Rain Note on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Rain is water
Rain is water
 Rain is water
Rain is water droplet
A drop or droplet is a small column of liquid, bounded completely or almost completely by free surfaces. A drop may form when liquid accumulates at the lower end of a tube or other surface boundary, producing a hanging drop called a pendant d ...
s that have condensed from atmospheric water vapor and then fall under gravity. Rain is a major component of the water cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly cons ...
and is responsible for depositing most of the fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
on the Earth. It provides water for hydroelectric power plants
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
, crop irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow Crop, crops, Landscape plant, landscape plants, and Lawn, lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,00 ...
, and suitable conditions for many types of ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syste ...
s.
The major cause of rain production is moisture moving along three-dimensional zones of temperature and moisture contrasts known as weather fronts. If enough moisture and upward motion is present, precipitation falls from convective
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convect ...
clouds (those with strong upward vertical motion) such as cumulonimbus (thunder clouds) which can organize into narrow rainbands. In mountainous areas, heavy precipitation is possible where upslope flow An anabatic wind, from the Greek '' anabatos'', verbal of ''anabainein'' meaning moving upward, is a warm wind which blows up a steep slope or mountain side, driven by heating of the slope through insolation.windward sides of the
 Air contains water vapor, and the amount of water in a given mass of dry air, known as the ''mixing ratio'', is measured in grams of water per kilogram of dry air (g/kg). The amount of moisture in air is also commonly reported as
Air contains water vapor, and the amount of water in a given mass of dry air, known as the ''mixing ratio'', is measured in grams of water per kilogram of dry air (g/kg). The amount of moisture in air is also commonly reported as  There are four main mechanisms for cooling the air to its dew point: adiabatic cooling, conductive cooling, radiational cooling, and evaporative cooling. Adiabatic cooling occurs when air rises and expands. The air can rise due to
There are four main mechanisms for cooling the air to its dew point: adiabatic cooling, conductive cooling, radiational cooling, and evaporative cooling. Adiabatic cooling occurs when air rises and expands. The air can rise due to

 As these larger water droplets descend, coalescence continues, so that drops become heavy enough to overcome air resistance and fall as rain. Coalescence generally happens most often in clouds above freezing, and is also known as the warm rain process. In clouds below freezing, when ice crystals gain enough mass they begin to fall. This generally requires more mass than coalescence when occurring between the crystal and neighboring water droplets. This process is temperature dependent, as supercooled water droplets only exist in a cloud that is below freezing. In addition, because of the great temperature difference between cloud and ground level, these ice crystals may melt as they fall and become rain.
Raindrops have sizes ranging from mean diameter but develop a tendency to break up at larger sizes. Smaller drops are called cloud droplets, and their shape is spherical. As a raindrop increases in size, its shape becomes more oblate, with its largest cross-section facing the oncoming airflow. Large rain drops become increasingly flattened on the bottom, like
As these larger water droplets descend, coalescence continues, so that drops become heavy enough to overcome air resistance and fall as rain. Coalescence generally happens most often in clouds above freezing, and is also known as the warm rain process. In clouds below freezing, when ice crystals gain enough mass they begin to fall. This generally requires more mass than coalescence when occurring between the crystal and neighboring water droplets. This process is temperature dependent, as supercooled water droplets only exist in a cloud that is below freezing. In addition, because of the great temperature difference between cloud and ground level, these ice crystals may melt as they fall and become rain.
Raindrops have sizes ranging from mean diameter but develop a tendency to break up at larger sizes. Smaller drops are called cloud droplets, and their shape is spherical. As a raindrop increases in size, its shape becomes more oblate, with its largest cross-section facing the oncoming airflow. Large rain drops become increasingly flattened on the bottom, like  Intensity and duration of rainfall are usually inversely related, i.e., high intensity storms are likely to be of short duration and low intensity storms can have a long duration.
Intensity and duration of rainfall are usually inversely related, i.e., high intensity storms are likely to be of short duration and low intensity storms can have a long duration.
 Convective rain, or showery precipitation, occurs from convective clouds (e.g., cumulonimbus or cumulus congestus). It falls as showers with rapidly changing intensity. Convective precipitation falls over a certain area for a relatively short time, as convective clouds have limited horizontal extent. Most precipitation in the
Convective rain, or showery precipitation, occurs from convective clouds (e.g., cumulonimbus or cumulus congestus). It falls as showers with rapidly changing intensity. Convective precipitation falls over a certain area for a relatively short time, as convective clouds have limited horizontal extent. Most precipitation in the
A Bow Echo and Severe Weather Associated with a Kona Low in Hawaii.
Retrieved on 22 May 2007. Local climates vary considerably on each island due to their topography, divisible into windward (''Koolau'') and leeward (''Kona'') regions based upon location relative to the higher mountains. Windward sides face the east to northeast
 The wet, or rainy, season is the time of year, covering one or more months, when most of the average annual rainfall in a region falls. The term ''green season'' is also sometimes used as a
The wet, or rainy, season is the time of year, covering one or more months, when most of the average annual rainfall in a region falls. The term ''green season'' is also sometimes used as a
 The fine particulate matter produced by car exhaust and other human sources of pollution forms
The fine particulate matter produced by car exhaust and other human sources of pollution forms

Objective Dvorak Technique.
Retrieved on 29 May 2006.
 The phrase ''acid rain'' was first used by Scottish chemist Robert Augus Smith in 1852. The pH of rain varies, especially due to its origin. On America's East Coast, rain that is derived from the Atlantic Ocean typically has a pH of 5.0–5.6; rain that comes across the continental from the west has a pH of 3.8–4.8; and local thunderstorms can have a pH as low as 2.0. Rain becomes acidic primarily due to the presence of two strong acids,
The phrase ''acid rain'' was first used by Scottish chemist Robert Augus Smith in 1852. The pH of rain varies, especially due to its origin. On America's East Coast, rain that is derived from the Atlantic Ocean typically has a pH of 5.0–5.6; rain that comes across the continental from the west has a pH of 3.8–4.8; and local thunderstorms can have a pH as low as 2.0. Rain becomes acidic primarily due to the presence of two strong acids,
 The Köppen classification depends on average monthly values of temperature and precipitation. The most commonly used form of the Köppen classification has five primary types labeled A through E. Specifically, the primary types are A, tropical; B, dry; C, mild mid-latitude; D, cold mid-latitude; and E, polar. The five primary classifications can be further divided into secondary classifications such as rain forest,
The Köppen classification depends on average monthly values of temperature and precipitation. The most commonly used form of the Köppen classification has five primary types labeled A through E. Specifically, the primary types are A, tropical; B, dry; C, mild mid-latitude; D, cold mid-latitude; and E, polar. The five primary classifications can be further divided into secondary classifications such as rain forest,
 Rain is measured in units of length per unit time, typically in millimeters per hour, or in countries where imperial units are more common, inches per hour. The "length", or more accurately, "depth" being measured is the depth of rain water that would accumulate on a flat, horizontal and impermeable surface during a given amount of time, typically an hour. One millimeter of rainfall is the equivalent of one liter of water per square meter.
The standard way of measuring rainfall or snowfall is the standard rain gauge, which can be found in 100-mm (4-in) plastic and 200-mm (8-in) metal varieties. The inner cylinder is filled by of rain, with overflow flowing into the outer cylinder. Plastic gauges have markings on the inner cylinder down to resolution, while metal gauges require use of a stick designed with the appropriate markings. After the inner cylinder is filled, the amount inside it is discarded, then filled with the remaining rainfall in the outer cylinder until all the fluid in the outer cylinder is gone, adding to the overall total until the outer cylinder is empty. Other types of gauges include the popular wedge gauge (the cheapest rain gauge and most fragile), the tipping bucket rain gauge, and the weighing rain gauge. For those looking to measure rainfall the most inexpensively, a can that is cylindrical with straight sides will act as a rain gauge if left out in the open, but its accuracy will depend on what ruler is used to measure the rain with. Any of the above rain gauges can be made at home, with enough know-how.
When a precipitation measurement is made, various networks exist across the United States and elsewhere where rainfall measurements can be submitted through the Internet, such as
Rain is measured in units of length per unit time, typically in millimeters per hour, or in countries where imperial units are more common, inches per hour. The "length", or more accurately, "depth" being measured is the depth of rain water that would accumulate on a flat, horizontal and impermeable surface during a given amount of time, typically an hour. One millimeter of rainfall is the equivalent of one liter of water per square meter.
The standard way of measuring rainfall or snowfall is the standard rain gauge, which can be found in 100-mm (4-in) plastic and 200-mm (8-in) metal varieties. The inner cylinder is filled by of rain, with overflow flowing into the outer cylinder. Plastic gauges have markings on the inner cylinder down to resolution, while metal gauges require use of a stick designed with the appropriate markings. After the inner cylinder is filled, the amount inside it is discarded, then filled with the remaining rainfall in the outer cylinder until all the fluid in the outer cylinder is gone, adding to the overall total until the outer cylinder is empty. Other types of gauges include the popular wedge gauge (the cheapest rain gauge and most fragile), the tipping bucket rain gauge, and the weighing rain gauge. For those looking to measure rainfall the most inexpensively, a can that is cylindrical with straight sides will act as a rain gauge if left out in the open, but its accuracy will depend on what ruler is used to measure the rain with. Any of the above rain gauges can be made at home, with enough know-how.
When a precipitation measurement is made, various networks exist across the United States and elsewhere where rainfall measurements can be submitted through the Internet, such as
 One of the main uses of weather radar is to be able to assess the amount of precipitations fallen over large basins for hydrological purposes. For instance, river
One of the main uses of weather radar is to be able to assess the amount of precipitations fallen over large basins for hydrological purposes. For instance, river
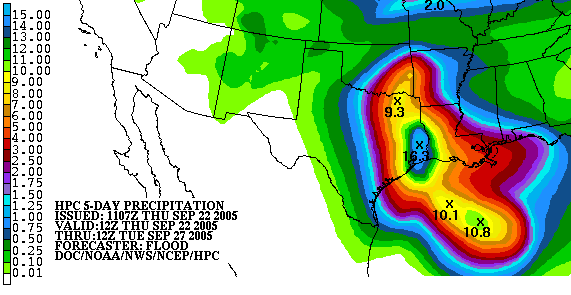
 Rainfall intensity is classified according to the rate of precipitation, which depends on the considered time.(pdf)
Rainfall intensity is classified according to the rate of precipitation, which depends on the considered time.(pdf)
The following categories are used to classify rainfall intensity: * Light rain — when the precipitation rate is < per hour * Moderate rain — when the precipitation rate is between – or per hour * Heavy rain — when the precipitation rate is > per hour, or between and per hour * Violent rain — when the precipitation rate is > per hour Euphemisms for a heavy or violent rain include gully washer, trash-mover and toad-strangler. The intensity can also be expressed by rainfall erosivity ''R-factor'' or in terms of the rainfall time-structure ''n-index''.
 The Quantitative Precipitation Forecast (abbreviated QPF) is the expected amount of liquid precipitation accumulated over a specified time period over a specified area. A QPF will be specified when a measurable precipitation type reaching a minimum threshold is forecast for any hour during a QPF valid period. Precipitation forecasts tend to be bound by synoptic hours such as 0000, 0600, 1200 and 1800 GMT. Terrain is considered in QPFs by use of topography or based upon climatological precipitation patterns from observations with fine detail. Starting in the mid to late 1990s, QPFs were used within hydrologic forecast models to simulate impact to rivers throughout the United States.
Forecast models show significant sensitivity to humidity levels within the planetary boundary layer, or in the lowest levels of the atmosphere, which decreases with height. QPF can be generated on a quantitative, forecasting amounts, or a qualitative, forecasting the probability of a specific amount, basis. Radar imagery forecasting techniques show higher
The Quantitative Precipitation Forecast (abbreviated QPF) is the expected amount of liquid precipitation accumulated over a specified time period over a specified area. A QPF will be specified when a measurable precipitation type reaching a minimum threshold is forecast for any hour during a QPF valid period. Precipitation forecasts tend to be bound by synoptic hours such as 0000, 0600, 1200 and 1800 GMT. Terrain is considered in QPFs by use of topography or based upon climatological precipitation patterns from observations with fine detail. Starting in the mid to late 1990s, QPFs were used within hydrologic forecast models to simulate impact to rivers throughout the United States.
Forecast models show significant sensitivity to humidity levels within the planetary boundary layer, or in the lowest levels of the atmosphere, which decreases with height. QPF can be generated on a quantitative, forecasting amounts, or a qualitative, forecasting the probability of a specific amount, basis. Radar imagery forecasting techniques show higher
 Precipitation, especially rain, has a dramatic effect on agriculture. All plants need at least some water to survive, therefore rain (being the most effective means of watering) is important to agriculture. While a regular rain pattern is usually vital to healthy plants, too much or too little rainfall can be harmful, even devastating to crops.
Precipitation, especially rain, has a dramatic effect on agriculture. All plants need at least some water to survive, therefore rain (being the most effective means of watering) is important to agriculture. While a regular rain pattern is usually vital to healthy plants, too much or too little rainfall can be harmful, even devastating to crops.
 Cultural attitudes towards rain differ across the world. In
Cultural attitudes towards rain differ across the world. In  Rain holds an important religious significance in many cultures. The ancient
Rain holds an important religious significance in many cultures. The ancient
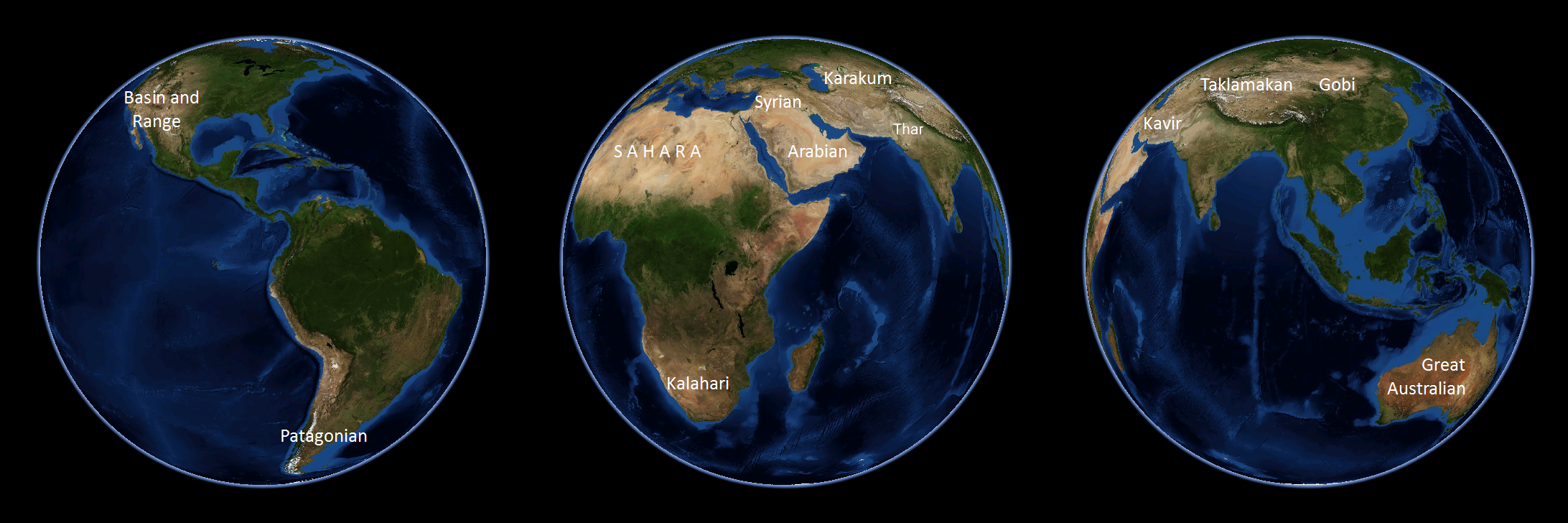
 The northern half of Africa is dominated by the world's most extensive hot, dry region, the Sahara Desert. Some deserts also occupy much of southern Africa: the Namib and the Kalahari. Across Asia, a large annual rainfall minimum, composed primarily of deserts, stretches from the
The northern half of Africa is dominated by the world's most extensive hot, dry region, the Sahara Desert. Some deserts also occupy much of southern Africa: the Namib and the Kalahari. Across Asia, a large annual rainfall minimum, composed primarily of deserts, stretches from the
Precipitation of the Individual States and of the Conterminous States.
Retrieved on 9 March 2008.
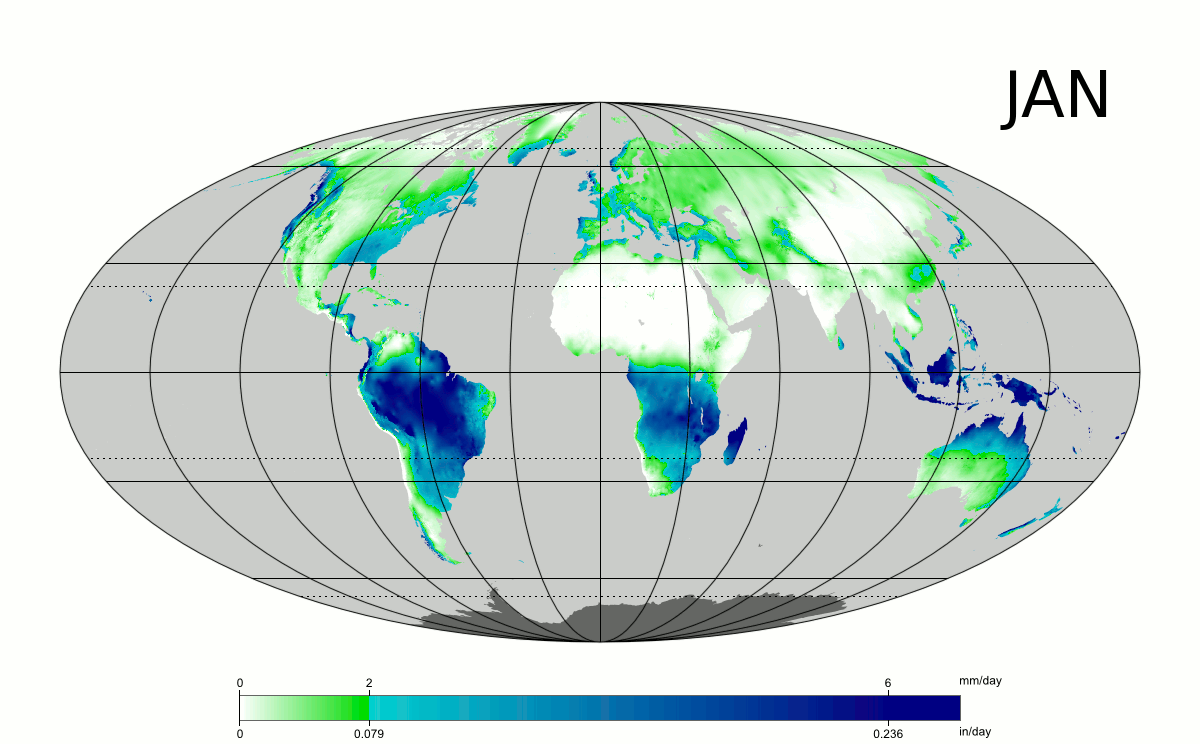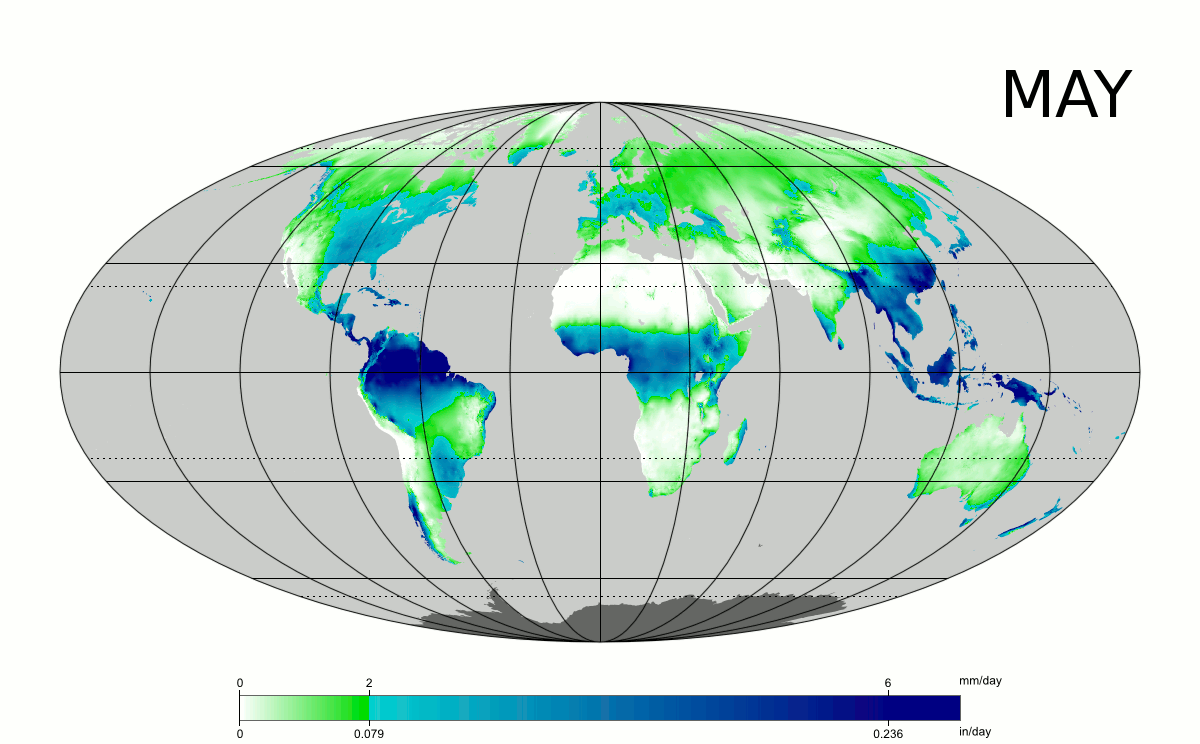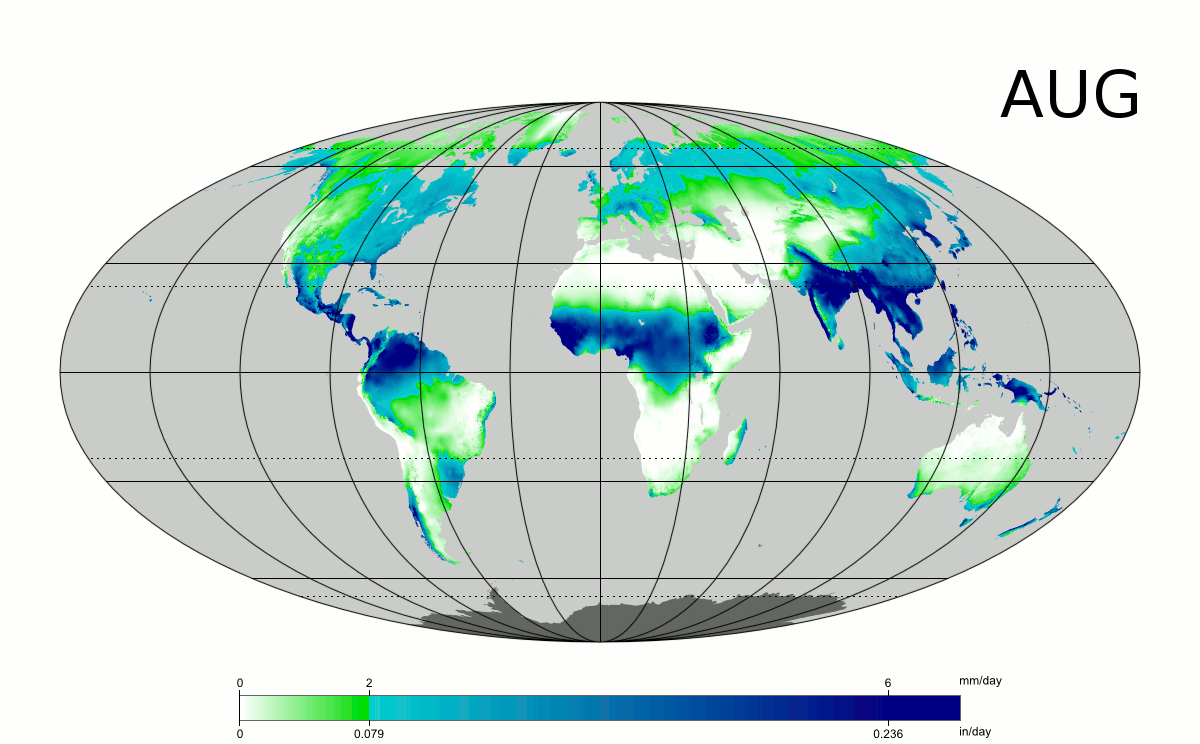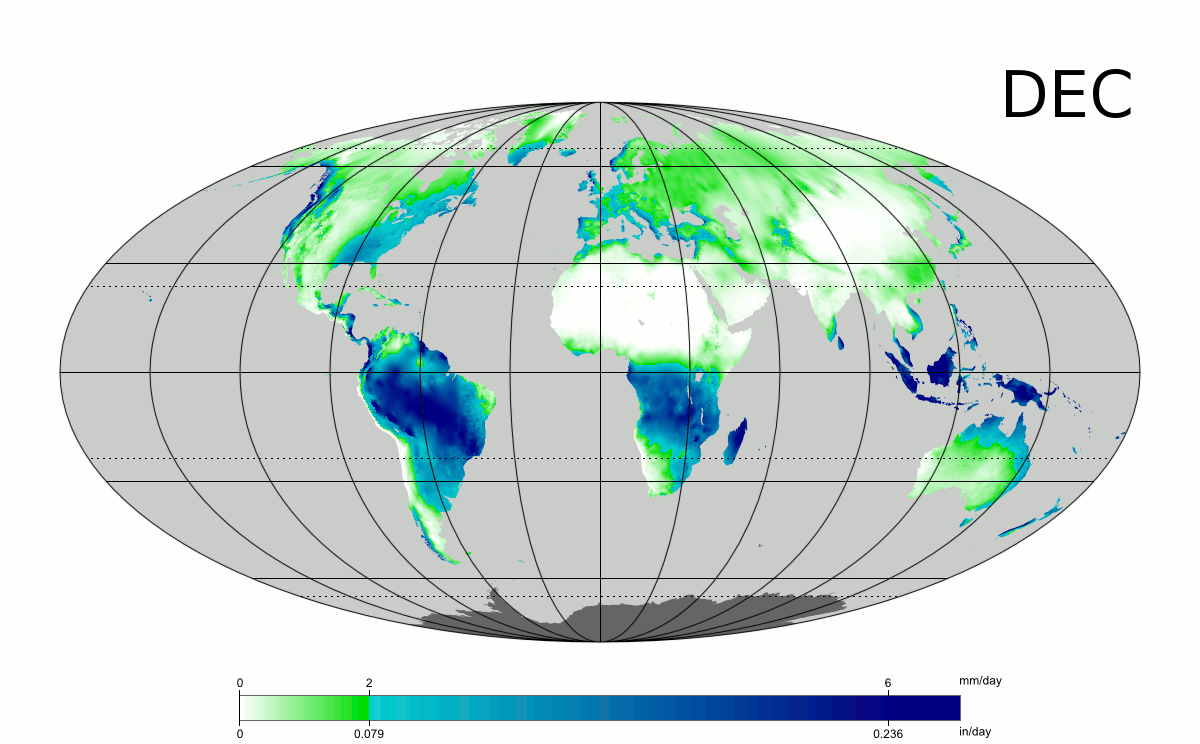 Westerly flow from the mild north Atlantic leads to wetness across western Europe, in particular Ireland and the United Kingdom, where the western coasts can receive between , at sea level and , on the mountains of rain per year.
Westerly flow from the mild north Atlantic leads to wetness across western Europe, in particular Ireland and the United Kingdom, where the western coasts can receive between , at sea level and , on the mountains of rain per year.
Normal Monthly Precipitation, Inches.
Retrieved on 19 March 2008. Over the top of the ridge, the jet stream brings a summer precipitation maximum to the
Distribution of Mesoscale Convective Complex Rainfall in the United States.
Retrieved on 2 March 2008. The
"Finding distant chips from distant maria"
pp. 8–9, ''Planetary Science Research Discoveries'', 30 April 2006.
BBC article on the weekend rain effectBBC article on rain-makingBBC article on the mathematics of running in the rain
{{Authority control Articles containing video clips
terrain
Terrain or relief (also topographical relief) involves the vertical and horizontal dimensions of land surface. The term bathymetry is used to describe underwater relief, while hypsometry studies terrain relative to sea level. The Latin word ...
at elevation which forces moist air to condense and fall out as rainfall along the sides of mountains. On the leeward
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference ...
side of mountains, desert climates can exist due to the dry air caused by downslope flow which causes heating and drying of the air mass. The movement of the monsoon trough, or intertropical convergence zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal e ...
, brings rainy seasons
The wet season (sometimes called the Rainy season) is the time of year when most of a region's average annual rainfall occurs. It is the time of year where the majority of a country's or region's annual precipitation occurs. Generally, the sea ...
to savannah
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the Canopy (forest), canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to rea ...
climes.
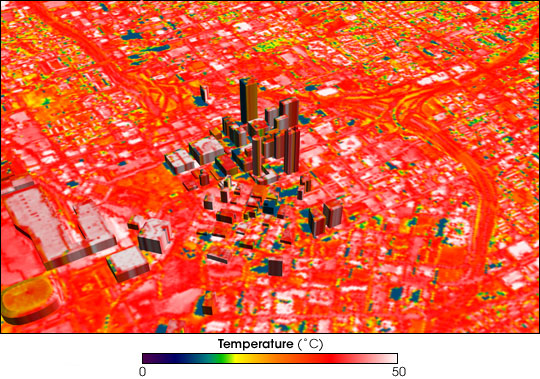
The urban heat island
An urban heat island (UHI) is an urban or metropolitan area that is significantly warmer than its surrounding rural areas due to human activities. The temperature difference is usually larger at night than during the day, and is most apparen ...
effect leads to increased rainfall, both in amounts and intensity, downwind of cities. Global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
is also causing changes in the precipitation pattern globally, including wetter conditions across eastern North America and drier conditions in the tropics. Antarctica is the driest continent. The globally averaged annual precipitation over land is , but over the whole Earth it is much higher at . Climate classification
Climate classifications are systems that categorize the world's climates. A climate classification may correlate closely with a biome classification, as climate is a major influence on life in a region. One of the most used is the Köppen climate ...
systems such as the Köppen classification system use average annual rainfall to help differentiate between differing climate regimes. Rainfall is measured using rain gauges. Rainfall amounts can be estimated by weather radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar (WSR) and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, and estimate its type (rain, snow, hail etc.). Modern weather radars are mostly puls ...
.
Rain is also known or suspected on other planets, where it may be composed of methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Eart ...
, neon
Neon is a chemical element with the symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is a noble gas. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with about two-thirds the density of air. It was discovered (along with krypton ...
, sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
, or even iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
rather than water.
Formation
Water-saturated air
 Air contains water vapor, and the amount of water in a given mass of dry air, known as the ''mixing ratio'', is measured in grams of water per kilogram of dry air (g/kg). The amount of moisture in air is also commonly reported as
Air contains water vapor, and the amount of water in a given mass of dry air, known as the ''mixing ratio'', is measured in grams of water per kilogram of dry air (g/kg). The amount of moisture in air is also commonly reported as relative humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depe ...
; which is the percentage of the total water vapor air can hold at a particular air temperature. How much water vapor a parcel of air can contain before it becomes saturated (100% relative humidity) and forms into a cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may co ...
(a group of visible and tiny water and ice particle
In the Outline of physical science, physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscule in older texts) is a small wikt:local, localized physical body, object which can be described by several physical property, physical or chemical property, chemical ...
s suspended above the Earth's surface) depends on its temperature. Warmer air can contain more water vapor than cooler air before becoming saturated. Therefore, one way to saturate a parcel of air is to cool it. The dew point
The dew point is the temperature to which air must be cooled to become saturated with water vapor, assuming constant air pressure and water content. When cooled below the dew point, moisture capacity is reduced and airborne water vapor will cond ...
is the temperature to which a parcel must be cooled in order to become saturated.
 There are four main mechanisms for cooling the air to its dew point: adiabatic cooling, conductive cooling, radiational cooling, and evaporative cooling. Adiabatic cooling occurs when air rises and expands. The air can rise due to
There are four main mechanisms for cooling the air to its dew point: adiabatic cooling, conductive cooling, radiational cooling, and evaporative cooling. Adiabatic cooling occurs when air rises and expands. The air can rise due to convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convec ...
, large-scale atmospheric motions, or a physical barrier such as a mountain ( orographic lift). Conductive cooling occurs when the air comes into contact with a colder surface, usually by being blown from one surface to another, for example from a liquid water surface to colder land. Radiational cooling occurs due to the emission of infrared radiation, either by the air or by the surface underneath. Evaporative cooling occurs when moisture is added to the air through evaporation, which forces the air temperature to cool to its wet-bulb temperature
The wet-bulb temperature (WBT) is the temperature read by a thermometer covered in water-soaked (water at ambient temperature) cloth (a wet-bulb thermometer) over which air is passed. At 100% relative humidity, the wet-bulb temperature is equal ...
, or until it reaches saturation.
The main ways water vapor is added to the air are: wind convergence into areas of upward motion, precipitation or virga falling from above, daytime heating evaporating water from the surface of oceans, water bodies or wet land, transpiration from plants, cool or dry air moving over warmer water, and lifting air over mountains. Water vapor normally begins to condense on condensation nuclei
Cloud condensation nuclei (CCNs), also known as cloud seeds, are small particles typically 0.2 µm, or one hundredth the size of a cloud droplet. CCNs are a unique subset of aerosols in the atmosphere on which water vapour condenses. This ca ...
such as dust, ice, and salt in order to form clouds. Elevated portions of weather fronts (which are three-dimensional in nature) force broad areas of upward motion within the Earth's atmosphere which form clouds decks such as altostratus or cirrostratus. Stratus
Stratus may refer to:
Weather
*Stratus cloud, a cloud type
**Nimbostratus cloud, a cloud type
**Stratocumulus cloud, a cloud type
**Altostratus cloud, a cloud type
**Altostratus undulatus cloud, a cloud type
**Cirrostratus cloud, a cloud type
Mus ...
is a stable cloud deck which tends to form when a cool, stable air mass is trapped underneath a warm air mass. It can also form due to the lifting of advection fog
In the field of physics, engineering, and earth sciences, advection is the transport of a substance or quantity by bulk motion of a fluid. The properties of that substance are carried with it. Generally the majority of the advected substance is al ...
during breezy conditions.
Coalescence and fragmentation
Coalescence
Coalescence may refer to:
* Coalescence (chemistry), the process by which two or more separate masses of miscible substances seem to "pull" each other together should they make the slightest contact
* Coalescence (computer science), the merging of ...
occurs when water droplets fuse to create larger water droplets. Air resistance typically causes the water droplets in a cloud to remain stationary. When air turbulence occurs, water droplets collide, producing larger droplets.
 As these larger water droplets descend, coalescence continues, so that drops become heavy enough to overcome air resistance and fall as rain. Coalescence generally happens most often in clouds above freezing, and is also known as the warm rain process. In clouds below freezing, when ice crystals gain enough mass they begin to fall. This generally requires more mass than coalescence when occurring between the crystal and neighboring water droplets. This process is temperature dependent, as supercooled water droplets only exist in a cloud that is below freezing. In addition, because of the great temperature difference between cloud and ground level, these ice crystals may melt as they fall and become rain.
Raindrops have sizes ranging from mean diameter but develop a tendency to break up at larger sizes. Smaller drops are called cloud droplets, and their shape is spherical. As a raindrop increases in size, its shape becomes more oblate, with its largest cross-section facing the oncoming airflow. Large rain drops become increasingly flattened on the bottom, like
As these larger water droplets descend, coalescence continues, so that drops become heavy enough to overcome air resistance and fall as rain. Coalescence generally happens most often in clouds above freezing, and is also known as the warm rain process. In clouds below freezing, when ice crystals gain enough mass they begin to fall. This generally requires more mass than coalescence when occurring between the crystal and neighboring water droplets. This process is temperature dependent, as supercooled water droplets only exist in a cloud that is below freezing. In addition, because of the great temperature difference between cloud and ground level, these ice crystals may melt as they fall and become rain.
Raindrops have sizes ranging from mean diameter but develop a tendency to break up at larger sizes. Smaller drops are called cloud droplets, and their shape is spherical. As a raindrop increases in size, its shape becomes more oblate, with its largest cross-section facing the oncoming airflow. Large rain drops become increasingly flattened on the bottom, like hamburger
A hamburger, or simply burger, is a food consisting of fillings—usually a patty of ground meat, typically Ground beef, beef—placed inside a sliced bun or bread roll. Hamburgers are often served with cheese, lettuce, tomato, onion, pickles ...
buns; very large ones are shaped like parachute
A parachute is a device used to slow the motion of an object through an atmosphere by creating drag or, in a ram-air parachute, aerodynamic lift. A major application is to support people, for recreation or as a safety device for aviators, who ...
s. Contrary to popular belief, their shape does not resemble a teardrop. The biggest raindrops on Earth were recorded over Brazil and the Marshall Islands
The Marshall Islands ( mh, Ṃajeḷ), officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands ( mh, Aolepān Aorōkin Ṃajeḷ),'' () is an independent island country and microstate near the Equator in the Pacific Ocean, slightly west of the Internati ...
in 2004 — some of them were as large as . The large size is explained by condensation on large smoke particles or by collisions between drops in small regions with particularly high content of liquid water.
Rain drops associated with melting hail tend to be larger than other rain drops.
Droplet size distribution
The final droplet size distribution is anexponential distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the exponential distribution is the probability distribution of the time between events in a Poisson point process, i.e., a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average ...
. The number of droplets with diameter between and per unit volume of space is . This is commonly referred to as the Marshall–Palmer law after the researchers who first characterized it.
* The parameters are somewhat temperature-dependent, and the slope also scales with the rate of rainfall (d in centimeters and R in millimeters per hour).
Deviations can occur for small droplets and during different rainfall conditions. The distribution tends to fit averaged rainfall, while instantaneous size spectra often deviate and have been modeled as gamma distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the gamma distribution is a two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. The exponential distribution, Erlang distribution, and chi-square distribution are special cases of the gamma distri ...
s. The distribution has an upper limit due to droplet fragmentation.
Raindrop impacts
Raindrops impact at their terminal velocity, which is greater for larger drops due to their larger mass to drag ratio. At sea level and without wind, drizzle impacts at or , while large drops impact at around or . Rain falling on loosely packed material such as newly fallen ash can produce dimples that can be fossilized, calledraindrop impressions
Raindrop impressions are a geological feature characterized by small crater-like pits with slightly raised edges that are the result of the impact of Rain#Raindrop impacts, raindrop impacts on soft sediment surfaces.
Sedimentary structures with si ...
. The air density dependence of the maximum raindrop diameter together with fossil raindrop imprints has been used to constrain the density of the air 2.7 billion years ago.
The sound of raindrops hitting water is caused by bubbles of air oscillating underwater.
The METAR
METAR is a format for reporting weather information. A METAR weather report is predominantly used by aircraft pilots, and by meteorologists, who use aggregated METAR information to assist in weather forecasting.
Raw METAR is the most common form ...
code for rain is RA, while the coding for rain showers is SHRA.
Virga
In certain conditions precipitation may fall from a cloud but then evaporate orsublime
Sublime may refer to:
Entertainment
* SuBLime, a comic imprint of Viz Media for BL manga
* Sublime (band), an American ska punk band
** ''Sublime'' (album), 1996
* ''Sublime'' (film), a 2007 horror film
* SubLime FM, a Dutch radio station dedic ...
before reaching the ground. This is termed virga and is more often seen in hot and dry climates.
Causes
Frontal activity
Stratiform (a broad shield of precipitation with a relatively similar intensity) and dynamic precipitation (convective precipitation which is showery in nature with large changes in intensity over short distances) occur as a consequence of slow ascent of air in synoptic systems (on the order of cm/s), such as in the vicinity of cold fronts and near and poleward of surface warm fronts. Similar ascent is seen aroundtropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
s outside the eyewall, and in comma-head precipitation patterns around mid-latitude cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of ...
s. A wide variety of weather can be found along an occluded front, with thunderstorms possible, but usually their passage is associated with a drying of the air mass. Occluded fronts usually form around mature low-pressure areas. What separates rainfall from other precipitation types, such as ice pellets
Ice pellets are a form of precipitation consisting of small, hard, translucent balls of ice. Ice pellets are different from graupel ("soft hail") which is made of frosty white opaque rime, and from a mixture of rain and snow which is a slushy ...
and snow, is the presence of a thick layer of air aloft which is above the melting point of water, which melts the frozen precipitation well before it reaches the ground. If there is a shallow near surface layer that is below freezing, freezing rain (rain which freezes on contact with surfaces in subfreezing environments) will result. Hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fal ...
becomes an increasingly infrequent occurrence when the freezing level within the atmosphere exceeds above ground level.
Convection
 Convective rain, or showery precipitation, occurs from convective clouds (e.g., cumulonimbus or cumulus congestus). It falls as showers with rapidly changing intensity. Convective precipitation falls over a certain area for a relatively short time, as convective clouds have limited horizontal extent. Most precipitation in the
Convective rain, or showery precipitation, occurs from convective clouds (e.g., cumulonimbus or cumulus congestus). It falls as showers with rapidly changing intensity. Convective precipitation falls over a certain area for a relatively short time, as convective clouds have limited horizontal extent. Most precipitation in the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
appears to be convective; however, it has been suggested that stratiform precipitation also occurs. Graupel
Graupel (; ), also called soft hail, hominy snow, or snow pellets, is precipitation that forms when supercooled water droplets in air are collected and freeze on falling snowflakes, forming balls of crisp, opaque rime.
Graupel is distinct from ...
and hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fal ...
indicate convection. In mid-latitudes, convective precipitation is intermittent and often associated with baroclinic boundaries such as cold fronts, squall lines, and warm fronts.
Orographic effects
Orographic precipitation occurs on the windward side of mountains and is caused by the rising air motion of a large-scale flow of moist air across the mountain ridge, resulting in adiabatic cooling and condensation. In mountainous parts of the world subjected to relatively consistent winds (for example, the trade winds), a more moistclimate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologic ...
usually prevails on the windward side of a mountain than on the leeward
Windward () and leeward () are terms used to describe the direction of the wind. Windward is ''upwind'' from the point of reference, i.e. towards the direction from which the wind is coming; leeward is ''downwind'' from the point of reference ...
or downwind side. Moisture is removed by orographic lift, leaving drier air (see katabatic wind) on the descending and generally warming, leeward side where a rain shadow
A rain shadow is an area of significantly reduced rainfall behind a mountainous region, on the side facing away from prevailing winds, known as its leeward side.
Evaporated moisture from water bodies (such as oceans and large lakes) is carrie ...
is observed.
In Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
, Mount Waiʻaleʻale
Mount Waialeale is a shield volcano and the second highest point on the island of Kauai in the Hawaiian Islands. Its name literally means "rippling water" or "overflowing water"
The mountain, at an elevation of , averages more than of rain a ...
, on the island of Kauai, is notable for its extreme rainfall, as it is amongst the places in the world with the highest levels of rainfall, with . Systems known as Kona storm
Kona storms (also called Kona lows) are a type of seasonal cyclone in the Hawaiian Islands, usually formed in the winter from winds coming from the westerly "kona" (normally leeward) direction. They are mainly cold core cyclones, which places the ...
s affect the state with heavy rains between October and April.Steven Businger and Thomas Birchard JrA Bow Echo and Severe Weather Associated with a Kona Low in Hawaii.
Retrieved on 22 May 2007. Local climates vary considerably on each island due to their topography, divisible into windward (''Koolau'') and leeward (''Kona'') regions based upon location relative to the higher mountains. Windward sides face the east to northeast
trade winds
The trade winds or easterlies are the permanent east-to-west prevailing winds that flow in the Earth's equatorial region. The trade winds blow mainly from the northeast in the Northern Hemisphere and from the southeast in the Southern Hemisph ...
and receive much more rainfall; leeward sides are drier and sunnier, with less rain and less cloud cover.
In South America, the Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
mountain range blocks Pacific moisture that arrives in that continent, resulting in a desertlike climate just downwind across western Argentina. The Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily ...
range creates the same effect in North America forming the Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic basin, endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California ...
and Mojave Desert
The Mojave Desert ( ; mov, Hayikwiir Mat'aar; es, Desierto de Mojave) is a desert in the rain shadow of the Sierra Nevada mountains in the Southwestern United States. It is named for the indigenous Mojave people. It is located primarily in ...
s.
Within the tropics
euphemism
A euphemism () is an innocuous word or expression used in place of one that is deemed offensive or suggests something unpleasant. Some euphemisms are intended to amuse, while others use bland, inoffensive terms for concepts that the user wishes ...
by tourist authorities. Areas with wet seasons are dispersed across portions of the tropics
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
and subtropics
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north and ...
. Savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to ...
climates and areas with monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
regimes have wet summers and dry winters. Tropical rainforests technically do not have dry or wet seasons, since their rainfall is equally distributed through the year. Some areas with pronounced rainy seasons will see a break in rainfall mid-season when the intertropical convergence zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal e ...
or monsoon trough move poleward of their location during the middle of the warm season. When the wet season occurs during the warm season, or summer
Summer is the hottest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, the earliest sunrise and latest sunset occurs, daylight hours are longest and dark hours are shortest, wit ...
, rain falls mainly during the late afternoon and early evening hours. The wet season is a time when air quality improves, freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
quality improves, and vegetation grows significantly.
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
s, a source of very heavy rainfall, consist of large air masses several hundred miles across with low pressure at the centre and with winds blowing inward towards the centre in either a clockwise direction (southern hemisphere) or counter clockwise (northern hemisphere). Although cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an anti ...
s can take an enormous toll in lives and personal property, they may be important factors in the precipitation regimes of places they impact, as they may bring much-needed precipitation to otherwise dry regions. Areas in their path can receive a year's worth of rainfall from a tropical cyclone passage.
Human influence

cloud condensation nuclei
Cloud condensation nuclei (CCNs), also known as cloud seeds, are small particles typically 0.2 µm, or one hundredth the size of a cloud droplet. CCNs are a unique subset of aerosols in the atmosphere on which water vapour condenses. This c ...
, leads to the production of clouds and increases the likelihood of rain. As commuters and commercial traffic cause pollution to build up over the course of the week, the likelihood of rain increases: it peaks by Saturday, after five days of weekday pollution has been built up. In heavily populated areas that are near the coast, such as the United States' Eastern Seaboard, the effect can be dramatic: there is a 22% higher chance of rain on Saturdays than on Mondays. The urban heat island effect warms cities 0.6 to 5.6 °C (1.1 to 10.1 °F) above surrounding suburbs and rural areas. This extra heat leads to greater upward motion, which can induce additional shower and thunderstorm activity. Rainfall rates downwind of cities are increased between 48% and 116%. Partly as a result of this warming, monthly rainfall is about 28% greater between downwind of cities, compared with upwind. Some cities induce a total precipitation increase of 51%.
Increasing temperatures tend to increase evaporation which can lead to more precipitation. Precipitation generally increased over land north of 30°N from 1900 through 2005 but has declined over the tropics since the 1970s. Globally there has been no statistically significant overall trend in precipitation over the past century, although trends have varied widely by region and over time. Eastern portions of North and South America, northern Europe, and northern and central Asia have become wetter. The Sahel, the Mediterranean, southern Africa and parts of southern Asia have become drier. There has been an increase in the number of heavy precipitation events over many areas during the past century, as well as an increase since the 1970s in the prevalence of droughts—especially in the tropics and subtropics. Changes in precipitation and evaporation over the oceans are suggested by the decreased salinity of mid- and high-latitude waters (implying more precipitation), along with increased salinity in lower latitudes (implying less precipitation and/or more evaporation). Over the contiguous United States, total annual precipitation increased at an average rate of 6.1 percent since 1900, with the greatest increases within the East North Central climate region (11.6 percent per century) and the South (11.1 percent). Hawaii was the only region to show a decrease (−9.25 percent).
Analysis of 65 years of United States of America rainfall records show the lower 48 states have an increase in heavy downpours since 1950. The largest increases are in the Northeast and Midwest, which in the past decade, have seen 31 and 16 percent more heavy downpours compared to the 1950s. Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
is the state with the largest increase, 104%. McAllen, Texas is the city with the largest increase, 700%. Heavy downpour in the analysis are the days where total precipitation exceeded the top one percent of all rain and snow days during the years 1950–2014.
The most successful attempts at influencing weather involve cloud seeding
Cloud seeding is a type of weather modification that aims to change the amount or type of precipitation that falls from clouds by dispersing substances into the air that serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei, which alter the microphysical p ...
, which include techniques used to increase winter precipitation over mountains and suppress hail
Hail is a form of solid precipitation. It is distinct from ice pellets (American English "sleet"), though the two are often confused. It consists of balls or irregular lumps of ice, each of which is called a hailstone. Ice pellets generally fal ...
.
Characteristics
Patterns

Rainband
A rainband is a cloud and precipitation structure associated with an area of rainfall which is significantly elongated. Rainbands can be stratiform or convective, and are generated by differences in temperature. When noted on weather radar ima ...
s are cloud and precipitation areas which are significantly elongated. Rainbands can be stratiform
Stratiform may refer to:
* Any of the stratus family of clouds (fog, stratus clouds, altostratus clouds, cirrostratus clouds, nimbostratus clouds) and the precipitation coming from them.
* Any occurrence of layered strata (see stratigraphic unit). ...
or convective
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convect ...
, and are generated by differences in temperature. When noted on weather radar
Weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar (WSR) and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation, calculate its motion, and estimate its type (rain, snow, hail etc.). Modern weather radars are mostly puls ...
imagery, this precipitation elongation is referred to as banded structure. Rainbands in advance of warm occluded front
In meteorology, an occluded front is a type of weather front formed during cyclogenesis. The classical and usual view of an occluded front is that it initiates when a cold front overtakes a warm front near a cyclone, such that the warm air is separ ...
s and warm fronts are associated with weak upward motion, and tend to be wide and stratiform in nature.
Rainbands spawned near and ahead of cold fronts can be squall lines which are able to produce tornado
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the Earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. It is often referred to as a twister, whirlwind or cyclone, altho ...
es. Rainbands associated with cold fronts can be warped by mountain barriers perpendicular to the front's orientation due to the formation of a low-level barrier jet
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow, meandering air currents in the atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. On Earth, the main jet streams are located near the altitude of the tropopause and are westerly winds (flowing west to east). ...
. Bands of thunderstorms can form with sea breeze
A sea breeze or onshore breeze is any wind that blows from a large body of water toward or onto a landmass; it develops due to differences in air pressure created by the differing heat capacities of water and dry land. As such, sea breezes ar ...
and land breeze boundaries, if enough moisture is present. If sea breeze rainbands become active enough just ahead of a cold front, they can mask the location of the cold front itself.
Once a cyclone occludes an occluded front
In meteorology, an occluded front is a type of weather front formed during cyclogenesis. The classical and usual view of an occluded front is that it initiates when a cold front overtakes a warm front near a cyclone, such that the warm air is separ ...
(a trough of warm air aloft) will be caused by strong southerly winds on its eastern periphery rotating aloft around its northeast, and ultimately northwestern, periphery (also termed the warm conveyor belt), forcing a surface trough to continue into the cold sector on a similar curve to the occluded front. The front creates the portion of an occluded cyclone known as its ''comma head'', due to the comma
The comma is a punctuation mark that appears in several variants in different languages. It has the same shape as an apostrophe or single closing quotation mark () in many typefaces, but it differs from them in being placed on the baseline ...
-like shape of the mid-tropospheric cloudiness that accompanies the feature. It can also be the focus of locally heavy precipitation, with thunderstorms possible if the atmosphere along the front is unstable enough for convection. Banding within the comma head precipitation pattern of an extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of ...
can yield significant amounts of rain. Behind extratropical cyclones during fall and winter, rainbands can form downwind of relative warm bodies of water such as the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
. Downwind of islands, bands of showers and thunderstorms can develop due to low level wind convergence downwind of the island edges. Offshore California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
, this has been noted in the wake of cold fronts.
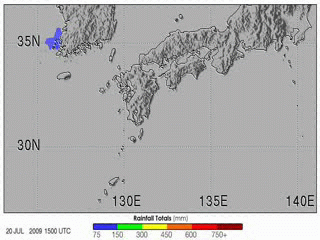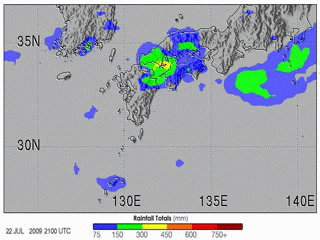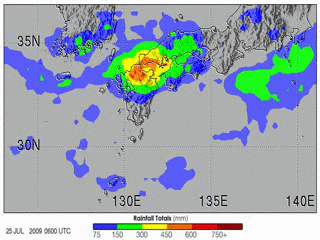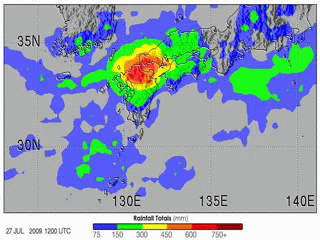
Rainbands within tropical cyclones are curved in orientation. Tropical cyclone rainbands contain showers and thunderstorms that, together with the eyewall and the eye, constitute a hurricane or tropical storm. The extent of rainbands around a tropical cyclone can help determine the cyclone's intensity.University of Wisconsin–Madison
A university () is an educational institution, institution of higher education, higher (or Tertiary education, tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several Discipline (academia), academic disciplines. Universities ty ...
(1998Objective Dvorak Technique.
Retrieved on 29 May 2006.
Acidity
sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
(H2SO4) and nitric acid
Nitric acid is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but older samples tend to be yellow cast due to decomposition into oxides of nitrogen. Most commercially available nitri ...
(HNO3). Sulfuric acid is derived from natural sources such as volcanoes, and wetlands (sulfate reducing bacteria); and anthropogenic sources such as the combustion of fossil fuels, and mining where H2S is present. Nitric acid is produced by natural sources such as lightning, soil bacteria, and natural fires; while also produced anthropogenically by the combustion of fossil fuels and from power plants. In the past 20 years the concentrations of nitric and sulfuric acid has decreased in presence of rainwater, which may be due to the significant increase in ammonium (most likely as ammonia from livestock production), which acts as a buffer
Buffer may refer to:
Science
* Buffer gas, an inert or nonflammable gas
* Buffer solution, a solution used to prevent changes in pH
* Buffering agent, the weak acid or base in a buffer solution
* Lysis buffer, in cell biology
* Metal ion buffer
* ...
in acid rain and raises the pH.
Köppen climate classification
monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
, tropical savanna, humid subtropical, humid continental, oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
, Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
, steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate grasslands, ...
, subarctic climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, ge ...
, tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless moun ...
, polar ice cap
A polar ice cap or polar cap is a high-latitude region of a planet, dwarf planet, or natural satellite that is covered in ice.
There are no requirements with respect to size or composition for a body of ice to be termed a polar ice cap, nor a ...
, and desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
.
Rain forests are characterized by high rainfall, with definitions setting minimum normal annual rainfall between . A tropical savanna is a grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur natur ...
biome
A biome () is a biogeographical unit consisting of a biological community that has formed in response to the physical environment in which they are found and a shared regional climate. Biomes may span more than one continent. Biome is a broader ...
located in semi-arid to semi-humid climate regions of subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical zone, geographical and Köppen climate classification, climate zones to the Northern Hemisphere, north and Southern Hemisphere, south of the tropics. Geographically part of the Geographical z ...
and tropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
latitudes
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
, with rainfall between a year. They are widespread on Africa, and are also found in India, the northern parts of South America, Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
, and Australia. The humid subtropical climate zone is where winter rainfall is associated with large storms that the westerlies
The westerlies, anti-trades, or prevailing westerlies, are prevailing winds from the west toward the east in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude. They originate from the high-pressure areas in the horse latitudes and trend to ...
steer from west to east. Most summer rainfall occurs during thunderstorms and from occasional tropical cyclones. Humid subtropical climates lie on the east side continents, roughly between latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
s 20° and 40° degrees away from the equator.
An oceanic (or maritime) climate is typically found along the west coasts at the middle latitudes of all the world's continents, bordering cool oceans, as well as southeastern Australia, and is accompanied by plentiful precipitation year-round. The Mediterranean climate regime resembles the climate of the lands in the Mediterranean Basin
In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin (; also known as the Mediterranean Region or sometimes Mediterranea) is the region of lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have mostly a Mediterranean climate, with mild to cool, rainy winters and w ...
, parts of western North America, parts of Western and South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
, in southwestern South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring countri ...
and in parts of central Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
. The climate is characterized by hot, dry summers and cool, wet winters. A steppe is a dry grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses (Poaceae). However, sedge (Cyperaceae) and rush (Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur natur ...
. Subarctic climates are cold with continuous permafrost
Permafrost is ground that continuously remains below 0 °C (32 °F) for two or more years, located on land or under the ocean. Most common in the Northern Hemisphere, around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surface ...
and little precipitation.
Pollution
Measurement
Gauges
 Rain is measured in units of length per unit time, typically in millimeters per hour, or in countries where imperial units are more common, inches per hour. The "length", or more accurately, "depth" being measured is the depth of rain water that would accumulate on a flat, horizontal and impermeable surface during a given amount of time, typically an hour. One millimeter of rainfall is the equivalent of one liter of water per square meter.
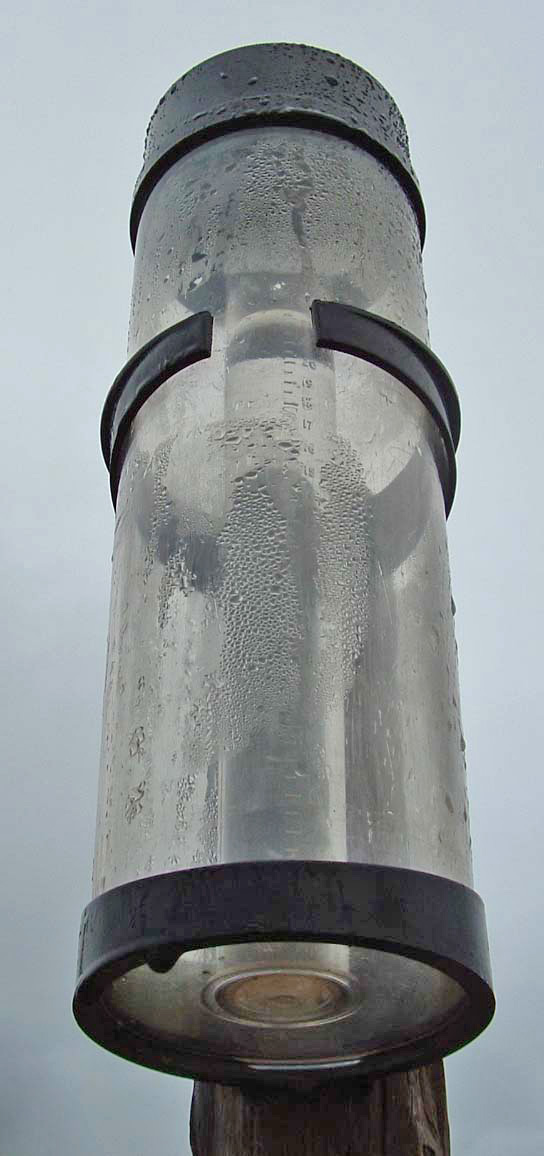
The standard way of measuring rainfall or snowfall is the standard rain gauge, which can be found in 100-mm (4-in) plastic and 200-mm (8-in) metal varieties. The inner cylinder is filled by of rain, with overflow flowing into the outer cylinder. Plastic gauges have markings on the inner cylinder down to resolution, while metal gauges require use of a stick designed with the appropriate markings. After the inner cylinder is filled, the amount inside it is discarded, then filled with the remaining rainfall in the outer cylinder until all the fluid in the outer cylinder is gone, adding to the overall total until the outer cylinder is empty. Other types of gauges include the popular wedge gauge (the cheapest rain gauge and most fragile), the tipping bucket rain gauge, and the weighing rain gauge. For those looking to measure rainfall the most inexpensively, a can that is cylindrical with straight sides will act as a rain gauge if left out in the open, but its accuracy will depend on what ruler is used to measure the rain with. Any of the above rain gauges can be made at home, with enough know-how.
When a precipitation measurement is made, various networks exist across the United States and elsewhere where rainfall measurements can be submitted through the Internet, such as
Rain is measured in units of length per unit time, typically in millimeters per hour, or in countries where imperial units are more common, inches per hour. The "length", or more accurately, "depth" being measured is the depth of rain water that would accumulate on a flat, horizontal and impermeable surface during a given amount of time, typically an hour. One millimeter of rainfall is the equivalent of one liter of water per square meter.
The standard way of measuring rainfall or snowfall is the standard rain gauge, which can be found in 100-mm (4-in) plastic and 200-mm (8-in) metal varieties. The inner cylinder is filled by of rain, with overflow flowing into the outer cylinder. Plastic gauges have markings on the inner cylinder down to resolution, while metal gauges require use of a stick designed with the appropriate markings. After the inner cylinder is filled, the amount inside it is discarded, then filled with the remaining rainfall in the outer cylinder until all the fluid in the outer cylinder is gone, adding to the overall total until the outer cylinder is empty. Other types of gauges include the popular wedge gauge (the cheapest rain gauge and most fragile), the tipping bucket rain gauge, and the weighing rain gauge. For those looking to measure rainfall the most inexpensively, a can that is cylindrical with straight sides will act as a rain gauge if left out in the open, but its accuracy will depend on what ruler is used to measure the rain with. Any of the above rain gauges can be made at home, with enough know-how.
When a precipitation measurement is made, various networks exist across the United States and elsewhere where rainfall measurements can be submitted through the Internet, such as CoCoRAHS
The Community Collaborative Rain, Hail and Snow Network, or CoCoRaHS, is a network of volunteer weather observers in the United States, Canada, and the Bahamas that take daily readings of precipitation and report them to a central data store over ...
or GLOBE. If a network is not available in the area where one lives, the nearest local weather or met office will likely be interested in the measurement.
Remote sensing
 One of the main uses of weather radar is to be able to assess the amount of precipitations fallen over large basins for hydrological purposes. For instance, river
One of the main uses of weather radar is to be able to assess the amount of precipitations fallen over large basins for hydrological purposes. For instance, river flood control
Flood control methods are used to reduce or prevent the detrimental effects of flood waters."Flood Control", MSN Encarta, 2008 (see below: Further reading). Flood relief methods are used to reduce the effects of flood waters or high water level ...
, sewer management and dam construction are all areas where planners use rainfall accumulation data. Radar-derived rainfall estimates complement surface station data which can be used for calibration. To produce radar accumulations, rain rates over a point are estimated by using the value of reflectivity data at individual grid points. A radar equation is then used, which is
where Z represents the radar reflectivity, R represents the rainfall rate, and A and b are constants.
Satellite derived rainfall estimates use passive microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one meter to one millimeter corresponding to frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz respectively. Different sources define different frequency ran ...
instruments aboard polar orbiting as well as geostationary
A geostationary orbit, also referred to as a geosynchronous equatorial orbit''Geostationary orbit'' and ''Geosynchronous (equatorial) orbit'' are used somewhat interchangeably in sources. (GEO), is a circular geosynchronous orbit in altitude ...
weather satellite
A weather satellite or meteorological satellite is a type of Earth observation satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites can be polar orbiting (covering the entire Earth asynchronously), or ge ...
s to indirectly measure rainfall rates. If one wants an accumulated rainfall over a time period, one has to add up all the accumulations from each grid box within the images during that time.
Intensity
The following categories are used to classify rainfall intensity: * Light rain — when the precipitation rate is < per hour * Moderate rain — when the precipitation rate is between – or per hour * Heavy rain — when the precipitation rate is > per hour, or between and per hour * Violent rain — when the precipitation rate is > per hour Euphemisms for a heavy or violent rain include gully washer, trash-mover and toad-strangler. The intensity can also be expressed by rainfall erosivity ''R-factor'' or in terms of the rainfall time-structure ''n-index''.
Return period
The average time between occurrences of an event with a specified intensity and duration is called the return period. The intensity of a storm can be predicted for any return period and storm duration, from charts based on historic data for the location. The return period is often expressed as an ''n''-year event. For instance, a 10-year storm describes a rare rainfall event occurring on average once every 10 years. The rainfall will be greater and the flooding will be worse than the worst storm expected in any single year. A 100-year storm describes an extremely rare rainfall event occurring on average once in a century. The rainfall will be extreme and flooding worse than a 10-year event. The probability of an event in any year is the inverse of the return period (assuming the probability remains the same for each year). For instance a 10-year storm has a probability of occurring of 10 percent in any given year, and a 100-year storm occurs with a 1 percent probability in a year. As with all probability events, it is possible, though improbable, to have multiple 100-year storms in a single year.Forecasting
 The Quantitative Precipitation Forecast (abbreviated QPF) is the expected amount of liquid precipitation accumulated over a specified time period over a specified area. A QPF will be specified when a measurable precipitation type reaching a minimum threshold is forecast for any hour during a QPF valid period. Precipitation forecasts tend to be bound by synoptic hours such as 0000, 0600, 1200 and 1800 GMT. Terrain is considered in QPFs by use of topography or based upon climatological precipitation patterns from observations with fine detail. Starting in the mid to late 1990s, QPFs were used within hydrologic forecast models to simulate impact to rivers throughout the United States.
Forecast models show significant sensitivity to humidity levels within the planetary boundary layer, or in the lowest levels of the atmosphere, which decreases with height. QPF can be generated on a quantitative, forecasting amounts, or a qualitative, forecasting the probability of a specific amount, basis. Radar imagery forecasting techniques show higher
The Quantitative Precipitation Forecast (abbreviated QPF) is the expected amount of liquid precipitation accumulated over a specified time period over a specified area. A QPF will be specified when a measurable precipitation type reaching a minimum threshold is forecast for any hour during a QPF valid period. Precipitation forecasts tend to be bound by synoptic hours such as 0000, 0600, 1200 and 1800 GMT. Terrain is considered in QPFs by use of topography or based upon climatological precipitation patterns from observations with fine detail. Starting in the mid to late 1990s, QPFs were used within hydrologic forecast models to simulate impact to rivers throughout the United States.
Forecast models show significant sensitivity to humidity levels within the planetary boundary layer, or in the lowest levels of the atmosphere, which decreases with height. QPF can be generated on a quantitative, forecasting amounts, or a qualitative, forecasting the probability of a specific amount, basis. Radar imagery forecasting techniques show higher skill
A skill is the learned ability to act with determined results with good execution often within a given amount of time, energy, or both. Skills can often be divided into domain-general and domain-specific skills. For example, in the domain of wo ...
than model forecasts within 6 to 7 hours of the time of the radar image. The forecasts can be verified through use of rain gauge measurements, weather radar estimates, or a combination of both. Various skill scores can be determined to measure the value of the rainfall forecast.
Impact
Agricultural
 Precipitation, especially rain, has a dramatic effect on agriculture. All plants need at least some water to survive, therefore rain (being the most effective means of watering) is important to agriculture. While a regular rain pattern is usually vital to healthy plants, too much or too little rainfall can be harmful, even devastating to crops.
Precipitation, especially rain, has a dramatic effect on agriculture. All plants need at least some water to survive, therefore rain (being the most effective means of watering) is important to agriculture. While a regular rain pattern is usually vital to healthy plants, too much or too little rainfall can be harmful, even devastating to crops. Drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
can kill crops and increase erosion, while overly wet weather can cause harmful fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from th ...
growth. Plants need varying amounts of rainfall to survive. For example, certain cacti
A cactus (, or less commonly, cactus) is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word ''cactus'' derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Greek ...
require small amounts of water, while tropical plants may need up to hundreds of inches of rain per year to survive.
In areas with wet and dry seasons, soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former te ...
nutrients diminish and erosion increases during the wet season. Animals have adaptation and survival strategies for the wetter regime. The previous dry season leads to food shortages into the wet season, as the crops have yet to mature. Developing countries have noted that their populations show seasonal weight fluctuations due to food shortages seen before the first harvest, which occurs late in the wet season. Rain may be harvested through the use of rainwater tanks; treated to potable use or for non-potable use indoors or for irrigation. Excessive rain during short periods of time can cause flash flood
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice or snow flowing o ...
s.
Culture and religion
 Cultural attitudes towards rain differ across the world. In
Cultural attitudes towards rain differ across the world. In temperate climate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
s, people tend to be more stressed when the weather is unstable or cloudy, with its impact greater on men than women. Rain can also bring joy, as some consider it to be soothing or enjoy the aesthetic appeal of it. In dry places, such as India, or during periods of drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
, rain lifts people's moods. In Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label=Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kalahar ...
, the Setswana
Tswana, also known by its native name , and previously spelled Sechuana in English, is a Bantu language spoken in Southern Africa by about 8.2 million people. It belongs to the Bantu language family within the Sotho-Tswana branch of Zone ...
word for rain, ''pula'', is used as the name of the national currency, in recognition of the economic importance of rain in its country, since it has a desert climate. Several cultures have developed means of dealing with rain and have developed numerous protection devices such as umbrellas and raincoats, and diversion devices such as gutters and storm drain
A storm drain, storm sewer (United Kingdom, United States, U.S. and Canada), surface water drain/sewer (United Kingdom), or stormwater drain (Australia and New Zealand) is infrastructure designed to Drainage, drain excess rain and ground water ...
s that lead rains to sewers. Many people find the scent during and immediately after rain pleasant or distinctive. The source of this scent is petrichor
Petrichor () is the earthy olfaction, scent produced when rain falls on dry soil. The word is constructed , the ichor, ethereal fluid that is the blood of the gods in Greek mythology.
Origins
Long before this phenomenon received its name in 19 ...
, an oil produced by plants, then absorbed by rocks and soil, and later released into the air during rainfall.
 Rain holds an important religious significance in many cultures. The ancient
Rain holds an important religious significance in many cultures. The ancient Sumer
Sumer () is the earliest known civilization in the historical region of southern Mesopotamia (south-central Iraq), emerging during the Chalcolithic and early Bronze Ages between the sixth and fifth millennium BC. It is one of the cradles of c ...
ians believed that rain was the semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is an organic bodily fluid created to contain spermatozoa. It is secreted by the gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphroditic animals and can fertilize the female ovum. Semen i ...
of the sky-god
The sky often has important religious significance. Many religions, both polytheistic and monotheistic, have deities associated with the sky.
The daytime sky deities are typically distinct from the nighttime ones. Stith Thompson's ''Motif-In ...
An, which fell from the heavens to inseminate his consort, the earth-goddess Ki, causing her to give birth to all the plants of the earth. The Akkadians believed that the clouds were the breasts of Anu's consort Antu Antu may refer to:
* Antu (goddess), a goddess, in Akkadian mythology
* Antu (Mapuche mythology), the Pillan spirit in the Mapuche mythology
* Antu, India, a town in Pratapgarh District, Uttar Pradesh, India
* Antu County, in Jilin, China
* Alpha ...
and that rain was milk from her breasts. According to Jewish tradition, in the first century BC, the Jewish miracle-worker Honi ha-M'agel
Honi HaMe'agel (חוני המעגל Khoni, Choni, or Ḥoni; lit. Honi the Circle-drawer) was a Jewish scholar of the 1st-century BCE, during the age of the ''tannaim'', the scholars from whose teachings the Mishnah was derived.
During the 1st ce ...
ended a three-year drought in Judaea by drawing a circle in the sand and praying for rain, refusing to leave the circle until his prayer was granted. In his ''Meditations
''Meditations'' () is a series of personal writings by Marcus Aurelius, Roman Emperor from AD 161 to 180, recording his private notes to himself and ideas on Stoic philosophy.
Marcus Aurelius wrote the 12 books of the ''Meditations'' in Koine ...
'', the Roman emperor Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (Latin: áːɾkus̠ auɾέːli.us̠ antɔ́ːni.us̠ English: ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 AD and a Stoic philosopher. He was the last of the rulers known as the Five Good ...
preserves a prayer for rain made by the Athenians
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates a ...
to the Greek sky-god Zeus
Zeus or , , ; grc, Δῐός, ''Diós'', label=Genitive case, genitive Aeolic Greek, Boeotian Aeolic and Doric Greek#Laconian, Laconian grc-dor, Δεύς, Deús ; grc, Δέος, ''Déos'', label=Genitive case, genitive el, Δίας, ''D� ...
. Various Native American tribes are known to have historically conducted rain dances in effort to encourage rainfall. Rainmaking rituals are also important in many African cultures. In the present-day United States, various state governors have held Days of Prayer for rain, including the Days of Prayer for Rain in the State of Texas
The Days of Prayer for Rain in the State of Texas was a designated period from Friday, April 22, 2011, to Sunday, April 24, 2011, during which Texas governor Rick Perry asked that Texans pray for "the healing of our land exas and for an end to t ...
in 2011.
Global climatology
Approximately of water falls as precipitation each year across the globe with of it over the oceans. Given the Earth's surface area, that means the globally averaged annual precipitation is . Deserts are defined as areas with an average annual precipitation of less than per year, or as areas where more water is lost byevapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) is the combined processes by which water moves from the earth’s surface into the atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of water to the air directly from soil, canopies, and water bodies) and transpi ...
than falls as precipitation.
Deserts

 The northern half of Africa is dominated by the world's most extensive hot, dry region, the Sahara Desert. Some deserts also occupy much of southern Africa: the Namib and the Kalahari. Across Asia, a large annual rainfall minimum, composed primarily of deserts, stretches from the
The northern half of Africa is dominated by the world's most extensive hot, dry region, the Sahara Desert. Some deserts also occupy much of southern Africa: the Namib and the Kalahari. Across Asia, a large annual rainfall minimum, composed primarily of deserts, stretches from the Gobi Desert
The Gobi Desert (Chinese: 戈壁 (沙漠), Mongolian: Говь (ᠭᠣᠪᠢ)) () is a large desert or brushland region in East Asia, and is the sixth largest desert in the world.
Geography
The Gobi measures from southwest to northeast an ...
in Mongolia west-southwest through western Pakistan (Balochistan
Balochistan ( ; bal, بلۏچستان; also romanised as Baluchistan and Baluchestan) is a historical region in Western and South Asia, located in the Iranian plateau's far southeast and bordering the Indian Plate and the Arabian Sea coastline. ...
) and Iran into the Arabian Desert in Saudi Arabia. Most of Australia is semi-arid or desert, making it the world's driest inhabited continent. In South America, the Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
mountain range blocks Pacific moisture that arrives in that continent, resulting in a desertlike climate just downwind across western Argentina. The drier areas of the United States are regions where the Sonoran Desert
The Sonoran Desert ( es, Desierto de Sonora) is a desert in North America and ecoregion that covers the northwestern Mexican states of Sonora, Baja California, and Baja California Sur, as well as part of the southwestern United States (in Arizona ...
overspreads the Desert Southwest, the Great Basin and central Wyoming.
Polar deserts
Since rain only falls as liquid, it rarely falls when surface temperatures are below freezing, unless there is a layer of warm air aloft, in which case it becomes freezing rain. Due to the entire atmosphere being below freezing most of the time, very cold climates see very little rainfall and are often known aspolar desert
Polar deserts are the regions of Earth that fall under an ice cap climate (''EF'' under the Köppen classification). Despite rainfall totals low enough to normally classify as a desert, polar deserts are distinguished from true deserts (' or ' un ...
s. A common biome in this area is the tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless moun ...
which has a short summer thaw and a long frozen winter. Ice caps
In glaciology, an ice cap is a mass of ice that covers less than of land area (usually covering a highland area). Larger ice masses covering more than are termed ice sheets.
Description
Ice caps are not constrained by topographical features ...
see no rain at all, making Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
the world's driest continent.
Rainforests
Rainforests are areas of the world with very high rainfall. Bothtropical
The tropics are the regions of Earth surrounding the Equator. They are defined in latitude by the Tropic of Cancer in the Northern Hemisphere at N and the Tropic of Capricorn in
the Southern Hemisphere at S. The tropics are also referred to ...
and temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
rainforests exist. Tropical rainforests occupy a large band of the planet mostly along the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
. Most temperate rainforests are located on mountainous west coasts between 45 and 55 degrees latitude, but they are often found in other areas.
Around 40–75% of all biotic life is found in rainforests. Rainforests are also responsible for 28% of the world's oxygen turnover.
Monsoons
The equatorial region near theIntertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal e ...
(ITCZ), or monsoon trough, is the wettest portion of the world's continents. Annually, the rain belt within the tropics marches northward by August, then moves back southward into the Southern Hemisphere by February and March. Within Asia, rainfall is favored across its southern portion from India east and northeast across the Philippines and southern China into Japan due to the monsoon advecting moisture primarily from the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
into the region. The monsoon trough can reach as far north as the 40th parallel in East Asia during August before moving southward thereafter. Its poleward progression is accelerated by the onset of the summer monsoon which is characterized by the development of lower air pressure (a thermal low
Thermal lows, or heat lows, are non-frontal low-pressure areas that occur over the continents in the subtropics during the warm season, as the result of intense heating when compared to their surrounding environments.Glossary of Meteorology (200 ...
) over the warmest part of Asia. Similar, but weaker, monsoon circulations are present over North America and Australia. During the summer, the Southwest monsoon combined with Gulf of California
The Gulf of California ( es, Golfo de California), also known as the Sea of Cortés (''Mar de Cortés'') or Sea of Cortez, or less commonly as the Vermilion Sea (''Mar Bermejo''), is a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean that separates the Baja Ca ...
and Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
moisture moving around the subtropical ridge
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as Subtropics, subtropical ridges, or highs. It is a h ...
in the Atlantic Ocean bring the promise of afternoon and evening thunderstorms to the southern tier of the United States as well as the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
. The eastern half of the contiguous United States east of the 98th meridian, the mountains of the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
, and the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada () is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primarily ...
range are the wetter portions of the nation, with average rainfall exceeding per year.NationalAtlas.goPrecipitation of the Individual States and of the Conterminous States.
Retrieved on 9 March 2008.
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
s enhance precipitation across southern sections of the United States, as well as Puerto Rico
Puerto Rico (; abbreviated PR; tnq, Boriken, ''Borinquen''), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico ( es, link=yes, Estado Libre Asociado de Puerto Rico, lit=Free Associated State of Puerto Rico), is a Caribbean island and Unincorporated ...
, the United States Virgin Islands
The United States Virgin Islands,. Also called the ''American Virgin Islands'' and the ''U.S. Virgin Islands''. officially the Virgin Islands of the United States, are a group of Caribbean islands and an unincorporated and organized territory ...
, the Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI; ch, Sankattan Siha Na Islas Mariånas; cal, Commonwealth Téél Falúw kka Efáng llól Marianas), is an unincorporated territory and commonw ...
, Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
, and American Samoa
American Samoa ( sm, Amerika Sāmoa, ; also ' or ') is an unincorporated territory of the United States located in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of the island country of Samoa. Its location is centered on . It is east of the International ...
.
Impact of the Westerlies
 Westerly flow from the mild north Atlantic leads to wetness across western Europe, in particular Ireland and the United Kingdom, where the western coasts can receive between , at sea level and , on the mountains of rain per year.
Westerly flow from the mild north Atlantic leads to wetness across western Europe, in particular Ireland and the United Kingdom, where the western coasts can receive between , at sea level and , on the mountains of rain per year. Bergen
Bergen (), historically Bjørgvin, is a city and municipality in Vestland county on the west coast of Norway. , its population is roughly 285,900. Bergen is the second-largest city in Norway. The municipality covers and is on the peninsula of ...
, Norway is one of the more famous European rain-cities with its yearly precipitation of on average. During the fall, winter, and spring, Pacific storm systems bring most of Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
and the western United States much of their precipitation.J. HorelNormal Monthly Precipitation, Inches.
Retrieved on 19 March 2008. Over the top of the ridge, the jet stream brings a summer precipitation maximum to the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
. Large thunderstorm areas known as mesoscale convective complexes move through the Plains, Midwest, and Great Lakes during the warm season, contributing up to 10% of the annual precipitation to the region.Walker S. Ashley, Thomas L. Mote, P. Grady Dixon, Sharon L. Trotter, Emily J. Powell, Joshua D. Durkee, and Andrew J. GrundsteinDistribution of Mesoscale Convective Complex Rainfall in the United States.
Retrieved on 2 March 2008. The
El Niño-Southern Oscillation
EL, El or el may refer to:
Religion
* El (deity), a Semitic word for "God"
People
* EL (rapper) (born 1983), stage name of Elorm Adablah, a Ghanaian rapper and sound engineer
* El DeBarge, music artist
* El Franco Lee (1949–2016), American po ...
affects the precipitation distribution, by altering rainfall patterns across the western United States, Midwest, the Southeast, and throughout the tropics. There is also evidence that global warming
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
is leading to increased precipitation to the eastern portions of North America, while droughts are becoming more frequent in the tropics and subtropics.
Wettest known locations
Cherrapunji
Cherrapunji () or Sohra is a subdivisional town (Proposed District) East Khasi Hills district in the Indian state of Meghalaya. It is the traditional capital of ka ''hima'' Sohra (Khasi tribal kingdom).
Sohra has often been credited as being t ...
, situated on the southern slopes of the Eastern Himalaya
]
The Eastern Himalayas extend from eastern Nepal across Northeast India, Bhutan, the Tibet Autonomous Region to Yunnan in China and northern Myanmar. The climate of this region is influenced by the monsoon of South Asia from June to September. It ...
in Shillong
Shillong () is a hill station and the capital of Meghalaya, a Indian state, state in northeastern India, which means "The Abode of Clouds". It is the headquarters of the East Khasi Hills district. Shillong is the list of most populous cities in ...
, India is the confirmed wettest place on Earth, with an average annual rainfall of . The highest recorded rainfall in a single year was in 1861. The 38-year average at nearby Mawsynram, Meghalaya
Meghalaya (, or , meaning "abode of clouds"; from Sanskrit , "cloud" + , "abode") is a states and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. Meghalaya was formed on 21 January 1972 by carving out two districts from the state of As ...
, India is . The wettest spot in Australia is Mount Bellenden Ker
Mount Bellenden Ker is the second-highest mountain in Queensland, Australia, with a height of . It is named after the botanist John Bellenden Ker Gawler. Located south of Cairns, Queensland, Cairns near Babinda, Queensland, Babinda, it is adj ...
in the north-east of the country which records an average of per year, with over of rain recorded during 2000. The Big Bog on the island of Maui
The island of Maui (; Hawaiian: ) is the second-largest of the islands of the state of Hawaii at 727.2 square miles (1,883 km2) and is the 17th largest island in the United States. Maui is the largest of Maui County's four islands, which ...
has the highest average annual rainfall in the Hawaiian Islands, at . Mount Waiʻaleʻale
Mount Waialeale is a shield volcano and the second highest point on the island of Kauai in the Hawaiian Islands. Its name literally means "rippling water" or "overflowing water"
The mountain, at an elevation of , averages more than of rain a ...
on the island of Kauaʻi
Kauai, () anglicized as Kauai ( ), is geologically the second-oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands (after Niʻihau). With an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), it is the fourth-largest of these islands and the List of islands of th ...
achieves similar torrential rains, while slightly lower than that of the Big Bog, at of rain per year over the last 32 years, with a record in 1982. Its summit is considered one of the rainiest spots on earth, with a reported 350 days of rain per year. Lloró
Lloró is a municipality and town in the Chocó Department, Colombia. It claims the second world record for highest average annual precipitation with , after López de Micay, which holds an also disputed record with . The official record is held ...
, a town situated in Chocó, Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
, is probably the place with the largest rainfall in the world, averaging per year. The Department of Chocó is extraordinarily humid. Tutunendaó, a small town situated in the same department, is one of the wettest estimated places on Earth, averaging per year; in 1974 the town received , the largest annual rainfall measured in Colombia. Unlike Cherrapunji, which receives most of its rainfall between April and September, Tutunendaó receives rain almost uniformly distributed throughout the year. Quibdó
Quibdó () is the capital city of Chocó Department, in Western Colombia, and is located on the Atrato River. The municipality of Quibdó has an area of 3,337.5 km² and a population of 129,237, predominantly Afro Colombian, including Zambo C ...
, the capital of Chocó, receives the most rain in the world among cities with over 100,000 inhabitants: per year. Storms in Chocó can drop of rainfall in a day. This amount is more than what falls in many cities in a year's time.
Outside Earth
Rainfalls of diamonds have been suggested to occur on the gas giant planets,Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but ...
and Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
, as well as on the ice giant planets, Uranus
Uranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. Its name is a reference to the Greek god of the sky, Uranus (mythology), Uranus (Caelus), who, according to Greek mythology, was the great-grandfather of Ares (Mars (mythology), Mars), grandfather ...
and Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times ...
. There is likely to be rain of various compositions in the upper atmospheres of the gas giants, as well as precipitation of liquid neon
Neon is a chemical element with the symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is a noble gas. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with about two-thirds the density of air. It was discovered (along with krypton ...
in the deep atmospheres. On Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
, Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
's largest natural satellite, infrequent methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Eart ...
rain is thought to carve the moon's numerous surface channels. On Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never fa ...
, sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (American spelling and the preferred IUPAC name) or sulphuric acid ( Commonwealth spelling), known in antiquity as oil of vitriol, is a mineral acid composed of the elements sulfur, oxygen and hydrogen, with the molecular formu ...
virga evaporates from the surface. Extrasolar planet OGLE-TR-56b
OGLE-TR-56b is an extrasolar planet located approximately 1500 parsecs away in the constellation of Sagittarius, orbiting the star OGLE-TR-56. This planet was the first known exoplanet to be discovered with the transit method. The object was disc ...
in the constellation Sagittarius is hypothesized to have iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
rain. Accordingly, research carried out by the European Southern Observatory
The European Organisation for Astronomical Research in the Southern Hemisphere, commonly referred to as the European Southern Observatory (ESO), is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental research organisation made up of 16 mem ...
shows that WASP-76b
WASP-76b is a Hot Jupiter exoplanet orbiting the star WASP-76 in the constellation Pisces. Wasp-76b orbits its parent star at a distance of 0.033 AU with a period of 1.8 days. Its mass is 0.92 times that of Jupiter. WASP-76b was discovered on Oc ...
can produce showers of burning liquid iron droplets once temperature decreases during the planet's night hours. There is evidence from samples of basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
brought back by the Apollo missions
The Apollo program was a United States human spaceflight program carried out from 1961 to 1972 by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), which landed the first astronauts on the Moon. The program used the Saturn IB and Saturn ...
that the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
has been subject to lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
rain.Taylor, G. Jeffrey"Finding distant chips from distant maria"
pp. 8–9, ''Planetary Science Research Discoveries'', 30 April 2006.
See also
* Atmospheric river *Hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to Electricity generation, produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by energy transformation, converting the Pot ...
* Intensity-duration-frequency curve
* Precipitation types
* Rain dust
Rain dust or snow dust, traditionally known as muddy rain, red rain, or coloured rain, is a variety of rain (or any other form of precipitation) which contains enough desert dust for the dust to be visible without using a microscope.
History
T ...
* Rain sensor
* Rain water harvesting
* Rainbow
* Raining animals
A rain of animals is a rare meteorological phenomenon in which flightless animals fall from the sky. Such occurrences have been reported in many countries throughout history. One hypothesis is that tornadic waterspouts sometimes pick up creatur ...
* Red rain in Kerala
The Kerala red rain phenomenon was a blood rain event that occurred in Wayanad district region of Malabar on Monday, 15 July 1957 and the colour subsequently turned yellow and also 25 July to 23 September 2001, when heavy downpours of red-col ...
* Petrichor
Petrichor () is the earthy olfaction, scent produced when rain falls on dry soil. The word is constructed , the ichor, ethereal fluid that is the blood of the gods in Greek mythology.
Origins
Long before this phenomenon received its name in 19 ...
– the cause of the scent during and after rain
* Sanitary sewer overflow
Sanitary sewer overflow (SSO) is a condition in which untreated sewage is discharged from a sanitary sewer into the environment prior to reaching sewage treatment facilities. When caused by rainfall it is also known as wet weather overflow. Cause ...
* Sediment precipitation
Rain dust or snow dust, traditionally known as muddy rain, red rain, or coloured rain, is a variety of rain (or any other form of precipitation) which contains enough desert dust for the dust to be visible without using a microscope.
History
T ...
* Water resources
Water resources are natural resources of water that are potentially useful for humans, for example as a source of drinking water supply or irrigation water. 97% of the water on the Earth is salt water and only three percent is fresh water; slight ...
* Weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere, the ...
* Rainmaking
Rainmaking, also known as artificial precipitation, artificial rainfall and pluviculture, is the act of attempting to artificially induce or increase precipitation, usually to stave off drought or the wider global warming. According to the cloud ...
* Johad
Notes
* The value given is the continent's highest, and ''possibly'' the world's, depending on measurement practices, procedures and period of record variations. * The official greatest average annual precipitation for South America is at Quibdó, Colombia. The average at LloróSE and at a higher elevation than Quibdó
SE, Se, or Sé may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Sé'' (album), by Lúnasa, 2006
* Se (instrument), a traditional Chinese musical instrument
Businesses and organizations
* Sea Ltd (NYSE: SE), tech conglomerate headquartered in Singapore
...
is an estimated amount.
* Approximate elevation.
* Recognized as "The Wettest place on Earth" by the ''Guinness Book of World Records
''Guinness World Records'', known from its inception in 1955 until 1999 as ''The Guinness Book of Records'' and in previous United States editions as ''The Guinness Book of World Records'', is a reference book published annually, listing world ...
''.
* This is the highest figure for which records are available. The summit of Mount Snowdon
Snowdon () or (), is the highest mountain in Wales, at an elevation of above sea level, and the highest point in the British Isles outside the Scottish Highlands. It is located in Snowdonia National Park (') in Gwynedd (historic ...
, about from Glaslyn, is estimated to have at least per year.
References
External links
BBC article on the weekend rain effect
{{Authority control Articles containing video clips