were originally published between the 17th and early 20th centuries. Founded by Jagdish Lall Jetley in 1973, the selection of titles are over 1200 in number. Involvement This firm has a very active publication programme that aims to preserve knowledge, in the form of old books, from being lost. An extensive list of about 200 travelogues gives a vivid picture of India specifically, and Asia generally. Many of the big names in Asian exploration and in the field of history have been reprinted. W. W. Hunter, H. H. Wilson, Max Muller, Rhys Davids, H. H. Risley, Edgar Thurston, G. Forrest, G. B. Malleson, Nicholas Greenwood, William Muir, Vincent A. Smith, Emerson Tennent, Wilhelm Geiger, Monier-Willams, Sven Hedin, Richard F. Burton, Francis Younghusband, William Moorcroft, M. Auriel Stein, Marco Polo, Heuin Tsang, Al-Beruni, William of Rubr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |